Genomic Characterization and Resistance Mechanisms of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 Isolates from Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
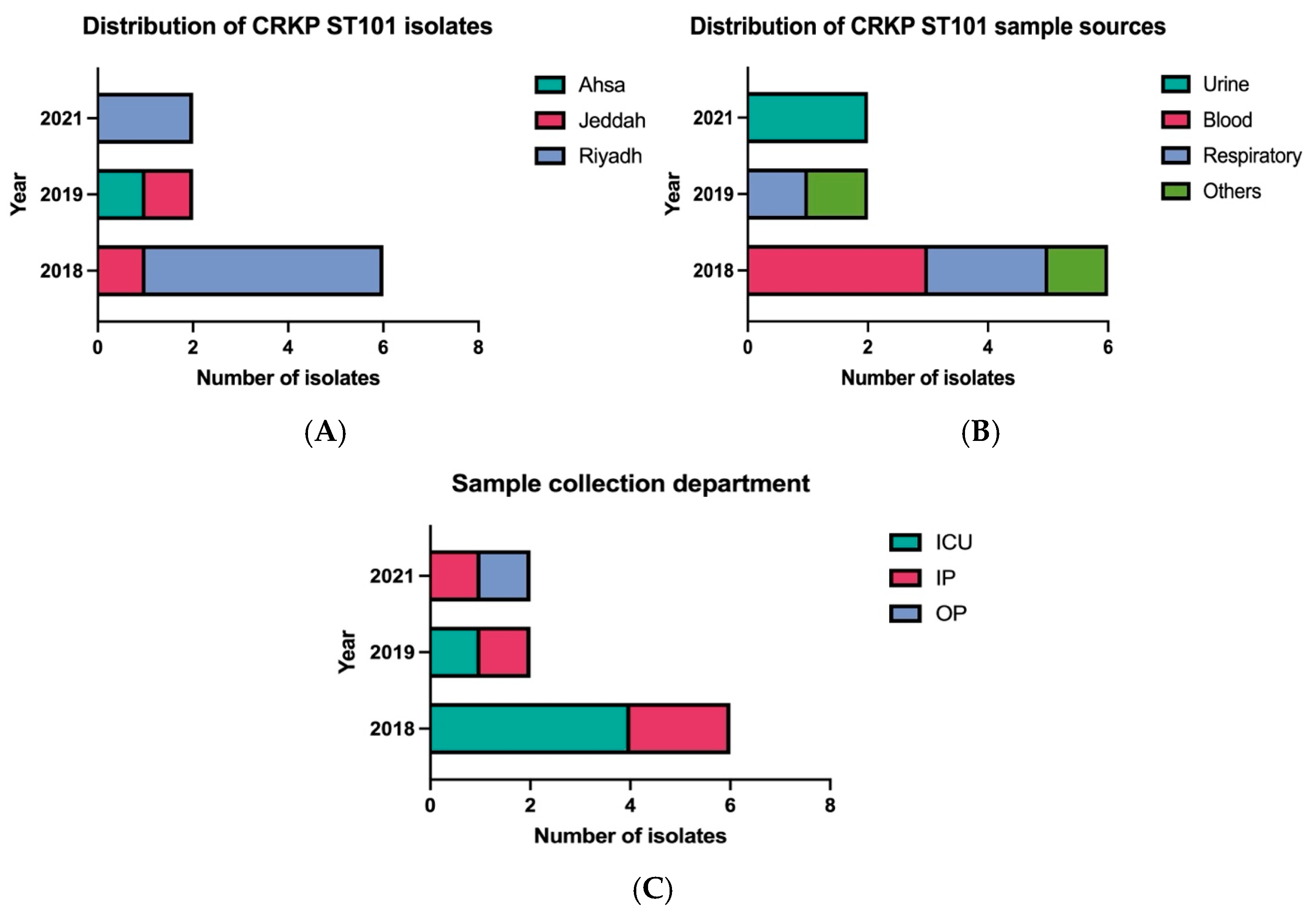
2.1. Clinical and Geographic Distribution of ST101 Isolates
2.2. Clinical Characteristics and Epidemiology of CRKP ST101 Isolates
2.3. Phenotypic Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles
2.4. Genomic Analysis of the ST101 Isolate
2.5. Antimicrobial Resistance Mechanisms
2.6. Virulence Associated Genes
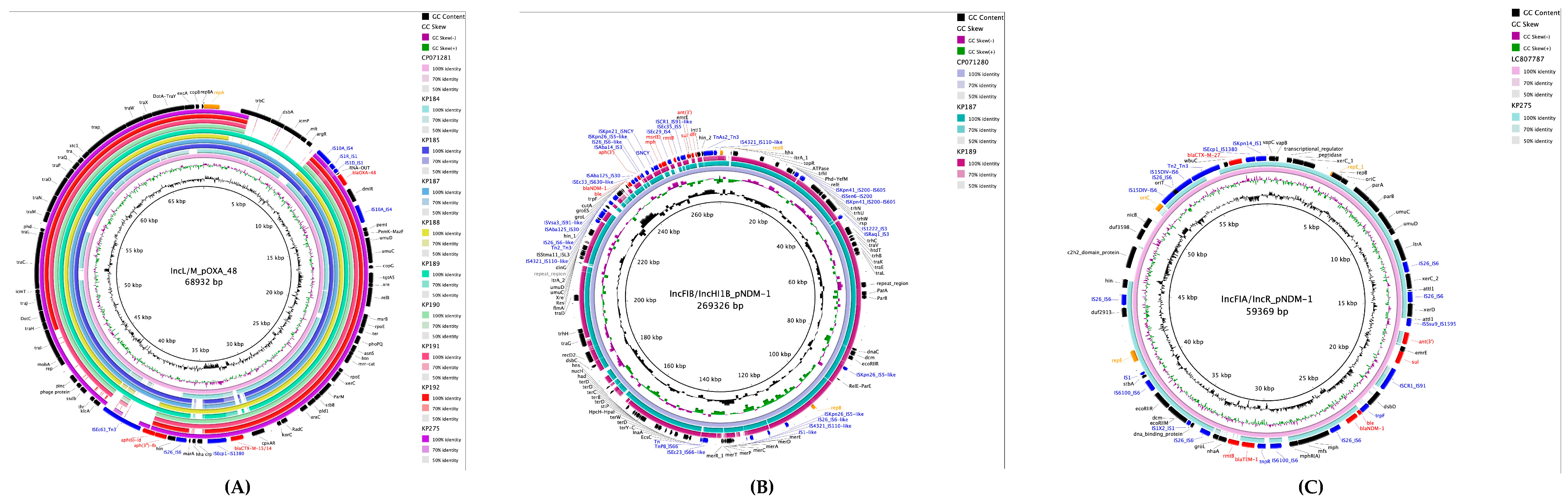
2.7. Plasmid Characterization and Resistance Gene Environments
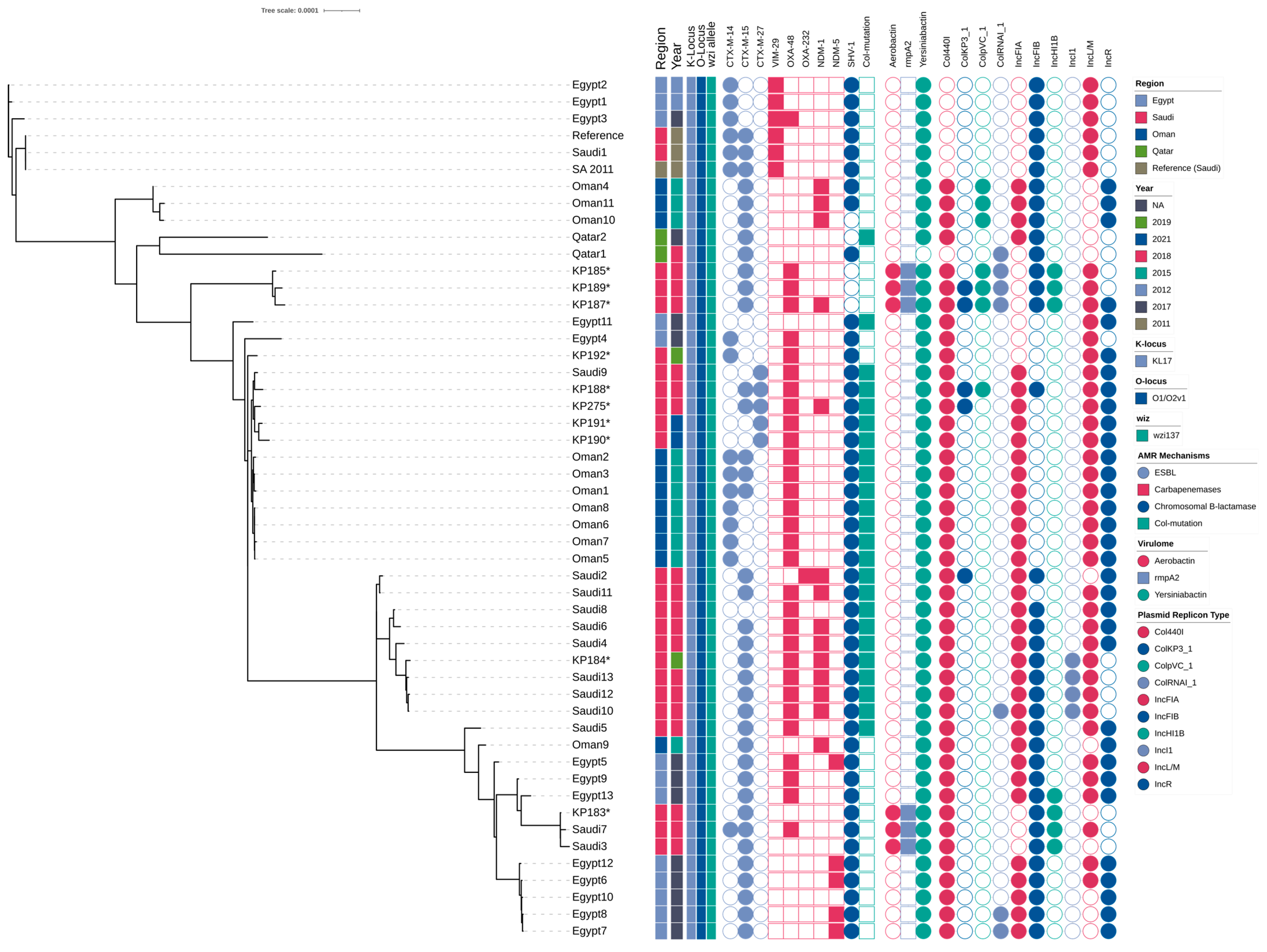
2.8. Phylogenetic Relationships of ST101 Isolates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Hospital Setting and Study Design
4.2. Bacterial Isolates and Phenotypic Testing
4.3. Bacterial Identification and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
4.4. Genotypic Screening of Carbapenemases
4.5. Whole Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.6. Plasmid Characterization
4.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Candan, E.D.; Aksöz, N. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Characteristics of carbapenem resistance and virulence factors. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 62, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosillo, N.; Taglietti, F.; Granata, G. Treatment options for colistin resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Present and future. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Santiago, J.; Cornejo-Juárez, P.; Silva-Sánchez, J.; Garza-Ramos, U. Polymyxin resistance in Enterobacterales: Overview and epidemiology in the Americas. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 58, 106426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Pan, F.; Wang, C.; Zhao, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H. Molecular epidemiology of Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in a paediatric hospital in China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Al Fadhli, A.H.; Mouftah, S.F.; Jamal, W.Y.; Rotimi, V.O.; Ghazawi, A. Cracking the Code: Unveiling the Diversity of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Clones in the Arabian Peninsula through Genomic Surveillance. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isler, B.; Özer, B.; Çınar, G.; Aslan, A.T.; Vatansever, C.; Falconer, C.; Dolapçı, I.; Şimşek, F.; Tülek, N.; Demirkaya, H.; et al. Characteristics and outcomes of carbapenemase harbouring carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella spp. bloodstream infections: A multicentre prospective cohort study in an OXA-48 endemic setting. