Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization and Multi-Omics Uncover Causal Serum Metabolites and Neuro-Related Mechanistic Pathways in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Strength of the Instrumental Variables
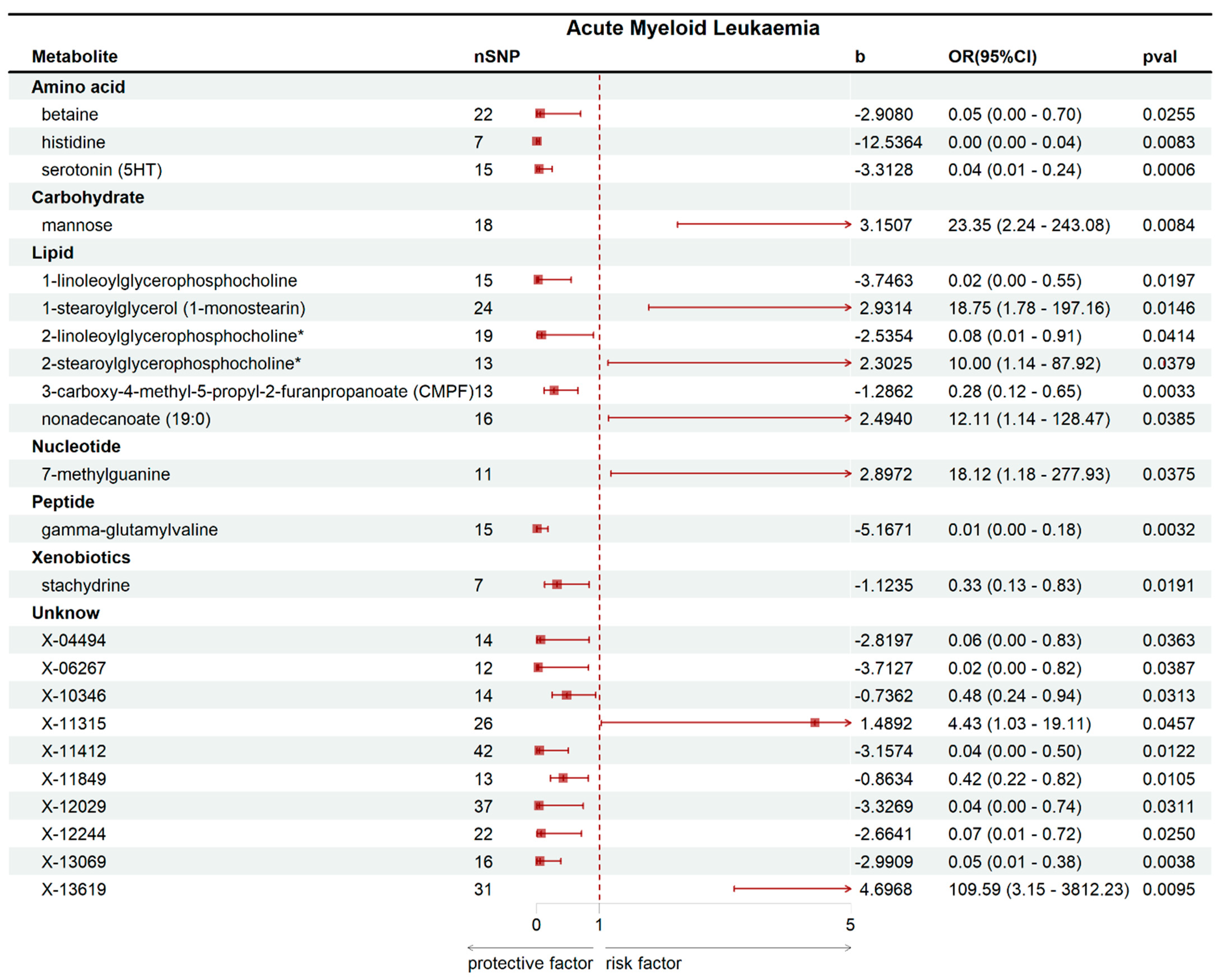
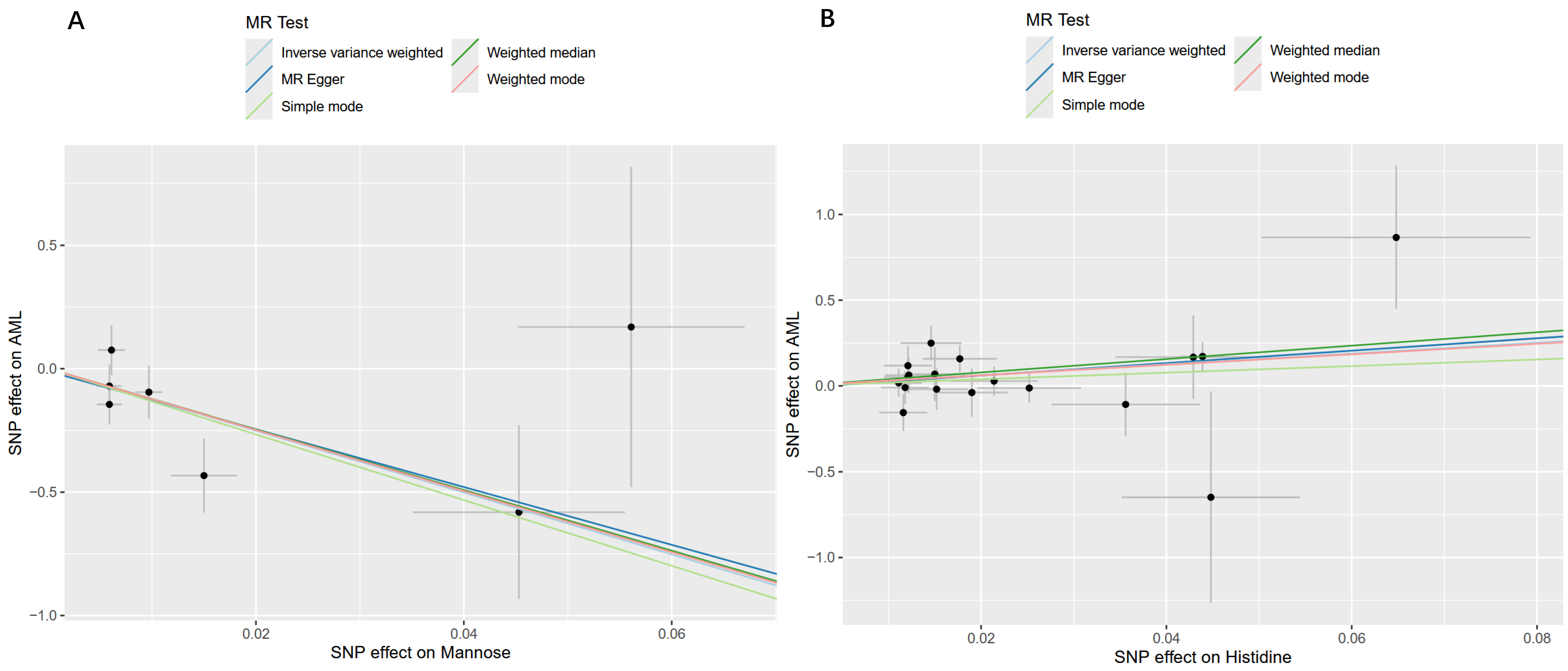
2.2. Mendelian Randomization Analysis Results
2.3. Sensitivity and Reverse Causality Analysis Results
2.4. Results of Metabolic Pathway Enrichment Analysis
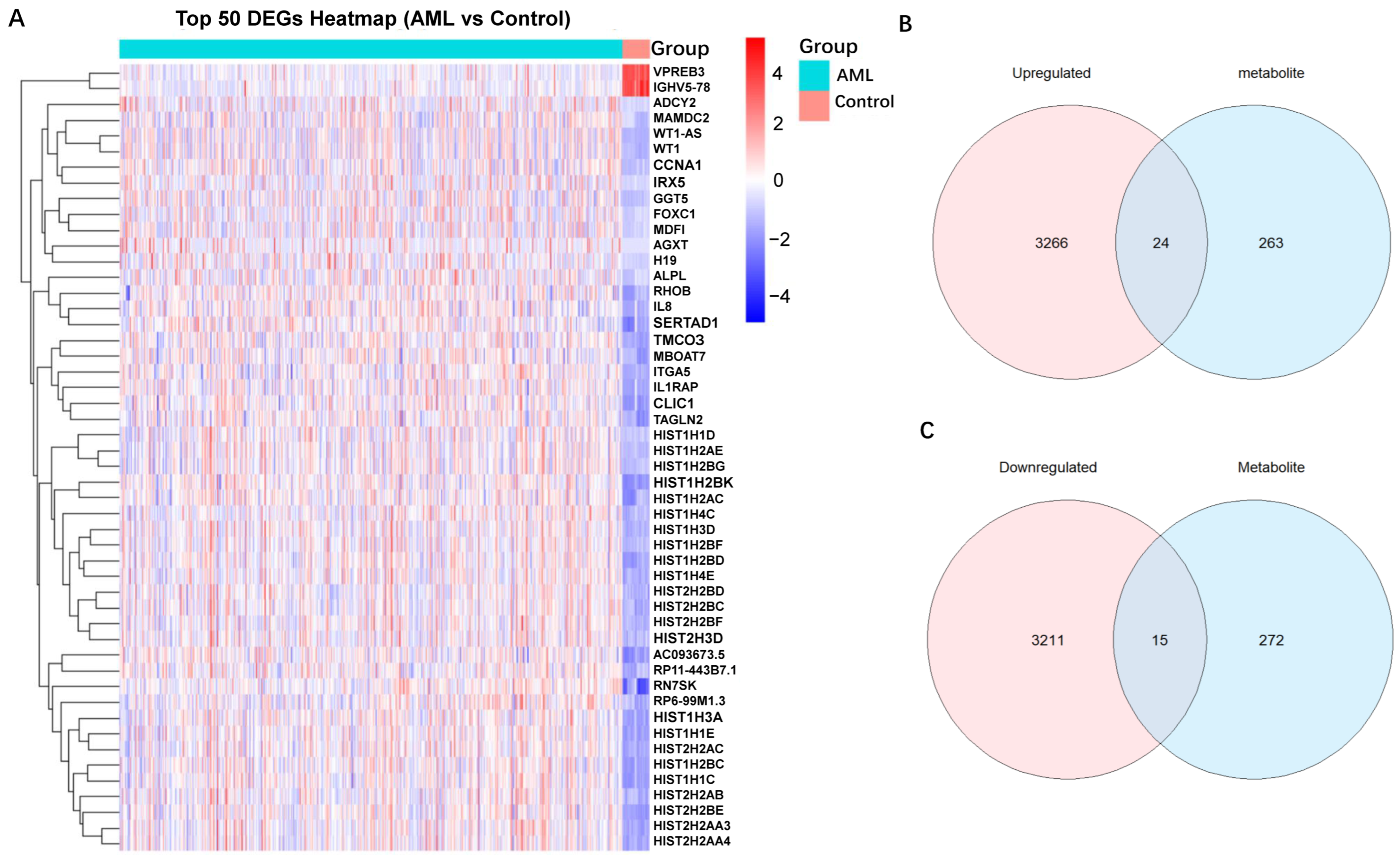
2.5. Mapping SNPs to Genes and DEGs Identification of AML
2.6. Identification and Functional Enrichment Analysis of Overlapping Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
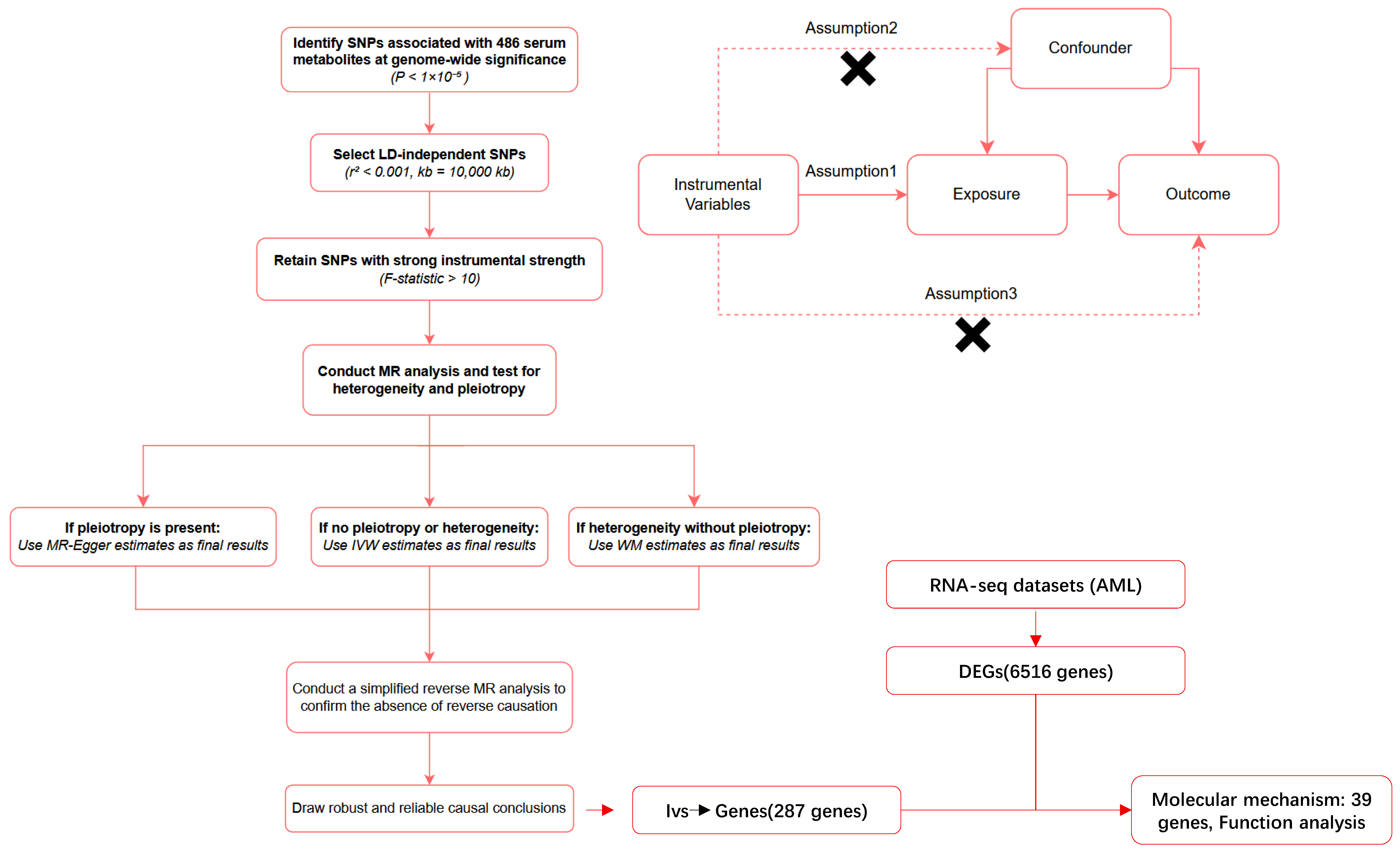
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Data Source
4.3. Selection of Instrumental Variables (IVs)
4.4. Mendelian Randomization Analyses
4.5. Sensitivity Analysis
4.6. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
4.7. Mapping SNPs to Genes and Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
4.8. Identification and Functional Enrichment Analysis of Overlapping Genes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.D.; Potter, N.E.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliusson, G.; Antunovic, P.; Derolf, A.; Lehmann, S.; Möllgård, L.; Stockelberg, D.; Tidefelt, U.; Wahlin, A.; Höglund, M. Age and Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Real World Data on Decision to Treat and Outcomes from the Swedish Acute Leukemia Registry. Blood 2009, 113, 4179–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Wei, A.H.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Craddock, C.; DiNardo, C.D.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Godley, L.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Aml in Adults: 2022 Recommendations from an International Expert Panel on Behalf of the Eln. Blood 2022, 140, 1345–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, C.; Vernarecci, C.; Minetto, P.; Goda, R.; Greppi, M.; Pesce, S.; Chies, M.; Zecchetti, G.; Ferro, B.; Maio, E.; et al. Harnessing Immune Response in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: Globocan Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kouchkovsky, I.; Abdul-Hay, M. ‘Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Comprehensive Review and 2016 Update’. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.F. Platelet Indices and the Causal Relationship with Myeloid Leukemia: A Mendelian Randomization Study with Dual Samples. Clin. Lab. 2025, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, A.Z.; Selek, S.; Bekiroglu, S.; Demirel, M.; Cakir, F.B.; Uyanik, B. Serum Nmr Metabolomics in Distinct Subtypes of Hematologic Malignancies. Exp. Hematol. 2025, 143, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockard, B.; Garrett, T.; Guingab-Cagmat, J.; Meshinchi, S.; Lamba, J. Distinct Metabolic Features Differentiating Flt3-Itd Aml from Flt3-Wt Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musharraf, S.G.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Shamsi, T.; Choudhary, M.I.; Rahman, A.U. Serum Metabonomics of Acute Leukemia Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R.M.; Mandrekar, S.J.; Sanford, B.L.; Laumann, K.; Geyer, S.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Thiede, C.; Prior, T.W.; Döhner, K.; Marcucci, G.; et al. Midostaurin Plus Chemotherapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia with a Flt3 Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Jonas, B.A.; Pullarkat, V.; Thirman, M.J.; Garcia, J.S.; Wei, A.H.; Konopleva, M.; Döhner, H.; Letai, A.; Fenaux, P.; et al. Azacitidine and Venetoclax in Previously Untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Ying, H.; Wang, X.; Hua, S.; Ligorio, M.; Perera, R.M.; Ferrone, C.R.; Mullarky, E.; Shyh-Chang, N.; et al. Glutamine Supports Pancreatic Cancer Growth through a Kras-Regulated Metabolic Pathway. Nature 2013, 496, 101–105, Erratum in Nature 2013, 499, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Adane, B.; Khan, N.; Alexeev, E.; Nusbacher, N.; Minhajuddin, M.; Stevens, B.M.; Winters, A.C.; Lin, X.; Ashton, J.M.; et al. Subversion of Systemic Glucose Metabolism as a Mechanism to Support the Growth of Leukemia Cells. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 659–673.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Son, S.Y.; Oh, J.S.; Song, Y.N.; Byun, J.M.; Koh, Y.; Hong, J.; Yoon, S.S.; Lee, C.H.; Shin, D.Y.; et al. Metabolic Profiling During Acute Myeloid Leukemia Progression Using Paired Clinical Bone Marrow Serum Samples. Metabolites 2021, 11, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenland, S. An Introduction to Instrumental Variables for Epidemiologists. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 29, 722–729, Erratum in Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales Berstein, F.; McCartney, D.L.; Lu, A.T.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Bouras, E.; Haycock, P.; Burrows, K.; Phipps, A.I.; Buchanan, D.D.; Cheng, I.; et al. Assessing the Causal Role of Epigenetic Clocks in the Development of Multiple Cancers: A Mendelian Randomization Study. eLife 2022, 11, e75374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Zhang, C.; Kilicarslan, M.; Piening, B.D.; Bjornson, E.; Hallström, B.M.; Groen, A.K.; Ferrannini, E.; Laakso, M.; Snyder, M.; et al. Integrated Network Analysis Reveals an Association between Plasma Mannose Levels and Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Su, Y.; Xie, E.; Cheng, H.; Du, J.; Xu, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, D.G.; Zhu, H.; et al. Mannose Metabolism Reshapes T cell Differentiation to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immunity. Cancer Cell 2025, 43, 103–121.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Granata, F.; Spadaro, G.; Genovese, A.; Triggiani, M. The Histamine-Cytokine Network in Allergic Inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112 (Suppl. 4), S83–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Wen, J.; Luo, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Ye, J. Causal Relationships of Metabolites with Allergic Diseases: A Trans-Ethnic Mendelian Randomization Study. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubahn, J.; Berndt, S.I.; Jin, C.H.; Klim, A.; Luly, J.; Wu, W.S.; Isaacs, S.; Wiley, K.; Isaacs, W.B.; Suarez, B.K.; et al. Association of Casp8 D302h Polymorphism with Reduced Risk of Aggressive Prostate Carcinoma. Prostate 2010, 70, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.; Blagih, J.; Zani, F.; Rees, A.; Hill, D.G.; Jenkins, B.J.; Bull, C.J.; Moreira, D.; Bantan, A.I.M.; Cronin, J.G.; et al. Fructose Reprogrammes Glutamine-Dependent Oxidative Metabolism to Support Lps-Induced Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, P.; Liu, Z.; He, Y. Single-Cell Analyses Reveal the Metabolic Heterogeneity and Plasticity of the Tumor Microenvironment During Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 2468–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Shi, S.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, M.; Shu, Q. Analysis of Signature Genes and Association with Immune Cells Infiltration in Pediatric Septic Shock. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1056750, Erratum in Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1241047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Ding, T.; Shao, Y. A Transient Receptor Potential Channel-Related Model Based on Machine Learning for Evaluating Tumor Microenvironment and Immunotherapeutic Strategies in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1040661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, C.; Tontonoz, P. Inter-Organ Cross-Talk in Metabolic Syndrome. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Thompson, J.W.; Yin, T.; Alexander, P.B.; Qin, D.; Mudgal, P.; Wu, H.; Liang, Y.; Tan, L.; et al. Cancer-Cell-Derived Gaba Promotes Β-Catenin-Mediated Tumour Growth and Immunosuppression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, J.; Lu, M.; Gao, Q.; Zeng, J.; Xiao, J. Transcriptome-Wide Association Studies: Recent Advances in Methods, Applications and Available Databases. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.Y.; Fauman, E.B.; Petersen, A.K.; Krumsiek, J.; Santos, R.; Huang, J.; Arnold, M.; Erte, I.; Forgetta, V.; Yang, T.P.; et al. An Atlas of Genetic Influences on Human Blood Metabolites. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Yang, H.; Deng, T.; Li, Y. A Cross-Tissue Transcriptome-Wide Association Study Identified Susceptibility Genes for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. JOR Spine 2025, 8, e70109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, M.K.; Kawachi, I.; Rehkopf, D.; Schooling, C.M. The Role of Cortisol in Ischemic Heart Disease, Ischemic Stroke, Type 2 Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: A Bi-Directional Mendelian Randomization Study. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z. Blood Metabolites and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. BMC Med. Genom. 2024, 17, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, N.; Dimou, N.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Banbury, B.; Martin, R.M.; Lewis, S.J.; Kazmi, N.; Robinson, T.M.; Albanes, D.; Aleksandrova, K.; et al. Physical Activity and Risks of Breast and Colorectal Cancer: A Mendelian Randomisation Analysis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian Randomization Analysis with Multiple Genetic Variants Using Summarized Data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagoni, P.; Korologou-Linden, R.S.; Howe, L.D.; Davey Smith, G.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Stergiakouli, E.; Anderson, E.L. Causal Effects of Circulating Cytokine Concentrations on Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease and Cognitive Function. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 104, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian Randomization with Invalid Instruments: Effect Estimation and Bias Detection through Egger Regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.R. Detecting Pleiotropy in Mendelian Randomisation Studies with Summary Data and a Continuous Outcome. Stat. Med. 2015, 34, 2926–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of Widespread Horizontal Pleiotropy in Causal Relationships Inferred from Mendelian Randomization between Complex Traits and Diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, J.M.B.; Wood, A.M.; Burgess, S. Extending the Mr-Egger Method for Multivariable Mendelian Randomization to Correct for Both Measured and