Protective Effects of Fucoidan on Iodoacetamide-Induced Functional Dyspepsia via Modulation of 5-HT Metabolism and Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
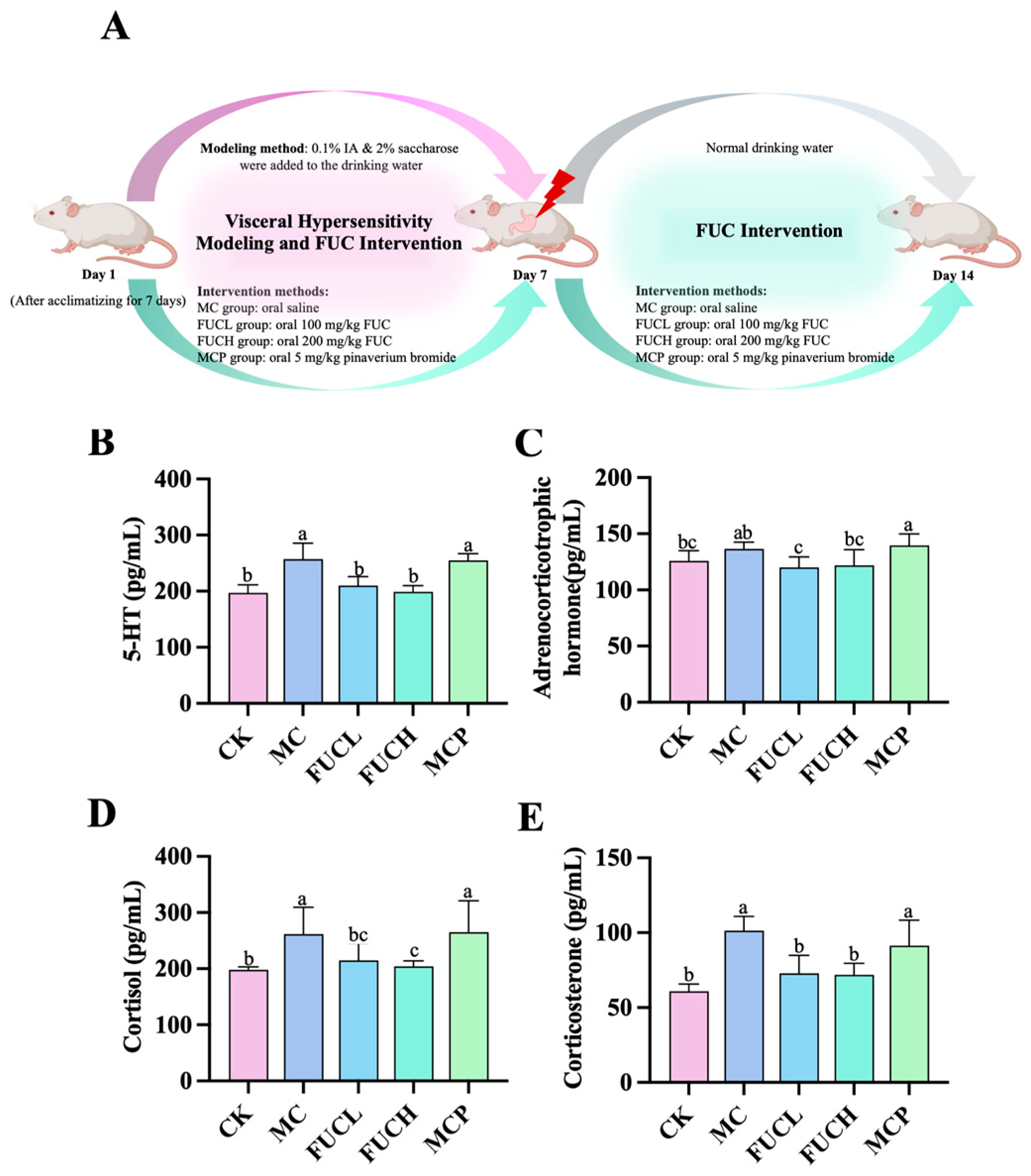
2.1. Effect on Serum 5-HT, ACHT, COL, and CORT
2.2. Effect on the Expression of the 5HT3 Receptor in Stomach, Duodenum, and Brain
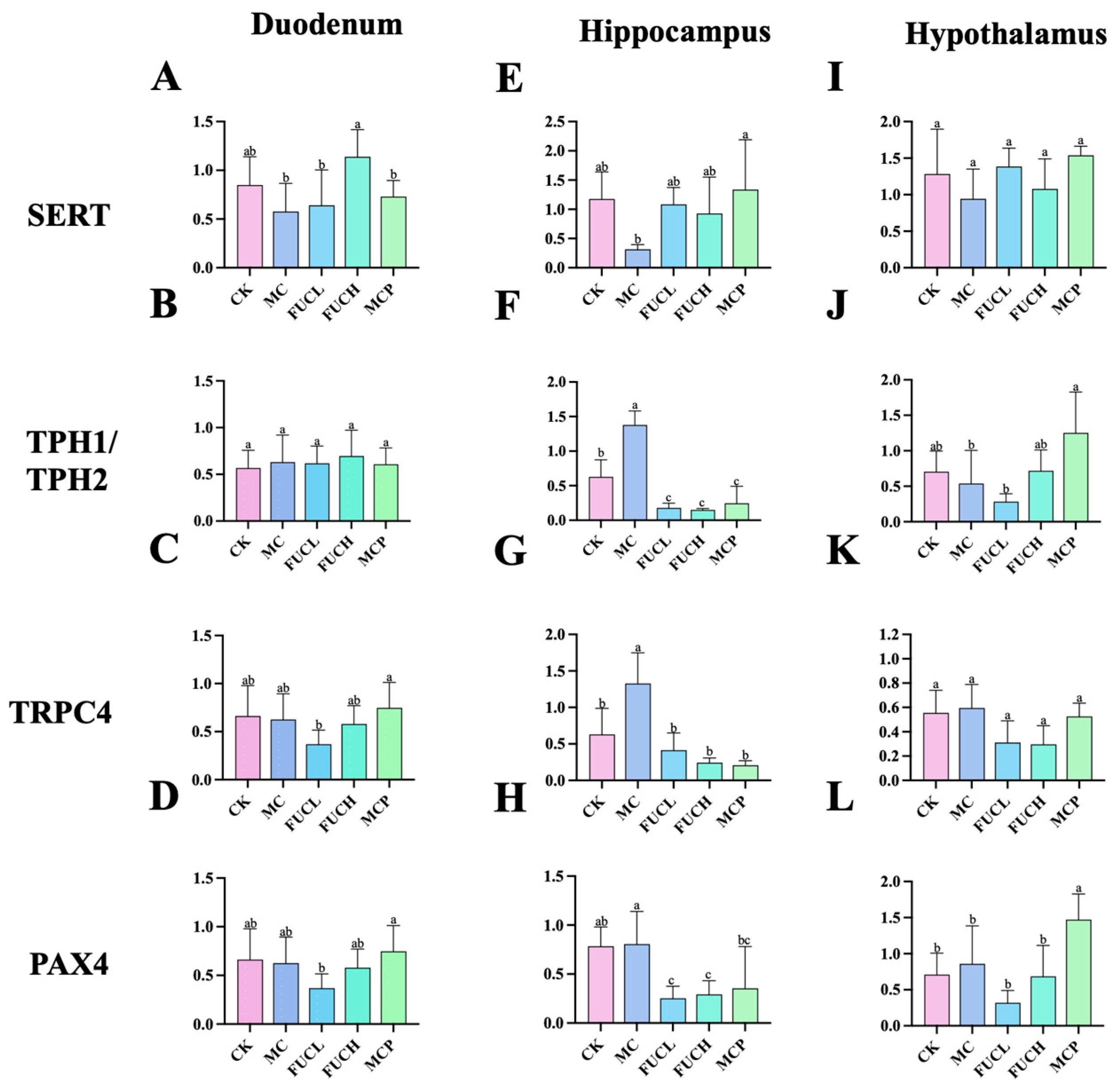
2.3. Effect on the Expression of Key Genes in the Duodenum and Brain
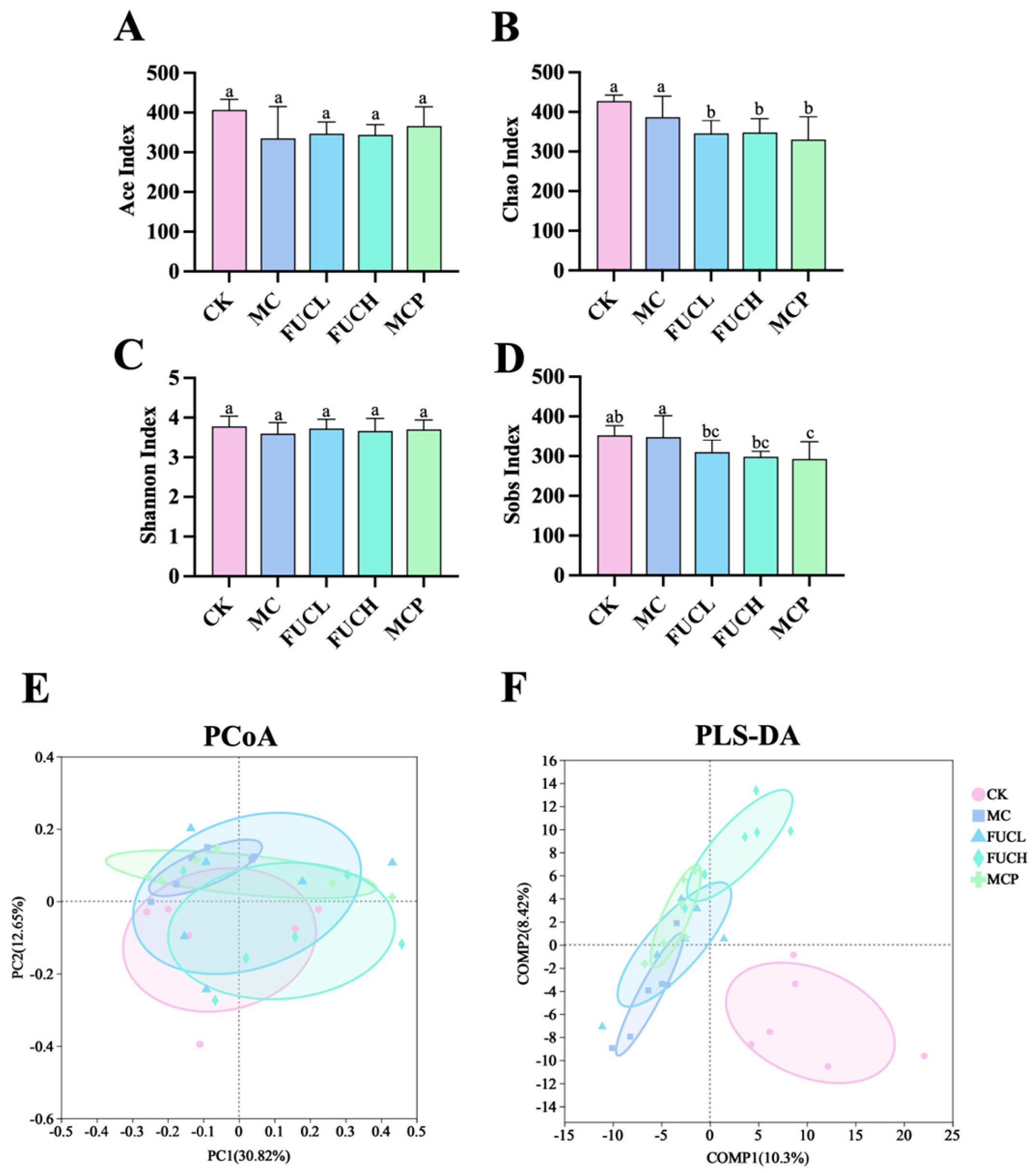
2.4. Effect on Gut Microbiota
2.4.1. Microbial Diversity and Richness
2.4.2. Microbial Composition
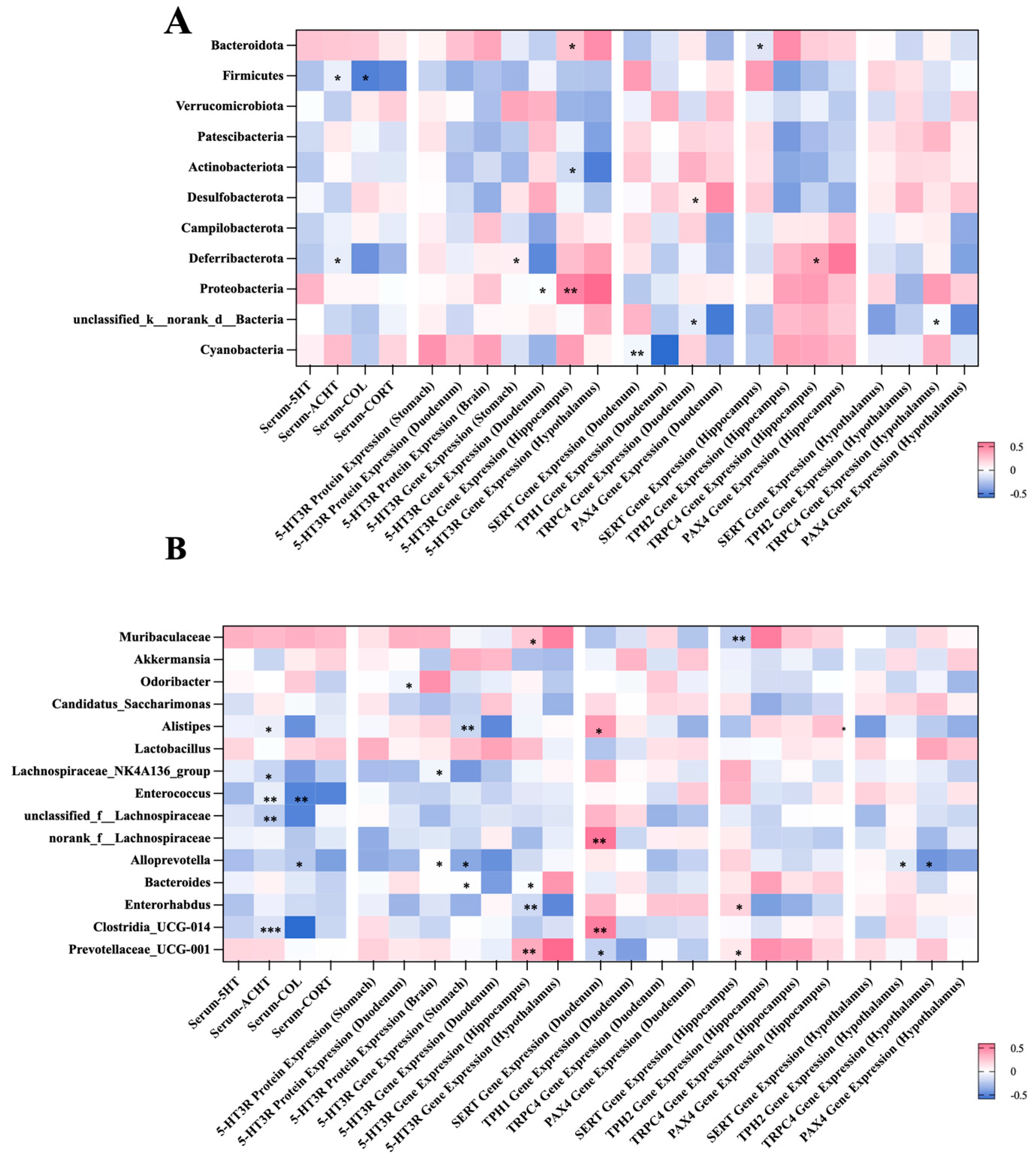
2.5. Correlation Between the Gut Microbial Composition and Visceral Hypersensitivity-Related Indicators
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Animal Experiment: Grouping Design and Intervention Strategy
4.2.1. Animal Maintenance
4.2.2. Animal Treatment
4.3. Serum Biochemical Analysis
4.4. Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence Staining
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.6. Western Blot
4.7. Gut Microbiota Analysis by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Black, C.J.; Drossman, D.A.; Talley, N.J.; Ruddy, J.; Ford, A.C. Functional gastrointestinal disorders: Advances in understanding and management. Lancet 2020, 396, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Kwon, C.I.; Yeniova, A.; Koyanagi, A.; Jacob, L.; Smith, L.; Lee, S.W.; Rahmati, M.; Shin, J.Y.; Shin, J.I.; et al. Global prevalence of functional dyspepsia according to Rome criteria, 1990–2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wauters, L.; Talley, N.J.; Walker, M.M.; Tack, J.; Vanuytsel, T. Novel concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gut 2020, 69, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, B.E.; Everhart, K.; Crowell, M.D. Functional Dyspepsia: Clinical Symptoms, Psychological Findings, and GCSI Scores. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguli, S.C.; Cawdron, R.; Irvine, E.J. Alternative medicine use by Canadian ambulatory gastroenterology patients: Secular trend or epidemic? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahner, E.; Bellentani, S.; Bastiani, R.D.; Tosetti, C.; Cicala, M.; Esposito, G.; Arullani, P.; Annibale, B. A survey of pharmacological and nonpharmacological treatment of functional gastrointestinal disorders. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2013, 1, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, S.H.; Nagle, V.L.; Jagtap, T.G. Antifouling potential of some marine organisms from India against species of Bacillus and Pseudomonas. Mar. Biotechnol. 