Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Transcriptional Regulator ZEB1 in Liver Cancer: Oncogenic Roles and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
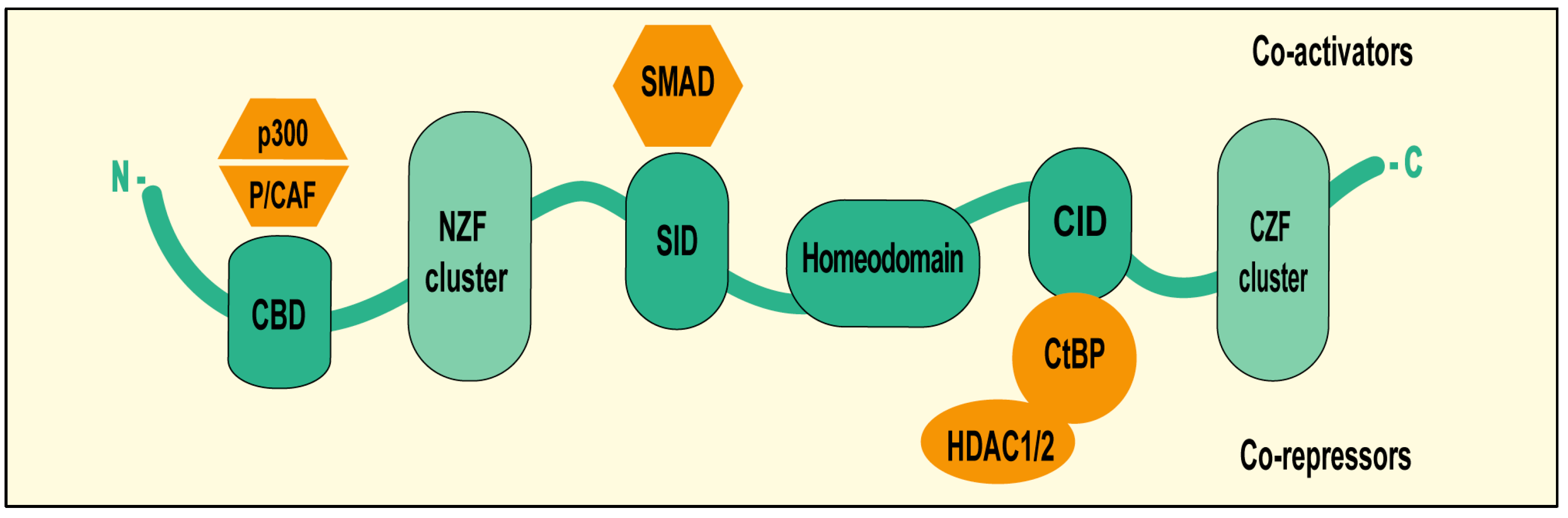
2. ZEB1 Structural Features and Functional Domains
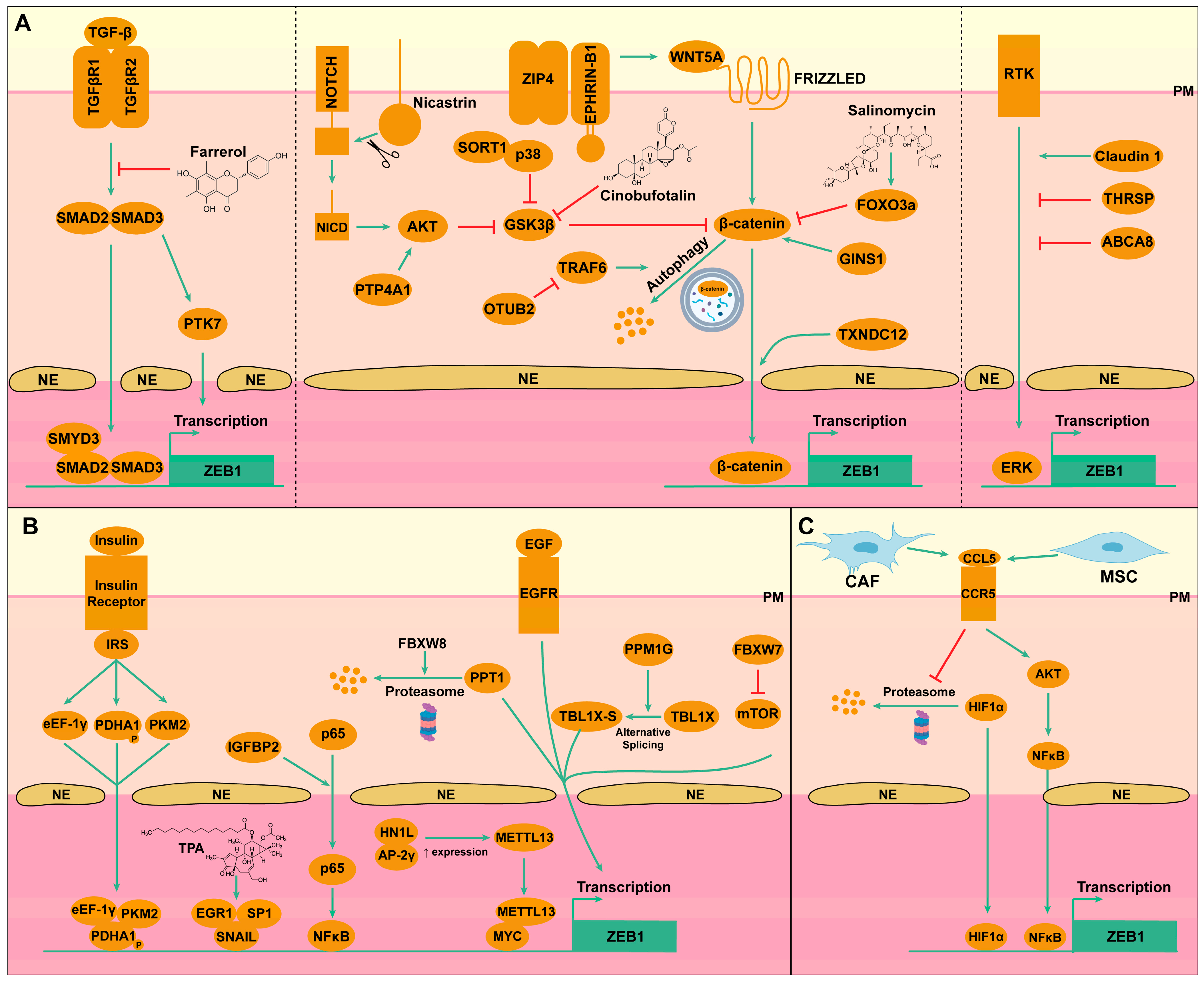
3. Regulation of ZEB1 Expression in Liver Cancer
3.1. Transcriptional Regulation
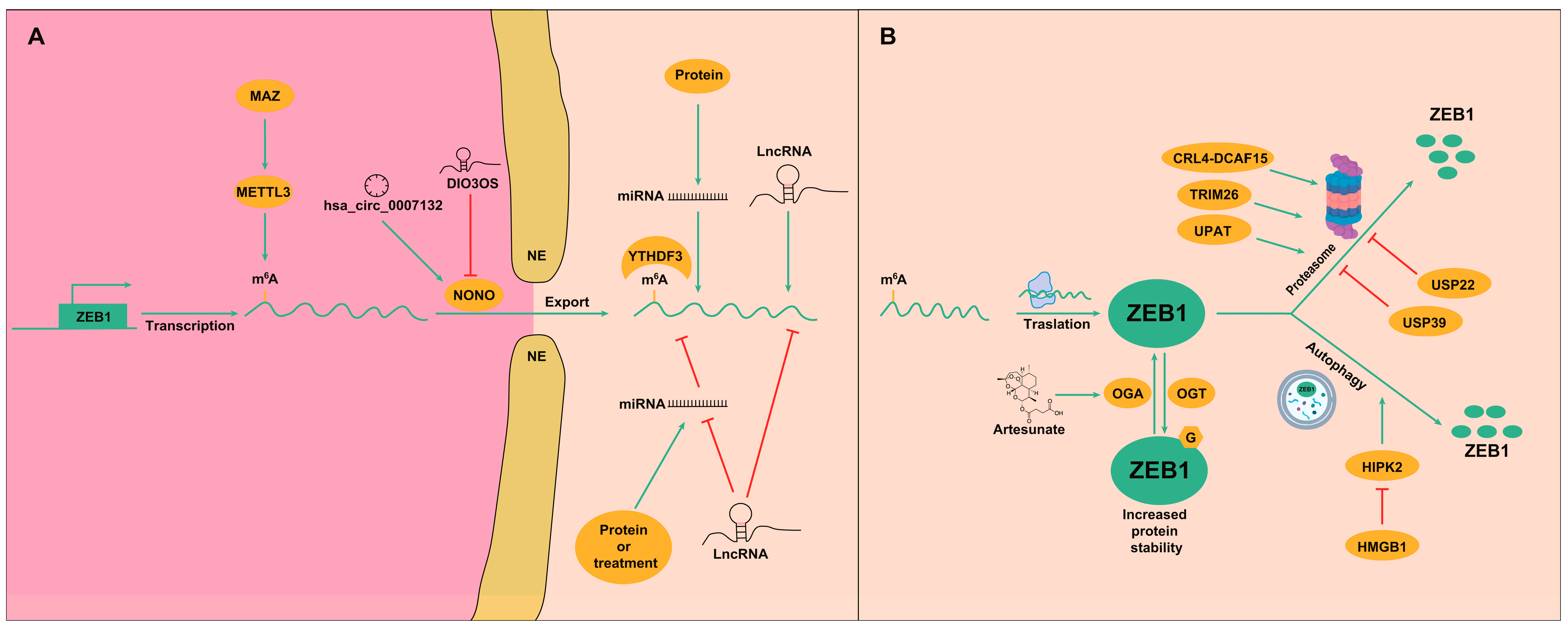
3.2. Post-Transcriptional Regulation
3.3. Post-Translational Regulation
| Tumor | Factor | Regulates | miRNA | Regulates | Factor | Result | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC | Lnc-RP11-422N16.3 | Negatively | miR-23b-3p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [62] |
| HCC | LncRNA-SNHG6 | Negatively | miR-101-3p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [63] |
| HCC | - | - | miR-139-5p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↓ ZEB1 | [64] |
| HCC | LncRNA-TUG1 | Negatively | miR-142-3p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [65] |
| HCC | Lnc-MALAT1 | Negatively | miR-143-3p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [66] |
| HCC | circ-100338 | Negatively | miR-143-3p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [67] |
| HCC | ELF3 | Negatively | miR-141-3p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [68] |
| HCC | ATRA | Positively | miR-141-3p miR-200a-3p miR-200c-3p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↓ ZEB1 | [69] |
| HCC | LncRNA-ZFAS1 | Negatively | miR-150 | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [70] |
| HCC | TGF-β | Positively | miR-155 | Positively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [71] |
| HCC | LncRNE-PE | Negatively | miR-200a miR-200b | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [72] |
| HCC | Gα12 | Negatively | miR-200a miR-200b | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [73] |
| CCA | Lnc-ZEB1-AS1 | Negatively | miR-200a | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [74] |
| HCC | Lnc-HULC | Negatively | miR-200a-3p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [75] |
| HCC | Genomic deletion, promoter methylation | Negatively | miR-200b | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [76] |
| HCC | Lnc-CARLo-5 | Negatively | miR-200b | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [77] |
| HCC | KLF4 | Positively | miR-200b | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↓ ZEB1 | [78] |
| HCC | YB1 | Negatively | miR-200b miR-205 | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [79] |
| HCC | LncRNA-XIST | Negatively | miR-200b-3p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [80] |
| CCA | - | - | miR-200c | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↓ ZEB1 | [81] |
| CCA | Lnc-ATB | Negatively | miR-200c | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [82] |
| HCC | p53 | Positively | miR-200 | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↓ ZEB1 | [54] |
| HCC | LncRNA-ATB | Negatively | miR-200 | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [53] |
| HCC | LINC00273 | Negatively | miR-200 | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [83] |
| CCA | Lnc-NNT-AS1 | Negatively | miR-203 | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [84] |
| HCC | Lnc-SNHG3 | Negatively | miR-326 | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [85] |
| HCC | - | - | miR-369 | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↓ ZEB1 | [86] |
| HCC | LncRNA-PRNCR1 | Negatively | miR-411-3p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [87] |
| HCC | Lnc-MAPKAPK5 | Negatively | miR-429 | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [88] |
| CCA | DMY | Positively | miR-455-3p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↓ ZEB1 | [89] |
| HCC | - | - | miR-590-3p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↓ ZEB1 | [90] |
| HCC | - | - | miR-708 | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↓ ZEB1 | [91] |
| HCC | Lnc171 | Negatively | miR-873-5p | Negatively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [43] |
| HCC | Lnc-HCCL5 | - | - | Positively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [92] |
| HCC | LncPNUTS | - | - | Positively | ZEB1 | ↑ ZEB1 | [93] |
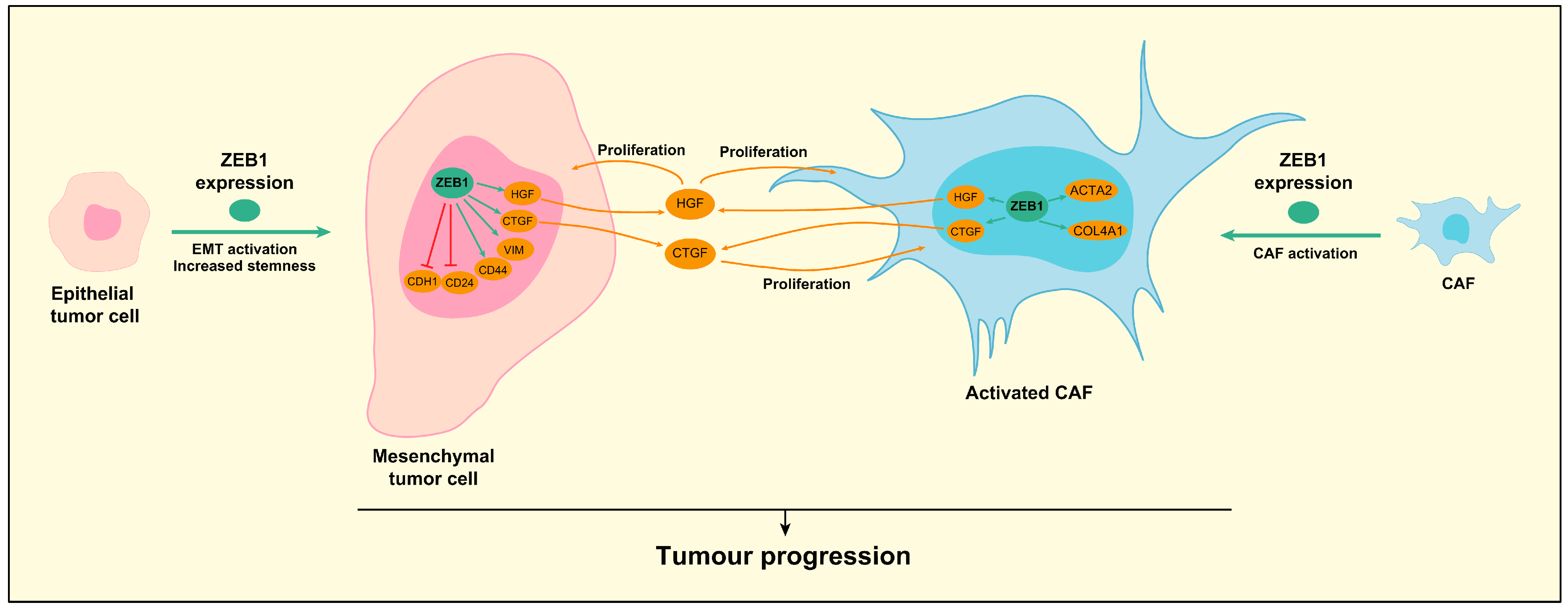
4. Role of ZEB1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
5. Role of ZEB1 in Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA)
6. Future Perspectives and Therapeutic Opportunities
6.1. Chemical Compounds
6.2. Neutralizing Antibodies
6.3. miRNAs
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCA8 | ATP binding cassette subfamily A member 8 |
| ACTA2 | Actin alpha 2, smooth muscle |
| ADM | Adrenomedullin |
| AKT | AKT serine/threonine kinase |
| AP-2γ | Activator Protein-2 gamma |
| AXL | AXL receptor tyrosine kinase |
| CAF | Cancer-associated fibroblasts |
| CAPZA1 | F-actin-capping protein subunit alpha-1 |
| CBD | P300-P/CBP-associated factor (P/CAF) binding domain |
| CBX6 | Chromobox 6 |
| CCA | Cholangiocarcinoma |
| CCL5 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 |
| CCR5 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 Receptor |
| CID | CtBP interaction domain |
| circRNA | Circular RNA |
| COL4A1 | Collagen 4A1 |
| CTGF | Connective tissue growth factor |
| CUL4A | Cullin 4A |
| DDX56 | DEAD-Box 56 |
| DEN | Diethylnitrosamine |
| DMY | Dihydromyricetin |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| EGR1 | Early growth response 1 |
| eEF-1γ | Eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 gamma |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal Transition |
| EMT-TF | EMT-inducing transcription factor |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| FBXW7 | F-Box and WD repeat domain containing 7 |
| FBXW8 | F-box and WD repeat domain containing 8 |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factor |
| FGG | Fibrinogen gamma chain |
| FOXO3a | Forkhead box O3 |
| GINS1 | GINS complex subunit 1 |
| GSK3β | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HDAC | Histone deacetylase |
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor |
| HIF1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha |
| HIPK2 | Homeodomain Interacting Protein Kinase 2 |
| HMGB1 | High mobility group box 1 |
| HMGB2 | High mobility group box 1 |
| HN1L | Hematological and neurological expressed 1-like |
