In Vitro Analysis of Probiotic Properties Related to the Adaptation of Levilactobacillus brevis to Intestinal Microenvironment and Involvement of S-Layer Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Genome Features of L. brevis Strains
2.2. Role of S-proteins in the Properties Important for Intestinal Adaptation of L. brevis Strains
2.3. Capacity of L. brevis Strains and Their S-proteins to Improve Epithelial Barrier Function In Vitro

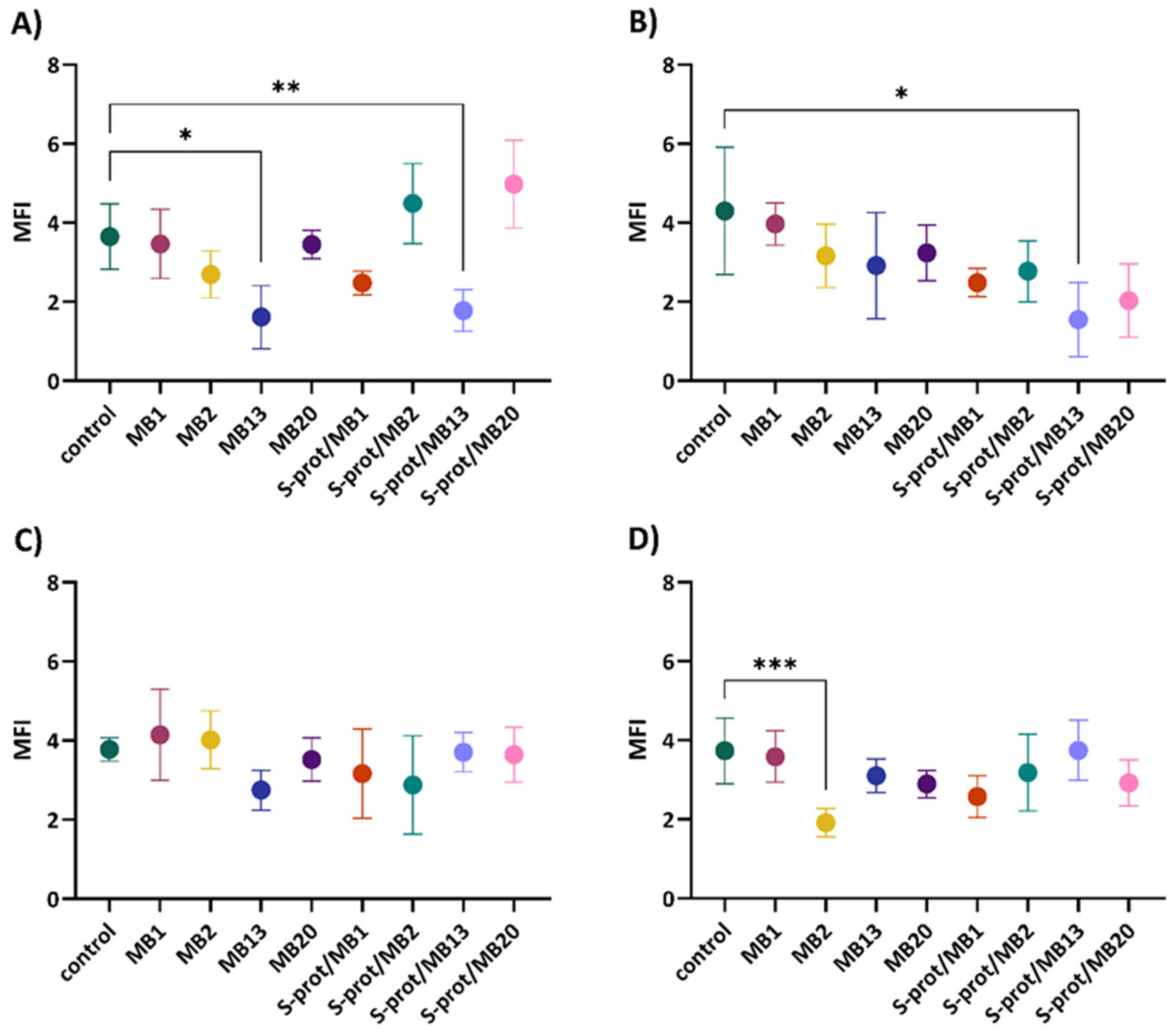
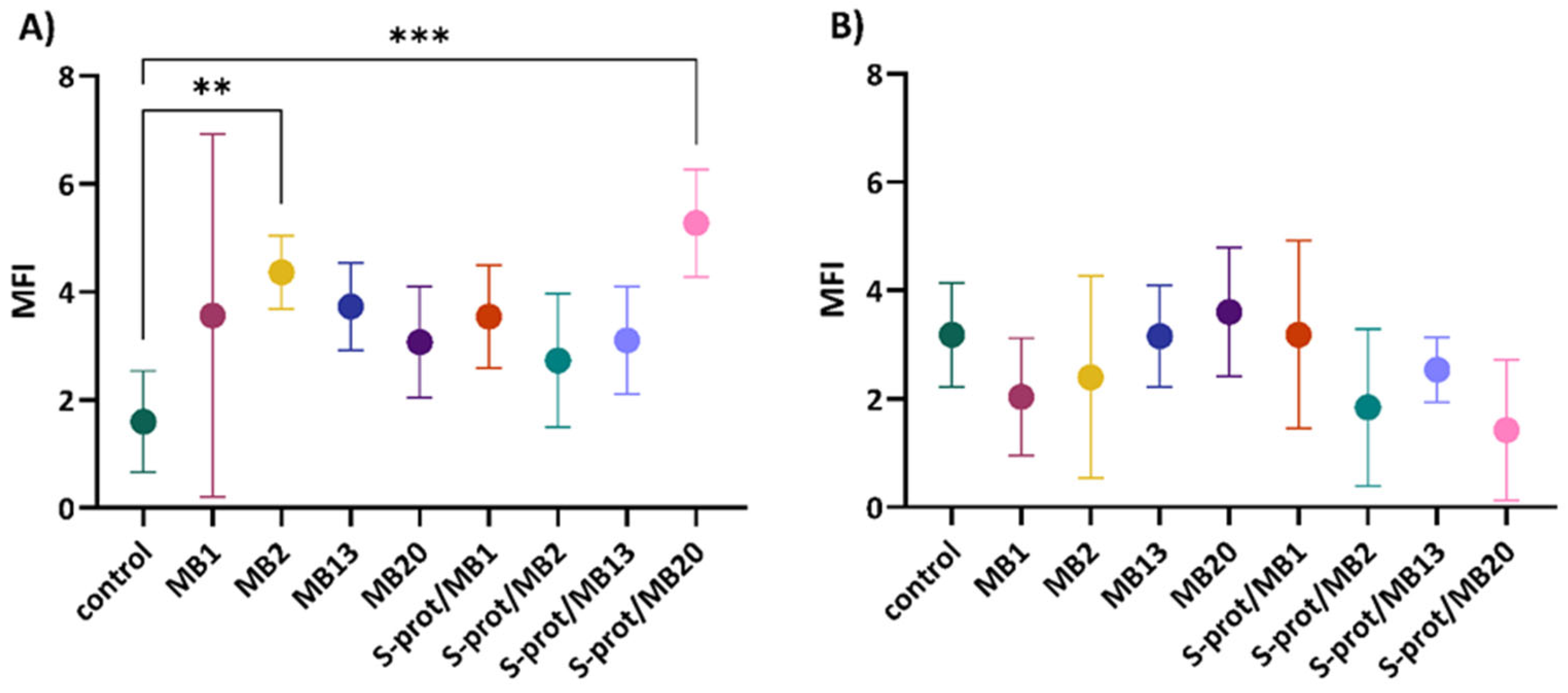
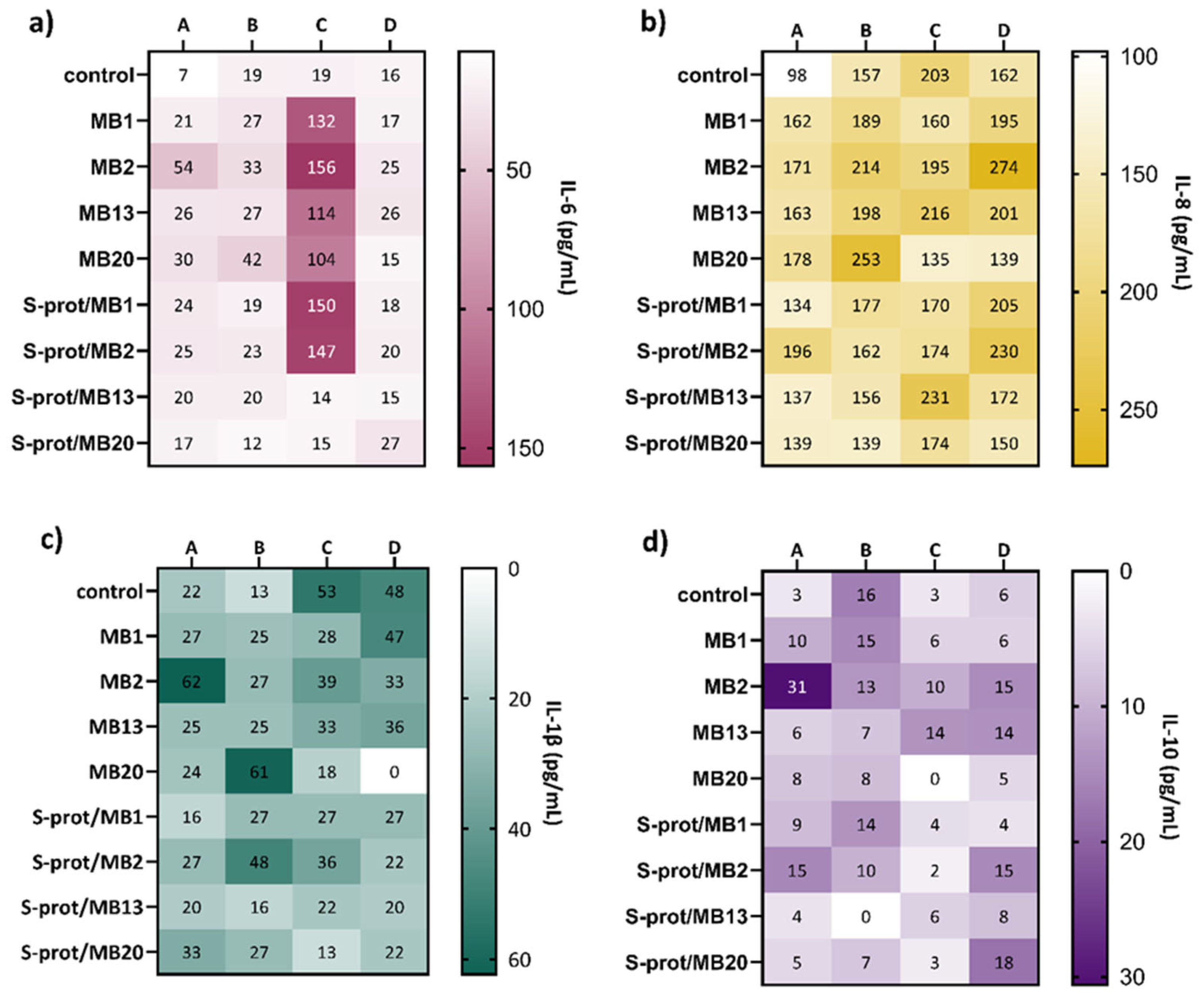
2.4. The Immunomodulatory Effect of L. brevis Strains and S-proteins In Vitro
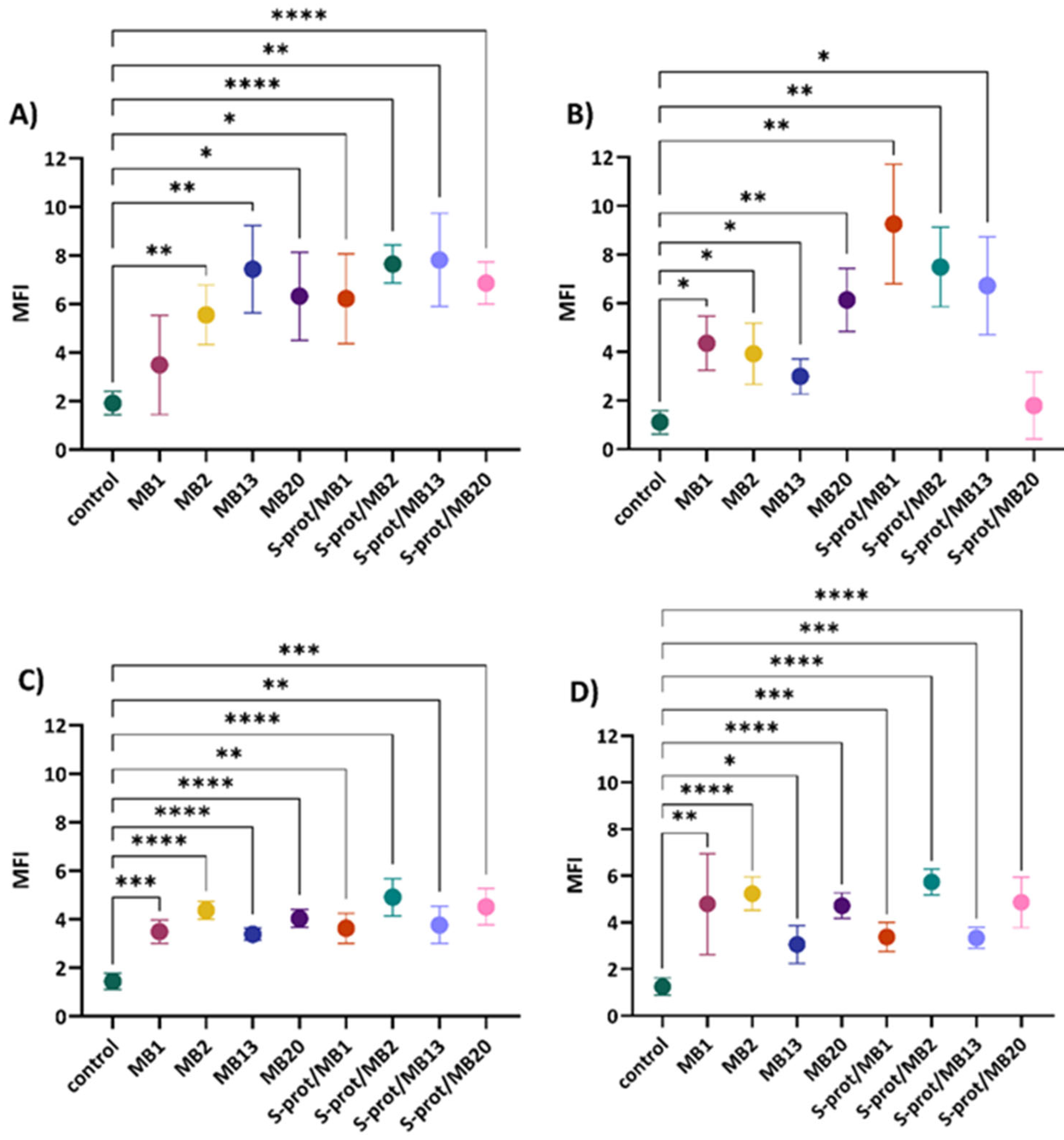
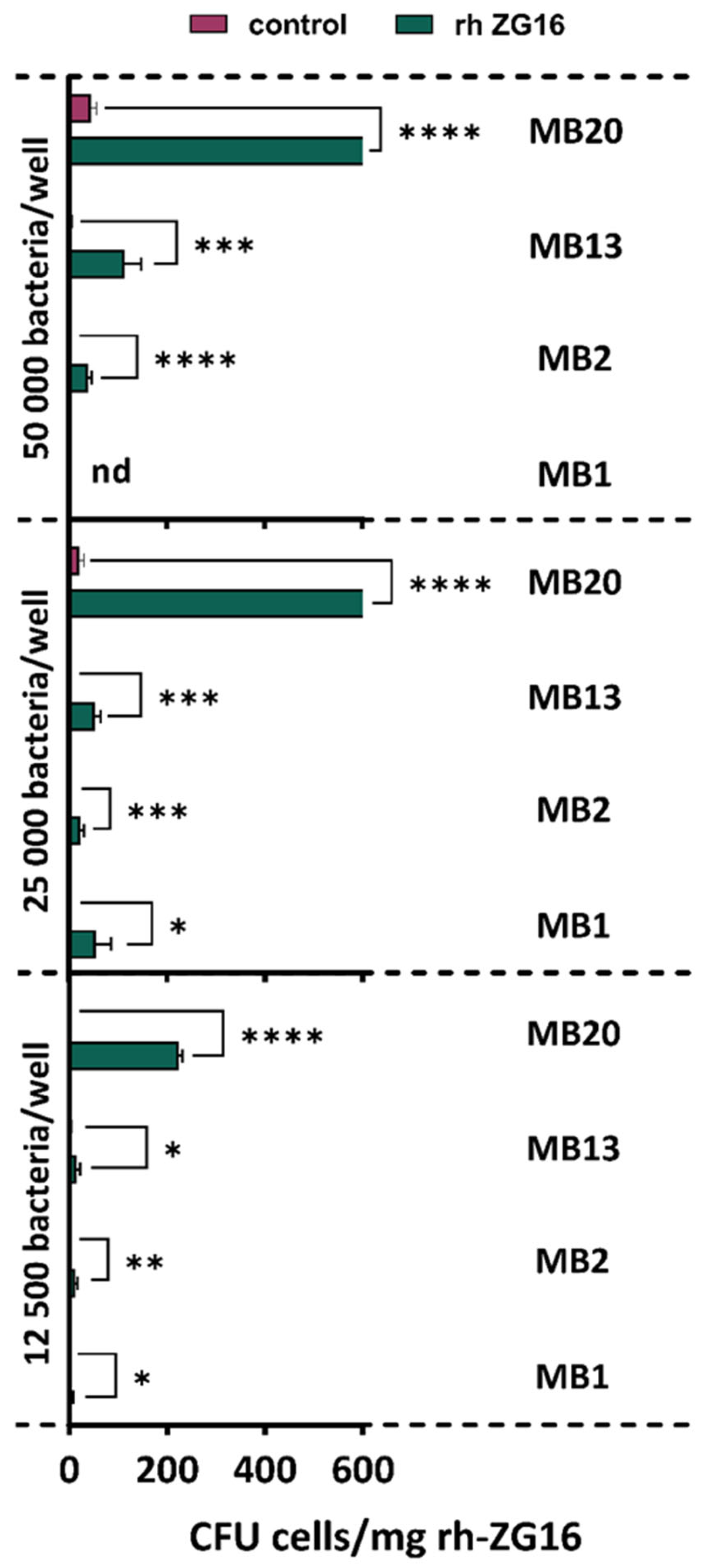
2.5. Adhesion to ZG16 Protein
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bacterial Strains and Cell Lines
3.2. Functional Annotation of L. brevis Genomes
3.3. Extraction of S-Layer Proteins from the Surface of L. brevis Strains
3.4. Autoaggregation and Coaggregation Assay
3.5. Competitive Exclusion Assay
3.6. The Effect of L. brevis and Their S-proteins on the Improvement of Epithelial Barrier Function In Vitro
3.6.1. Cell Treatments
3.6.2. Immunofluorescent Microscopic Analysis of TJ Protein Expression
3.7. Flow Cytometric Measurement of Cytokines
3.8. Ability of L. brevis Strains to Adhere to Recombinant Human ZG16 Protein
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E. The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Shadan, A.; Ma, Y. Biotechnological applications of probiotics: A multifarious weapon to disease and metabolic abnormality. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2022, 14, 1184–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, C.P.; Guimaraes, J.T.; Esmerino, E.A.; Duarte, M.C.K.; Silva, M.C.; Silva, R.; Ferreira, B.M.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Freitas, M.Q.; Cruz, A.G. Paraprobiotics and postbiotics: Concepts and potential applications in dairy products. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.S.; Schnorr, C.E.; Pasquali, M.A.D.B. Paraprobiotics and Postbiotics-Current State of Scientific Research and Future Trends toward the Development of Functional Foods. Foods 2023, 12, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas-González, P.F.; Liceaga, A.M.; Aguilar-Toalá, J.E. Postbiotics and Paraprobiotics: From concepts to applications. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banić, M.; Butorac, K.; Čuljak, N.; Butorac, A.; Novak, J.; Pavunc, A.L.; Rušanac, A.; Stanečić, Ž.; Lovrić, M.; Šušković, J.; et al. An Integrated Comprehensive Peptidomics and In Silico Analysis of Bioactive Peptide-Rich Milk Fermented by Three Autochthonous Cocci Strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assandri, M.H.; Malamud, M.; Trejo, F.M.; de los A Serradell, M. S-layer proteins as immune players: Tales from pathogenic and non-pathogenic bacteria. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2023, 4, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banić, M.; Uroić, K.; Pavunc, A.L.; Novak, J.; Zorić, K.; Durgo, K.; Petković, H.; Jamnik, P.; Kazazić, S.; Kazazić, S.; et al. Characterization of S-layer proteins of potential probiotic starter culture Lactobacillus brevis SF9B isolated from sauerkraut. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 93, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelin, J.; Kavitha, M. Exopolysaccharides from probiotic bacteria and their health potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butorac, K.; Banić, M.; Novak, J.; Pavunc, A.L.; Uroić, K.; Durgo, K.; Oršolić, N.; Kukolj, M.; Radović, S.; Scalabrin, S.; et al. The functional capacity of plantaricin-producing Lactobacillus plantarum SF9C and S-layer-carrying Lactobacillus brevis SF9B to withstand gastrointestinal transit. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čuljak, N.; Bellich, B.; Pedron, A.; Butorac, K.; Pavunc, A.L.; Novak, J.; Banić, M.; Šušković, J.; Cescutti, P.; Kos, B. Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains MC1 and D12: Functional properties and exopolysaccharides characterization. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 133215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butorac, K.; Novak, J.; Bellich, B.; Terán, L.C.; Banić, M.; Pavunc, A.L.; Zjalić, S.; Cescutti, P.; Šušković, J.; Kos, B. Lyophilized alginate-based microspheres containing Lactobacillus fermentum D12, an exopolysaccharides producer, contribute to the strain’s functionality in vitro. Microb. Cell Factories 2021, 20, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banić, M.; Butorac, K.; Čuljak, N.; Pavunc, A.L.; Novak, J.; Bellich, B.; Kazazić, S.; Kazazić, S.; Cescutti, P.; Šušković, J.; et al. The Human Milk Microbiota Produces Potential Therapeutic Biomolecules and Shapes the Intestinal Microbiota of Infants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čuljak, N.; Pavunc, A.L.; Dučkić, K.; Butorac, K.; Banić, M.; Novak, J.; Šušković, J.; Kos, B. Functionality and protective effect of S-layer proteins in microencapsulated freeze-dried probiotic Levilactobacillus brevis strains. Mljekarstvo 2024, 74, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, R.; Uroić, K.; Hynonen, U.; Kos, B.; Šušković, J.; Palva, A. Genome Sequence of Lactobacillus brevis Strain D6, Isolated from Smoked Fresh Cheese. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00264-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausova, G.; Hyrslova, I.; Hynstova, I. In vitro evaluation of adhesion capacity, hydrophobicity, and auto-aggregation of newly isolated potential probiotic strains. Fermentation 2019, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, Z.C.; Langa, R.L.S.; Aiyegoro, O.A.; Okoh, A.I. Safety Evaluation and Colonisation Abilities of Four Lactic Acid Bacteria as Future Probiotics. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alp, D.; Kuleaşan, H.; Altıntaş, A.K. The importance of the S-layer on the adhesion and aggregation ability of lactic acid bacteria. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 3449–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zyl, W.F.; Deane, S.M.; Dicks, L.M.T. Molecular insights into probiotic mechanisms of action employed against intestinal pathogenic bacteria. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, e1831339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytgat, H.L.; Douillard, F.P.; Reunanen, J.; Rasinkangas, P.; Hendrickx, A.P.; Laine, P.K.; Paulin, L.; Satokari, R.; de Vos, W.M. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG outcompetes Enterococcus faecium via mucus-binding pili: Evidence for a novel and heterospecific probiotic mechanism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5756–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, D.I.; Cook, P.W.; Franco, J.G.; Bugarel, M.; Kottapalli, K.R.; Loneragan, G.H.; Brashears, M.M.; Nightingale, K.K. A Systematic Approach to Identify and Characterize the Effectiveness and Safety of Novel Probiotic Strains to Control Foodborne Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Guo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Pan, D. Extraction of Lactobacillus acidophilus CICC 6074 S-layer proteins and their ability to inhibit enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, A.; Turner, J.R. Cell biology of tight junction barrier regulation and mucosal disease. CHS Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a029314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, L.J.; Arboleda, S.; Angelov, N.; Arce, R.M. Oral Versus Gastrointestinal Mucosal Immune Niches in Homeostasis and Allostasis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 705206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, T.; Furuse, M. Tight junction structure and function revisited. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landy, J.; Ronde, E.; English, N.; Clark, S.K.; Hart, A.L.; Knight, S.C.; Ciclitira, P.J.; Al-Hassi, H.O. Tight junctions in inflammatory bowel diseases and inflammatory bowel disease associated colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ren, L.F.; Li, Z.J.; Zhabg, L. How do intestinal probiotics restore the intestinal barrier? Front. Micriobiol. 2022, 13, 929346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Li, W.; Boardman, L.A.; Wang, L. Loss of ZG16 is associated with molecular and clinicopathological phenotypes of colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, J.H.; Birchenough, G.M.; Katona, G.; Schroeder, B.O.; Schütte, A.; Ermund, A.; Johansson, M.E.; Hansson, G.C. Gram-positive bacteria are held at a distance in the colon mucus by the lectin-like protein ZG16. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13833–13838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Zhao, K.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Nie, L.; Wei, H.; Wan, C. Effect of 3 lactobacilli on immunoregulation and intestinal microbiota in a β-lactoglobulin–induced allergic mouse model. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1943–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tommaso, N.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ponziani, F.R. Intestinal Barrier in Human Health and Disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Yan, X.; Weng, W.; Yang, Y.; Gao, R.; Liu, M.; Pan, C.; Zhu, Q.; Li, H.; Wei, Q.; et al. Micro integral membrane protein (MIMP), a newly discovered anti-inflammatory protein of Lactobacillus plantarum, enhances the gut barrier and modulates microbiota and inflammatory cytokines. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 474–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendinelli, P.; De Noni, I.; Cattaneo, S.; Silvetti, T.; Brasca, M.; Piazzalunga, F.; Donetti, E.; Ferraretto, A. Surface layer proteins from Lactobacillus helveticus ATCC® 15009™ affect the gut barrier morphology and function. Tissue Barriers 2023, 12, 2289838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T. Regulation of the intestinal barrier by nutrients: The role of tight junctions. Anim. Sci. J. 2020, 91, e13357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Post, S.; Jabbar, K.S.; Birchenough, G.; Arike, L.; Akhtar, N.; Sjovall, H.; Johansson, M.E.V.; Hansson, G.C. Structural weakening of the colonic mucus barrier is an early event in ulcerative colitis pathogenesis. Gut 2019, 68, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javitt, G.; Kinzel, A.; Reznik, N.; Fass, D. Conformational switches and redox properties of the colon cancer-associated human lectin ZG16. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 6465–6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Meng, G.; Yang, G.; Li, H. ZG16 impacts gut microbiota-associated intestinal inflammation and pulmonary mucosal function through bacterial metabolites. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 141, 112995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.H.; Crawley, S.C.; Hokari, R.; Kato, S.; Yang, S.C.; Li, J.D.; Kim, Y.S. TNF-alpha activates MUC2 transcription via NF-kappaB but inhibits via JNK activation. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 15, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmani, P.; Leung, P.; Chadee, K. Tumor necrosis factor-α and Muc2 mucin play major roles in disease onset and progression in dextran sodium sulphate-induced colitis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, M.P.; Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Scheffel, J.; Dudeck, A.; Ruland, J.; Lepenies, B. S-Layer from Lactobacillus brevis modulates antigen-presenting cell functions via the Mincle-Syk-Card9 Axis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.; Selle, K.; O’Flaherty, S.; Goh, Y.J.; Klaenhammer, T. Identification of extracellular surface-layer