2002, 4, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlikova, B.; Legrand, N.; Panning, J.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Anti-inflammatory and anticancer drugs from nature. Cancer Treat. Res. 2014, 159, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dring, M.J. The Biology of Marine Plants; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Holdt, S.L.; Kraan, S. Bioactive compounds in seaweed: Functional food applications and legislation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 543–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.D.; Amarante, S.J.; Mateus, N.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Brown Algae Phlorotannins: A Marine Alternative to Break the Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Cancer Network. Foods 2021, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wei, Z.; Xue, C. Alginate-based delivery systems for food bioactive ingredients: An overview of recent advances and future trends. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5345–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, S.L.; Babić Radić, M.M.; Vuković, J.S.; Filipović, V.V.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J.; Vukomanović, M. Alginate-Based Hydrogels and Scaffolds for Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesus Raposo, M.F.; de Morais, A.M.; de Morais, R.M. Marine polysaccharides from algae with potential biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2967–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisha, G.S.; Padmakumari, S.; Patel, A.K.; Pandey, A.; Singhania, R.R. Fucoidan from Marine Macroalgae: Biological Actions and Applications in Regenerative Medicine, Drug Delivery Systems and Food Industry. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xin, S.; Zheng, X.; Lou, L.; Ye, S.; Li, S.; Wu, Q.; Ding, Q.; Ji, L.; Nan, C.; et al. Inhibition of the Occurrence and Development of Inflammation-Related Colorectal Cancer by Fucoidan Extracted from Sargassum fusiforme. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 9463–9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.; Ishaq, M.; Karpiniec, S.; Park, A.; Stringer, D.; Singh, N.; Ratanpaul, V.; Wolfswinkel, K.; Fitton, H.; Caruso, V.; et al. Oral Macrocystis pyrifera Fucoidan Administration Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties and Improves DSS-Induced Colitis in C57BL/6J Mice. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Ko, S.C.; Oh, G.W.; Heo, S.Y.; Jeon, Y.J.; Park, W.S.; Choi, I.W.; Choi, S.W.; Jung, W.K. Anti-inflammatory effects of sodium alginate/gelatine porous scaffolds merged with fucoidan in murine microglial BV2 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1620–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Asif, I.M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Wang, L. Laminarin ameliorates iodoacetamide-induced functional dyspepsia via modulation of 5-HT(3) receptors and the gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268, 131640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piqueras, L.; Corpa, J.M.; Martínez, J.; Martínez, V. Gastric hypersecretion associated to iodoacetamide-induced mild gastritis in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2003, 367, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubashina, O.A.; Sivachenko, I.B.; Busygina, I.I.; Panteleev, S.S. Colitis-induced alterations in response properties of visceral nociceptive neurons in the rat caudal medulla oblongata and their modulation by 5-HT3 receptor blockade. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 142, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakan, T.; Ozkul, C.; Küpeli Akkol, E.; Bilici, S.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Capasso, R. Gut-Brain-Microbiota Axis: Antibiotics and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Nutrients 2021, 13, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarnelli, G.; Vandenberghe, J.; Tack, J. Visceral hypersensitivity in functional disorders of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2004, 36, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarioni, G.; Pesce, M.; Fantin, A.; Sarnelli, G. Complementary and alternative treatment in functional dyspepsia. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, M.; Asif, I.M.; Wu, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, L. The regulatory effects of fucoidan and laminarin on functional dyspepsia mice induced by loperamide. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 6513–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, E.; Wang, T.; Guo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.; Tang, D.; Wei, J.; Yang, H.; Xian, M. Xiaoerfupi alleviates the symptoms of functional dyspepsia by regulating the HTR3A and c-FOS. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Rong, P.; Yang, Y.; Fang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.D.Z.; et al. Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation Improves Visceral Hypersensitivity and Gastric Motility and Depression-like Behaviors via Vago-Vagal Pathway in a Rat Model of Functional Dyspepsia. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oustamanolakis, P.; Tack, J. Dyspepsia: Organic versus functional. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Ye, F.; Foreman, R.D.; Chen, J.D.Z. Effects of electroacupuncture on stress-induced gastric dysrhythmia and mechanisms involving autonomic and central nervous systems in functional dyspepsia. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2020, 319, R106–R113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershon, M.D.; Tack, J. The serotonin signaling system: From basic understanding to drug development for functional GI disorders. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, F.; Zhang, J. Metabolic kinetics of 5-hydroxytryptamine and the research targets of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 2642–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.X.; Chen, Y.; Fu, R.; Liu, S.Y.; Yang, Q.Q.; Shen, T.B. Activation of 5-HT and NR2B contributes to visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome in rats. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 5580–5590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.P.; Figueiredo, H.; Mueller, N.K.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.; Ostrander, M.M.; Choi, D.C.; Cullinan, W.E. Central mechanisms of stress integration: Hierarchical circuitry controlling hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical responsiveness. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2003, 24, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightman, S.L. The neuroendocrinology of stress: A never ending story. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winston, J.H.; Sarna, S.K. Developmental origins of functional dyspepsia-like gastric hypersensitivity in rats. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 570–579.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.W.; Fang, J.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.Y.; Wu, M.Z.; Rong, P.J. Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation Ameliorates Functional Dyspepsia with Depressive-Like Behavior and Inhibits the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis in a Rat Model. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 4719–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Huang, Q.; Tang, X.; Qu, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, L.; Wu, P.; Gong, H.; Xu, Y.; et al. ZhiShiXiaoPi tang inhibits autophagy induced by corticosterone and functional dyspepsia through blockade of the mTOR pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 238, 111836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Tan, R.; Chen, L.; Liang, X.; Li, A.; Qi, C.; Wang, Z. Electroacupuncture can Modify Stress, Low-Grade Inflammation in the Duodenum, and Damage to the Intestinal Barrier in Rats with Functional Dyspepsia through the CRF Signaling Pathway. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2025, 28, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasi, C.; Bellini, M.; Bassotti, G.; Blandizzi, C.; Milani, S. Serotonin receptors and their role in the pathophysiology and therapy of irritable bowel syndrome. Tech. Coloproctol. 2014, 18, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machu, T.K. Therapeutics of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists: Current uses and future directions. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 130, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, K.N. Role of central vagal 5-HT3 receptors in gastrointestinal physiology and pathophysiology. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Lin, M.; Tang, Y.; Chen, A.; Wu, B.; Lin, C. Dorsoventral hippocampus distinctly modulates visceral sensitivity and anxiety behaviors in male IBS-like rats. J. Neurosci. Res. 2024, 102, e25288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.Y.; Ku, S.K.; Kim, H.J.; Han, J.S. Low molecular weight fucoidan ameliorating the chronic cisplatin-induced delayed gastrointestinal motility in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 4468–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Pan, H.; Rothman, T.P.; Wade, P.R.; Gershon, M.D. Guinea pig 5-HT transporter: Cloning, expression, distribution, and function in intestinal sensory reception. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, G433–G448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, K.B.; Parry, L.J.; Bornstein, J.C. Strain-specific genetics, anatomy and function of enteric neural serotonergic pathways in inbred mice. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, S.; Kohen, R.; Cain, K.C.; Jarrett, M.E.; Heitkemper, M.M. Associations of tryptophan hydroxylase gene polymorphisms with irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 233–239.e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Kang, C.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, P.; Liu, H.; Hou, Y.; Su, P.; Yang, F.; Wei, Y.; et al. Association study of serotonin transporter SLC6A4 gene with Chinese Han irritable bowel syndrome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; Sun, T.; Jiang, W.; Hu, N.; Yang, P.; Luo, L.; Ren, J.; et al. Costunolide ameliorates intestinal dysfunction and depressive behaviour in mice with stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome via colonic mast cell activation and central 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4142–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, X.; Tian, J.; Xiao, Y.; Tian, T.; Xu, F.; Hong, X.; Zhu, M.X. TRPC channels: Structure, function, regulation and recent advances in small molecular probes. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 209, 107497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Sung, T.S.; Jeon, D.; Park, K.J.; Jun, J.Y.; So, I.; Hong, C. Inhibition of TRPC4 channel activity in colonic myocytes by tricyclic antidepressants disrupts colonic motility causing constipation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 4911–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beucher, A.; Gjernes, E.; Collin, C.; Courtney, M.; Meunier, A.; Collombat, P.; Gradwohl, G. The homeodomain-containing transcription factors Arx and Pax4 control enteroendocrine subtype specification in mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, C. Modified Liu-Jun-Zi decoction alleviates visceral hypersensitivity in functional dyspepsia by regulating EC cell-5HT3r signaling in duodenum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 250, 112468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, F.A.; Sachs, D.; Costa, V.V.; Fagundes, C.T.; Cisalpino, D.; Cunha, T.M.; Ferreira, S.H.; Cunha, F.Q.; Silva, T.A.; Nicoli, J.R.; et al. Commensal microbiota is fundamental for the development of inflammatory pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2193–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouzet, L.; Gaultier, E.; Del’Homme, C.; Cartier, C.; Delmas, E.; Dapoigny, M.; Fioramonti, J.; Bernalier-Donadille, A. The hypersensitivity to colonic distension of IBS patients can be transferred to rats through their fecal microbiota. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, e272–e282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusceddu, M.M.; Murray, K.; Gareau, M.G. Targeting the Microbiota, from Irritable Bowel Syndrome to Mood Disorders: Focus on Probiotics and Prebiotics. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2018, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, X.; Ding, F.; Mo, X.; Zhu, W.; Bian, Q.; Zou, X.; et al. Qi-Zhi-Wei-Tong granules alleviates chronic non-atrophic gastritis in mice by altering the gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, G.; Shu, Y.; Hou, X.; Yang, L.; Jin, Y. Circadian dysregulation induces alterations of visceral sensitivity and the gut microbiota in Light/Dark phase shift mice. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 935919. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, F.; Zhou, H.; Song, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, H. Sodium alginate and galactooligosaccharides ameliorate metabolic disorders and alter the composition of the gut microbiota in mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 215, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Pan, R.; Lin, G.; Liang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, G. Lactic acid bacteria alleviate liver damage caused by perfluorooctanoic acid exposure via antioxidant capacity, biosorption capacity and gut microbiota regulation. Ecotoxicol Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.Y.; Liu, H.M.; Leu, Y.L.; Hsu, C.H.; Lee, T.Y. Modulation of Gut Microbiota Combined with Upregulation of Intestinal Tight Junction Explains Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Corylin on Colitis-Associated Cancer in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; McLean, J.S.; Edlund, A.; Yooseph, S.; Hall, A.P.; Liu, S.Y.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Esquenazi, E.; Hunter, R.C.; Cheng, G.; et al. Cultivation of a human-associated TM7 phylotype reveals a reduced genome and epibiotic parasitic lifestyle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Su, T.; Chen, W.; Wang, D.; Xue, Y.; Lu, Q.; Jiang, C.; Ni, Q.; Mao, E.; Peng, Y. Clostridioides difficile aggravates dextran sulfate solution (DSS)-induced colitis by shaping the gut microbiota and promoting neutrophil recruitment. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2192478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, E.; Ono, E. Differential effects of different diets on depressive-like phenotypes in C57BL/JJmsSLc mice. Physiol. Behav. 2022, 243, 113623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Yan, J.; Yu, Y.; Shan, X.; Zhang, R.; Xing, H.; Zhang, T.; et al. Alterations of intestinal mucosal barrier, cecal microbiota diversity, composition, and metabolites of yellow-feathered broilers under chronic corticosterone-induced stress: A possible mechanism underlying the anti-growth performance and glycolipid metabolism disorder. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0347323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Yin, J.; Liuqi, S.; Wang, J.; Peng, B.; Wang, S. Fucoidan Ameliorated Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 14864–14876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liang, X.; Xue, M. Fucoidan Oligosaccharide Supplementation Relieved Kidney Injury and Modulated Intestinal Homeostasis in D-Galactose-Exposed Rats. Nutrients 2025, 17, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Liu, S.; Luo, Y.; Pu, J.; Deng, X.; Zhou, W.; Dong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, F.; et al. Procyanidin B2 alleviates uterine toxicity induced by cadmium exposure in rats: The effect of oxidative stress, inflammation, and gut microbiota. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arseneau, J.R.; Steeves, R.; Laflamme, M. Modified low-salt CTAB extraction of high-quality DNA from contaminant-rich tissues. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| 5-HT3R | (5′-3′)-forward GCTATCCTCCATCCGCCACTTC |
| (5′-3′)-reverse CGAGCACAGCCAGCAGGTAG | |
| 5-HT4R | (5′-3′)-forward GCTATCCTCCATCCGCCACTTC |
| (5′-3′)-reverse CGAGCACAGCCAGCAGGTAG | |
| SERT | (5′-3′)-forward ATGGCTGAGATGAGGAACGAAGAC |
| (5′-3′)-reverse AAGAATGTGGATGCTGGCATGTTAG | |
| TPH1 | (5′-3′)-forward GGCTGAGGATGCGTCAACATTAAC |
| (5′-3′)-reverse CCTCTTAGTCGCTGTCTGCTGTC | |
| TPH2 | (5′-3′)-forward CCTGATGTGGCAATGACCTAAGTG |
| (5′-3′)-reverse CAGAGACAGAGACAGAGACAGAGAG | |
| TRPC4 | (5′-3′)-forward AGAGCGAAGGTAATGGCAAGGAC |
| (5′-3′)-reverse GCACCACCAGGGCGAAC | |
| PAX4 | (5′-3′)-forward CTCCTGAGTGAAGGCTCTGTGAAG |
| (5′-3′)-reverse TGCTGGTGGTCTGGTCTTGTAAC | |
| -actin | (5′-3′)-forward GATGGTGGGAATGGGTCAGAAGG |
| (5′-3′)-reverse TTGTAGAAGGTGTGGTGCCAGATC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Ma, M.; Wu, Y.; Asif, I.M.; Chen, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, L. Protective Effects of Fucoidan on Iodoacetamide-Induced Functional Dyspepsia via Modulation of 5-HT Metabolism and Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073273
Liu T, Ma M, Wu Y, Asif IM, Chen D, Liu L, Zhang M, Chen Y, Li B, Wang L. Protective Effects of Fucoidan on Iodoacetamide-Induced Functional Dyspepsia via Modulation of 5-HT Metabolism and Microbiota. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073273
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tianxu, Muyuan Ma, Yonglin Wu, Ismail Muhammad Asif, Daosen Chen, Lichong Liu, Minghui Zhang, Yijie Chen, Bin Li, and Ling Wang. 2025. "Protective Effects of Fucoidan on Iodoacetamide-Induced Functional Dyspepsia via Modulation of 5-HT Metabolism and Microbiota" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073273
APA StyleLiu, T., Ma, M., Wu, Y., Asif, I. M., Chen, D., Liu, L., Zhang, M., Chen, Y., Li, B., & Wang, L. (2025). Protective Effects of Fucoidan on Iodoacetamide-Induced Functional Dyspepsia via Modulation of 5-HT Metabolism and Microbiota. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073273






