Canagliflozin Promotes Structural and Functional Changes in Proximal Tubular Cell Mitochondria of Hypertensive–Diabetic Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CANA Lowers Blood Glucose and Protects Against Albuminuria in Hypertensive–Diabetic Mice
2.2. Mitochondria Morphology and Networking in PTECs
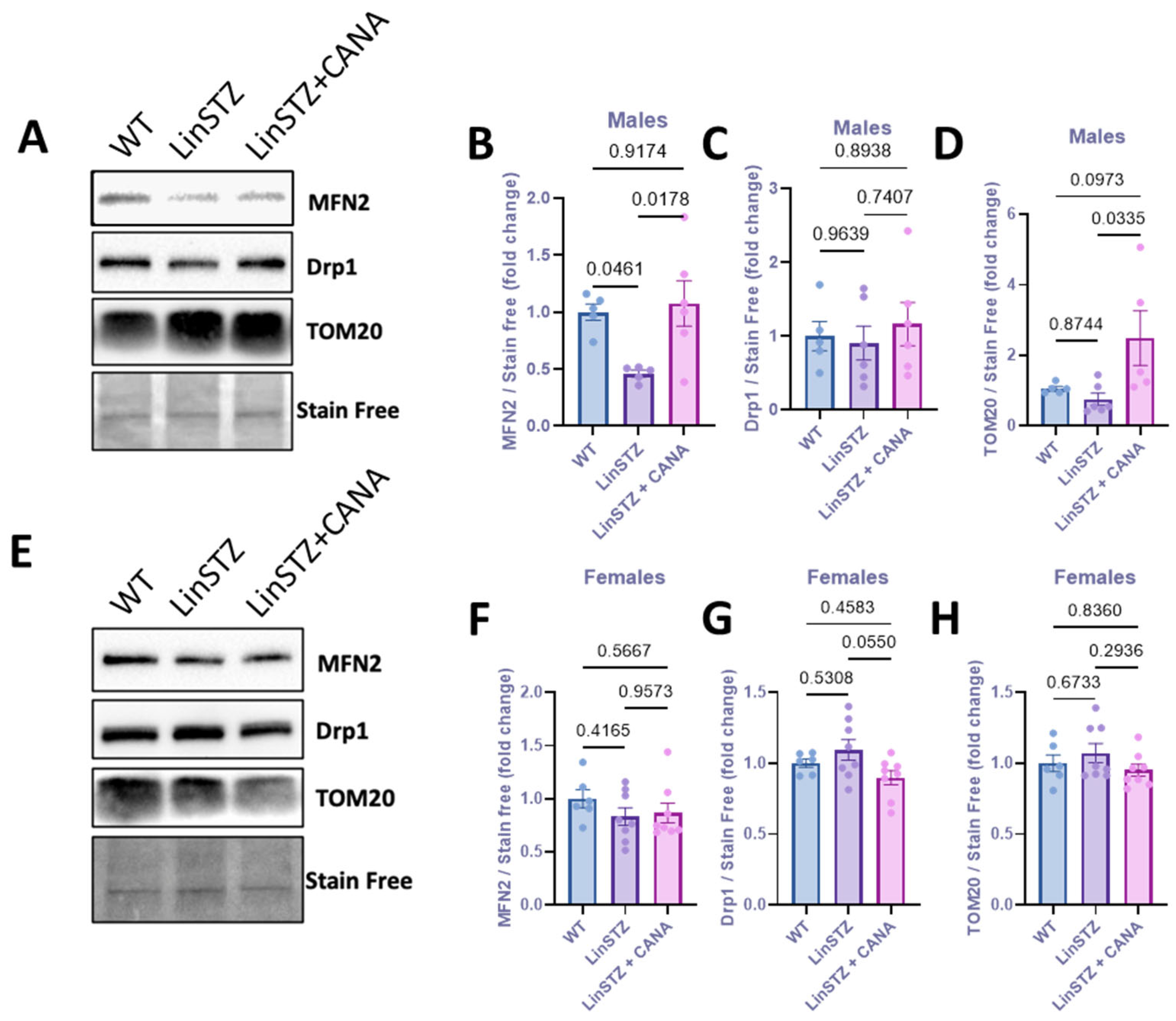
2.3. CANA Treatment and Mitochondria Fission and Fusion Markers
2.4. CANA Treatment Alters Ratio of TMRE/MT
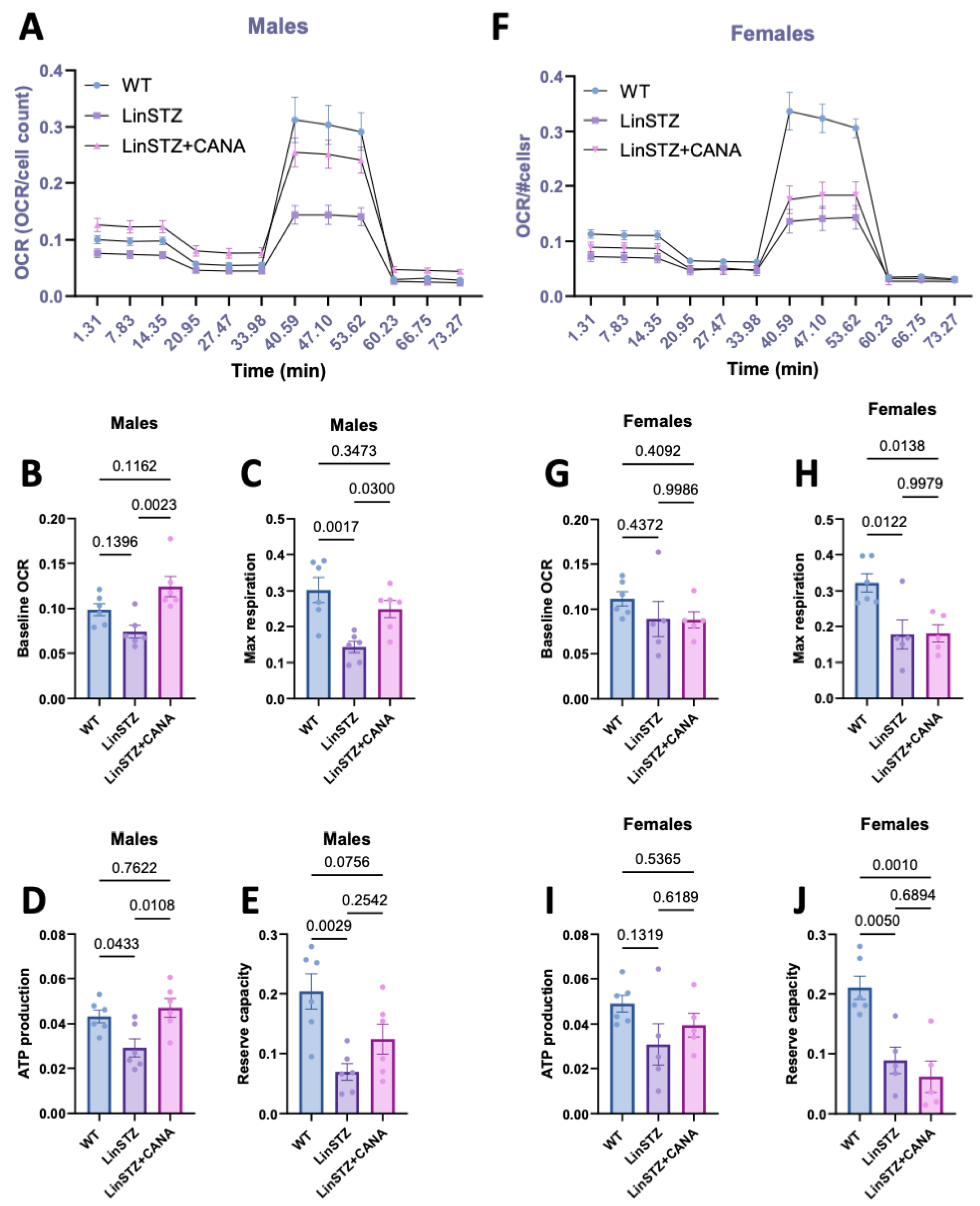
2.5. CANA Treatment Improves Mitochondrial Respiration in LinSTZ Mice
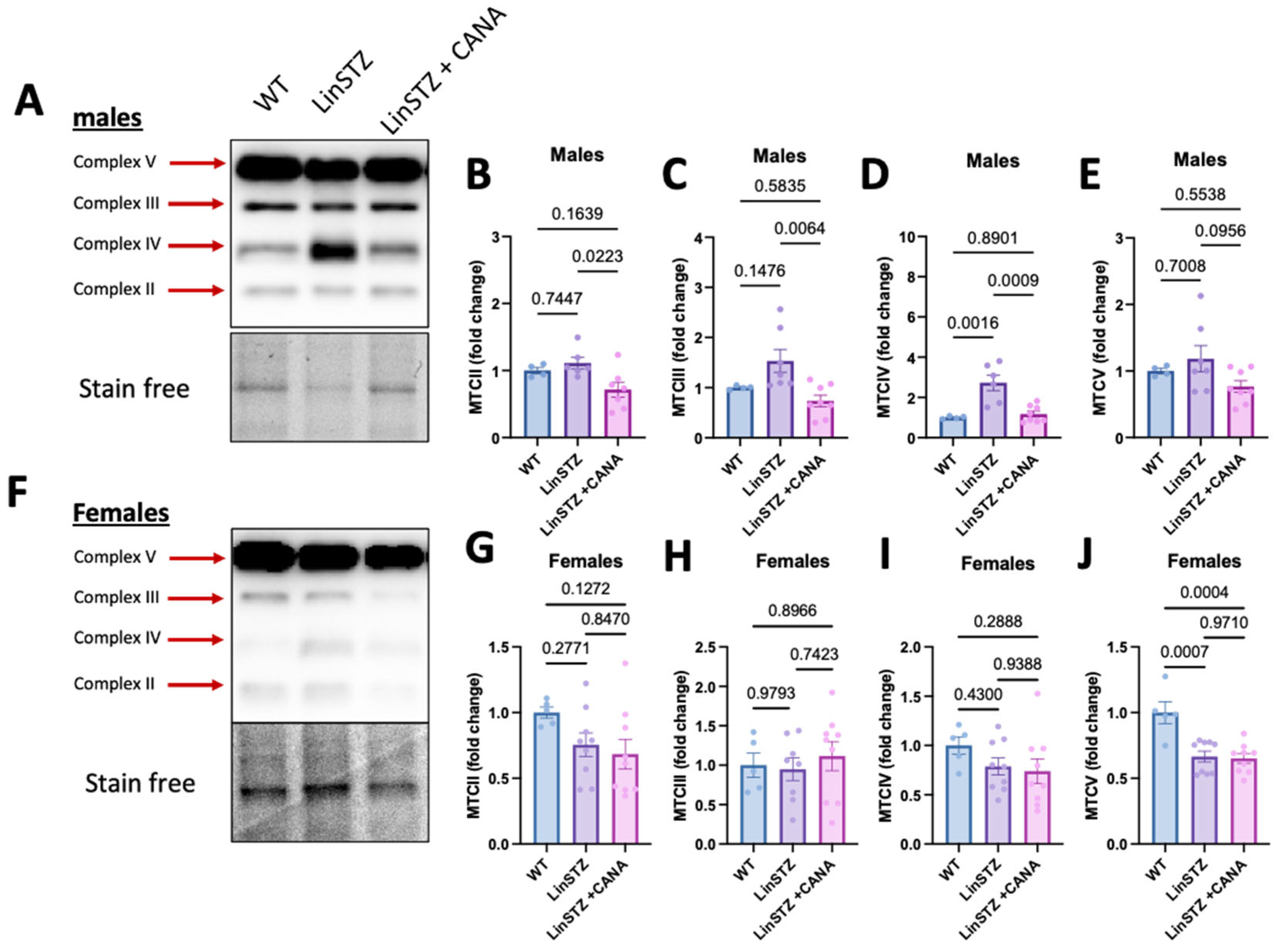
2.6. CANA Treatment Promotes OXPHOS Remodeling in Males
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
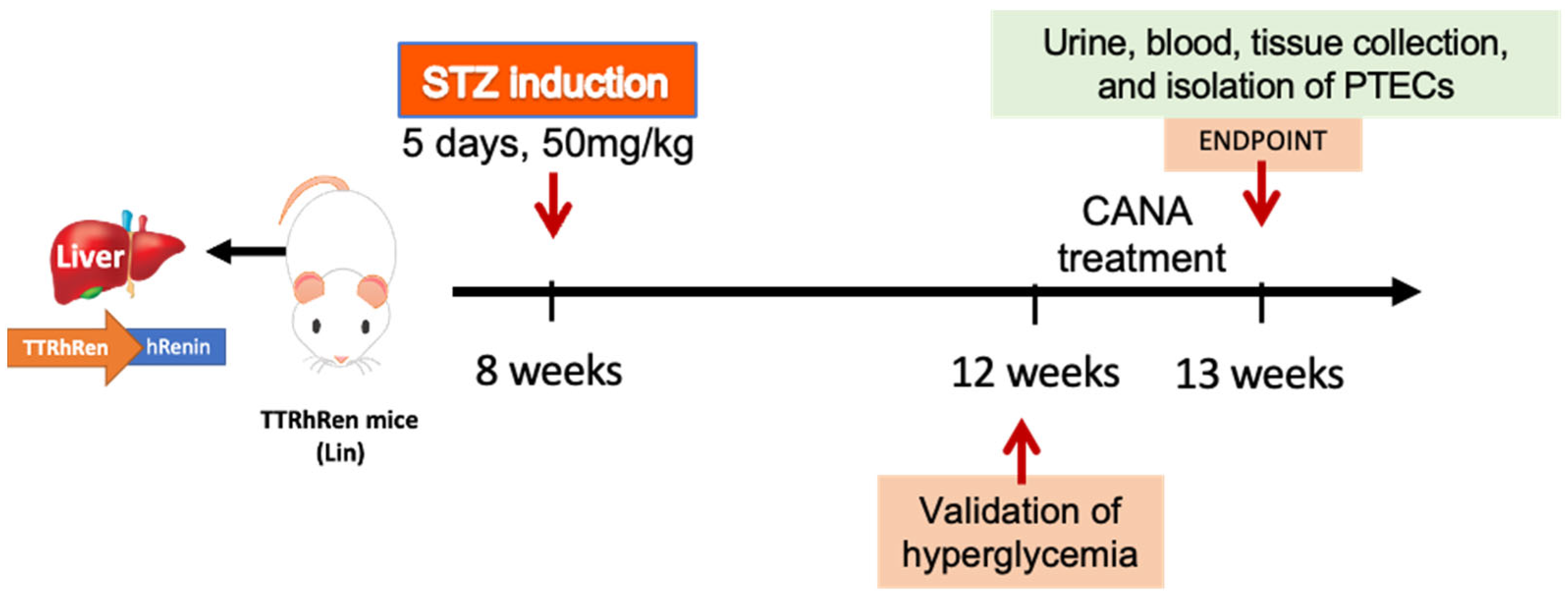
4.1. In Vivo Study
4.2. Biochemistry Analysis
4.3. Blood Glucose
4.4. Albuminuria
4.5. Injury Score
4.6. KIM-1 Expression
4.7. Proximal Tubular Cells Isolation
4.8. MitoTracker Staining and Mitochondria Morphology
4.9. Seahorse MitoStress Test
4.10. Immunoblotting
4.11. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.12. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BG | Blood glucose |
| CANA | Canagliflozin |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DKD | Diabetic kidney disease |
| EMPA | Empagliflozin |
| FCCP | Trifluoromethoxy carbonyl cyanide phenylhydrazone |
| MT | MitoTracker |
| OCR | Oxygen consumption rate |
| OXPHOS | Oxidative phosphorylation |
| PTEC | Proximal tubular epithelial cell |
| SGLT2 | Sodium–glucose co-transporter 2 |
| STZ | Streptozocin |
| TMRE | Tetramethylrhodamine |
| WT | Wild-type |
References
- Chang, J.; Yan, J.; Li, X.; Liu, N.; Zheng, R.; Zhong, Y. Update on the Mechanisms of Tubular Cell Injury in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 661076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group Tight Blood Pressure Control and Risk of Macrovascular and Microvascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes: UKPDS 38. UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. BMJ 1998, 317, 703–713. [CrossRef]