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 41, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitout, J.D.D.; Peirano, G.; Kock, M.M.; Strydom, K.A.; Matsumura, Y. The Global Ascendency of OXA-48-Type Carbapenemases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 33, e00102-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Walsh, T.R.; Cuvillier, V.; Nordmann, P. Multiplex PCR for detection of acquired carbapenemase genes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Price, L.S.; Poirel, L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Schwaber, M.J.; Daikos, G.L.; Cormican, M.; Cornaglia, G.; Garau, J.; Gniadkowski, M.; Hayden, M.K.; et al. Clinical epidemiology of the global expansion of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L.; Dortet, L. Rapid detection of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgincar, N.; Iyer, S.; Stacey, A.; Maharjan, S.; Pike, R.; Perry, C.; Wyeth, J.; Woodford, N. Klebsiella pneumoniae producing KPC carbapenemase in a district general hospital in the UK. J. Hosp. Infect. 2011, 78, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Agamy, M.H.; Shibl, A.M.; Elkhizzi, N.A.; Meunier, D.; Turton, J.F.; Livermore, D.M. Persistence of Klebsiella pneumoniae clones with OXA-48 or NDM carbapenemases causing bacteraemias in a Riyadh hospital. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 76, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamohammad, S.; Khazani Asforooshani, M.; Malek Mohammadi, Y.; Sholeh, M.; Badmasti, F. Decoding the genetic structure of conjugative plasmids in international clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae: A deep dive into blaKPC, blaNDM, blaOXA-48, and blaGES genes. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0292288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.W.; Quyen, T.L.T.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wu, L.T.; Pan, Y.J. Investigation of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan revealed strains co-harbouring bla(NDM) and bla(OXA-48-like) and a novel plasmid co-carrying bla(NDM-1) and bla(OXA-181). Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solgi, H.; Nematzadeh, S.; Giske, C.G.; Badmasti, F.; Westerlund, F.; Lin, Y.-L.; Goyal, G.; Nikbin, V.S.; Nemati, A.H.; Shahcheraghi, F. Molecular epidemiology of OXA-48 and NDM-1 producing Enterobacterales species at a University Hospital in Tehran, Iran, between 2015 and 2016. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülmez, D.; Woodford, N.; Palepou, M.-F.I.; Mushtaq, S.; Metan, G.; Yakupogullari, Y.; Kocagoz, S.; Uzun, O.; Hascelik, G.; Livermore, D.M. Carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from Turkey with OXA-48-like carbapenemases and outer membrane protein loss. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 31, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dautzenberg, M.; Ossewaarde, J.; De Kraker, M.; Van Der Zee, A.; Van Burgh, S.; De Greeff, S.; A Bijlmer, H.; Grundmann, H.; Stuart, J.W.C.; Fluit, A.C.; et al. Successful control of a hospital-wide outbreak of OXA-48 producing Enterobacteriaceae in the Netherlands, 2009 to 2011. Eurosurveillance 2014, 19, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, A.; Haenni, M.; Bouallègue, O.; Saras, E.; Chatre, P.; Chaouch, C.; Boujâafar, N.; Mansour, W.; Madec, J.-Y. Dynamics and molecular features of OXA-48-like-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae lineages in a Tunisian hospital. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 20, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Koster, S.; Rodriguez Ruiz, J.P.; Rajakani, S.G.; Lammens, C.; Glupczynski, Y.; Goossens, H.; Xavier, B.B. Diversity in the characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 of human, environmental, and animal origin. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 838207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, C.C.; Vazquez, A.J.; Esposito, E.P.; Zarrilli, R.; Sahl, J.W. Diversity, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in isolates from the newly emerging Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 lineage. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loconsole, D.; Accogli, M.; De Robertis, A.L.; Capozzi, L.; Bianco, A.; Morea, A.; Mallamaci, R.; Quarto, M.; Parisi, A.; Chironna, M. Emerging high-risk ST101 and ST307 carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clones from bloodstream infections in Southern Italy. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero, M.; Cuervo, G.; Dominguez, M.Á.; Tubau, F.; Martí, S.; Sevillano, E.; Gallego, L.; Ayats, J.; Peña, C.; Pujol, M.; et al. Carbapenem-resistant and carbapenem-susceptible isogenic isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 causing infection in a tertiary hospital. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Alhejaili, A.Y.; Alkherd, U.H.; Milner, M.; Zhou, G.; Alzahrani, D.; Banzhaf, M.; Alzaidi, A.A.; Rajeh, A.A.; Al-Otaiby, M.A.; et al. The dissemination of multidrug-resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clones across the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2427793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 34th ed.; CLSI supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann, P.; Dortet, L.; Poirel, L. Carbapenem resistance in Enterobacteriaceae: Here is the storm! Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, F.; Menekse, S.; Ispir, P.; Atac, N.; Albayrak, O.; Demir, T.; Karaaslan, D.C.; Karahan, S.N.; Kapmaz, M.; Azap, O.K.; et al. Impact of the ST101 clone on fatality among patients with colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröding, I.; David, S.; Yeats, C.; Abu-Dahab, K.; Albiger, B.