Formulation Optimization of Sinomenine-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Evaluation of Pharmacological Efficacy in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Excipient Screening
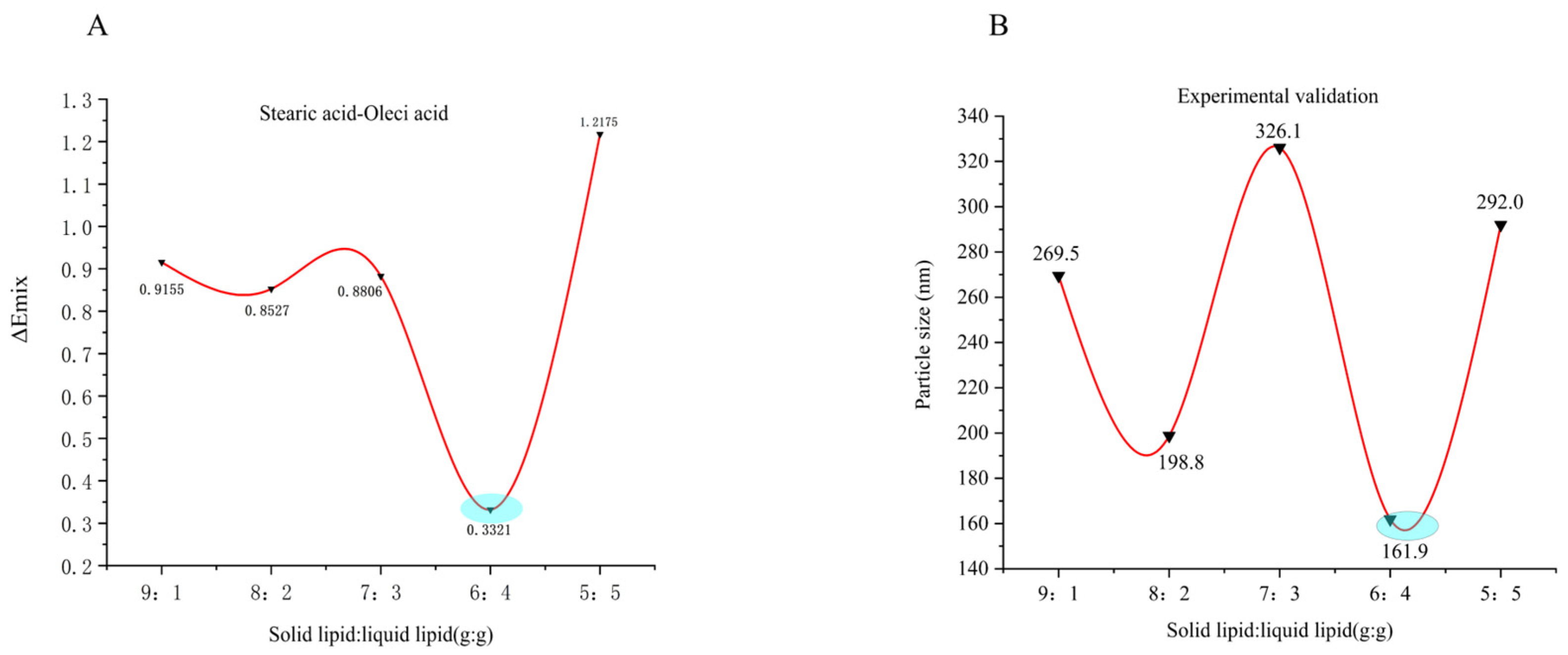
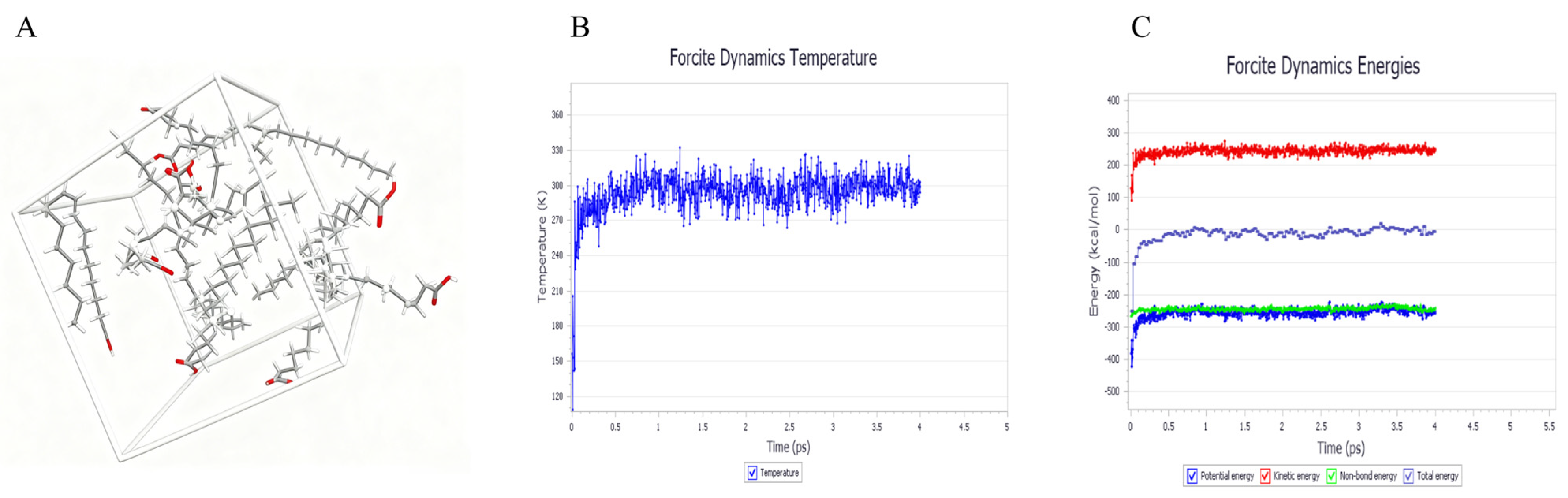
2.2. Simulation of Lipid Carrier Blending Systems
2.3. Formulation and Process Optimization of SIN-NLCs
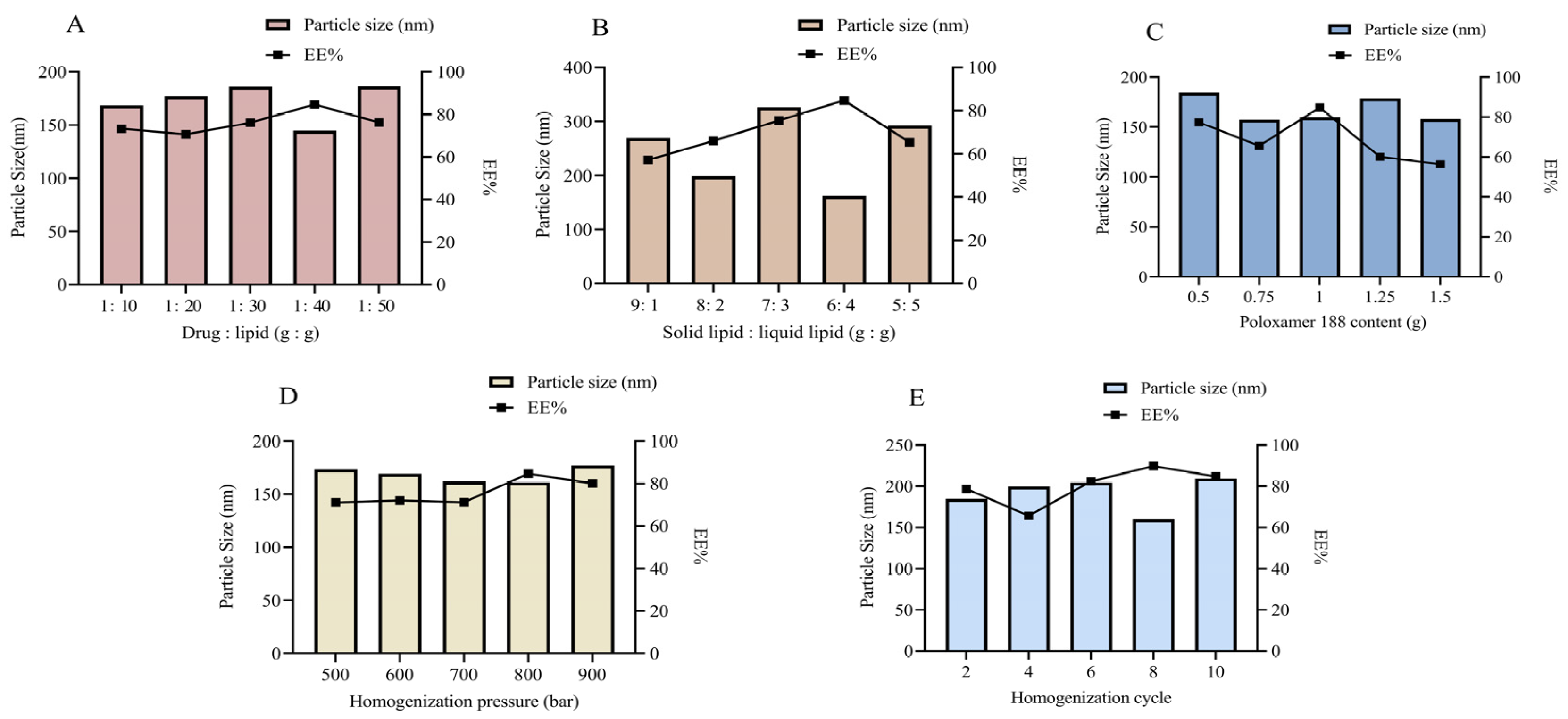
2.3.1. Single-Factor Optimization Formulation
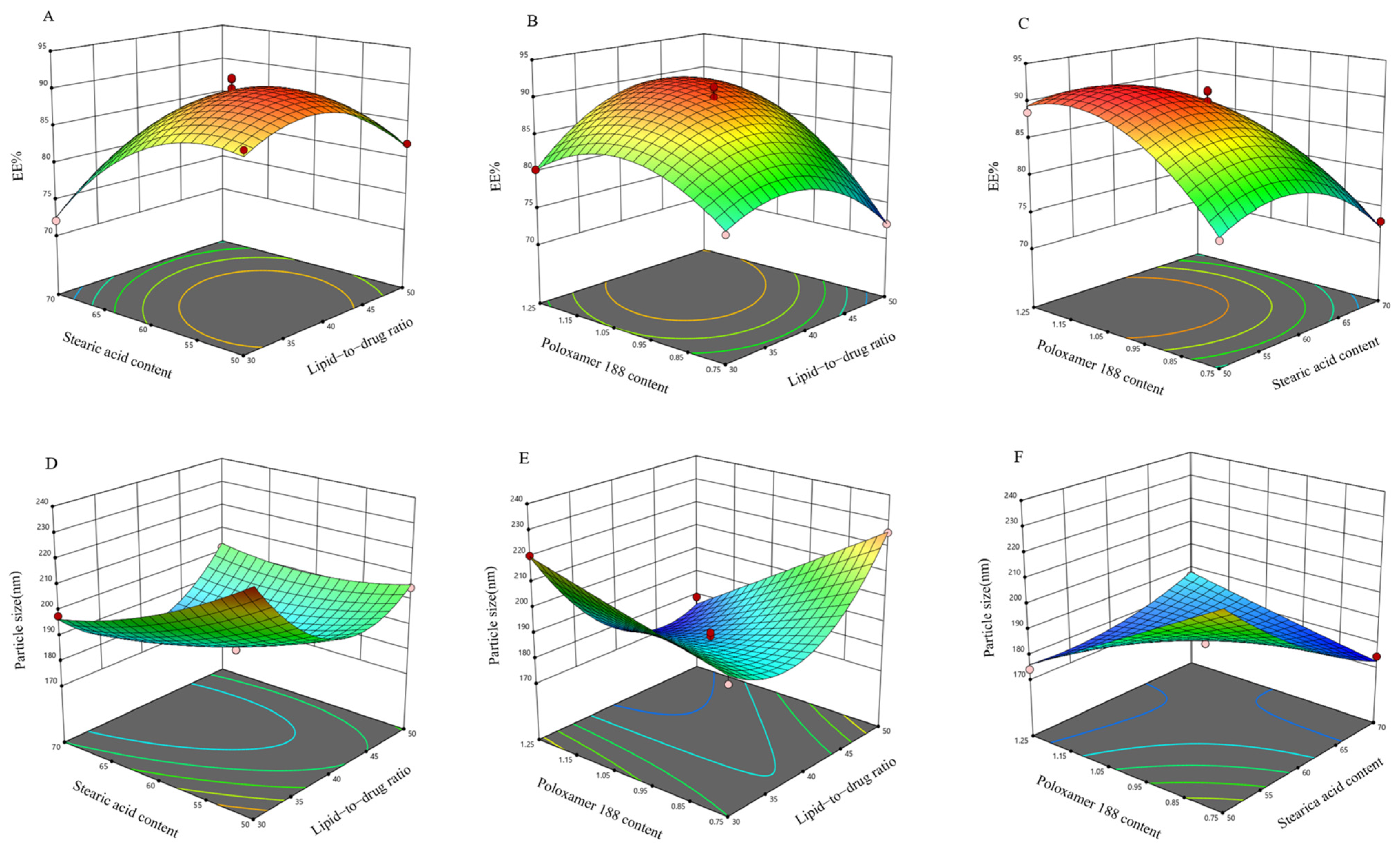
2.3.2. Box–Behnken Design (BBD) Experiment for Further Optimization of the Formulation
2.4. Characterization of SIN-NLCs
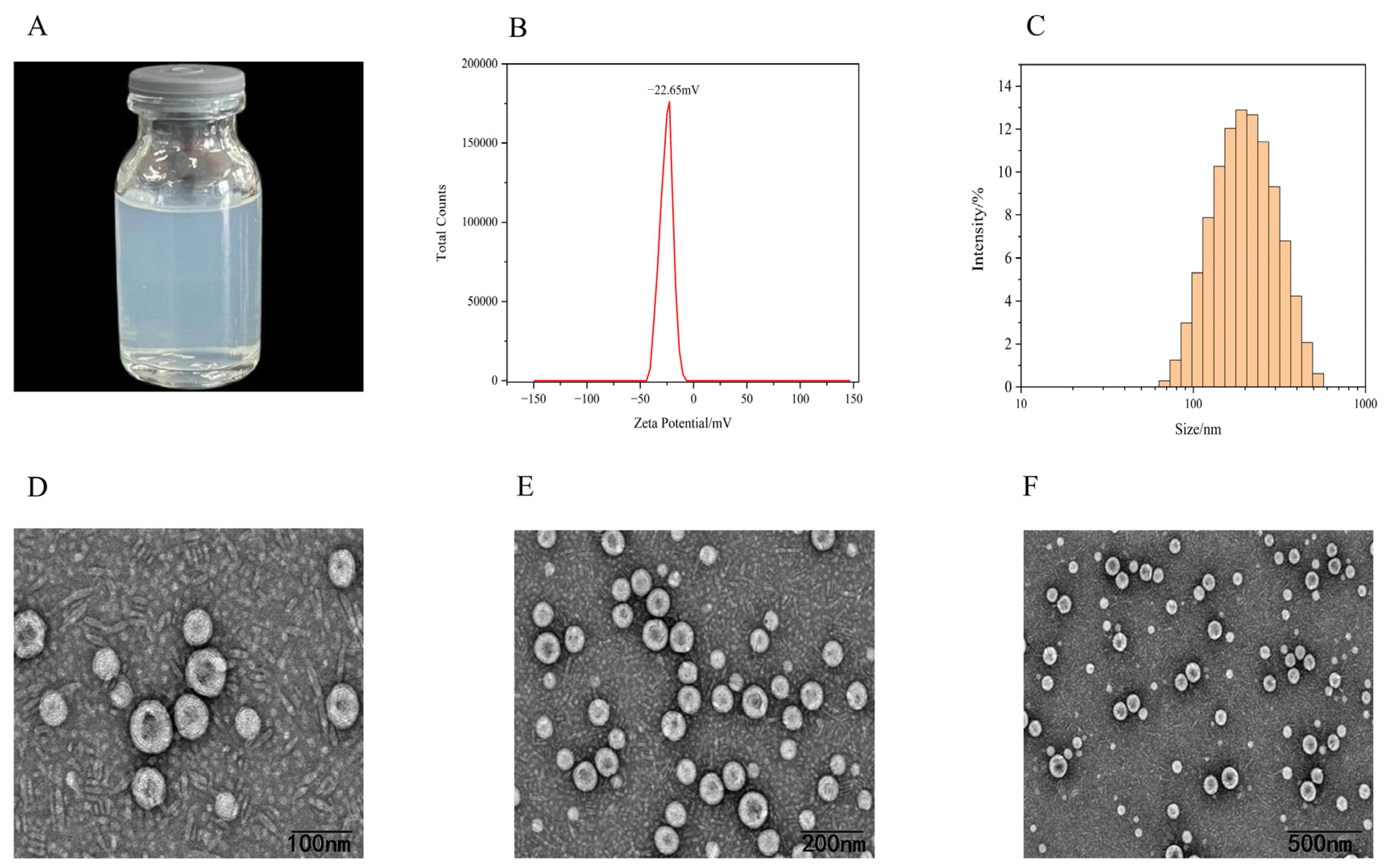
2.4.1. Appearance, Zeta Potential, and Particle Size Distribution
2.4.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.5. Spectral Analysis of SIN-NLCs
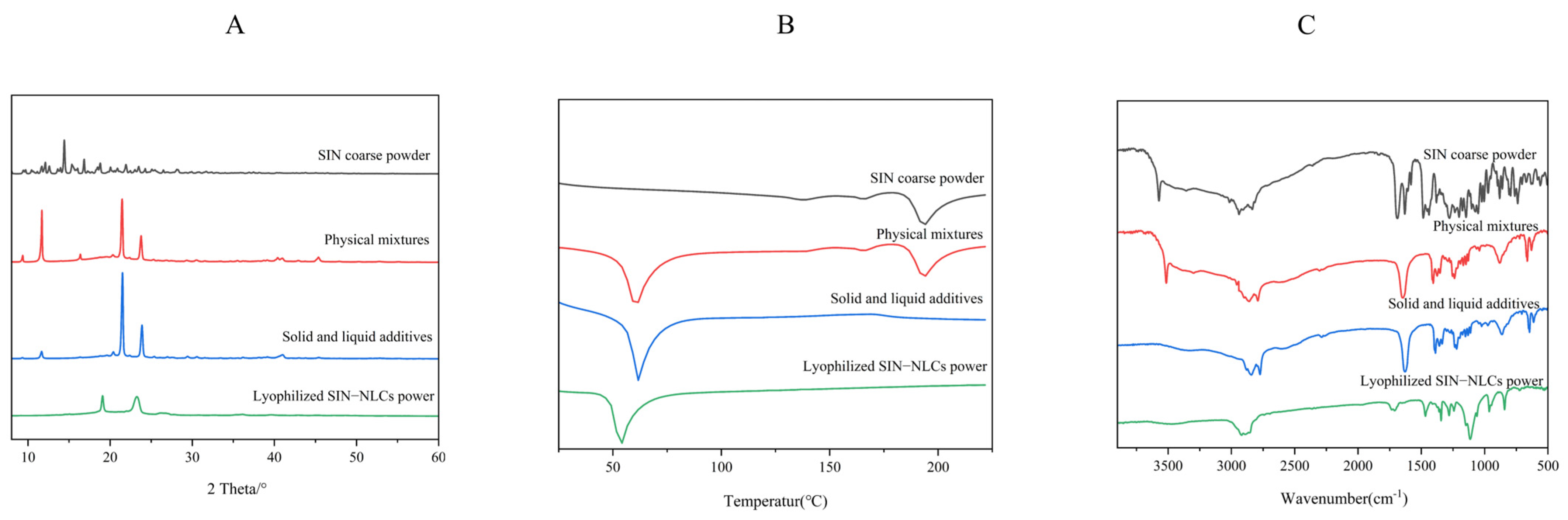
2.5.1. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
2.5.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.6. In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Studies
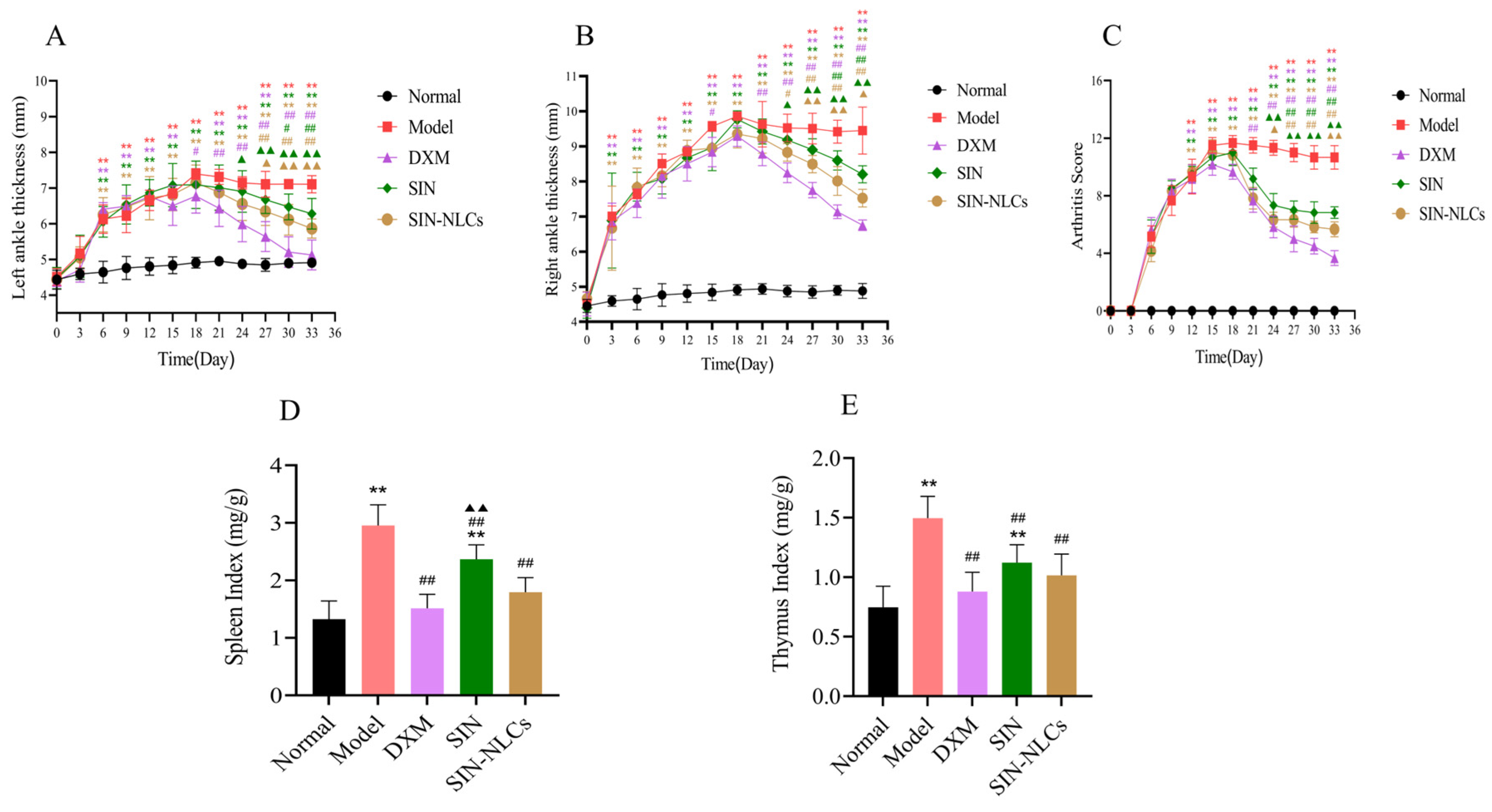
2.6.1. Paw Swelling Rate in Rats
2.6.2. Arthritis Scoring in Rats
2.6.3. Immune Organ Index in Rats
2.6.4. Inflammatory Mediators in Rats
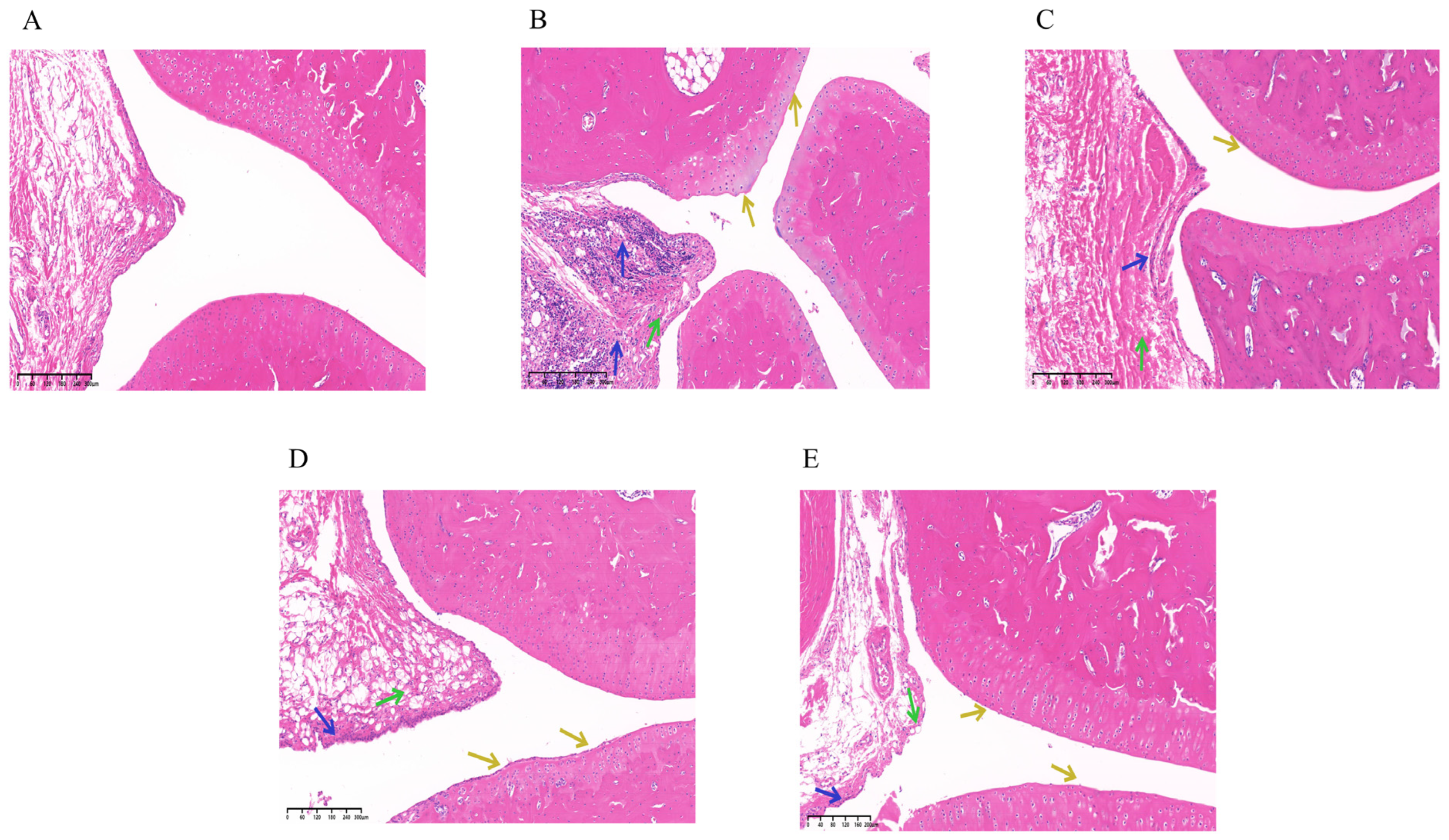
2.6.5. Histopathological Examination (HE)
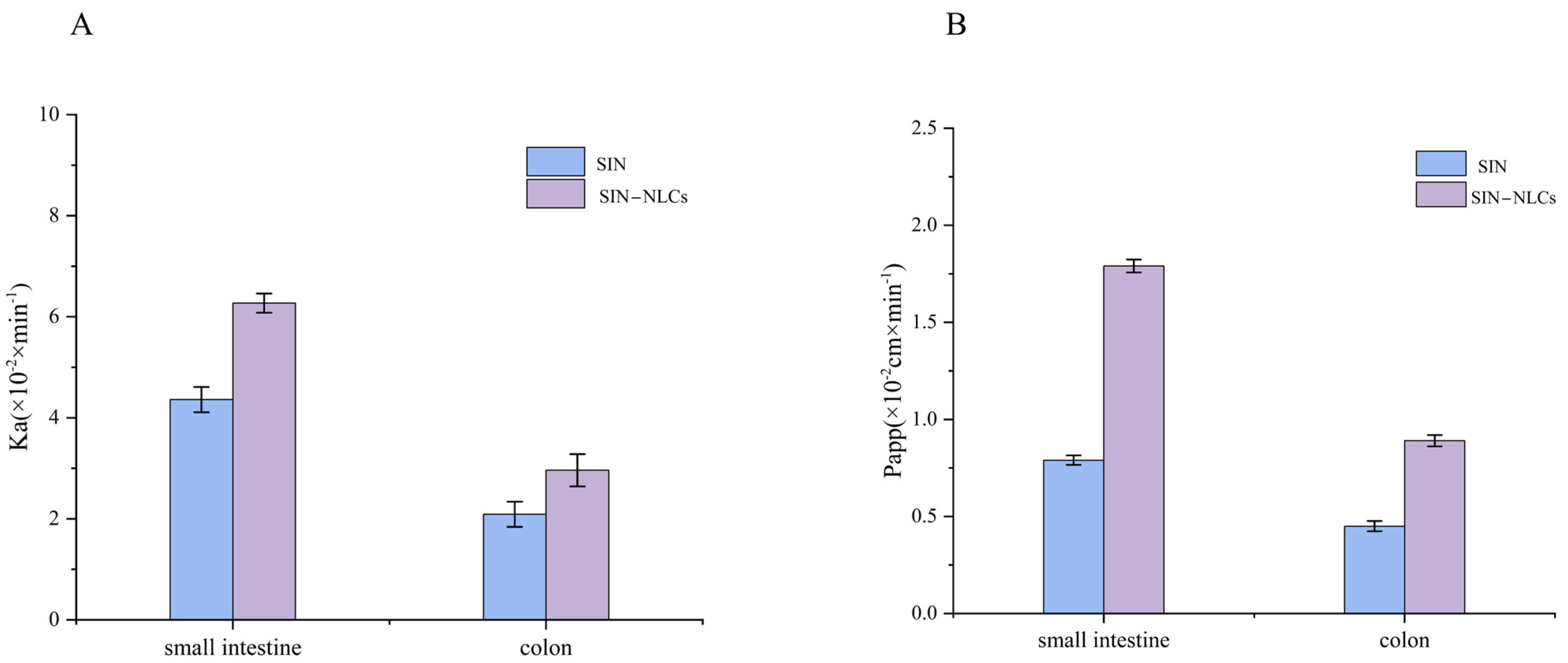
2.7. Single-Pass Intestinal Perfusion Study (SPIP)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Excipient Screening
4.3. Simulations of Solid–Liquid Lipid Carrier Mixture Systems
4.4. Formulation Optimization
4.5. Preparation of SIN-NLCs
4.6. Characterization of SIN-NLCs
4.6.1. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
4.6.2. EE%
4.6.3. TEM
4.7. Spectral Analysis of SIN-NLCs
4.7.1. XRD
4.7.2. DSC
4.7.3. FT-IR
4.8. In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Studies
4.8.1. Ethical Statement
4.8.2. Complete Freund’s Adjuvant-Induced (CFA) and Animal Treatment
4.8.3. Paw Edema Index, Arthritis Score, Immune Organ Indicators, Inflammatory Cytokine Detection, and HE Analysis in Rats
4.9. SPIP
