Chronic Overexpression of Neuronal NRG1-III in Mice Causes Long-Term Detrimental Changes in Lower Motor Neurons, Neuromuscular Synapses and Motor Behaviour
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
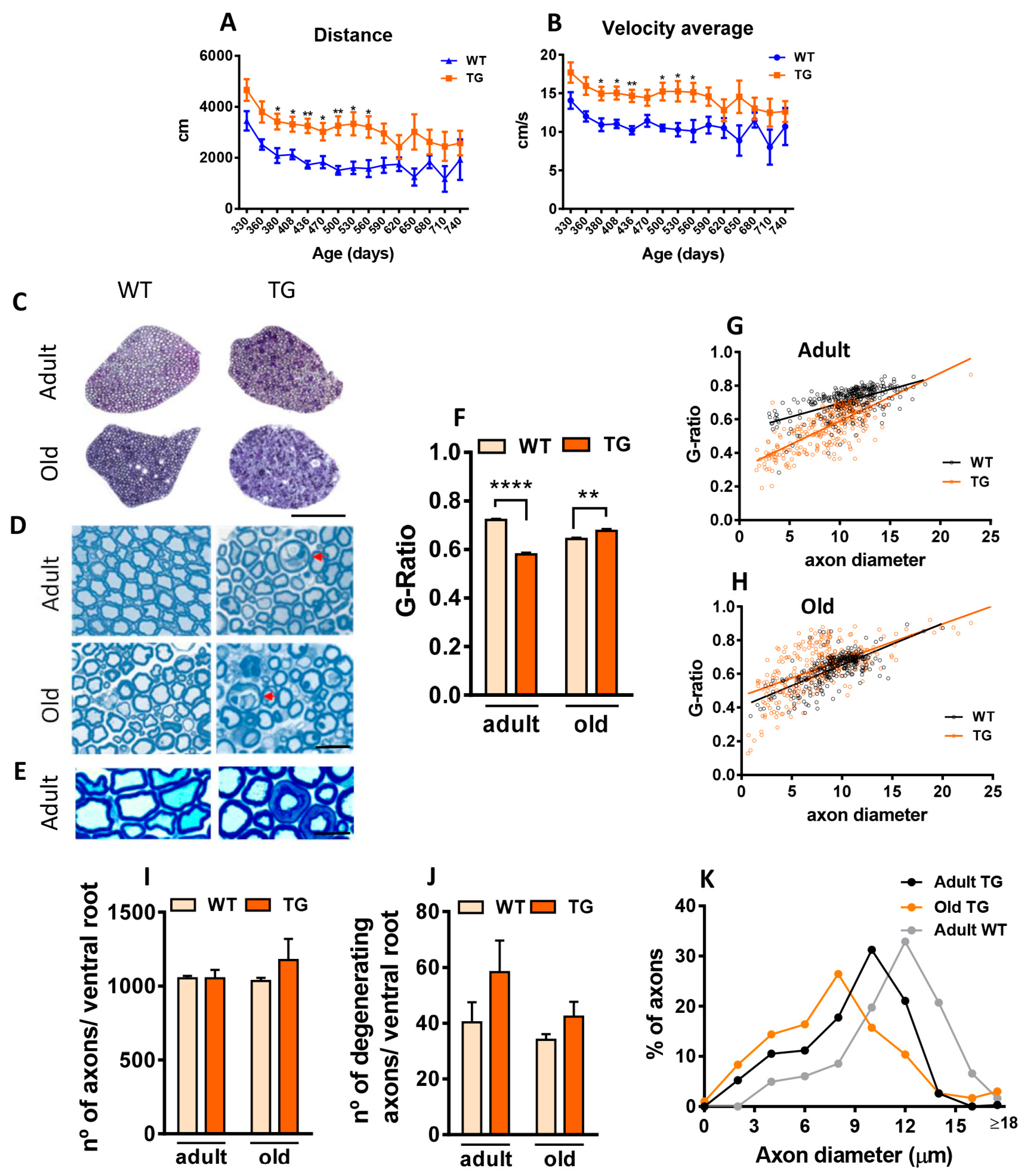
2.1. Neuregulin Type III (NRG1-III) Overexpression in Mice Increases Motor Activity and Alters Ventral Root Axon Myelination
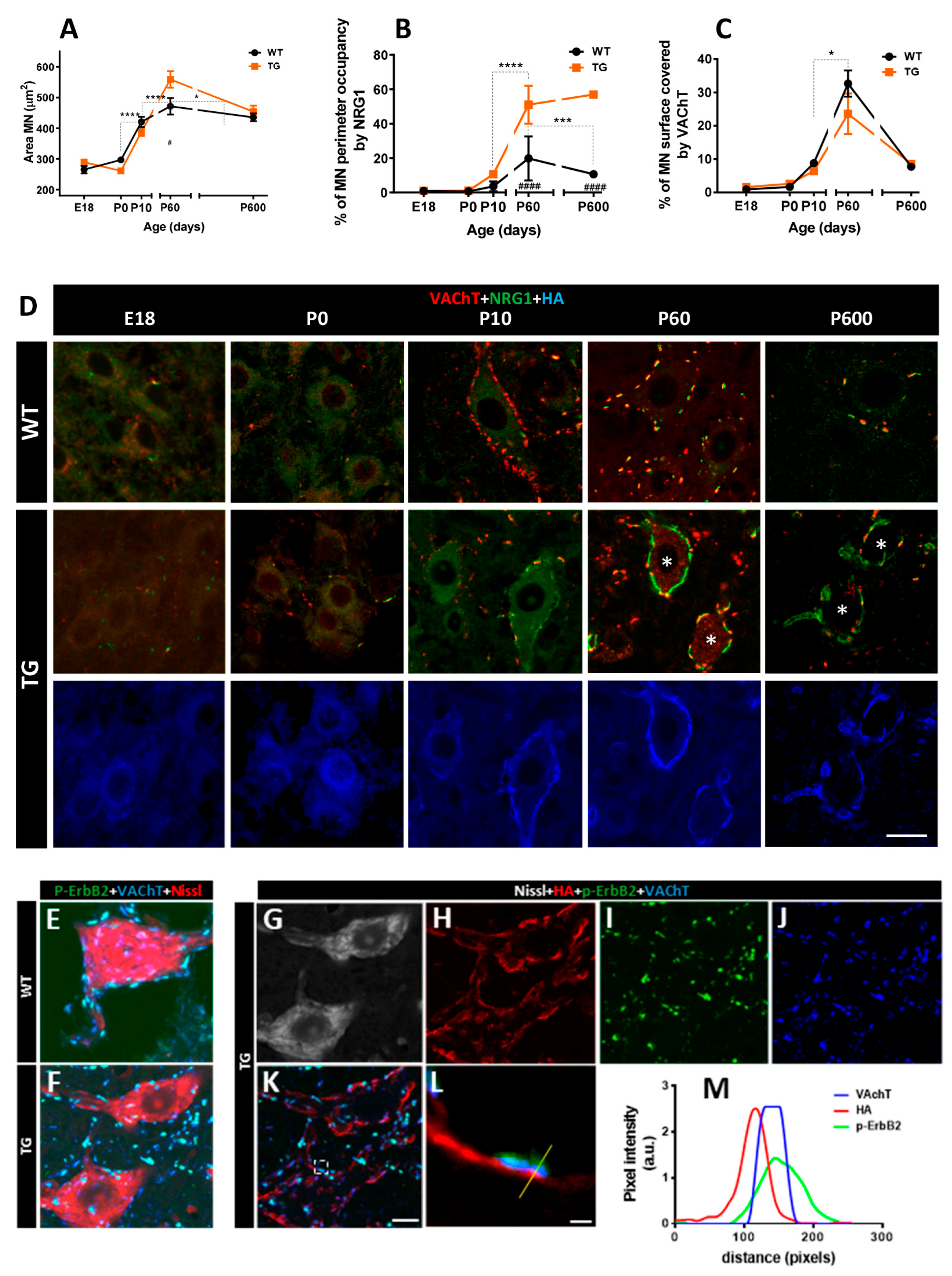
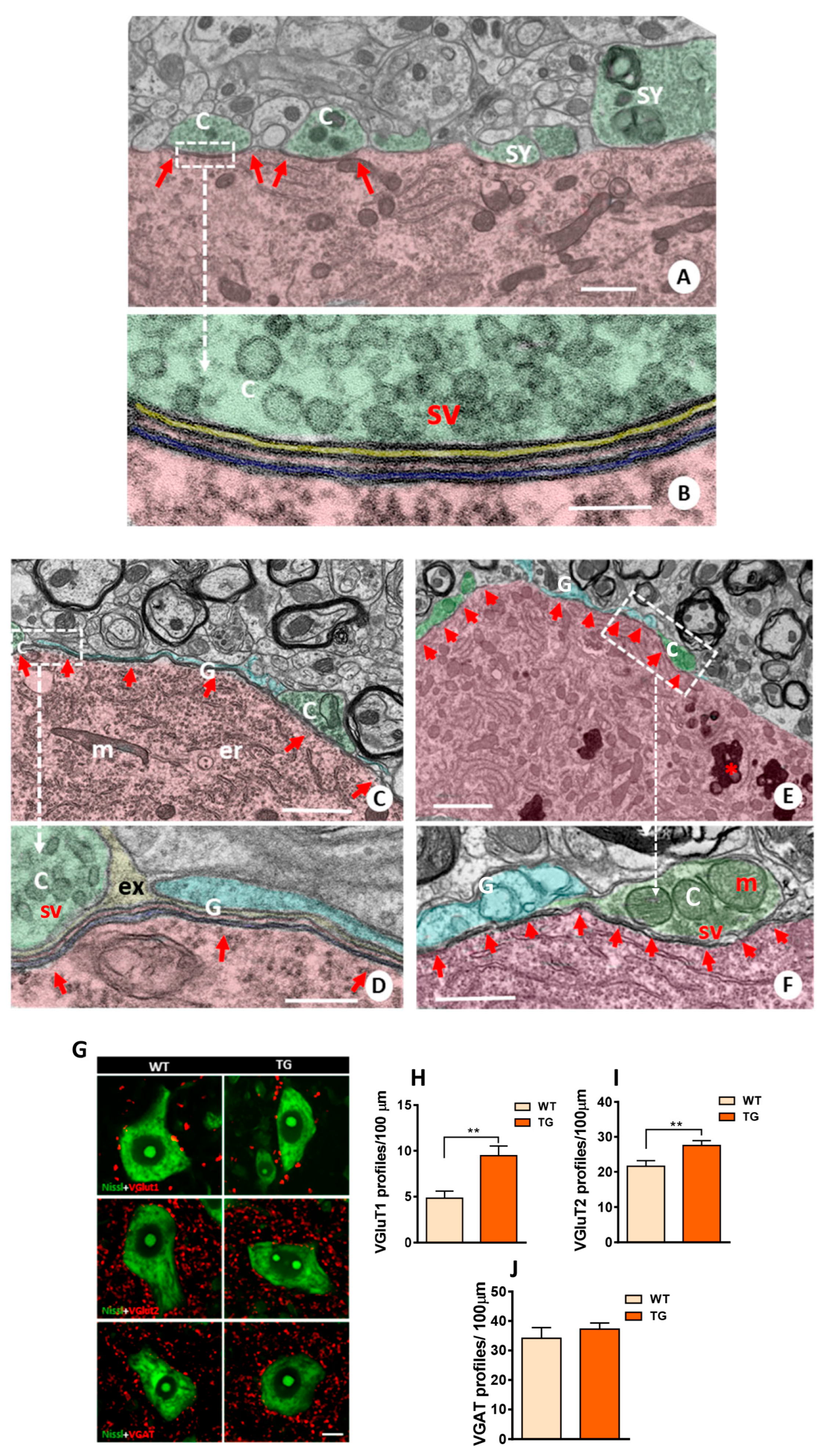
2.2. Impact of Long-Term NRG1-III Overexpression on Motor Neuron (MN) Synaptic Afferents and C-Bouton Organization
2.3. Sustained NRG1-III Overexpression Promotes MN Plasticity and the Development of a Fast-Fatigable MN Phenotype
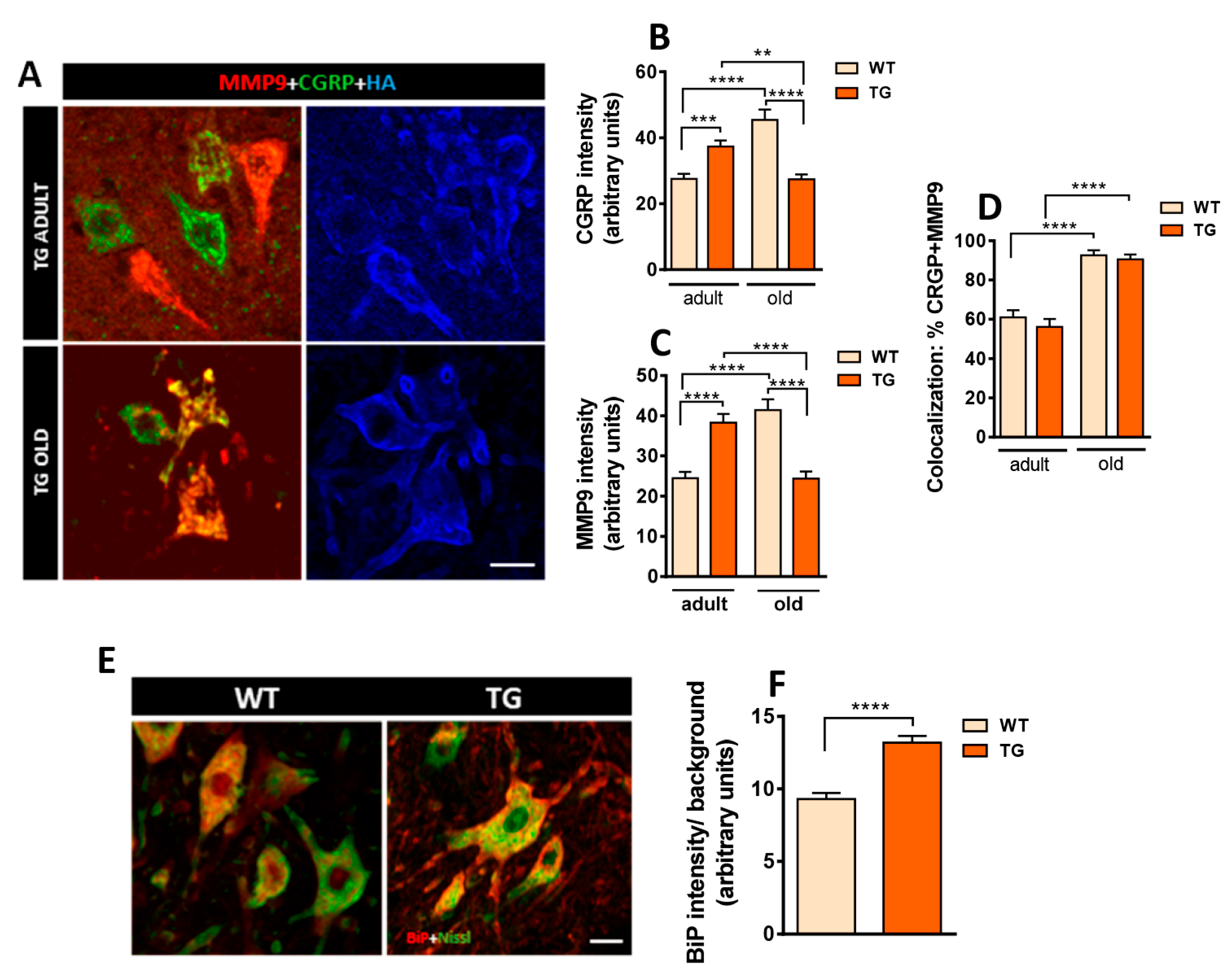
2.4. Axotomized MNs in Transgenic Mice Exhibit Disrupted NRG1 Compartmentalization and Exacerbated Microglial Recruitment
2.5. In Vitro Expression of C-Bouton-Associated Molecules in MNs from NRG1-III Overexpressing Mice
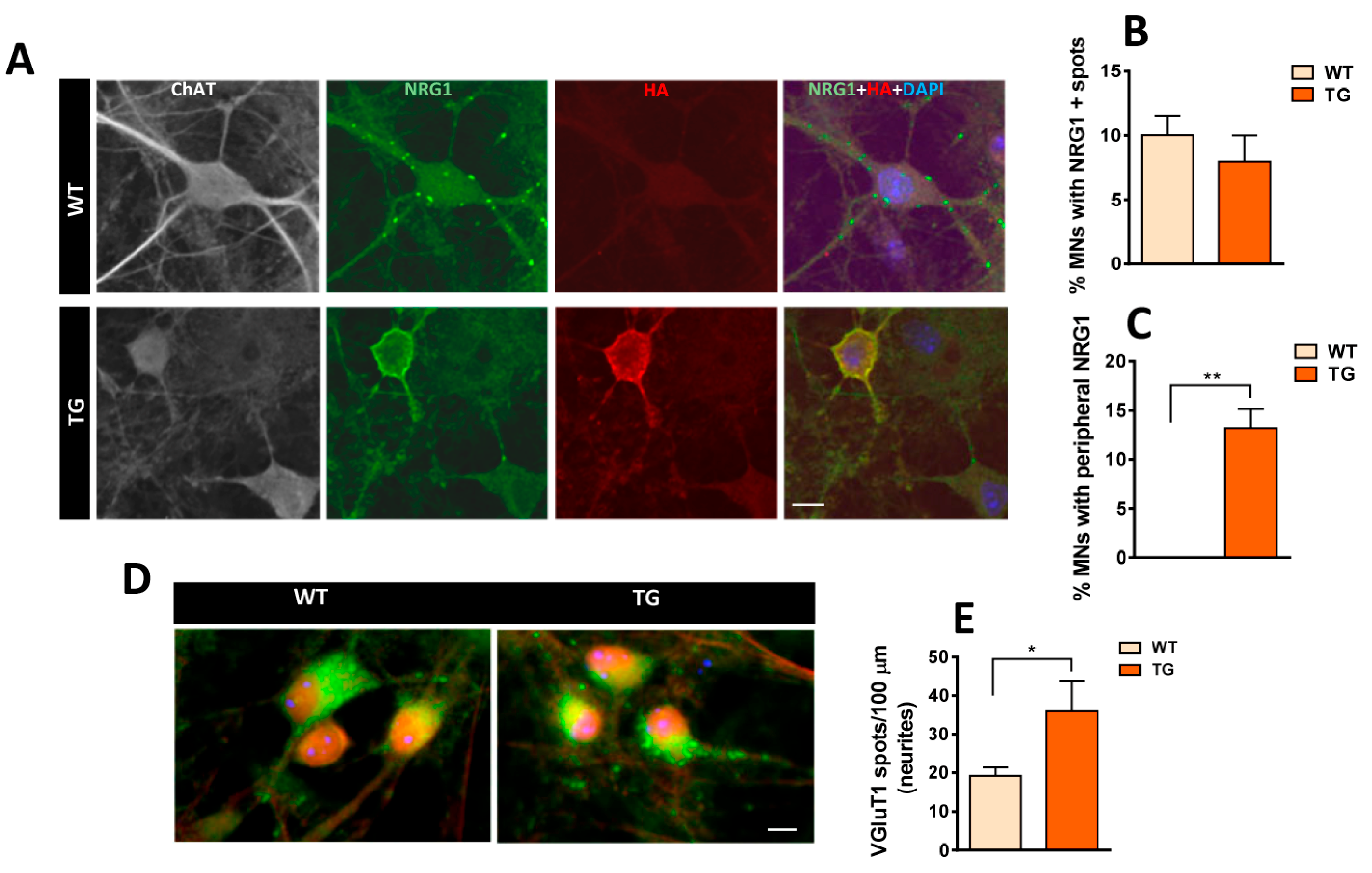
2.6. In Vitro Development of Excitatory Inputs to MNs from NRG1-III-Overexpressing Mice and Changes in Glutamate Receptor-Mediated Vulnerability
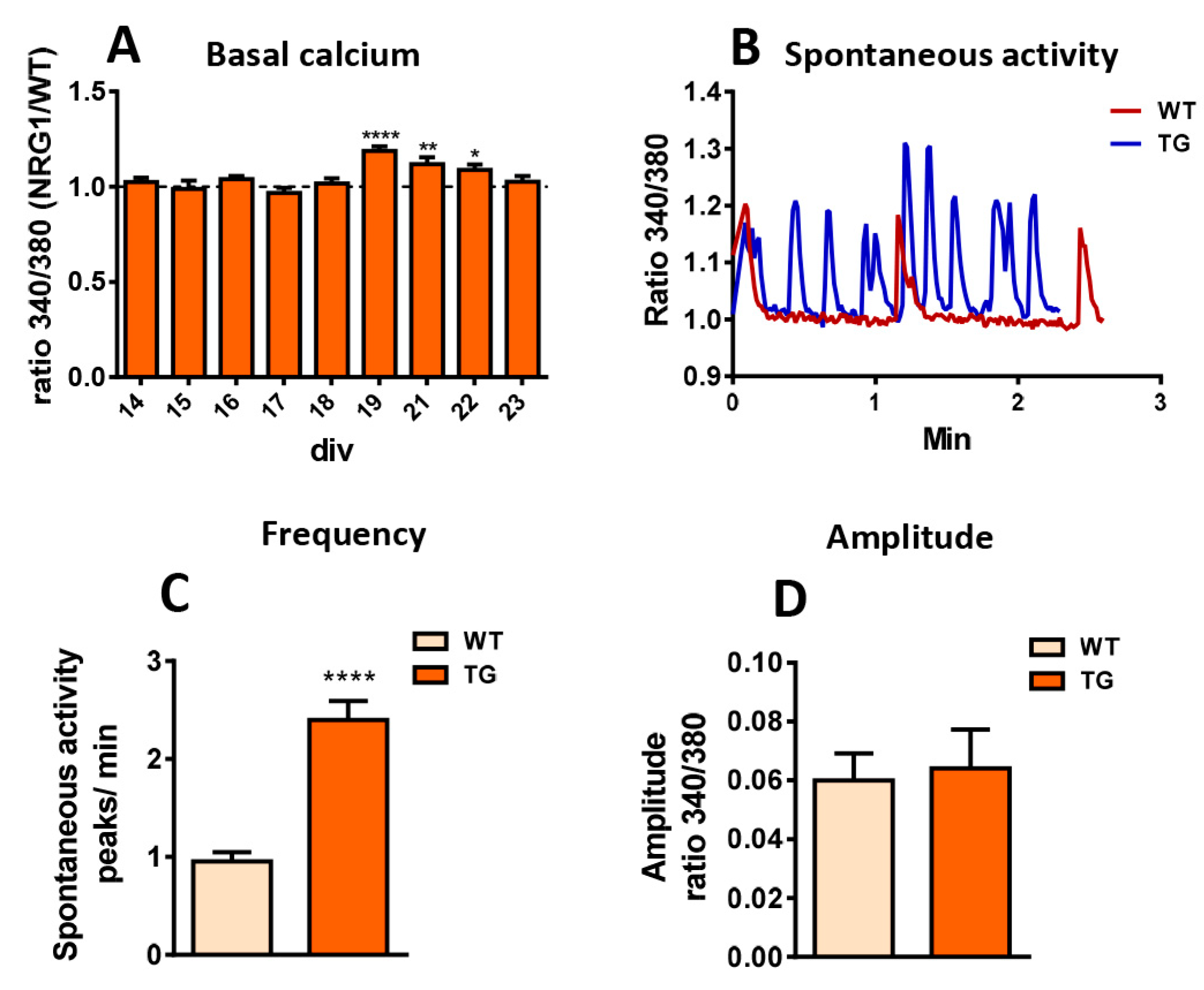
2.7. Dysregulation of Calcium Homeostasis in MNs from NRG1-III Overexpressing Mice
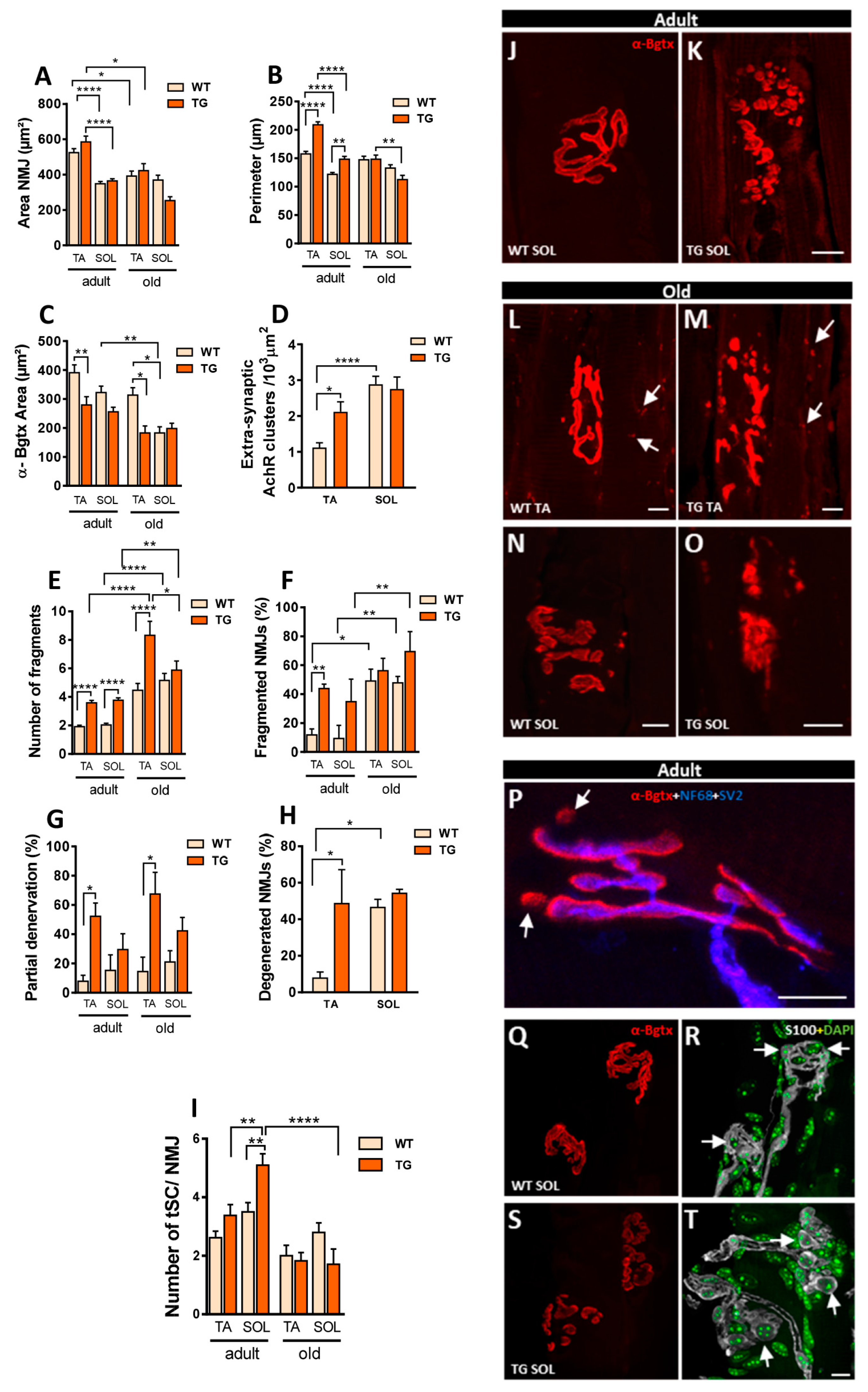
2.8. Overexpression of NRG1 in MNs Leads to Plastic Changes in Neuromuscular Junctions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice Colony and Animal Facilities
4.2. Motor Behavior Analysis
4.3. Nerve Transection Experiments
4.4. Spinal Cord Cultures
4.5. Tissue Preparation, Immunohistochemistry, and Image Analysis for Confocal Microscopy
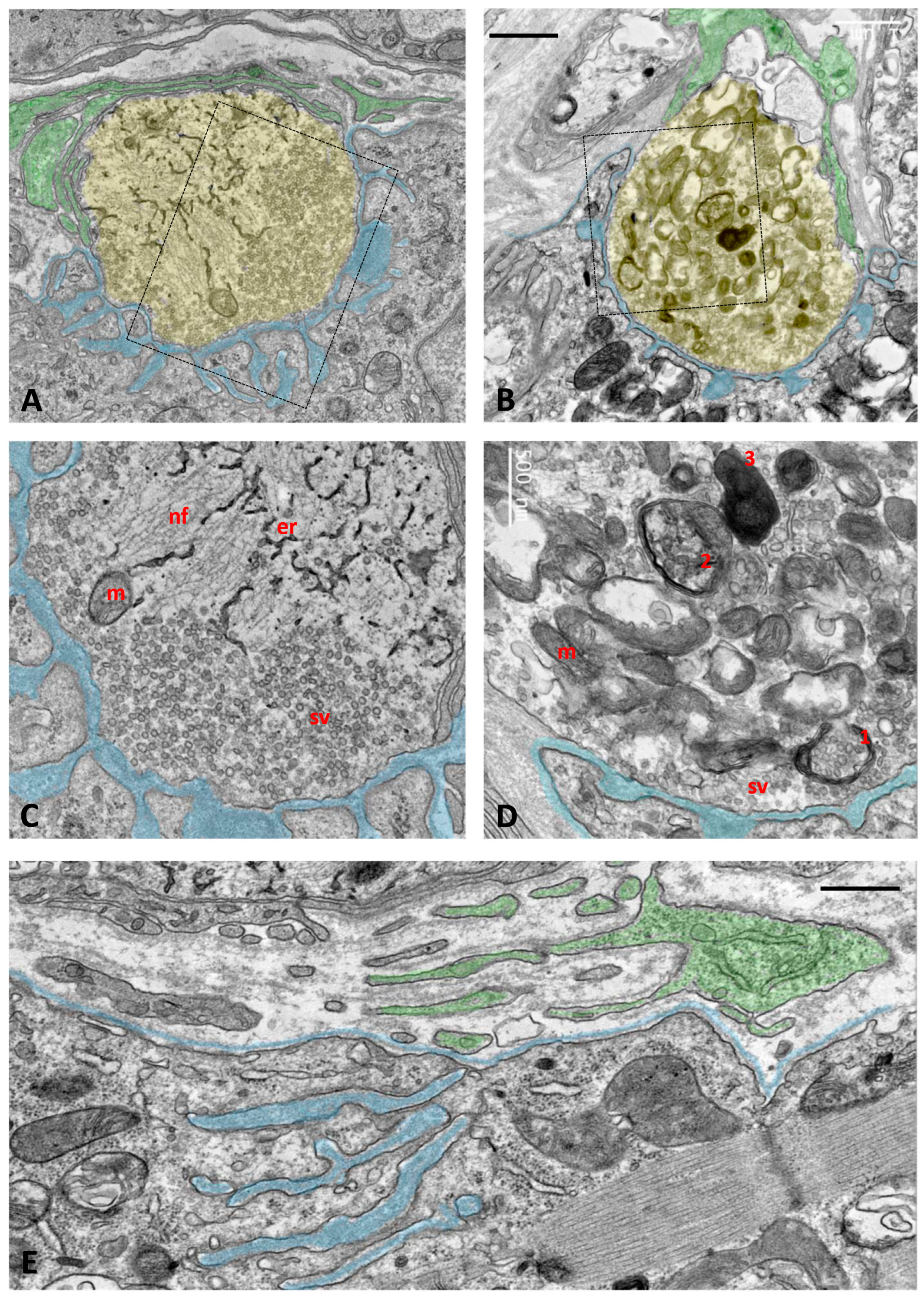
4.6. Electron Microscopy and Ventral Nerve Root (VR) Analysis
4.7. Calcium Imaging
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AChR | Acetylcholine receptor |
| ALS | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| BiP | Immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein |
| DIV | Days in vitro |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| ER-PM | ER-plasma membrane |
| α-Bgtx | α-bungarotoxin |
| CGRP | Calcitonin gene-related peptide |
| ChAT | Choline acetyltransferase |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride |
| DRG | Dorsal root ganglion |
| GAP-43 | Growth-associated protein 43 |
| HA | Hemagglutinin |
| Iba1 | Ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 |
| KA | Kainic acid |
| Kv2.1 | Voltage-gated K+ channel 2.1 |
| M2 | M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor |
| mGluR | Metabotropic glutamate receptor |
| MMP9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| MN | Motor neuron |
| NF68 | 68kDa neurofilament-L |
| NMDA | N-Methyl-D-aspartate acid |
| NMJ | Neuromuscular junction |
| NRGs | Neuregulins |
| NRG type I, II, III | NRG1-I, -II, and -III |
| PB | Phosphate buffer |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| RT | Room temperature |
| SMA | Spinal muscular atrophy |
| SYN | Synaptophysin |
| SOL | Soleus |
| SSC | Subsynaptic cistern |
| SV2 | Synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A |
| TA | Tibialis anterior |
| TBST | Tris-buffered saline |
| TG | Transgenic |
| t-SC | Terminal Schwann cell |
| VAChT | Vesicular acetylcholine transporter |
| VGAT | Vesicular GABA transporter |
| VGluT1 | Vesicular glutamate transporter 1 |
| VGluT2 | Vesicular glutamate transporter 2 |
| VR | Ventral nerve root |
| WT | Wild-type |
References