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Alm, E.; Byfors, S.; Couto, N.; Diaz Caballero, J.; et al. Persistent Spread of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Acute Care Hospitals in 36 European Countries: Results from the Survey of Carbapenem-and/or Colistin-Resistant Enterobacterales (CCRE Survey). 2019. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5275521 (accessed on 20 November 2025).
- Kang, C.-I.; Kim, S.-H.; Bang, J.-W.; Kim, H.-B.; Kim, N.-J.; Kim, E.-C.; Oh, M.D.; Choe, K.W. Community-acquired versus nosocomial Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia: Clinical features, treatment outcomes, and clinical implication of antimicrobial resistance. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2006, 21, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coolen, J.P.M.; den Drijver, E.P.M.; Kluytmans, J.; Verweij, J.J.; Lamberts, B.A.; Soer, J.; Verhulst, C.; Wertheim, H.F.L.; Kolwijck, E. Development of an algorithm to discriminate between plasmid- and chromosomal-mediated AmpC β-lactamase production in Escherichia coli by elaborate phenotypic and genotypic characterization. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 3481–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.T.; Lewin, C.S. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance and implications for epidemiology. Vet. Microbiol. 1993, 35, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-F.; Chuang, C.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chan, Y.-J.; Lin, J.-C.; Lu, P.-L.; Huang, C.-T.; Wang, J.-T.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Siu, L.K.; et al. Treatment outcome of non-carbapenemase-producing carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections: A multicenter study in Taiwan. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, I.; Puzari, M.; Chetia, P. Porin-Mediated Carbapenem Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae: An Alarming Threat to Global Health. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2023, 10, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Santiago, J.; Alvarado-Delgado, A.; Rodríguez-Medina, N.; Garza-González, E.; Tellez-Sosa, J.; Duarte-Zambrano, L.; Nava-Domínguez, N.; Sohlenkamp, C.; Vences-Guzmán, M.A.; López-Jácome, L.E.; et al. Colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae species complex: The scenario in Mexico. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2025, 43, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditti, C.; Butera, O.; Proia, A.; Rigacci, L.; Mariani, B.; Parisi, G.; Messina, F.; Capone, A.; Nisii, C.; Di Caro, A. Reduced susceptibility to carbapenems in a Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolate producing SCO-1 and CTX-M-15 β-lactamases together with OmpK35 and OmpK36 Porin deficiency. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00556-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerón, S.; Salem-Bango, Z.; Contreras, D.A.; Ranson, E.L.; Yang, S. Clinical and Genomic Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with Concurrent Production of NDM and OXA-48-like Carbapenemases in Southern California, 2016–2022. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junaid, K. Molecular Diversity of NDM-1, NDM-5, NDM-6, and NDM-7 Variants of New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamases and Their Impact on Drug Resistance. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67, 1897–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElMahallawy, H.; Zafer, M.M.; Al-Agamy, M.; Amin, M.A.; Mersal, M.M.; Booq, R.Y.; Alyamani, E.; Radwan, S. Dissemination of ST101 blaOXA-48 producing Klebsiella pneumoniae at tertiary care setting. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2018, 12, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miro, E.; Rossen, J.W.A.; Chlebowicz, M.A.; Harmsen, D.; Brisse, S.; Passet, V.; Navarro, F.; Friedrich, A.W.; García-Cobos, S. Core/Whole Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing and Core Genome SNP-Based Typing of OXA-48-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates From Spain. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcade, G.; Brisse, S.; Bialek, S.; Marcon, E.; Leflon-Guibout, V.; Passet, V.; Moreau, R.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.-H. The emergence of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae of international clones ST13, ST16, ST35, ST48 and ST101 in a teaching hospital in the Paris region. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hala, S.; Malaikah, M.; Huang, J.; Bahitham, W.; Fallatah, O.; Zakri, S.; Antony, C.P.; Alshehri, M.; Ghazzali, R.N.; Ben-Rached, F.; et al. The emergence of highly resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae CC14 clone in a tertiary hospital over 8 years. Genome Med. 2024, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, B.; Salvador, C.; Tormo, N.; García-González, N.; Gimeno, C.; González-Candelas, F. Molecular epidemiology and drug-resistance mechanisms in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated in patients from a tertiary hospital in Valencia, Spain. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes de novo assembler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 70, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C.J. BIGSdb: Scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, D.