- Isomaa, B.; Almgren, P.; Tuomi, T.; Forsén, B.; Lahti, K.; Nissén, M.; Taskinen, M.-R.; Groop, L. Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality Associated with the Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallon, V.; Platt, K.A.; Cunard, R.; Schroth, J.; Whaley, J.; Thomson, S.C.; Koepsell, H.; Rieg, T. SGLT2 Mediates Glucose Reabsorption in the Early Proximal Tubule. JASN 2011, 22, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallon, V.; Rose, M.; Gerasimova, M.; Satriano, J.; Platt, K.A.; Koepsell, H.; Cunard, R.; Sharma, K.; Thomson, S.C.; Rieg, T. Knockout of Na-Glucose Transporter SGLT2 Attenuates Hyperglycemia and Glomerular Hyperfiltration but Not Kidney Growth or Injury in Diabetes Mellitus. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2013, 304, F156–F167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, E.C. SGLT-2 Inhibitors: A New Mechanism for Glycemic Control. Clin. Diabetes 2014, 32, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Arnott, C.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; MBiostat, Q.L.; Cannon, C.P.; Wheeler, D.C.; Charytan, D.M.; Barraclough, J.; Figtree, G.A.; Agarwal, R.; et al. Effect of Canagliflozin on Total Cardiovascular Burden in Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Post Hoc Analysis from the CREDENCE Trial. JAHA 2022, 11, e025045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.-F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassis, P.; Locatelli, M.; Cerullo, D.; Corna, D.; Buelli, S.; Zanchi, C.; Villa, S.; Morigi, M.; Remuzzi, G.; Benigni, A.; et al. SGLT2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin Limits Podocyte Damage in Proteinuric Nondiabetic Nephropathy. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Delic, D.; Chu, C.; Xiong, Y.; Luo, T.; Chen, X.; Gaballa, M.M.S.; Xue, Y.; Chen, X.; Cao, Y.; et al. Antifibrotic Effects of Low Dose SGLT2 Inhibition with Empagliflozin in Comparison to Ang II Receptor Blockade with Telmisartan in 5/6 Nephrectomised Rats on High Salt Diet. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Delić, D.; Cao, Y.; Shen, L.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Hasan, A.A.; Reichetzeder, C.; Gaballa, M.M.S.; et al. Renoprotective Effects of Empagliflozin Are Linked to Activation of the Tubuloglomerular Feedback Mechanism and Blunting of the Complement System. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2023, 324, C951–C962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryml, E.; Lanktree, M.B. Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors in Patients without Diabetes. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2023, 195, E619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Sarafidis, P.; Kanbay, M.; Navarro-González, J.F.; Soler, M.J.; Górriz, J.L.; Ortiz, A. SGLT2 Inhibitors for Non-Diabetic Kidney Disease: Drugs to Treat CKD That Also Improve Glycaemia. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrallah, R.; Zimpelmann, J.; Cheff, V.; Thibodeau, J.; Burns, K.; Hébert, R. Collecting Duct PGE2 Responses Reduce Water Loss with Empagliflozin in Mice with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Nephrol. 2021, 5, 023–030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaimani, M.; Sridhar, V.S.; Cherney, D.Z.I. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition in Non-Diabetic Kidney Disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2021, 30, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, K.; Goldberg, I.J.; Susztak, K. The Evolving Understanding of the Contribution of Lipid Metabolism to Diabetic Kidney Disease. Curr. Diab Rep. 2015, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.M.; Ahn, S.H.; Choi, P.; Ko, Y.-A.; Han, S.H.; Chinga, F.; Park, A.S.D.; Tao, J.; Sharma, K.; Pullman, J.; et al. Defective Fatty Acid Oxidation in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells Has a Key Role in Kidney Fibrosis Development. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudaliar, S.; Alloju, S.; Henry, R.R. Can a Shift in Fuel Energetics Explain the Beneficial Cardiorenal Outcomes in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME Study? A Unifying Hypothesis. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporters and Their Inhibition: Clinical Physiology. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, J.M.; Heo, J.H.; Kim, D.-J.; Park, S.H.; Sung, M.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Yang, D.H.; et al. Empagliflozin Attenuates Diabetic Tubulopathy by Improving Mitochondrial Fragmentation and Autophagy. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2019, 317, F767–F780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Li, J.; Takagaki, Y.; Kitada, M.; Nitta, K.; Takasu, T.; Kanasaki, K.; Koya, D. Ipragliflozin Improves Mitochondrial Abnormalities in Renal Tubules Induced by a High-fat Diet. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, R.L.; García Menéndez, S.; Inserra, F.; Ferder, L.; Manucha, W. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Protect Tissues via Cellular and Mitochondrial Pathways: Experimental and Clinical Evidence. World J. Exp. Med. 2024, 14, 91519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mone, P.; Varzideh, F.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Pansini, A.; Lombardi, A.; Frullone, S.; Santulli, G. SGLT2 Inhibition via Empagliflozin Improves Endothelial Function and Reduces Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress: Insights from Frail Hypertensive and Diabetic Patients. Hypertension 2022, 79, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secker, P.F.; Beneke, S.; Schlichenmaier, N.; Delp, J.; Gutbier, S.; Leist, M.; Dietrich, D.R. Canagliflozin Mediated Dual Inhibition of Mitochondrial Glutamate Dehydrogenase and Complex I: An off-Target Adverse Effect. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, L.A.; Smith, B.K.; Marcinko, K.; Ford, R.J.; Broadfield, L.A.; Green, A.E.; Houde, V.P.; Muti, P.; Tsakiridis, T.; Steinberg, G.R. The Diabetes Medication Canagliflozin Reduces Cancer Cell Proliferation by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Complex-I Supported Respiration. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, S.A.; Ford, R.J.; Smith, B.K.; Gowans, G.J.; Mancini, S.J.; Pitt, R.D.; Day, E.A.; Salt, I.P.; Steinberg, G.R.; Hardie, D.G. The Na+/Glucose Cotransporter Inhibitor Canagliflozin Activates AMPK by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Function and Increasing Cellular AMP Levels. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2784–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibodeau, J.-F.; Holterman, C.E.; Burger, D.; Read, N.C.; Reudelhuber, T.L.; Kennedy, C.R.J. A Novel Mouse Model of Advanced Diabetic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheff, V.; Trentin-Sonoda, M.; Blais, A.; Thibodeau, J.