Diabetes Mellitus and Lipoprotein(a): A Determinant Interaction in Micro- and Macrovascular Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
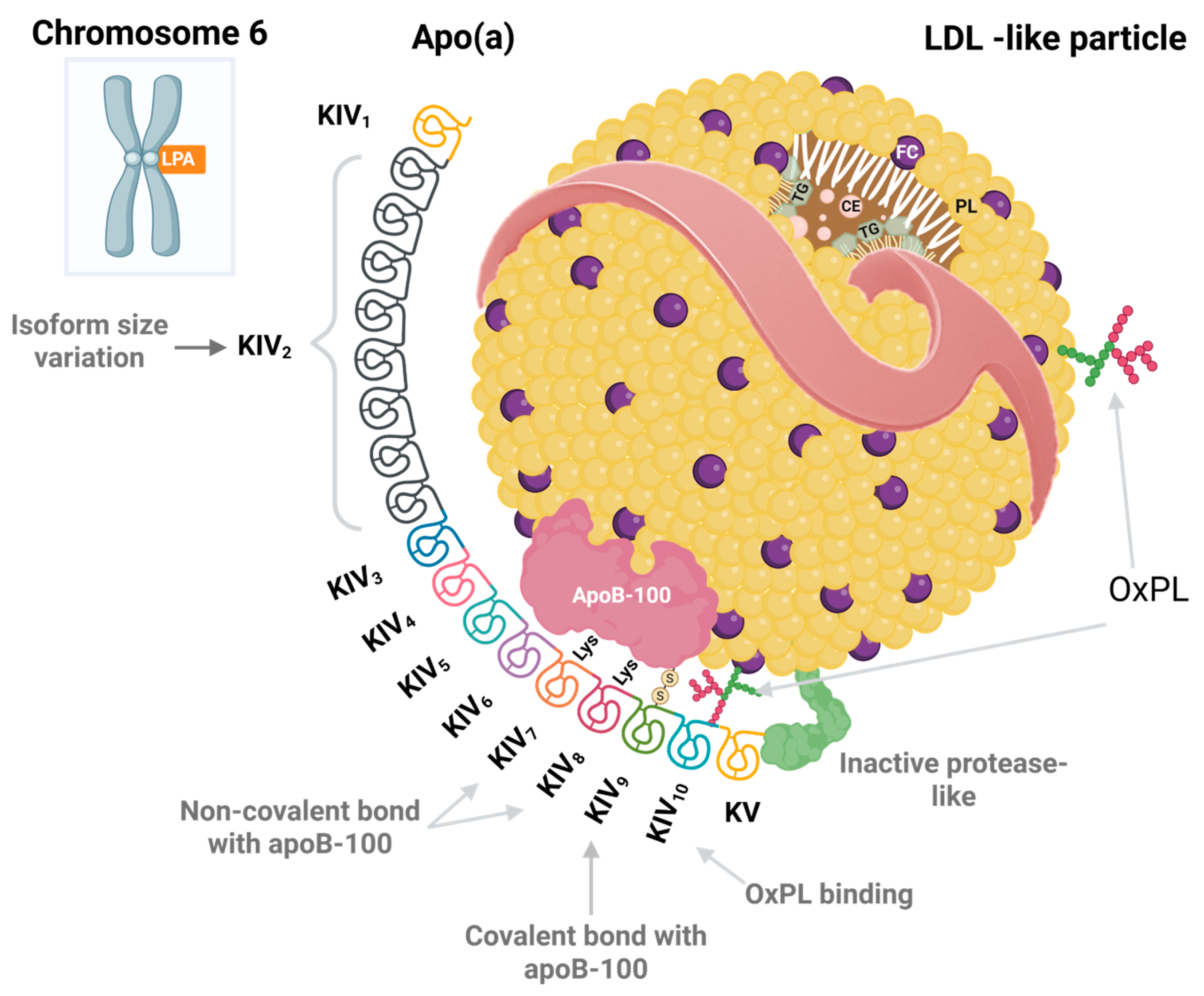
2. Chemical Structure of Lipoprotein(a)
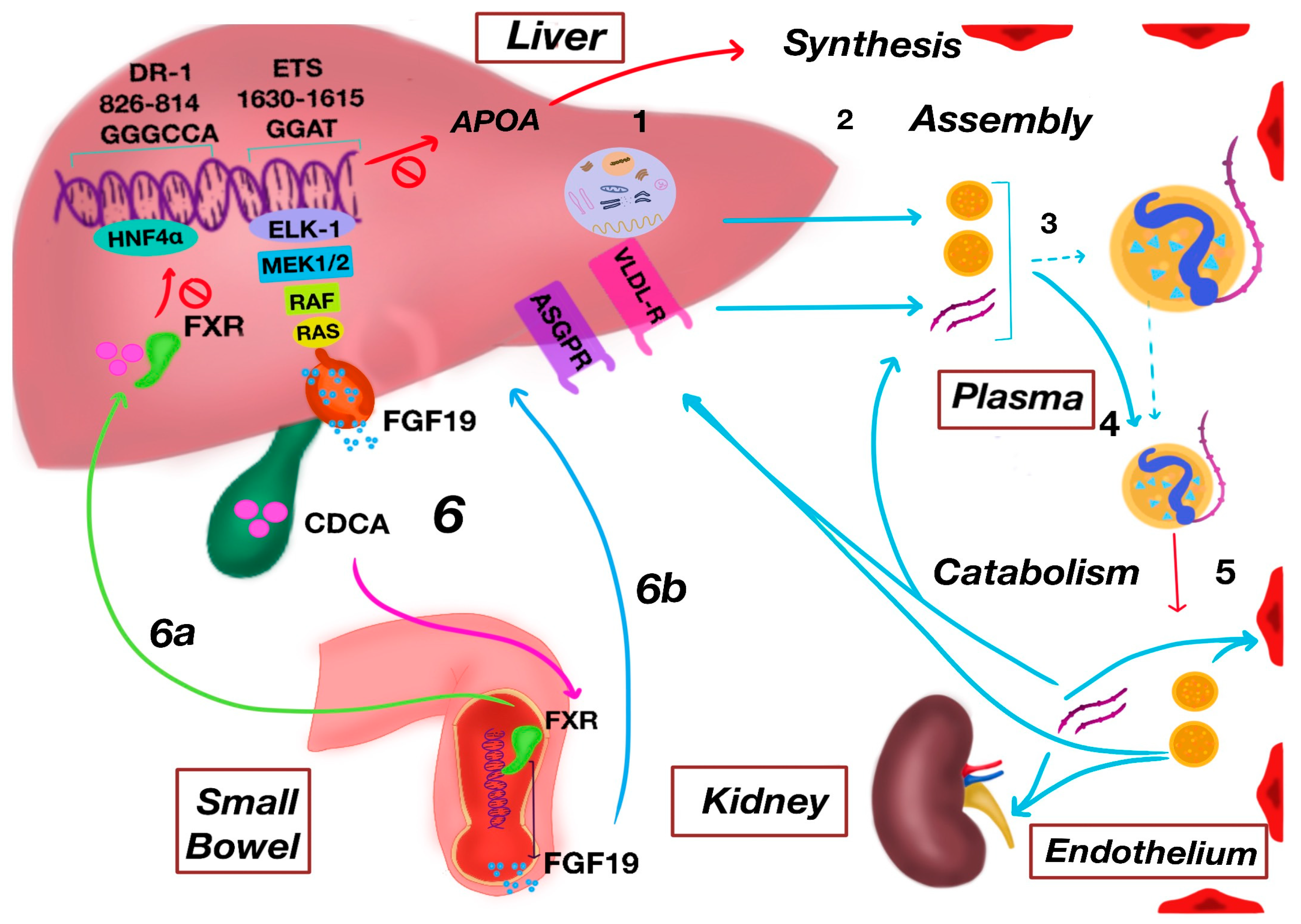
3. Metabolism of Lipoprotein(a)
3.1. Biosynthesis
3.2. Assembly
3.3. Catabolism
4. Behavior of Lipoprotein(a) According to Diabetic Phenotype
4.1. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
4.2. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
4.3. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)
5. Molecular Mechanisms of Lipoprotein(a) in DM: From Intimal Retention to Lipid Signaling
5.1. Vascular Retention of Lipoprotein(a): Intima, Proteoglycans, and Macrophage Uptake
5.2. Early Inflammatory Activation: Endothelium, Adhesion, and Chemotaxis
5.3. Lipoprotein(a)–Oxidized Phospholipid Axis: Signaling and Immune Amplification
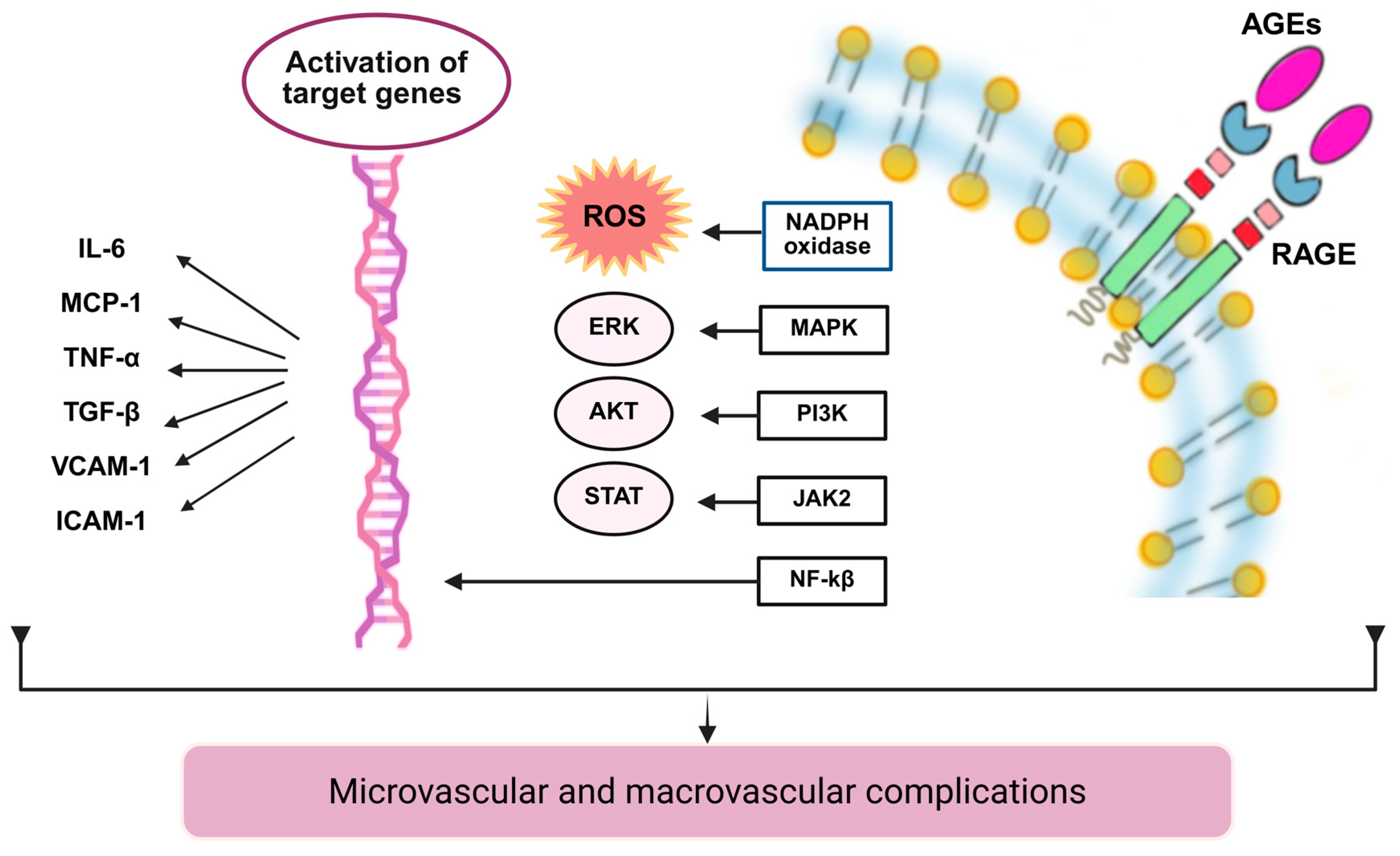
5.4. Non-Enzymatic Protein Glycation
5.5. Atherothrombosis and Antifibrinolysis Measured by Apo(a)
6. Macrovascular Complications
6.1. Atherosclerotic Coronary Artery Disease
6.2. Ischemic Cerebrovascular Disease
7. Microvascular Complications
7.1. Diabetic Retinopathy
7.2. Diabetic Nephropathy
7.3. Diabetic Neuropathy
8. Clinical Utility of Lipoprotein(a) in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
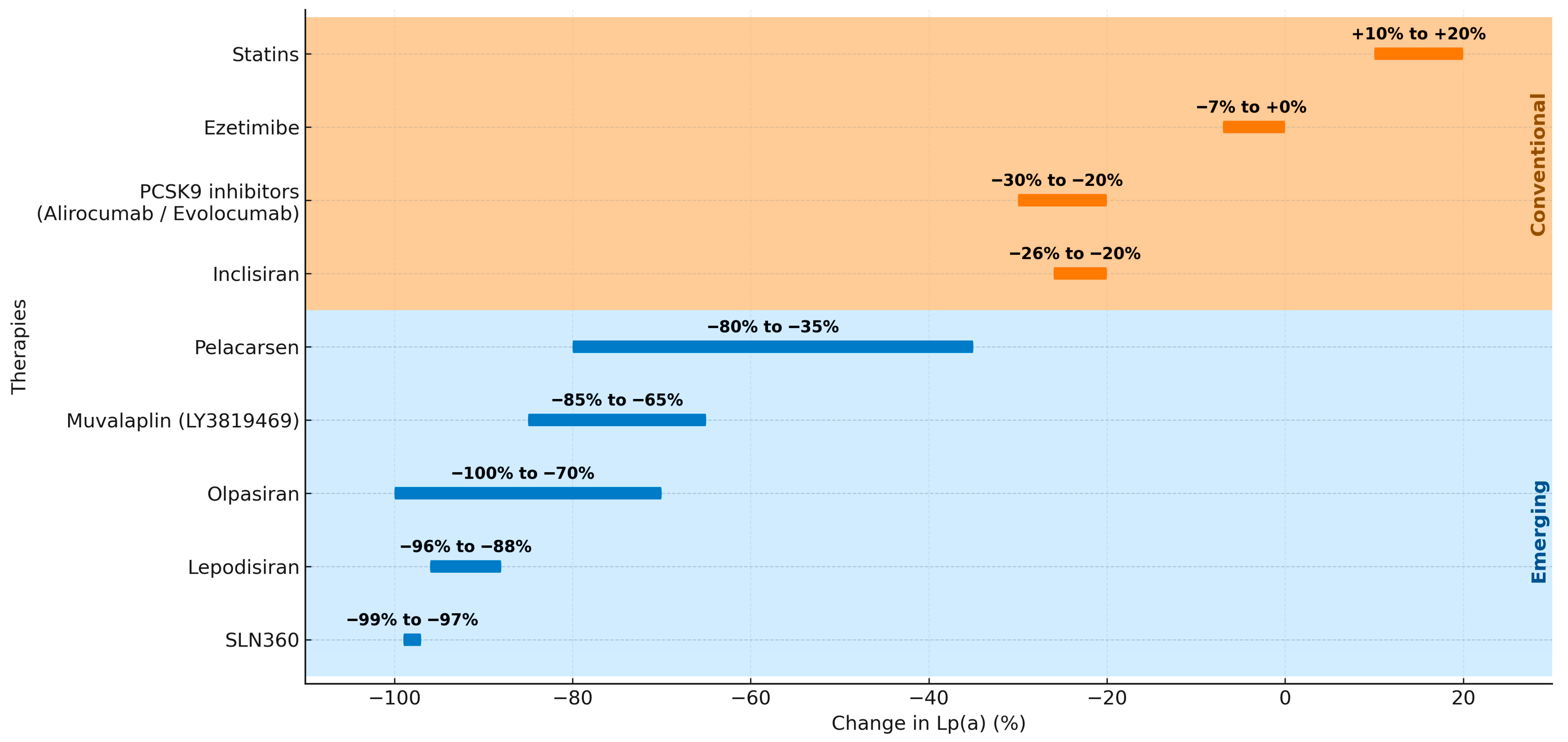
9. Therapeutic Perspectives and Future Directions
9.1. Conventional Lipid-Lowering Therapies
9.2. Emerging Lp(a)-Targeted Therapies
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGEs | Advanced glycation end-products |
| Apo(a) | Apolipoprotein(a) |
| Apo(B) | Apolipoprotein B |
| ApoB100 | Apolipoprotein B100 |
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease |
| ASGP-R | Asialoglycoprotein receptor |
| CDCA | Chenodeoxycholic acid |
| DAMPs | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| DR-1 | Downregulator of Transcription 1 |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| FGF19 | Fibroblast growth factor 19 |
| FXR | Farnesoid X receptor |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| HbA1C | Glycosylated hemoglobin |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HNF4α | Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-γ |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-18 | Interleukin-18 |
