Mechanism of Tumor Budding in Patient-Derived Metachronous Oral Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Case Presentation
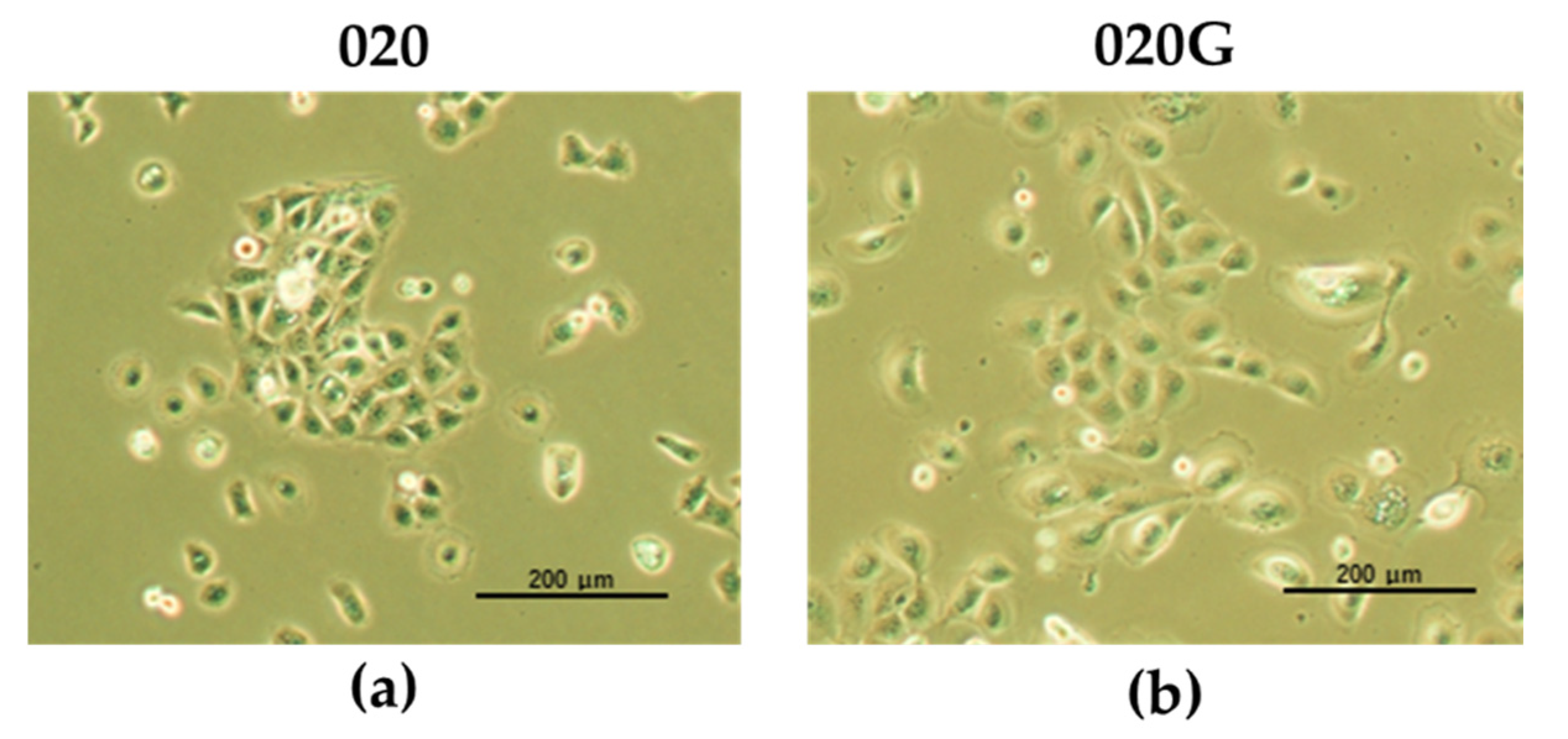
2.2. Establishment of Cultured Oral Metachronous Carcinoma