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2016: Hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis—10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D694–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, P.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Y. A global perspective on the convergence of hypervirulence and carbapenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berriman, M.; Rutherford, K. Viewing and annotating sequence data with Artemis. Brief. Bioinform. 2003, 4, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carver, T.; Berriman, M.; Tivey, A.; Patel, C.; Böhme, U.; Barrell, B.G.; Parkhill, J.; Rajandream, M.-A. Artemis and ACT: Viewing, annotating and comparing sequences stored in a relational database. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2672–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, T.; Harris, S.R.; Berriman, M.; Parkhill, J.; McQuillan, J.A. Artemis: An integrated platform for visualization and analysis of high-throughput sequence-based experimental data. Bioinformatics 2011, 28, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, K.; Parkhill, J.; Crook, J.; Horsnell, T.; Rice, P.; Rajandream, M.A.; Barrell, B. Artemis: Sequence visualization and annotation. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 944–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhan, N.-F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghoribi, M.F.; Alqurashi, M.; Okdah, L.; Alalwan, B.; AlHebaishi, Y.S.; Almalki, A.; Alzayer, M.A.; Alswaji, A.A.; Doumith, M.; Barry, M. Successful treatment of infective endocarditis due to pandrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with ceftazidime-avibactam and aztreonam. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, T.T.; Sugawara, Y.; Hamaguchi, S.; Takeuchi, D.; Abe, R.; Kuroda, E.; Morita, M.; Zuo, H.; Ueda, A.; Nishi, I.; et al. Genomic characterization of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales from Dhaka food markets unveils the spread of high-risk antimicrobial-resistant clones and plasmids co-carrying blaNDM and mcr-1.1. JAC-Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 6, dlae124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croucher, N.J.; Page, A.J.; Connor, T.R.; Delaney, A.J.; Keane, J.A.; Bentley, S.D.; Parkhill, J.; Harris, S.R. Rapid phylogenetic analysis of large samples of recombinant bacterial whole genome sequences using Gubbins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 43, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534, Erratum in Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Strains | Collection Department | Outcome | Admission Reason/Visit | Death Reason | Death During Admission | HAI | CAI | Death Due to Infection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KP183 | ICU | Died | Mucormycosis status post FESS and debridement with excision of hard palate/ maxillary sinus | Severe pulmonary edema, septic shock | Yes | Yes | - | Yes |