| IP3 | Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate |
| IVGTT | Intravenous glucose tolerance test |
| KIV | Kringle IV |
| KIV-1 | Kringle IV type 1 |
| KIV-2 | Kringle IV type 2 |
| KIV-3 | Kringle IV type 3 |
| KIV-4 | Kringle IV type 4 |
| KIV-5 | Kringle IV type 5 |
| KIV-6 | Kringle IV type 6 |
| KIV-7 | Kringle IV type 7 |
| KIV-8 | Kringle IV type 8 |
| KIV-9 | Kringle IV type 9 |
| KIV-10 | Kringle IV type 10 |
| KV | Kringle V |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| LDL-R | Low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| Lp(a) | Lipoprotein(a) |
| LPA | Apolipoprotein(a) gene |
| MACE | Major adverse cardiovascular events |
| MMP-9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| MODY | Maturity-onset diabetes of the young |
| NF-κB | Factor nuclear factor kappa B |
| ox-LDL | Oxidized low-density lipoprotein |
| OxPL | Oxidized phospholipids |
| PAF | Platelet-activating factor |
| PAF-AH | Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase |
| PCSK9 | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 |
| PLC | Phospholipase C |
| PPARγ/α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors |
| PRRs | Pattern recognition receptors |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| sdLDL | Dense low-density lipoprotein |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| SNPs | Single-nucleotide polymorphisms |
| T1DM | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| TLRs | Toll-like receptors |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| tPA | Tissue-type plasminogen activator |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| VLDL | Very-low-density lipoprotein |
| VLDL-R | Very-low-density lipoprotein receptor |
References
- Cuevas, M.A.; Alonso, K.R. Dislipidemia Diabética. Rev. Médica Clínica Condes 2016, 27, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antini, C.; Caixeta, R.; Luciani, S.; Hennis, A.J.M. Diabetes Mortality: Trends and Multi-Country Analysis of the Americas from 2000 to 2019. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2024, 53, dyad182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 30 October 2025).