Unmeasured Pleiotropy. Stat. Med. 2017, 36, 4705–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. A Causal Relationship between Childhood Obesity and Risk of Osteoarthritis: Results from a Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 1636–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Hui, F.; Xu, L.; Viau, C.; Spigelman, A.F.; MacDonald, P.E.; Wishart, D.S.; Li, S.; et al. Metaboanalyst 6.0: Towards a Unified Platform for Metabolomics Data Processing, Analysis and Interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W398–W406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oscanoa, J.; Sivapalan, L.; Gadaleta, E.; Dayem Ullah, A.Z.; Lemoine, N.R.; Chelala, C. Snpnexus: A Web Server for Functional Annotation of Human Genome Sequence Variation (2020 Update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W185–W192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. Clusterprofiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes among Gene Clusters. Omics 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Metabolite | nSNP | Cochran’s Q Test | MR-Egger Intercept | MR-Presso | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVW | MR Egger | Egger Intercept | p | Global Test RSSobs | p | ||
| 1-linoleoylglycerophosphocholine | 15 | 0.8486 | 0.8081 | −0.0343 | 0.6631 | 9.6823 | 0.8850 |
| 1-stearoylglycerol (1-monostearin) | 24 | 0.4880 | 0.4975 | 0.0561 | 0.2931 | 25.0529 | 0.4780 |
| 2-linoleoylglycerophosphocholine* | 19 | 0.4243 | 0.4240 | 0.0812 | 0.3312 | 20.5221 | 0.4520 |
| 2-stearoylglycerophosphocholine* | 13 | 0.7440 | 0.7082 | 0.0852 | 0.5142 | 9.7489 | 0.7800 |
| 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furanpropanoate (CMPF) | 13 | 0.5016 | 0.4208 | −0.0152 | 0.8307 | 13.2670 | 0.5190 |
| 7-methylguanine | 11 | 0.1743 | 0.1569 | −0.0680 | 0.4662 | 17.6698 | 0.2050 |
| betaine | 22 | 0.8676 | 0.8863 | −0.0540 | 0.2752 | 15.0725 | 0.8750 |
| gamma-glutamylvaline | 15 | 0.6318 | 0.5545 | 0.0087 | 0.9317 | 12.9875 | 0.6810 |
| histidine | 7 | 0.2744 | 0.1854 | −0.0108 | 0.9069 | 9.9380 | 0.3410 |
| mannose | 18 | 0.4115 | 0.3479 | −0.0116 | 0.8398 | 19.3056 | 0.4870 |
