Chronic Administration with FAD012 (3,5-Dimethyl-4-hydroxycinnamic Acid) Maintains Cerebral Blood Flow and Ameliorates Swallowing Dysfunction After Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Body Weights and Survival Rates
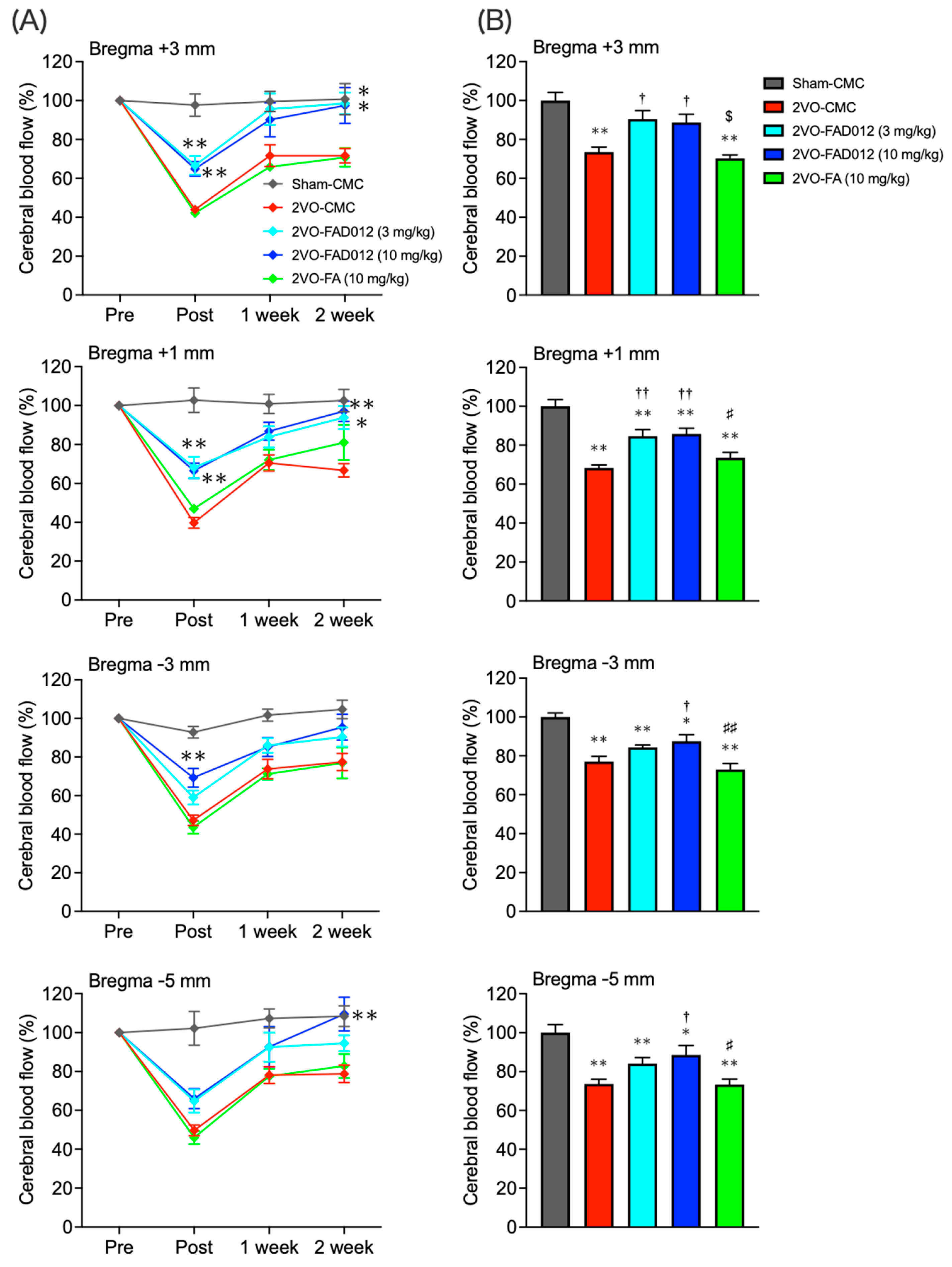
2.2. Changes in Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF) After Bilateral Common Carotid Artery Occlusion (2VO)
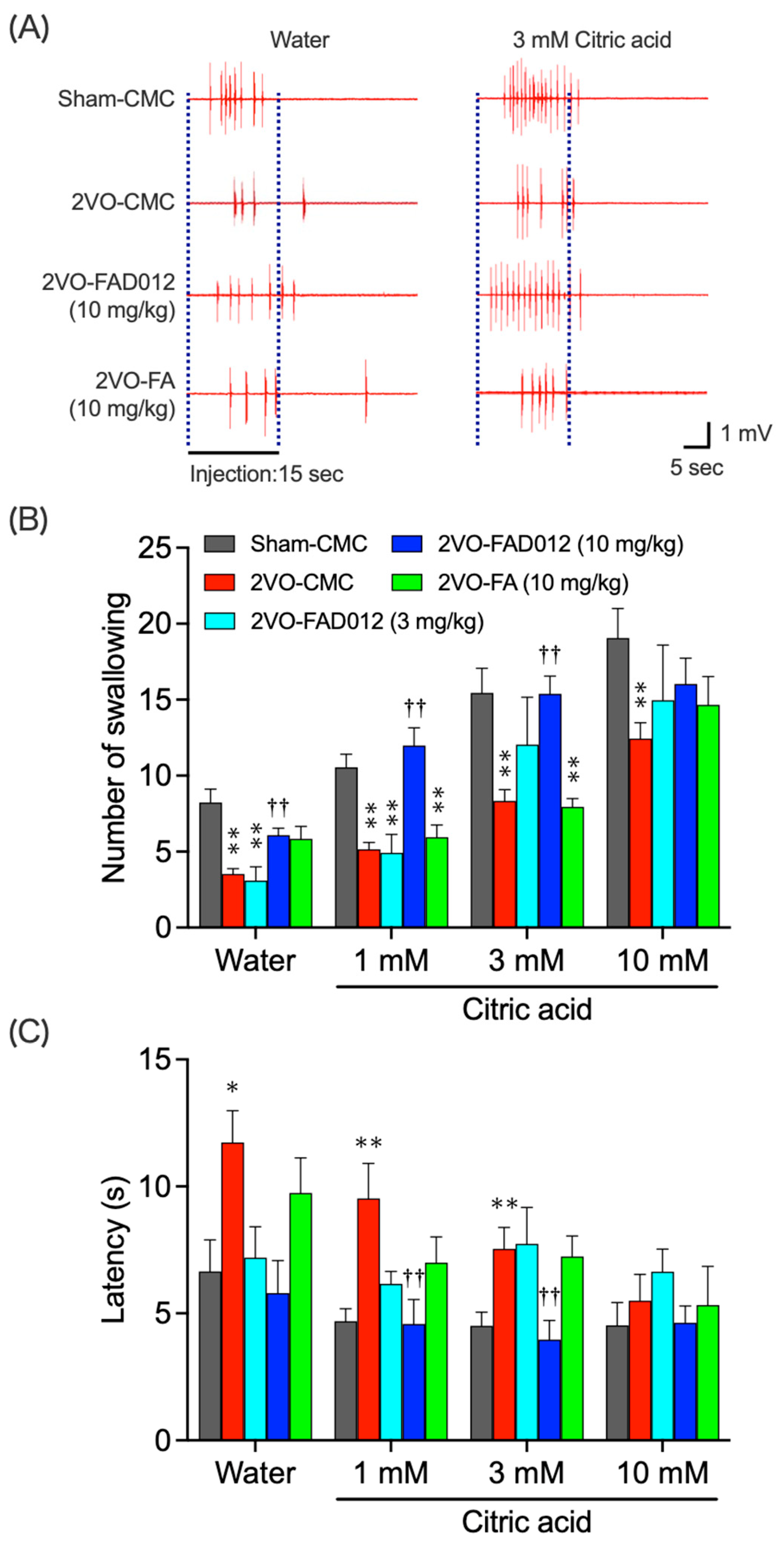
2.3. 2VO-Induced Swallowing Dysfunction
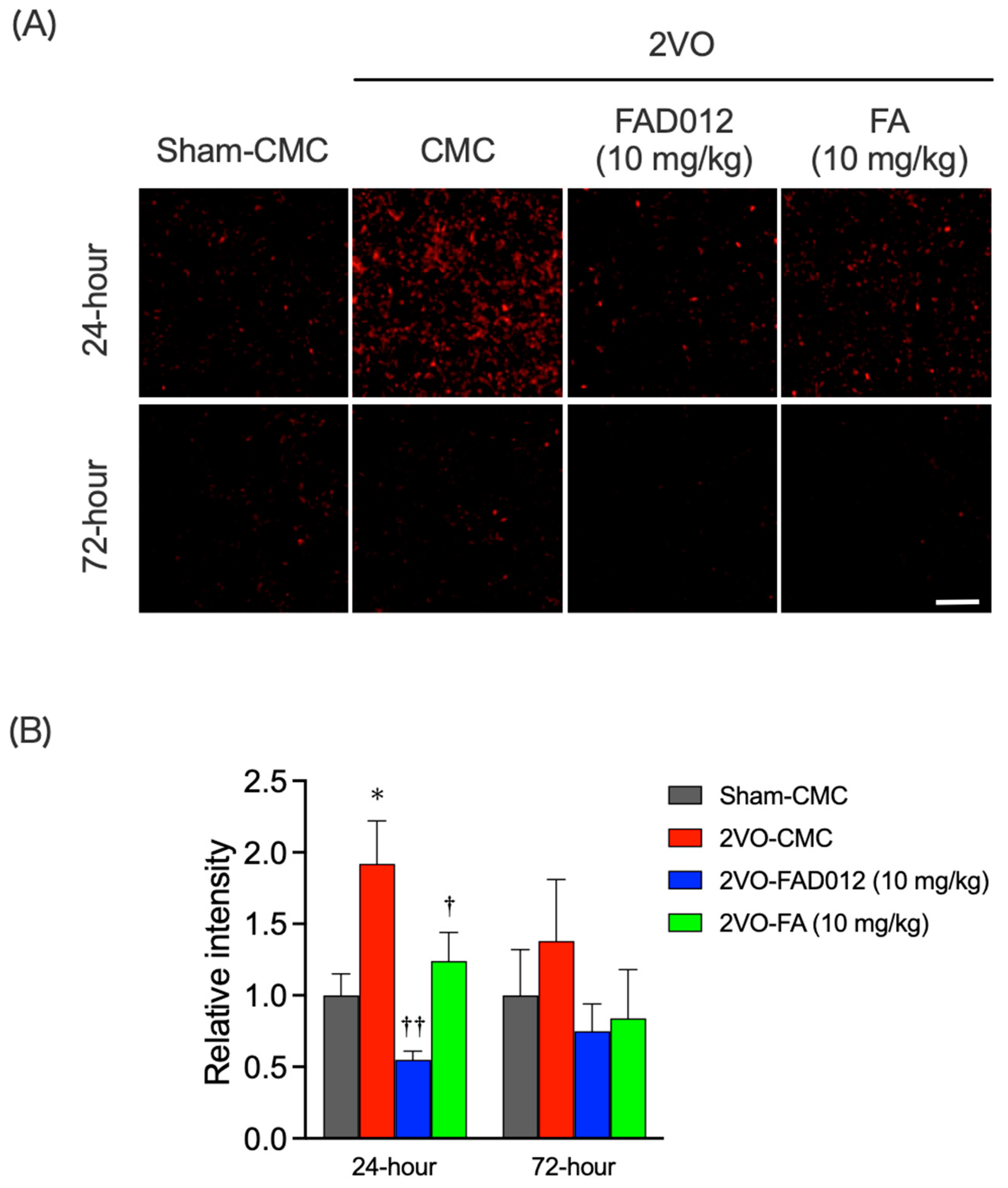
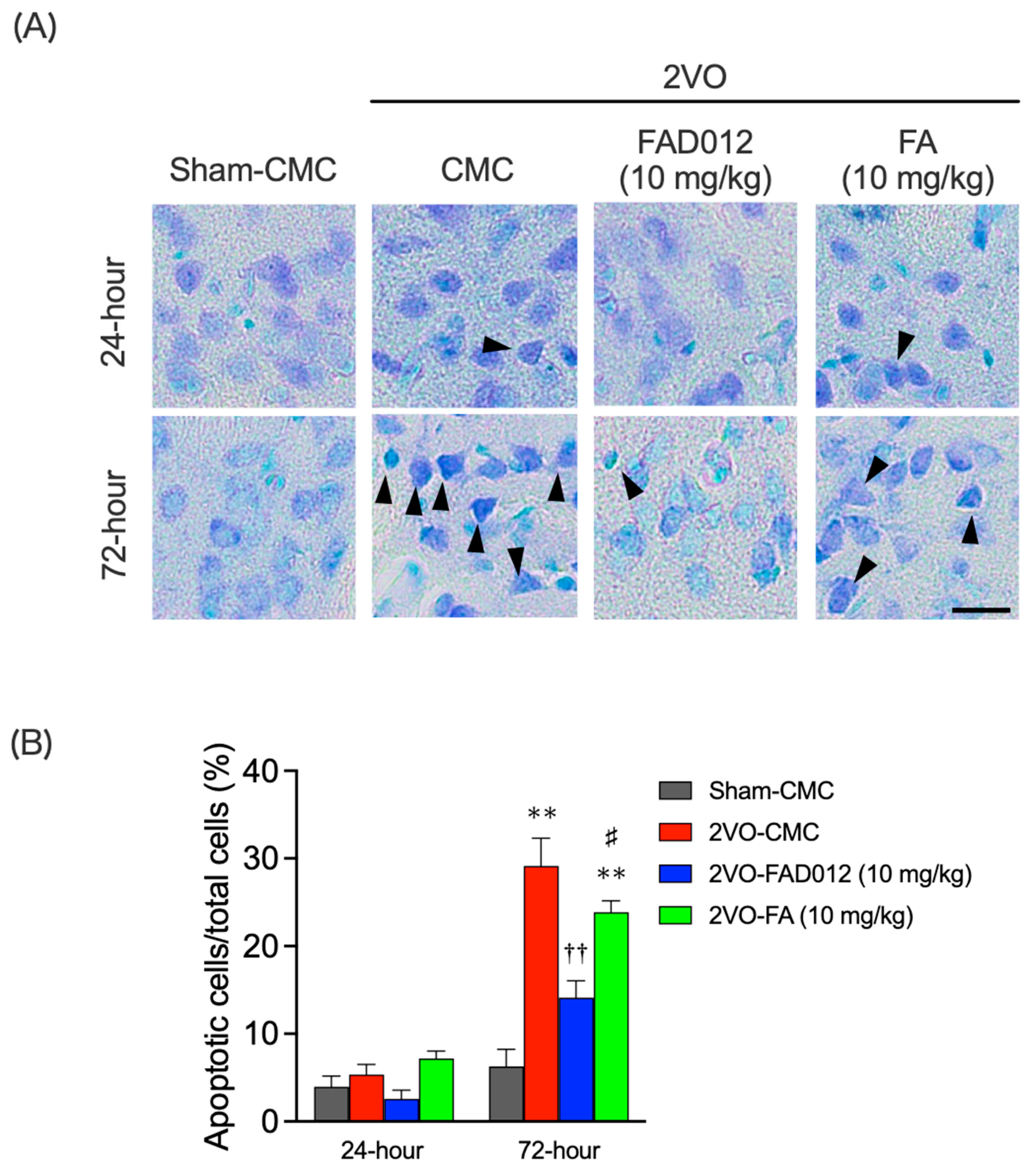
2.4. Oxidative Stress and Apoptotic Cell Death in the Striatum
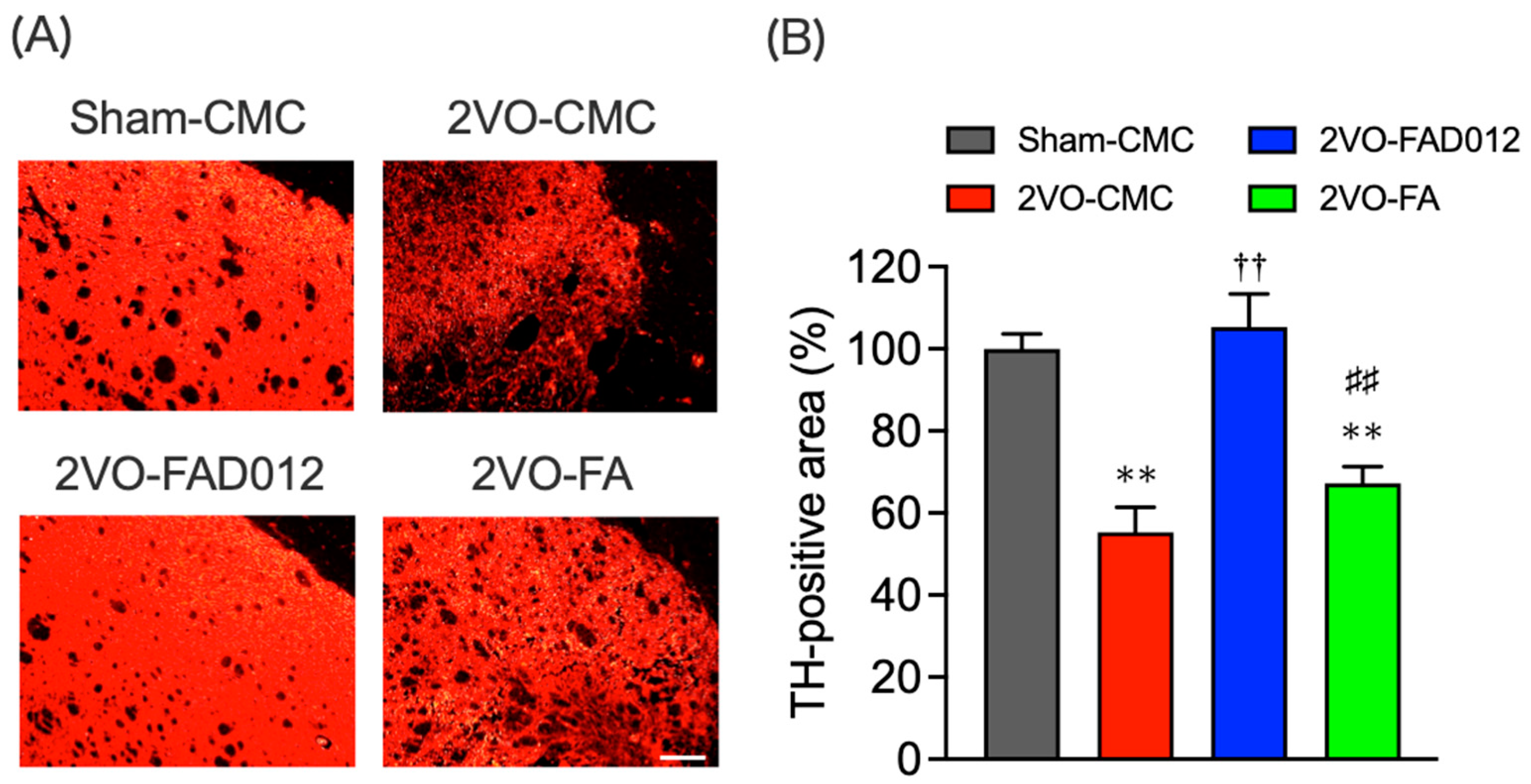
2.5. Tyrosine Hydroxylase (TH) Expression in the Striatum
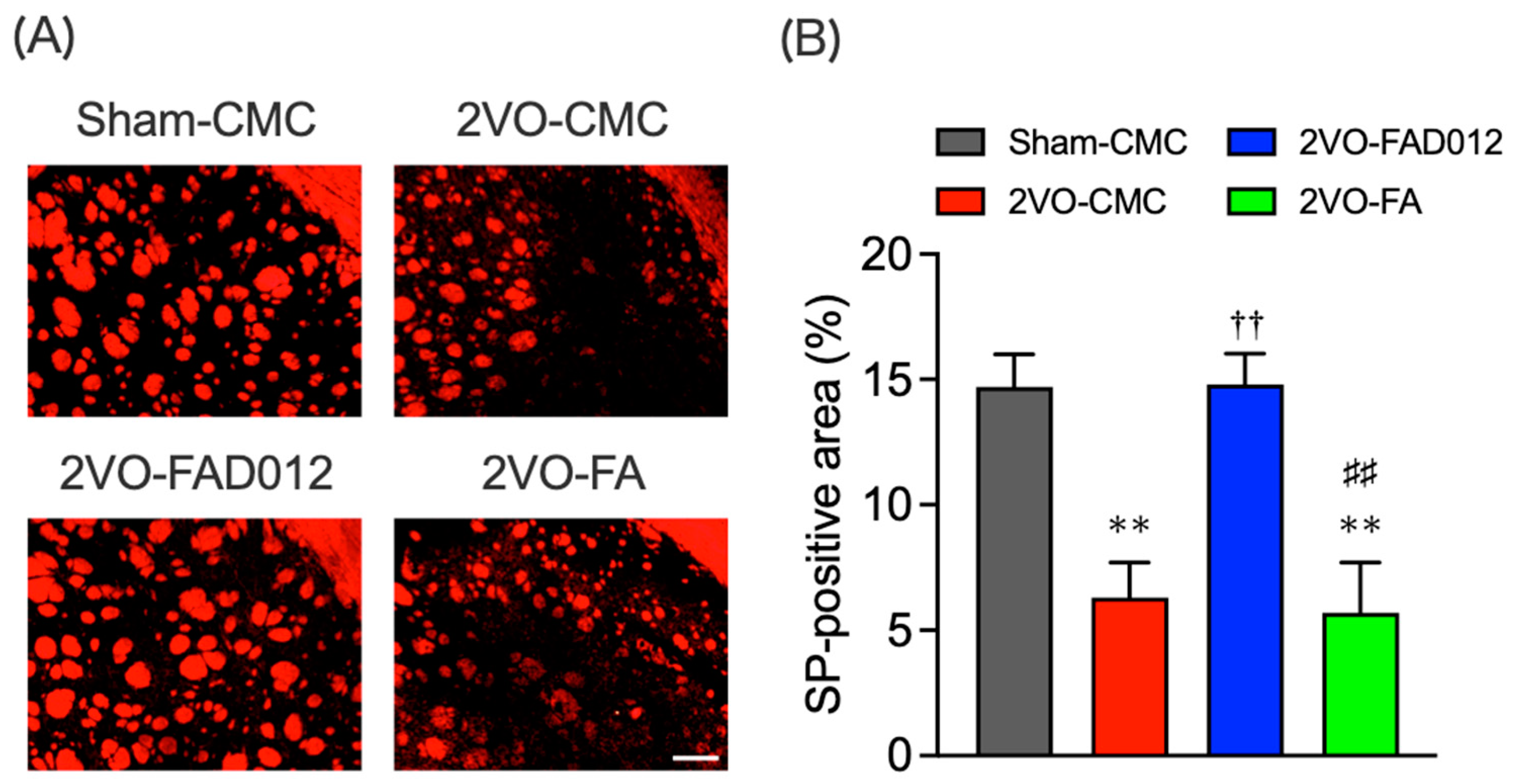
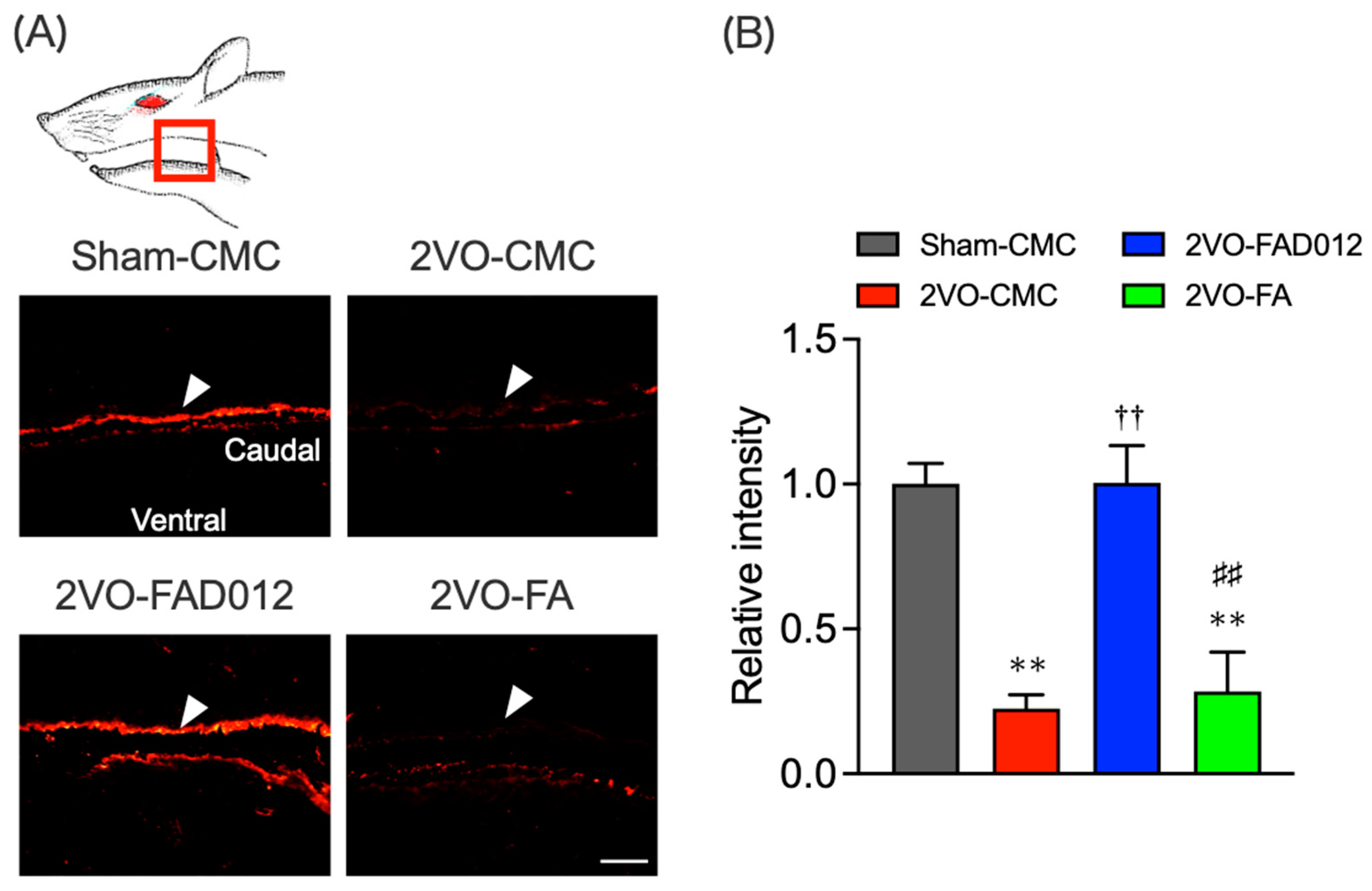
2.6. Substance P (SP) Expression in the Striatum and Laryngopharyngeal Region
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
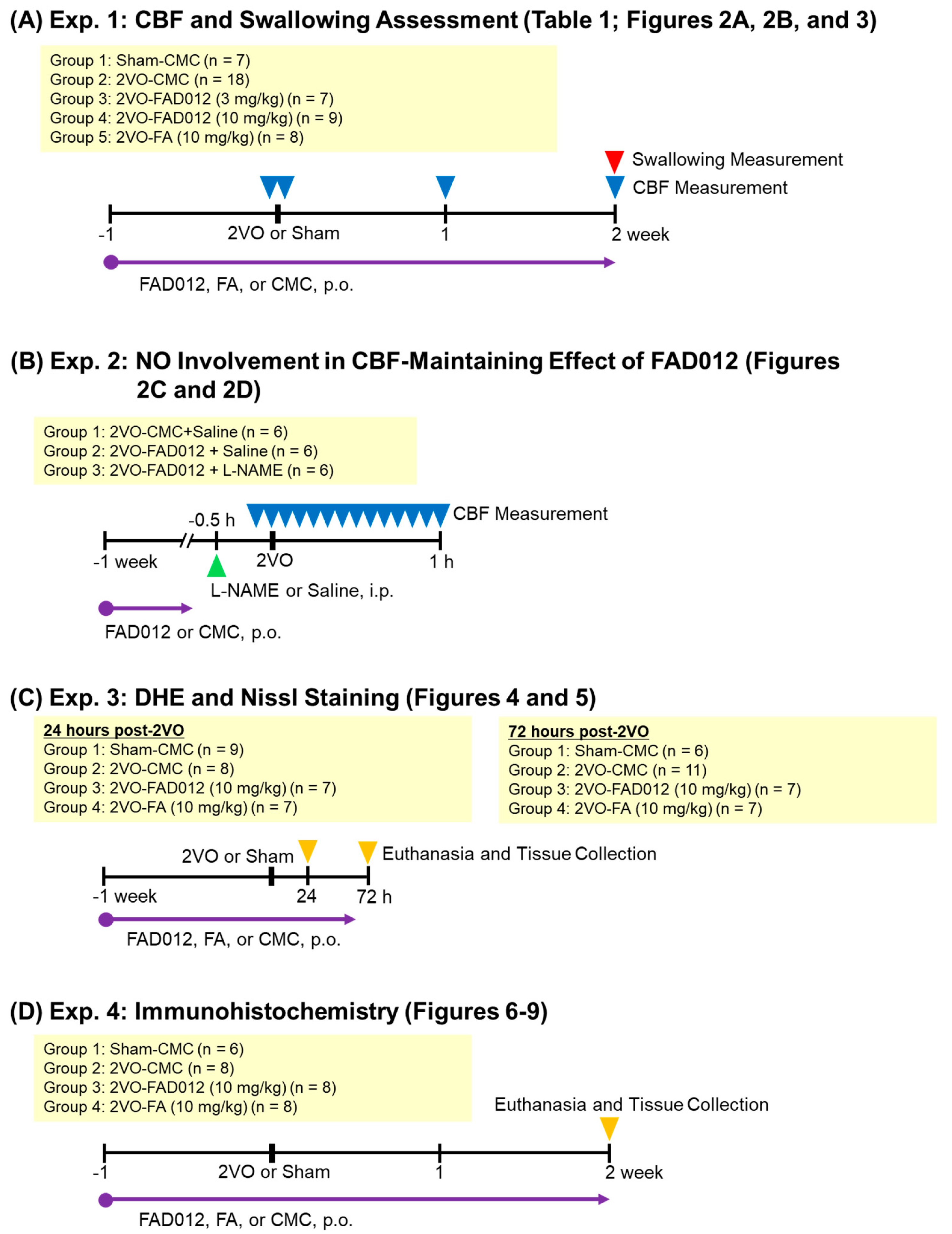
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Animals
4.3. 2VO Procedure [13]
4.4. Measurement of CBF [13]
4.5. Measurement of Swallowing [13,14]
4.6. Perfusion Fixation and Coronal Section Preparation [13]
4.7. Evaluation of O2− Production by Dihydroethidium (DHE) Staining [13]
4.8. Nissl Staining [44]
4.9. Immunohistochemistry [13]
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| CBF | Cerebral blood flow |
| CMC | Carboxymethyl cellulose |
| CPG | Swallowing central pattern generator |
| DHE | Dihydroethidium |
| EMG | Electromyogram |
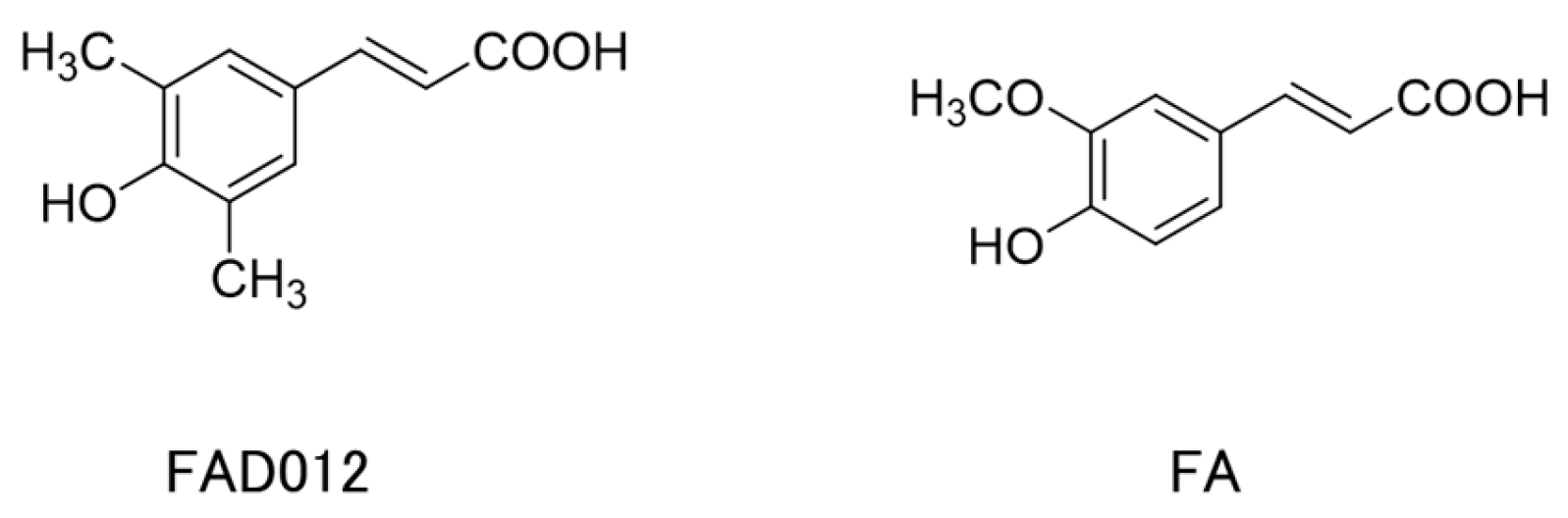
| FA | Ferulic acid; 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid |
| FAD012 | 3,5-Dimethyl-4-hydroxy cinnamic acid |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| MCAO | Middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| L-NAME | NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NOS | NO synthase |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| t-PA | Tissue plasminogen activator |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SP | Substance P |
| TH | Tyrosine hydroxylase |
| 2VO | Ligation of bilateral common carotid arteries |
References
- Johnson, C.O.; Nguyen, M.; Roth, G.A.; Nichols, E.; Alam, T.; Abate, D.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abraha, H.N.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.S.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Barone Gibbs, B.; Beaton, A.Z.; Boehme, A.K.; et al. 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of US and Global Data From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 149, e347–e913. [Google Scholar]
- Hankey, G.J. Long-term outcome after ischaemic stroke/transient ischaemic attack. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2003, 16 (Suppl. S1), 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, R.; Foley, N.; Bhogal, S.; Diamant, N.; Speechley, M.; Teasell, R. Dysphagia after stroke: Incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Stroke 2005, 36, 2756–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.L.; Roffe, C.; Beavan, J.; Blackett, B.; Fairfield, C.A.; Hamdy, S.; Havard, D.; McFarlane, M.; McLauglin, C.; Randall, M.; et al. Post-stroke dysphagia: A review and design considerations for future trials. Int. J. Stroke 2016, 11, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, K.J.; Chu, H.; Kang, X.L.; Liu, D.; Pien, L.C.; Jen, H.J.; Hsiao, S.S.; Chou, K.R. Prevalence of dysphagia and risk of pneumonia and mortality in acute stroke patients: A meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcerak, P.; Corbiere, S.; Zubal, R.; Kägi, G. Post-stroke