| IGFBP2 | Insulin like growth factor binding protein 2 |
| IL4 | Interleukin 4 |
| LKB1 | Liver kinase B1 |
| lncRNA | long non-coding RNA |
| m6A | N6-methyladenosine |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MAZ | MYC associated zinc finger protein |
| METTL3 | Methyltransferase-like protein 3 |
| METTL13 | Methyltransferase 13 |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| MIST | Muscle, intestine and stomach expression 1 |
| MMP2 | Matrix metallopeptidase 2 |
| MSC | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| mTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase |
| ncRNAs | Non-coding RNAs |
| NCSTN | Nicastrin |
| NFκB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NONO | Non-POU domain containing octamer binding |
| OTUB2 | OTU deubiquitinase, ubiquitin aldehyde binding 2 |
| PDHA-1 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 subunit alpha 1 |
| PFKM | Phosphofructokinase-1, muscle |
| PHGDH | Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase |
| PIM1 | Pim-1 proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase |
| PKCA | Protein kinase C alpha |
| PKM2 | Pyruvate kinase M2 |
| POU2F1 | POU class 2 homeobox 1 |
| PPM1G | Protein phosphatase 1G |
| PPT1 | Palmitoyl-Protein Thioesterase 1 |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| PTK7 | Tyrosine-protein kinase-like 7 |
| PTP4A1 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase type 4A1 |
| RBMY | RNA-binding motif, Y chromosome |
| SDPR | Serum deprivation response |
| SET | Suppressor of variegation, enhancer of zeste, trithorax |
| SID | Smad interaction domain |
| SMYD3 | MYND (Myeloid-Nervy-DEAF1) domain containing 3 |
| SNAI1/2 | Snail family transcriptional repressor 1/2 |
| SORT1 | Sortilin 1 |
| SP1 | Specificity protein 1 |
| SSEA3 | Stage-specific embryonic antigen 3 |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| TBL1X | Transducin beta like 1 X-linked |
| TCF | T-cell factor |
| TF | Transcription factor |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-beta |
| THRSP | Thyroid Hormone Responsive Protein |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| TPA | O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol 13-acetate |
| TRAF6 | TNF receptor associated factor 6 |
| TRIM26 | Tripartite motif containing 26 |
| TRPV1 | Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 |
| TWIST1/2 | Twist family bHLH transcription factor 1/2 |
| TXNDC12 | Thioredoxin domain containing 12 |
| UPAT | Ubiquitin-like plant homeodomain (PHD) and really interesting new gene (RING) finger domain-containing protein 1 (UHRF1) protein associated transcript |
| USP22 | Ubiquitin specific peptidase 22 |
| USP39 | Ubiquitin specific peptidase 39 |
| VEGFA | Vascular endothelial growth factor A |
| Wnt | Wingless/integrated |
| YAP | Yes-associated protein |
| YTHDF3 | YTH domain-containing family protein 3 |
| ZEB1/2 | Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1/2 |
| ZIP4 | Zrt- and irt-like protein 4 |
References
- Yang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, A.X.; Bernards, R.; Qin, W.; Wang, C. Evolving therapeutic landscape of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banales, J.M.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Marzioni, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Invernizzi, P.; Lind, G.E.; Folseraas, T.; Forbes, S.J.; Fouassier, L.; et al. Expert consensus document: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA). Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hong, W.; Wei, X. The molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression and metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero, J.; Guedj, N.; Claperon, A.; Nguyen Ho-Bouldoires, T.H.; Paradis, V.; Fouassier, L. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cholangiocarcinoma: From clinical evidence to regulatory networks. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 424–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derynck, R.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT and Cancer: More Than Meets the Eye. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Sunkara, R.R.; Parmar, M.Y.; Shaikh, S.; Waghmare, S.K. EMT imparts cancer stemness and plasticity: New perspectives and therapeutic potential. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2021, 26, 238–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, S.; Quader, S.; Cabral, H.; Ono, R. Interplay of EMT and CSC in Cancer and the Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenyev, S.E.; Daks, A.A.; Shuvalov, O.Y.; Fedorova, O.A.; Pestov, N.B.; Korneenko, T.V.; Barlev, N.A. Dualistic role of ZEB1 and ZEB2 in tumor progression. Biol. Direct 2025, 20, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postigo, A.A. Opposing functions of ZEB proteins in the regulation of the TGFbeta/BMP signaling pathway. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2443–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soen, B.; Vandamme, N.; Berx, G.; Schwaller, J.; Van Vlierberghe, P.; Goossens, S. ZEB Proteins in Leukemia: Friends, Foes, or Friendly Foes? Hemasphere 2018, 2, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramel, J.; Ligier, M.; Puisieux, A. Pleiotropic Roles for ZEB1 in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashiguchi, M.; Ueno, S.; Sakoda, M.; Iino, S.; Hiwatashi, K.; Minami, K.; Ando, K.; Mataki, Y.; Maemura, K.; Shinchi, H.; et al. Clinical implication of ZEB-1 and E-cadherin expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobe, C.; Vallette, M.; Arbelaiz, A.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, E.; Izquierdo, L.; Pellat, A.; Guedj, N.; Louis, C.; Paradis, V.; Banales, J.M.; et al. Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox 1 Promotes Cholangiocarcinoma Progression Through Tumor Dedifferentiation and Tumor-Stroma Paracrine Signaling. Hepatology 2021, 74, 3194–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.M.; Montoya, G.; Wu, Y.; Eddy, R.L.; Byers, M.G.; Shows, T.B. The TCF8 gene encoding a zinc finger protein (Nil-2-a) resides on human chromosome 10p11.2. Genomics 1992, 14, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remacle, J.E.; Kraft, H.; Lerchner, W.; Wuytens, G.; Collart, C.; Verschueren, K.; Smith, J.C.; Huylebroeck, D. New mode of DNA binding of multi-zinc finger transcription factors: DeltaEF1 family members bind with two hands to two target sites. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 5073–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postigo, A.A.; Depp, J.L.; Taylor, J.J.; Kroll, K.L. Regulation of Smad signaling through a differential recruitment of coactivators and corepressors by ZEB proteins. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sawada, J.; Sui, G.; Affar, E.B.; Whetstine, J.R.; Lan, F.; Ogawa, H.; Luke, M.P.; Nakatani, Y.; Shi, Y. Coordinated histone modifications mediated by a CtBP co-repressor complex. Nature 2003, 422, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, J.; Nasarre, P.; Gemmill, R.; Baldys, A.; Pontis, J.; Korch, C.; Guilhot, J.; Ait-Si-Ali, S.; Drabkin, H. Global Decrease of Histone H3K27 Acetylation in ZEB1-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Lung Cancer Cells. Cancers 2013, 5, 334–356, Erratum in Cancers 2016, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, H.; Liang, L.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, P.; Xiang, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S. ZEB1 induces ER-alpha promoter hypermethylation and confers antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; You, X.; Liu, X.; Fengwei, Z.; Zhou, H.; Shang, X.; Cai, L. SMYD3 induces sorafenib resistance by activating SMAD2/3-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. iScience 2023, 26, 106994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.L.M.; Wong, T.L.; Zhou, L.; Man, K.; Purcell, J.; Lee, T.K.; Yun, J.P.; Ma, S. Protein Tyrosine Kinase 7 (PTK7) Promotes Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via SOX9 Regulation and TGF-beta Signaling. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Su, R.; Lu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wei, X.; Xu, X. ZIP4 inhibits Ephrin-B1 ubiquitination, activating Wnt5A/JNK/ZEB1 to promote liver cancer metastasis. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 101312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Xie, K.; Lan, T.; Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Liao, M.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Zeng, Y.; et al. TXNDC12 promotes EMT and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via activation of beta-catenin. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 1355–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lan, T.; Xu, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Yuan, K.; et al. NCSTN promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth and metastasis via beta-catenin activation in a Notch1/AKT dependent manner. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 128, Correction in J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liao, W.; Jiang, Y.; Liao, G.; Gao, X.; Cen, S.; Liu, L.; Peng, J.; Shaohang, C. SORT1 promote the metastasis and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma via p38/beta-catenin/ZEB1 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Yao, N.; Deng, B.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, T.; Hu, Y.; Cao, M.; Hong, J. GINS1 promotes ZEB1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis via beta-catenin signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell Physiol. 2024, 239, e31237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, C.; Xue, F.; Chen, W.; Zhi, X.; Feng, X.; Bai, X.; Liang, T. Salinomycin decreases doxorubicin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting the beta-catenin/TCF complex association via FOXO3a activation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10350–10365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dong, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zi, R.; Hao, J.; Liang, H.; et al. Deubiquitinase OTUB2 promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma progression by stabilizing the CTNNB1-ZEB1 axis. Exp. Cell Res. 2023, 425, 113537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Z.; He, Y.Z.; Dong, P.P.; Ma, L.J.; Wang, Z.C.; Liu, X.Y.; Duan, M.; Yang, L.X.; Shi, J.Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP4A1 promotes proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 75210–75220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Song, R.; Wang, J.; Yin, D.; et al. ABCA8 is regulated by miR-374b-5p and inhibits proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through the ERK/ZEB1 pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Ma, X.; Li, C.; Zhou, C.; Chen, J.; Gu, X. Downregulation of THRSP Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Triggering ZEB1 Transcription in an ERK-dependent Manner. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 4247–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, Y.; Yoon, C.H.; Kim, R.K.; Lim, E.J.; Oh, Y.S.; Hwang, S.G.; An, S.; Yoon, G.; Gye, M.C.; Yi, J.M.; et al. Claudin-1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of the c-Abl-ERK signaling pathway in human liver cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4873–4882, Correction in Oncogene 2017, 36, 1167–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.J.; Hamza, A.; Islam, R.; Dogsom, O.; Park, J.B. Function of eEF-1gamma in the nucleus in response to insulin in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yu, D.Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Liu, D.Y.; Cao, H.Q.; Liao, X.W. IGFBP2 upregulates ZEB1 expression and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zheng, Y.L.; Jiang, C.; Fang, S.; Zeng, T.T.; Zhu, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Xie, D.; Guan, X.Y. HN1L-mediated transcriptional axis AP-2gamma/METTL13/TCF3-ZEB1 drives tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 2268–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Shi, X.; Yuan, X.; Liu, D.; Zheng, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, F.; Zhang, M.; Su, S.G.; Zhang, C.Z. PPM1G-mediated TBL1X mRNA splicing promotes cell migration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2025, 116, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.S.; You, R.I.; Cheng, C.C.; Lee, M.C.; Lin, T.Y.; Hu, C.T. Snail collaborates with EGR-1 and SP-1 to directly activate transcription of MMP 9 and ZEB1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17753, Correction in Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Zou, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Ma, S.; Shen, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, B. FBXW8-mediated degradation of PPT1 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2025, 1871, 167985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lu, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, G.; Chen, Y. FBXW7 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stemness and metastatic potential of cholangiocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6310–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; Cui, Z.; Liu, R.; Lu, R.; Yao, Z.; Xu, Q. Cancer associated fibroblast-derived CCL5 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through activating HIF1alpha/ZEB1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahine, J.J.; Davis, S.S.; Culfaci, S.; Kallakury, B.V.; Tuma, P.L. Chromosome 8q24 amplification associated with human hepatocellular carcinoma predicts MYC/ZEB1/MIZ1 transcriptional regulation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liao, Z.; He, X.; Song, Z.; Fang, X.; Wen, S.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Mo, W.; et al. Ethanol responsive lnc171 promotes migration and invasion of HCC cells via mir-873-5p/ZEB1 axis. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwapisz, O.; Gorka, J.; Korlatowicz, A.; Kotlinowski, J.; Waligorska, A.; Marona, P.; Pydyn, N.; Dobrucki, J.W.; Jura, J.; Miekus, K. Fatty Acids and a High-Fat Diet Induce Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Activating TGFbeta and beta-Catenin in Liver Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Ma, Y.; Shrivastava, S.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Shankar, S. Chronic alcohol exposure induces hepatocyte damage by inducing oxidative stress, SATB2 and stem cell-like characteristics, and activating lipogenesis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 2119–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, M.S.; Suk, F.M.; Chiu, W.C.; Lee, C.Y.; Hsu, F.Y.; Liao, Y.J. Long-term di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure reduces sorafenib treatment efficacy by enhancing mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 273, 116161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, L.; Liu, R.; Yao, Z.; Zheng, C.; Jin, S.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, S.; Zhu, X. MAZ-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of ZEB1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating METTL3. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Zhu, X.; Liu, W.; Ren, Y.; Bei, C.; Qin, L.; Miao, X.; Tang, F.; Tang, G.; Tan, S. MYC associated zinc finger protein promotes the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing epithelial mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 86420–86432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.; Han, S. circ_KIAA1429 accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma advancement through the mechanism of m(6)A-YTHDF3-Zeb1. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorecki, I.; Rak, B. The role of microRNAs in epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancers; focusing on mir-200 family. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2021, 28, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.R.; Diao, L.T.; Hu, Y.X.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Lv, G.; Tao, S.; Xu, W.Y.; Xie, S.J.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, Z.D. The Conserved LncRNA DIO3OS Restricts Hepatocellular Carcinoma Stemness by Interfering with NONO-Mediated Nuclear Export of ZEB1 mRNA. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2301983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Li, Y.; Su, X.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Ren, Y.; Deng, M.; Yao, Z. Exosome-derived hsa_circ_0007132 promotes lenvatinib resistance by inhibiting the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of NONO. Noncoding RNA Res. 2025, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.H.; Yang, F.; Wang, F.; Ma, J.Z.; Guo, Y.J.; Tao, Q.F.; Liu, F.; Pan, W.; Wang, T.T.; Zhou, C.C.; et al. A long noncoding RNA activated by TGF-beta promotes the invasion-metastasis cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Veronese, A.; Pichiorri, F.; Lee, T.J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Volinia, S.; Pineau, P.; Marchio, A.; Palatini, J.; Suh, S.S.; et al. p53 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition through microRNAs targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.K.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.H. Post-Translational Modification of ZEB Family Members in Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W.; Chen, Y.; Qian, X. Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1. Open Life Sci. 2025, 20, 20251109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, J.; Song, C.; Lei, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W.; Song, G. Deubiquitinase USP39 and E3 ligase TRIM26 balance the level of ZEB1 ubiquitination and thereby determine the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2315–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Xie, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Su, Y.; Lin, L.; Zou, R.; Sun, G.; Zhou, B.; et al. USP22 upregulates ZEB1-mediated VEGFA transcription in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, E.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Zhong, L.; Li, Q. Tumor suppressor DCAF15 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 for proteasomal degradation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging 2021, 13, 10603–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Ou, H.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, D. Deficiency of pseudogene UPAT leads to hepatocellular carcinoma progression and forms a positive feedback loop with ZEB1. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 4102–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, H.; Lin, Y.; Hu, A.; Zhou, J.; Ren, H.; Shi, X. Inhibition of HMGB1 Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via HIPK2-Mediated Autophagic Degradation of ZEB1. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 599124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, Q. LncRNA RP11-422N16.3 Inhibits Cell Proliferation and EMT, and Induces Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Sponging miR-23b-3p. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 10943–10961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, T.; Qi, H.; Xiao, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q. Upregulation of SNHG6 exhibits an oncogenic effect, regulating ZEB1 expression by competitively binding miR-101-3p and interacting with UPF1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 183–194, Corrigendum in Cancer Lett. 2023, 555, 216045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, D. miR-139-5p inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Jin, L.; Zhang, F.; Peng, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Lyu, Q.; Cai, X. lncRNA TUG1-Mediated Mir-142-3p Downregulation Contributes to Metastasis and the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting ZEB1. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 1928–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yao, H.; Wang, K.; Liu, X. Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1 Regulates ZEB1 Expression by Sponging miR-143-3p and Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. J. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 4836–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Tian, P.; Zheng, W.; Yan, X. Piplartine attenuates the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via regulating hsa_circ_100338 expression. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4265–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Xu, M.; Xu, J.; Wu, K.; Fang, Q.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Cen, D.; Ji, L.; Han, W.; et al. ELF3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by protecting ZEB1 from miR-141-3p-mediated silencing in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Gong, M.; Fang, S.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, N.; He, Y. All-trans retinoic acid reverses malignant biological behavior of hepatocarcinoma cells by regulating miR-200 family members. Genes Dis. 2021, 8, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Xie, J.; Shen, C.; Cheng, D.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Shen, B.; Peng, C.; et al. Amplification of Long Noncoding RNA ZFAS1 Promotes Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3181–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.P.; Fan, J.; Wu, Y.J.; Xie, Y.F.; Zha, J.M.; Zhou, X.M. MiR-155 up-regulated by TGF-beta promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2956–2965. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, S.; Yuan, H.; Ying, X.; Fu, H.; Zheng, X. A long non-coding RNA lncRNA-PE promotes invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma through the miR-200a/b-ZEB1 pathway. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317705756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.M.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, C.G.; An, J.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, C.H.; Dhanasekaran, D.N.; Moon, A.; et al. Galpha12 gep oncogene deregulation of p53-responsive microRNAs promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2910–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Ning, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Jiao, M.; Cui, Z.; Guo, L.; Mu, W.; Yang, H. Long non-coding RNA ZEB1-AS1 predicts a poor prognosis and promotes cancer progression through the miR-200a/ZEB1 signaling pathway in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Xu, H.X.; Yu, Y.; He, J.D.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Zhang, R.X.; Zhang, J.J.; et al. LncRNA HULC enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote tumorigenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via the miR-200a-3p/ZEB1 signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42431–42446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.C.; Lin, C.C.; Shih, T.C.; Tseng, R.J.; Yu, M.C.; Lin, Y.J.; Hsieh, S.Y. The miR-200b-ZEB1 circuit regulates diverse stemness of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 2035–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, C.; Sun, L.; Jin, X.; Han, M.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.; Lv, J.; Li, T. Long non-coding RNA CARLo-5 promotes tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma via suppressing miR-200b expression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 70172–70182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Song, W.; Wang, W.; Yao, S.; Tian, C.; Cai, X.; Wang, L. Suppression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by Kruppel-like factor 4. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 29749–29760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, D.; Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, C.; Ning, Z.; Guo, X.; Otkur, W.; et al. YB1 regulates miR-205/200b-ZEB1 axis by inhibiting microRNA maturation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 576–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jiang, H.; Pan, H.; Zhu, X. LncRNA XIST promotes liver cancer progression by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-200b-3p to regulate ZEB1/2 expression. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 3000605211016211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.H.; Chou, W.; Wang, F.; Yeh, C.N.; Chen, T.C.; Yeh, T.S. Expression profile of microRNA-200 family in cholangiocarcinoma arising from choledochal cyst. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Yang, L.; Tian, F.; Nie, S.; Zhou, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, W. Up-regulated LncRNA-ATB regulates the growth and metastasis of cholangiocarcinoma via miR-200c signals. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 7561–7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.J.; Islam, R.; Kim, J.G.; Dogsom, O.; Cap, K.C.; Park, J.B. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase A1 Phosphorylated by Insulin Associates with Pyruvate Kinase M2 and Induces LINC00273 through Histone Acetylation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Pei, H.; Xu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, L. Long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 promotes cholangiocarcinoma cells proliferation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through down-regulating miR-203. Aging 2020, 12, 2333–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Fan, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, K. LncRNA SNHG3 Promotes Hepatocellular Tumorigenesis by Targeting miR-326. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2019, 249, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Gu, Y.; Feng, Y. miR-369 inhibits Liver Cancer progression by targeting ZEB1 pathway and predicts the prognosis of HCC patients. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 3067–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G.; Lu, K.; Zhao, T.; Yang, L. LincRNA PRNCR1 activates the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway to drive the deterioration of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating miR-411-3p/ZEB1 axis. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2024, 40, 4809–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Ouyang, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Q. MAPKAPK5-AS1 drives the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating miR-429/ZEB1 axis. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Z.S.; Cai, W.W.; Deng, Y.; Chen, L.; Tan, S.L. Dihydromyricetin Inhibits Tumor Growth and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through regulating miR-455-3p in Cholangiocarcinoma. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 6058–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.I.; Khaled, G.M.; Amleh, A. Functional role and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of the miR-590-3p/MDM2 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Yang, J.F.; Rong, F.; Luo, Z.P.; Hu, S.; Fang, H.; Wu, Y.; Yao, R.; Kong, W.H.; Feng, X.W.; et al. ZEB1 serves an oncogenic role in the tumourigenesis of HCC by promoting cell proliferation, migration, and inhibiting apoptosis via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1676–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Jiang, B.; Yuan, X.; Qiu, Y.; Peng, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Super-Enhancer-Associated Long Noncoding RNA HCCL5 Is Activated by ZEB1 and Promotes the Malignancy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, C.; Zhao, C.; Che, C.; Liu, W.; Mei, Y. Alternatively-spliced lncRNA-PNUTS promotes HCC cell EMT via regulating ZEB1 expression. Tumori J. 2023, 109, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.A.; Jan, Y.J.; Ko, B.S.; Liang, S.M.; Chen, S.C.; Wang, J.; Hsu, C.; Wu, Y.M.; Liou, J.Y. 14-3-3epsilon overexpression contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Zhao, T.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, X.; Cui, L.; Zhang, Y. HMGB2 upregulation promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the activation of ZEB1/vimentin axis. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2023, 14, 2178–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, M.; Huang, J.; Wu, Q.; Yan, G.R.; Chen, D. POU2F1 over-expression correlates with poor prognoses and promotes cell growth and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44082–44095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, H.H.; Chang, M.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Tsuei, D.J.; Jeng, Y.M.; Lee, P.H.; Ni, Y.H. PIM1-Induced Cytoplasmic Expression of RBMY Mediates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 121–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, T.H.; Huang, Y.; Yeh, C.T.; Yeh, C.N.; Yu, J.; Lin, C.C.; Chiou, S.P.; Chiang, P.Y.; Hung, J.T.; Yu, A.L. High expression of embryonic stem cell marker SSEA3 confers poor prognosis and promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. J. 2024, 47, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, H.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jia, S. CBX6 Promotes HCC Metastasis Via Transcription Factors Snail/Zeb1-Mediated EMT Mechanism. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 12489–12500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Huang, Y.; Ke, K.; Zhao, B.; Chen, L.; Liao, N.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; et al. FGG promotes migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through activating epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 1653–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Cao, L.; Zheng, S. CAPZA1 modulates EMT by regulating actin cytoskeleton remodelling in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, B.; Wei, W.; Zhu, J.; Fu, G.; Lu, D. EMT induced by loss of LKB1 promotes migration and invasion of liver cancer cells through ZEB1-induced YAP signaling. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6465–6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Liu, G.; Li, M.; Fang, Y.; Qian, K.; Tang, Y.; Wu, X.; Lei, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; et al. Targeting TRPV1 on cellular plasticity regulated by Ovol 2 and Zeb 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claperon, A.; Mergey, M.; Nguyen Ho-Bouldoires, T.H.; Vignjevic, D.; Wendum, D.; Chretien, Y.; Merabtene, F.; Frazao, A.; Paradis, V.; Housset, C.; et al. EGF/EGFR axis contributes to the progression of cholangiocarcinoma through the induction of an epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.J.; Xue, D.; Zhang, C.D.; Zhang, Z.D.; Liu, Q.R.; Wang, J.Q. Cullin 4A is associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition and poor prognosis in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 2318–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zheng, Y.; Li, L.; Zhai, W.; Li, R.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, L. Adrenomedullin promotes intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma metastasis and invasion by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhashem, N.S.; Elwan, A.; El Hefnawy, A.S.; Atwa, H.A. Expression of HnRNP A1, ZEB1, and E-cadherin in Hepatocellular carcinoma and their impact on patients’ prognosis and survival. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2022, 65, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, S.; Lu, G.; Wang, D. The aberrant expressions of MACC1, ZEB1, and KLF4 in hepatocellular carcinoma and their clinical significance. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 3653–3661. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, M.; Qin, F.; Lan, X. ZEB1 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the expression of vimentin. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 2297–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Cao, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, R.X.; Sui, C.J.; Yin, Z.F.; Yang, J.M. Clinicopathological significance of ZEB1 protein in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 1700–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashita, K.; Chuma, M.; Hatanaka, Y.; Hatanaka, K.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Yokoo, H.; Ohmura, T.; Ishizu, H.; Muraoka, S.; Nagasaka, A.; et al. ZEB1 expression is associated with prognosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lin, F.; Xu, Z.; Yu, S.; Li, G.; Liao, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; et al. ZEB1 Transcriptionally Activates PHGDH to Facilitate Carcinogenesis and Progression of HCC. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 16, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Lin, F.; Wan, T.; Chen, A.; Wang, H.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, W.; Liao, S.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; et al. ZEB1 enhances Warburg effect to facilitate tumorigenesis and metastasis of HCC by transcriptionally activating PFKM. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5926–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, W.; Mossmann, D.; Kleemann, J.; Mock, K.; Meisinger, C.; Brummer, T.; Herr, R.; Brabletz, S.; Stemmler, M.P.; Brabletz, T. ZEB1 turns into a transcriptional activator by interacting with YAP1 in aggressive cancer types. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Du, Y.; Wei, X.; Song, C.; Song, J.; Xu, N.; Huang, W.; Chen, L.; Yao, F.; Du, D.; et al. DDX56 transcriptionally activates MIST1 to facilitate tumorigenesis of HCC through PTEN-AKT signaling. Theranostics 2022, 12, 6069–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Liu, J.Y.; Li, J.L.; Wang, F.Z.; Sun, B.L. ZEB1 causes the production of hsa-microRNA-99b/let-7e/microRNA-125a cluster and promotes invasion of liver cancer cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedele, M.; Sgarra, R.; Battista, S.; Cerchia, L.; Manfioletti, G. The Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition at the Crossroads between Metabolism and Tumor Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.; Mi, B.; Huang, G. The emerging co-regulatory role of long noncoding RNAs in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the Warburg effect in aggressive tumors. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 126, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hao, W.; Shi, K. Preclinical efficacy of CBR-5884 against epithelial ovarian cancer cells by targeting the serine synthesis pathway. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Qi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, C.; Yang, L.; et al. PHGDH activation fuels glioblastoma progression and radioresistance via serine synthesis pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 44, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Hao, Y.; Feng, J.; Liu, H.; Li, S.T.; Feng, J.; Jiang, Z.; Ye, L.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Non-canonical phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase activity promotes liver cancer growth via mitochondrial translation and respiratory metabolism. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e111550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, R.; Emaduddin, M.; Al-Saihati, H.; Moutasim, K.; Chan, J.; Spampinato, M.; Bhome, R.; Yuen, H.M.; Mescoli, C.; Vitale, A.; et al. Protein kinase C inhibitors override ZEB1-induced chemoresistance in HCC. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Jia, M.; Gao, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, T.; Dai, R.; Wang, M.; Miao, H. Cisplatin Disrupts Proteasome Bounce-Back Effect through Suppressing ZEB1/Nfe2l1 in Cholangiocarcinoma. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2024, 29, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luan, G.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, T. Exosomal miR-200b-3p induce macrophage polarization by regulating transcriptional repressor ZEB1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Int. 2023, 17, 889–903, Correction in Hepatol. Int. 2024, 18, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, T.; Tsuchikawa, T.; Hatanaka, K.C.; Hatanaka, Y.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Noji, T.; Nakamura, T.; Okamura, K.; Matsuno, Y.; et al. Prognostic impact of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression and its association with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20034–20047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirbel, C.; Durand, S.; Boivin, F.; Plaschka, M.; Benboubker, V.; Grimont, M.; Barbollat-Boutrand, L.; Tondeur, G.; Balme, B.; Harou, O.; et al. ZEB1 transcription factor induces tumor cell PD-L1 expression in melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2025, 74, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruna, T.; Kudo, M.; Ishino, K.; Ueda, J.; Shintani-Domoto, Y.; Yoshimori, D.; Fuji, T.; Kawamoto, Y.; Teduka, K.; Kitamura, T.; et al. Molecular biological role of epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2024, 55, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, Y.; Isse, K.; Specht, S.; Lunz, J.G., 3rd; Corbitt, N.; Takizawa, T.; Demetris, A.J. Small proline rich protein 2a in benign and malignant liver disease. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1130–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.J.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M.; et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaquero, J.; Lobe, C.; Tahraoui, S.; Claperon, A.; Mergey, M.; Merabtene, F.; Wendum, D.; Coulouarn, C.; Housset, C.; Desbois-Mouthon, C.; et al. The IGF2/IR/IGF1R Pathway in Tumor Cells and Myofibroblasts Mediates Resistance to EGFR Inhibition in Cholangiocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4282–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Long, Z.; Gu, X. Farrerol suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via suppression of TGF-beta1/Smad2/3 signaling. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 264, 155719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Pei, S.; Zhang, X.; Qi, D.; Zhang, W.; Dou, Y.; Yang, R.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, S.; et al. Cinobufotalin inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through down-regulate beta-catenin in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 922, 174886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Tong, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, J.; Hu, S.; Hu, T.; Song, G. Mesenchymal stem cells in inflammatory microenvironment potently promote metastatic growth of cholangiocarcinoma via activating Akt/NF-kappaB signaling by paracrine CCL5. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 73693–73704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Tumor | Sample Size | Detection Method | Cut Off | % ZEB1 Positive/ High Expression | PFS/OS | HR | 95%CI | p-Value | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC | 54 | IHC | Expression > 1% | 29.6 | PFS (MV) | 15.5 | 10.1–20.9 | <0.001 | [107] |
| OS (MV) | 9.6 | 4.34–14.86 | <0.001 | ||||||
| HCC | 153 | IHC | Score > 2 | 59.4 | OS (MV) | 1.812 | 1.060–3.097 | 0.030 | [108] |
| HCC | 110 | WB | - | 65.4 | PFS (MV) | 1.814 | 1.002–3.284 | 0.048 | [110] |
| OS (MV) | 2.222 | 1.097–4.503 | 0.027 | ||||||
| HCC | 108 | IHC | - | 23.0 | OS (MV) | 1.45 | 1.02–2.00 | 0.037 | [13] |
| OS (UV) | 1.20 | 0.83–1.71 | 0.320 | ||||||
| CCA | 102 | IHC | Score 0–300 | 46.1 | OS (UV) | 0.911 | 0.493–1.686 | 0.027 | [111] |
| Tumor | Parameter | Sample Size | ZEB1 Negative | ZEB1 Positive | p-Value | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC | Grade | 54 | 38 | 16 | [107] | |
| I | 12 | 11 | 1 | 0.006 | ||
| II | 28 | 21 | 7 | |||
| III | 14 | 6 | 8 | |||
| Staging | 54 | 38 | 16 | |||
| I | 9 | 8 | 1 | 0.001 | ||
| II | 20 | 19 | 1 | |||
| III | 16 | 7 | 9 | |||
| IV | 9 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Vascular Invasion | 54 | 38 | 16 | |||
| No | 21 | 19 | 2 | 0.01 | ||
| Yes | 33 | 19 | 14 | |||
| Number of metastases | 54 | 38 | 16 | |||
| Uni-focal | 28 | 26 | 2 | 0.001 | ||
| Multi-focal | 26 | 12 | 14 | |||
| Child pough class | 54 | 38 | 16 | |||
| A | 19 | 18 | 1 | 0.003 | ||
| B | 28 | 17 | 11 | |||
| C | 7 | 3 | 4 | |||
| HCC | Number of tumors | 153 | 62 | 91 | [108] | |
| 1 | 82 | 58 | 24 | <0.001 | ||
| >1 | 71 | 4 | 67 | |||
| Grade | 153 | 62 | 91 | |||
| Well + moderate | 77 | 44 | 33 | <0.001 | ||
| Poor | 76 | 18 | 58 | |||
| Staging | 153 | 62 | 91 | |||
| I | 52 | 44 | 8 | <0.001 | ||
| II | 64 | 7 | 57 | |||
| III | 42 | 11 | 20 | |||
| IV | 6 | 0 | 6 | |||
| HCC | Staging | 80 | 38 | 42 | [109] | |
| I–II | 43 | 14 | 29 | 0.04 | ||
| III–IV | 37 | 24 | 13 | |||
| HCC | Staging | [110] | ||||
| I | 12 | 8 | 4 | 0.010 | ||
| II | 30 | 13 | 17 | |||
| III–IV | 68 | 17 | 51 | |||
| Tumor size | ||||||
| <5 | 37 | 18 | 19 | 0.027 | ||
| >5 | 73 | 20 | 53 | |||
| Intrahepatic metastases | ||||||
| Absent | 82 | 33 | 49 | 0.031 | ||
| Present | 28 | 5 | 23 | |||
| Vascular invasion | ||||||
| Absent | 47 | 23 | 24 | 0.006 | ||
| Present | 63 | 15 | 48 | |||
| Early recurrence | ||||||
| Yes | 34 | 6 | 28 | 0.013 | ||
| No | 76 | 32 | 44 | |||
| HCC | Vascular invasion | 108 | [13] | |||
| Absent | 70 | 10 | 60 | 0.016 | ||
| Present | 38 | 13 | 25 | |||
| Staging | 108 | |||||
| I + II + III | 88 | 15 | 73 | 0.023 | ||
| IV | 20 | 8 | 12 | |||
| CCA | Sex | 102 | 55 | 47 | [111] | |
| Men | 63 | 29 | 34 | 0.042 | ||
| Women | 39 | 26 | 13 | |||
| Age (years) | 102 | 55 | 47 | |||
| <64 | 51 | 20 | 31 | 0.003 | ||
| >64 | 51 | 35 | 16 | |||
| Staging | 102 | 55 | 47 | |||
| I + II + III | 59 | 37 | 22 | 0.037 | ||
| IV | 43 | 18 | 25 | |||
| Differentiation | 102 | 55 | 47 | |||
| Well | 20 | 16 | 4 | 0.017 | ||
| Moderately | 58 | 30 | 48 | |||
| Poorly | 24 | 9 | 15 | |||
| Lymph node metastasis | 102 | 55 | 47 | |||
| Absent | 70 | 43 | 27 | 0.024 | ||
| Present | 32 | 12 | 20 | |||
| Portal vein invasion | 102 | 55 | 47 | |||
| Absent | 59 | 37 | 22 | 0.037 | ||
| Present | 43 | 18 | 25 | |||
| CCA | Grade | 45 | 35 | 10 | [14] | |
| I | 17 | 15 | 2 | <0.05 | ||
| II | 18 | 15 | 3 | |||
| III | 10 | 5 | 5 | |||
| Vascular Invasion | 45 | 35 | 10 | |||
| Absent | 13 | 13 | 0 | <0.05 | ||
| Present | 32 | 22 | 10 |
| Tumor | Strategy | Molecule | Target | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC | Chemical compound | Farrerol | SMAD2/3 | [131] |
| HCC | Chemical compound | Cinobufotalin | β-catenin | [132] |
| HCC | Chemical compound | Salinomycin | FOXO3a | [28] |
| CCA | Chemical compound | Dihydromyricetin | miR-455-3p | [89] |
| HCC | Chemical compound | Artesunate | O-GlcNAcase | [56] |
| HCC | Chemical compound | PKC inhibitors | PKCA | [122] |
| CCA | Chemical compound | Maraviroc | CCR5 | [133] |
| CCA | Neutralizing antibody | - | CCL5 | [133] |
| HCC | miRNA | miR-708 | ZEB1 | [91] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzalez-Sanchez, E.; Roldan-Hernandez, C.A.; Martin-Ramirez, A.; Garcia-Collado, L.; Fouassier, L.; Vaquero, J. Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Transcriptional Regulator ZEB1 in Liver Cancer: Oncogenic Roles and Therapeutic Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211135
Gonzalez-Sanchez E, Roldan-Hernandez CA, Martin-Ramirez A, Garcia-Collado L, Fouassier L, Vaquero J. Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Transcriptional Regulator ZEB1 in Liver Cancer: Oncogenic Roles and Therapeutic Potential. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211135
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzalez-Sanchez, Ester, Carlos Andres Roldan-Hernandez, Ana Martin-Ramirez, Lucia Garcia-Collado, Laura Fouassier, and Javier Vaquero. 2025. "Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Transcriptional Regulator ZEB1 in Liver Cancer: Oncogenic Roles and Therapeutic Potential" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211135
APA StyleGonzalez-Sanchez, E., Roldan-Hernandez, C. A., Martin-Ramirez, A., Garcia-Collado, L., Fouassier, L., & Vaquero, J. (2025). Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Transcriptional Regulator ZEB1 in Liver Cancer: Oncogenic Roles and Therapeutic Potential. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211135