- Dal Canto, E.; Ceriello, A.; Rydén, L.; Ferrini, M.; Hansen, T.B.; Schnell, O.; Standl, E.; Beulens, J.W. Diabetes as a Cardiovascular Risk Factor: An Overview of Global Trends of Macro and Micro Vascular Complications. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoluci, M.C.; Rocha, V.Z. Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Patients with Diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2017, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskinen, M.-R.; Borén, J. New Insights into the Pathophysiology of Dyslipidemia in Type 2 Diabetes. Atherosclerosis 2015, 239, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiter, L.A.; Lundman, P.; da Silva, P.M.; Drexel, H.; Jünger, C.; Gitt, A.K. Persistent Lipid Abnormalities in Statin-treated Patients with Diabetes Mellitus in Europe and Canada: Results of the Dyslipidaemia International Study. Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschinsky, M.L.; Bajaj, A.; Boffa, M.B.; Dixon, D.L.; Ferdinand, K.C.; Gidding, S.S.; Gill, E.A.; Jacobson, T.A.; Michos, E.D.; Safarova, M.S.; et al. A Focused Update to the 2019 NLA Scientific Statement on Use of Lipoprotein(a) in Clinical Practice. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2024, 18, e308–e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; McCoy, R.G.; Aleppo, G.; Balapattabi, K.; Beverly, E.A.; Briggs Early, K.; Bruemmer, D.; Das, S.R.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Ekhlaspour, L.; et al. 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, S207–S238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Wong, N.D. Epidemiology, Control, and Cardiovascular Outcomes of Dyslipidemia in Diabetes. In Lipoproteins in Diabetes Mellitus; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 891–913. [Google Scholar]
- Mooradian, A.D. Dyslipidemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergès, B. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Dyslipidaemia: Where Are We? Diabetologia 2015, 58, 886–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Dyslipidemia. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive Blood-Glucose Control with Sulphonylureas or Insulin Compared with Conventional Treatment and Risk of Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.L.; Durand, A.; McCormack, T.; Hughes, E.; Berni, T.R.; Lahoz, R. Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events Associated with Elevated Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in a Population with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease with and without Type 2 Diabetes: A UK Database Analysis Using the Clinical Practice Resea. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e064541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamina, C.; Ward, N.C. Lipoprotein (a) and Diabetes Mellitus. Atherosclerosis 2022, 349, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durlach, V.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Boccara, F.; Varret, M.; Di-Filippo Charcosset, M.; Cariou, B.; Valero, R.; Charriere, S.; Farnier, M.; Morange, P.E.; et al. Lipoprotein(a): Pathophysiology, Measurement, Indication and Treatment in Cardiovascular Disease. A Consensus Statement from the Nouvelle Société Francophone d’Athérosclérose (NSFA). Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 114, 828–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, P.; Di Girolamo, F.G.; Panizon, E.; Tosoni, L.M.; Cerrato, C.; Pellicori, F.; Altamura, N.; Pirulli, A.; Zaccari, M.; Biasinutto, C.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) as a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Diseases: Pathophysiology and Treatment Perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimikas, S.; Karwatowska-Prokopczuk, E.; Gouni-Berthold, I.; Tardif, J.-C.; Baum, S.J.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Shapiro, M.D.; Stroes, E.S.; Moriarty, P.M.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) Reduction in Persons with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyrbuś, K.; Mędrala, Z.; Konsek, K.; Nowowiejska-Wiewióra, A.; Trzeciak, P.; Skrzypek, M.; Cieśla, D.; Banach, M.; Gąsior, M. Lipoprotein(a) and Its Impact on Cardiovascular Disease—The Polish Perspective: Design and First Results of the Zabrze-Lipoprotein(a) Registry. Arch. Med. Sci. 2024, 20, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, W.; Lobo, M.; Barbagelata, L.; Lavalle-Cobo, A.; Nogueira, J.P. Acute Pancreatitis due to Different Semaglutide Regimens: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2024, 71, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, F. Human Genetics and the Causal Role of Lipoprotein(a) for Various Diseases. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2016, 30, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinder, M.; Zekavat, S.M.; Uddin, M.M.; Pampana, A.; Natarajan, P. Apolipoprotein B Is an Insufficient Explanation for the Risk of Coronary Disease Associated with Lipoprotein(a). Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1245–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Ference, B.A.; Staley, J.R.; Freitag, D.F.; Mason, A.M.; Nielsen, S.F.; Willeit, P.; Young, R.; Surendran, P.; Karthikeyan, S.; et al. Association of LPA Variants With Risk of Coronary Disease and the Implications for Lipoprotein(a)-Lowering Therapies. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poznyak, A.V.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Surkova, R.; Orekhov, N.A.; Orekhov, A.N. Glycation of LDL: AGEs, Impact on Lipoprotein Function, and Involvement in Atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1094188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, A.J.; Best, J.D.; Klein, R.L.; Lyons, T.J. Lipoproteins, Glycoxidation and Diabetic Angiopathy. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2004, 20, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengstie, M.A.; Chekol Abebe, E.; Behaile Teklemariam, A.; Tilahun Mulu, A.; Agidew, M.M.; Teshome Azezew, M.; Zewde, E.A.; Agegnehu Teshome, A. Endogenous Advanced Glycation End Products in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Diabetic Complications. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1002710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.W.; Kang, T.S.; Lee, B.K.; Chang, W.; Hwang, K.-C.; Rhee, J.-H.; Min, P.-K.; Hong, B.-K.; Rim, S.-J.; Kwon, H.M. Pathobiological Role of Advanced Glycation Endproducts via Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Dependent Pathway in the Diabetic Vasculopathy. Exp. Mol. Med. 2008, 40, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrecher, U.P.; Parthasarathy, S.; Leake, D.S.; Witztum, J.L.; Steinberg, D. Modification of Low Density Lipoprotein by Endothelial Cells Involves Lipid Peroxidation and Degradation of Low Density Lipoprotein Phospholipids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3883–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pan, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Role of Advanced Glycation End Products in Diabetic Vascular Injury: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yun, J.-S.; Ko, S.-H. Advanced Glycation End Products and Their Effect on Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirban, A.; Gawlowski, T.; Roden, M. Vascular Effects of Advanced Glycation Endproducts: Clinical Effects and Molecular Mechanisms. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimikas, S. A Test in Context: Lipoprotein(a). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 692–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte Lau, F.; Giugliano, R.P. Lipoprotein(a) and Its Significance in Cardiovascular Disease. JAMA Cardiol. 2022, 7, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gries, A.; Nimpf, J.; Nimpf, M.; Wurm, H.; Kostner, G.M. Free and Apo B-Associated Lpa-Specific Protein in Human Serum. Clin. Chim. Acta 1987, 164, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, J.W.; Nagaswami, C.; Woodhead, J.L.; Higazi, A.A.-R.; Cain, W.J.; Marcovina, S.M.; Koschinsky, M.L.; Cines, D.B.; Bdeir, K. The Structure of Lipoprotein(a) and Ligand-Induced Conformational Changes. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 10424–10435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanu, A.M.; Nakajima, K.; Edelstein, C. Apolipoprotein(a): Structure and Biology. Front. Biosci. 2001, 6, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronenberg, F.; Utermann, G. Lipoprotein(a): Resurrected by Genetics. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 273, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volgman, A.S.; Koschinsky, M.L.; Mehta, A.; Rosenson, R.S. Genetics and Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Lipoprotein(a)-Associated Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e033654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argraves, K.M.; Kozarsky, K.F.; Fallon, J.T.; Harpel, P.C.; Strickland, D.K. The Atherogenic Lipoprotein Lp(a) Is Internalized and Degraded in a Process Mediated by the VLDL Receptor. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2170–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson-Paul, A.M.; Gillespie, C.; Wall, H.K.; Loustalot, F.; Sperling, L.; Hong, Y. Recommended and Observed Statin Use among U.S. Adults—National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2011—2018. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2023, 17, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcovina, S.M.; Koschinsky, M.L. Lipoprotein(a) Concentration and Apolipoprotein(a) Size. Circulation 1999, 100, 1151–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, S.; Coassin, S.; Rueedi, R.; Yousri, N.A.; Seppälä, I.; Gieger, C.; Schönherr, S.; Forer, L.; Erhart, G.; Marques-Vidal, P.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Meta-Analysis on Lipoprotein (a) Concentrations Adjusted for Apolipoprotein (a) Isoforms. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, M.; Chen, H.Y.; Rong, J.; Dufresne, L.; Yao, J.; Guo, X.; Tsai, M.Y.; Tsimikas, S.; Post, W.S.; Vasan, R.S.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Highlights APOH as a Novel Locus for Lipoprotein(a) Levels—Brief Report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostakou, P.M.; Hatzigeorgiou, G.; Kolovou, V.; Mavrogeni, S.; Kolovou, G.D. Lipoprotein (a) Evolution: Possible Benefits and Harm. Genetic and Non-Genetic Factors Influencing Its Plasma Levels. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, J.M.; Milberg, J.A.; Pearce, G.L.; Sprecher, D.L. Lipoprotein(a) Associated with Coronary Artery Disease in Older Women: Age and Gender Analysis. Atherosclerosis 2000, 153, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordestgaard, B.G.; Langsted, A. Lipoprotein(a) and Cardiovascular Disease. Lancet 2024, 404, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guertin, J.; Kaiser, Y.; Manikpurage, H.; Perrot, N.; Bourgeois, R.; Couture, C.; Wareham, N.J.; Bossé, Y.; Pibarot, P.; Stroes, E.S.G.; et al. Sex-Specific Associations of Genetically Predicted Circulating Lp(a) (Lipoprotein(a)) and Hepatic LPA Gene Expression Levels With Cardiovascular Outcomes: Mendelian Randomization and Observational Analyses. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2021, 14, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Soffer, G.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Berglund, L.; Duell, P.B.; Heffron, S.P.; Kamstrup, P.R.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Marcovina, S.M.; Yeang, C.; Koschinsky, M.L.; et al. Lipoprotein(a): A Genetically Determined, Causal, and Prevalent Risk Factor for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2022, 42, E48–E60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostner, K.M.; Marz, W.; Kostner, G.M. When Should We Measure Lipoprotein (A)? Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 3268–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, A.; Repa, J.J.; Evans, R.M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Nuclear Receptors and Lipid Physiology: Opening the X-Files. Science 2001, 294, 1866–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chennamsetty, I.; Claudel, T.; Kostner, K.M.; Trauner, M.; Kostner, G.M. FGF19 Signaling Cascade Suppresses APOA Gene Expression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, T.; Choi, M.; Moschetta, A.; Peng, L.; Cummins, C.L.; McDonald, J.G.; Luo, G.; Jones, S.A.; Goodwin, B.; Richardson, J.A.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 15 Functions as an Enterohepatic Signal to Regulate Bile Acid Homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2005, 2, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.L.; Lanford, R.E. Biosynthesis and Metabolism of Lipoprotein (a). Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 1995, 6, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, T.A. Lipoprotein(a), Cardiovascular Disease, and Contemporary Management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 1294–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostner, K.M.; Kostner, G.M. Lp(a) and the Risk for Cardiovascular Disease: Focus on the Lp(a) Paradox in Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frischmann, M.E.; Ikewaki, K.; Trenkwalder, E.; Lamina, C.; Dieplinger, B.; Soufi, M.; Schweer, H.; Schaefer, J.R.; König, P.; Kronenberg, F.; et al. In Vivo Stable-Isotope Kinetic Study Suggests Intracellular Assembly of Lipoprotein(a). Atherosclerosis 2012, 225, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HRZENJAK, A.; FRANK, S.; WO, X.; ZHOU, Y.; van BERKEL, T.; KOSTNER, G.M. Galactose-Specific Asialoglycoprotein Receptor Is Involved in Lipoprotein (a) Catabolism. Biochem. J. 2003, 376, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostner, K.M.; Kostner, G.M. Lipoprotein (a): A Historical Appraisal. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostner, G.M.; Wo, X.; Frank, S.; Kostner, K.; Zimmermann, R.; Steyrer, E. Metabolism of Lp(a): Assembly and Excretion. Clin. Genet. 1997, 52, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, F.; Trenkwalder, E.; Lingenhel, A.; Friedrich, G.; Lhotta, K.; Schober, M.; Moes, N.; König, P.; Utermann, G.; Dieplinger, H. Renovascular Arteriovenous Differences in Lp[a] Plasma Concentrations Suggest Removal of Lp[a] from the Renal Circulation. J. Lipid Res. 1997, 38, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostner, K.M.; Maurer, G.; Huber, K.; Stefenelli, T.; Dieplinger, H.; Steyrer, E.; Kostner, G.M. Urinary Excretion of Apo(a) Fragments. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1996, 16, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KOSTNER, K.M.; JANSEN, M.; MAURER, G.; DERFLER, K. LDL-apheresis Significantly Reduces Urinary Apo(a) Excretion. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 27, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmena, R. Riesgo Elevado de Disfunción Lipoproteica En La Diabetes Mellitus Tipo 2. Rev. Española Cardiol. Supl. 2008, 8, 19C–26C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandstätter, A.; Lingenhel, A.; Zwiauer, K.; Strobl, W.; Kronenberg, F. Decrease of Lp(a) during Weight Reduction in Obese Children Is Modified by the Apo(a) Kringle-IV Copy Number Variation. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcovina, S.M.; Lippi, G.; Bagatell, C.J.; Bremner, W.J. Testosterone-Induced Suppression of Lipoprotein(a) in Normal Men; Relation to Basal Lipoprotein(a) Level. Atherosclerosis 1996, 122, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estellés, A.; Falcó, C.; Gilabert-Estellés, J. La Influencia Del Tratamiento Hormonal Sustitutivo En La Lipoproteína (A), La Coagulación Y La Fibrinólisis. Clínica Investig. Arterioscler. 2001, 13, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, M.C.; Cano, A.; Hermenegildo, C. Metabolismo Lipídico Y Aterogénesis Femenina: Acción de Hormonas, SERM Y Fitoestrógenos. Prog. Obstet. Ginecol. 2001, 44, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Radu, C.C.; Gliga, M. Lipoprotein(a) Levels in Thyroid Disorders. Acta Medica Marisiensis 2013, 59, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, M.; Crook, D.; Godsland, I.F.; Walton, C.; Wynn, V.; Oliver, M.F. Inverse Relationship Between Serum Lp(a) Levels and First-Phase Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 1992, 41, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaverková, H.; Karásek, D.; Halenka, M.; Cibíčková, L.; Kubíčková, V. Inverse Association of Lipoprotein (a) With Markers of Insulin Resistance in Dyslipidemic Subjects. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66, S113–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskinen, M.-R. Quantitative and Qualitative Lipoprotein Abnormalities in Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes 1992, 41, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krempler, F.; Kostner, G.M.; Bolzano, K.; Sandhofer, F. Turnover of Lipoprotein (a) in Man. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 65, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejawa, M.; Goławski, M.; Fronczek, M.; Osadnik, T.; Paneni, F.; Ruscica, M.; Pawlas, N.; Lisik, M.; Banach, M. Causal Associations between Insulin and Lp(a) Levels in Caucasian Population: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainwater, D.L.; Haffner, S.M. Insulin and 2-Hour Glucose Levels Are Inversely Related to Lp(a) Concentrations Controlled for LPA Genotype. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neele, D.M.; de Wit, E.C.M.; Princen, H.M.G. Insulin Suppresses Apolipoprotein(a) Synthesis by Primary Cultures of Cynomolgus Monkey Hepatocytes (Short Communication). Diabetologia 1999, 42, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz Naya, L.; Delgado Álvarez, E. Diabetes Mellitus. Criterios Diagnósticos Y Clasificación. Epidemiología. Etiopatogenia. Evaluación Inicial Del Paciente Con Diabetes. Med.-Programa Form. Médica Contin. Acreditado 2016, 12, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antar, S.A.; Ashour, N.A.; Sharaky, M.; Khattab, M.; Ashour, N.A.; Zaid, R.T.; Roh, E.J.; Elkamhawy, A.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A. Diabetes Mellitus: Classification, Mediators, and Complications; A Gate to Identify Potential Targets for the Development of New Effective Treatments. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, S.M. Lipoprotein(a) and Diabetes: An Update. Diabetes Care 1993, 16, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, K.; Yutani, S.; Miyake, H.; Onigata, K.; Yagi, H.; Kuroume, T. Lipoprotein(a) Levels in Japanese Children With IDDM. Diabetes Care 1993, 16, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.S.; Aslam, M.; Shah, S.F.A.; Naveed, A.K. Lipoproteína (a) Está Associada Com Níveis Basais de Insulina Em Pacientes Com Diabetes Mellitus Tipo 2. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2009, 93, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groop, P.-H.; Viberti, G.C.; Elliott, T.G.; Friedman, R.; Mackie, A.; Ehnholm, C.; Jauhiainen, M.; Taskinen, M.-R. Lipoprotein(a) in Type 1 Diabetic Patients with Renal Disease. Diabet. Med. 1994, 11, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botana López, M.A. Lipoproteína (a): ¿está Indicada Su Determinación Sistemática? Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2024, 71, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhofer, K.G.; Demant, T.; Ritter, M.M.; Geiss, H.C.; Donner, M.; Schwandt, P. Lipoprotein (a) Metabolism Estimated by Nonsteady-state Kinetics. Lipids 1999, 34, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracz, A.; Madzio, J.; Gnys, P.; Malachowska, B.; Borowiec, M.; Wyka, K.; Jarosz-Chobot, P.; Mysliwiec, M.; Szadkowska, A.; Mlynarski, W.; et al. Genetic Variability of GCKR Alters Lipid Profiles in Children with Monogenic and Autoimmune Diabetes. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2014, 122, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, D.Q.; Dansky, H.M.; Fleisher, M.; Assmann, G.; Fajans, S.S.; Stoffel, M. Genotype/phenotype Relationships in HNF-4alpha/MODY1: Haploinsufficiency Is Associated with Reduced Apolipoprotein (AII), Apolipoprotein (CIII), Lipoprotein(a), and Triglyceride Levels. Diabetes 2000, 49, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajans, S.S. Maturity-onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY). Diabetes Metab. Rev. 1989, 5, 579–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carral, F.; Tomé, M.; Fernández, J.J.; Piñero, A.; Expósito, C.; Jiménez, A.I.; García, C.; Ayala, C. La Presencia de Complicaciones Microvasculares Se Asocia Con Un Mal Control Metabólico Evolutivo En Pacientes Con Diabetes Tipo 1. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2021, 68, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jin, X.; Kei Lam, C.W.; Yan, S.-K. Oxidative Stress and Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2011, 49, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzobo, K.E.; Kraaijenhof, J.M.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Nurmohamed, N.S.; Kroon, J. Lipoprotein(a): An Underestimated Inflammatory Mastermind. Atherosclerosis 2022, 349, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rider, D.A.; Eisermann, M.; Löffler, K.; Aleku, M.; Swerdlow, D.I.; Dames, S.; Hauptmann, J.; Morrison, E.; Lindholm, M.W.; Schubert, S.; et al. Pre-Clinical Assessment of SLN360, a Novel siRNA Targeting LPA, Developed to Address Elevated Lipoprotein (a) in Cardiovascular Disease. Atherosclerosis 2022, 349, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catapano, A.L.; Daccord, M.; Damato, E.; Humphries, S.E.; Neely, R.D.G.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Pistollato, M.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E. How Should Public Health Recommendations Address Lp(a) Measurement, a Causative Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)? Atherosclerosis 2022, 349, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampsas, S.; Xenou, M.; Oikonomou, E.; Pantelidis, P.; Lysandrou, A.; Sarantos, S.; Goliopoulou, A.; Kalogeras, K.; Tsigkou, V.; Kalpis, A.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) in Atherosclerotic Diseases: From Pathophysiology to Diagnosis and Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugovšek, S.; Šebeštjen, M. Lipoprotein(a)—The Crossroads of Atherosclerosis, Atherothrombosis and Inflammation. Biomolecules 2021, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hoek, Y.Y.; Sangrar, W.; Côté, G.P.; Kastelein, J.J.; Koschinsky, M.L. Binding of Recombinant Apolipoprotein(a) to Extracellular Matrix Proteins. Arterioscler. Thromb. J. Vasc. Biol. 1994, 14, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, L.A.; Fless, G.M.; Scanu, A.M.; Baynham, P.; Sebald, M.T.; Skocir, P.; Curtiss, L.K.; Levin, E.G.; Hoover-Plow, J.L.; Plow, E.F. Interaction of Lp(a) with Plasminogen Binding Sites on Cells. Thromb. Haemost. 1995, 73, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klezovitch, O.; Edelstein, C.; Zhu, L.; Scanu, A.M. Apolipoprotein(a) Binds via Its C-Terminal Domain to the Protein Core of the Proteoglycan Decorin. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 23856–23865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bdeir, K.; Cane, W.; Canziani, G.; Chaiken, I.; Weisel, J.; Koschinsky, M.L.; Lawn, R.M.; Bannerman, P.G.; Sachais, B.S.; Kuo, A.; et al. Defensin Promotes the Binding of Lipoprotein(a) to Vascular Matrix. Blood 1999, 94, 2007–2019. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10477730/ (accessed on 30 October 2025).
- Trpkovic, A.; Resanovic, I.; Stanimirovic, J.; Radak, D.; Mousa, S.A.; Cenic-Milosevic, D.; Jevremovic, D.; Isenovic, E.R. Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein as a Biomarker of Cardiovascular Diseases. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 52, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiechl, S.; Willeit, J. The Mysteries of Lipoprotein(a) and Cardiovascular Disease Revisited**Editorials Published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiologyreflect the Views of the Authors and Do Not Necessarily Represent the Views of JACCor the American College of Ca. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2168–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, E.M.; Jauhiainen, M.; Zardi, L.; Vaheri, A.; Ehnholm, C. Lipoprotein(a) Binds to Fibronectin and Has Serine Proteinase Activity Capable of Cleaving It. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 4035–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, S.; Khan, S.; Tam, S.-P.; Koschinsky, M.; Taylor, P.; Yacoub, M. Expression of Adhesion Molecules by Lp(a): A Potential Novel Mechanism for Its Atherogenicity. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, S.N.; Orlova, V.V.; Al-Fakhri, N.; Ihanus, E.; Economopoulou, M.; Isermann, B.; Bdeir, K.; Nawroth, P.P.; Preissner, K.T.; Gahmberg, C.G.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) in Atherosclerotic Plaques Recruits Inflammatory Cells through Interaction with Mac-1 Integrin. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrovets, T.; Thillet, J.; Chapman, M.J.; Simmet, T. Lipoprotein(a) Is a Potent Chemoattractant for Human Peripheral Monocytes. Blood 1997, 90, 2027–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Størling, J.; Juntti-Berggren, L.; Olivecrona, G.; Prause, M.C.; Berggren, P.-O.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Apolipoprotein CIII Reduces Proinflammatory Cytokine-Induced Apoptosis in Rat Pancreatic Islets via the Akt Prosurvival Pathway. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3040–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, N.A.; East, C.; Zhang, J.; McCullough, P.A. ApoCIII as a Cardiovascular Risk Factor and Modulation by the Novel Lipid-Lowering Agent Volanesorsen. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, N.; Jaisson, S.; Garnotel, R.; Anglés-Cano, E.; Gillery, P. Small Size Apolipoprotein(a) Isoforms Enhance Inflammatory and Proteolytic Potential of Collagen-Primed Monocytes. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, J.A.; Orbe, J.; Páramo, J.A. Metaloproteasas, Remodelado Vascular Y Syndromes Aterotrombóticos. Rev. Española Cardiol. 2007, 60, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, M.; Niendorf, A.; Reblin, T.; Dietel, M.; Krebber, H.J.; Beisiegel, U. Detection and Quantification of Lipoprotein(a) in the Arterial Wall of 107 Coronary Bypass Patients. Arterioscler. Off. J. Am. Heart Assoc. Inc. 1989, 9, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhwirth, G.O.; Loidl, A.; Hermetter, A. Oxidized Phospholipids: From Molecular Properties to Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2007, 1772, 718–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Palinski, W.; Rosenfeld, M.E.; Parthasarathy, S.; Carew, T.E.; Butler, S.; Witztum, J.L.; Steinberg, D. Evidence for the Presence of Oxidatively Modified Low Density Lipoprotein in Atherosclerotic Lesions of Rabbit and Man. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wang, Z.; Dong, J.; Yu, M.; Zhou, Y. Lipoprotein(a) and Panvascular Disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2025, 24, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketelhuth, D.F.J.; Hansson, G.K. Adaptive Response of T and B Cells in Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Jin, K.; Pang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Luo, J.; Xu, R.; Jiao, L.; et al. Mechanism of Oxidized Phospholipid-Related Inflammatory Response in Vascular Ageing. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 86, 101888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsironis, L.D.; Katsouras, C.S.; Lourida, E.S.; Mitsios, J.V.; Goudevenos, J.; Elisaf, M.; Tselepis, A.D. Reduced PAF-Acetylhydrolase Activity Associated with Lp(a) in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Atherosclerosis 2004, 177, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSIRONIS, L.; MITSIOS, J.; MILIONIS, H.; ELISAF, M.; TSELEPIS, A. Effect of Lipoprotein (a) on Platelet Activation Induced by Platelet-Activating Factor: Role of Apolipoprotein (a) and Endogenous PAF-Acetylhydrolase. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 63, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, Y.; McConnell, J.P.; Jaffe, A.S.; Weston, S.A.; Killian, J.M.; Roger, V.L. Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A 2 and Prognosis After Myocardial Infarction in the Community. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2517–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, W.; Twardella, D.; Brenner, H.; Rothenbacher, D. Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A 2 Predicts Future Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Coronary Heart Disease Independently of Traditional Risk Factors, Markers of Inflammation, Renal Function, and Hemodynamic Stress. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassara, H. The AGE-receptor in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Complications. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2001, 17, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, T.; Edelstein, D.; Du, X.L.; Yamagishi, S.; Matsumura, T.; Kaneda, Y.; Yorek, M.A.; Beebe, D.; Oates, P.J.; Hammes, H.-P.; et al. Normalizing Mitochondrial Superoxide Production Blocks Three Pathways of Hyperglycaemic Damage. Nature 2000, 404, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadai, G.R.Z.; Nahomy, G.G.; Andree, O.A.; Leonor, S.B.N.; Llelena, S.L.V.; Eduardo, A.M.M. Prevalencia de Complicaciones Micro Y Macrovasculares En Derechohabientes Con Diabetes Mellitus, Salina Cruz, Oaxaca 2022–2024. South Fla. J. Dev. 2024, 5, e4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, D.J.; Bajaj, A. Lipoprotein(a) and Oxidized Phospholipids. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 1793–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskolkova, O.V.; Birukova, A.A.; Birukov, K.G.; Bochkov, V.N. Oxidized Phospholipids Are Biomarkers, Drug Targets, and Drug Leads. Front. Drug Discov. 2022, 2, 1043708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimikas, S.; Brilakis, E.S.; Miller, E.R.; McConnell, J.P.; Lennon, R.J.; Kornman, K.S.; Witztum, J.L.; Berger, P.B. Oxidized Phospholipids, Lp(a) Lipoprotein, and Coronary Artery Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.R.; Hill, E.G. Inactivation of Nutrients by Heating With Glucose. Science 1948, 107, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.S.; Minanni, C.A.; de Araújo Lira, A.L.; Passarelli, M. Advanced Glycation End Products: A Sweet Flavor That Embitters Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, L.; Stancu, C.S.; Sima, A.V. Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes Is Aggravated by Glycated Lipoproteins; Novel Molecular Therapies. Biomedicines 2020, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, K.; Furbee, J.W.; Scanu, A.M.; Fless, G.M. Effect of Glycation on the Properties of Lipoprotein(a). Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbrecher, U.P.; Witztum, J.L. Glucosylation of Low-Density Lipoproteins to an Extent Comparable to That Seen in Diabetes Slows Their Catabolism. Diabetes 1984, 33, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, C.; Jacobs, K.; Haucke, E.; Navarrete Santos, A.; Grune, T.; Simm, A. Role of Advanced Glycation End Products in Cellular Signaling. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senatus, L.M.; Schmidt, A.M. The AGE-RAGE Axis: Implications for Age-Associated Arterial Diseases. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.K.; Bierhaus, A.; Schiekofer, S.; Tritschler, H.; Ziegler, R.; Nawroth, P.P. The Role of Oxidative Stress and NF-κB Activation in Late Diabetic Complications. BioFactors 1999, 10, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, H.M.; Tauras, J.M.; Ogiste, J.S.; Hori, O.; Moss, R.A.; Schmidt, A.M. Activation of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products Triggers a p21 -Dependent Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway Regulated by Oxidant Stress. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 17810–17814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Ren, S.; Moghadasain, M.H.; Rempel, J.D.; Shen, G.X. Involvement of Fibrinolytic Regulators in Adhesion of Monocytes to Vascular Endothelial Cells Induced by Glycated LDL and to Aorta from Diabetic Mice. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2014, 95, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toma, L.; Sanda, G.M.; Deleanu, M.; Stancu, C.S.; Sima, A.V. Glycated LDL Increase VCAM-1 Expression and Secretion in Endothelial Cells and Promote Monocyte Adhesion through Mechanisms Involving Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 417, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanajou, D.; Ghorbani Haghjo, A.; Argani, H.; Aslani, S. AGE-RAGE Axis Blockade in Diabetic Nephropathy: Current Status and Future Directions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 833, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patthy, L. Evolution of the Proteases of Blood Coagulation and Fibrinolysis by Assembly from Modules. Cell 1985, 41, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.W.; Tomlinson, J.E.; Kuang, W.-J.; Eaton, D.L.; Chen, E.Y.; Fless, G.M.; Scanu, A.M.; Lawn, R.M. cDNA Sequence of Human Apolipoprotein(a) Is Homologous to Plasminogen. Nature 1987, 330, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utermann, G. The Mysteries Of Lipoprotein(a). Science 1989, 246, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patthy, L.; Trexler, M.; Váli, Z.; Bányai, L.; Váradi, A. Kringles: Modules Specialized for Protein Binding. FEBS Lett. 1984, 171, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulinsky, A.; Park, C.H.; Mao, B.; Llináas, M. Lysine/fibrin Binding Sites of Kringles Modeled after the Structure of Kringle 1 of Prothrombin. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 1988, 3, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangrar, W.; Marcovina, S.M.; Koschinsky, M.L. Expression and Characterization of Apolipoprotein(a) Kringle IV Types 1, 2 and 10 in Mammalian Cells. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1994, 7, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoylaerts, M.; Rijken, D.C.; Lijnen, H.R.; Collen, D. Kinetics of Plasminogen Activation by Tissue Plasminogen Activator. Role of Fibrin. Thromb. Haemost. 1981, 46, 0494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredenburgh, J.C.; Nesheim, M.E. Lys-Plasminogen Is a Significant Intermediate in the Activation of Glu-Plasminogen during Fibrinolysis in Vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 26150–26156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feric, N.T.; Boffa, M.B.; Johnston, S.M.; Koschinsky, M.L. Apolipoprotein(a) Inhibits the Conversion of Glu-plasminogen to Lys-plasminogen: A Novel Mechanism for Lipoprotein(a)-mediated Inhibition of Plasminogen Activation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoylaerts, M.; Rijken, D.C.; Lijnen, H.R.; Collen, D. Kinetics of the Activation of Plasminogen by Human Tissue Plasminogen Activator. Role of Fibrin. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 2912–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenson, E.; Petersen, L.C. Fibrin and Plasminogen Structures Essential to Stimulation of Plasmin Formation by Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1986, 870, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnuolo, R.; Marcovina, S.M.; Boffa, M.B.; Koschinsky, M.L. Inhibition of Plasminogen Activation by Apo(a): Role of Carboxyl-Terminal Lysines and Identification of Inhibitory Domains in Apo(a). J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, L.A.; Fless, G.M.; Levin, E.G.; Scanu, A.M.; Plow, E.F. A Potential Basis for the Thrombotic Risks Associated with Lipoprotein(a). Nature 1989, 339, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjar, K.A.; Gavishi, D.; Breslow, J.L.; Nachman, R.L. Lipoprotein(a) Modulation of Endothelial Cell Surface Fibrinolysis and Its Potential Role in Atherosclerosis. Nature 1989, 339, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahoz, C.; Mostaza, J.M. La Aterosclerosis Como Enfermedad Sistémica. Rev. Española Cardiol. 2007, 60, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajoolabady, A.; Pratico, D.; Lin, L.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Bahijri, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Ren, J. Inflammation in Atherosclerosis: Pathophysiology and Mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurdasani, D.; Sjouke, B.; Tsimikas, S.; Hovingh, G.K.; Luben, R.N.; Wainwright, N.W.J.; Pomilla, C.; Wareham, N.J.; Khaw, K.-T.; Boekholdt, S.M.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) and Risk of Coronary, Cerebrovascular, and Peripheral Artery Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 3058–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littmann, K.; Wodaje, T.; Alvarsson, M.; Bottai, M.; Eriksson, M.; Parini, P.; Brinck, J. The Association of Lipoprotein(a) Plasma Levels With Prevalence of Cardiovascular Disease and Metabolic Control Status in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.; Peden, J.F.; Hopewell, J.C.; Kyriakou, T.; Goel, A.; Heath, S.C.; Parish, S.; Barlera, S.; Franzosi, M.G.; Rust, S.; et al. Genetic Variants Associated with Lp(a) Lipoprotein Level and Coronary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, J.; Collins, R.; Peto, R. Lipoprotein(a) and Coronary Heart Disease. Circulation 2000, 102, 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holanda, M.M.d.A.; Filizola, R.G.; Costa, M.J.d.C.; de Andrade, R.V.C.L.; da Silva, J.A.G. Plasma Lipoprotein(a) Levels: A Comparison between Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2004, 62, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyden, P.D. Thrombolytic Therapy for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 2597–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisler, K.; Nelson, A.R.; Montagne, A.; Zlokovic, B.V. Cerebral Blood Flow Regulation and Neurovascular Dysfunction in Alzheimer Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenillas, J.F.; Molina, C.A.; Chacón, P.; Rovira, A.; Montaner, J.; Coscojuela, P.; Sánchez, E.; Quintana, M.; Álvarez-Sabín, J. High Lipoprotein (A), Diabetes, and the Extent of Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerosis. Neurology 2004, 63, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nave, A.H.; Lange, K.S.; Leonards, C.O.; Siegerink, B.; Doehner, W.; Landmesser, U.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Endres, M.; Ebinger, M. Lipoprotein (a) as a Risk Factor for Ischemic Stroke: A Meta-Analysis. Atherosclerosis 2015, 242, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Romero, J.A.; Castro Gomez, K.G.; Morales Ortigoza, M.P.; Saavedra López, H.F. Lipoproteína (a) Y Oligonucleótidos Antisentido. Rev. Colomb. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2023, 10, 218–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, M.Y.; Toh, K.Z.; Loh, E.D.; Teo, Y.N.; Joon, K.C.; Tan, Q.X.; Sharma, V.K.; Yeo, L.L.; Sia, C.-H.; Loh, W.J.; et al. Association of Elevated Lipoprotein(a) Levels with Ischemic Stroke in Young Patients—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2024, 33, 107960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaiodimou, L.; Melanis, K.; Stefanou, M.-I.; Theodorou, A.; Giannopoulos, S.; Lambadiari, V.; de Sousa, D.A.; Sacco, S.; Katan, M.; Siasos, G.; et al. The Association of Lipoprotein(a) and Stroke Recurrence: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Stroke 2025, 27, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization Blindness and Vision Impairment. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/blindness-and-visual-impairment (accessed on 30 October 2025).