Dysphagia: Prognosis and Treatment–A Systematic Review of, R.C.T on Interventional Treatments for Dysphagia Following Subacute Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 823189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2019, 50, e344–e418. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, S.; Ogasawara, K.; Kuroda, S.; Itabashi, R.; Toyoda, K.; Itoh, Y.; Iguchi, Y.; Shiokawa, Y.; Takagi, Y.; Ohtsuki, T.; et al. Japan Stroke Society Guideline 2021 for the Treatment of Stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2022, 17, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Rui, Y.X.; Guo, S.D.; Luan, F.; Liu, R.; Zeng, N. Ferulic acid: A review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and derivatives. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Su, S.Y.; Tang, N.Y.; Ho, T.Y.; Chiang, S.Y.; Hsieh, C.L. Ferulic acid provides neuroprotection against oxidative stress-related apoptosis after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ICAM-1 mRNA expression in rats. Brain Res. 2008, 1209, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, E.; Calabrese, V.; Mancuso, C. Ferulic acid and its therapeutic potential as a hormetin for age-related diseases. Biogerontology 2009, 10, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Matsuzaki, H.; Iwata, N.; Xuan, M.; Kamiuchi, S.; Hibino, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Okazaki, M. Protective effects of ferulic acid against chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced swallowing dysfunction in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajii, Y.; Shingai, T.; Kitagawa, J.I.; Takahashi, Y.; Taguchi, Y.; Noda, T.; Yamada, Y. Sour taste stimulation facilitates reflex swallowing from the pharynx and larynx in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 2002, 77, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertekin, C.; Aydogdu, I. Neurophysiology of swallowing. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114, 2226–2244. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Sanchez, F.F.; Cardozo, A.; Castejon, C.; Tolosa, E.; Rossi, M.L. Aging and the nigro-striatal pathway. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 1997, 51, 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.X.; Sekizawa, K.; Ohrui, T.; Nakayama, K.; Sasaki, H. Dopamine D1 receptor antagonist inhibits swallowing reflex in guinea pigs. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1998, 274, R76–R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeon, J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.M.; Cheon, M.; Kim, J.Y. Striatal Dopaminergic Loss and Dysphagia in Parkinson Disease. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2023, 48, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Sekizawa, K.; Fukushima, T.; Morikawa, M.; Nakazawa, H.; Sasaki, H. Capsaicin desensitization inhibits swallowing reflex in guinea pigs. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 149, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, J.; Massey, E.W. Silent aspiration following stroke. Neurology 1988, 38, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takizawa, C.; Gemmell, E.; Kenworthy, J.; Speyer, R. A Systematic Review of the Prevalence of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Stroke, Parkinson’s Disease, Alzheimer’s Disease, Head Injury, and Pneumonia. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suttrup, I.; Warnecke, T. Dysphagia in Parkinson’s Disease. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, T.; Xuan, M.; Iwata, N.; Takayama, J.; Hayashi, K.; Kato, Y.; Aoyama, T.; Sugo, H.; Matsuzaki, H.; Yuan, B.; et al. Involvement of the Restoration of Cerebral Blood Flow and Maintenance of eNOS Expression in the Prophylactic Protective Effect of the Novel Ferulic Acid Derivative FAD012 against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injuries in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramae, H.; Xuan, M.; Yamashita, T.; Takayama, J.; Okazaki, M.; Sakamoto, T. Theoretical study on antioxidant properties of ferulic acid. J. Comput. Chem. Jpn 2018, 17, 150–152. [Google Scholar]
- Osawa, A.; Maeshima, S.; Tanahashi, N. Efficacy of cilostazol in preventing aspiration pneumonia in acute cerebral infarction. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 22, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, N.; Inoue, Y.; Ogata, Y.; Murata, I.; Meiyan, X.; Takayama, J.; Sakamoto, T.; Okazaki, M.; Kanamoto, I. Improvement of the Solubility and Evaluation of the Physical Properties of an Inclusion Complex Formed by a New Ferulic Acid Derivative and γ-Cyclodextrin. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12073–12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Miyamoto, N.; Tanaka, R.; Mochizuki, H.; Hattori, N.; Urabe, T. Activation of tyrosine hydroxylase prevents pneumonia in a rat chronic cerebral hypoperfusion model. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 665–672. [Google Scholar]
- Sivam, S.P.; Cox, J. Postnatal administration of D1 dopamine agonist reverses neonatal dopaminergic lesion-induced changes in striatal enkephalin and substance P systems. Brain Res. 2006, 1073–1074, 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yang, H. Ferulic acid exerts neuroprotective