Pulsatilla koreana Nakai Extract Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis-like Symptoms by Regulating Skin Barrier Factors and Inhibiting the JAK/STAT Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
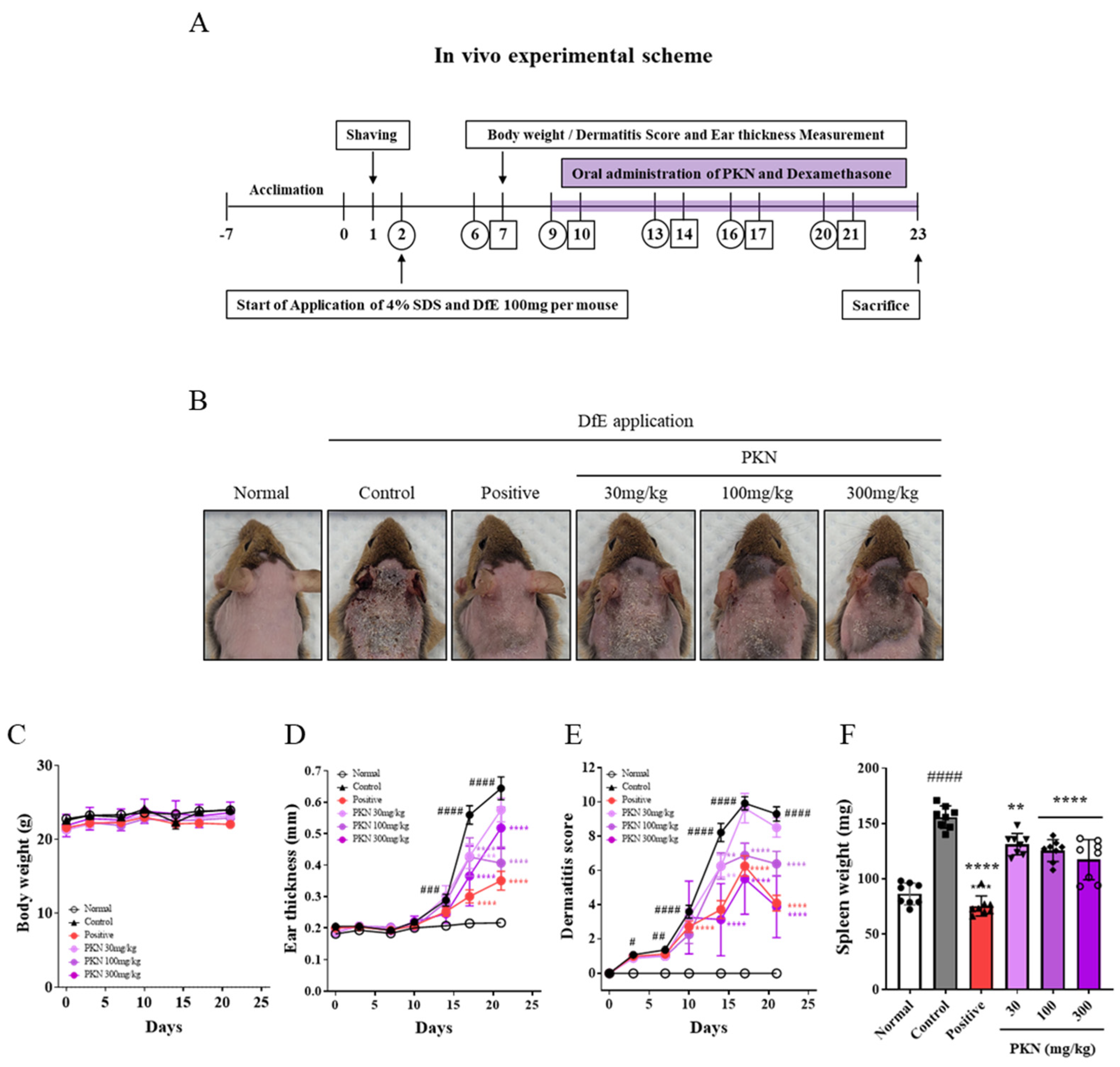
2.1. PKN Extract Improves Atopic Symptoms in DfE-Induced NC/Nga Mice
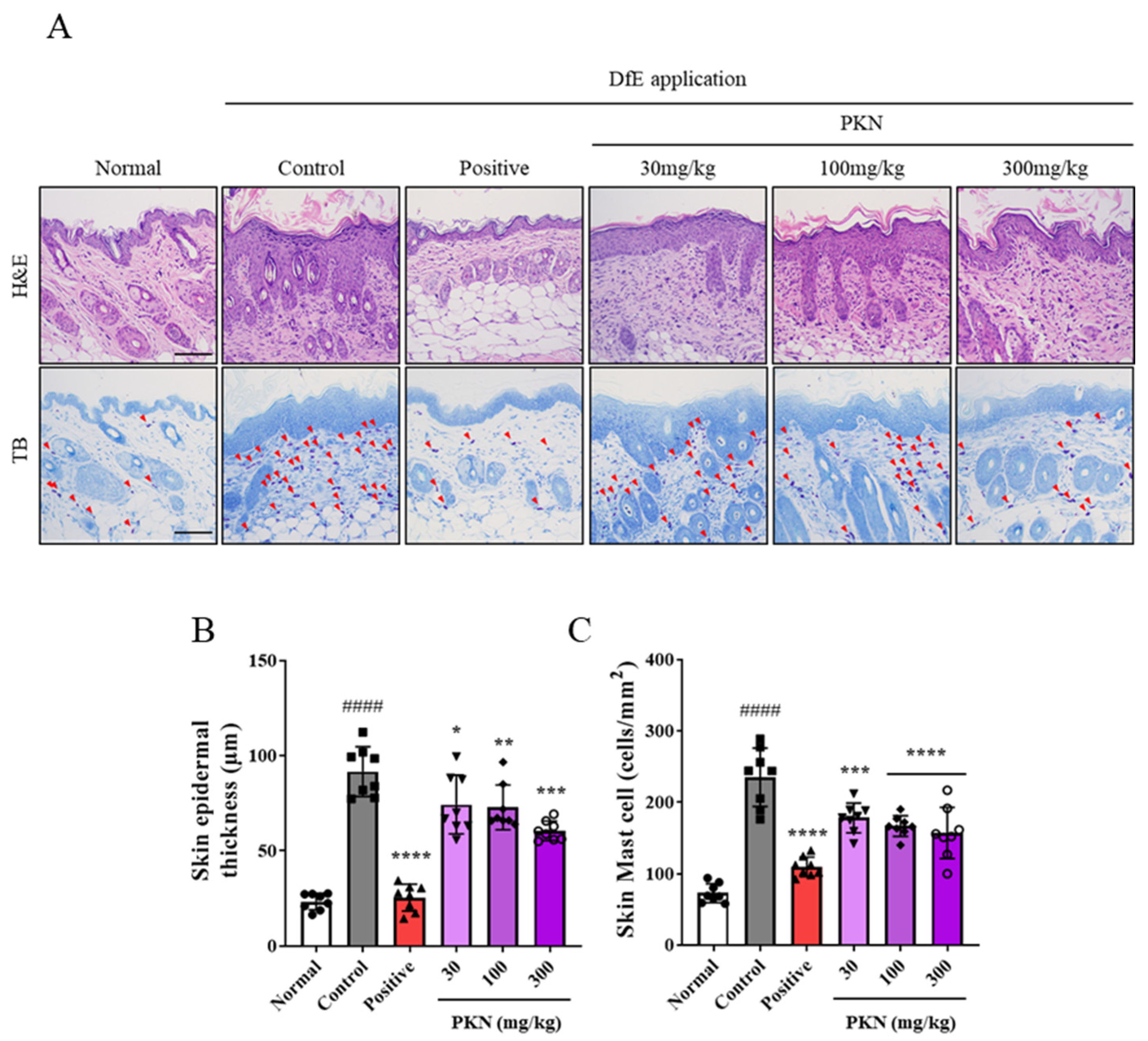
2.2. PKN Extract Decreases Epidermal Thickness and Mast Cell Infiltration in DfE-Induced AD-like Mice
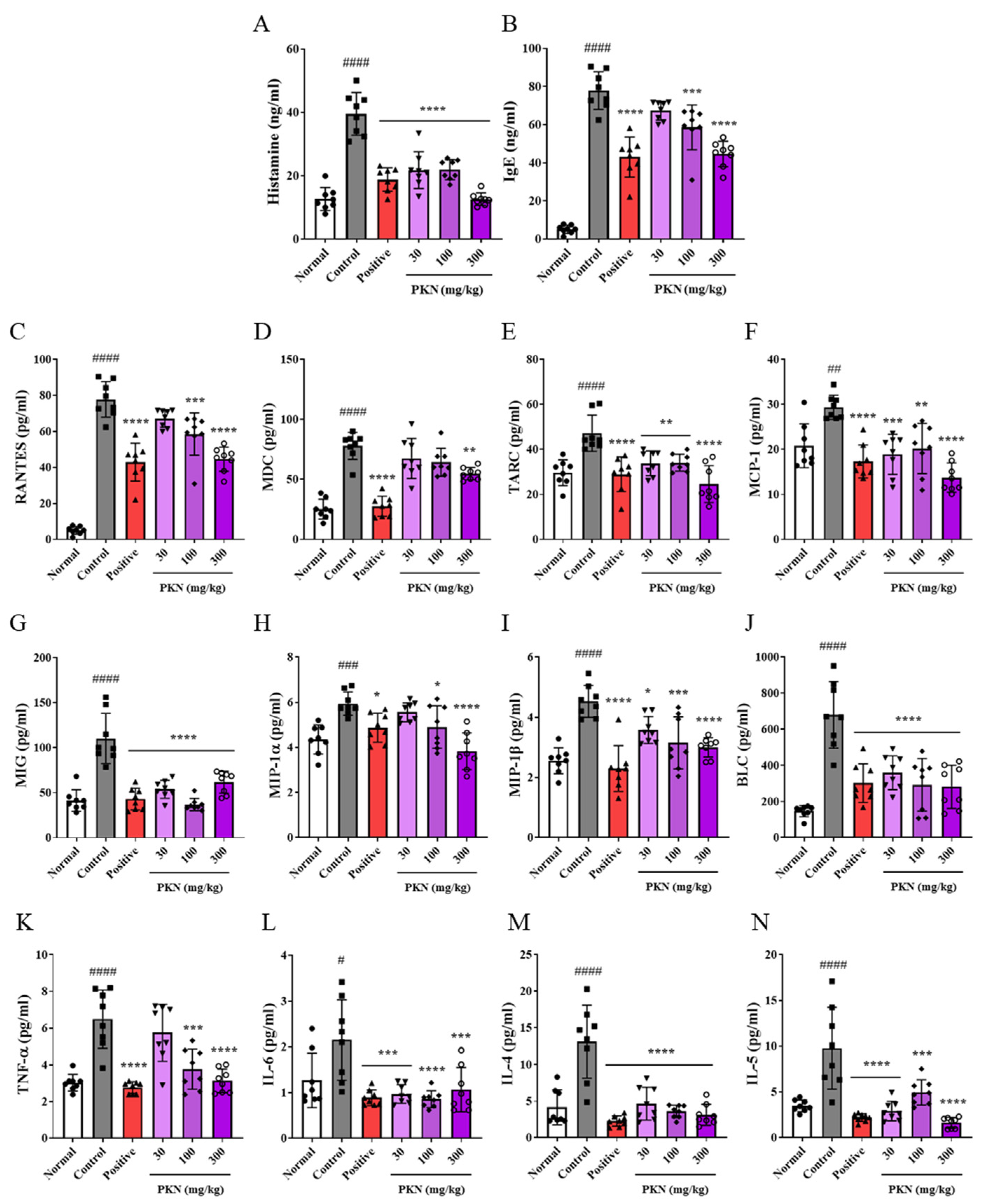
2.3. PKN Extract Suppresses Production of Inflammatory Factors in Serum of DfE-Induced AD-like Mice
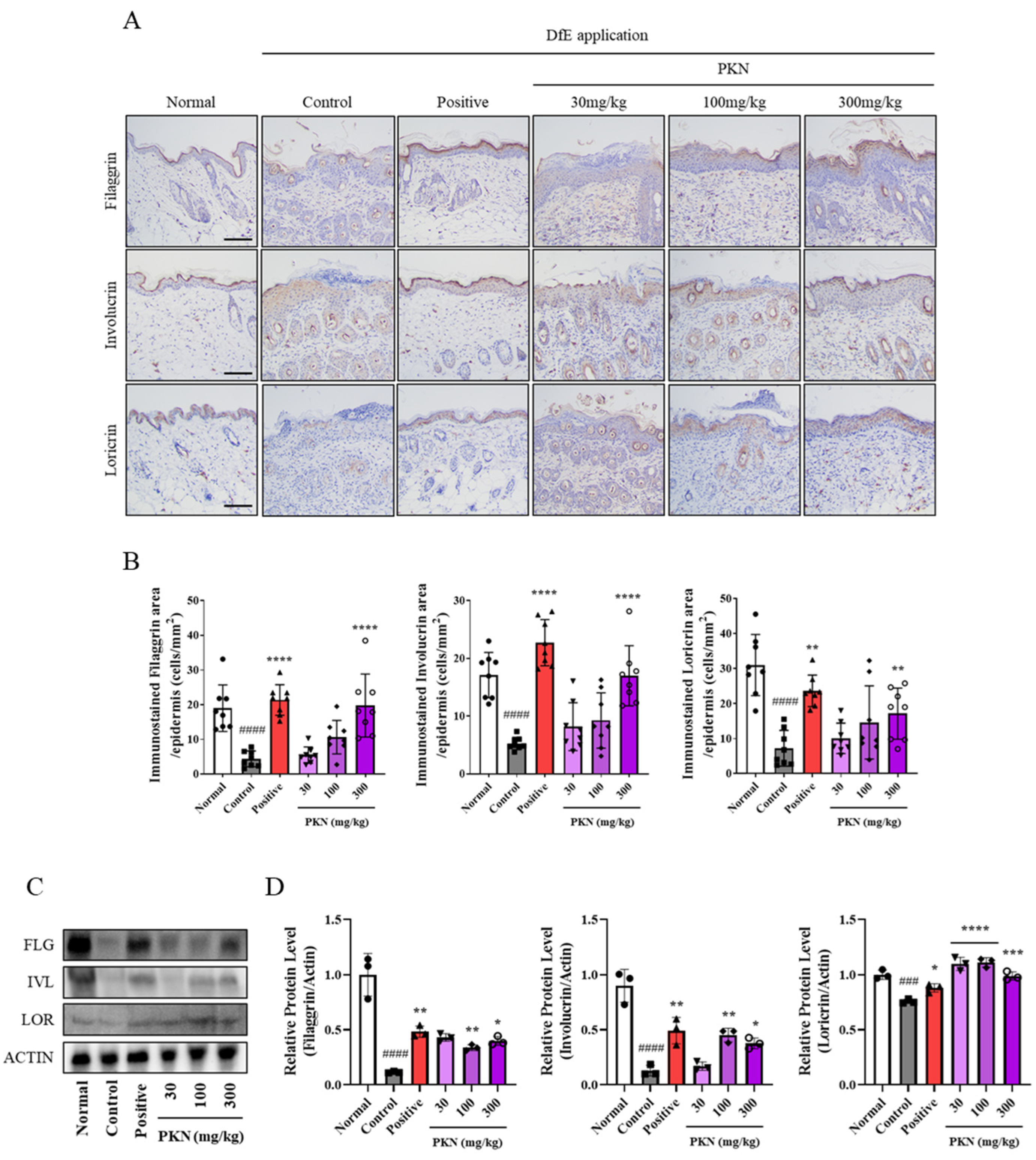
2.4. PKN Extract Restores Decreased Skin Barrier Factors in DfE-Induced AD-like Mice
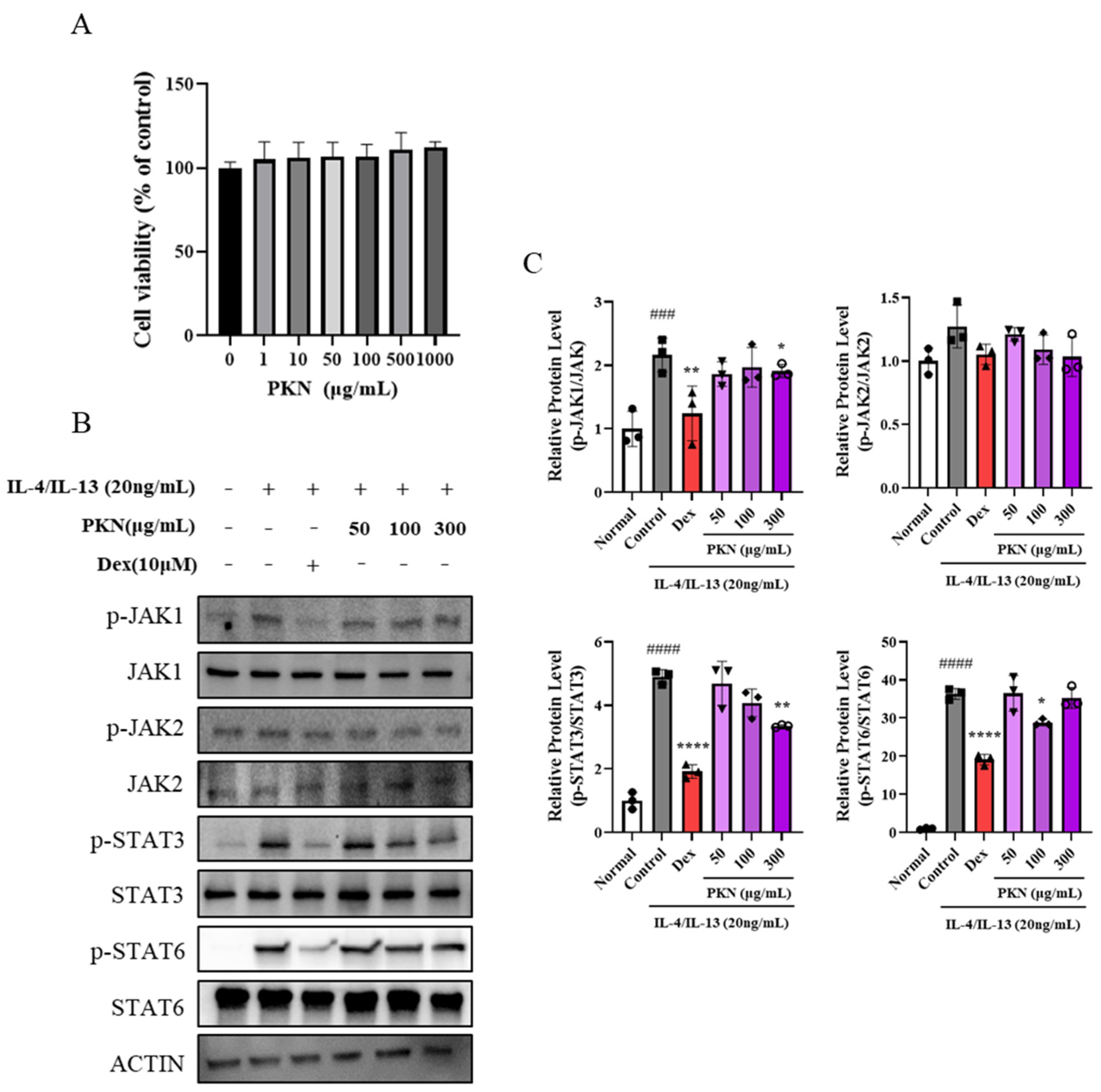
2.5. PKN Suppresses Production of Inflammatory Factors and JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway In Vitro
2.6. Quantitative Analysis of Pulsatilla Koreana Nakai
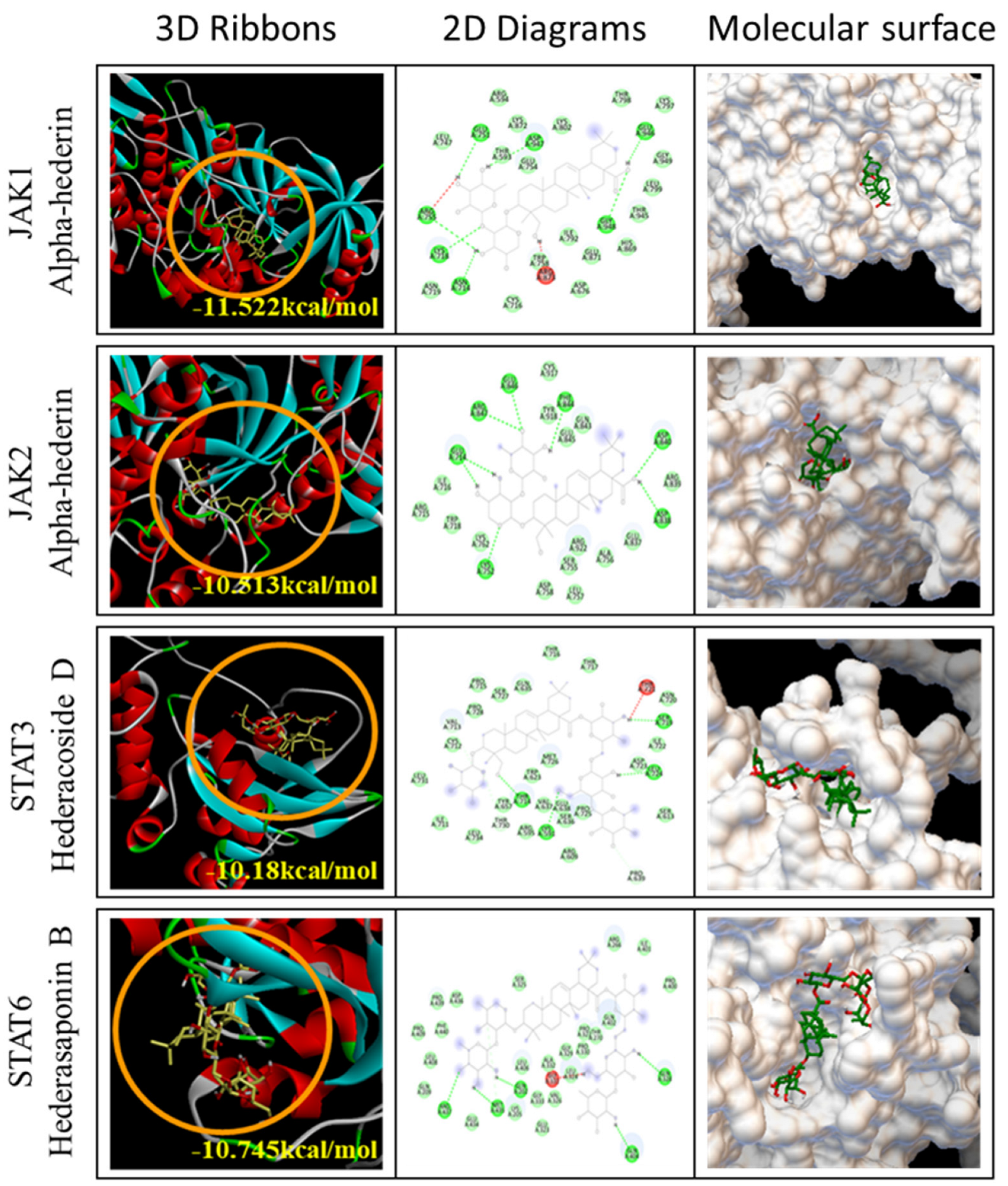
2.7. Docking Analysis of Seven Compounds
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Preparation of PKN Extract
4.2. Animals and DfE-Induced AD Mouse Model
4.3. Measurement of Ear Thickness and Evaluation of Dermatitis Severity
4.4. Histopathological Studies
4.5. Immunoassay
4.6. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assay
4.7. Sampling and Western Blotting
4.8. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