- Kropp, M.; Golubnitschaja, O.; Mazurakova, A.; Koklesova, L.; Sargheini, N.; Vo, T.-T.K.S.; de Clerck, E.; Polivka, J.; Potuznik, P.; Polivka, J.; et al. Diabetic Retinopathy as the Leading Cause of Blindness and Early Predictor of Cascading Complications—Risks and Mitigation. EPMA J. 2023, 14, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami Chahkand, M.S.; Esmaeilpour Moallem, F.; Qezelgachi, A.; Seifouri, K.; Pesaran Afsharian, A.; Sheikhzadeh, F.; Poursalehi, A.; Fani Sadrabadi, F.S.; Saghab Torbati, M.; Ramezanzade, M.; et al. Lipoprotein (a) as a Predictor of Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2023, 20, 14791641231197114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaruso, C.; Garzaniti, A.; Buscaglia, P.; D’Annunzio, G.; Porta, A.; Vandelli, G.; Lorini, R.; Finardi, G.; Fratino, P.; Geroldi, D. Lipoprotein(a) Levels and Apolipoprotein(a) Polymorphism in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Relationships to Microvascular and Neurological Complications. Acta Diabetol. 1998, 35, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhou, K.K.; Lee, K.; Gao, G.; Lyons, T.J.; Kowluru, R.; Ma, J. The Role of Lipid Peroxidation Products and Oxidative Stress in Activation of the Canonical Wingless-Type MMTV Integration Site (WNT) Pathway in a Rat Model of Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Y.; Du, M.; Elliott, M.H.; Wu, M.; Fu, D.; Yang, S.; Basu, A.; Gu, X.; Ma, J.-X.; Aston, C.E.; et al. Extravascular Modified Lipoproteins: A Role in the Propagation of Diabetic Retinopathy in a Mouse Model of Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2026–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogan, D.G.; Toussaint, D.; Kuwabara, T. Retinal Vascular Patterns. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1961, 66, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scipione, C.A.; Sayegh, S.E.; Romagnuolo, R.; Tsimikas, S.; Marcovina, S.M.; Boffa, M.B.; Koschinsky, M.L. Mechanistic Insights into Lp(a)-Induced IL-8 Expression: A Role for Oxidized Phospholipid Modification of Apo(a). J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 2273–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, I.H.; Khunti, K.; Sadusky, T.; Tuttle, K.R.; Neumiller, J.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G. Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 3075–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Piscitelli, P.; Giandalia, A.; Viazzi, F.; Pontremoli, R.; Fioretto, P.; De Cosmo, S. Atherogenic Dyslipidemia and Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor Valero, J. Características de La Enfermedad Renal Diabética. Diabetes Práctica 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondorf, U.F.; Piiper, A.; Herrero, M.; Olbrich, H.-G.; Bender, M.; Gross, W.; Scheuermann, E.; Geiger, H. Lipoprotein(a) Stimulates Growth of Human Mesangial Cells and Induces Activation of Phospholipase C via Pertussis Toxin-Sensitive G Proteins. Kidney Int. 1999, 55, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Cui, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Can Lipoprotein(a) Predict the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus?: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2025, 57, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobini, C.; Menini, S.; Ricci, C.; Scipioni, A.; Sansoni, V.; Mazzitelli, G.; Cordone, S.; Pesce, C.; Pugliese, F.; Pricci, F.; et al. Advanced Lipoxidation End-products Mediate Lipid-induced Glomerular Injury: Role of Receptor-mediated Mechanisms. J. Pathol. 2009, 218, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucher, C.; Doucet, C.; Baumelou, A.; Chapman, J.; Jacobs, C.; Thillet, J. Elevated Lipoprotein (a) Levels in Primary Nephrotic Syndrome. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1993, 22, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.E.; Freestone, A.; Varghese, Z.; Persaud, J.W.; Moorhead, J.F. Lipoprotein (a) in Patients with Proteinuria. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1992, 7, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimbürger, O.; Stenvinkel, P.; Berglund, L.; Tranæus, A.; Lindholm, B. Increased Plasma Lipoprotein(a) in Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Is Related to Peritoneal Transport of Proteins and Glucose. Nephron 1996, 72, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P.; Heimbürger, O.; Tuck, C.H.; Berglund, L. Apo(a)-Isoform Size, Nutritional Status and Inflammatory Markers in Chronic Renal Failure. Kidney Int. 1998, 53, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Z. Association Between Lipoprotein (A) and Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 633529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Khetarpal, S.A.; Terembula, K.; Reilly, M.P.; Wilson, F.P. Relation of Atherogenic Lipoproteins with Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Decline: A Longitudinal Study. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, W.; Du, X.; Luo, Z.; Hu, J.; Peng, S. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1265372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Association between Lipoprotein(a) and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2025, 17, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.C.; Yang, S. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Essentials: A Narrative Review. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2023, 12, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlassara, H.; Uribarri, J. Advanced Glycation End Products (AGE) and Diabetes: Cause, Effect, or Both? Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fusco, S.A.; Maggioni, A.P.; Scicchitano, P.; Zuin, M.; D’Elia, E.; Colivicchi, F. Lipoprotein (A), Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca, A.; Ketenci, A.; Sahin, I.; Sengun, I.S.; Oner, R.I.; Erdem Tilki, H.; Adas, M.; Soyleli, H.; Demir, T. Expert Opinion on Screening, Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Multidisciplinary Approach. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1380929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.P.; Mulder, H.; Lydon, E.; Chiswell, K.; Hu, X.; Lampron, Z.; Cohen, L.; Patel, M.R.; Taubes, S.; Song, W.; et al. Lipoprotein (a) Testing in Patients With Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in 5 Large US Health Systems. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e035610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, J.-L.; Cao, Y.-X.; Zhang, H.-W.; Guo, Y.-L.; Wu, N.-Q.; Zhu, C.-G.; Gao, Y.; Hua, Q.; Li, Y.-F.; et al. Lipoprotein (a) Predicts Recurrent Worse Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Prior Cardiovascular Events: A Prospective, Observational Cohort Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Soffer, G.; Yeang, C.; Michos, E.D.; Boatwright, W.; Ballantyne, C.M. High Lipoprotein(a): Actionable Strategies for Risk Assessment and Mitigation. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2024, 18, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Qiu, H.; Zhao, K.