PTEN: A Novel Diabetes Nephropathy Protective Gene Related to Cellular Senescence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
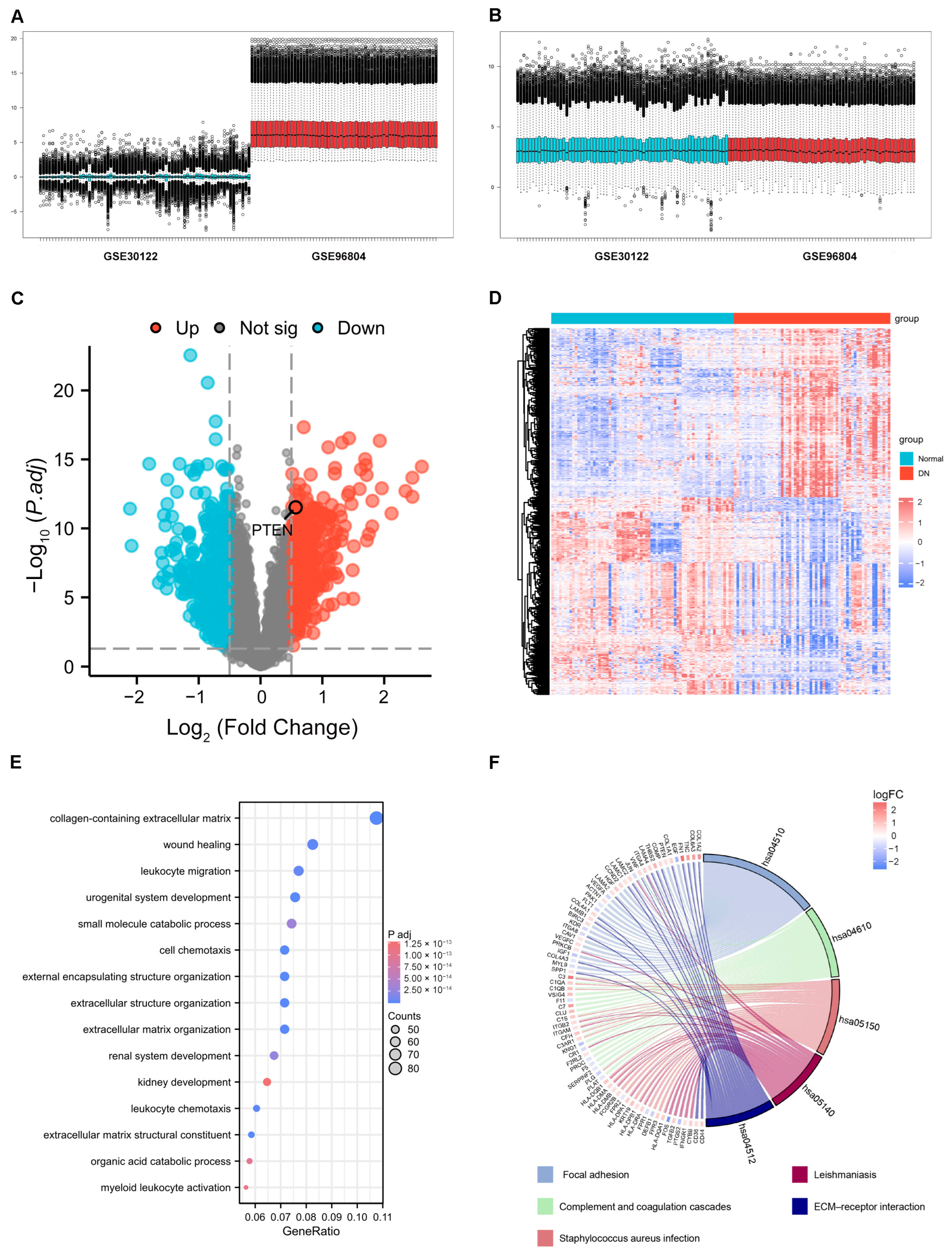
2.1. Identification of DEGs
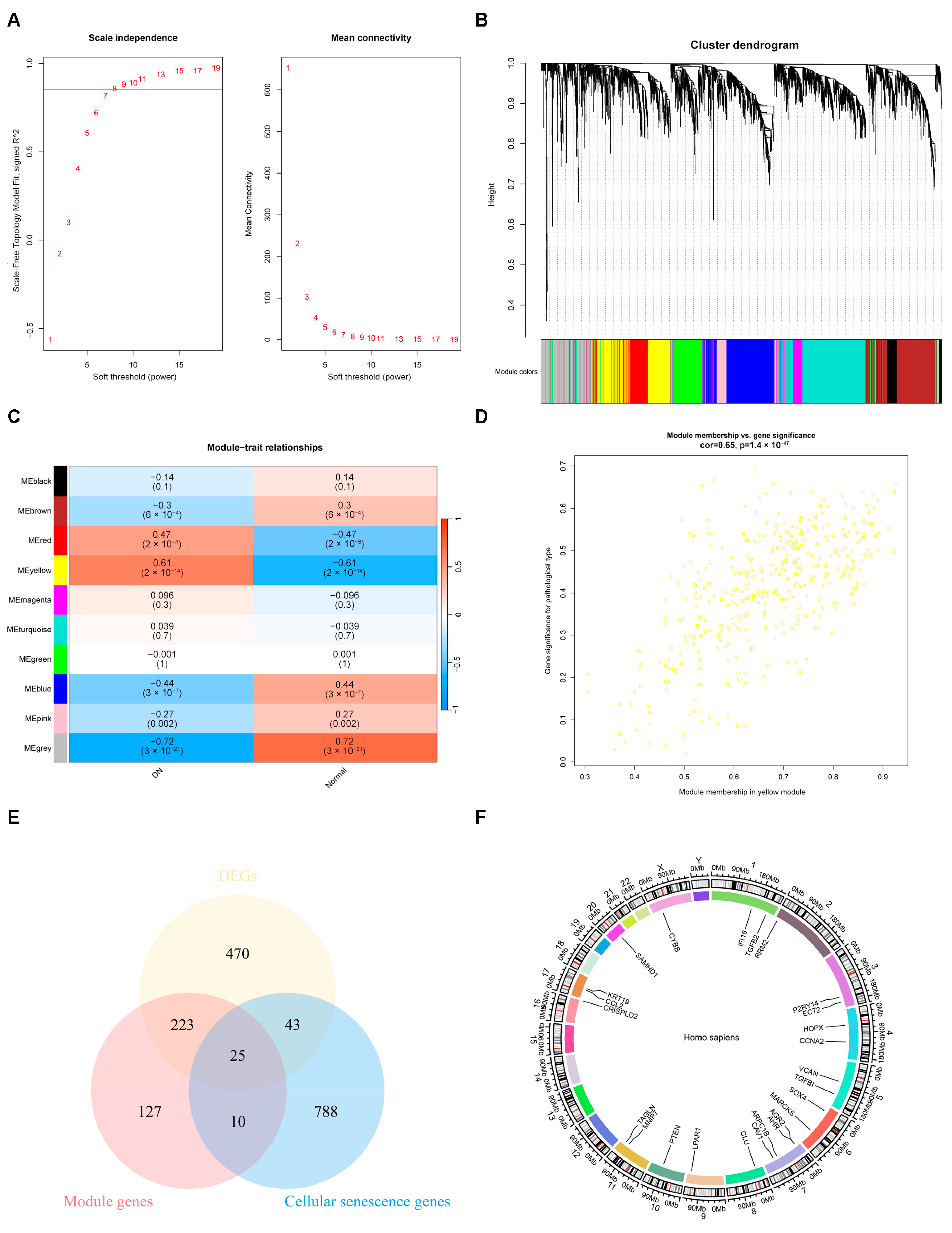
2.2. The Result of Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis
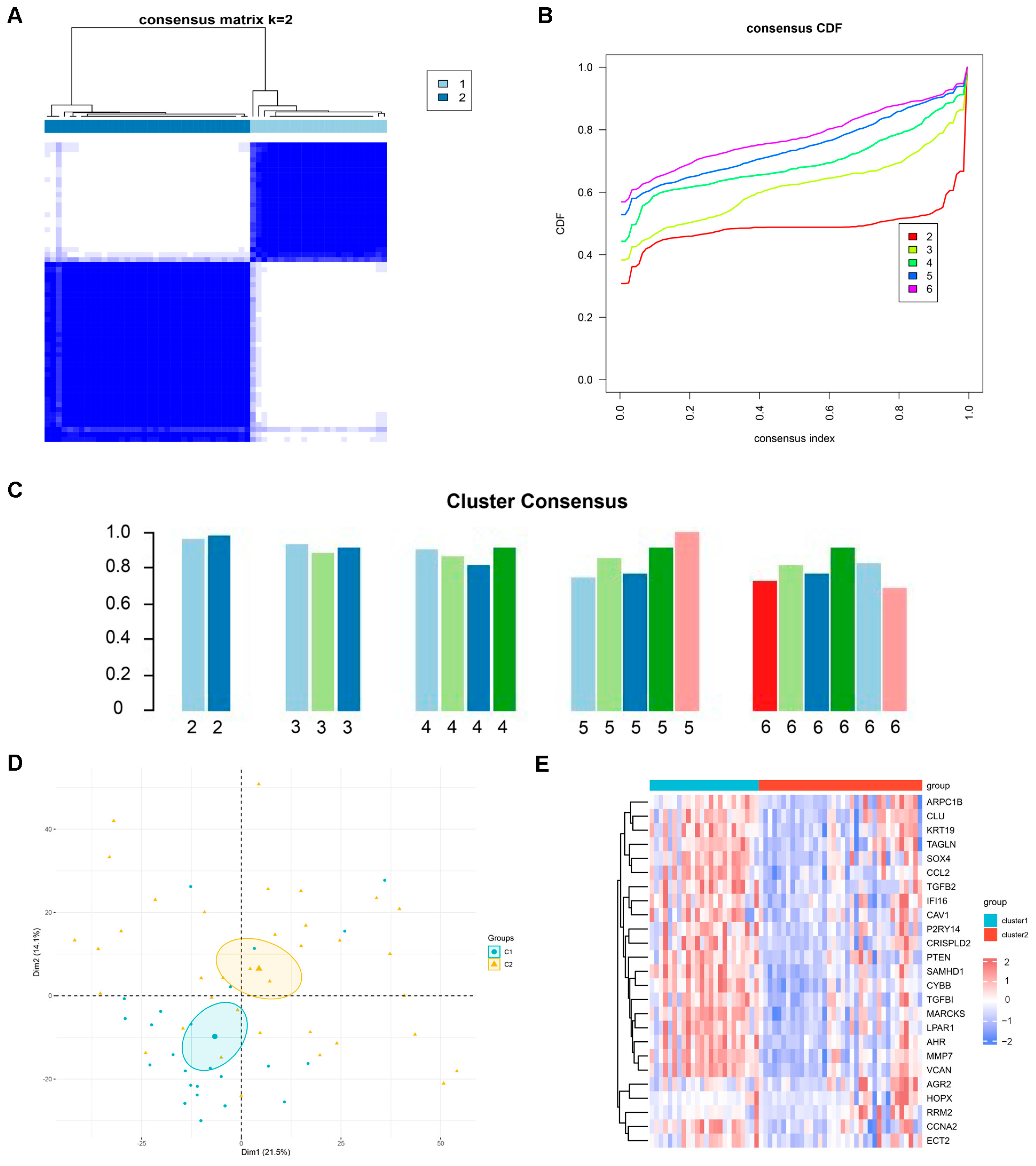
2.3. Identification of Potential Subtypes of DN
2.4. Identification Diagnosis Genes Through Machine Learning and Validation
2.5. PPI Network Construction and Important Module Analysis
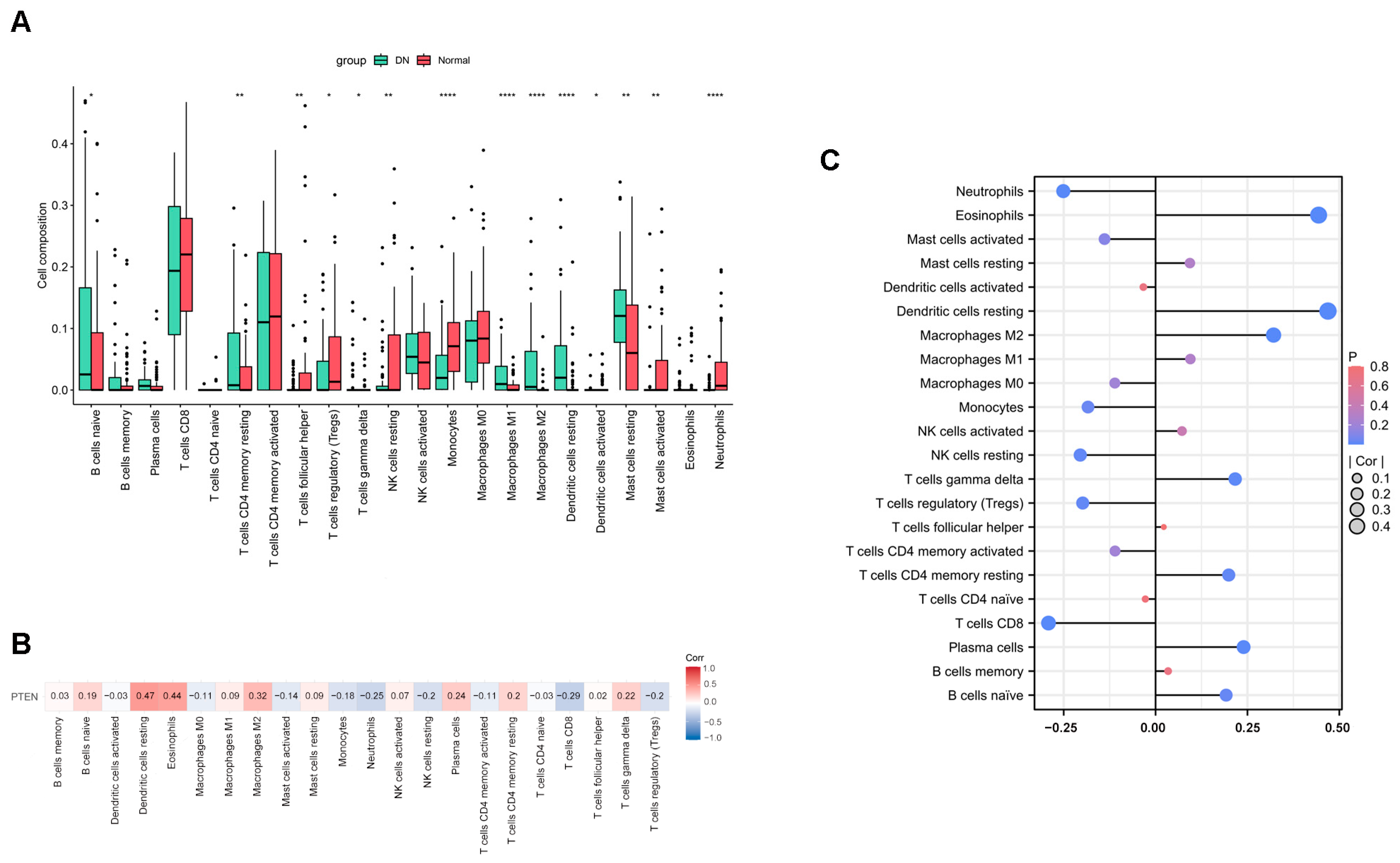
2.6. The Result of Immune Infiltration Analysis
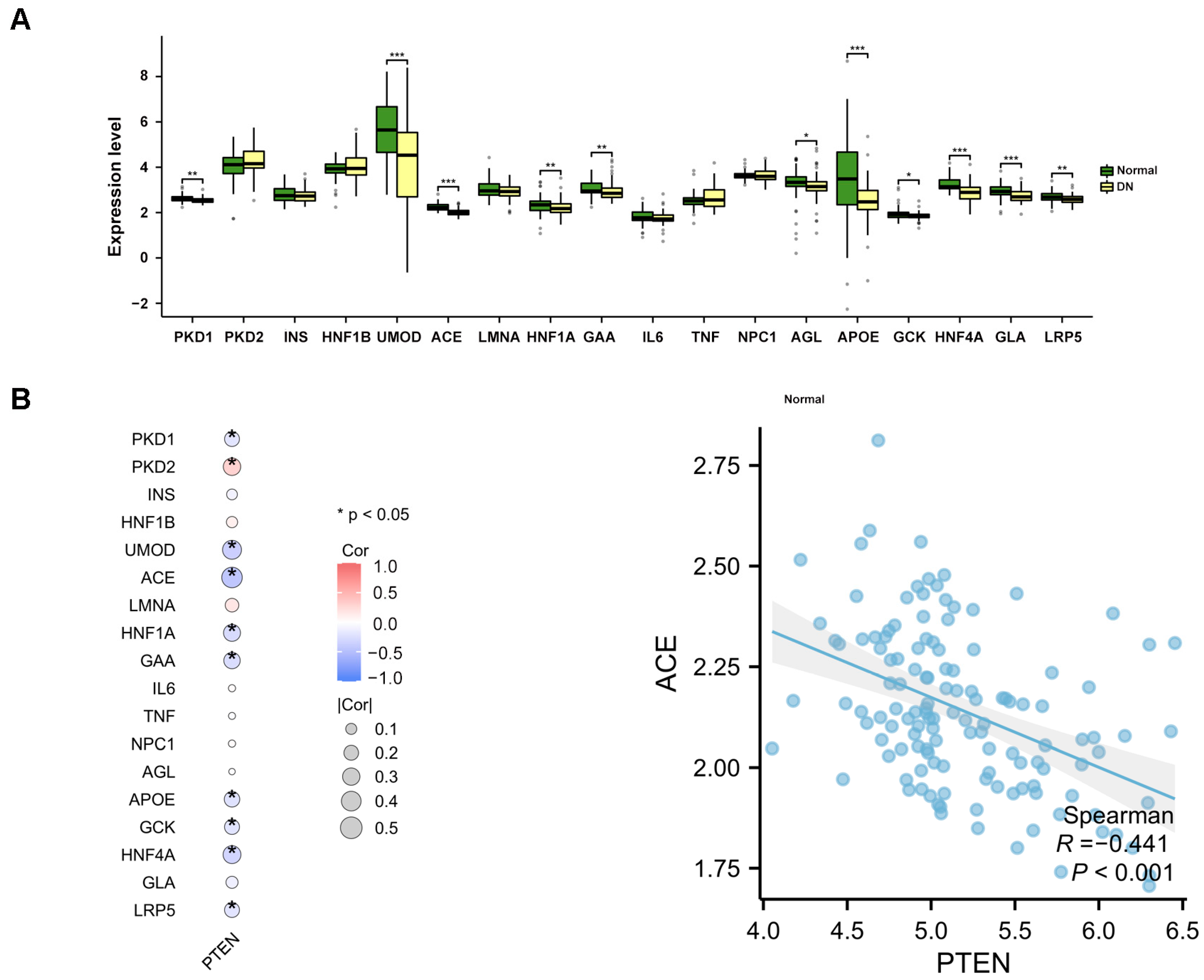
2.7. The Study of Disease Gene Expression Levels
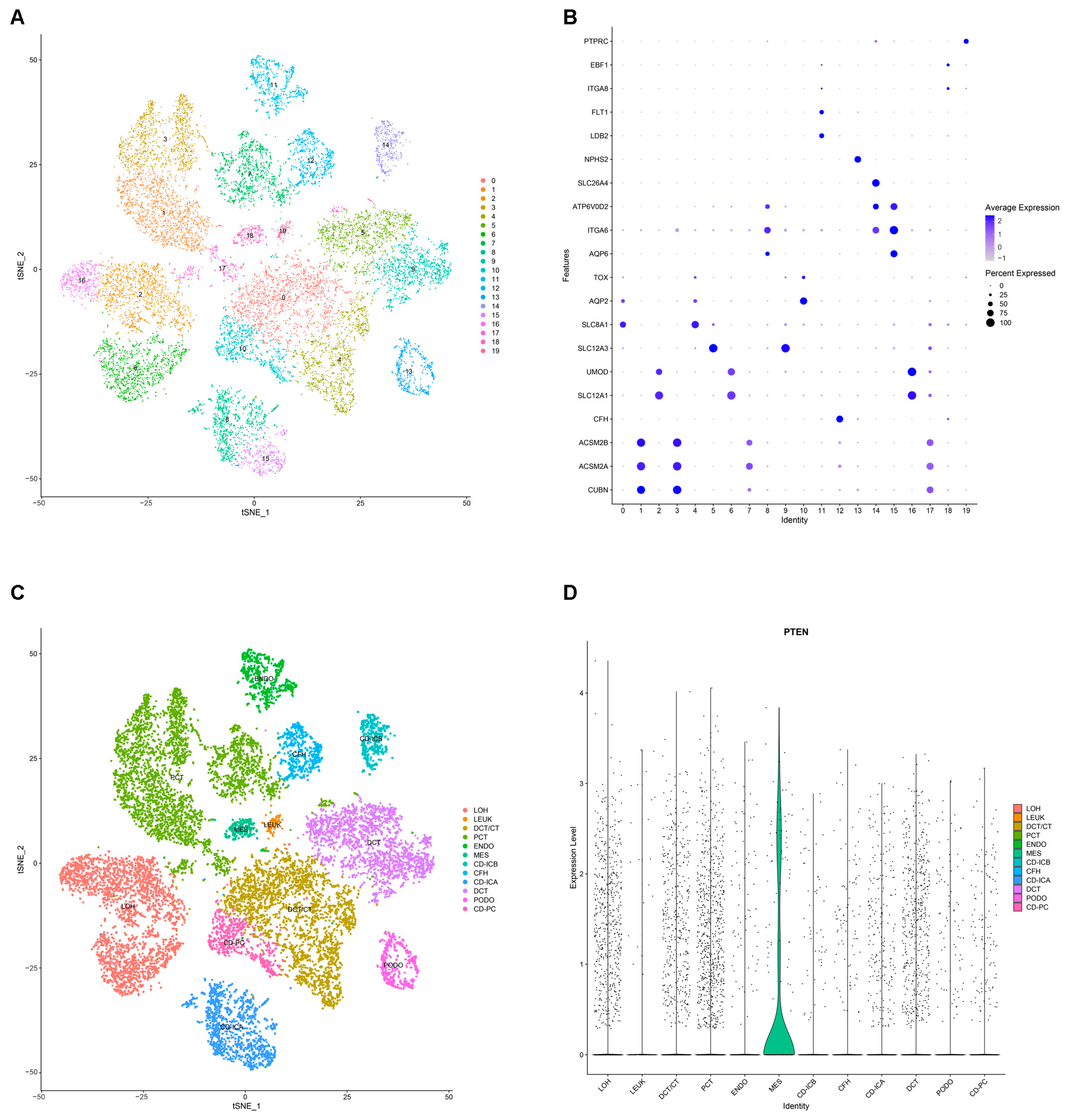
2.8. Annotation and Analysis of Cluster Subtypes of Single-Cell Data
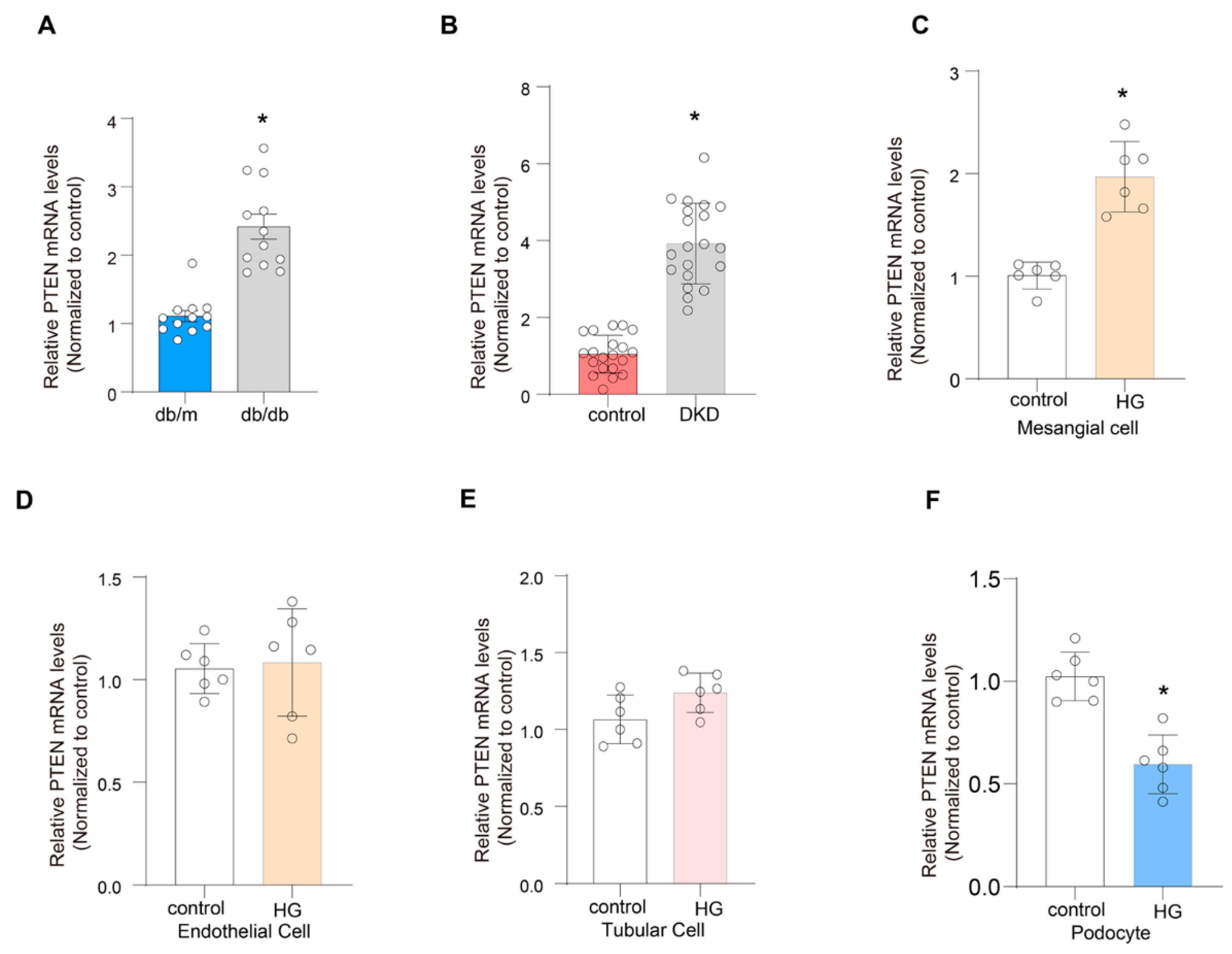
2.9. Validation of the Expression of PTEN
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Renal Biopsy Samples
4.2. Animal Studies
4.3. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.4. Data Sources
4.5. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes and Functional Enrichment Analysis
4.6. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis
4.7. Clustering Analysis to Identify the Potential Subtypes of DN
4.8. The Construction of a PPI Network
4.9. Diagnostic Genes Identified via Machine Learning
4.10. Immune Infiltration Analysis
4.11. Single Nucleus RNA Sequencing
4.12. Real-Time RT-PCR
4.13. Quantification and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liao, L.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z. Identification and Validation of Immune and Cuproptosis—Related Genes for Diabetic Nephropathy by WGCNA and Machine Learning. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1332279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Zhou, T.; Hou, W.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, S.; Song, Y. Isoliquiritigenin Protects Against Diabetic Nephropathy in db/db Mice by Inhibiting Advanced Glycation End Product-Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Product Axis. Drug Dev. Res. 2025, 86, e70051. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Xu, H.; Su, C.; Dong, W.; Xiao, M.; Xiao, N.; Jia, Y.; Xue, Y. Polo-like Kinase2 Regulates Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis via Notch Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Kidney Disease. FASEB J. 2025, 39, e70455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandelbrot, D.A.; Reese, P.P.; Garg, N.; Thomas, C.P.; Rodrigue, J.R.; Schinstock, C.; Doshi, M.; Cooper, M.; Friedewald, J.; Naik, A.S.; et al. KDOQI US Commentary on the 2017 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline on the Evaluation and Care of Living Kidney Donors. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 299–316. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, J.; Xu, P.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Liang, H.