effects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury via antioxidant and anti-apoptotic mechanisms in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugundhan, V.; Arthanari, A.; Parthasarathy, P.R. Protective Effect of Ferulic Acid on Acetylcholinesterase and Amyloid Beta Peptide Plaque Formation in Alzheimer’s Disease: An In Vitro Study. Cureus 2024, 16, e54103. [Google Scholar]
- Karademir, Y.; Mackie, A.; Tuohy, K.; Dye, L. Effects of Ferulic Acid on Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, 2300526. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Peng, Q.; Liu, J.; Alolga, R.N.; Zhou, W. A novel ferulic acid derivative attenuates myocardial cell hypoxia reoxygenation injury through a succinate dehydrogenase dependent antioxidant mechanism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 856, 172417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchetti, D.; Borghi, V.; Gaitan, G.; Herrero, J.F.; Impagnatiello, F. NCX 2057, a novel NO-releasing derivative of ferulic acid, suppresses inflammatory and nociceptive responses in in vitro and in vivo models. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, J.I.; Kojima, N.; Saeki, K.; Ishihara, M.; Takayama, M. Perindopril increases the swallowing reflex by inhibiting substance P degradation and tyrosine hydroxylase activation in a rat model of dysphagia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 746, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, P.O. Ferulic acid modulates nitric oxide synthase expression in focal cerebral ischemia. Lab. Anim. Res. 2012, 28, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.J.; Hu, J.F.