associated proteins in Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. Microbiology 2013, 159, 2269–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Mu, J.; Zalan, Z.; Hegyi, F.; Takács, K.; Zhao, X.; Du, M. Protective effect of Lactobacillus fermentum CQPC04 on dextran sulfate sodium–induced colitis in mice is associated with modulation of the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9570–9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayivi, R.D.; Gyawali, R.; Krastanov, A.; Aljaloud, S.O.; Worku, M.; Tahergorabi, R.; da Silva, R.C.; Ibrahim, S.A. Lactic acid bacteria: Food safety and human health applications. Dairy 2020, 1, 202–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Chai, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Intestinal mucus components and secretion mechanisms: What we do and do not know. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phùng, T.T.T.; Dupont, S.; Beney, L.; Moundanga, S.; Denimal, E.; Hồ, P.H.; Karbowiak, T. Ex-vivo investigation of probiotic bacterial adhesion to the intestinal mucus. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurina, I.B.; Blažević, I.; Jurina, T.; Pavunc, A.L.; Božanić, R.; Jakopović, K.L. Evaluation of heat-induced changes and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural formation in mare milk—A comparative study to cow milk. Mljekarstvo 2024, 74, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavunc, A.L.; Penava, L.; Ranilović, J.; Novak, J.; Banić, M.; Butorac, K.; Petrović, E.; Mihaljević-Herman, V.; Bendelja, K.; Savić-Mlakar, A.; et al. Influence of Dehydrated Wheat/Rice Cereal Matrices on Probiotic Activity of Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis BB-12®. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Kingdom, One-Way ANOVA Calculator and Tukey HSD, Statistics Kingdom: Website for Statistics Calculators. 2024. Available online: http://www.statskingdom.com (accessed on 2 September 2024).