Cell Lines HCM-SqCC020 (020) and HCM-SqCC020G (020G) from Each Tumor
2.3. Exome Sequence Analysis
2.4. Expression of p-EMT Marker at Deepest Site of Tumor Invasion and TB Expression
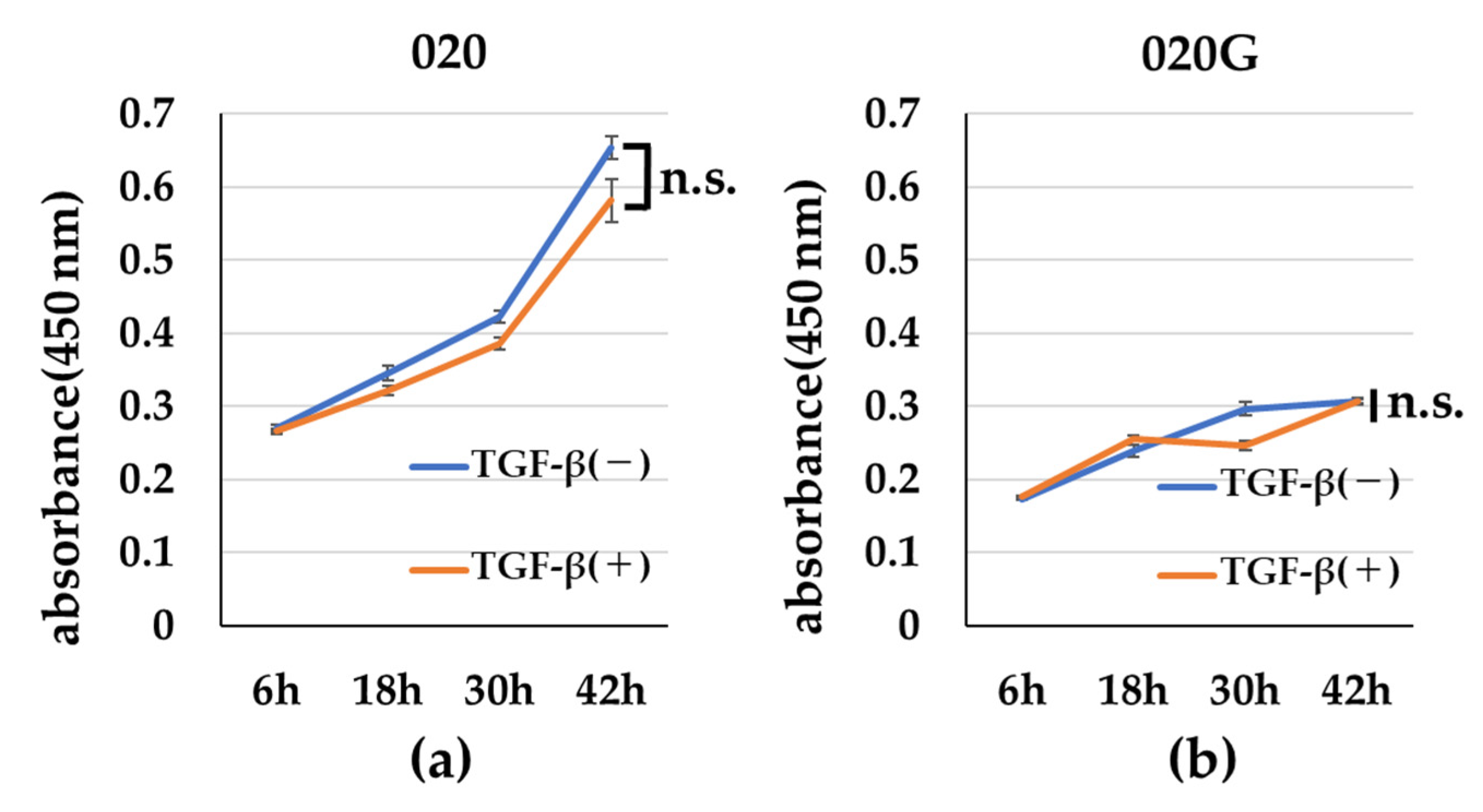