4.9. Molecular Docking Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ong, P.Y. Atopic dermatitis: Is innate or adaptive immunity in control? A clinical perspective. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 943640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Adalsteinsson, J.; Whitaker-Worth, D.L. Atopic dermatitis and nutrition. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 40, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohr, C.; Mann, J. New insights into the epidemiology of childhood atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2014, 69, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, A.M. Atopic dermatitis: Burden of illness, quality of life, and associated complications. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2017, 38, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, M.; Takamori, K. Peripheral itch sensitization in atopic dermatitis. Allergol. Int. 2022, 71, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, N.A.; Pirozzi, G.; Graham, N.M.H. Commonality of the IL-4/IL-13 pathway in atopic diseases. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, M. Regulation of Filaggrin, Loricrin, and Involucrin by IL-4, IL-13, IL-17A, IL-22, AHR, and NRF2: Pathogenic Implications in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, D.S.; Griffiths, C.E.; Yuspa, S.H.; Roop, D.R.; Voorhees, J.J. Acute or chronic topical retinoic acid treatment of human skin in vivo alters the expression of epidermal transglutaminase, loricrin, involucrin, filaggrin, and keratins 6 and 13 but not keratins 1, 10, and 14. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1992, 98, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.H. Epidermal permeability barrier defects and barrier repair therapy in atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2014, 6, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.H.; Chung, W.H.; Wu, P.C.; Chen, C.B. JAK-STAT signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis: An updated review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1068260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.E.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Stats: Transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovatiya, R.; Paller, A.S. JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Kim, K.; Shin, K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, B.; Kim, M.B.; Ko, H.C.; Kim, Y.H. The safety of systemic Janus kinase inhibitors in atopic dermatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampa, M.; Mitran, C.I.; Mitran, M.I.; Georgescu, S.R. A New Horizon for Atopic Dermatitis Treatments: JAK Inhibitors. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.H.; Lee, A.; Hwang, Y.H.; Jung, M.A.; Pyun, B.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, T.; Song, K.H.; Ji, K.Y. Therapeutic effects of Pulsatilla koreana Nakai extract on ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis by inhibition of Th2 cell activation and differentiation via