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, Y. Construction of a Diagnostic Model Utilizing m7G Regulatory Factors for the Characterization of Diabetic Nephropathy and the Immune Microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9208. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, D.; Ren, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hao, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Song, C.; et al. Identification of a Non-Invasive Urinary Exosomal Biomarker for Diabetic Nephropathy Using Data-Independent Acquisition Proteomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Cao, S.; Sasaki, K.; Harris, R.C. Podocyte EGFR Inhibits Autophagy through Upregulation of Rubicon in Type II Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes 2020, 70, 562–576. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Deng, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, Y. Diabetic Nephropathy: Focusing on Pathological Signals, Clinical Treatment, and Dietary Regulation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 159, 114252. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, S.C.; Tendal, B.; Mustafa, R.A.; Vandvik, P.O.; Li, S.; Hao, Q.; Tunnicliffe, D.; Ruospo, M.; Natale, P.; Saglimbene, V.; et al. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter Protein-2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists for Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. BMJ 2021, 372, m4573. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.; Wang, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.; Cao, M. Bioinformatics Analysis Identifies Immune-Related Gene Signatures and Subtypes in Diabetic Nephropathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1048139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Guo, B.; Chang, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ma, Y.; Fu, S. Identification and Validation of Glycolysis-Related Diagnostic Signatures in Diabetic Nephropathy: A Study Based on Integrative Machine Learning and Single-Cell Sequence. Front. Immunol. 2025, 15, 1427626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luo, Z.; He, P.; Ma, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, L.; Tian, N.; Dong, S.; et al. VCAM1: An Effective Diagnostic Marker Related to Immune Cell Infiltration in Diabetic Nephropathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1426913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Zhou, H.; Hu, P.; Pan, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Liu, X. Identification and Validation of Immune and Oxidative Stress-Related Diagnostic Markers for Diabetic Nephropathy by WGCNA and Machine Learning. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1084531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, R.; Jat, P. Mechanisms of Cellular Senescence: Cell Cycle Arrest and Senescence Associated Secretory Phenotype. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 645593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Fang, Y.P.; Sun, L.; Wei, S.Z.; Zhu, X.D.; Zhang, X.L. High Glucose Induces Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Senescence by Inhibiting Autophagic Flux. Hum. Cell 2025, 38, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Ke-Hong, C.; Fei, X.; Huan-Zi, D.; Jie, Y.; Li-Ming, W.; Xiao-Yue, W.; Jian-Guo, Z.; Ya-Ni, H. Decoy Receptor 2 Mediation of the Senescent Phenotype of Tubular Cells by Interacting with Peroxiredoxin 1 Presents a Novel Mechanism of Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Mou, S.; Yang, Q.; Liu, F.; Cooper, M.E.; Chai, Z. To Target Cellular Senescence in Diabetic Kidney Disease: The Known and the Unknown. Clin. Sci. 2024, 138, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Huang, W.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, R.; Liu, F.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, F.; Wang, B. Melatonin Attenuates Cellular Senescence and Apoptosis in Diabetic Nephropathy by Regulating STAT3 Phosphorylation. Life Sci. 2023, 332, 122108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Yang, C.; Wang, P.; Li, L.; Lin, Y.; Yi, Q.; Tang, F.; Liu, L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, D.; et al. Identification and Validation of Glomeruli Cellular Senescence-Related Genes in Diabetic Nephropathy by Multiomics. Adv. Biol. 2024, 8, e2300453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Moru, P.; Liao, K.; Song, W.; Yang, P.; Zang, D.; Cai, C.; Zhou, H. High Glucose-Induced Senescence Contributes to Tubular Epithelial Cell Damage in Diabetic Nephropathy. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 197, 112609. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Mei, G.; Jiang, C.; Cheng, X.; Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Wan, C.; Yao, P.; Gao, C.; et al. Carbon Monoxide Alleviates Senescence in Diabetic Nephropathy by Improving Autophagy. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e13052. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verzola, D.; Gandolfo, M.T.; Gaetani, G.; Ferraris, A.; Mangerini, R.; Ferrario, F.; Villaggio, B.; Gianiorio, F.; Tosetti, F.; Weiss, U.; et al. Accelerated Senescence in the Kidneys of Patients with Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2008, 295, F1563–F1573. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Guo, L.; Chen, J.; Liang, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhou, L.; Shan, L.; Wang, H. Intravenous Injection of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorates Not Only Blood Glucose but Also Nephrotic Complication of Diabetic Rats Through Autophagy-Mediated Anti-Senescent Mechanism. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 14, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Dai, H.; Yuan, J.; Chen, J.; Lin, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; He, Y. Optineurin-Mediated Mitophagy Protects Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells against Accelerated Senescence in Diabetic Nephropathy. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, D.