| KP184 | ICU | Died | Shortness of breath | Multiorgan failure, cardiac arrest | Yes | - | Yes | Yes |
| KP185 | ICU | Died | Hemorrhagic stroke | Septic shock due to CRKP, multiorgan failure | Yes | Yes | - | Yes |
| KP187 | ICU | Died | Stoma closure | Septic shock with multiorgan failure | Yes | Yes | - | Yes |
| KP188 | IP | Improved | Shortness of breath | - | - | - | Yes | - |
| KP189 | ICU | Died | Complete paralysis of his right leg | Septic shock | Yes | Yes | - | Yes |
| KP190 | IP | Improved | gastrointestinal bleeding, melena | - | - | Yes | - | - |
| KP191 | OP | Improved | Urinary Tract Infection | - | - | - | Yes | - |
| KP192 | IP | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| KP275 | ICU | Died | Cardiac arrest | Fulminant sepsis, multiorgan failure, septic shock | Yes | Yes | - | Yes |
| Strain | Year of Isolation | Region | Specimen Type | Plasmid-Associated Genes | Plasmid Replicon Typing | Chromosome-Associated Genes | Serotyping | Virulence Determinants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbapenemases | ESBL | Other Resistance Genes | ß-Lactamases | Colistin | Yersiniabactin | Aerobactin | rmpA2 | ||||||
| KP183 | 2018 | Jeddah | Respiratory | - | blaCTX-M-15 | aph3-Ia; armA; mphA; mphE; msrE; sul1; sul2; dfrA | Col440I, IncFIB, IncHI1B | blaSHV-1 | - | KL17; O1/O2v1 | ybt9; ICEKp3 | iuc1 | rmpA2_6-60% |
| KP184 | 2019 | Jeddah | Respiratory | blaNDM-1; blaOXA-48 | blaCTX-M-15 | aac(6′)-Ib; aadA12; aph(3′)-VI; qnrS; ermB; mphA; sul1; tet(D), dfrA | Col440I, IncFIA, IncFIB, IncL/M, IncI1 | blaSHV-1 | mgrB (altered) | KL17; O1/O2v1 | ybt9; ICEKp3 | - | - |
| KP185 | 2018 | Riyadh | Blood | blaOXA-48 | blaCTX-M-15 | aac(3)-IId; aac(6′)-Ib; aadA; aph(3′)-VI; catA; sul2; dfrA | Col440I, ColpVC, ColRNAI, IncFIB, IncHI1B, IncL/M | - | - | KL17; O1/O2v1 | ybt9; ICEKp3 | iuc1 | rmpA2_6-60% |
| KP187 | 2018 | Riyadh | Respiratory | blaNDM-1; blaOXA-48 | blaCTX-M-15 | aac(3)-IId; aac(6′)-Ib; aadA; aadA2; sat-2; strB.v1; catA; sul2; dfrA | Col440I, ColKP3, ColpVC, ColRNAI, IncFIB, IncHI1B, IncL/M, IncR | - | - | KL17; O1/O2v1 | ybt9; ICEKp3 | iuc1 | rmpA2_6-60% |
| KP188 | 2018 | Riyadh | Rectal swab | blaOXA-48 | blaCTX-M-15, blaCTX-M-27 | aac(3)-IIa; aac(6′)-Ib; aadA2; strA; mphA; cmlA; sul3; dfrA | Col440I; ColKP3, ColpVC, IncFIA, IncFIB, IncL/M, IncR | blaSHV-1 | mgrB (altered) | KL17; O1/O2v1 | ybt9; ICEKp3 | - | - |
| KP189 | 2018 | Riyadh | Blood | blaOXA-48 | blaCTX-M-15 | aac(3)-IId; aac(6′)-Ib; aadA; aadA2; sat-2; strB.v1; mphE; catA; sul2; dfrA | Col440I, ColKP3; ColpVC; ColRNAI; IncFIB, IncHI1B, IncL/M | - | - | KL17; O1/O2v1 | ybt9; ICEKp3 | iuc1 | rmpA2_6-60% |
