The Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Dercum’s Disease: Exploring the Intersection of Obesity, Pain, and Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Characteristics and Differential Diagnosis
2.1. Clinical Features
2.2. Clinical Subtypes
2.3. Differential Diagnosis
3. Proposed Pathophysiology of Dercum’s Disease
3.1. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction
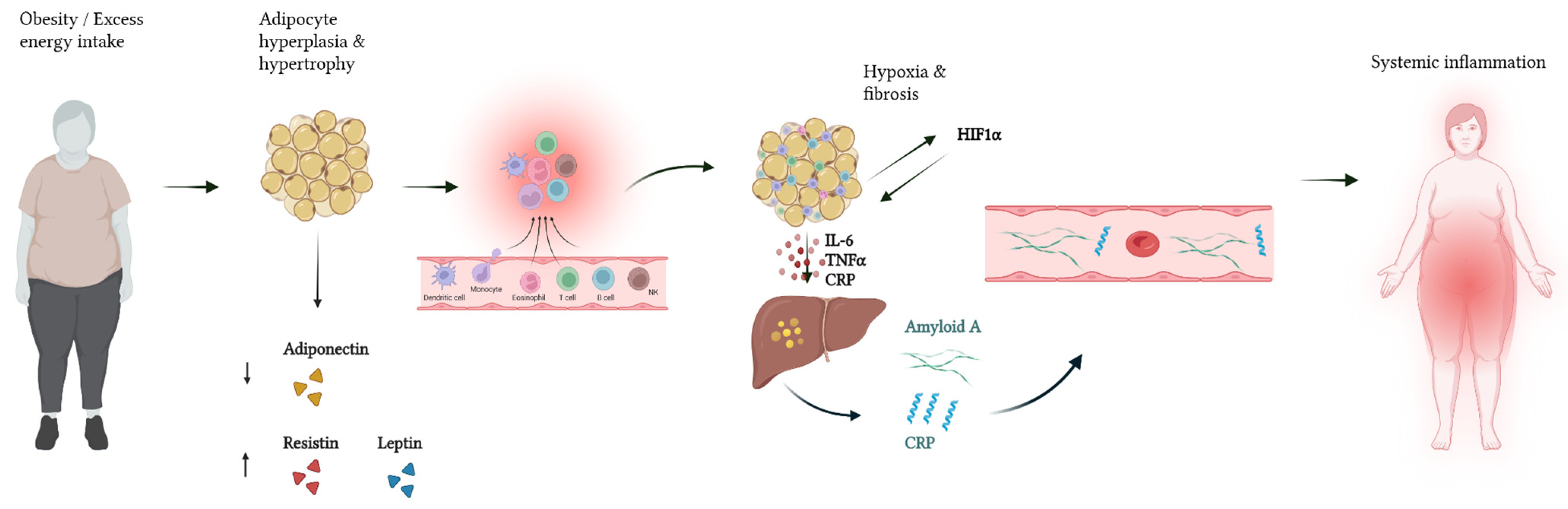
3.2. Systemic Low-Grade Inflammation
3.3. Neuroinflammation and Nociceptor Activation
4. Molecular Mechanisms of Pain
4.1. Peripheral Sensitization
4.2. Pain Mediators
5. Genetic and Epigenetic Considerations
6. Therapeutic Approaches and Future Perspectives
6.1. Current Symptom-Based Treatments
6.2. Molecular Targets and Novel Therapies
6.3. Metabolic Regulators and Lipid-Lowering Agents
6.4. Nutritional Modulation as a Complementary Therapy
7. Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| ASIC | Acid-Sensing Ion Channel |
| CAV1 | Caveolin-1 |
| COX | Cyclooxygenase |
| CR | Caloric Restriction |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| DD | Dercum’s Disease |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| ERα | Estrogen Receptor Alpha |
| ESR | Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate |
| FML | Familial Multiple Lipomatosis |
| HIF1α | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-Alpha |
| HMGA2 | High Mobility Group AT-Hook 2 |
| IF | Intermittent Fasting |
| IFN-γ | Interferon Gamma |
| IgG2c | Immunoglobulin G2c |
| IL | Interleukin |
| JAK-STAT | Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| KD | Ketogenic Diet |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MD | Mediterranean Diet |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa-light-chain-enhancer of Activated B Cells |
| NGF | Nerve Growth Factor |
| NK | Natural Killer (cell) |
| NOS2 | nitric oxide synthase 2 |
| NSAID | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| PKA | Protein Kinase A |
| SAT | Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| Th2 | T Helper 2 |
| TRPV1 | Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| VLCKD | Very Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet |
References
- Flegal, K.M.; Kruszon-Moran, D.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Trends in Obesity Among Adults in the United States, 2005 to 2014. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 315, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Caprio, M.; Watanabe, M.; Cammarata, G.; Feraco, A.; Muscogiuri, G.; Verde, L.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Could very low-calorie ketogenic diets turn off low grade inflammation in obesity? Emerging evidence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 8320–8336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Bettini, S.; Boschetti, M.; Barrea, L.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. Low-grade inflammation, CoVID-19, and obesity: Clinical aspect and molecular insights in childhood and adulthood. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Laudisio, D.; Frias-Toral, E.; Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. Anti-Inflammatory Nutrients and Obesity-Associated Metabolic-Inflammation: State of the Art and Future Direction. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinna, L.; Verde, L.; Di Tolla, M.F.; Barrea, L.; Parascandolo, A.; D’alterio, F.; Colao, A.; Formisano, P.; D’esposito, V.; Muscogiuri, G. Chronodisruption enhances inflammatory cytokine release from visceral adipose tissue in obesity. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Verde, L.; Vetrani, C.; Barrea, L.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. Obesity: A gender-view. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2023, 47, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verde, L.; Barrea, L.; Bowman-Busato, J.; Yumuk, V.D.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Obesogenic environments as major determinants of a disease: It is time to re-shape our cities. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2024, 40, e3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JKucharz, E.; Kopeć-Mędrek, M.; Kramza, J.; Chrzanowska, M.; Kotyla, P. Dercum’s disease (adiposis dolorosa): A review of clinical presentation and management. Rheumatology 2019, 57, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsal, S.A.; Kumar, A.; Soomro, M.; Shafique, M.A. Dercum’s disease: A rare adipose tissue disorder. J. Med. Surg. Public Health 2023, 1, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munguia, N.; Mozayeni, B.R.; Wright, T.F.; Herbst, K.L. Dercum’s Disease: Estimating the Prevalence of a Rare Painful Loose Connective Tissue Disease. Future Rare Dis. 2021, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Housni, O.; Boufeas, C.; Slane, V. Dercum’s Disease: The Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, Radiological Findings, and Treatment of a Rare, Debilitating Inflammatory Disorder. HCA Healthc. J. Med. 2024, 5, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.D.; Nai, G.A.; de Andrade, T.C.P.C.; de Abreu, M.A.M.M. Dercum’s disease: A rare and underdiagnosed disease. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2019, 94, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.S. Dercum’s Disease (Adiposis Dolorosa). Int. J. Nurs. Educ. Res. 2018, 6, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moattari, C.; Giovane, R.A.; DiGiovanni Kinsely, S. Dercum’s Disease: A Case Report of a Patient Having Both Type 1 and Type 2 Dercum’s Disease. Case Rep. Dermatol. Med. 2020, 2020, 6129706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.W.; Zhang, G.; Haith, L.R. Dercum’s disease: A unique case of recrudescent lipomas necessitating surgery. J. Med. Surg. Public Health 2025, 5, 100185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.A. An unusual presentation of Dercum’s disease to the emergency department. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2023, 2023, 284–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiesenga, F.; Farooqui, H.; Kaur, K.; Niazi, S.; Nijjar, K. Dercum’s Disease (adiposis dolorosa) & Associated Obesity. J. Med. Case Rep. Case Ser. 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, K.L.; Asare-Bediako, S. Adiposis Dolorosa Is More Than Painful Fat. Endocrinologist 2007, 17, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, E.; Svensson, H.; Brorson, H. Review of Dercum’s disease and proposal of diagnostic criteria, diagnostic methods, classification and management. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2012, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petry, N.M.; Barry, D.; Pietrzak, R.H.; Wagner, J.A. Overweight and Obesity Are Associated with Psychiatric Disorders: Results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Psychosom. Med. 2008, 70, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, F. Dercums Disease/Adiposis Dolorosa. J. Pigment. Disord. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wipf, A.; Lofgreen, S.; Miller, D.D.; Farah, R.S. Novel Use of Deoxycholic Acid for Adiposis Dolorosa (Dercum Disease). Dermatol. Surg. 2019, 45, 1718–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, A.; Aukerman, W.; Winegarden, B.; Morrissey, S. Lurking Under the Surface: Dercum’s Disease. Cureus 2021, 13, e17649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Z.; Kan, C.F.K.; Webb-Detiege, T.A. Differential Diagnosis of a Case of Dercum’s Disease with Possible Familial Involvement and Review of Literature. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2021, 94, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández Pellicer, F.J.; Vázquez Díaz, F.J.; Rodríguez, F.A. Adiposis dolorosa o enfermedad de Dercum. A propósito de un caso. Semer. Med. Fam. 2000, 26, 552–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Mohindra, N.; Mehndiratta, A.; Chaturvedi, P. Case 312: Dercum Disease. Radiology 2023, 307, e213044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, K.M.; Gaw, R.; MacLean, M.R. Obesity, estrogens and adipose tissue dysfunction—Implications for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2020, 10, 204589402095201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Wadhawan, G.; Singh, R.; Thakkar, K. Study on the Correlation between Hyperlipidemia and Lipoma. Int. J. Pharm. Clin. Res. Orig. Res. Artic. 2024, 16, 1525. [Google Scholar]