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Feng, Z.; Cai, G.; Fu, B.; Hong, Q.; Du, J. Downregulation of Connexin 43 Expression by High Glucose Induces Senescence in Glomerular Mesangial Cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y. Ageing, Cellular Senescence and Chronic Kidney Disease: Experimental Evidence. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2022, 31, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Meng, P.; Ling, X.; Zhou, L. Advancements in Therapeutic Drugs Targeting of Senescence. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2020, 11, 2040622320964125. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland, J.L.; Tchkonia, T. Senolytic Drugs: From Discovery to Translation. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 518–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Senolytics for Kidney Repair. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Dominguez, M.; Golestaneh, L. Diabetic Kidney Disease: An Update. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 107, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Y.; Lin, T.W.; Hong, Z.X.; Lim, L.M. Vitamin D and Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Ji, C.; Wei, K. Cellular Senescence and Regulated Cell Death of Tubular Epithelial Cells in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 924299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eppard, M.; Passos, J.F.; Victorelli, S. Telomeres, Cellular Senescence, and Aging: Past and Future. Biogerontology 2024, 25, 329–339. [Google Scholar]
- Lans, H.; Hoeijmakers, J.H.J. Genome Stability, Progressive Kidney Failure and Aging. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 836–838. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yang, J.R.; Chen, X.M.; Cai, G.Y.; Lin, L.R.; He, Y.N. Impact of ER Stress-Regulated ATF4/p16 Signaling on the Premature Senescence of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells in Diabetic Nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2015, 308, 621–630. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, S.L.; Kouzarides, T.; Shiekhattar, R.; Shilatifard, A. An Operational Definition of Epigenetics. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 781–783. [Google Scholar]
- Wanner, N.; Bechtel-Walz, W. Epigenetics of Kidney Disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 369, 75–92. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, I.; Dutta, R.K.; Singh, N.K.; Kanwar, Y.S. High Glucose-Induced Hypomethylation Promotes Binding of Sp-1 to Myo-Inositol Oxygenase. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 724–739. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.Y.; Shi, Y.Y.; Cui, X.W.; Pan, Y.F.; Lin, Y.K.; Feng, X.F.; Ding, Z.W.; Yang, C.; Tan, Y.X.; Dong, L.W.; et al. PTEN Deficiency Facilitates Exosome Secretion and Metastasis in Cholangiocarcinoma by Impairing TFEB—mediated Lysosome Biogenesis. Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 424–438. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.Y.; Cui, X.W.; Zeng, T.M.; Pan, Y.F.; Lin, Y.K.; Feng, X.F.; Tan, Y.X.; Yuan, Z.G.; Dong, L.W.; Wang, H.Y. PTEN Deficiency Facilitates Gemcitabine Efficacy in Cancer by Modulating the Phosphorylation of PP2Ac and DCK. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eadd7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Shi, Y.; Peng, H.; Shen, X.; Thomas, S.; Wang, Y.; Truong, L.D.; Dryer, S.E.; Hu, Z.; Xu, J. Loss of PTEN Promotes Podocyte Cytoskeletal Rearrangement, Aggravating Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Pathol. 2015, 236, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Wang, Y.; Shi, M.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Guo, B. Regulation of PTEN/AKT/FAK Pathways by PPARγ Impacts on Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 6998–7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Liu, H.; Jiang, X.; Tang, N.; Fan, W.; Ji, W.; Zhou, Z. Effect of miR-1297 on Kidney Injury in Rats with Diabetic Nephropathy through the PTEN/PI3K/AKT Pathway. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2024, 77, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaoka, T.; Wada, T.; Tsuneki, H. Lipid Phosphatases as a Possible Therapeutic Target in Cases of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 112, 799–809. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, M.J.; An, H.J.; Ha, M.H.; Park, S.H.; Jeong, H.Y.; Baek, J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, S.Y. PTEN-induced Kinase 1 Exerts Protective Effects in Diabetic Kidney Disease by Attenuating Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Necroptosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 5145–5159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L. Study of Serum FABP4, PTEN Levels and HLA-DRB1 Alleles in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mahimainathan, L.; Das, F.; Venkatesan, B.; Choudhury, G.G. Mesangial Cell Hypertrophy by High Glucose Is Mediated by Downregulation of the Tumor Suppressor PTEN. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zheng, C.; Hua, Z.; Ci, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, L. Diosmin Mitigates High Glucose-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress through PI3K/AKT Pathway in HK-2 Cells. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lv, X.; Li, S.; Qin, X.; Yang, H.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y. Surface Chemistry Induces Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells via PTEN/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 172–185. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Han, Z.; Han, F.; Chang, Y.P.; Yang, Y.; Xue, M.; Sun, B.; Chen, L.M. Triptolide Restores Autophagy to Alleviate Diabetic Renal Fibrosis through the miR-141-3p/PTEN/Akt/mTOR Pathway. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 9, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemesh, I.I.; Rozen-Zvi, B.; Kalechman, Y.; Gafter, U.; Sredni, B. AS101 Prevents Diabetic Nephropathy Progression and Mesangial Cell Dysfunction: Regulation of the AKT Downstream Pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 114287. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Shen, E.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Cheng, D.; Chen, Y.; Gui, D.; Wang, N. Cross Talk between miR-214 and PTEN Attenuates Glomerular Hypertrophy under Diabetic Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31506. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yao, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L. Oleanolic Acid Attenuated Diabetic Mesangial Cell Injury by Activation of Autophagy via miRNA-142-5p/PTEN Signaling. Cytotechnology 2019, 71, 925–933. [Google Scholar]