the IL-4/STAT6/GATA3 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yan, X.T.; Sun, Y.N.; Ngan, T.T.; Shim, S.H.; Kim, Y.H. Anti-Inflammatory and PPAR Transactivational Effects of Oleanane-Type Triterpenoid Saponins from the Roots of Pulsatilla koreana. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, C.F.t.; Billi, A.C.; Maverakis, E.; Tsoi, L.C.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Novel insights into atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, S.; Miraglia del Giudice, M.; La Rosa, M.; Bellanti, J.A. Atopic disease, immune system, and the environment. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2007, 28, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka-Tomaszewska, J.; Trzeciak, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Atopic Dermatitis Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, W.; Bhardwaj, N. Atopic Dermatitis: Diagnosis and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 101, 590–598. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, H.F.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Lack, G.; Sindher, S.; Ciaccio, C.E.; Chan, S.; Nadeau, K.C.; Brough, H.A. Topical steroid withdrawal and atopic dermatitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024, 132, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; He, R.; Oyoshi, M.; Geha, R.S. Animal models of atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Seok, J.K.; Kang, H.C.; Cho, Y.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.Y. Skin Barrier Abnormalities and Immune Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.I.; Mizutani, H. The role of cytokines/chemokines in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2011, 41, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, E. The TH1/TH2 paradigm in allergy. Immunotechnology 1998, 3, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, C.; Del Duca, E.; Guttman-Yassky, E. The IL-4, IL-13 and IL-31 pathways in atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 835–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miot, H.A.; Criado, P.R.; de Castro, C.C.S.; Ianhez, M.; Talhari, C.; Ramos, P.M. JAK-STAT pathway inhibitors in dermatology. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2023, 98, 656–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Yi, J.M.; Kim, N.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, H. Effect of Poria cocos Terpenes: Verifying Modes of Action Using Molecular Docking, Drug-Induced Transcriptomes, and Diffusion Network Analyses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.R.; Han, Q.; Zou, M.; Chen, F.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Zhong, Y.M.; Wu, Q.Y.; Tomlinson, B.; Li, Y.H. Identification of potential immunomodulators from Pulsatilla decoction that act on therapeutic targets for ulcerative colitis based on pharmacological activity, absorbed ingredients, and in-silico molecular docking. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.Y.; An, W.G. Systems Pharmacological Approach of Pulsatillae Radix on Treating Crohn’s Disease. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 4198035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Kasim, V.N.K.; Noble, S.M.; Liew, K.Y.; Tan, J.W.; Israf, D.A.; Tham, C.L. Management of Atopic Dermatitis Via Oral and Topical Administration of Herbs in Murine Model: A Systematic Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 785782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Song, H.K.; Park, S.H.; Jang, S.; Park, K.S.; Song, K.H.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, T. Terminalia chebula Retz. extract ameliorates the symptoms of atopic dermatitis by regulating anti-inflammatory factors in vivo and suppressing STAT1/3 and NF-kB signaling in vitro. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, K.S.; Kim, H.J.; Ji, K.Y.; Jung, D.H.; Park, S.H.; Song, H.K.; Kim, T.; Kim, K.M. Rosmarinic Acid Ameliorates Dermatophagoides farinae Extract-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Inflammation by Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Lee, A.; Hwang, Y.H. Qualitative Profiling and Quantitative Analysis of Major Constituents in Jinmu-tang by UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-MS and UPLC-TQ-MS/MS. Molecules 2022, 27, 7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadi, M.; Anyango, S.; Deshpande, M.; Nair, S.; Natassia, C.; Yordanova, G.; Yuan, D.; Stroe, O.; Wood, G.; Laydon, A.