- Kuryłowicz, A. Estrogens in Adipose Tissue Physiology and Obesity-Related Dysfunction. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, F.; Wang, S.; Jing, J.; Cui, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Carrillo, J.A.; Ding, Z.; Song, J.; et al. Epigenetic programming of estrogen receptor in adipocytes by high-fat diet regulates obesity-induced inflammation. JCI Insight 2025, 10, e173423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, B.M.; Berry, D.C. The Regulation of Adipose Tissue Health by Estrogens. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 889923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M.R.; Rus, M.J.; Areal-Quecuty, V.; Lubián-López, D.M.; Simon-Soro, A. Menopausal shift on women’s health and microbial niches. npj Women’s Health 2025, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, M.; Aubert, S.; Chevalier, B.; Jannin, A.; Bourry, J.; Prévost, G.; Lefebvre, H.; Vantyghem, M.-C. Rare Forms of Lipomatosis: Dercum’s Disease and Roch-Leri Mesosomatous Lipomatosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchiatto, B.; Castro, T.L.; Ferreira, N.J.R.; Evangelista, F.S. Healthy adipose tissue after menopause: Contribution of balanced diet and physical exercise. Explor. Endocr. Metab. Dis. 2025, 2, 101424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, A.; Birk, R. Adipose Tissue Hyperplasia and Hypertrophy in Common and Syndromic Obesity—The Case of BBS Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, M.B.; Landeros, R.V.; Chen, D.; Magness, R.R. Structural analysis of estrogen receptors: Interaction between estrogen receptors and cav-1 within the caveolae†. Biol. Reprod. 2019, 100, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Feola, A.; Porcellini, A.; Gigantino, V.; Di Bonito, M.; Di Mauro, A.; Caggiano, R.; Faraonio, R.; Zuchegna, C. Estrogen Induces Selective Transcription of Caveolin1 Variants in Human Breast Cancer through Estrogen Responsive Element-Dependent Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltran, K.; Wadeea, R.; Herbst, K.L. Infections preceding the development of Dercum disease. IDCases 2020, 19, e00682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosseifi, S.; Anaya, E.; Dronovalli, G.; Leicht, S. Dercum’s Disease: An Unusual Presentation. Pain Med. 2010, 11, 1430–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, K.L. Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Diseases: Dercum Disease, Lipedema, Familial Multiple Lipomatosis, and Madelung Disease; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis, H.; Lemaitre, M.; Jannin, A.; Douillard, C.; Espiard, S.; Vantyghem, M.-C. Lipomatoses. Ann. Endocrinol. 2024, 85, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri Palisetty, B.; Pinisetti, A.; Kumar Mugada, V.; Rao Yarguntla, S. An in-Depth Review of Dercum’s disease: Aetiology, Epidemiology, and Treatment. Asian J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 13, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, D.B.; Zhra, M.; Nassar, W.K.; Altemyatt, H.; Naureen, A.; Abotouk, N.; Elahi, M.A.; Aljada, A. Adipose tissue dysfunction disrupts metabolic homeostasis: Mechanisms linking fat dysregulation to disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1592683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, D.; Bi, Y. Adipose Morphology: A Critical Factor in Regulation of Human Metabolic Diseases and Adipose Tissue Dysfunction. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 5086–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakers, A.; De Siqueira, M.K.; Seale, P.; Villanueva, C.J. Adipose-tissue plasticity in health and disease. Cell 2022, 185, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Sharma, Y.; Elahi, A.; Khan, F. Macrophage polarization: The link between inflammation and related diseases. Inflamm. Res. 2016, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, H.; Su, M.; Wang, Y. Macrophage polarization: An important role in inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1352946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis, J.B.; Balda Noria, G.; García, A.H. Exploring How Adipose Tissue, Obesity, and Gender Influence the Immune Response to Vaccines: A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.C.; Herbst, K.L.; Aldrich, M.B.; Darne, C.D.; Tan, I.