- Buonanno, A.; Fischbach, G.D. Neuregulin and ErbB Receptor Signaling Pathways in the Nervous System. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001, 11, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledonne, A.; Mercuri, N.B. On the Modulatory Roles of Neuregulins/ErbB Signaling on Synaptic Plasticity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falls, D. Neuregulins: Functions, Forms, and Signaling Strategies. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 284, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, L.; Xiong, W.-C. Neuregulin 1 in Neural Development, Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nave, K.-A.; Salzer, J.L. Axonal Regulation of Myelination by Neuregulin 1. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2006, 16, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallart-Palau, X.; Tarabal, O.; Casanovas, A.; Sábado, J.; Correa, F.J.; Hereu, M.; Piedrafita, L.; Calderó, J.; Esquerda, J.E. Neuregulin-1 Is Concentrated in the Postsynaptic Subsurface Cistern of C-bouton Inputs to A-motoneurons and Altered During Motoneuron Diseases. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 3618–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagoraiou, L.; Akay, T.; Martin, J.F.; Brownstone, R.M.; Jessell, T.M.; Miles, G.B. A Cluster of Cholinergic Premotor Interneurons Modulates Mouse Locomotor Activity. Neuron 2009, 64, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deardorff, A.S.; Romer, S.H.; Deng, Z.; Bullinger, K.L.; Nardelli, P.; Cope, T.C.; Fyffe, R.E.W. Expression of Postsynaptic Ca2+-activated K+ (SK) Channels at C-bouton Synapses in Mammalian Lumbar A-motoneurons. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 875–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, J.; Oliveira, A.L.R.; Meister, B.; Cullheim, S. Large Cholinergic Nerve Terminals on Subsets of Motoneurons and Their Relation to Muscarinic Receptor Type 2. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 460, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavlyutov, T.A.; Epstein, M.L.; Andersen, K.A.; Ziskind-Conhaim, L.; Ruoho, A.E. The Sigma-1 Receptor Is Enriched in Postsynaptic Sites of C-Terminals in Mouse Motoneurons. An Anatomical and Behavioral Study. Neuroscience 2010, 167, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muennich, E.A.L.; Fyffe, R.E.W. Focal Aggregation of Voltage-gated, Kv2.1 Subunit-containing, Potassium Channels at Synaptic Sites in Rat Spinal Motoneurones. J. Physiol. 2004, 554, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatius, A.; Tarabal, O.; Cayuela, P.; Casanovas, A.; Piedrafita, L.; Salvany, S.; Hernández, S.; Soler, R.M.; Esquerda, J.E.; Calderó, J. The Y172 Monoclonal Antibody Against P-c-Jun (Ser63) Is a Marker of the Postsynaptic Compartment of C-Type Cholinergic Afferent Synapses on Motoneurons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanovas, A.; Salvany, S.; Lahoz, V.; Tarabal, O.; Piedrafita, L.; Sabater, R.; Hernández, S.; Calderó, J.; Esquerda, J.E. Neuregulin 1-ErbB Module in C-Bouton Synapses on Somatic Motor Neurons: Molecular Compartmentation and Response to Peripheral Nerve Injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deardorff, A.S.; Romer, S.H.; Fyffe, R.E.W. Location, Location, Location: The Organization and Roles of Potassium Channels in Mammalian Motoneurons. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 1391–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blinzinger, K.; Kreutzberg, G. Displacement of Synaptic Terminals from Regenerating Motoneurons by Microglial Cells. Z. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat. 1968, 85, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvany, S.; Casanovas, A.; Tarabal, O.; Piedrafita, L.; Hernández, S.; Santafé, M.; Soto-Bernardini, M.C.; Calderó, J.; Schwab, M.H.; Esquerda, J.E. Localization and Dynamic Changes of Neuregulin-1 at C-type Synaptic Boutons in Association with Motor Neuron Injury and Repair. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 7833–7851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vullhorst, D.; Ahmad, T.; Karavanova, I.; Keating, C.; Buonanno, A. Structural Similarities between Neuregulin 1–3 Isoforms Determine Their Subcellular Distribution and Signaling Mode in Central Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 5232–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willem, M. Proteolytic Processing of Neuregulin-1. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 126, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassart, R.M.; Fledrich, R.; Velanac, V.; Brinkmann, B.G.; Schwab, M.H.; Meijer, D.; Sereda, M.W.; Nave, K.-A. A Role for Schwann Cell–Derived Neuregulin-1 in Remyelination. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailov, G.V.; Sereda, M.W.; Brinkmann, B.G.; Fischer, T.M.; Haug, B.; Birchmeier, C.; Role, L.; Lai, C.; Schwab, M.H.; Nave, K.-A. Axonal Neuregulin-1 Regulates Myelin Sheath Thickness. Science 2004, 304, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velanac, V.; Unterbarnscheidt, T.; Hinrichs, W.; Gummert, M.N.; Fischer, T.M.; Rossner, M.J.; Trimarco, A.; Brivio, V.; Taveggia, C.; Willem, M.; et al. Bace1 Processing of NRG1 Type III Produces a Myelin-Inducing Signal but Is Not Essential for the Stimulation of Myelination. Glia 2012, 60, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.I.; Li, Y.; Mikesh, M.; Smith, I.; Nave, K.-A.; Schwab, M.H.; Thompson, W.J. Neuregulin1 Displayed on Motor Axons Regulates Terminal Schwann Cell-Mediated Synapse Elimination at Developing Neuromuscular Junctions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E479–E487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Zhang, M.; Trembak-Duff, I.; Unterbarnscheidt, T.; Radyushkin, K.; Dibaj, P.; de Souza, D.M.; Boretius, S.; Brzózka, M.M.; Steffens, H.; et al. Dysregulated Expression of Neuregulin-1 by Cortical Pyramidal Neurons Disrupts Synaptic Plasticity. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1130–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Fukuda, Y.; Yoshimura, J.; Toyoda, A.; Kurppa, K.; Moritoyo, H.; Belzil, V.V.; Dion, P.A.; Higasa, K.; Doi, K.; et al. ERBB4 Mutations That Disrupt the Neuregulin-ErbB4 Pathway Cause Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Type 19. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, S.; Roselli, F.; Singh, K.; Leptien, K.; Julien, J.-P.; Gros-Louis, F.; Caroni, P. Neuroprotection Through Excitability and mTOR Required in ALS Motoneurons to Delay Disease and Extend Survival. Neuron 2013, 80, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, M.; Misawa, H.; Kato, S.; Hirai, S. Loss of Cholinergic Synapses on the Spinal Motor Neurons of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1998, 57, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullen, A.H.; Athanasiou, D. Increase in Presynaptic Territory of C-Terminals on Lumbar Motoneurons of G93A SOD1 Mice During Disease Progression. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, L.; Courtand, G.; Cardoit, L.; Masmejean, F.; Barrière, G.; Cazalets, J.-R.; Garret, M.; Bertrand, S.S. Age-Related Changes in Pre- and Postsynaptic Partners of the Cholinergic C-Boutons in Wild-Type and SOD1G93A Lumbar Motoneurons. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasiene, J.; Komine, O.; Fujimori-Tonou, N.; Powers, B.; Endo, F.; Watanabe, S.; Shijie, J.; Ravits, J.; Horner, P.; Misawa, H.; et al. Neuregulin 1 Confers Neuroprotection in SOD1-Linked Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Mice via Restoration of C-Boutons of Spinal Motor Neurons. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mòdol-Caballero, G.; García-Lareu, B.; Verdés, S.; Ariza, L.; Sánchez-Brualla, I.; Brocard, F.; Bosch, A.; Navarro, X.; Herrando-Grabulosa, M. Therapeutic Role of Neuregulin 1 Type III in SOD1-Linked Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 1048–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Allender, E.; Wang, J.; Simpson, E.H.; Loeb, J.A.; Song, F. Slowing Disease Progression in the SOD1 Mouse Model of ALS by Blocking Neuregulin-Induced Microglial Activation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 111, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, S.; Salvany, S.; Casanovas, A.; Piedrafita, L.; Soto-Bernardini, M.C.; Tarabal, O.; Blasco, A.; Gras, S.; Gatius, A.; Schwab, M.H.; et al. Persistent NRG1 Type III Overexpression in Spinal Motor Neurons Has No Therapeutic Effect on ALS-Related Pathology in SOD1G93A Mice. Neurotherapeutics 2023, 20, 1820–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Hassinan, C.W.; Gerstner, F.; Buettner, J.M.; Petigrow, J.B.; Valdivia, D.O.; Chan-Cortés, M.H.; Mistri, A.; Cao, A.; McGaugh, S.A.; et al. Boosting Neuregulin 1 Type-III Expression Hastens SMA Motor Axon Maturation. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehr, M.C.; Hinrichs, W.; Brzózka, M.M.; Unterbarnscheidt, T.; Herholt, A.; Wintgens, J.P.; Papiol, S.; Soto-Bernardini, M.C.; Kravchenko, M.; Zhang, M.; et al. Spironolactone Is an Antagonist of NRG1-ERBB4 Signaling and Schizophrenia-relevant Endophenotypes in Mice. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 1448–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, M.G.; Mermod, J.J.; Amara, S.G.; Swanson, L.W.; Sawchenko, P.E.; Rivier, J.; Vale, W.W.; Evans, R.M. Production of a Novel Neuropeptide Encoded by the Calcitonin Gene via Tissue-Specific RNA Processing. Nature 1983, 304, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, C.; Andreose, J.S.; Fumagalli, G.; Lømo, T. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide: Possible Role in Formation and Maintenance of Neuromuscular Junctions. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabal, O.; Calderó, J.; Ribera, J.; Sorribas, A.; López, R.; Molgó, J.; Esquerda, J.E. Regulation of Motoneuronal Calcitonin Gene–Related Peptide (CGRP) During Axonal Growth and Neuromuscular Synaptic Plasticity Induced by Botulinum Toxin in Rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabal, O.; Calderó, J.; Esquerda, J.E. Intramuscular Nerve Sprouting Induced by CNTF Is Associated with Increases in CGRP Content in Mouse Motor Nerve Terminals. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 219, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, A.; Gras, S.; Mòdol-Caballero, G.; Tarabal, O.; Casanovas, A.; Piedrafita, L.; Barranco, A.; Das, T.; Pereira, S.L.; Navarro, X.; et al. Motoneuron Deafferentation and Gliosis Occur in Association with Neuromuscular Regressive Changes During Ageing in Mice. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 1628–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.; Spiller, K.J.; Towne, C.; Kanning, K.C.; Choe, G.T.; Geber, A.; Akay, T.; Aebischer, P.; Henderson, C.E. Neuronal Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Is a Determinant of Selective Neurodegeneration. Neuron 2014, 81, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Chin, E.R. Activation of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response in Skeletal Muscle of G93A*SOD1 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Mice. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Motor Neurons of the Spinal Cord in Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 69, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayalakshmi, K.; Alladi, P.A.; Ghosh, S.; Prasanna, V.K.; Sagar, B.C.; Nalini, A.; Sathyaprabha, T.N.; Raju, T.R. Evidence of Endoplasmic Reticular Stress in the Spinal Motor Neurons Exposed to CSF from Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 41, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.J.; Rotterman, T.M.; Akhter, E.T.; Lane, A.R.; English, A.W.; Cope, T.C. Synaptic Plasticity on Motoneurons After Axotomy: A Necessary Change in Paradigm. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.J.; Titus-Mitchell, H.E.; Bullinger, K.L.; Kraszpulski, M.; Nardelli, P.; Cope, T.C. Permanent Central Synaptic Disconnection of Proprioceptors After Nerve Injury and Regeneration. I. Loss of VGLUT1/IA Synapses on Motoneurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 106, 2450–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vullhorst, D.; Mitchell, R.M.; Keating, C.; Roychowdhury, S.; Karavanova, I.; Tao-Cheng, J.-H.; Buonanno, A. A Negative Feedback Loop Controls NMDA Receptor Function in Cortical Interneurons via Neuregulin 2/ErbB4 Signalling. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, G.B.; Hartley, R.; Todd, A.J.; Brownstone, R.M. Spinal Cholinergic Interneurons Regulate the Excitability of Motoneurons During Locomotion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2448–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usachev, Y.; Shmigol, A.; Pronchuk, N.; Kostyuk, P.; Verkhratsky, A. Caffeine-Induced Calcium Release from Internal Stores in Cultured Rat Sensory Neurons. Neuroscience 1993, 57, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thastrup, O.; Cullen, P.J.; Drøbak, B.K.; Hanley, M.R.; Dawson, A.P. Thapsigargin, a Tumor Promoter, Discharges Intracellular Ca2+ Stores by Specific Inhibition of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 2466–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fambrough, D.M. Acetylcholine Receptors. Revised Estimates of Extrajunctional Receptor Density in Denervated Rat Diaphragm. J. Gen. Physiol. 1974, 64, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willadt, S.; Nash, M.; Slater, C.R. Age-Related Fragmentation of the Motor Endplate Is Not Associated with Impaired Neuromuscular Transmission in the Mouse Diaphragm. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holahan, M.R. A Shift from a Pivotal to Supporting Role for the Growth-Associated Protein (GAP-43) in the Coordination of Axonal Structural and Functional Plasticity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Yeo, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Zhou, W.; Tan, J.Y.; Chi, L.; Chia, S.