| nonadecanoate (19:0) | 16 | 0.6602 | 0.6815 | −0.0546 | 0.2937 | 13.9014 | 0.6900 |
| serotonin (5HT) | 15 | 0.3151 | 0.2509 | −0.0027 | 0.9552 | 19.0807 | 0.3560 |
| stachydrine | 7 | 0.8902 | 0.8169 | 0.0421 | 0.7988 | 2.9697 | 0.9170 |
| X-04494 | 14 | 0.6025 | 0.6016 | −0.0435 | 0.3526 | 12.3367 | 0.6670 |
| X-06267 | 12 | 0.3642 | 0.2871 | 0.0100 | 0.8938 | 14.0074 | 0.4160 |
| X-10346 | 14 | 0.4221 | 0.3450 | 0.0012 | 0.9842 | 14.4879 | 0.5270 |
| X-11315 | 26 | 0.6334 | 0.5944 | −0.0169 | 0.5934 | 2.9697 | 0.9170 |
| X-11412 | 42 | 0.3686 | 0.4152 | 0.0494 | 0.1560 | 45.1492 | 0.3860 |
| X-11849 | 13 | 0.6487 | 0.5765 | −0.0223 | 0.7216 | 11.6005 | 0.6570 |
| X-12029 | 37 | 0.4456 | 0.4488 | 0.0466 | 0.3075 | 38.5584 | 0.5010 |
| X-12244 | 22 | 0.3725 | 0.3544 | −0.0410 | 0.4223 | 24.2208 | 0.4590 |
| X-13069 | 16 | 0.8026 | 0.7424 | 0.0021 | 0.9835 | 11.5354 | 0.8040 |
| X-13619 | 31 | 0.5595 | 0.5816 | −0.0624 | 0.2479 | 30.2791 | 0.5500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, H.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, X. Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization and Multi-Omics Uncover Causal Serum Metabolites and Neuro-Related Mechanistic Pathways in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311307
Ye H, Liu Y, Tang J, Li X. Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization and Multi-Omics Uncover Causal Serum Metabolites and Neuro-Related Mechanistic Pathways in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311307
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Haohan, Yuanheng Liu, Jun Tang, and Xiaoli Li. 2025. "Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization and Multi-Omics Uncover Causal Serum Metabolites and Neuro-Related Mechanistic Pathways in Acute Myeloid Leukemia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311307
APA StyleYe, H., Liu, Y., Tang, J., & Li, X. (2025). Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization and Multi-Omics Uncover Causal Serum Metabolites and Neuro-Related Mechanistic Pathways in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311307