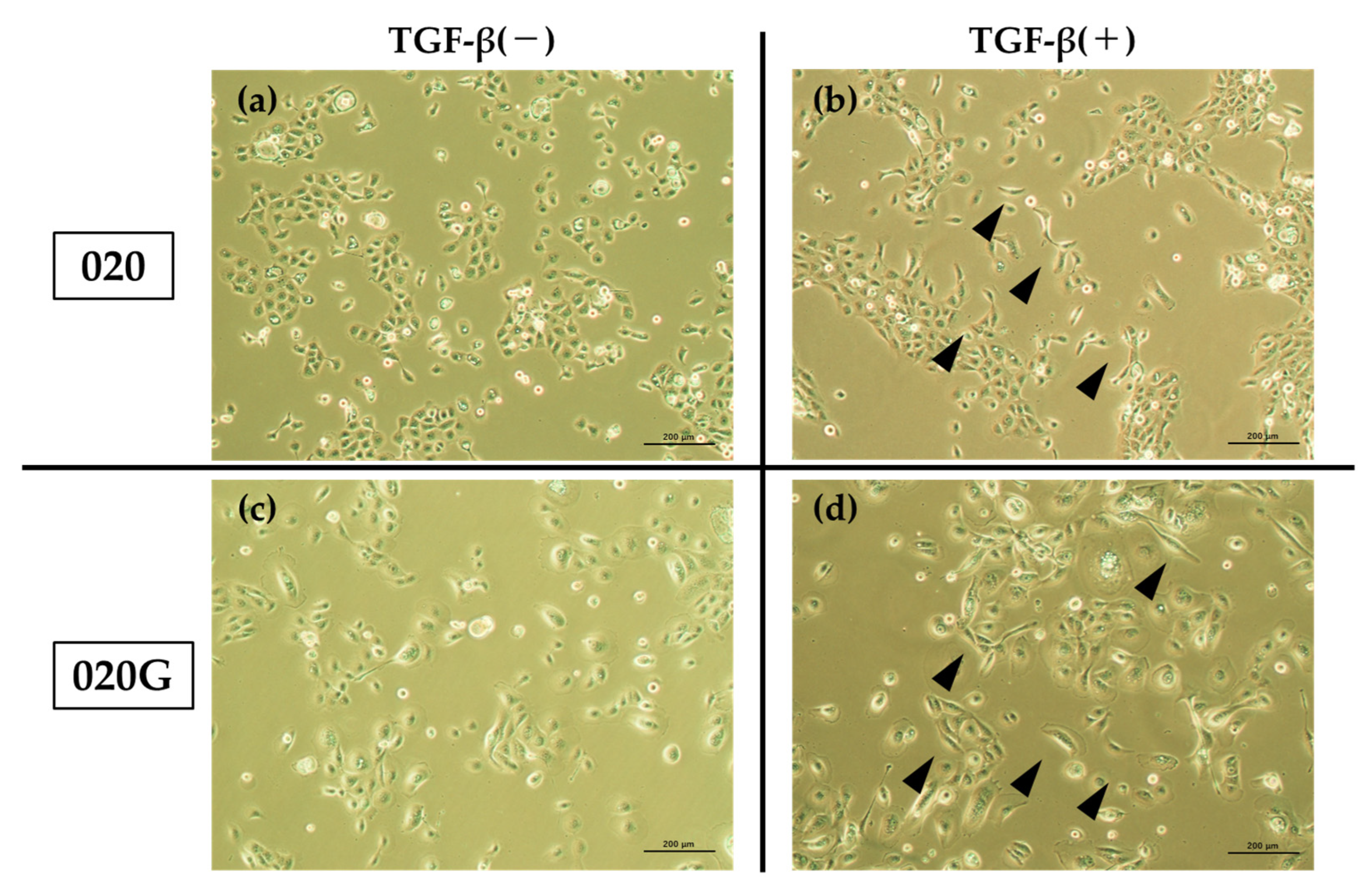
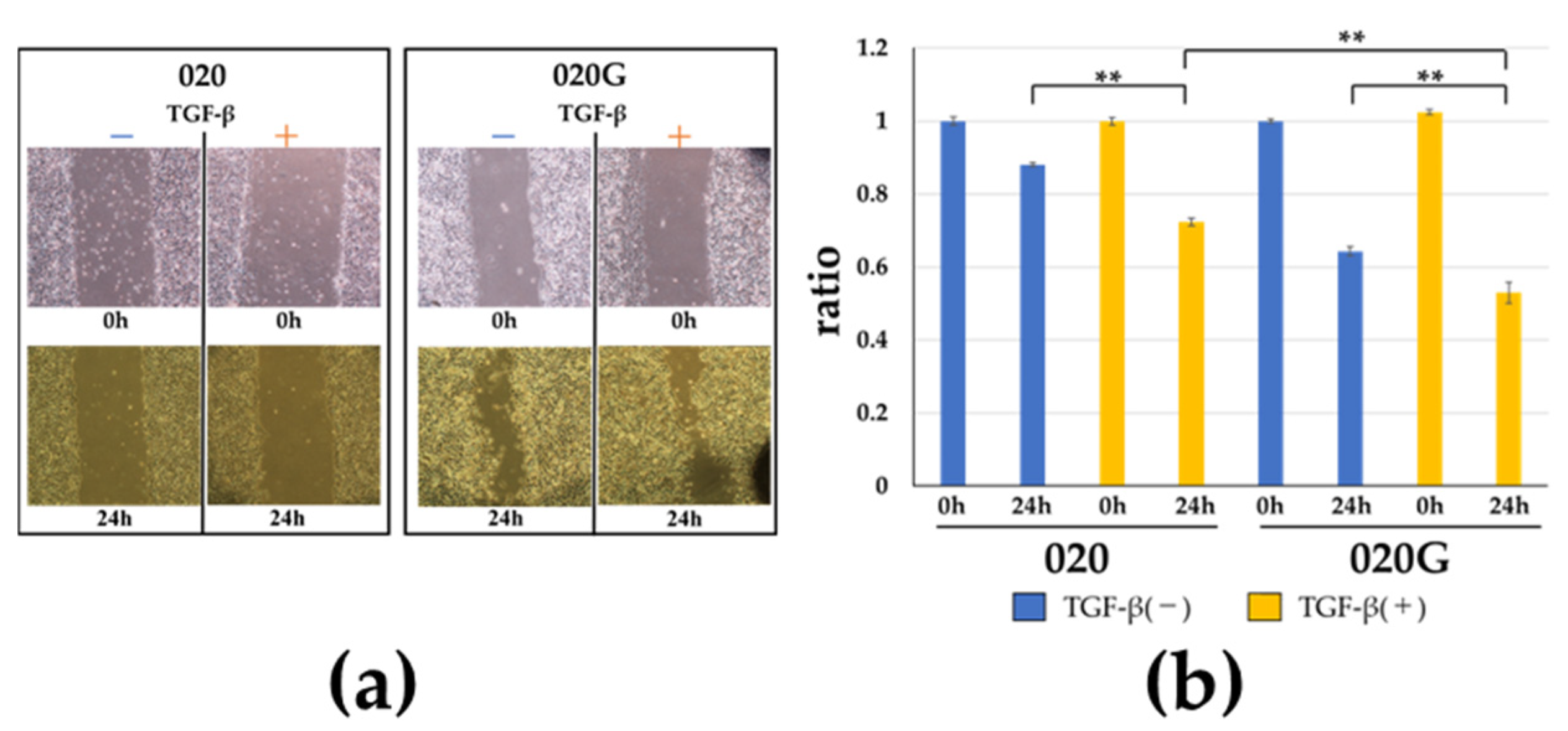
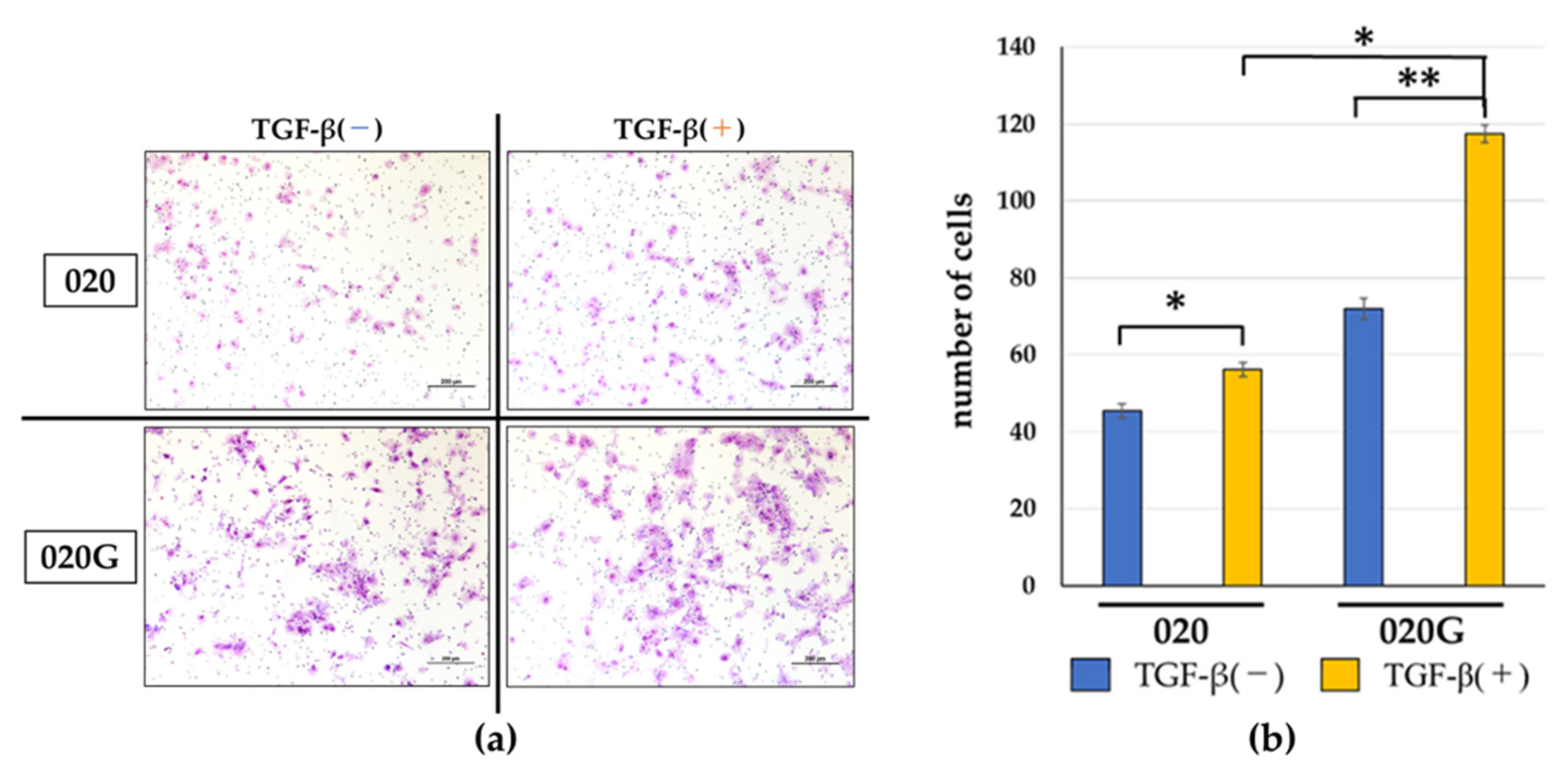
2.5. Effects of TGF-β on Proliferative, Migratory, and Invasive Abilities, and Cell Morphology of 020 and 020G Cells