-C.; Zhu, B.; Guilliod, R.; Fife, C.E.; Maus, E.A.; Sevick-Muraca, E.M. An abnormal lymphatic phenotype is associated with subcutaneous adipose tissue deposits in Dercum’s disease. Obesity 2014, 22, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, E.; Svensson, H.; Stenram, U.; Brorson, H. Histology of adipose tissue inflammation in Dercum’s disease, obesity and normal weight controls: A case control study. J. Inflamm. 2011, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, K.L.; Coviello, A.D.; Chang, A.; Boyle, D.L. Lipomatosis-associated inflammation and excess collagen may contribute to lower relative resting energy expenditure in women with adiposis dolorosa. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajkić, A.; Jahić, R.; Ejubović, M.; Đešević, M.; Ejubović, A.J.; Lepara, O. The Trend of Changes in Adiponectin, Resistin, and Adiponectin–Resistin Index Values in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with the Development of Metabolic Syndrome. Medicina 2024, 60, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, E.; Deng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Yan, Y.; Han, J.-Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Immunological roles for resistin and related adipokines in obesity-associated tumors. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 142, 112911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, K.; Kallies, A.; Vasanthakumar, A. Resident and migratory adipose immune cells control systemic metabolism and thermogenesis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 421–431, Erratum in Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.M.; Levings, M.K. Immune Regulation in Obesity-Associated Adipose Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szypula, I.; Kotulska, A.; Szopa, M.; Pieczyrak, R.; Kucharz, E.J. Adiposis dolorosa with hypercholesterolemia and premature severe generalized atherosclerosis. Wiad. Lek. 2009, 62, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amine, B.; Leguilchard, F.; Benhamou, C.L. Dercum’s disease (adiposis dolorosa): A new case-report. Jt. Bone Spine 2004, 71, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, J.; Schiltz, K.; Heidenreich, F.; Weissenborn, K. Lipomatosis dolorosa—Ein häufig übersehenes Krankheitsbild. Nervenarzt 2002, 73, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, U.; Oelzner, P.; Uhlemann, C. Dercum’s disease (Lipomatosis dolorosa): Successful therapy with pregabalin and manual lymphatic drainage and a current overview. Rheumatol. Int. 2008, 29, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poojari, A.; Dev, K.; Rabiee, A. Lipedema: Insights into Morphology, Pathophysiology, and Challenges. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamaluddin, M.S.; Weakley, S.M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Resistin: Functional roles and therapeutic considerations for cardiovascular disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, C.M. Omentin: A Key Player in Glucose Homeostasis, Atheroprotection, and Anti-Inflammatory Potential for Cardiovascular Health in Obesity and Diabetes. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Alam, R.; Ahsan, H.; Khan, S. Role of adipokines (omentin and visfatin) in coronary artery disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 33, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemat Jouy, S.; Mohan, S.; Scichilone, G.; Mostafa, A.; Mahmoud, A.M. Adipokines in the Crosstalk between Adipose Tissues and Other Organs: Implications in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, E.; Gao, K. Mast cells: A double-edged sword in inflammation and fibrosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1466491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, M.; Chevalier, B.; Jannin, A.; Le Mapihan, K.; Boury, S.; Lion, G.; Labalette, M.; Vantyghem, M.