| KP190 | 2021 | Riyadh | Urine | blaOXA-48 | blaCTX-M-27 | aac(3)-IIa; strA; mphA; dfrA | Col440I, IncFIA, IncL/M, IncR | blaSHV-1 | mgrB (altered) | KL17; O1/O2v1 | ybt9; ICEKp3 | - | - |
| KP191 | 2021 | Riyadh | Urine | blaOXA-48 | blaCTX-M-27 | aac(3)-IIa; strA; mphA; dfrA | Col440I, IncFIA, IncL/M, IncR | blaSHV-1 | mgrB (altered) | KL17; O1/O2v1 | ybt9; ICEKp3 | - | - |
| KP192 | 2019 | Ahsa | Wound | blaOXA-48 | blaCTX-M-14 | aac(6′)-Ib; aadA; aph(3′)-VI; strA; mphA; dfrA | Col440I, ColKP3, IncFIA, IncL/M, IncR | blaSHV-1 | - | KL17; O1/O2v1 | ybt9; ICEKp3 | - | - |
| KP275 | 2018 | Riyadh | Blood | blaNDM-1; blaOXA-48 | blaCTX-M-15, blaCTX-M-27 | aac(3)-IIa; aac(6′)-Ib; aadA; strA; mphA; dfrA | Col440I, IncL/M, IncR | blaSHV-1 | mgrB (altered) | KL17; O1/O2v1 | ybt9; ICEKp3 | - | - |
| Resistance Gene | Primer a | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| blaOXA-48 | OXA-F OXA-R | GGTTAAGGATGAACACCAAGTC TTGTGATGGCTTGGCGCAG |
| blaNDM | NDM-F NDM-R | ACCGAATGTCTGGCAGCACA GGGCCGTATGAGTGATTGC |
| blaKPC | KPC-F KPC-R | TCTGCTGTCTTGTCTCTCATG CTTGTCATCCTTGTTAGGCG |
| blaIMP | IMP-F IMP-R | GGAATAGAGTGGCTTAAYTCTC GGTTTAAYAAAACAACCACC |
| blaVIM | VIM-F VIM-R | GATGGTGTTTGGTCGCATA CGAATGCGCAGCACCAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Idrees, E.K.; Alkhulaifi, M.M.; Aldriwesh, M.G.; Alqurainy, N.; Okdah, L.; Alswaji, A.A.; Alrashidi, E.T.; Alshahrani, A.S.; Al Johani, S.M.; MNGHA Surveillance Group; et al. Genomic Characterization and Resistance Mechanisms of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 Isolates from Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311518
Idrees EK, Alkhulaifi MM, Aldriwesh MG, Alqurainy N, Okdah L, Alswaji AA, Alrashidi ET, Alshahrani AS, Al Johani SM, MNGHA Surveillance Group, et al. Genomic Characterization and Resistance Mechanisms of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 Isolates from Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311518
Chicago/Turabian StyleIdrees, Enaam K., Manal M. Alkhulaifi, Marwh G. Aldriwesh, Nasser Alqurainy, Liliane Okdah, Abdulrahman A. Alswaji, Eisa T. Alrashidi, Alhanouf S. Alshahrani, Sameera M. Al Johani, MNGHA Surveillance Group, and et al. 2025. "Genomic Characterization and Resistance Mechanisms of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 Isolates from Saudi Arabia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311518
APA StyleIdrees, E. K., Alkhulaifi, M. M., Aldriwesh, M. G., Alqurainy, N., Okdah, L., Alswaji, A. A., Alrashidi, E. T., Alshahrani, A. S., Al Johani, S. M., MNGHA Surveillance Group, Balkhy, H. H., & Alghoribi, M. F. (2025). Genomic Characterization and Resistance Mechanisms of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 Isolates from Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311518