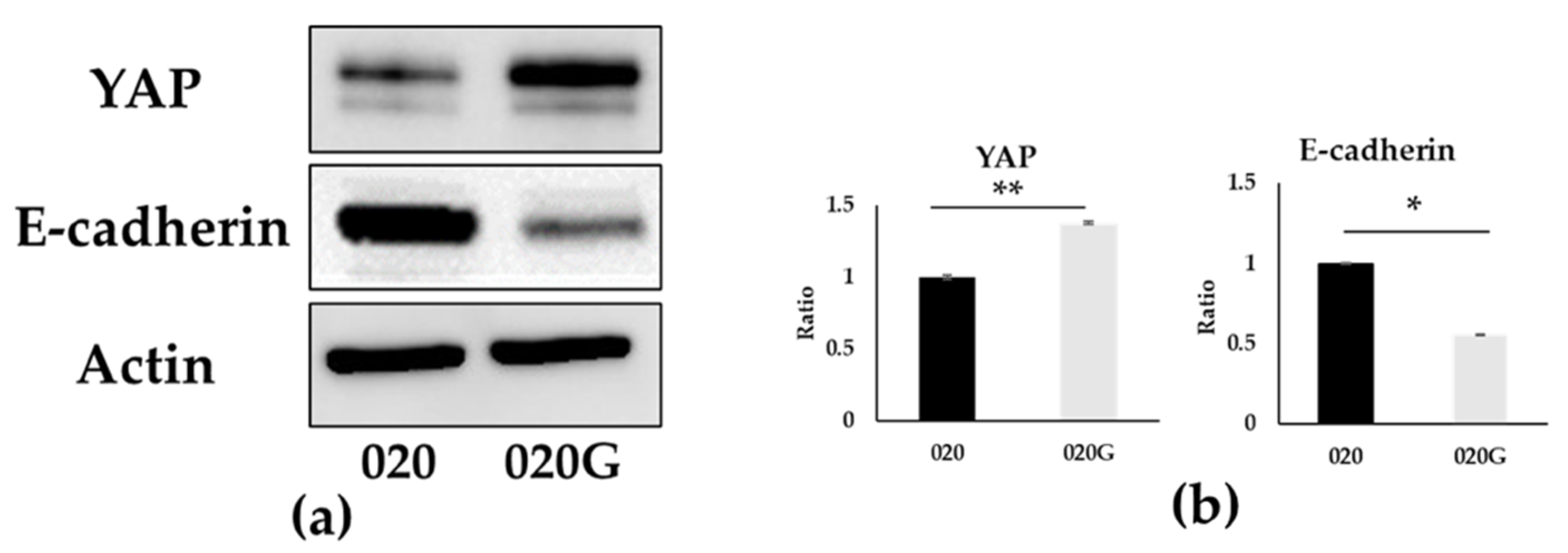
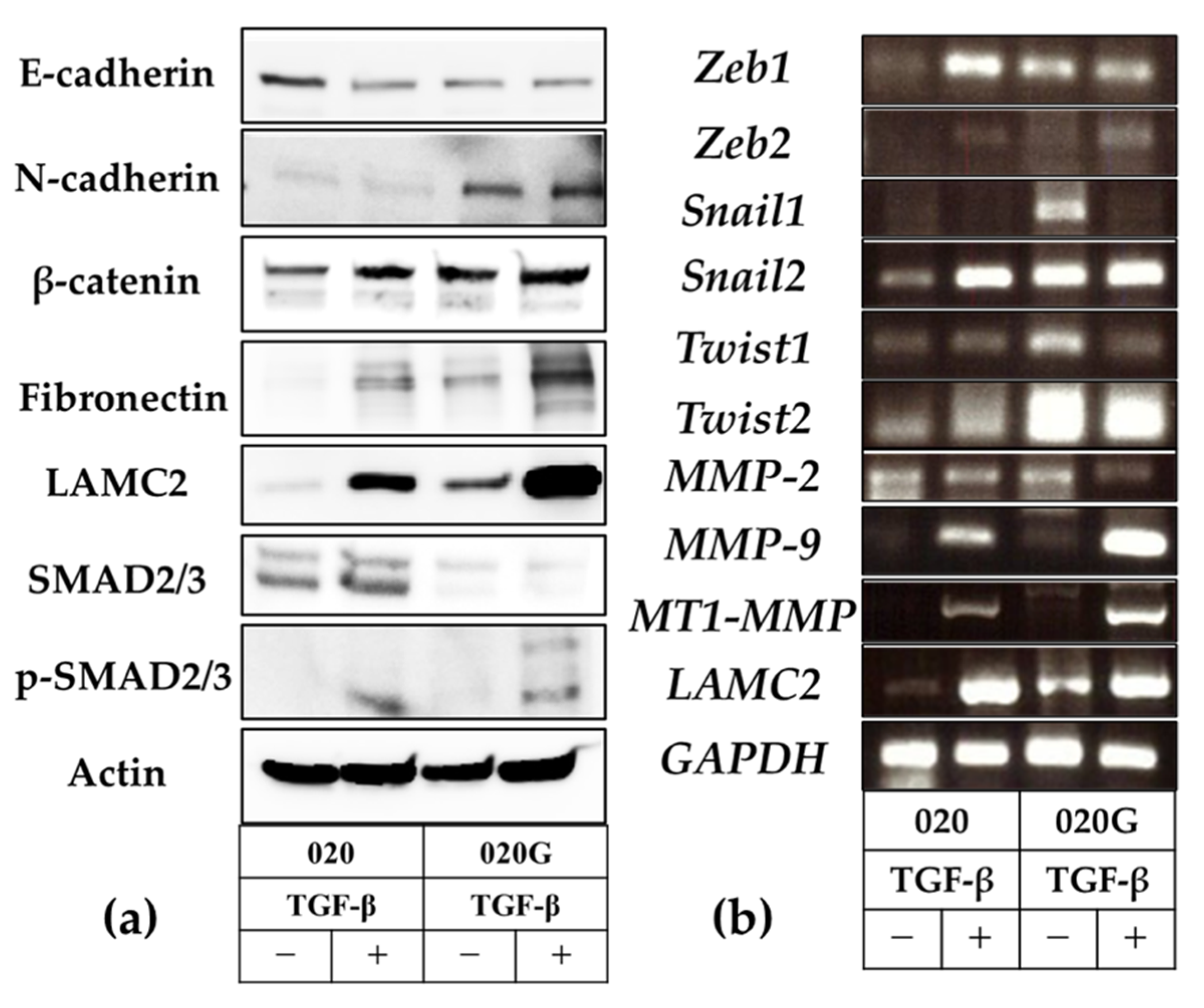
2.6. Evaluation of EMT and p-EMT in 020 and 020G Cells with and Without TGF-β
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Establishment of HCM-SqCC020 and HCM-SqCC020G Cell Lines
4.2. Short Tandem Repeat Authentication of HCM-SqCC020 and SqCC020G Cell Lines
4.3. Exome Capture and Sequencing
4.4. Exome Sequencing
- Alignment and Somatic Variant Calling
- 2.