| Autoaggregation % | ||
|---|---|---|
| L. brevis | Untreated (S+) | GHCl-Treated (S−) |
| MB1 | 73.57 ± 5.91 a | 26.44 ± 4.57 b |
| MB2 | 66.04 ± 8.33 a | 42.53 ± 7.18 b |
| MB13 | 77.15 ± 4.89 a | 41.51 ± 12.57 b |
| MB20 | 69.65 ± 5.27 a | 21.92 ± 3.26 b |
| L. brevis | Coaggregation % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. Typhimurium FP1 | E. coli 3014 | |||
| Untreated (S+) | GHCl-Treated (S−) | Untreated (S+) | GHCl-Treated (S−) | |
| MB1 | 47.07 ± 8.05 a | 19.62 ± 2.71 b | 41.54 ± 2.96 a | 28.02 ± 3.74 b |
| MB2 | 46.73 ± 8.04 a | 16.97 ± 0.96 b | 32.41 ± 4.35 a | 18.59 ± 2.69 b |
| MB13 | 26.36 ± 1.14 a | 16.35 ± 0.94 b | 26.34 ± 4.07 a | 36.72 ± 5.06 a |
| MB20 | 34.63 ± 3.17 a | 22.20 ± 1.64 b | 35.12 ± 8.42 a | 23.55 ± 4.43 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čuljak, N.; Bendelja, K.; Leboš Pavunc, A.; Butorac, K.; Banić, M.; Savić Mlakar, A.; Cvetić, Ž.; Hrsan, J.; Novak, J.; Šušković, J.; et al. In Vitro Analysis of Probiotic Properties Related to the Adaptation of Levilactobacillus brevis to Intestinal Microenvironment and Involvement of S-Layer Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062425
Čuljak N, Bendelja K, Leboš Pavunc A, Butorac K, Banić M, Savić Mlakar A, Cvetić Ž, Hrsan J, Novak J, Šušković J, et al. In Vitro Analysis of Probiotic Properties Related to the Adaptation of Levilactobacillus brevis to Intestinal Microenvironment and Involvement of S-Layer Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062425
Chicago/Turabian StyleČuljak, Nina, Krešo Bendelja, Andreja Leboš Pavunc, Katarina Butorac, Martina Banić, Ana Savić Mlakar, Željko Cvetić, Jana Hrsan, Jasna Novak, Jagoda Šušković, and et al. 2025. "In Vitro Analysis of Probiotic Properties Related to the Adaptation of Levilactobacillus brevis to Intestinal Microenvironment and Involvement of S-Layer Proteins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062425
APA StyleČuljak, N., Bendelja, K., Leboš Pavunc, A., Butorac, K., Banić, M., Savić Mlakar, A., Cvetić, Ž., Hrsan, J., Novak, J., Šušković, J., & Kos, B. (2025). In Vitro Analysis of Probiotic Properties Related to the Adaptation of Levilactobacillus brevis to Intestinal Microenvironment and Involvement of S-Layer Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062425






