Neural Circuit Connections and Functions of Locus Coeruleus–Norepinephrine System
Abstract
1. Evolution of Norepinephrine System in Locus Coeruleus
1.1. Evolutionary Conservation of the Locus Coeruleus
1.2. Evolutionary Features of the LC from Non-Mammalian to Mammalian Vertebrates
1.2.1. Number of Cells
1.2.2. Anatomical Projections
1.2.3. Physiological Functions
1.3. Sex Differences in the LC of Mammalian Vertebrates
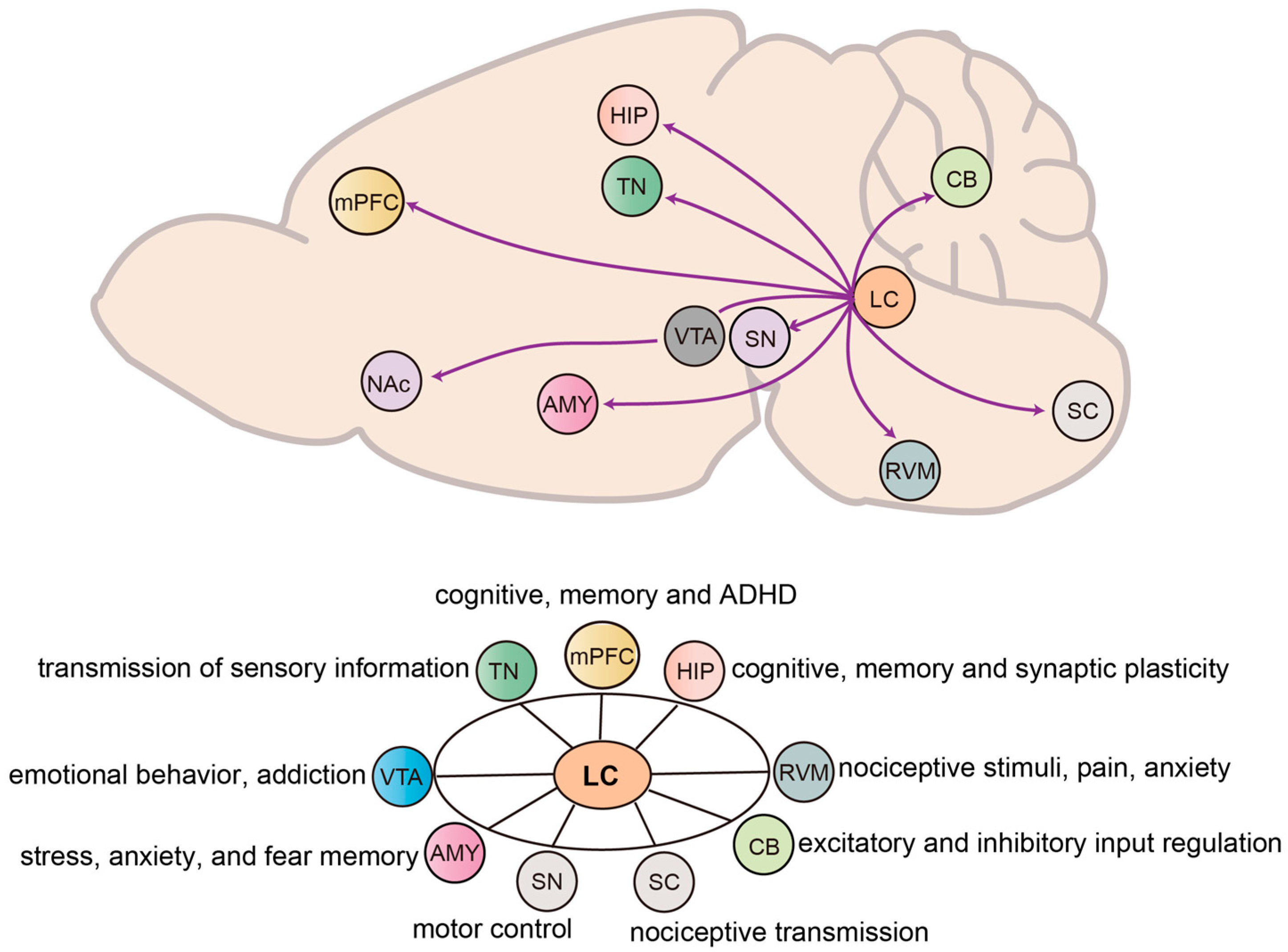
2. Efferent and Functions of NE Neurons in the LC
2.1. Forebrain
2.1.1. LC to Medial Prefrontal Cortex
2.1.2. LC to Hippocampus
2.1.3. LC to Amygdala
2.1.4. LC to Thalamic Nuclei
2.2. Midbrain
2.2.1. LC to Ventral Tegmental Area
2.2.2. LC to Substantia Nigra
2.3. Hindbrain
2.3.1. LC to Rostral Ventromedial Medulla
2.3.2. LC to Cerebellum
2.4. Spinal Cord
LC to Spinal Cord
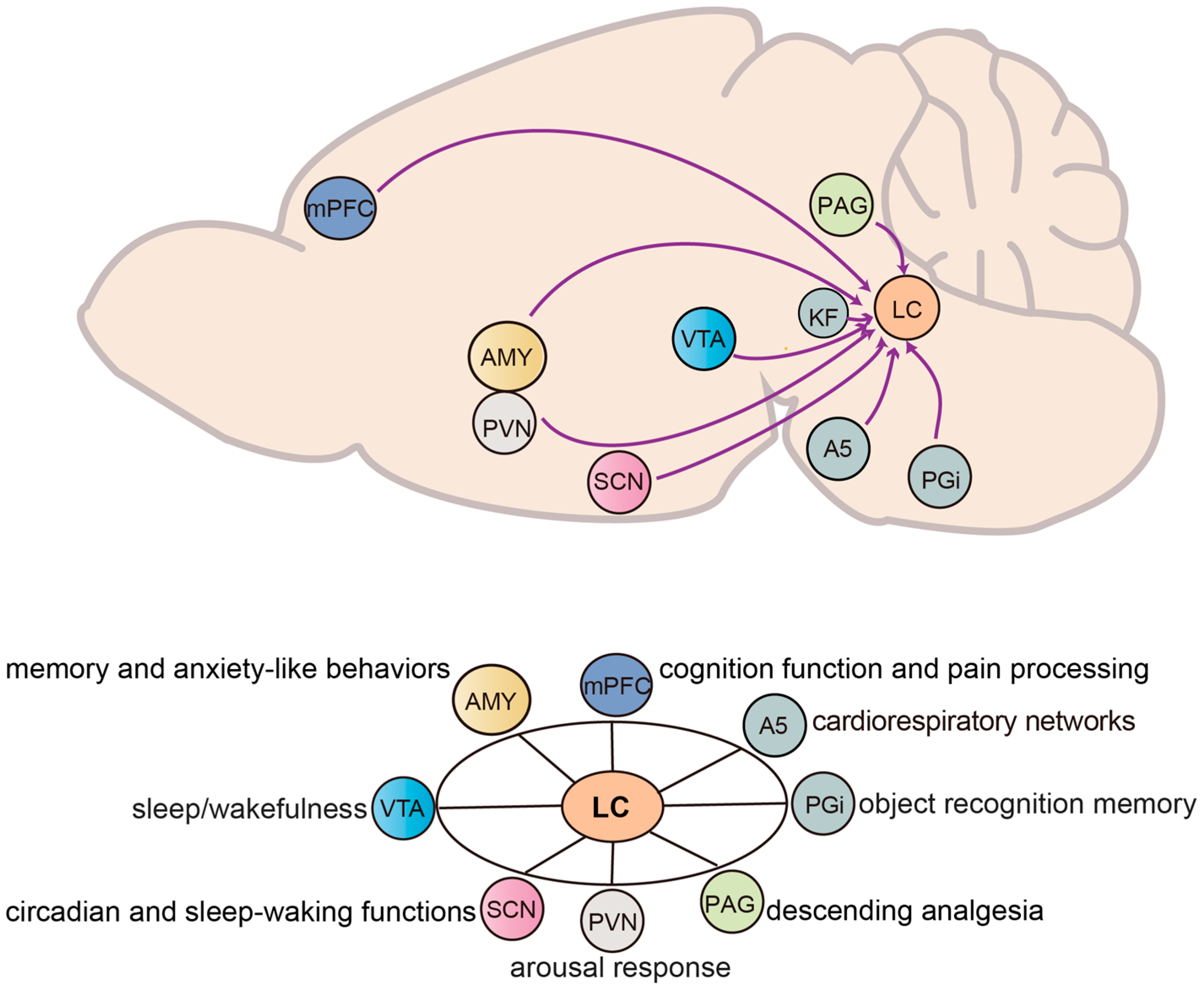
3. Inputs and Functions of NE Neurons in the LC
3.1. Midbrain and Brainstem
3.1.1. Paragigantocellularis to LC
3.1.2. Ventral Tegmental Area to LC
3.1.3. Suprachiasmatic Nucleus to LC
3.1.4. Periaqueductal Gray to LC
3.1.5. Pontine and Cardiorespiratory Networks
3.2. Cortical and Subcortical
3.2.1. Amygdala to LC
3.2.2. Medial Prefrontal Cortex to LC
3.2.3. Paraventricular Nucleus to LC
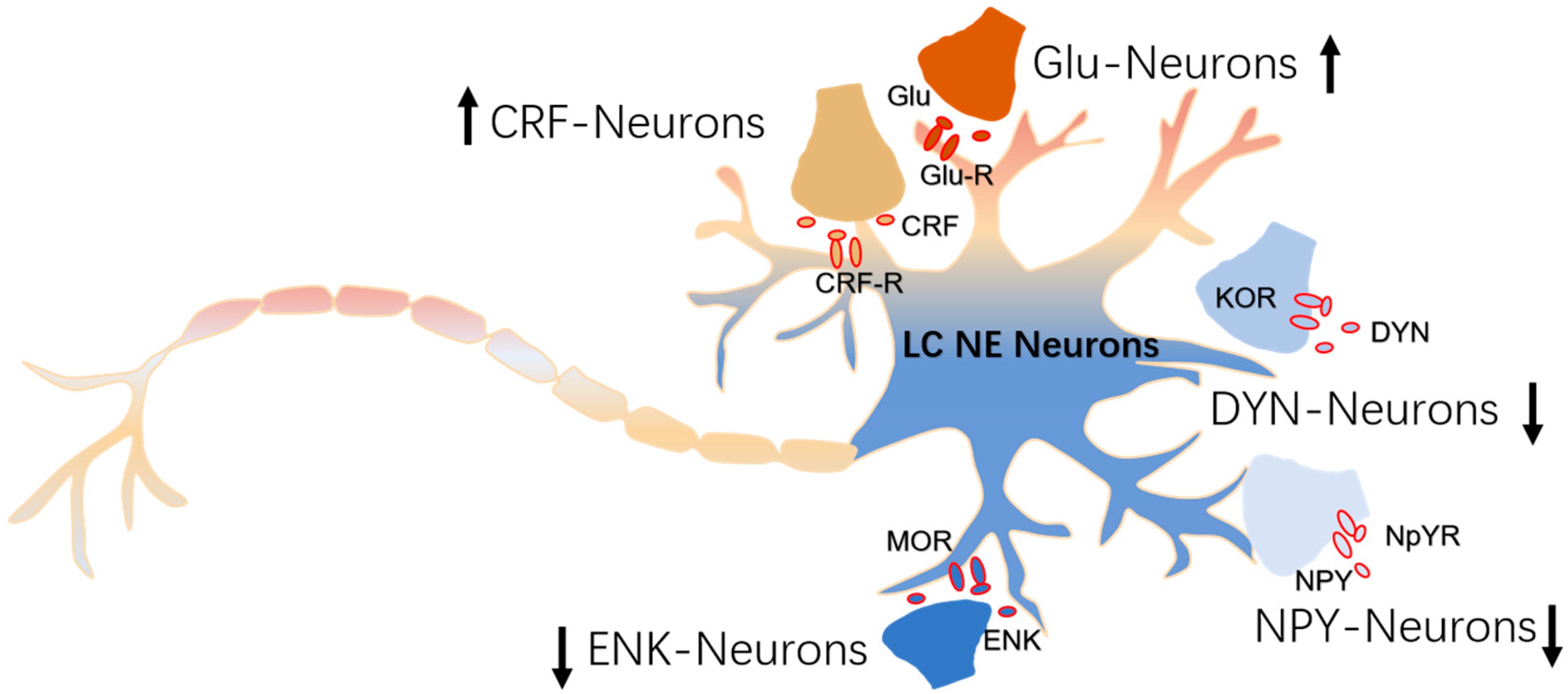
4. The Modulation of Inputs to NE Neurons
4.1. CRF-Afferents
4.2. ENK-Afferents
4.3. DYN-Afferents
4.4. Neuropeptide Y-Afferents
5. Conclusions and Future Direction
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwarz, L.A.; Miyamichi, K.; Gao, X.J.; Beier, K.T.; Weissbourd, B.; DeLoach, K.E.; Ren, J.; Ibanes, S.; Malenka, R.C.; Kremer, E.J.; et al. Viral-genetic tracing of the input-output organization of a central noradrenaline circuit. Nature 2015, 524, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbi, V.; Floriou-Servou, A.; Markicevic, M.; Vermeiren, Y.; Sturman, O.; Privitera, M.; von Ziegler, L.; Ferrari, K.D.; Weber, B.; De Deyn, P.P.; et al. Rapid Reconfiguration of the Functional Connectome after Chemogenetic Locus Coeruleus Activation. Neuron 2019, 103, 702–718.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, C.; Duss, S.N.; Privitera, M.; Munn, B.R.; Karalis, N.; Frässle, S.; Wilhelm, M.; Patriarchi, T.; Razansky, D.; Wenderoth, N.; et al. Tonic and burst-like locus coeruleus stimulation distinctly shift network activity across the cortical hierarchy. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Oikonomou, G.; Prober, D.A. Norepinephrine is required to promote wakefulness and for hypocretin-induced arousal in zebrafish. eLife 2015, 4, e07000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maness, E.B.; Burk, J.A.; McKenna, J.T.; Schiffino, F.L.; Strecker, R.E.; McCoy, J.G. Role of the locus coeruleus and basal forebrain in arousal and attention. Brain Res. Bull. 2022, 188, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrar, M.J.; Kolkman, K.E.; Fetcho, J.R. Features of the structure, development, and activity of the zebrafish noradrenergic system explored in new CRISPR transgenic lines. J. Comp. Neurol. 2018, 526, 2493–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzschuh, J.; Ryu, S.; Aberger, F.; Driever, W. Dopamine transporter expression distinguishes dopaminergic neurons from other catecholaminergic neurons in the developing zebrafish embryo. Mech. Dev. 2001, 101, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelino, C.B.; Schmidt, M.F. What birdsong can teach us about the central noradrenergic system. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2010, 39, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.; Xu, T.; Graf, W.M.; Fobbs, A.; Sherwood, C.C.; Hof, P.R.; Allman, J.M.; Manaye, K.F. Comparative anatomy of the locus coeruleus in humans and nonhuman primates. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010, 518, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, P.R.; Pakkenberg, B.; Gundersen, H.J.; Price, D.L. Absolute number and size of pigmented locus coeruleus neurons in young and aged individuals. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1994, 7, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkowicz, S.; Kocourek, M.; Lučan, R.K.; Porteš, M.; Fitch, W.T.; Herculano-Houzel, S.; Němec, P. Birds have primate-like numbers of neurons in the forebrain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7255–7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herculano-Houzel, S.; Lent, R. Isotropic fractionator: A simple, rapid method for the quantification of total cell and neuron numbers in the brain. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2518–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.M. Catecholaminergic systems in the zebrafish. I. Number, morphology, and histochemical characteristics of neurons in the locus coeruleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 344, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.E.; Friedman, L. Atlas of catecholamine perikarya, varicosities and pathways in the brainstem of the cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1983, 215, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, T.L.; Ronneberger, O.; Ryu, S.; Nitschke, R.; Driever, W. Comprehensive catecholaminergic projectome analysis reveals single-neuron integration of zebrafish ascending and descending dopaminergic systems. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rink, E.; Wullimann, M.F. Connections of the ventral telencephalon (subpallium) in the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Brain Res. 2004, 1011, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Camacho, C.; Peña, J.J.; González, A. Catecholaminergic innervation of the septum in the frog: A combined immunohistochemical and tract-tracing study. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 455, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogland, P.V. Brainstem afferents to the thalamus in a lizard, Varanus exanthematicus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1982, 210, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangma, G.C.; ten Donkelaar, H. Afferent connections of the cerebellum in various types of reptiles. J. Comp. Neurol. 