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Firestein, G.S.; McInnes, I.B. Immunopathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunity 2017, 46, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, T.; Lafforgue, P.; Pham, T. NSAID: Current limits to prescription. Jt. Bone Spine 2024, 91, 105685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salliot, C.; van der Heijde, D. Long-term safety of methotrexate monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic literature research. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.D.; Baker, J.F.; Winthrop, K.; Curtis, J.R. Risk of Biologics and Glucocorticoids in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Undergoing Arthroplasty. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, V.; Rachapalli, S.; Choy, E.H. Safety of medium- to long-term glucocorticoid therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.M.; Deng, H.S.; Yao, Y.D.; Wang, W.T.; Hu, J.Q.; Dong, Y.; Wang, P.X.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Xie, Y.; et al. Sinomenine ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by targeting GBP5 and regulating the P2X7 receptor to suppress NLRP3-related signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 2504–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, K.; Gao, K.; Fu, M.; Lyu, C.; Quan, Z. Sinomenine Ameliorates IL-1β-Induced Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Rats Through Suppressing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Keap1/Nrf2/NF-κB Signaling Pathways. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 4777–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Bhatia, D.; Dave, V.; Sutariya, V.; Varghese Gupta, S. Salts of Therapeutic Agents: Chemical, Physicochemical, and Biological Considerations. Molecules 2018, 23, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Li, F.; Ma, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Le, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J. Highly Efficient Oral Iguratimod/Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanodrugs Fabricated by High-Gravity Nanoprecipitation Technique for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Small 2024, 20, e2304150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Cyclodextrins as functional excipients: Methods to enhance complexation efficiency. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 3019–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Sun, X.; Chen, J.; Cai, T. Pharmaceutical cocrystals: A review of preparations, physicochemical properties and applications. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2537–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.; Zhang, L.; Liao, W.; Liu, J.; Mao, L.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) stabilized by natural or synthetic emulsifiers for lutein delivery: Improved physicochemical stability, antioxidant activity, and bioaccessibility. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhao, L.; Su, X.; Zhang, P.; Ling, G. Repaglinide-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers with different particle sizes for improving oral absorption: Preparation, characterization, pharmacokinetics, and in situ intestinal perfusion. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Asghar, S.; Wu, Y.; Kambere Amerigos, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yin, L.; Huang, L.; Ping, Q.; Xiao, Y. N-acetyl-L-cysteine functionalized nanostructured lipid carrier for improving oral bioavailability of curcumin: Preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.R.; Lúcio, M.; Martins, S.; Lima, J.L.; Reis, S. Novel resveratrol nanodelivery systems based on lipid nanoparticles to enhance its oral bioavailability. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Jin, Y.; Bao, W.; Gao, H.; Xu, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Yao, P.; Liu, L. In vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation of nanostructured lipid curcumin carriers for intragastric administration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5395–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alatawi, H.M.; Alhwiti, S.S.; Alsharif, K.A.; Albalawi, S.S.; Abusaleh, S.M.; Sror, G.K.; Qushawy, M. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) as Effective Drug Delivery Systems: Methods of Preparation and their Therapeutic Applications. Recent. Pat. Nanotechnol. 2024, 18, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzadi, I.; Fürst, A.; Knoll, P.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) for Oral Peptide Drug Delivery: About the Impact of Surface Decoration. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liang, X.; Lu, C.; Kong, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, T.; Gou, J.; Wang, Y.; He, H. Nanostructured lipid carriers as oral delivery systems for improving oral bioavailability of nintedanib by promoting intestinal absorption. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latham, A.P.; Levy, E.S.; Sellers, B.D.; Leung, D.H. Utilizing Molecular Simulations to Examine Nanosuspension Stability. Pharmaceutics 2023, 16, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Pan, S.; Li, J.; Ding, X.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, W. Formulation Design and Evaluation of Ginsenoside Compound K Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Pharm. Innov. 2024, 19, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoni, P.A.; Ranchhod, J.; WaKasongo, K.; Khamanga, S.M.; Walker, R.B. The use of quantitative analysis and Hansen solubility parameter predictions for the selection of excipients for lipid nanocarriers to be loaded with water soluble and insoluble compounds. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathi, R.; Balamurugan, K.; Shi, J.; Subramanian, V.; Simmons, B.A.; Singh, S. Theoretical Insights into the Role of Water in the Dissolution of Cellulose Using IL/Water Mixed Solvent Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 14339–14349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madkhali, O.A. Perspectives and Prospective on Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems. Molecules 2022, 27, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.; Engers, D.; Bates, S.; Ivanisevic, I.; Kelly, R.C.; Zografi, G. Characterization of amorphous API:Polymer mixtures using X-ray powder diffraction. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4840–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteyne, T.; Heeze, L.; Mortier, S.T.; Oldörp, K.; Cardinaels, R.; Nopens, I.; Vervaet, C.; Remon, J.P.; De Beer, T. The use of Rheology Combined with Differential Scanning Calorimetry to Elucidate the Granulation Mechanism of an Immiscible Formulation During Continuous Twin-Screw Melt Granulation. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2481–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoni, S.; Passerini, N.; Albertini, B. Liquid Lipids Act as Polymorphic Modifiers of Tristearin-Based Formulations Produced by Melting Technologies. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, C.O., 3rd. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: Pivotal cytokines involved in bone degradation and inflammation. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 2002, 65, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.H.; Wen, W.L.; Zhang, W.Y.; Liang, X.; Sun, X.; Xiao, Z.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Li, A.Q.; Zhao, P.R.; Bai, H.T.; et al. [Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis by injection of sinomenine solid lipid nanoparticles under a fluorescence endoscopic laser confocal microscope]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2023, 48, 3786–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardy, J.; Chiew, K.S.; Galica, J.; Pond, G.R.; Tannock, I.F. Side effects associated with the use of dexamethasone for prophylaxis of delayed emesis after moderately emetogenic chemotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.; Tharmalingam, S.; Nguyen, P.; Tai, T.C. Untargeted metabolomics reveals sex-specific differences in lipid metabolism of adult rats exposed to dexamethasone in utero. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigfridsson, K.; Nordmark, A.; Theilig, S.; Lindahl, A. A formulation comparison between micro- and nanosuspensions: The importance of particle size for absorption of a model compound, following repeated oral administration to rats during early development. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 37, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, B.J.; Clulow, A.J. The influence of lipid digestion on the fate of orally administered drug delivery vehicles. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2021, 49, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuche, K.; Bhargavi, N.; Dora, C.P.; Jain, S. Drug-Phospholipid Complex-a Go Through Strategy for Enhanced Oral Bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskarinec, S.A.; Hannig, J.; Lee, R.C.; Lee, K.Y. Direct observation of poloxamer 188 insertion into lipid monolayers. Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayehunie, S.; Landry, T.; Stevens, Z.; Armento, A.; Hayden, P.; Klausner, M. Human Primary Cell-Based Organotypic Microtissues for Modeling Small Intestinal Drug Absorption. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrdadi, S. Lipid-Based Nanoparticles as Oral Drug Delivery Systems: Overcoming Poor Gastrointestinal Absorption and Enhancing Bioavailability of Peptide and Protein Therapeutics. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 14, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.S.; Yang, C.H.; Rhee, J.D.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, D.C.; Kim, D.D.; Kim, C.K.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, H.G. Enhanced rectal bioavailability of ibuprofen in rats by poloxamer 188 and menthol. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 269, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, J.; Nunes, C.; Vyas, S.; Jonnalagadda, S. Prediction of solubility parameters and miscibility of pharmaceutical compounds by molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 2014–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higginbotham, T.; Meier, K.; Ramírez, J.; Garaizar, A. Predicting Drug-Polymer Compatibility in Amorphous Solid Dispersions by MD Simulation: On the Trap of Solvation Free Energies. Mol. Pharm. 