- Khokhar, M.; Roy, D.; Modi, A.; Agarwal, R.; Yadav, D.; Purohit, P.; Sharma, P. Perspectives on the Role of PTEN in Diabetic Nephropathy: An Update. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 470–483. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Feng, Z.; Xie, J.; Wen, F.; Jv, M.; Liang, T.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Podocyte-Specific Knockin of PTEN Protects Kidney from Hyperglycemia. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2018, 314, F1096–F1107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Tao, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Yan, D.; et al. Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 Promotes Renal Fibrosis after Acute Kidney Injury by Inducing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Activation of M2 Macrophage Polarization. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moses, C.; Nugent, F.; Waryah, C.B.; Garcia-Bloj, B.; Harvey, A.R.; Blancafort, P. Activating PTEN Tumor Suppressor Expression with the CRISPR/dCas9 System. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 14, 287–300. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Chao, P.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Cui, X.; Wang, S.; Wusiman, M.; Jiang, H.; Lu, C. Single-Cell RNA and Transcriptome Sequencing Profiles Identify Immune-Associated Key Genes in the Development of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1030198. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.; Ping, F.; Mu, W.; Hill, P.; Atkins, R.C.; Chadban, S.J. Macrophage Accumulation in Human Progressive Diabetic Nephropathy. Nephrology 2006, 11, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Klessens, C.Q.F.; Zandbergen, M.; Wolterbeek, R.; Bruijn, J.A.; Rabelink, T.J.; Bajema, I.M.; IJpelaar, D.H.T. Macrophages in Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, G.; Nakano, K.; Sawada, M.; Uno, K.; Shibayama, Y.; Ienaga, K.; Kondo, M. Possible Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor and Interleukin—1 in the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1991, 40, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Kalantarinia, K.; Awad, A.S.; Siragy, H.M. Urinary and Renal Interstitial Concentrations of TNF-alpha Increase Prior to the Rise in Albuminuria in Diabetic Rats. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 1208–1213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Navarro-González, J.F.; Mora-Fernández, C.; Muros de Fuentes, M.; Chahin, J.; Méndez, M.L.; Gallego, E.; Macía, M.; del Castillo, N.; Rivero, A.; Getino, M.A.; et al. Effect of Pentoxifylline on Renal Function and Urinary Albumin Excretion in Patients with Diabetic Kidney Disease: The PREDIAN Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hiramoto, K.; Imai, M.; Tanaka, S.; Ooi, K. Changes in the AGE/Macrophage/TNF—α Pathway Affect Skin Dryness during KK—Ay/Tajcl Mice Aging. Life 2023, 13, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.S.; You, H.; Gao, T.; Cooper, T.K.; Nedospasov, S.A.; Vacher, J.; Wilkinson, P.F.; Farrell, F.X.; Brian Reeves, W. Macrophage-Derived Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Mediates Diabetic Renal Injury. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 722–733. [Google Scholar]
- Prattichizzo, F.; De Nigris, V.; Spiga, R.; Mancuso, E.; La Sala, L.; Antonicelli, R.; Testa, R.; Procopio, A.D.; Olivieri, F.; Ceriello, A. Inflammageing and metaflammation: The Yin and Yang of Type 2 Diabetes. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 41, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prattichizzo, F.; De Nigris, V.; Mancuso, E.; Spiga, R.; Giuliani, A.; Matacchione, G.; Lazzarini, R.; Marcheselli, F.; Recchioni, R.; Testa, R.; et al. Short-term Sustained Hyperglycaemia Fosters an Archetypal Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype in Endothelial Cells and Macrophages. Redox Biol. 2018, 15, 170–181. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Nie, L.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, X.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Q. Diabetes Fuels Periodontal Lesions via GLUT1-Driven Macrophage Inflammaging. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2021, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verreck, F.A.; de Boer, T.; Langenberg, D.M.; Hoeve, M.A.; Kramer, M.; Vaisberg, E.; Kastelein, R.; Kolk, A.; de Waal-Malefyt, R.; Ottenhoff, T.H. Human IL-23-producing Type 1 Macrophages Promote but IL-10-producing Type 2 Macrophages Subvert Immunity to (Myco)bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4560–4565. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, S.; Martinez, F.O. Alternative Activation of Macrophages: Mechanism and Functions. Immunity 2010, 32, 593–604. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Yu, M.; Xie, D.; Wang, L.; Ye, C.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, F.; Yang, L. Melatonin-Stimulated MSC-Derived Exosomes Improve Diabetic Wound Healing through Regulating Macrophage M1 and M2 Polarization by Targeting the PTEN/AKT Pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Tsichlis, P.N. Regulation of the Akt Kinase by Interacting Proteins. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7401–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Guo, Y.F.; Song, Z.X.; Zhou, M. Vitamin D Prevents Podocyte Injury via Regulation of Macrophage M1/M2 Phenotype in Diabetic Nephropathy Rats. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 4939–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.S.; Qiu, D.D.; Le, W.B.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.H.; Jiang, S. Identification of Transcription Regulatory Relationships in Diabetic Nephropathy. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 2886–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Woroniecka, K.I.; Park, A.S.; Mohtat, D.; Thomas, D.B.; Pullman, J.M.; Susztak, K. Transcriptome Analysis of Human Diabetic Kidney Disease. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2354–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Gene Ontology Consortium. The Gene Ontology Resource: 20 Years and Still GOing Strong. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D330–D338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes among Gene Clusters. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R Package for Weighted Correlation Network Analysis. BMC Bioinf. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Li, W.; Wei, R.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Q. Identification of Pyroptosis-Related Genes and Potential Drugs in Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, M.D.; Hayes, D.N. Consensus Cluster Plus: A Class Discovery Tool with Confidence Assessments and Item Tracking. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1572–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Zu, Y. Unveiling the Potential of Migrasomes: A Machine-Learning-Driven Signature for Diagnosing Acute Myocardial Infarction. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimaiti, A.; Turhon, M.; Abulaiti, A.; Dilixiati, Y.; Zhang, F.; Axieer, A.; Kadeer, K.; Zhang, Y.; Maimaitili, A.; Yang, X. DNA Methylation Regulator-Mediated Modification Patterns and Risk of Intracranial Aneurysm: A Multi-omics and Epigenome-wide Association Study Integrating Machine Learning, Mendelian Randomization, eQTL and mQTL Data. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangiola, S.; Doyle, M.A.; Papenfuss, A.T. Interfacing Seurat with the R Tidy Universe. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 4100–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; He, K.; Zhao, J.; You, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J. Co-differential Genes between DKD and Aging: Implications for a Diagnostic Model of DKD. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Tang, H.; Cao, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. PTEN: A Novel Diabetes Nephropathy Protective Gene Related to Cellular Senescence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073088
Li K, Tang H, Cao X, Zhang X, Wang X. PTEN: A Novel Diabetes Nephropathy Protective Gene Related to Cellular Senescence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073088
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kang, Huidi Tang, Xiaoqing Cao, Xiaoli Zhang, and Xiaojie Wang. 2025. "PTEN: A Novel Diabetes Nephropathy Protective Gene Related to Cellular Senescence" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073088
APA StyleLi, K., Tang, H., Cao, X., Zhang, X., & Wang, X. (2025). PTEN: A Novel Diabetes Nephropathy Protective Gene Related to Cellular Senescence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073088