1982, 207, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuinhof, R.; Artero, C.; Fasolo, A.; Franzoni, M.F.; Ten Donkelaar, H.J.; Wismans, P.G.; Roubos, E.W. Involvement of retinohypothalamic input, suprachiasmatic nucleus, magnocellular nucleus and locus coeruleus in control of melanotrope cells of Xenopus laevis: A retrograde and anterograde tracing study. Neuroscience 1994, 61, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, H.J.; Wall, E.M.; Woolley, S.C. Dopamine in the songbird auditory cortex shapes auditory preference. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 4547–4559.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutgeb, S.; Husband, S.; Riters, L.V.; Shimizu, T.; Bingman, V.P. Telencephalic afferents to the caudolateral neostriatum of the pigeon. Brain Res. 1996, 730, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnoli, P.; Burkhalter, A. Organization of the afferent projections to the Wulst in the pigeon. J. Comp. Neurol. 1983, 214, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodman, H.R.; Karten, H.J. Laminar distribution and sources of catecholaminergic input to the optic tectum of the pigeon (Columbia livia). J. Comp. Neurol. 1995, 359, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Duszkiewicz, A.J.; Sonneborn, A.; Spooner, P.A.; Yamasaki, M.; Watanabe, M.; Smith, C.C.; Fernández, G.; Deisseroth, K.; Greene, R.W.; et al. Locus coeruleus and dopaminergic consolidation of everyday memory. Nature 2016, 537, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, A.; Tan, B.Z.; Ycu, E.A.; Cuevas, J.S.; Koivumaa, J.; Junyent, F.; Kremer, E.J.; Witten, I.B.; Deisseroth, K.; Johansen, J.P. Modular organization of the brainstem noradrenaline system coordinates opposing learning states. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.J.; Zhang, R.W.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.B.; Peng, X.L.; Cao, S.; Yuan, J.; Yuan, C.D.; Yu, T.; Du, J.L. The Locus Coeruleus Modulates Intravenous General Anesthesia of Zebrafish via a Cooperative Mechanism. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 3146–3155.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.E.; de Lecea, L.; Adamantidis, A. Functional wiring of hypocretin and LC-NE neurons: Implications for arousal. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.E.; Yizhar, O.; Chikahisa, S.; Nguyen, H.; Adamantidis, A.; Nishino, S.; Deisseroth, K.; de Lecea, L. Tuning arousal with optogenetic modulation of locus coeruleus neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, C.; Boumans, T.; Vellema, M.; De Groof, G.; Charlier, T.D.; Verhoye, M.; Van der Linden, A.; Balthazart, J. Own song selectivity in the songbird auditory pathway: Suppression by norepinephrine. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsutani, K.; Tsuruoka, M.; Shinya, A.; Furuya, R.; Kawawa, T. Stimulation of the locus coeruleus suppresses trigeminal sensorimotor function in the rat. Brain Res. Bull. 2000, 53, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruoka, M.; Willis, W.D., Jr. Bilateral lesions in the area of the nucleus locus coeruleus affect the development of hyperalgesia during carrageenan-induced inflammation. Brain Res. 1996, 726, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.L.; Gebhart, G.F. Characterization of coeruleospinal inhibition of the nociceptive tail-flick reflex in the rat: Mediation by spinal alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Brain Res. 1986, 364, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, W.L.; Yeomans, D.C.; Proudfit, H.K. The function of noradrenergic neurons in mediating antinociception induced by electrical stimulation of the locus coeruleus in two different sources of Sprague-Dawley rats. Brain Res. 1993, 626, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangasser, D.A.; Wiersielis, K.R.; Khantsis, S. Sex differences in the locus coeruleus-norepinephrine system and its regulation by stress. Brain Res. 2016, 1641 Pt B, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinos, H.; Collado, P.; Rodríguez-Zafra, M.; Rodríguez, C.; Segovia, S.; Guillamón, A. The development of sex differences in the locus coeruleus of the rat. Brain Res. Bull. 2001, 56, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Falgueras, A.; Pinos, H.; Collado, P.; Pasaro, E.; Fernandez, R.; Segovia, S.; Guillamon, A. The expression of brain sexual dimorphism in artificial selection of rat strains. Brain Res. 2005, 1052, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Falgueras, A.; Pinos, H.; Fernández, R.; Collado, P.; Pasaro, E.; Segovia, S.; Guillamon, A. Sexual dimorphism in hybrids rats. Brain Res. 2006, 1123, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, C.; Bohl, J.; Ohm, T.G. Spatial, temporal and numeric analysis of Alzheimer changes in the nucleus coeruleus. Neurobiol. Aging 1997, 18, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohm, T.G.; Busch, C.; Bohl, J. Unbiased estimation of neuronal numbers in the human nucleus coeruleus during aging. Neurobiol. Aging 1997, 18, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvey, B.; Bhatti, D.L.; Gyawali, S.; Lake, A.M.; Kriaucionis, S.; Ford, C.P.; Bruchas, M.R.; Heintz, N.; Dougherty, J.D. Molecular and Functional Sex Differences of Noradrenergic Neurons in the Mouse Locus Coeruleus. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2225–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Duan, X.; Wei, Y.; Xu, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Sex-Related Differential Whole-Brain Input Atlas of Locus Coeruleus Noradrenaline Neurons. Front. Neural Circuits 2020, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Mu, Y. Locus Coeruleus in Non-Mammalian Vertebrates. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodovitsyna, O.; Flamini, M.; Chandler, D. Noradrenergic Modulation of Cognition in Health and Disease. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 6031478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agster, K.L.; Clark, B.D.; Gao, W.J.; Shumsky, J.S.; Wang, H.X.; Berridge, C.W.; Waterhouse, B.D. Experimental strategies for investigating psychostimulant drug actions and prefrontal cortical function in ADHD and related attention disorders. Anat. Rec. 2011, 294, 1698–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschberg, S.; Li, Y.; Randall, A.; Kremer, E.J.; Pickering, A.E. Functional dichotomy in spinal- vs prefrontal-projecting locus coeruleus modules splits descending noradrenergic analgesia from ascending aversion and anxiety in rats. eLife 2017, 6, e29808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnsten, A.F. Stress weakens prefrontal networks: Molecular insults to higher cognition. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Song, J.; Ma, C.; Lv, Y.; Wang, F.; Ma, L.; Liu, X. Noradrenergic signaling mediates cortical early tagging and storage of remote memory. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapiz, M.D.; Morilak, D.A. Noradrenergic modulation of cognitive function in rat medial prefrontal cortex as measured by attentional set shifting capability. Neuroscience 2006, 137, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaughy, J.; Ross, R.S.; Eichenbaum, H. Noradrenergic, but not cholinergic, deafferentation of prefrontal cortex impairs attentional set-shifting. Neuroscience 2008, 153, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, R.C.; Berridge, C.W. Receptor and circuit mechanisms underlying differential procognitive actions of psychostimulants. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnsten, A.F. Catecholamine and second messenger influences on prefrontal cortical networks of “representational knowledge”: A rational bridge between genetics and the symptoms of mental illness. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17 (Suppl. S1), i6–i15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radley, J.J.; Rocher, A.B.; Janssen, W.G.; Hof, P.R.; McEwen, B.S.; Morrison, J.H. Reversibility of apical dendritic retraction in the rat medial prefrontal cortex following repeated stress. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 196, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, R.; Koziell, D.A.; Lindsey, J.D.; Moore, R.Y. Noradrenergic innervation of the adult rat hippocampal formation. J. Comp. Neurol. 1980, 189, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, N.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Hippocampal long-term potentiation that is elicited by perforant path stimulation or that occurs in conjunction with spatial learning is tightly controlled by beta-adrenoreceptors and the locus coeruleus. Hippocampus 2015, 25, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, D.G.; Foss, J.A. Locus coeruleus lesions and learning. Science 1975, 188, 377–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coradazzi, M.; Gulino, R.; Fieramosca, F.; Falzacappa, L.V.; Riggi, M.; Leanza, G. Selective noradrenaline depletion impairs working memory and hippocampal neurogenesis. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 48, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, C. Noradrenergic and locus coeruleus modulation of the perforant path-evoked potential in rat dentate gyrus supports a role for the locus coeruleus in attentional and memorial processes. Prog. Brain Res. 1991, 88, 307–321. [Google Scholar]
- Lemon, N.; Aydin-Abidin, S.; Funke, K.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Locus coeruleus activation facilitates memory encoding and induces hippocampal LTD that depends on beta-adrenergic receptor activation. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 2827–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devauges, V.; Sara, S.J. Memory retrieval enhancement by locus coeruleus stimulation: Evidence for mediation by beta-receptors. Behav. Brain Res. 1991, 43, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, N.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Locus Coeruleus Stimulation Facilitates Long-Term Depression in the Dentate Gyrus That Requires Activation of β-Adrenergic Receptors. Cereb. Cortex 2015, 25, 1889–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babushkina, N.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Frequency-dependency of the involvement of dopamine D1/D5 and beta-adrenergic receptors in hippocampal LTD triggered by locus coeruleus stimulation. Hippocampus 2022, 32, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempadoo, K.A.; Mosharov, E.V.; Choi, S.J.; Sulzer, D.; Kandel, E.R. Dopamine release from the locus coeruleus to the dorsal hippocampus promotes spatial learning and memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14835–14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsetsenis, T.; Badyna, J.K.; Li, R.; Dani, J.A. Activation of a Locus Coeruleus to Dorsal Hippocampus Noradrenergic Circuit Facilitates Associative Learning. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 887679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ul Haq, R.; Anderson, M.; Liotta, A.; Shafiq, M.; Sherkheli, M.A.; Heinemann, U. Pretreatment with β-adrenergic receptor agonists facilitates induction of LTP and sharp wave ripple complexes in rodent hippocampus. Hippocampus 2016, 26, 1486–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.P.; Tan, C.H.; Jay, T.M.; Dawe, G.S. Locus coeruleus stimulation and noradrenergic modulation of hippocampo-prefrontal cortex long-term potentiation. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 13, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, M.J.; Kulesza, A.; Werkle-Bergner, M.; Mather, M. Declining locus coeruleus-dopaminergic and noradrenergic modulation of long-term memory in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 153, 105358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaouane, N.; Porte, Y.; Vallée, M.; Brayda-Bruno, L.; Mons, N.; Calandreau, L.; Marighetto, A.; Piazza, P.V.; Desmedt, A. Glucocorticoids can induce PTSD-like memory impairments in mice. Science 2012, 335, 1510–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, J.G.; Siuda, E.R.; Bhatti, D.L.; Lawson, L.A.; McElligott, Z.A.; Stuber, G.D.; Bruchas, M.R. Locus coeruleus to basolateral amygdala noradrenergic projections promote anxiety-like behavior. eLife 2017, 6, e18247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fast, C.D.; McGann, J.P. Amygdalar Gating of Early Sensory Processing through Interactions with Locus Coeruleus. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 3085–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorca-Torralba, M.; Suárez-Pereira, I.; Bravo, L.; Camarena-Delgado, C.; Garcia-Partida, J.A.; Mico, J.A.; Berrocoso, E. Chemogenetic Silencing of the Locus Coeruleus-Basolateral Amygdala Pathway Abolishes Pain-Induced Anxiety and Enhanced Aversive Learning in Rats. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Cai, Z.; Lei, C.; Guo, X.; Cui, D.; Yuan, Y.; Lai, B.; Zheng, P. Inputs from paraventricular nucleus of thalamus and locus coeruleus contribute to the activation of central nucleus of amygdala during context-induced retrieval of morphine withdrawal memory. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 338, 113600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubrich, J.; Bernabo, M.; Nader, K. Noradrenergic projections from the locus coeruleus to the amygdala constrain fear memory reconsolidation. eLife 2020, 9, e57010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromer, L.F.; Moore, R.Y. A study of the organization of the locus coeruleus projections to the lateral geniculate nuclei in the albino rat. Neuroscience 1980, 5, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogawski, M.A.; Aghajanian, G.K. Modulation of lateral geniculate neurone excitability by noradrenaline microiontophoresis or locus coeruleus stimulation. Nature 1980, 287, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayama, Y.; Negi, T.; Sugitani, M.; Iwama, K. Effects of locus coeruleus stimulation on neuronal activities of dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus and perigeniculate reticular nucleus of the rat. Neuroscience 1982, 7, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogawski, M.A.; Aghajanian, G.K. Activation of lateral geniculate neurons by norepinephrine: Mediation by an alpha-adrenergic receptor. Brain Res. 1980, 182, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Xu, H. Application of quinpirole in the paraventricular thalamus facilitates emergence from isoflurane anesthesia in mice. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e01903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooiker, C.L.; Birnie, M.T.; Baram, T.Z. The Paraventricular Thalamus: A Potential Sensor and Integrator of Emotionally Salient Early-Life Experiences. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 673162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, C.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X.; Xing, D.; Xu, H. Locus Coeruleus to Paraventricular Thalamus Projections Facilitate Emergence from Isoflurane Anesthesia in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beas, B.S.; Wright, B.J.; Skirzewski, M.; Leng, Y.; Hyun, J.H.; Koita, O.; Ringelberg, N.; Kwon, H.B.; Buonanno, A.; Penzo, M.A. The locus coeruleus drives disinhibition in the midline thalamus via a dopaminergic mechanism. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Carrión, O.; Stamelou, M.; Murillo-Rodríguez, E.; Menéndez-González, M.; Pöppel, E. Dopaminergic reward system: A short integrative review. Int. Arch. Med. 2010, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isingrini, E.; Perret, L.; Rainer, Q.; Amilhon, B.; Guma, E.; Tanti, A.; Martin, G.; Robinson, J.; Moquin, L.; Marti, F.; et al. Resilience to chronic stress is mediated by noradrenergic regulation of dopamine neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chaudhury, D.; Nectow, A.R.; Friedman, A.K.; Zhang, S.; Juarez, B.; Liu, H.; Pfau, M.L.; Aleyasin, H.; Jiang, C.; et al. α(1)- and β(3)-Adrenergic Receptor-Mediated Mesolimbic Homeostatic Plasticity Confers Resilience to Social Stress in Susceptible Mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradel, K.; Blasiak, T.; Solecki, W.B. Adrenergic Receptor Agonists’ Modulation of Dopaminergic and Non-dopaminergic Neurons in the Ventral Tegmental Area. Neuroscience 2018, 375, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenhoff, J.; Nisell, M.; Ferré, S.; Aston-Jones, G.; Svensson, T.H. Noradrenergic modulation of midbrain dopamine cell firing elicited by stimulation of the locus coeruleus in the rat. J. Neural Transm. Gen. Sect. 1993, 93, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, C.A.; Williams, J.T. Noradrenergic inhibition of midbrain dopamine neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 4568–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, G.F.; Volkow, N.D. Neurobiology of addiction: A neurocircuitry analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solecki, W.B.; Kielbinski, M.; Wilczkowski, M.; Zajda, K.; Karwowska, K.; Joanna, B.; Rajfur, Z.; Przewłocki, R. Regulation of cocaine seeking behavior by locus coeruleus noradrenergic activity in the ventral tegmental area is time- and contingency-dependent. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 967969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, P.; Wang, Y.; Vit, J.P.; Novinbakht, E.; Morones, N.; Hogg, E.; Tagliati, M.; Riera, C.E. Sustained chemogenetic activation of locus coeruleus norepinephrine neurons promotes dopaminergic neuron survival in synucleinopathy. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, M.; Parent, A. Substantia nigra and Parkinson’s disease: A brief history of their long and intimate relationship. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 37, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.I.; Qiu, D.; Zhao, L.; Hu, W.T.; Duong, D.M.; Higginbotham, L.; Dammer, E.B.; Seyfried, N.T.; Wingo, T.S.; Hales, C.M.; et al. A phase II study repurposing atomoxetine for neuroprotection in mild cognitive impairment. Brain J. Neurol. 2022, 145, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondetti, E.; Gaurav, R.; Yahia-Cherif, L.; Mangone, G.; Pyatigorskaya, N.; Valabrègue, R.; Ewenczyk, C.; Hutchison, M.; François, C.; Arnulf, I.; et al. Spatiotemporal changes in substantia nigra neuromelanin content in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2020, 143, 2757–2770, Erratum in Brain 2020, 144, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.S.; Biagioni, F.; Galgani, A.; Pavese, N.; Lazzeri, G.; Fornai, F. Locus Coeruleus Modulates Neuroinflammation in Parkinsonism and Dementia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinstroop, E.; Cano, G.; Vanderhorst, V.G.; Cavalcante, J.C.; Wirth, J.