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhou, R.; Chen, N.H. Osthole improves chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced cognitive deficits and neuronal damage in hippocampus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 636, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Niizuma, K.; Yoshioka, H.; Chen, H.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.E.; Katsu, M.; Okami, N.; Chan, P.H. Mitochondrial and apoptotic neuronal death signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2010, 1802, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.; Wang, T.; Fu, Y.; Yu, T.; Ding, Y.; Nie, H. Ferulic Acid: A Review of Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutic Effects on Pulmonary Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Sekizawa, K.; Arai, H.; Sasaki, H. Levodopa and swallowing reflex. Lancet 1996, 348, 1320–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, T.; Sekizawa, K.; Yoshimi, N.; Toshima, S.; Fujiwara, H. Cabergoline and silent aspiration in elderly patients with stroke. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51, 1815–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, M.; Isono, C.; Sakamoto, H.; Ueno, S.; Kusunoki, S.; Nakamura, Y. Rotigotine Transdermal Patch Improves Swallowing in Dysphagic Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Dysphagia 2015, 30, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Zhang, N.; Liu, M.; Tanaka, R.; Mizuno, Y.; Urabe, T. Cilostazol protects against brain white matter damage and cognitive impairment in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Stroke 2006, 37, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Komine-Kobayashi, M.; Tanaka, R.; Liu, M.; Mizuno, Y.; Urabe, T. Edaravone reduces early accumulation of oxidative products and sequential inflammatory responses after transient focal ischemia in mice brain. Stroke 2005, 36, 2220–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotactic Coordinates; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]