- Variant Annotation and Filtering
4.5. IHC to Evaluate TB
4.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.7. Scratch Assay
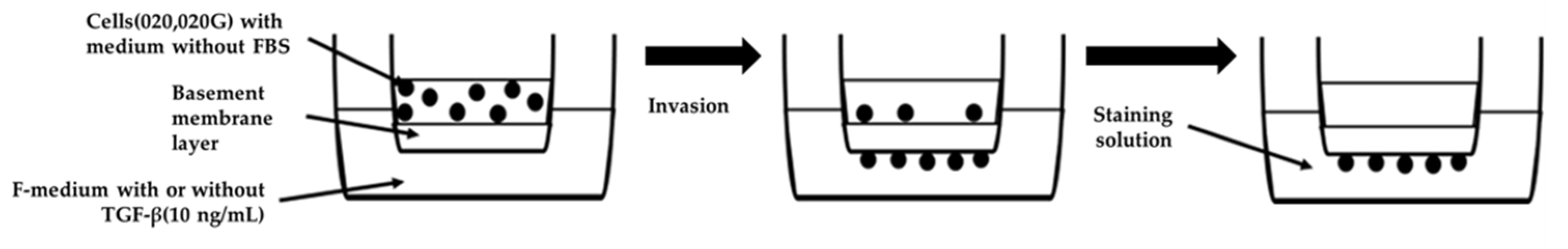
4.8. Invasion Assay
4.9. Western Blotting
4.10. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Ali, K. Oral cancer—The fight must go on against all odds…. Evid. Based Dent. 2022, 23, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerjes, W.; Upile, T.; Petrie, A.; Riskalla, A.; Hamdoon, Z.; Vourvachis, M.; Karavidas, K.; Jay, A.; Sandison, A.; Thomas, G.J.; et al. Clinicopathological parameters, recurrence, locoregional and distant metastasis in 115 T1–T2 oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Head Neck Oncol. 2010, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wutzl, A.; Ploder, O.; Kermer, C.; Millesi, W.; Ewers, R.; Klug, C. Mortality and causes of death after multimodality treatment for advanced oral and oropharyngeal cancer. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 65, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobdey, S.; Sathwara, J.; Jain, A.; Saoba, S.; Balasubramaniam, G. Squamous cell carcinoma of buccal mucosa: An analysis of prognostic factors. S. Asian J. Cancer 2018, 7, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Nishimine, M.; Kishi, M.; Kirita, T.; Sugimura, M.; Nakamura, M.; Konishi, N. Prediction of delayed neck metastasis in patients with stage I/II squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2002, 31, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Cruz, A.K.; Vaish, R.; Kapre, N.; Dandekar, M.; Gupta, S.; Hawaldar, R.; Agarwal, J.P.; Pantvaidya, G.; Chaukar, D.; Deshmukh, A.; et al. Elective versus therapeutic neck dissection in node-negative oral cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, H.; Price, A.B.; Wilkinson, K.H.; Jass, J.R.; Mochizuki, H.; Talbot, I.C. A new prognostic staging system for rectal cancer. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Karhunen, M.; Hautaniemi, S.; Salo, T.; Leivo, I. Prognostic value of tumour budding in oesophageal cancer: A meta-analysis. Histopathology 2016, 68, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarioglu, S.; Acara, C.; Akman, F.C.; Dag, N.; Ecevit, C.; Ikiz, A.O.; Cetinayak, O.H.; Ada, E. Tumor budding as a prognostic marker in laryngeal carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2010, 206, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.R.; Gao, F.; Li, S.Y.; Yao, K.T. Tumour budding and the expression of cancer stem cell marker aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Histopathology 2012, 61, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T. Growth patterns in human carcinoma. Their classification and relation to prognosis. Obstet. Gynecol. 1960, 16, 296–308. [Google Scholar]
- Almangush, A.; Coletta, R.D.; Bello, I.O.; Bitu, C.; Keski-Säntti, H.; Mäkinen, L.K.; Kauppila, J.H.; Pukkila, M.; Hagström, J.; Laranne, J.; et al. A simple novel prognostic model for early stage oral tongue cancer. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Kubota, A.; Yokose, T.; Furukawa, M.; Matsushita, T.; Takita, M.; Mitsunaga, S.; Mizoguchi, N.; Nonaka, T.; Nakayama, Y.; et al. Predictive significance of tumor depth and budding for late lymph node metastases in patients with clinical N0 early oral tongue carcinoma. Head Neck Pathol. 2017, 11, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, R.; Hou, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, H. Tumor budding correlates with occult cervical lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in clinical early-stage tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2015, 44, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Salo, T.; Hagström, J.; Leivo, I. Tumour budding in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma—A systematic review. Histopathology 2014, 65, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, N.; Kirita, T.; Umeda, M.; Yanamoto, S.; Ota, Y.; Otsuru, M.; Okura, M.; Kurita, H.; Yamada, S.I.; Hasegawa, T.; et al. Tumor budding and adjacent tissue at the invasive front correlate with delayed neck metastasis in clinical early-stage tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 119, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlobec, I.; Lugli, A. Tumour budding in colorectal cancer: Molecular rationale for clinical translation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, D.H.; Dabelsteen, E.; Specht, L.; Fiehn, A.M.; Therkildsen, M.H.; Jønson, L.; Vikesaa, J.; Nielsen, F.C.; von Buchwald, C. Molecular profiling of tumour budding implicates TGFβ-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition as a therapeutic target in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2015, 236, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.O.; Oh, K.Y.; Shin, W.J.; Yoon, H.J.; Lee, J.I.; Hong, S.D. Tumor budding is associated with poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma and histologically represents an epithelial-mesenchymal transition process. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 80, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M.A.; Huang, R.Y.; Jackson, R.A.; Thiery, J.P. EMT: 2016. Cell 2016, 166, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puram, S.V.; Tirosh, I.; Parikh, A.S.; Patel, A.P.; Yizhak, K.; Gillespie, S.; Rodman, C.; Luo, C.L.; Mroz, E.A.; Emerick, K.S.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of primary and metastatic tumor ecosystems in head and neck cancer. Cell 2017, 171, 1611–1624.e1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puram, S.V.; Parikh, A.S.; Tirosh, I. Single cell RNA-seq highlights a role for a partial EMT in head and neck cancer. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 5, e1448244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argon, A.; Öz, Ö.; Kebat, T.A. Evaluation and prognostic significance of tumor budding in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2023, 66, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, A.S.; Puram, S.V.; Faquin, W.C.; Richmon, J.D.; Emerick, K.S.; Deschler, D.G.; Varvares, M.A.; Tirosh, I.; Bernstein, B.E.; Lin, D.T. Immunohistochemical quantification of partial-EMT in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma primary tumors is associated with nodal metastasis. Oral Oncol. 