-Y.; Li, Z.; Sim, A.Y.; Singh, B.K.; et al. NOTCH2NLC GGC Intermediate Repeat with Serine Induces Hypermyelination and Early Parkinson’s Disease-like Phenotypes in Mice. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adlkofer, K.; Martini, R.; Aguzzi, A.; Zielasek, J.; Toyka, K.V.; Suter, U. Hypermyelination and Demyelinating Peripheral Neuropathy in Pmp22-Deficient Mice. Nat. Genet. 1995, 11, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Luo, R.; Li, X.; Lin, M.; Qiu, M. Hypermyelination and Overexpression of Neuregulin-1 in Thoracic Sympathetic Nerves in Patients with Primary Palmar Hyperhidrosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 19, 1651–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odierna, G.L.; Vucic, S.; Dyer, M.; Dickson, T.; Woodhouse, A.; Blizzard, C. How Do We Get from Hyperexcitability to Excitotoxicity in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis? Brain 2024, 147, 1610–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, T.A.; Muir, D. MMP-2 and MMP-9 Increase the Neurite-Promoting Potential of Schwann Cell Basal Laminae and Are Upregulated in Degenerated Nerve. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2000, 16, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, M.; Zhu, N.; Tsantoulas, C.; Ma, Z.; Grist, J.; Loeb, J.A.; Bennett, D.L.H. Neuregulin-ErbB Signaling Promotes Microglial Proliferation and Chemotaxis Contributing to Microgliosis and Pain After Peripheral Nerve Injury. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 5437–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, A.R. The Axon Reaction: A Review of the Principal Features of Perikaryal Responses to Axon Injury. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 1971, 14, 49–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregno, G.; Zamburlin, P.; Gambarotta, G.; Farcito, S.; Licheri, V.; Fregnan, F.; Perroteau, I.; Lovisolo, D.; Bovolin, P. Neuregulin1/ErbB4-Induced Migration in ST14A Striatal Progenitors: Calcium-Dependent Mechanisms and Modulation by NMDA Receptor Activation. BMC Neurosci. 2011, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vullhorst, D.; Buonanno, A. NMDA Receptors Regulate Neuregulin 2 Binding to ER-PM Junctions and Ectodomain Release. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 8345–8363, Correction in Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Fu, A.K.Y.; Ip, N.Y.; Yan, Z. Regulation of NMDA Receptors by Neuregulin Signaling in Prefrontal Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 4974–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, A.C.; Dammerman, R.S.; Kriegstein, A.R. Endogenous Activation of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Neocortical Development Causes Neuronal Calcium Oscillations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12144–12149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuta, S.; Iguchi, Y.; Kakizaki, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Yanagawa, Y.; Takada, M.; Osanai, M. Store-Operated Calcium Channels Are Involved in Spontaneous Slow Calcium Oscillations in Striatal Neurons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, R.; Hardy, W.R.; Laing, M.A.; Hardy, S.E.; Muller, W.J. The Catalytic Activity of the ErbB-2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Is Essential for Embryonic Development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Lai, C.; Thomas, S.; Burden, S.J. Neuregulin Receptors, erbB3 and erbB4, Are Localized at Neuromuscular Synapses. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 5842–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.A.; Zhu, X.; Marchionni, M.A.; Burden, S.J. Neuregulins Are Concentrated at Nerve-Muscle Synapses and Activate ACh-Receptor Gene Expression. Nature 1995, 373, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpowitz, D.; Mason, T.B.; Dietrich, P.; Mendelsohn, M.; Talmage, D.A.; Role, L.W. Cysteine-Rich Domain Isoforms of the Neuregulin-1 Gene Are Required for Maintenance of Peripheral Synapses. Neuron 2000, 25, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Sanchez, H.B.; Deerinck, T.; Morris, J.K.; Ellisman, M.; Lee, K.F. Aberrant Development of Motor Axons and Neuromuscular Synapses in erbB2-Deficient Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan, S.L.; Rygiel, K.; Purves-Smith, F.M.; Solbak, N.M.; Turnbull, D.M.; Hepple, R.T. Denervation Causes Fiber Atrophy and Myosin Heavy Chain Co-Expression in Senescent Skeletal Muscle. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Khurana, S.; Vats, A.; Sahu, B.; Ganguly, N.K.; Chakraborti, P.; Gourie-Devi, M.; Taneja, V. Neuromuscular Junction Dysfunction in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 1502–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, V.; Verstreken, P. Autophagy in the Presynaptic Compartment in Health and Disease. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 1895–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukup, S.-F.; Kuenen, S.; Vanhauwaert, R.; Manetsberger, J.; Hernández-Díaz, S.; Swerts, J.; Schoovaerts, N.; Vilain, S.; Gounko, N.V.; Vints, K.; et al. A LRRK2-Dependent EndophilinA Phosphoswitch Is Critical for Macroautophagy at Presynaptic Terminals. Neuron 2016, 92, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Varo, R.; Trujillo-Estrada, L.; Sanchez-Mejias, E.; Torres, M.; Baglietto-Vargas, D.; Moreno-Gonzalez, I.; De Castro, V.; Jimenez, S.; Ruano, D.; Vizuete, M.; et al. Abnormal Accumulation of Autophagic Vesicles Correlates with Axonal and Synaptic Pathology in Young Alzheimer’s Mice Hippocampus. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordi, M.; Berg, M.J.; Mohan, P.S.; Peterhoff, C.M.; Alldred, M.J.; Che, S.; Ginsberg, S.D.; Nixon, R.A. Autophagy Flux in CA1 Neurons of Alzheimer Hippocampus: Increased Induction Overburdens Failing Lysosomes to Propel Neuritic Dystrophy. Autophagy 2016, 12, 2467–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castets, P.; Ham, D.J.; Rüegg, M.A. The TOR Pathway at the Neuromuscular Junction: More Than a Metabolic Player? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.; Minotti, S.; Dong, L.; Figlewicz, D.A.; Durham, H.D. Glutamate Potentiates the Toxicity of Mutant Cu/Zn-Superoxide Dismutase in Motor Neurons by Postsynaptic Calcium-Dependent Mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 9673–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Target | Source | Host Species | Used Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|
| CGRP | Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) (C-81989) | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:1000 |
| ChAT | MilliporeSigma (Temecula, CA, USA) (AB144) | Goat polyclonal | 1:250 |
| Glucose-regulated protein78 (Grp78/BiP) | Enzo Life Sciences (Farmingdale, NY, USA) (SPA-826) | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:1000 |
| GluR2 (GluA2) | Invitrogen (Waltham, MA, USA) (71-8600) | Mouse monoclonal | 1:125 |
| GAP-43 | Novusbio (Centennial, CO, USA) (NB300-143) | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:500 |