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Saper, C.B. Spinal projections of the A5, A6 (locus coeruleus), and A7 noradrenergic cell groups in rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 520, 1985–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Obata, H.; Iriuchijima, N.; Saito, S. An increase in spinal cord noradrenaline is a major contributor to the antihyperalgesic effect of antidepressants after peripheral nerve injury in the rat. Pain 2012, 153, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertovaara, A.; Wei, H.; Hämäläinen, M.M. Lidocaine in the rostroventromedial medulla and the periaqueductal gray attenuates allodynia in neuropathic rats. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 218, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Heinricher, M.M. Plasticity in the Link between Pain-Transmitting and Pain-Modulating Systems in Acute and Persistent Inflammation. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 2065–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, P.; Pan, C.; Deng, H.; Xu, S.; Tang, D.; Xiao, J.; Jiao, Y.; Yu, W.; et al. The locus coeruleus input to the rostral ventromedial medulla mediates stress-induced colorectal visceral pain. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbe, H.; Kimura, A. Repeated forced swim stress affects the expression of pCREB and ΔFosB and the acetylation of histone H3 in the rostral ventromedial medulla and locus coeruleus. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 127, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aston-Jones, G.; Waterhouse, B. Locus coeruleus: From global projection system to adaptive regulation of behavior. Brain Res. 2016, 1645, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheun, J.E.; Yeh, H.H. Modulation of GABAA receptor-activated current by norepinephrine in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuroscience 1992, 51, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheun, J.E.; Yeh, H.H. Noradrenergic potentiation of cerebellar Purkinje cell responses to GABA: Cyclic AMP as intracellular intermediary. Neuroscience 1996, 74, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moises, H.C.; Waterhouse, B.D.; Woodward, D.J. Locus coeruleus stimulation potentiates Purkinje cell responses to afferent input: The climbing fiber system. Brain Res. 1981, 222, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickford, P.C.; Hoffer, B.J.; Freedman, R. Interaction of norepinephrine with Purkinje cell responses to cerebellar afferent inputs in aged rats. Neurobiol. Aging 1985, 6, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, A.T.; Post, M.R.; Lacefield, C.; Sulzer, D.; Miniaci, M.C. Norepinephrine release in the cerebellum contributes to aversive learning. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorca-Torralba, M.; Borges, G.; Neto, F.; Mico, J.A.; Berrocoso, E. Noradrenergic Locus Coeruleus pathways in pain modulation. Neuroscience 2016, 338, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Micheli, L.; Crocetti, L.; Giovannoni, M.P.; Vergelli, C.; Ghelardini, C. α2 Adrenoceptor: A Target for Neuropathic Pain Treatment. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zou, H.; Ma, L.; Liu, C.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, X.; Tan, X.; Yu, T.; et al. Activation of locus coeruleus-spinal cordnoradrenergic neurons alleviates neuropathic pain in mice via reducing neuroinflammation from astrocytes and microglia in spinal dorsal horn. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, L.; Li, Y.; Fyson, S.J.; Watson, T.C.; Perrins, R.; Hewinson, J.; Teschemacher, A.G.; Furue, H.; Lumb, B.M.; Pickering, A.E. Optoactivation of locus ceruleus neurons evokes bidirectional changes in thermal nociception in rats. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 4148–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drolet, G.; Van Bockstaele, E.J.; Aston-Jones, G. Robust enkephalin innervation of the locus coeruleus from the rostral medulla. J. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 3162–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, M.; Aston-Jones, G. Two physiologically distinct populations of neurons in the ventrolateral medulla innervate the locus coeruleus. Brain Res. 1987, 425, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, R.J.; Page, M.; Van Bockstaele, E.; Aston-Jones, G. Corticotropin-releasing factor innervation of the locus coeruleus region: Distribution of fibers and sources of input. Neuroscience 1992, 48, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieribone, V.A.; Aston-Jones, G.; Bohn, M.C. Adrenergic and non-adrenergic neurons in the C1 and C3 areas project to locus coeruleus: A fluorescent double labeling study. Neurosci. Lett. 1988, 85, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bockstaele, E.J.; Colago, E.E.; Aicher, S. Light and electron microscopic evidence for topographic and monosynaptic projections from neurons in the ventral medulla to noradrenergic dendrites in the rat locus coeruleus. Brain Res. 1998, 784, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennis, M.; Aston-Jones, G.; Shiekhattar, R. Activation of locus coeruleus neurons by nucleus paragigantocellularis or noxious sensory stimulation is mediated by intracoerulear excitatory amino acid neurotransmission. Brain Res. 1992, 598, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennis, M.; Aston-Jones, G. Activation of locus coeruleus from nucleus paragigantocellularis: A new excitatory amino acid pathway in brain. J. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 3644–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aston-Jones, G.; Astier, B.; Ennis, M. Inhibition of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons by C1 adrenergic cells in the rostral ventral medulla. Neuroscience 1992, 48, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello-Carpes, P.B.; Izquierdo, I. The Nucleus of the Solitary Tract → Nucleus Paragigantocellularis → Locus Coeruleus → CA1 region of dorsal hippocampus pathway is important for consolidation of object recognition memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2013, 100, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, B.A.S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Dufourt, E.C.; Bhatnagar, S.; Valentino, R.J.; Van Bockstaele, E.J. Neurochemically distinct circuitry regulates locus coeruleus activity during female social stress depending on coping style. Brain Struct. Funct. 