-F.; Holterman, C.E.; Gutsol, A.; Kennedy, C.R.J.; Hébert, R.L. High Fat Diet Is Protective against Kidney Injury in Hypertensive-Diabetic Mice, but Leads to Liver Injury. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trentin-Sonoda, M.; Cheff, V.; Gutsol, A.; Hébert, R.L. Sex-Dependent Effects of Canagliflozin on Kidney Protection in Mice with Combined Hypertension-Type 1 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuen, B.L.; Ohkuma, T.; Neal, B.; Matthews, D.R.; de Zeeuw, D.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Fulcher, G.; Li, Q.; Jardine, M.; Oh, R.; et al. Effect of Canagliflozin on Renal and Cardiovascular Outcomes across Different Levels of Albuminuria: Data from the CANVAS Program. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 2229–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Tian, Y.; Liang, X.; Wu, X.; Yao, C.; Chen, X. SGLT2i Relieve Proteinuria in Diabetic Nephropathy Patients Potentially by Inhibiting Renal Oxidative Stress Rather than through AGEs Pathway. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 16, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, T.; Langer, T. Mitochondrial Dynamics and Metabolic Regulation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clotet-Freixas, S.; Soler, M.J.; Palau, V.; Anguiano, L.; Gimeno, J.; Konvalinka, A.; Pascual, J.; Riera, M. Sex Dimorphism in ANGII-Mediated Crosstalk between ACE2 and ACE in Diabetic Nephropathy. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, K.M.; Kayampilly, P.; Byun, J.; Nair, V.; Hinder, L.M.; Hur, J.; Zhang, H.; Lin, C.; Qi, N.R.; Michailidis, G.; et al. Tissue-Specific Metabolic Reprogramming Drives Nutrient Flux in Diabetic Complications. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e86976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narongkiatikhun, P.; Choi, Y.J.; Hampson, H.; Gotzamanis, J.; Zhang, G.; Van Raalte, D.H.; De Boer, I.H.; Nelson, R.G.; Tommerdahl, K.L.; McCown, P.J.; et al. Unraveling Diabetic Kidney Disease: The Roles of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Immunometabolism. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 3386–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Park, E.-S.; Lee, J.-S.; Suh, J.-G. Outbred Mice with Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Show Sex Differences in Glucose Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clotet-Freixas, S.; Zaslaver, O.; Kotlyar, M.; Pastrello, C.; Quaile, A.T.; McEvoy, C.M.; Saha, A.D.; Farkona, S.; Boshart, A.; Zorcic, K.; et al. Sex Differences in Kidney Metabolism May Reflect Sex-Dependent Outcomes in Human Diabetic Kidney Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16, eabm2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcińczyk, N.; Misztal, T.; Chabielska, E.; Gromotowicz-Popławska, A. Sex-Dependent Effects of Canagliflozin and Dapagliflozin on Hemostasis in Normoglycemic and Hyperglycemic Mice. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Wood, S.; Bell, J.S.; De Blasio, M.J.; Ilomäki, J.; Ritchie, R.H. Sex Differences in Risk of Cardiovascular Events and Mortality with Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibitors versus Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists in Australians with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Lancet Reg. Health–West. Pac. 2023, 33, 100692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.W.; Smyth, B.; Di Tanna, G.L.; Arnott, C.; Cardoza, K.; Kang, A.; Pollock, C.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Charytan, D.M.; et al. Kidney and Cardiovascular Effects of Canagliflozin According to Age and Sex: A Post Hoc Analysis of the CREDENCE Randomized Clinical Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2023, 82, 84–96.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, F.B.; Tang, V.A.S.; De Luna, D.V.; Lerma, E.V.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Kazory, A.; Shah, N.S.; Volgman, A.S. Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Outcomes of SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure Randomized Controlled Trials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. Heart J. Plus Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2023, 26, 100261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepard, B.D. Sex Differences in Diabetes and Kidney Disease: Mechanisms and Consequences. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2019, 317, F456–F462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prescott, G.; Silversides, D.W.; Chiu, S.M.L.; Reudelhuber, T.L. Contribution of Circulating Renin to Local Synthesis of Angiotensin Peptides in the Heart. Physiol. Genom. 2000, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Zimpelmann, J.; Agaybi, S.; Gurley, S.B.; Puente, L.; Burns, K.D. Characterization of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Ectodomain Shedding from Mouse Proximal Tubular Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, A.; Shi, R.; Luciani, D.S. A Pipeline for Multidimensional Confocal Analysis of Mitochondrial Morphology, Function, and Dynamics in Pancreatic β-Cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E87–E101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trentin-Sonoda, M.; Burelle, Y.; Gutsol, A.; Myette, R.L.; Hébert, R.L. Canagliflozin Promotes Structural and Functional Changes in Proximal Tubular Cell Mitochondria of Hypertensive–Diabetic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11988. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411988
Trentin-Sonoda M, Burelle Y, Gutsol A, Myette RL, Hébert RL. Canagliflozin Promotes Structural and Functional Changes in Proximal Tubular Cell Mitochondria of Hypertensive–Diabetic Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(24):11988. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411988
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrentin-Sonoda, Mayra, Yan Burelle, Alex Gutsol, Robert L. Myette, and Richard L. Hébert. 2025. "Canagliflozin Promotes Structural and Functional Changes in Proximal Tubular Cell Mitochondria of Hypertensive–Diabetic Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 24: 11988. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411988
APA StyleTrentin-Sonoda, M., Burelle, Y., Gutsol, A., Myette, R. L., & Hébert, R. L. (2025). Canagliflozin Promotes Structural and Functional Changes in Proximal Tubular Cell Mitochondria of Hypertensive–Diabetic Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(24), 11988. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411988