| HA | Roche (Basel, Switzerland) (11 867 423 001) | Rat monoclonal | 1:500 |
| Ionised calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba1) | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) (ab5076) | Goat polyclonal | 1:500 |
| Voltage gated potassium channel 2.1 (Kv2.1) | NeuroMAB (Davis, CA, USA) (73-014) | Mouse monoclonal | 1:100 |
| M2 muscarinic receptor (M2) | Alomone Labs (Jerusalem, Israel) (AMR-002) | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:100 |
| MMP9 | Sigma-Aldrich (M9570) | Goat polyclonal | 1:10 |
| 1α/β1/2 NRG1 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA) (sc-348) | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:300 |
| NF68 | Abcam (ab72997) | Chicken polyclonal | 1:1000 |
| NMDAR1 (GluN1) | Invitrogen (PA5-34599) | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:1000 (W) |
| NMDAR2A (GluN2A) | Invitrogen (480031) | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:1000 (W) |
| NMDAR2B (GluN2B) | Invitrogen (71-8600) | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:125 1:1000 (W) |
| phospho-Neu try1248 (p-ErbB2) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology (sc-293110) | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:100 |
| S100 | Dako Agilent (Santa Clara, CA, USA) (Z311) | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:500 |
| SV2 | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (Iowa City, IA, USA) (SV2) | Mouse monoclonal | 1:1000 |
| Synaptophysin (SYN) | Synaptic Systems (Goettingen, Germany) (101 004) | Guinea pig polyclonal | 1/500 |
| Tubulin | Sigma-Aldrich (T5168) | Mouse monoclonal | 1:20,000 (W) |
| VAChT | Synaptic Systems (139 105) | Guinea pig polyclonal | 1:500 |
| VGAT | Synaptic Systems (131 004) | Guinea pig polyclonal | 1:200 |
| VGluT1 | Synaptic Systems (135 304) | Guinea pig polyclonal | 1:500 |
| VGluT2 | Synaptic Systems (135 404) | Guinea pig polyclonal | 1:500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salvany, S.; Hernández, S.; Casanovas, A.; Gras, S.; Piedrafita, L.; Bosch-Queralt, M.; Schwab, M.H.; Calderó, J.; Esquerda, J.E.; Tarabal, O. Chronic Overexpression of Neuronal NRG1-III in Mice Causes Long-Term Detrimental Changes in Lower Motor Neurons, Neuromuscular Synapses and Motor Behaviour. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311421
Salvany S, Hernández S, Casanovas A, Gras S, Piedrafita L, Bosch-Queralt M, Schwab MH, Calderó J, Esquerda JE, Tarabal O. Chronic Overexpression of Neuronal NRG1-III in Mice Causes Long-Term Detrimental Changes in Lower Motor Neurons, Neuromuscular Synapses and Motor Behaviour. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311421
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalvany, Sara, Sara Hernández, Anna Casanovas, Sílvia Gras, Lídia Piedrafita, Mar Bosch-Queralt, Markus H. Schwab, Jordi Calderó, Josep E. Esquerda, and Olga Tarabal. 2025. "Chronic Overexpression of Neuronal NRG1-III in Mice Causes Long-Term Detrimental Changes in Lower Motor Neurons, Neuromuscular Synapses and Motor Behaviour" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311421
APA StyleSalvany, S., Hernández, S., Casanovas, A., Gras, S., Piedrafita, L., Bosch-Queralt, M., Schwab, M. H., Calderó, J., Esquerda, J. E., & Tarabal, O. (2025). Chronic Overexpression of Neuronal NRG1-III in Mice Causes Long-Term Detrimental Changes in Lower Motor Neurons, Neuromuscular Synapses and Motor Behaviour. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311421