2019, 99, 104458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.Y.; Shin, D.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Ko, Y.H.; Kim, S.; Jeong, H.S. Prognostic significance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition of extracapsular spread tumors in lymph node metastases of head and neck cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 1904–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, K.; Kanda, S.; Yoshida, K.; Funaoka, Y.; Yamanegi, K.; Yoshikawa, K.; Takaoka, K.; Kishimoto, H.; Nakano, Y. Establishment of a patient-derived mucoepidermoid carcinoma cell line with the CRTC1-MAML2 fusion gene. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 16, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki-Maeda, H.; Kawabe, M.; Omori, Y.; Yamanegi, K.; Yoshida, K.; Yoshikawa, K.; Takaoka, K.; Noguchi, K.; Nakano, Y.; Kishimoto, H. Establishment of an oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line expressing vascular endothelial growth factor a and its two receptors. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Noguchi, K.; Yamanegi, K.; Yoshikawa, K.; Kanda, S.; Omori, Y.; Omae, T.; Takaoka, K.; Terada, T.; Nakano, Y.; et al. LAMB3 and TACSTD2, both highly expressed in salivary gland mucoepidermoid carcinoma, represent potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Med. Pathol. 2023, 35, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature 2015, 517, 576–582. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Liu, H.; Liao, C.T.; Huang, P.J.; Huang, Y.; Hsu, A.; Tang, P.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, H.C.; Yen, T.C. Ultra-deep targeted sequencing of advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma identifies a mutation-based prognostic gene signature. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18066–18080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyodo, T.; Kuribayashi, N.; Fukumoto, C.; Komiyama, Y.; Shiraishi, R.; Kamimura, R.; Sawatani, Y.; Yaguchi, E.; Hasegawa, T.; Izumi, S.; et al. The mutational spectrum in whole exon of p53 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical implications. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yanamoto, S. Relationship between tumor budding and partial epithelial-mesenchymal transition in head and neck cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massagué, J. TGFβ signalling in context. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Kadam, P.; Helkin, A.; Cao, K.; Wu, S.; Samara, G.J.; Zhang, Q.; Zucker, S.; Cao, J. MT1-MMP activation of TGF-β signaling enables intercellular activation of an epithelial-mesenchymal transition program in cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2016, 16, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, X.J.; Xing, J. Signal transduction pathways of EMT induced by TGF-β, SHH, and WNT and their crosstalks. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulte, D.; Brenner, H. Changes in survival in head and neck cancers in the late 20th and early 21st century: A period analysis. Oncologist 2010, 15, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuirt, W.F.; Matthews, B.; Koufman, J.A. Multiple simultaneous tumors in patients with head and neck cancer: A prospective, sequential panendoscopic study. Cancer 1982, 50, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.Y.; Mukhopadhyay, T.; Kim, J.; Casson, A.; Ro, J.Y.; Goepfert, H.; Hong, W.K.; Roth, J.A. Discordant p53 gene mutations in primary head and neck cancers and corresponding second primary cancers of the upper aerodigestive tract. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt, M.S.; Bennett, W.P.; Hollstein, M.; Harris, C.C. Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: Clues to cancer etiology and molecular pathogenesis. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 4855–4878. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.H.; Cheng, H.W.; Liu, C.J. Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction for detection and quantification of cell-free DNA TP53 target somatic mutations in oral cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2022, 33, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhi, S.S.; Roy, S.; Kar, M.; Saha, A.; Adhya, A.; Baisakh, M.; Banerjee, B. Role of CDKN2A/p16 expression in the prognostication of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2017, 73, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Degese, M.S.; Vitale-Cross, L.; Iglesias-Bartolome, R.; Valera, J.L.C.; Wang, Z.; Feng, X.; Yeerna, H.; Vadmal, V.; Moroishi, T.; et al. Assembly and activation of the Hippo signalome by FAT1 tumor suppressor. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, H.; Nishio, M.; Masuda, M.; Miyachi, Y.; Ueda, F.; Nakano, T.; Sato, K.; Mimori, K.; Taguchi, K.; Hikasa, H.; et al. YAP1 is a potent driver of the onset and progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Jin, L.; Chen, Y.; Xi, X.; Guo, Y. YAP promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition by upregulating Slug expression in human colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 701–710. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, U.S.; Saravanan, K.; Wan, H. The role of YAP in the control of the metastatic potential of oral cancer. Oncol. Res. 2021, 29, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemans, C.R.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The molecular landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.; Lin, L.H.; Yu, S.Y.; Kao, S.Y.; Chang, K.W.; Cheng, H.W.; Liu, C.J. FAT1 somatic mutations in head and neck carcinoma are associated with tumor progression and survival. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Global epidemiology of oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massano, J.; Regateiro, F.S.; Januário, G.; Ferreira, A. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: Review of prognostic and predictive factors. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2006, 102, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.J.; Jensen, D.H.; Lelkaitis, G.; Kiss, K.; Charabi, B.; Specht, L.; von Buchwald, C. Construction of a pathological risk model of occult lymph node metastases for prognostication by semi-automated image analysis of tumor budding in early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 18227–18237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkitie, A.A.; Almangush, A.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Ferlito, A.; Leivo, I. Hallmarks of cancer: Tumor budding as a sign of invasion and metastasis in head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2019, 41, 3712–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.M.; Wang, L.; Shen, H.; Jiang, C.F.; Ge, X.; Li, D.M.; Wen, Y.Y.; Sun, H.R.; Pan, M.H.; Li, W.; et al. Downregulation of miR-218 contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis in lung cancer by targeting Slug/ZEB2 signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto da-Silva, J.; Lourenço, S.; Nico, M.; Silva, F.H.; Martins, M.T.; Costa-Neves, A. Expression of laminin-5 and integrins in actinic cheilitis and superficially invasive squamous cell carcinomas of the lip. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2012, 208, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangon Junior, H.; Rocha, V.N.; Leite, C.F.; de Aguiar, M.C.; Souza, P.E.; Horta, M.C. Laminin-5 gamma 2 chain expression is associated with intensity of tumor budding and density of stromal myofibroblasts in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2014, 43, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ory, V.; Chapman, S.; Yuan, H.; Albanese, C.; Kallakury, B.; Timofeeva, O.A.; Nealon, C.; Dakic, A.; Simic, V.; et al. ROCK inhibitor and feeder cells induce the conditional reprogramming of epithelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Scheffler, K.; Halpern, A.L.; Bekritsky, M.A.; Noh, E.; Källberg, M.; Chen, X.; Kim, Y.; Beyter, D.; Krusche, P.; et al. Strelka2: Fast and accurate calling of germline and somatic variants. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Schulz-Trieglaff, O.; Shaw, R.; Barnes, B.; Schlesinger, F.; Källberg, M.; Cox, A.J.; Kruglyak, S.; Saunders, C.T. Manta: Rapid detection of structural variants and indels for germline and cancer sequencing applications. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1220–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.J.; Amode, M.R.; Aneja, A.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barnes, I.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Berry, A.; Bhai, J.; et al. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D933–D941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.genome.med.kyoto-u.ac.jp/SnpDB/ (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Liang, C.C.; Park, A.Y.; Guan, J.L. In vitro scratch assay: A convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, S.E.; Quinley, C.; Kim, H.; Herdman, S.; Corr, M.; Raz, E. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) protein suppresses adenoma-to-carcinoma transition in Apcmin/+ mice via regulation of Snail-1 (SNAI) protein stability. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 18182–18189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Kalita, P.; Patil, O.; Mohanty, S. An investigation of folic acid-protein association sites and the effect of this association on folic acid self-assembly. J. Mol. Model. 2015, 21, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, K.; Wakai, K.; Kiyono, T.; Kawabe, M.; Yoshikawa, K.; Hashimoto-Tamaoki, T.; Kishimoto, H.; Nakano, Y. Molecular analysis of keratocystic odontogenic tumor cell lines derived from sporadic and basal cell nevus syndrome patients. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmae, T.; Noguchi, K.; Yamanegi, K.; Omori, Y.; Makihara, Y.; Yoshikawa, K.; Takaoka, K.; Nakano, Y.; Kishimoto, H. Huge glandular odontogenic cyst: Report of a case and use of CRTC1/3-MAML2 fusion gene analysis for diagnosis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Med. Pathol. 2024, 36, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cell | CHROM | POS | REF | Variant Type | Allele | Annotation | Gene Name | HGVS.c | HGVS.p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 020 | chr17 | 7676195 | T | INS | TG | Frameshift variant | TP53 | c.173dupC | p.Gly59fs |
| 020G | chr4 | 186614345 | C | SNV | G | Splice acceptor variant and intron variant | FAT1 | c.9082-1G>C | |
| chr4 | 186617884 | G | SNV | A | Missense variant | FAT1 | c.8708C>T | p.Thr2903Ile | |
| chr9 | 21971121 | G | SNV | A | Stop gained | CDKN2A | c.238C>T | p.Arg80* | |
| chr17 | 7676123 | C | INS | CG | Frameshift variant | TP53 | c.245dupC | p.Ala83fs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omae, T.; Omori, Y.; Makihara, Y.; Yamanegi, K.; Hanawa, S.; Yoshikawa, K.; Noguchi, K.; Kishimoto, H. Mechanism of Tumor Budding in Patient-Derived Metachronous Oral Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073347
Omae T, Omori Y, Makihara Y, Yamanegi K, Hanawa S, Yoshikawa K, Noguchi K, Kishimoto H. Mechanism of Tumor Budding in Patient-Derived Metachronous Oral Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073347
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmae, Takayuki, Yuji Omori, Yuna Makihara, Koji Yamanegi, Soutaro Hanawa, Kyohei Yoshikawa, Kazuma Noguchi, and Hiromitsu Kishimoto. 2025. "Mechanism of Tumor Budding in Patient-Derived Metachronous Oral Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073347
APA StyleOmae, T., Omori, Y., Makihara, Y., Yamanegi, K., Hanawa, S., Yoshikawa, K., Noguchi, K., & Kishimoto, H. (2025). Mechanism of Tumor Budding in Patient-Derived Metachronous Oral Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073347