2019, 224, 1429–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, B.A.; Zitnik, G.; Foster, C.; Van Bockstaele, E.J.; Valentino, R.J. Social Stress Engages Neurochemically-Distinct Afferents to the Rat Locus Coeruleus Depending on Coping Strategy. eNeuro. 2015, 2, ENEURO.0042-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouarab, C.; Thompson, B.; Polter, A.M. VTA GABA Neurons at the Interface of Stress and Reward. Front. Neural Circuits 2019, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, E.B.; Toy, B.; Himmels, P.; Morales, M.; Fields, H.L. Identification of rat ventral tegmental area GABAergic neurons. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutch, A.Y.; Goldstein, M.; Roth, R.H. Activation of the locus coeruleus induced by selective stimulation of the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res. 1986, 363, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, S.M.; Chowdhury, S.; Mukai, Y.; Ono, D.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yamanaka, A. Functional Interaction Between GABAergic Neurons in the Ventral Tegmental Area and Serotonergic Neurons in the Dorsal Raphe Nucleus. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 877054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deurveilher, S.; Semba, K. Indirect projections from the suprachiasmatic nucleus to major arousal-promoting cell groups in rat: Implications for the circadian control of behavioural state. Neuroscience 2005, 130, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legoratti-Sánchez, M.O.; Guevara-Guzmán, R.; Solano-Flores, L.P. Electrophysiological evidences of a bidirectional communication between the locus coeruleus and the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res. Bull. 1989, 23, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aston-Jones, G.; Chen, S.; Zhu, Y.; Oshinsky, M.L. A neural circuit for circadian regulation of arousal. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, V.A.; Gebhart, G.F. Evaluation of the periaqueductal central gray (PAG) as a morphine-specific locus of action and examination of morphine-induced and stimulation-produced analgesia at coincident PAG loci. Brain Res. 1977, 124, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, M.A.; Waterhouse, B.D. Retrograde double-labeling study of common afferent projections to the dorsal raphe and the nuclear core of the locus coeruleus in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 481, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Gangadharan, G.; Byun, J.; Choi, E.J.; Lee, C.J.; Shin, H.S. Yin-and-yang bifurcation of opioidergic circuits for descending analgesia at the midbrain of the mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11078–11083, Erratum in Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Franco, L.; González-García, M.; Morales-Luque, C.; Dawid-Milner, M.S.; López-González, M.V. Hypothalamic Regulation of Cardiorespiratory Functions: Insights into the Dorsomedial and Perifornical Pathways. Biology 2024, 13, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, I.; González-García, M.; Carrillo-Franco, L.; Dawid-Milner, M.S.; López-González, M.V. Influence of Brainstem’s Area A5 on Sympathetic Outflow and Cardiorespiratory Dynamics. Biology 2024, 13, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bockstaele, E.J.; Chan, J.; Pickel, V.M. Input from central nucleus of the amygdala efferents to pericoerulear dendrites, some of which contain tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity. J. Neurosci. Res. 1996, 45, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bockstaele, E.J.; Peoples, J.; Valentino, R.J. Anatomic basis for differential regulation of the rostrolateral peri-locus coeruleus region by limbic afferents. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 46, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassell, M.D.; Freedman, L.J.; Shi, C. The intrinsic organization of the central extended amygdala. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 877, 217–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmond, D.E., Jr.; Huang, Y.H. Current concepts. II. New Evid. A Locus Coeruleus-Norepinephrine Connect. anxiety. Life Sci. 1979, 25, 2149–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, J.G.; Al-Hasani, R.; Siuda, E.R.; Hong, D.Y.; Norris, A.J.; Ford, C.P.; Bruchas, M.R. CRH Engagement of the Locus Coeruleus Noradrenergic System Mediates Stress-Induced Anxiety. Neuron 2015, 87, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paretkar, T.; Dimitrov, E. The Central Amygdala Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) Neurons Modulation of Anxiety-like Behavior and Hippocampus-dependent Memory in Mice. Neuroscience 2018, 390, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.Y.; Stohler, C.S.; Herr, D.R. Role of the Prefrontal Cortex in Pain Processing. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 1137–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKlveen, J.M.; Myers, B.; Herman, J.P. The medial prefrontal cortex: Coordinator of autonomic, neuroendocrine and behavioural responses to stress. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 27, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eden, C.G.; Buijs, R.M. Functional neuroanatomy of the prefrontal cortex: Autonomic interactions. Prog. Brain Res. 2000, 126, 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Jodo, E.; Chiang, C.; Aston-Jones, G. Potent excitatory influence of prefrontal cortex activity on noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons. Neuroscience 1998, 83, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sara, S.J.; Hervé-Minvielle, A. Inhibitory influence of frontal cortex on locus coeruleus neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 6032–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, A.; Papadogiannis, A.; Dimitrov, E. The role of medial prefrontal cortex projections to locus ceruleus in mediating the sex differences in behavior in mice with inflammatory pain. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, B.A.; Valentino, R.J.; Xu, G.; Van Bockstaele, E.J. Hypothalamic projections to locus coeruleus neurons in rat brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, I.; Seki, Y.; Nakatani, Y.; Fumoto, M.; Oguri, M.; Sato-Suzuki, I.; Arita, H. Corticotropin-releasing factor neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus are involved in arousal/yawning response of rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2006, 169, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devilbiss, D.M. Consequences of tuning network function by tonic and phasic locus coeruleus output and stress: Regulating detection and discrimination of peripheral stimuli. Brain Res. 2019, 1709, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, K.; Wang, W.W.; Han, R.; McFadden, K.; Valentino, R.J. Corticotropin-releasing factor in the norepinephrine nucleus, locus coeruleus, facilitates behavioral flexibility. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bockstaele, E.J.; Reyes, B.A.; Valentino, R.J. The locus coeruleus: A key nucleus where stress and opioids intersect to mediate vulnerability to opiate abuse. Brain Res. 2010, 1314, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enman, N.M.; Reyes, B.A.S.; Shi, Y.; Valentino, R.J.; Van Bockstaele, E.J. Sex differences in morphine-induced trafficking of mu-opioid and corticotropin-releasing factor receptors in locus coeruleus neurons. Brain Res. 2019, 1706, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, A.M.; McElligott, Z.A. Noradrenergic circuits and signaling in substance use disorders. Neuropharmacology 2022, 208, 108997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.L.; Lechner, S.M.; Pavcovich, L.A.; Valentino, R.J. Activation of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system by intracoerulear microinfusion of corticotropin-releasing factor: Effects on discharge rate, cortical norepinephrine levels and cortical electroencephalographic activity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 281, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, R.J.; Wehby, R.G. Corticotropin-releasing factor: Evidence for a neurotransmitter role in the locus ceruleus during hemodynamic stress. Neuroendocrinology 1988, 48, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedema, H.P.; Grace, A.A. Corticotropin-releasing hormone directly activates noradrenergic neurons of the locus ceruleus recorded in vitro. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 9703–9713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.T.; Egan, T.M.; North, R.A. Enkephalin opens potassium channels on mammalian central neurones. Nature 1982, 299, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecilla, M.; Quillinan, N.; Williams, J.T.; Wickman, K. Pre- and postsynaptic regulation of locus coeruleus neurons after chronic morphine treatment: A study of GIRK-knockout mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecilla, M.; Marker, C.L.; Cintora, S.C.; Stoffel, M.; Williams, J.T.; Wickman, K. G-protein-gated potassium channels containing Kir3.2 and Kir3.3 subunits mediate the acute inhibitory effects of opioids on locus ceruleus neurons. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 4328–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Aghajanian, G.K. Excitation of locus coeruleus neurons by an adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate-activated inward current: Extracellular and intracellular studies in rat brain slices. Synapse 1987, 1, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alreja, M.; Aghajanian, G.K. Opiates suppress a resting sodium-dependent inward current and activate an outward potassium current in locus coeruleus neurons. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 3525–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alreja, M.; Aghajanian, G.K. QX-314 blocks the potassium but not the sodium-dependent component of the opiate response in locus coeruleus neurons. Brain Res. 1994, 639, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, R.S.; Tallman, J.F.; Nestler, E.J. Acute and chronic opiate-regulation of adenylate cyclase in brain: Specific effects in locus coeruleus. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1988, 246, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazei-Robison, M.S.; Nestler, E.J. Opiate-induced molecular and cellular plasticity of ventral tegmental area and locus coeruleus catecholamine neurons. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a012070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.L.; Vialou, V.F.; Lobo, M.K.; Robison, A.J.; Neve, R.L.; Cooper, D.C.; Nestler, E.J.; Han, M.H. Essential role of the cAMP-cAMP response-element binding protein pathway in opiate-induced homeostatic adaptations of locus coeruleus neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17011–17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.H.; Bolaños, C.A.; Green, T.A.; Olson, V.G.; Neve, R.L.; Liu, R.J.; Aghajanian, G.K.; Nestler, E.J. Role of cAMP response element-binding protein in the rat locus ceruleus: Regulation of neuronal activity and opiate withdrawal behaviors. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 4624–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Ahmadi Soleimani, S.; Azizi, H.; Pachenari, N.; Mirnajafi-Zadeh, J.; Semnanian, S. Enhancement of μ-opioid receptor desensitization by orexin-A in rat locus coeruleus neurons. Neuropeptides 2017, 63, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, M.R.K.; Kuo, C.C.; Kim, J.R.; Dunn, S.S.; Borges, G.; Thang, L.V.; McCall, J.G. Endogenous opioids gate the locus coeruleus pain generator. bioRxiv Prepr. Serv. Biol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, B.A.; Johnson, A.D.; Glaser, J.D.; Commons, K.G.; Van Bockstaele, E.J. Dynorphin-containing axons directly innervate noradrenergic neurons in the rat nucleus locus coeruleus. Neuroscience 2007, 145, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, B.A.; Drolet, G.; Van Bockstaele, E.J. Dynorphin and stress-related peptides in rat locus coeruleus: Contribution of amygdalar efferents. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 508, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, J.; Van Bockstaele, E.J. Vesicular glutamate transporter-1 colocalizes with endogenous opioid peptides in axon terminals of the rat locus coeruleus. Anat. record. Part A Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 2005, 284, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnock, R.D. A highly selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist, CI-977, reduces excitatory synaptic potentials in the rat locus coeruleus in vitro. Neuroscience 1992, 47, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreibich, A.; Reyes, B.A.; Curtis, A.L.; Ecke, L.; Chavkin, C.; Van Bockstaele, E.J.; Valentino, R.J. Presynaptic inhibition of diverse afferents to the locus ceruleus by kappa-opiate receptors: A novel mechanism for regulating the central norepinephrine system. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 6516–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, D.E., Jr.; Huang, Y.H. The primate locus coeruleus and effects of clonidine on opiate withdrawal. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1982, 43 Pt 2, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, Y.S.; Adrian, T.E.; Allen, J.M.; Tatemoto, K.; Crow, T.J.; Bloom, S.R.; Polak, J.M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science 1983, 221, 877–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Yan, J.; Liu, Q.; Ou, C.; Chen, M. A Promising Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Diseases: Neuropeptide Y Receptors in Humans. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larhammar, D.; Salaneck, E. Molecular evolution of NPY receptor subtypes. Neuropeptides 2004, 38, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedragosa-Badia, X.; Stichel, J.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Neuropeptide Y receptors: How to get subtype selectivity. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, M.C.; Beck-Sickinger, A.; Cox, H.; Doods, H.N.; Herzog, H.; Larhammar, D.; Quirion, R.; Schwartz, T.; Westfall, T. XVI. International Union of Pharmacology recommendations for the nomenclature of neuropeptide Y, peptide YY, and pancreatic polypeptide receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1998, 50, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrele, C.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Molecular characterization of the ligand-receptor interaction of the neuropeptide Y family. J. Pept. Sci. Off. Publ. Eur. Pept. Soc. 2000, 6, 97–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Murthy, K.S.; Zhou, H.; Grider, J.R. Coexpression of Y1, Y2, and Y4 receptors in smooth muscle coupled to distinct signaling pathways. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 311, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B.J.; Hökfelt, T.; Terenius, L.; Tatemoto, K.; Mutt, V.; Goldstein, M. Differential co-existence of neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity with catecholamines in the central nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience 1984, 11, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.S. Retrograde study of CART- or NPY-neuronal projection from the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus to the dorsal raphe and/or the locus coeruleus in the rat. Brain Res. 2013, 1519, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramia, M.; Romanov, R.A.; Sideromenos, S.; Hevesi, Z.; Zhao, M.; Krasniakova, M.; Xu, Z.D.; Harkany, T.; Hökfelt, T.G.M. Neuronal diversity of neuropeptide signaling, including galanin, in the mouse locus coeruleus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2222095120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitnik, G.A. Control of arousal through neuropeptide afferents of the locus coeruleus. Brain Res. 2016, 1641 Pt B, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enman, N.M.; Sabban, E.L.; McGonigle, P.; Van Bockstaele, E.J. Targeting the Neuropeptide Y System in Stress-related Psychiatric Disorders. Neurobiol. Stress 2015, 1, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, R.; Ekhator, N.N.; Jefferson-Wilson, L.; Horn, P.S.; Geracioti, T.D., Jr. Cerebrospinal fluid neuropeptide Y in combat veterans with and without posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehuda, R.; Brand, S.; Yang, R.K. Plasma neuropeptide Y concentrations in combat exposed veterans: Relationship to trauma exposure, recovery from PTSD, and coping. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barde, S.; Aguila, J.; Zhong, W.; Solarz, A.; Mei, I.; Prud’homme, J.; Palkovits, M.; Turecki, G.; Mulder, J.; Uhlén, M.; et al. NPY, CCK and their receptors in five brain regions in major depressive disorder with transcriptomic analysis of locus coeruleus neurons. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024, 78, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kask, A.; Rägo, L.; Harro, J. Anxiolytic-like effect of neuropeptide Y (NPY) and NPY13-36 microinjected into vicinity of locus coeruleus in rats. Brain Res. 1998, 788, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serova, L.I.; Tillinger, A.; Alaluf, L.G.; Laukova, M.; Keegan, K.; Sabban, E.L. Single intranasal neuropeptide Y infusion attenuates development of PTSD-like symptoms to traumatic stress in rats. Neuroscience 2013, 236, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabban, E.L.; Laukova, M.; Alaluf, L.G.; Olsson, E.; Serova, L.I. Locus coeruleus response to single-prolonged stress and early intervention with intranasal neuropeptide Y. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
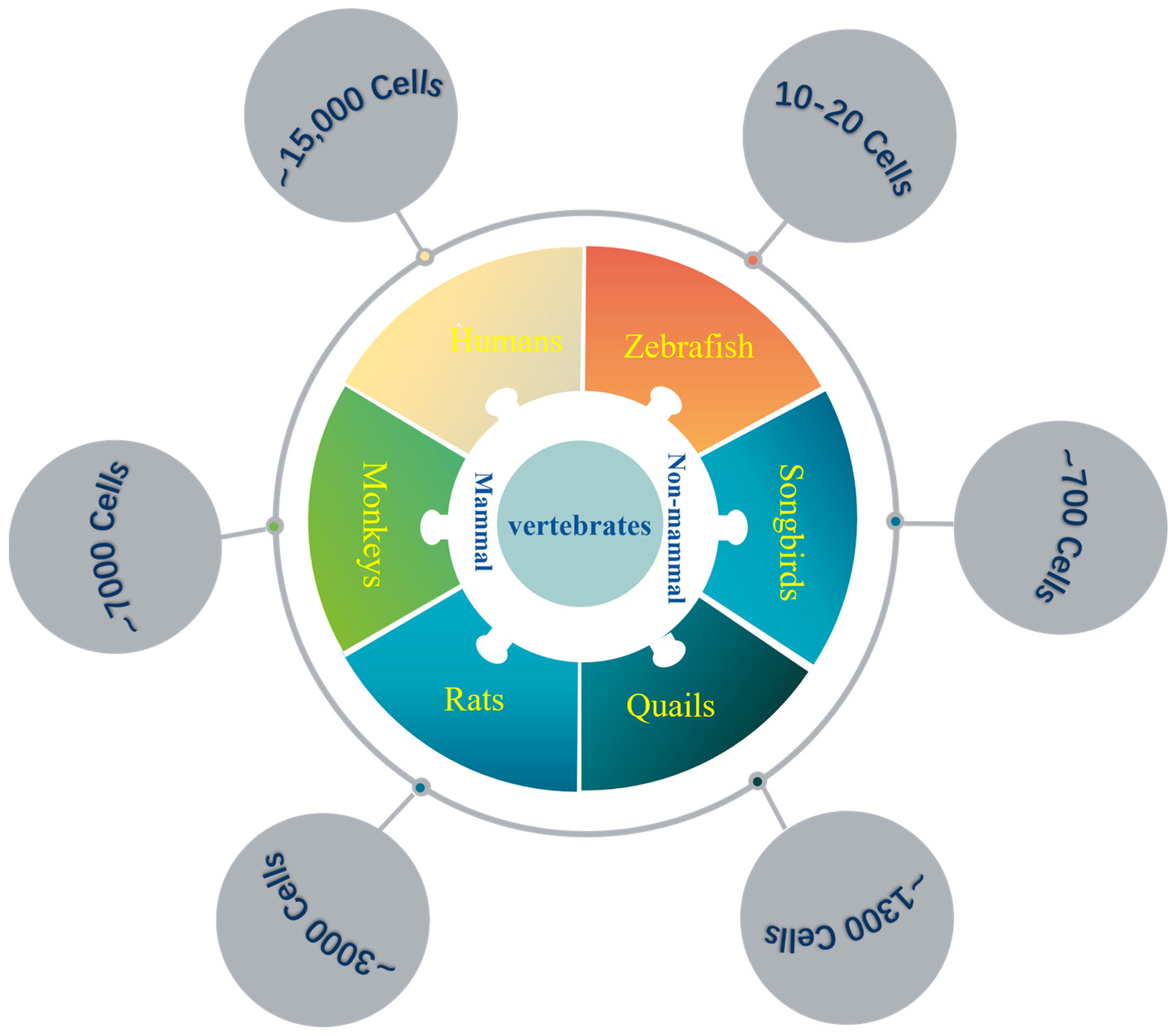
| Vertebrates | LC Neurons | Brain Neurons (×106) | Ratio (×10−6) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zebrafish | ~10−20 | ~0.1 | ~100–200 |
| Songbirds | ~700 | ~2171 (Raven) | ~0.32 |
| Rats | ~3000 | ~200 | ~15 |
| Monkeys | ~7000 | ~6391 (Rhesus) | ~1.09 |
| Humans | ~15,000 | ~86,060 | ~0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, M.; Li, F.; Duan, J.-W.; Han, M.-H. Neural Circuit Connections and Functions of Locus Coeruleus–Norepinephrine System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211163
Hao M, Li F, Duan J-W, Han M-H. Neural Circuit Connections and Functions of Locus Coeruleus–Norepinephrine System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211163
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Mei, Fang Li, Jia-Wen Duan, and Ming-Hu Han. 2025. "Neural Circuit Connections and Functions of Locus Coeruleus–Norepinephrine System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211163
APA StyleHao, M., Li, F., Duan, J.-W., & Han, M.-H. (2025). Neural Circuit Connections and Functions of Locus Coeruleus–Norepinephrine System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211163