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: Massively expanding the structural coverage of protein-sequence space with high-accuracy models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D439–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Smith, J.C. Speed vs Accuracy: Effect on Ligand Pose Accuracy of Varying Box Size and Exhaustiveness in AutoDock Vina. Mol. Inf. 2023, 42, e2200188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
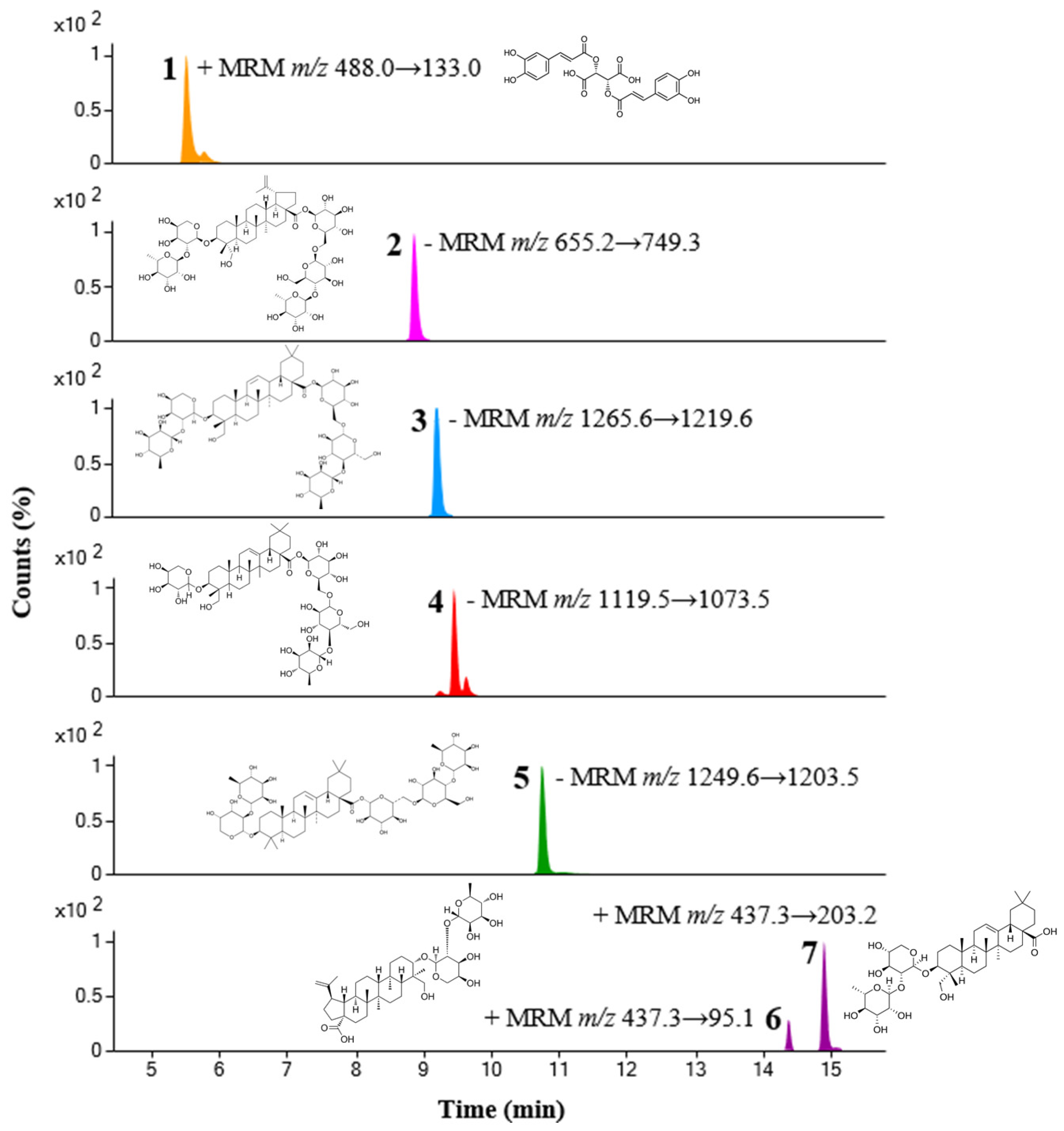
| No. | Compound Name | Rt (min) | Ion Mode | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Collision Energy (V) | Amount (mg/g ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chicoric acid | 5.53 | positive | 488.0 | 133.0 | 38 | 2.07 ± 0.01 |
| 2 | Anemoside B4 | 8.88 | negative | 655.2 | 749.3 | 26 | 20.68 ± 0.12 |
| 3 | Hederacoside C | 9.22 | negative | 1265.6 | 1219.6 | 22 | 9.63 ± 0.17 |
| 4 | Hederacoside D | 9.45 | negative | 1119.5 | 1073.5 | 22 | 1.05 ± 0.02 |
| 5 | Hederasaponin B | 10.75 | negative | 1249.6 | 1203.5 | 22 | 16.80 ± 0.11 |
| 6 | Anemoside A3 | 14.39 | positive | 437.3 | 95.1 | 38 | 0.38 ± 0.01 |
| 7 | α-Hederin | 14.91 | positive | 437.3 | 203.2 | 22 | 0.57 ± 0.01 |
| JAK/STAT Family | Binding Affinity (kcal/mol) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AH | AA3 | AB4 | CC | HC | HD | HB | |
| JAK1 | −11.522 | −9.589 | −10.029 | −8.741 | −10.537 | −10.923 | −9.915 |
| JAK2 | −10.513 | −9.665 | −10.122 | −9.358 | −10.483 | −11.147 | −10.57 |
| STAT3 | −9.232 | −8.861 | −9.951 | −7.819 | −9.975 | −10.18 | −10.23 |
| STAT6 | −10.099 | −9.037 | −10.373 | −8.449 | −9.816 | −10.648 | −10.745 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.J.; Park, M.; Jang, S.; Song, H.-K.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, T. Pulsatilla koreana Nakai Extract Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis-like Symptoms by Regulating Skin Barrier Factors and Inhibiting the JAK/STAT Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072994
Kim HJ, Park M, Jang S, Song H-K, Lee SK, Kim T. Pulsatilla koreana Nakai Extract Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis-like Symptoms by Regulating Skin Barrier Factors and Inhibiting the JAK/STAT Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072994
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hye Jin, Musun Park, Seol Jang, Hyun-Kyung Song, Sang Kook Lee, and Taesoo Kim. 2025. "Pulsatilla koreana Nakai Extract Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis-like Symptoms by Regulating Skin Barrier Factors and Inhibiting the JAK/STAT Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072994
APA StyleKim, H. J., Park, M., Jang, S., Song, H.-K., Lee, S. K., & Kim, T. (2025). Pulsatilla koreana Nakai Extract Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis-like Symptoms by Regulating Skin Barrier Factors and Inhibiting the JAK/STAT Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072994