| Group | Relative Body Weights (%) | Survival Rates (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sham-CMC | 112.6 ± 3.2 | 100 (7/7) |
| 2VO-CMC | 99.2 ± 2.2 * | 66.7 (12/18) |
| 2VO-FAD012 (3 mg/kg) | 102.3 ± 1.3 * | 85.7 (6/7) |
| 2VO-FAD012 (10 mg/kg) | 98.4 ± 1.9 * | 77.8 (7/9) |
| 2VO-FA (10 mg/kg) | 98.8 ± 1.6 * | 87.5 (7/8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asano, T.; Matsuzaki, H.; Xuan, M.; Yuan, B.; Takayama, J.; Sakamoto, T.; Okazaki, M. Chronic Administration with FAD012 (3,5-Dimethyl-4-hydroxycinnamic Acid) Maintains Cerebral Blood Flow and Ameliorates Swallowing Dysfunction After Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073277
Asano T, Matsuzaki H, Xuan M, Yuan B, Takayama J, Sakamoto T, Okazaki M. Chronic Administration with FAD012 (3,5-Dimethyl-4-hydroxycinnamic Acid) Maintains Cerebral Blood Flow and Ameliorates Swallowing Dysfunction After Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073277
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsano, Takashi, Hirokazu Matsuzaki, Meiyan Xuan, Bo Yuan, Jun Takayama, Takeshi Sakamoto, and Mari Okazaki. 2025. "Chronic Administration with FAD012 (3,5-Dimethyl-4-hydroxycinnamic Acid) Maintains Cerebral Blood Flow and Ameliorates Swallowing Dysfunction After Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073277
APA StyleAsano, T., Matsuzaki, H., Xuan, M., Yuan, B., Takayama, J., Sakamoto, T., & Okazaki, M. (2025). Chronic Administration with FAD012 (3,5-Dimethyl-4-hydroxycinnamic Acid) Maintains Cerebral Blood Flow and Ameliorates Swallowing Dysfunction After Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073277