2025, 22, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhu, J.; Chen, T.; Lin, S.; Cai, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, X.S. Drug releasing behavior of hybrid micelles containing polypeptide triblock copolymer. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeitler, R.; Glader, C.; König, G.; Kaplan, J.; Tetyczka, C.; Remmelgas, J.; Mußbacher, M.; Fröhlich, E.; Roblegg, E. On the Structure, Stability, and Cell Uptake of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 3674–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornputtapitak, W.; Thiangjit, Y.; Tantirungrotechai, Y. Effect of Functional Groups in Lipid Molecules on the Stability of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Experimental and Computational Investigations. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 11012–11024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolou, M.; Assi, S.; Fatokun, A.A.; Khan, I. The Effects of Solid and Liquid Lipids on the Physicochemical Properties of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 2859–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancic, R.J.S.; Audus, D.J. Predicting compatibilized polymer blend toughness. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadk6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeton, C.; Chandy, K.G. Induction and monitoring of active delayed type hypersensitivity (DTH) in rats. J. Vis. Exp. 2007, 6, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Ke, X.M.; Zhang, C.H.; Yang, R.P. Absorption mechanism of three curcumin constituents through in situ intestinal perfusion method. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, e6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.J.; Jiang, D.B.; Tian, L.L.; Yin, J.J.; Huang, J.M.; Weng, W.Y. Intestinal permeability of forskolin by in situ single pass perfusion in rats. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, O.I.; Gubbins, R.H.; O’Driscoll, C.M. Estimation of absorption parameters from the non-steady-state phase in the rat gut perfusion model. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Systems | CED ×108(J/m3) | δ (Calculated Value) (J/cm3)1/2 | δ (Literature Value) (J/cm3)1/2 | Δδ (J/cm3)1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIN | 4.41 | 21.17 | - | - |