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Elevated Plasma Concentrations of Lipoprotein (a) Are Associated with Cardiovascular Diseases in Patients with Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1434745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, J.J.; Slee, A.; O’Brien, K.D.; Robinson, J.G.; Kashyap, M.L.; Kwiterovich, P.O.; Xu, P.; Marcovina, S.M. Relationship of Apolipoproteins A-1 and B, and Lipoprotein(a) to Cardiovascular Outcomes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Steg, P.G.; Szarek, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.A.; Diaz, R.; Edelberg, J.M.; Goodman, S.G.; Hanotin, C.; Harrington, R.A.; et al. Alirocumab and Cardiovascular Outcomes after Acute Coronary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Keech, A.C.; Honarpour, N.; Wiviott, S.D.; Murphy, S.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Evolocumab and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.K.; Wright, R.S.; Kallend, D.; Koenig, W.; Leiter, L.A.; Raal, F.J.; Bisch, J.A.; Richardson, T.; Jaros, M.; Wijngaard, P.L.J.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Inclisiran in Patients with Elevated LDL Cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Rosenson, R.S.; Gencer, B.; López, J.A.G.; Lepor, N.E.; Baum, S.J.; Stout, E.; Gaudet, D.; Knusel, B.; Kuder, J.F.; et al. Small Interfering RNA to Reduce Lipoprotein(a) in Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidaemias: Lipid Modification to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, L.M.; Oorthuys, A.O.J.; Wiegman, A.; Langendam, M.W.; Kroon, J.; Spijker, R.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Hutten, B.A. Statin Therapy and Lipoprotein(a) Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, C.P.; Blazing, M.A.; Giugliano, R.P.; McCagg, A.; White, J.A.; Theroux, P.; Darius, H.; Lewis, B.S.; Ophuis, T.O.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Ezetimibe Added to Statin Therapy after Acute Coronary Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2387–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschinsky, M.L.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Kronenberg, F. Daring to Dream: Targeting Lipoprotein(a) as a Causal and Risk-Enhancing Factor. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 194, 106843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Li, Y.; Xue, X.; Yang, W.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; et al. Association of Statin Use and Increase in Lipoprotein(a): A Real-World Database Research. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeang, C.; Karwatowska-Prokopczuk, E.; Su, F.; Dinh, B.; Xia, S.; Witztum, J.L.; Tsimikas, S. Effect of Pelacarsen on Lipoprotein(a) Cholesterol and Corrected Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, L.; Nicholls, S.J.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Landmesser, U.; Tsimikas, S.; Blaha, M.J.; Leitersdorf, E.; Lincoff, A.M.; Lesogor, A.; Manning, B.; et al. Design and Rationale of Lp(a)HORIZON Trial: Assessing the Effect of Lipoprotein(a) Lowering With Pelacarsen on Major Cardiovascular Events in Patients With CVD and Elevated Lp(a). Am. Heart J. 2025, 287, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Nissen, S.E.; Fleming, C.; Urva, S.; Suico, J.; Berg, P.H.; Linnebjerg, H.; Ruotolo, G.; Turner, P.K.; Michael, L.F. Muvalaplin, an Oral Small Molecule Inhibitor of Lipoprotein(a) Formation. JAMA 2023, 330, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Linnebjerg, H.; Shen, X.; Wolski, K.; Ma, X.; Lim, S.; Michael, L.F.; Ruotolo, G.; Gribble, G.; Navar, A.M.; et al. Lepodisiran, an Extended-Duration Short Interfering RNA Targeting Lipoprotein(a). JAMA 2023, 330, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wolski, K.; Balog, C.; Swerdlow, D.I.; Scrimgeour, A.C.; Rambaran, C.; Wilson, R.J.; Boyce, M.; Ray, K.K.; Cho, L.; et al. Single Ascending Dose Study of a Short Interfering RNA Targeting Lipoprotein(a) Production in Individuals With Elevated Plasma Lipoprotein(a) Levels. JAMA 2022, 327, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulos, E.; Palaiodimou, L.; Theodorou, A.; Papagiannopoulou, G.; Bakola, E.; Chondrogianni, M.; Psychogios, K.; Kargiotis, O.; Safouris, A.; Vlachopoulos, C.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) as a Stroke Biomarker: Pathophysiological Pathways and Therapeutic Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Therapies | Class/Mechanism | Key Trial | Population | LDL-C Reduction % | Representative Reduction % ɟ | Reported Range % ɟ | Timepoint | Key Source (DOI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | ||||||||
| Alirocumab (PCSK9-mAb) | Anti-PCSK9 mAb | ODYSSEY (Ph3) | Hypercholesterolemia ± ASCVD | 46–61 | −25.6 | ~20–30 | 24–104 weeks | [197] |
| Evolocumab (PCSK9-mAb) | Anti-PCSK9 mAb | FOURIER (Ph3) | ASCVD | ~59 | −26.9 | IQR 6.2–46.7 | 48 weeks | [198] |
| Inclisiran (PCSK9-siRNA) | siRNA to PCSK9 (semiannual) | ORION-10/11 (Ph3) | ASCVD or equivalent | ~50–52 | −25.6 | ~18.6–25.6 | Day 510–540 | [199] |
| Statins | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors | Prospective studies and systematic reviews | Dyslipidemia/ASCVD | 20–55 | . | n.s. (slightly ↑) | 6 weeks–6 months | [202,205] |
| Ezetimibe | NPC1L1 inhibitors | IMPROVE-IT | Dyslipidemia/ASCVD | 18–25 (mono); ~24 add-on | n.s. | ~0–7 | Weeks–months | [203] |
| Emerging | ||||||||
| Olpasiran (siRNA-LPA) | siRNA to LPA | OCEAN(a)-DOSE (Ph2) | ASCVD + high Lp(a) | ~0–5 | −97.4 | ~70–100 | Week 36 | [200] |
| Pelacarsen (ASO-LPA) | Antisense oligonucleotide to LPA | NEJM 2020 (Ph2) | ASCVD + high Lp(a) | ~7–26 (2–19 LDL-C-corrected) | −80 | ~35–80 (dose–dependent) | Weeks 24–26 | [206,207] |
| Muvalaplin (LY3819469) | First-in-class oral small-molecule; Lp(a) assembly inhibitor (apo[a]-apoB100 blocker) | JAMA 2023 (Ph2) | ASCVD + high Lp(a) | n.s. | −75 | ~65–85 (dose–dependent) | Weeks 4–12 | [208] |
| Lepodisiran (siRNA-LPA) | Long-acting siRNA | JAMA (Ph1) | High Lp(a) | ≤5 | −94 | ~88–96 | 48–50 weeks (to day 360) | [209] |
| SLN360 (siRNA-LPA) | SiRNA to LPA | APOLLO (Ph1) | High Lp(a) | ~20–25 (higher doses) | −98 | Up to 98 | Day 150–210 | [210] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polo-Barranco, A.; Rebolledo-Maldonado, C.; Esquiaqui-Rangel, V.; Nuñez-Mejia, A.; Rambal-Torres, J.; Barraza-Ahumada, V.; Vargas-Cantillo, S.; Benavides-De la Cruz, W.; Liñán-Martínez, V.; Rada-Obeso, V.; et al. Diabetes Mellitus and Lipoprotein(a): A Determinant Interaction in Micro- and Macrovascular Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311427
Polo-Barranco A, Rebolledo-Maldonado C, Esquiaqui-Rangel V, Nuñez-Mejia A, Rambal-Torres J, Barraza-Ahumada V, Vargas-Cantillo S, Benavides-De la Cruz W, Liñán-Martínez V, Rada-Obeso V, et al. Diabetes Mellitus and Lipoprotein(a): A Determinant Interaction in Micro- and Macrovascular Damage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311427
Chicago/Turabian StylePolo-Barranco, Alberto, Carlos Rebolledo-Maldonado, Valeria Esquiaqui-Rangel, Andrea Nuñez-Mejia, Jeisón Rambal-Torres, Valentina Barraza-Ahumada, Shivleivy Vargas-Cantillo, Wylman Benavides-De la Cruz, Valentina Liñán-Martínez, Valentina Rada-Obeso, and et al. 2025. "Diabetes Mellitus and Lipoprotein(a): A Determinant Interaction in Micro- and Macrovascular Damage" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311427
APA StylePolo-Barranco, A., Rebolledo-Maldonado, C., Esquiaqui-Rangel, V., Nuñez-Mejia, A., Rambal-Torres, J., Barraza-Ahumada, V., Vargas-Cantillo, S., Benavides-De la Cruz, W., Liñán-Martínez, V., Rada-Obeso, V., Isaac-Escorcia, M., Martínez-Fontalvo, N., Correa-Guerrero, J., Rodelo-Barrios, D., & Osorio-Rodríguez, E. (2025). Diabetes Mellitus and Lipoprotein(a): A Determinant Interaction in Micro- and Macrovascular Damage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311427







