Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Bone-Related Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
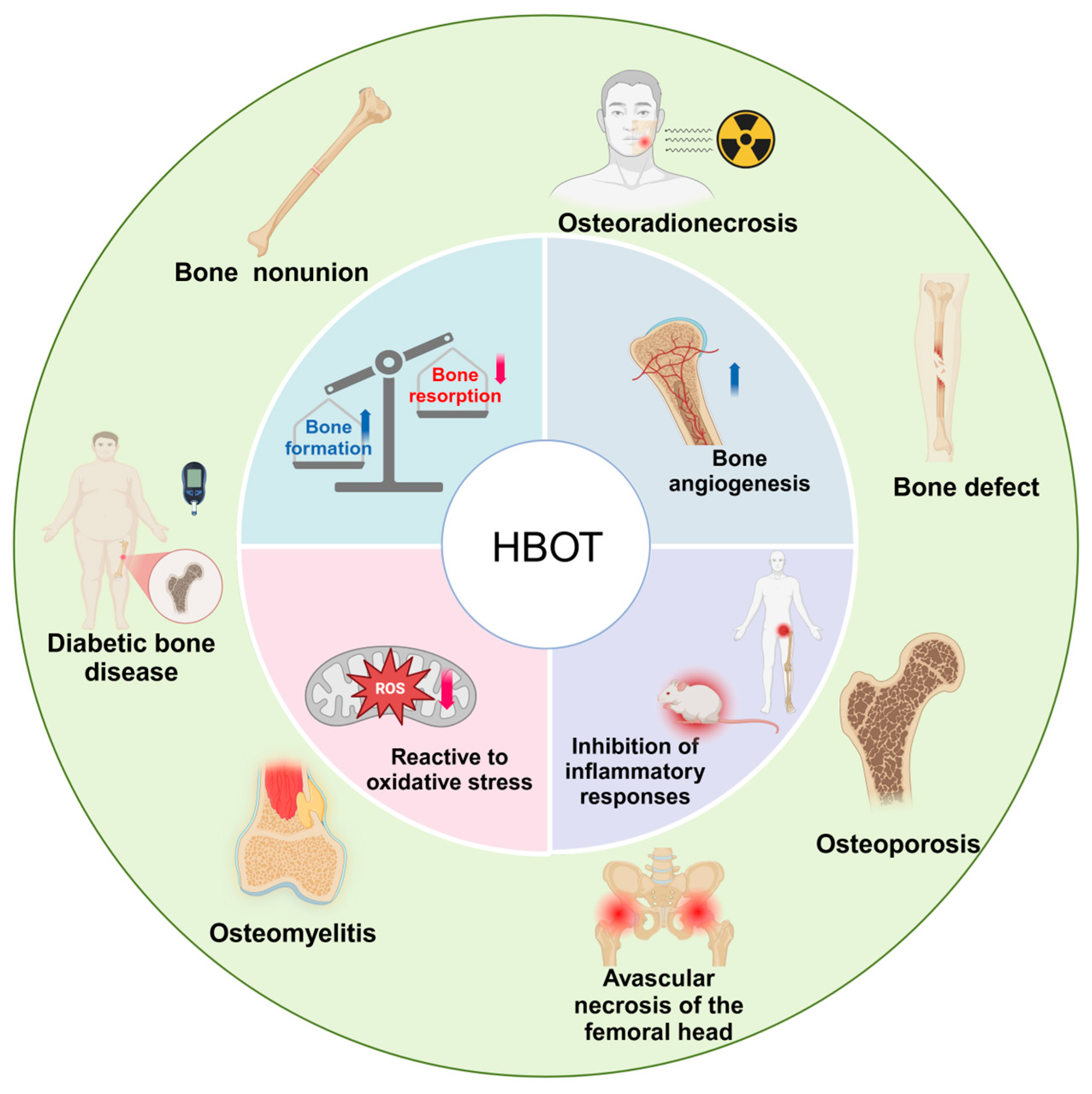
2. Mechanism of HBOT on the Bone
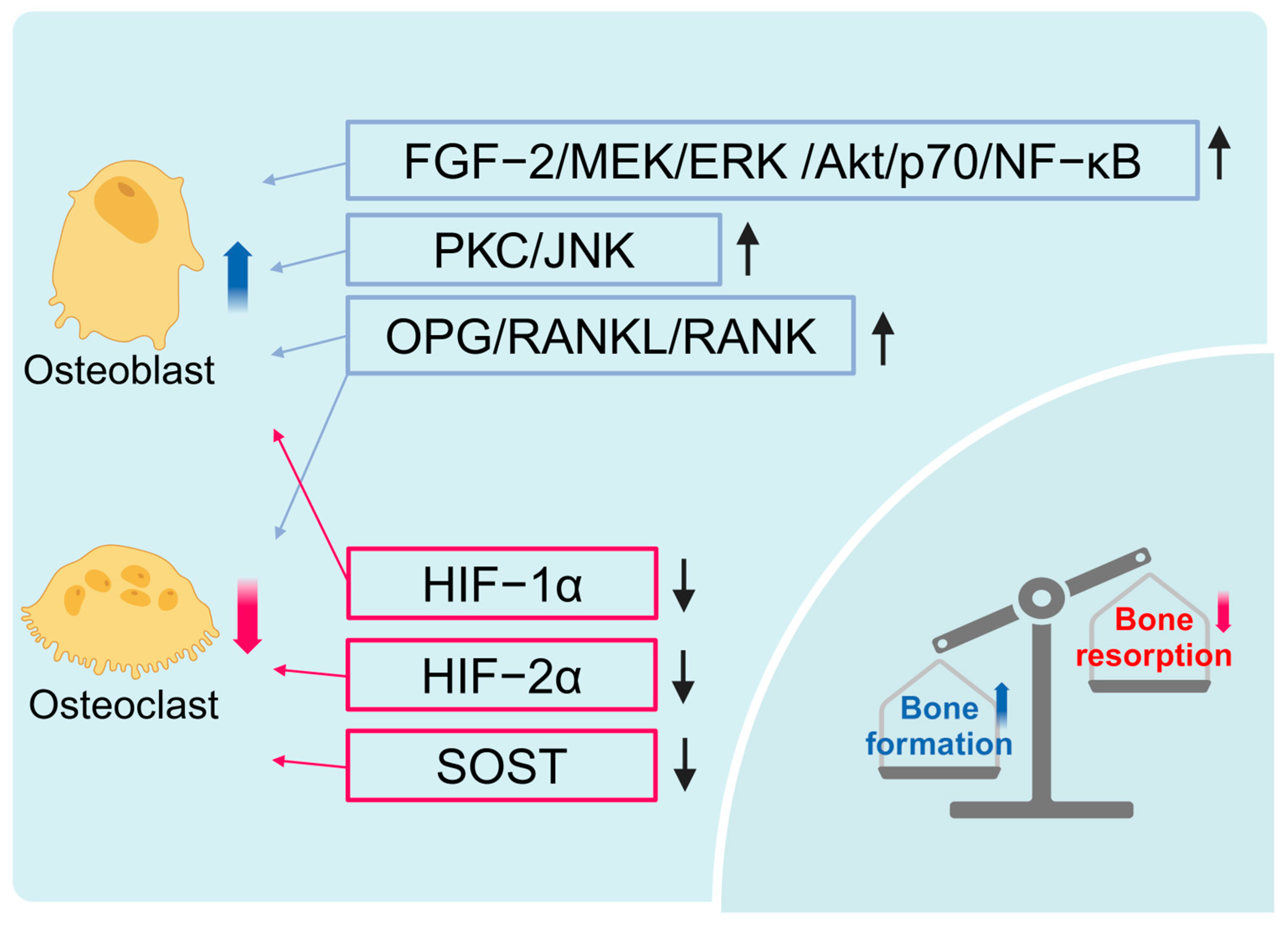
2.1. HBOT Promotes Bone Formation and Inhibits Bone Resorption
2.2. HBOT Promotes Bone Vascularization
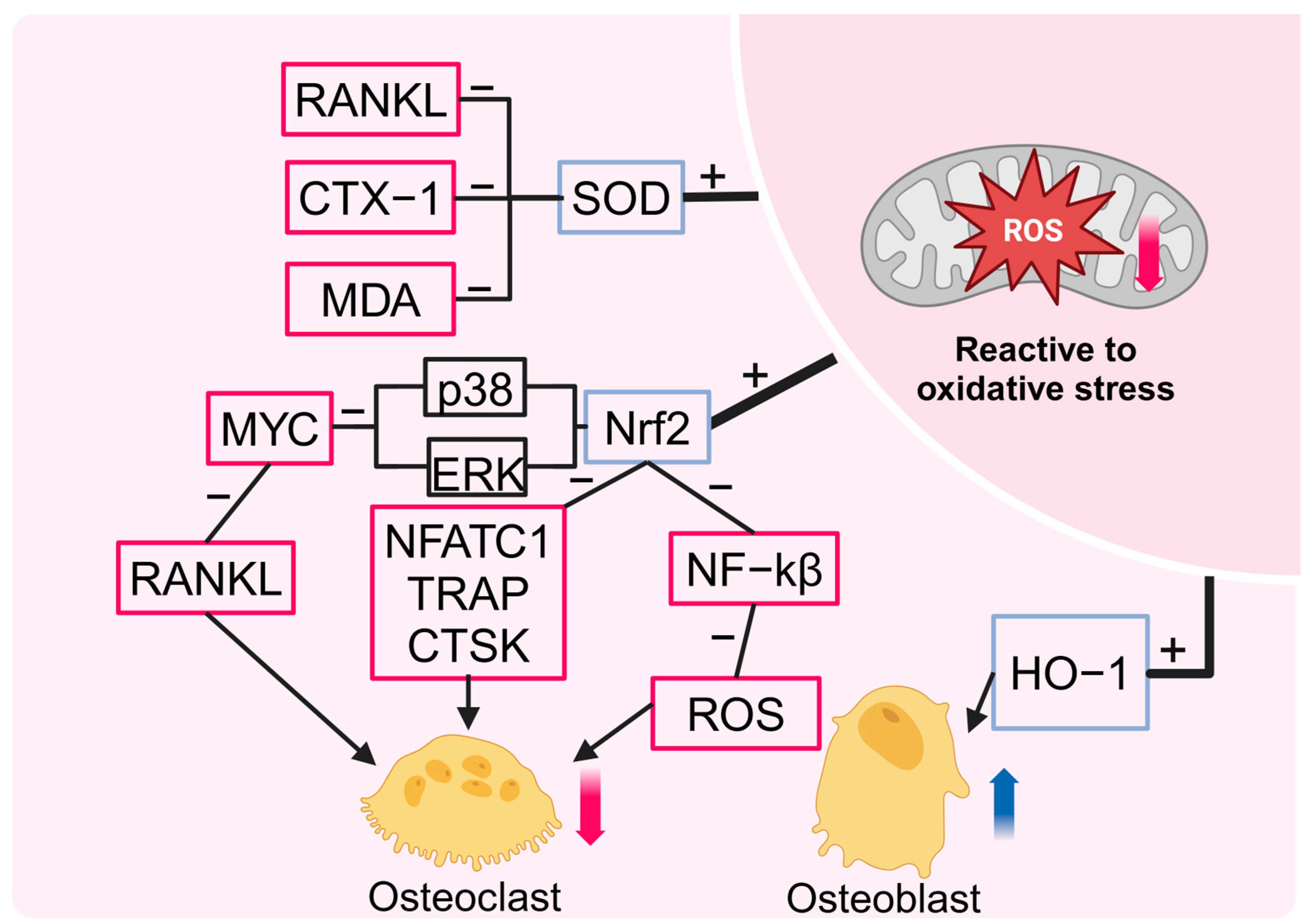
2.3. HBOT Reduces Oxidative Stress
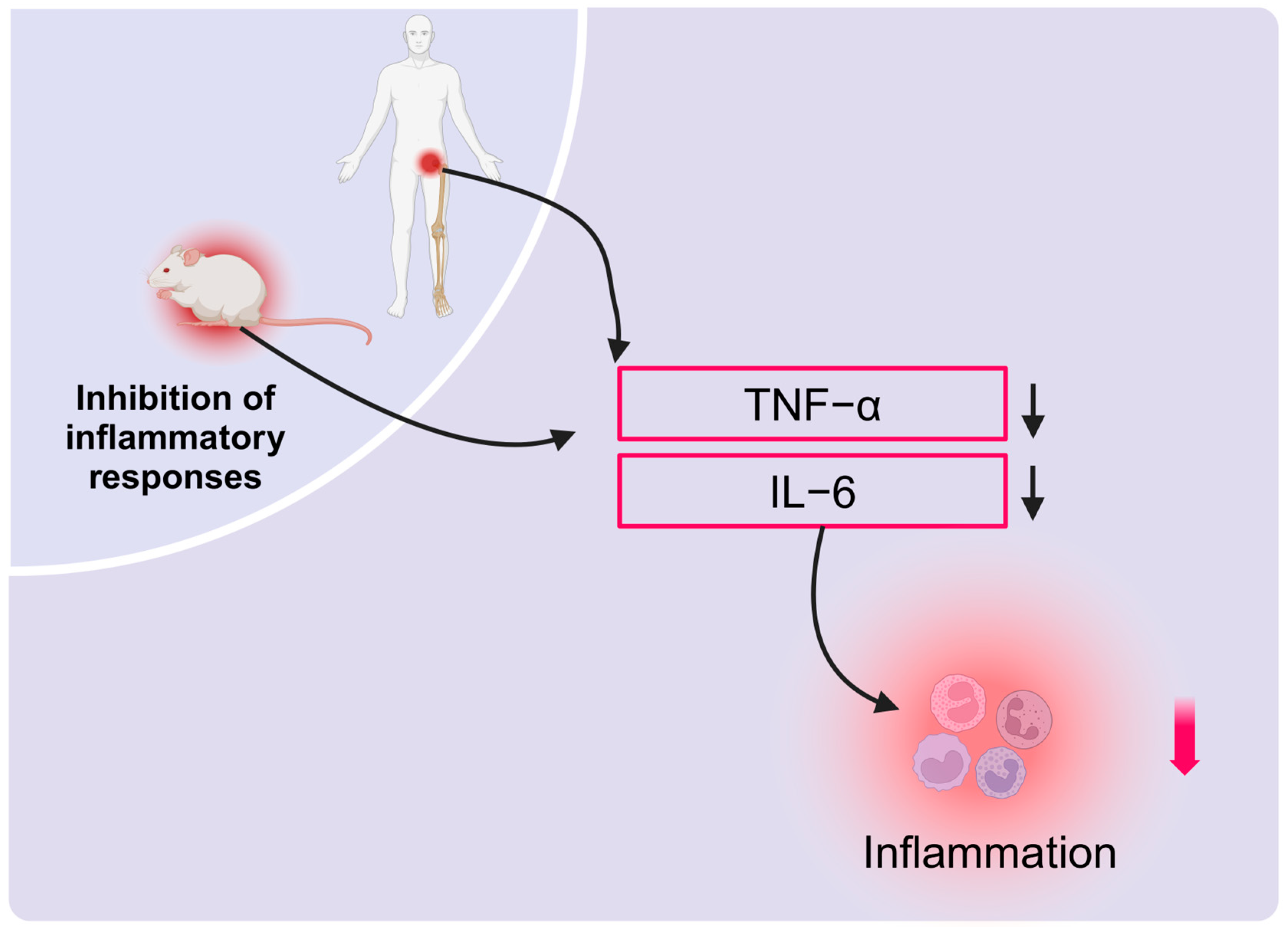
2.4. HBOT Effectively Suppresses Inflammation
3. HBOT in Clinical Skeletal Diseases
3.1. Osteoporosis
3.2. Diabetic Bone Disease
3.3. Bone Defect
3.4. Bone Nonunion
3.5. Osteoradionecrosis
3.6. Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head
3.7. Osteomyelitis
| Species | Time | Frequency | Pressure (bar) | Duration (min) | Adaptation Disease | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse | 60 | 5 days/week | 2.5 | 90 | Cranial bone defects | [126] |
| Rat | 14 | Once per day | 2 | 80 | Osteoporosis | [62] |
| Rat | 40 | Twice daily (Initial course) Once daily (Subsequent courses) | 2.2 | 40 | Osteoporosis | [102] |
| Rat | 15 | Once every two days | 2.5 | 90 | Type 1 diabetic bone disease | [65] |
| Rat | 15 | 5 days/week | 2.4 | 90 | Type 1 diabetic bone disease | [115] |
| Rat | 1–7 | Once per day | 2.5 | 90 | Femoral bone defect | [122] |
| Rat | 7 | Once per day | 2.5 | 90 | Diabetes mellitus combined with femoral bone defects | [114] |
| Rat | 20 | 5 days/week | 2 | 90 | Femoral bone defect | [36] |
| Rat | 2–42 | Once per day | 2.5 | 90 | Ischemic necrosis of the femoral head | [160] |
| Rabbit | 10 | Once per day | 2.4 | 90 | Diabetic Bone Disease Implant Integration | [116] |
| Rabbit | 20 | Once per day | 2.4 | 90 | Cranial bone defects | [120] |
| Rabbit | 15–30 | 5 days/week | 2.4 | 90 | Radial stem bone defect | [119] |
| Rabbit | 20 | 5 days/week | 2.4 | 90 | Cranial bone defects | [47] |
| Rabbit | 20 | Once per day | 2.5 | 120 | Atrophic tibial nonunion | [133] |
| Rabbit | 18 | Once per day | 2.5 | 90 | Traction osteogenesis of the irradiated mandible | [37] |
| Rabbit | 30 | Once per day | 2.0 | 45 | Ischemic necrosis of the femoral head | [158] |
| Human | 40, 90 | 5 days/week | 2.5 | 90 | Transient osteoporosis of the hip joint | [105] |
| Human | 20 | Once per day | 2.5 | 90 | Aseptic tibial nonunion | [132] |
| Human | 30–60 (determined based on the course of the disease) | 5 days/week | 2.4 | 90 | Radiation-induced osteonecrosis and irradiation-induced wounds | [143] |
| Human | 20–40 | 3–4 times/week | 2.2 | 90 | Ischemic necrosis of the femoral head | [156] |
| Human | 30 | 6 days/week | 2.4 | 120 | Osteonecrosis of the hip | [157] |
| Human | 60 (2 cycles) | Once a day, with a 30-day interval between weeks | 2.5 | 90 | Ischemic necrosis of the femoral head | [60] |
| Human | 60 (2 cycles) | 5 days/week | 2.4 | 90 | Ischemic necrosis of the femoral head | [22] |
| Human | Treatment is stopped in the presence of signs of recovery and the condition has clearly stopped for two weeks | 5 days/week | 2 | 120 | Refractory osteomyelitis | [173] |
| Human | 50 | 5 days/week | 2.5 | 120 | Refractory osteomyelitis | [174] |
4. Limitations: Adverse Events in HBOT
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carreau, A.; El Hafny-Rahbi, B.; Matejuk, A.; Grillon, C.; Kieda, C. Why is the partial oxygen pressure of human tissues a crucial parameter? Small molecules and hypoxia. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipowska, J.; Tomaszewski, K.A.; Niedźwiedzki, Ł.; Walocha, J.A.; Niedźwiedzki, T. The role of vasculature in bone development, regeneration and proper systemic functioning. Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, C.; Gilbert, S.R.; Clemens, T.L. Oxygen sensing and osteogenesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1117, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, C.; Carmeliet, G.; Schipani, E. Hypoxia-driven pathways in bone development, regeneration and disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grim, P.S.; Gottlieb, L.J.; Boddie, A.; Batson, E. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy. JAMA 1990, 263, 2216–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibbles, P.M.; Edelsberg, J.S. Hyperbaric-oxygen therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, K.; Patel, S.; Gandhi, J.; Suh, Y.; Reid, I.; Joshi, G.; Smith, N.L.; Khan, S.A. Clinical utility of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in dentistry. Med. Gas. Res. 2019, 9, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wolde, S.D.; Hulskes, R.H.; Weenink, R.P.; Hollmann, M.W.; Van Hulst, R.A. The Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygenation on Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Angiogenesis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottfried, I.; Schottlender, N.; Ashery, U. Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment—From Mechanisms to Cognitive Improvement. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, M.H.; Stanford, R.E.; Turner, R. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for promoting fracture healing and treating fracture non-union. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 11, CD004712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmann, J.; Kamolz, L.; Graier, W.; Smolle, J.; Smolle-Juettner, F.-M. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy and Tissue Regeneration: A Literature Survey. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducy, P.; Zhang, R.; Geoffroy, V.; Ridall, A.L.; Karsenty, G. Osf2/Cbfa1: A transcriptional activator of osteoblast differentiation. Cell 1997, 89, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, S.; Rodan, G.A. Control of osteoblast function and regulation of bone mass. Nature 2003, 423, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Duan, N.; Zhu, G.; Schwarz, E.M.; Xie, C. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect. Tissue Res. 2018, 59, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roodman, G.D. Advances in bone biology: The osteoclast. Endocr. Rev. 1996, 17, 308–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, W.J.; Simonet, W.S.; Lacey, D.L. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 2003, 423, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-M.; Lin, C.; Stavre, Z.; Greenblatt, M.B.; Shim, J.-H. Osteoblast-Osteoclast Communication and Bone Homeostasis. Cells 2020, 9, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Malda, J.; Crawford, R.; Xiao, Y. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts from human alveolar bone. Connect. Tissue Res. 2007, 48, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hadi, H.; Smerdon, G.R.; Fox, S.W. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy accelerates osteoblast differentiation and promotes bone formation. J. Dent. 2015, 43, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.P.; Chiou, Y.L.; Lin, C.Y. Hyperbaric oxygen-stimulated proliferation and growth of osteoblasts may be mediated through the FGF-2/MEK/ERK 1/2/NF-κB and PKC/JNK pathways. Connect. Tissue Res. 2010, 51, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemura, A.; Pajevic, P.D.; Egawa, T.; Teshigawara, R.; Hayashi, T.; Ishihara, A. Effects of mild hyperbaric oxygen on osteoporosis induced by hindlimb unloading in rats. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2020, 38, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, G.; Quartesan, S.; Cancellara, P.; Camporesi, E.; Mangar, D.; Bernasek, T.; Dalvi, P.; Yang, Z.; Paoli, A.; Rizzato, A.; et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy modulates serum OPG/RANKL in femoral head necrosis patients. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, B.F.; Xing, L. The RANKL/RANK/OPG pathway. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2007, 5, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hadi, H.; Smerdon, G.R.; Fox, S.W. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy suppresses osteoclast formation and bone resorption. J. Orthop. Res. 2013, 31, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, H.A.; Smerdon, G.; Fox, S.W. Osteoclastic resorptive capacity is suppressed in patients receiving hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Gao, B.; Wang, X.; Qin, X.; Peng, M.; Zeng, X. Hyperbaric oxygen and treadmill exercise partially prevented bone loss and bone microarchitecture deterioration in ovariectomized rats. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2023, 53, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imerb, N.; Thonusin, C.; Pratchayasakul, W.; Chanpaisaeng, K.; Aeimlapa, R.; Charoenphandhu, N.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy exerts anti-osteoporotic effects in obese and lean D-galactose-induced aged rats. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Liu, M.; Li, M.; Zhai, S.; Quni, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Jia, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y. The Role of HIF-1α in Bone Regeneration: A New Direction and Challenge in Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Miao, R.; Liu, G.; Qiu, X.; Yang, B.; Tan, X.; Liu, L.; Long, J.; Tang, W.; Jing, W. Spatiotemporal correlation between HIF-1α and bone regeneration. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaku, M.; Izumino, J.; Yamamoto, T.; Yashima, Y.; Shimoe, S.; Tanimoto, K. Functional regulation of osteoblastic MC3T3E-1 cells by hyperbaric oxygen treatment. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2022, 138, 105410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, R.E.; Silva, M.J. Skeletal Blood Flow in Bone Repair and Maintenance. Bone Res. 2013, 1, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisby, R.D. Bone Marrow Microvasculature. Compr. Physiol. 2020, 10, 1009–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsenty, G.; Wagner, E.F. Reaching a genetic and molecular understanding of skeletal development. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Crane, J.L. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics 2020, 10, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopf, H.W.; Gibson, J.J.; Angeles, A.P.; Constant, J.S.; Feng, J.J.; Rollins, M.D.; Zamirul Hussain, M.; Hunt, T.K. Hyperoxia and angiogenesis. Wound Repair. Regen. 2005, 13, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, E.; Sullivan, T.; Berg, E. Animal model for evaluating bone repair with and without adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO): Comparing dose schedules. J. Invest. Surg. 1990, 3, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhonen, A.; Haaparanta, M.; Grönroos, T.; Bergman, J.; Knuuti, J.; Hinkka, S.; Happonen, R.P. Osteoblastic activity and neoangiogenesis in distracted bone of irradiated rabbit mandible with or without hyperbaric oxygen treatment. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 33, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inokuchi, T.; Kawamoto, T.; Aoki, K.; Aoki, A.; Nagahama, K.; Baba, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Shibayama, M.; Mano, Y.; Ohya, K.; et al. The effects of hyperbaric oxygen on tooth movement into the regenerated area after distraction osteogenesis. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2010, 47, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, T.; Tsuchiya, E.; Abe, M.; Amizuka, N. Cellular interplay of bone cells and vascular endothelial cells in bone. Clin. Calcium 2016, 26, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, C.; Wu, S.; Yang, K.; Yang, X.; Chen, Q.; Fu, G.; Liu, C. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy enhances osteointegration of reimplanted cranial flap by regulating osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling. J. Orthop. Res. 2024, 42, 2197–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, T.O.; Xing, Z.; Finne-Wistrand, A.; Hellem, S.; Mustafa, K. Hyperbaric oxygen stimulates vascularization and bone formation in rat calvarial defects. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 42, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.Y.; Tu, Y.K.; Ma, C.H.; Yeh, J.H.; Kao, F.C.; Yu, S.W.; Lee, M.S.; Chou, Y.C.; Ueng, S.W. Measurement of tibial endothelial cell function after cigarette smoking, cessation of smoking and hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Injury 2008, 39 (Suppl. 4), 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueng, S.W.; Lee, S.S.; Lin, S.S.; Wang, C.R.; Liu, S.J.; Tai, C.L.; Shih, C.H. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy mitigates the adverse effect of cigarette smoking on the bone healing of tibial lengthening: An experimental study on rabbits. J. Trauma. 1999, 47, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shao, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, H.; Miao, C. S100A8/A9(hi) neutrophils induce mitochondrial dysfunction and PANoptosis in endothelial cells via mitochondrial complex I deficiency during sepsis. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Yu, J.; Luo, Y.; Xie, M.; Qu, C.; Shi, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Kong, L.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Deficiency of S100 calcium binding protein A9 attenuates vascular dysfunction in aged mice. Redox Biol. 2023, 63, 102721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.-W.; Lian, W.-S.; Kuo, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-S.; Ko, J.-Y.; Wang, F.-S. S100 Calcium Binding Protein A9 Represses Angiogenic Activity and Aggravates Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fok, T.C.; Jan, A.; Peel, S.A.; Evans, A.W.; Clokie, C.M.; Sándor, G.K. Hyperbaric oxygen results in increased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) protein expression in rabbit calvarial critical-sized defects. Oral. Surg. Oral Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. 2008, 105, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Ren, J.; Qing, W.; Mu, Y.D.; Li, P. Impact of Hyperbaric Oxygen on the Healing of Teeth Extraction Sockets and Alveolar Ridge Preservation. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 2591–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautch, V.L. VEGF-directed blood vessel patterning: From cells to organism. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Q. HIF-1α increases the osteogenic capacity of ADSCs by coupling angiogenesis and osteogenesis via the HIF-1α/VEGF/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.; Lee, M.G. Oxidative stress and antioxidant strategies in dermatology. Redox Rep. 2016, 21, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolfi-Donegan, D.; Braganza, A.; Shiva, S. Mitochondrial electron transport chain: Oxidative phosphorylation, oxidant production, and methods of measurement. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auten, R.L.; Davis, J.M. Oxygen toxicity and reactive oxygen species: The devil is in the details. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 66, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarzi, S.; Romagnoli, C.; Marcucci, G.; Favilli, F.; Iantomasi, T.; Vincenzini, M.T. Redox regulation of ERK1/2 activation induced by sphingosine 1-phosphate in fibroblasts: Involvement of NADPH oxidase and platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1810, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, K. NADPH oxidases in bone homeostasis and osteoporosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 132, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, J.S.; Johnson, J.P.; Carlson, D.A. Oxidative Stress and Osteoporosis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2021, 103, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.H.; Oh, K.W.; Lee, W.Y.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, M.K.; Kwon, H.S.; Rhee, E.J.; Han, J.H.; Song, K.H.; Cha, B.Y.; et al. Association of oxidative stress with postmenopausal osteoporosis and the effects of hydrogen peroxide on osteoclast formation in human bone marrow cell cultures. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2010, 87, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.K.; Choi, Y.G.; Baik, J.Y.; Han, S.Y.; Jeong, D.W.; Bae, Y.S.; Kim, N.; Lee, S.Y. A crucial role for reactive oxygen species in RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Blood 2005, 106, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Duan, R.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for healthy aging: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Redox Biol. 2022, 53, 102352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, G.; Vezzani, G.; Mrakic Sposta, S.; Rizzato, A.; Enten, G.; Abou-Samra, A.; Malacrida, S.; Quartesan, S.; Vezzoli, A.; Camporesi, E. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy ameliorates osteonecrosis in patients by modulating inflammation and oxidative stress. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezgin, D.; Giardina, C.; Perdrizet, G.A.; Hightower, L.E. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen on mitochondrial and glycolytic energy metabolism: The caloristasis concept. Cell Stress. Chaperones 2020, 25, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imerb, N.; Thonusin, C.; Pratchayasakul, W.; Arunsak, B.; Nawara, W.; Aeimlapa, R.; Charoenphandhu, N.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves age induced bone dyshomeostasis in non-obese and obese conditions. Life Sci. 2022, 295, 120406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguz, E.; Ekinci, S.; Eroglu, M.; Bilgic, S.; Koca, K.; Durusu, M.; Kaldirim, U.; Sadir, S.; Yurttas, Y.; Cakmak, G.; et al. Evaluation and comparison of the effects of hyperbaric oxygen and ozonized oxygen as adjuvant treatments in an experimental osteomyelitis model. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 171, e61–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureda, A.; Batle, J.M.; Martorell, M.; Capó, X.; Tejada, S.; Tur, J.A.; Pons, A. Antioxidant Response of Chronic Wounds to Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limirio, P.H.J.O.; da Rocha Junior, H.A.; Morais, R.B.d.; Hiraki, K.R.N.; Balbi, A.P.C.; Soares, P.B.F.; Dechichi, P. Influence of hyperbaric oxygen on biomechanics and structural bone matrix in type 1 diabetes mellitus rats. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schottlender, N.; Gottfried, I.; Ashery, U. Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment: Effects on Mitochondrial Function and Oxidative Stress. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Chopra, A.; Giardina, C.; Sabbisetti, V.; Smyth, J.A.; Hightower, L.E.; Perdrizet, G.A. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) suppresses biomarkers of cell stress and kidney injury in diabetic mice. Cell Stress. Chaperones 2015, 20, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Shi, J.; Chen, O.; Li, J.; Sun, X. Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning ameliorates hypoxia-ischemia brain damage by activating Nrf2 expression in vivo and in vitro. Free Radic. Res. 2016, 50, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, X.; Meng, M.; Pan, X.; Huang, L.; Chen, C. Hyperbaric oxygen improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats via inhibition of ferroptosis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2023, 32, 107395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.E.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Fan, D.F.; Yang, C.; Li, H.; Guo, D.Z.; Pan, S.Y. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on the Nrf2 signaling pathway in secondary injury following traumatic brain injury. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, 15016933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, F.; Huang, J.W.; Ding, P.Y.; Zang, H.G.; Kou, Z.J.; Li, T.; Fan, J.; Peng, Z.W.; Yan, W.J. Nrf2/antioxidant defense pathway is involved in the neuroprotective effects of Sirt1 against focal cerebral ischemia in rats after hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 309, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.H.; Zhang, P.X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Yin, N. Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning protects the lung against acute pancreatitis induced injury via attenuating inflammation and oxidative stress in a nitric oxide dependent manner. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, C.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, Q. Protective effects of hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning against LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2018, 45, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhamodharan, U.; Karan, A.; Sireesh, D.; Vaishnavi, A.; Somasundar, A.; Rajesh, K.; Ramkumar, K.M. Tissue-specific role of Nrf2 in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers during hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 138, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, T.; Rea, S.L.; Goode, A.; Bennett, A.J.; Ratajczak, T.; Long, J.E.; Searle, M.S.; Goldring, C.E.; Park, B.K.; Copple, I.M.; et al. The S349T mutation of SQSTM1 links Keap1/Nrf2 signalling to Paget’s disease of bone. Bone 2013, 52, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, J.; Yang, X.; Jin, Z.; Xu, C. Nrf2: A promising therapeutic target in bone-related diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, T.; Schultz, M.A.; Freeman, M.L.; Biswas, S. Loss of Nrf2 accelerates ionizing radiation-induced bone loss by upregulating RANKL. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 2298–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzaki, H.; Shinohara, F.; Kajiya, M.; Kodama, T. The Keap1/Nrf2 protein axis plays a role in osteoclast differentiation by regulating intracellular reactive oxygen species signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23009–23020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.Y.H.; Li, Z.; Jones, M.M.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Fu, C.; Tu, C.; Oursler, M.J.; Qu, J.; Yang, S. Regulator of G protein signaling 12 enhances osteoclastogenesis by suppressing Nrf2-dependent antioxidant proteins to promote the generation of reactive oxygen species. Elife 2019, 8, e42951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzaki, H.; Shinohara, F.; Itohiya, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Katsumata, Y.; Matsuzawa, M.; Fukaya, S.; Miyamoto, Y.; Wada, S.; Nakamura, Y. RANKL induces Bach1 nuclear import and attenuates Nrf2-mediated antioxidant enzymes, thereby augmenting intracellular reactive oxygen species signaling and osteoclastogenesis in mice. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.S.U.; Mun, S.H.; Zeng, S.L.; Kim, H.; Bae, S.; Park-Min, K.-H. NRF2 Is an Upstream Regulator of MYC-Mediated Osteoclastogenesis and Pathological Bone Erosion. Cells 2020, 9, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Bao, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Song, T.; Sun, Y.; Pi, J. Nrf2 Mitigates RANKL and M-CSF Induced Osteoclast Differentiation via ROS-Dependent Mechanisms. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; He, C. Nrf2-mediated anti-inflammatory polarization of macrophages as therapeutic targets for osteoarthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 967193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Niu, X.; Wang, M.; Yu, S.; Wang, M.; Mu, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y. Anemoside B4 attenuates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by upregulating Nrf2 and dampens ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.-N.; Trang, N.M.; Kang, H.; Kim, K.H.; Jeong, G.-S. Phytol Suppresses Osteoclast Differentiation and Oxidative Stress through Nrf2/HO-1 Regulation in RANKL-Induced RAW264.7 Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yuan, W.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. HO-1 in Bone Biology: Potential Therapeutic Strategies for Osteoporosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 791585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönrock, N.; Tillmans, F.; Sebens, S.; Kähler, W.; Klapa, S.; Rieger, B.; Scherthan, H.; Koch, A. Analysis of Single- and Double-Stranded DNA Damage in Osteoblastic Cells after Hyperbaric Oxygen Exposure. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothfuss, A.; Radermacher, P.; Speit, G. Involvement of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in the adaptive protection of human lymphocytes after hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) treatment. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Xiong, L. Preconditioning with hyperbaric oxygen induces tolerance against oxidative injury via increased expression of heme oxygenase-1 in primary cultured spinal cord neurons. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Bauer, I. Heme oxygenase-1: Redox regulation and role in the hepatic response to oxidative stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2002, 4, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cheng, X.; Ma, W.; Chen, C. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on open tibial fractures in rabbits after transient seawater immersion. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2017, 44, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Fei, W.; Gao, W.; Fan, C.; Li, Y.; Hong, Y.; Cui, R. SOD3 regulates FLT1 to affect bone metabolism by promoting osteogenesis and inhibiting adipogenesis through PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 212, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.S.; Hu, X.F.; Wu, X.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yang, M.; Shen, C.L. Ganoderic Acid A prevents bone loss in lipopolysaccharide-treated male rats by reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2024, 401, 111164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Liu, Y. The Role of the Immune Microenvironment in Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 3697–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mountziaris, P.M.; Spicer, P.P.; Kasper, F.K.; Mikos, A.G. Harnessing and modulating inflammation in strategies for bone regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part. B Rev. 2011, 17, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, L.; Recknagel, S.; Ignatius, A. Fracture healing under healthy and inflammatory conditions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toosi, S.; Behravan, J. Osteogenesis and bone remodeling: A focus on growth factors and bioactive peptides. Biofactors 2020, 46, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, R.; Gravallese, E.M. Impact of inflammation on the osteoblast in rheumatic diseases. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2014, 12, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardin, C.; Bosco, G.; Ferroni, L.; Quartesan, S.; Rizzato, A.; Tatullo, M.; Zavan, B. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Improves the Osteogenic and Vasculogenic Properties of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Presence of Inflammation In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armas, L.A.; Recker, R.R. Pathophysiology of osteoporosis: New mechanistic insights. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 41, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Chen, H.; Tong, M.; Zhou, J.; Wu, X. Effects of Ultra-early Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Femoral Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Bone Metabolism of Rats With Complete Spinal Transection. Spine 2018, 43, E919–E926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanis, A.; Dimopoulou, S.; Karampinas, P.; Vavourakis, M.; Papagrigorakis, E.; Sakellariou, E.; Karampitianis, S.; Zachariou, D.; Theodora, M.; Antsaklis, P.; et al. The correlation between transient osteoporosis of the hip and pregnancy: A review. Medicine 2023, 102, e35475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesikburun, S.; Uran, A.; Demir, Y.; Güzelküçük, ü.; ErgöZen, S.; Tan, A.K. Transient osteoporosis of the hip and hyperbaric oxygen therapy: A report of two cases. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 57, e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Domachevsky, L.; Keynan, Y.; Militianu, D.; Goldenberg, I.; Adir, Y. Transient osteoporosis associated with hyperhomocystinemia: A possible role for hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2004, 31, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sahni, T.; Gupta, S. Case report: Treatment of bone marrow edema of femoral head with hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Apollo Med. 2016, 13, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, A.H.; Costa, A.B.; Engel, J.D.G.; Rezin, G.T. Mitochondrial dysfunction in obesity. Life Sci. 2018, 192, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Meouchy, P.; Wahoud, M.; Allam, S.; Chedid, R.; Karam, W.; Karam, S. Hypertension Related to Obesity: Pathogenesis, Characteristics and Factors for Control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilmeier, U.; Patsch, J.M. Diabetes and Bone. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2016, 20, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kume, S.; Kato, S.; Yamagishi, S.; Inagaki, Y.; Ueda, S.; Arima, N.; Okawa, T.; Kojiro, M.; Nagata, K. Advanced glycation end-products attenuate human mesenchymal stem cells and prevent cognate differentiation into adipose tissue, cartilage, and bone. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2005, 20, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhani, M.; Alikhani, Z.; Boyd, C.; MacLellan, C.M.; Raptis, M.; Liu, R.; Pischon, N.; Trackman, P.C.; Gerstenfeld, L.; Graves, D.T. Advanced glycation end products stimulate osteoblast apoptosis via the MAP kinase and cytosolic apoptotic pathways. Bone 2007, 40, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adil, M.; Khan, R.A.; Kalam, A.; Venkata, S.K.; Kandhare, A.D.; Ghosh, P.; Sharma, M. Effect of anti-diabetic drugs on bone metabolism: Evidence from preclinical and clinical studies. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 1328–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, P.C.; Limirio, P.; Linhares, C.R.B.; Bergamini, M.L.; Rocha, F.S.; Morais, R.B.; Balbi, A.P.C.; Hiraki, K.R.N.; Dechichi, P. Hyperbaric Oxygen therapy effects on bone regeneration in Type 1 diabetes mellitus in rats. Connect. Tissue Res. 2018, 59, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldisoky, R.H.; Younes, S.A.; Omar, S.S.; Gharib, H.S.; Tamara, T.A. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy efficacy on mandibular defect regeneration in rats with diabetes mellitus: An animal study. BMC Oral. Health 2023, 23, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altug, H.A.; Tatli, U.; Coskun, A.T.; Erdogan, Ö.; Özkan, A.; Sencimen, M.; Kürkçü, M. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen treatment on implant osseointegration in experimental diabetes mellitus. J. Appl. Oral. Sci. 2018, 26, e20180083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, J.; Liporace, A.; Egol, A.; McLaurin, M. Management of Bone Defects in Orthopedic Trauma. Bull. NYU Hosp. Jt. Dis. 2018, 76, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Karalashvili, L.; Kakabadze, A.; Uhryn, M.; Vyshnevska, H.; Ediberidze, K.; Kakabadze, Z. Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Bone Defects (Review). Georgian Med. News 2018, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Grassmann, J.P.; Schneppendahl, J.; Hakimi, A.R.; Herten, M.; Betsch, M.; Lögters, T.T.; Thelen, S.; Sager, M.; Wild, M.; Windolf, J.; et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves angiogenesis and bone formation in critical sized diaphyseal defects. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, A.M.; Sándor, G.K.; Iera, D.; Mhawi, A.; Peel, S.; Evans, A.W.; Clokie, C.M. Hyperbaric oxygen results in an increase in rabbit calvarial critical sized defects. Oral. Surg. Oral Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. 2006, 101, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, A.; Sándor, G.K.; Brkovic, B.B.; Peel, S.; Evans, A.W.; Clokie, C.M. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on grafted and nongrafted calvarial critical-sized defects. Oral. Surg. Oral Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. 2009, 107, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, F.S.; Gomes Moura, C.C.; Rocha Rodrigues, D.B.; Zanetta-Barbosa, D.; Nakamura Hiraki, K.R.; Dechichi, P. Influence of hyperbaric oxygen on the initial stages of bone healing. Oral. Surg. Oral Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. 2015, 120, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, H.; Lin, M.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Fu, G.; Liu, C. Hyperbaric oxygen promotes bone regeneration by activating the mechanosensitive Piezo1 pathway in osteogenic progenitors. J. Orthop. Translat 2024, 48, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirckx, N.; Van Hul, M.; Maes, C. Osteoblast recruitment to sites of bone formation in skeletal development, homeostasis, and regeneration. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today 2013, 99, 170–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, K.A.; Goldstein, L.J.; Thom, S.R.; Velazquez, O.C. Hyperbaric oxygen and bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells in diabetic wound healing. Vascular 2006, 14, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumino, J.; Kaku, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Yashima, Y.; Kagawa, H.; Ikeda, K.; Shimoe, S.; Tanimoto, K. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen treatment on calvarial bone regeneration in young and adult mice. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2020, 117, 104828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Barrena, E.; Ehrnthaller, C. Long bone uninfected non-union: Grafting techniques. EFORT Open Rev. 2024, 9, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderkarr, M.F.; Ruppenkamp, J.W.; Vanderkarr, M.; Holy, C.E.; Blauth, M. Risk factors and healthcare costs associated with long bone fracture non-union: A retrospective US claims database analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impieri, L.; Pezzi, A.; Hadad, H.; Peretti, G.M.; Mangiavini, L.; Rossi, N. Orthobiologics in delayed union and non-union of adult long bones fractures: A systematic review. Bone Rep. 2024, 21, 101760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tall, M. Treatment of aseptic tibial shaft non-union without bone defect. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2018, 104, S63–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atesalp, A.S.; Komurcu, M.; Basbozkurt, M.; Kurklu, M. The treatment of infected tibial nonunion with aggressive debridement and internal bone transport. Mil. Med. 2002, 167, 978–981. [Google Scholar]
- Rollo, G.; Bonura, E.M.; Falzarano, G.; Bisaccia, M.; Ribes Iborra, J.; Grubor, P.; Filipponi, M.; Pichierri, P.; Hitov, P.; Leonetti, D.; et al. Platet Rich Plasma or Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy as callus accellerator in aseptic tibial non union. Evaluate of outcomes. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, e2020188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kürklü, M.; Yurttaş, Y.; Köse, O.; Demiralp, B.; Yüksel, H.Y.; Kömürcü, M. Adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen therapy in the treatment of atrophic tibial nonunion with Ilizarov external fixator: A radiographic and scintigraphic study in rabbits. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2012, 46, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendenhall, W.M. Mandibular osteoradionecrosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 4867–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuther, T.; Schuster, T.; Mende, U.; Kübler, A. Osteoradionecrosis of the jaws as a side effect of radiotherapy of head and neck tumour patients--a report of a thirty year retrospective review. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 32, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, A.S.; Buchbinder, D.; Hu, K.; Urken, M.L. Paradigm shifts in the management of osteoradionecrosis of the mandible. Oral. Oncol. 2010, 46, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahidi, N.; Lee, T.S.; Daggumati, S.; Shokri, T.; Wang, W.; Ducic, Y. Osteoradionecrosis of the Midface and Mandible: Pathogenesis and Management. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2020, 34, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, G.H. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Promoting healing in difficult cases. Postgrad. Med. 1986, 79, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, R.E. Osteoradionecrosis: A new concept of its pathophysiology. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1983, 41, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronje, F.J. A review of the Marx protocols: Prevention and management of osteoradionecrosis by combining surgery and hyperbaric oxygen therapy. SADJ 1998, 53, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marx, R.E. A new concept in the treatment of osteoradionecrosis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1983, 41, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenwitheesuk, K.; Mahakkanukrauh, A.; Punjaruk, W.; Jenwitheesuk, K.; Chowchuen, B.; Jinaporntham, S.; Uraiwan, K.; Limrattanapimpa, P. Efficacy of Adjunctive Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Osteoradionecrosis. BioRes. Open Access 2018, 7, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korambayil, P.M.; Ambookan, P.V.; Pillai, S.; Karangath, R.R.; George, D. Role of Hyperbaric Medicine for Osteoradionecrosis and Post Irradiation Wounds: An Institutional Experience. Indian. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 11, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, D.E.; Koyfman, S.A.; Yarom, N.; Lynggaard, C.D.; Ismaila, N.; Forner, L.E.; Fuller, C.D.; Mowery, Y.M.; Murphy, B.A.; Watson, E.; et al. Prevention and Management of Osteoradionecrosis in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer Treated With Radiation Therapy: ISOO-MASCC-ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 1975–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raggio, B.S.; Winters, R. Modern management of osteoradionecrosis. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2018, 26, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, L.E.; Dieleman, F.J.; Shaw, R.J.; Kanatas, A.; Butterworth, C.J.; Kjeller, G.; Alsner, J.; Overgaard, J.; Hillerup, S.; Hyldegaard, O.; et al. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment of mandibular osteoradionecrosis: Combined data from the two randomized clinical trials DAHANCA-21 and NWHHT2009-1. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 166, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, A.; Hanna, G.J.; Margalit, D.N.; Chau, N.; Goguen, L.A.; Marty, F.M.; Rabinowits, G.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Sonis, S.T.; Thomas, T.; et al. The Use of Hyperbaric Oxygen for the Prevention and Management of Osteoradionecrosis of the Jaw: A Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center Multidisciplinary Guideline. Oncologist 2017, 22, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitak-Arnnop, P.; Sader, R.; Dhanuthai, K.; Masaratana, P.; Bertolus, C.; Chaine, A.; Bertrand, J.C.; Hemprich, A. Management of osteoradionecrosis of the jaws: An analysis of evidence. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 34, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenwitheesuk, K.; Mahakkanukrauh, A.; Punjaruk, W.; Vatanasapt, P.; Jenwitheesuk, K.; Surakunprapha, P.; Jinaporntham, S.; Uraiwan, K.; Limrattanapimpa, P. Is Adjunctive Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment Alone or with Surgery the Proper Management for Active and Persistent Osteoradionecrosis? Adv. Skin. Wound Care 2021, 34, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid, C.; Abarca, M.; Bouferrache, K. Osteoradionecrosis: An update. Oral. Oncol. 2010, 46, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, E.N.; Koval, O.A.; Nikolaevich Bezuglov, E.; Aleksandrovich Vetoshkin, A.; Gavriilovich Goncharov, N.; Encarnación Ramirez, M.D.J.; Montemurro, N. Conservative Treatment in Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head: A Systematic Review. Med. Sci. 2024, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerado, E.; Caso, E. The physiopathology of avascular necrosis of the femoral head: An update. Injury 2016, 47 (Suppl. 6), S16–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, M.; Milena, F.; Ruggero, C.; Stefania, S.; Giancarlo, T. Biophysical stimulation in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Indian. J. Orthop. 2009, 43, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theopold, J.; Armonies, S.; Pieroh, P.; Hepp, P.; Roth, A. Nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head: Arthroscopic and navigation-supported core decompression. Oper. Orthop. Traumatol. 2020, 32, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckmann, J.; Schmidt, T.; Schaumburger, J.; Rath, B.; Lüring, C.; Tingart, M.; Grifka, J. Infusion, core decompression, or infusion following core decompression in the treatment of bone edema syndrome and early avascular osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghamis, I.; Alhammoud, A.A.; Kokash, O.; Alhaneedi, G.A. The outcome of hyperbaric oxygen therapy versus core decompression in the non-traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head: Retrospective Cohort Study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 62, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, I.; Yalcin, N.; Uluyardimci, E.; Akgul, E.A. Combination of hyperbaric oxygen and core decompression therapies improve outcomes in the treatment of hip osteonecrosis. Hip Int. 2022, 32, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Pan, Z.Y.; Gu, H.; Li, N.; Qian, X.J.; Zhai, R.Y.; Wu, L.H.; Gao, C.J. Quantitative study of therapeutic efficacy on early intervention of hyperbaric oxygen to model of steroid-induced avascular osteonecrosis of femoral head by multi-slice perfusion imaging. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2008, 88, 3210–3216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Camporesi, E.M.; Bosco, G. Mechanisms of action of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2014, 41, 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, D.; Norman, D.; Zinman, C.; Rubinstein, L.; Sabo, E.; Misselevich, I.; Reis, D.; Boss, J.H. Treatment of experimental avascular necrosis of the femoral head with hyperbaric oxygen in rats: Histological evaluation of the femoral heads during the early phase of the reparative process. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 1999, 67, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dym, H.; Zeidan, J. Microbiology of Acute and Chronic Osteomyelitis and Antibiotic Treatment. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 61, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, D.P.; Waldvogel, F.A. Osteomyelitis. Lancet 2004, 364, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urish, K.L.; Cassat, J.E. Staphylococcus aureus Osteomyelitis: Bone, Bugs, and Surgery. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00932-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, M.E.; Hendriksen, S.; Cooper, J.S. Hyperbaric Treatment of Chronic Refractory Osteomyelitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mader, J.T.; Adams, K.R.; Wallace, W.R.; Calhoun, J.H. Hyperbaric oxygen as adjunctive therapy for osteomyelitis. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1990, 4, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costerton, J.W. Biofilm theory can guide the treatment of device-related orthopaedic infections. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2005, 437, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpen, M.; Mousavi, N.; Sams, T.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Ciofu, O.; Moser, C.; Kühl, M.; Høiby, N.; Jensen, P. Reinforcement of the bactericidal effect of ciprofloxacin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm by hyperbaric oxygen treatment. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, J.T.; Guckian, J.C.; Glass, D.L.; Reinarz, J.A. Therapy with hyperbaric oxygen for experimental osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus in rabbits. J. Infect. Dis. 1978, 138, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendel, V.; Reichert, B.; Simanowski, H.J.; Scholz, H.C. Therapy with hyperbaric oxygen and cefazolin for experimental osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus in rats. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 1999, 26, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mendel, V.; Simanowski, H.J.; Scholz, H. Synergy of HBO2 and a local antibiotic carrier for experimental osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus in rats. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2004, 31, 407–416. [Google Scholar]
- Memar, M.Y.; Yekani, M.; Alizadeh, N.; Baghi, H.B. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Antimicrobial mechanisms and clinical application for infections. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvidou, O.D.; Kaspiris, A.; Bolia, I.K.; Chloros, G.D.; Goumenos, S.D.; Papagelopoulos, P.J.; Tsiodras, S. Effectiveness of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Management of Chronic Osteomyelitis: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Orthopedics 2018, 41, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingham, E.L.; Hart, G.B. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment of refractory osteomyelitis. Postgrad. Med. 1977, 61, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menekse, S. Outcome of Chronic Foot Osteomyelitis Treated With Hyperbaric Oxygen: An Observational Study. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2024, 23, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edinguele, W.; Barberon, B.; Poussard, J.; Thomas, E.; Reynier, J.C.; Coulange, M. Middle-ear barotrauma after hyperbaric oxygen therapy: A five-year retrospective analysis on 2,610 patients. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2020, 47, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Minami, T.; Okuno, Y.; Kakuda, Y.; Tsutsumi, T.; Kogame, T.; Ohtsuru, S.; Sato, N.; Koike, K. Convulsive seizure and pulmonary edema during hyperbaric oxygen therapy: A case report. J. Med. Invest. 2018, 65, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalbano, C.; Kiorpes, C.; Elam, L.; Miscioscia, E.; Shmalberg, J. Common Uses and Adverse Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in a Cohort of Small Animal Patients: A Retrospective Analysis of 2,792 Treatment Sessions. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 764002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMonnies, C.W. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and the possibility of ocular complications or contraindications. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2015, 98, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.G.; Sloan, E.P.; Hart, R.G.; Narasimhan, K.; Barreca, R.S. Tension pneumothorax associated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 1991, 9, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, T.; Battal, B.; Kara, K.; Metin, S.; Demirbas, S.; Yildiz, S.; Uzun, G. A case of tension pneumothorax during hyperbaric oxygen therapy in an earthquake survivor with crush injury complicated by ARDS (adult respiratory distress syndrome). Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2015, 42, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Guenneugues, R.; Henckes, A.; Mansourati, V.; Mansourati, J. Effects of hyperbaric exposure on mechanical and electronic parameters of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. Europace 2023, 25, euad134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, K.; Banham, N.; Bonnington, S.; Gawthrope, I. Oxygen toxicity seizure mimics. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2021, 51, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, M.J.; Hampson, N.B. Partial seizure provoked by hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Possible mechanisms and implications. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 974–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, N.; Atik, D. Central nervous system oxygen toxicity during routine hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2003, 30, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riedl, P.; Škiljić, D.; Arnell, P.; Wannholt, R.; Zetterberg, M.; Andersson Grönlund, M. Myopic shift and lens turbidity following hyperbaric oxygen therapy—A prospective, longitudinal, observational cohort study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019, 97, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, J.; Zhu, C.; Zou, J.; Zhang, L. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Bone-Related Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031067
Feng J, Zhu C, Zou J, Zhang L. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Bone-Related Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031067
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Jie, Chenyu Zhu, Jun Zou, and Lingli Zhang. 2025. "Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Bone-Related Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031067
APA StyleFeng, J., Zhu, C., Zou, J., & Zhang, L. (2025). Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Bone-Related Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031067