| GMS | 4.42 | 20.00 | - | 1.17 |
| Stearic acid | 4.28 | 20.52 | - | 0.65 |
| Glycerol tristearate | 3.27 | 18.44 | 17.37 | 3.33 |
| α-tocopherol | 3.75 | 17.52 | - | 3.65 |
| Oleci acid | 3.91 | 21.41 | 18.50 | 0.24 |
| Glycerol tricaprylate | 3.19 | 18.80 | 17.76 | 2.37 |
| Poloxamer 188 | 4.91 | 19.20 | - | 1.97 |
| Lecithin | 5.19 | 23.21 | - | 2.04 |
| PVA 0486 | 5.25 | 24.36 | 24.34 | 3.19 |
| Ethanol | 3.94 | 27.90 | 26.42 | 6.73 |
| Water | 2.46 | 48.26 | 47.04 | 27.09 |
| Factors | Drug-To-Lipid Ratio (g/g) | Solid Lipid–Liquid Lipid (g/g) | Poloxamer 188 Content (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levels | ||||
| −1 | 1:30 | 5:5 | 0.75 | |
| 0 | 1:40 | 6:4 | 1.00 | |
| 1 | 1:50 | 7:3 | 1.25 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, X.; Ding, X.; Zou, Y.; Sheng, M.; Li, J.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, W. Formulation Optimization of Sinomenine-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Evaluation of Pharmacological Efficacy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311449
Lin X, Ding X, Zou Y, Sheng M, Li J, Xiao Y, Xu J, Li J, Wang L, Xu W. Formulation Optimization of Sinomenine-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Evaluation of Pharmacological Efficacy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311449
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Xinmeng, Xuehui Ding, Yunlu Zou, Mingyang Sheng, Jingying Li, Yinghao Xiao, Jiahui Xu, Jixin Li, Lin Wang, and Wei Xu. 2025. "Formulation Optimization of Sinomenine-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Evaluation of Pharmacological Efficacy in Rheumatoid Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311449
APA StyleLin, X., Ding, X., Zou, Y., Sheng, M., Li, J., Xiao, Y., Xu, J., Li, J., Wang, L., & Xu, W. (2025). Formulation Optimization of Sinomenine-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Evaluation of Pharmacological Efficacy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311449