-C. Metabolic and immunological phenotype of rare lipomatoses: Dercum’s disease and Roch-Leri mesosomatic lipomatosis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divoux, A.; Moutel, S.; Poitou, C.; Lacasa, D.; Veyrie, N.; Aissat, A.; Arock, M.; Guerre-Millo, M.; Clément, K. Mast Cells in Human Adipose Tissue: Link with Morbid Obesity, Inflammatory Status, and Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 9, E1677–E1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabut, J.M.; Crane, J.D.; Green, A.E.; Keating, D.J.; Khan, W.I.; Steinberg, G.R. Emerging Roles for Serotonin in Regulating Metabolism: New Implications for an Ancient Molecule. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1092–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cîmpeanu, R.-C.; Caragea, E.-M.; Mustață, L.-M.; Forțofoiu, D.; Dragne, I.-G.; Alexa, R.-E.; Balta, A.; Ceasovschih, A.; Șorodoc, L.; Săndulescu, L.-D. The Involvement of Serotonin in the Obesity Pathway—A Last Decade Systematic Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Gao, Y. New insights into roles of basophils in initiating T helper type 2 immunity. Chin. Herb. Med. 2020, 12, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, E.; Svensson, H.; Brorson, H. Liposuction May Reduce Pain in Dercum’s Disease (Adiposis Dolorosa). Pain. Med. 2011, 12, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliason, A.H.; Seo, Y.I.; Murphy, D.; Beal, C. Adiposis Dolorosa Pain Management. Fed. Pract. 2019, 36, 529–533. [Google Scholar]
- Basbaum, A.I.; Bautista, D.M.; Scherrer, G.; Julius, D. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Pain. Cell 2009, 139, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, I.M.; von Hehn, C.A.; Woolf, C.J. Neurogenic inflammation and the peripheral nervous system in host defense and immunopathology. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, P.M.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. Pathological pain and the neuroimmune interface. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassimtabar, A. The Neurobiology of Nociception. In Pain Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 19–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozmanova, M.; Pavelkova, N. The Prospect for Potent Sodium Voltage-Gated Channel Blockers to Relieve an Excessive Cough. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, S7–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolignier, S.; Amsalem, M.; Maingret, F.; Padilla, F.; Gabriac, M.; Chapuy, E.; Eschalier, A.; Delmas, P.; Busserolles, J. Nav1.9 Channel Contributes to Mechanical and Heat Pain Hypersensitivity Induced by Subacute and Chronic Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, T.; Ishibashi, F.; Takada, Y.; Ohno, A.; Tani, N.; Ikeda, K.; Oyamada, Y. A novel Nav1.7, Nav1.8, and Nav1.9 blocker, ANP-230, has broad analgesic efficacy in preclinical pain models with favorable safety margins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2025, 777, 152197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, R.E.; Sluka, K.A. ASICs Mediate Pain and Inflammation in Musculoskeletal Diseases. Physiology 2015, 30, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judl, T.; Popelka, S.; Tomšík, E.; Hrubý, M.; Daniel, M.; Fojt, J.; Melicherčík, P.; Landor, I.; Jahoda, D. Acidity Is an Excellent Marker of Infection in Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, L.A.F.; Sluka, K.A.; McMullen, T.; Lee, J.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Acidic buffer induced muscle pain evokes referred pain and mechanical hyperalgesia in humans. Pain 2008, 140, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, V.S.; Rash, L.D.; King, G.F.; Rank, M.M. Acid-Sensing Ion Channels: Expression and Function in Resident and Infiltrating Immune Cells in the Central Nervous System. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 738043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-H.; Chin, Y.; Fong, Y.-O.; Lee, C.-H.; Han, D.-S.; Lin, J.-H.; Sun, W.-H.; Chen, C.-C. Acidosis-related pain and its receptors as targets for chronic pain. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 247, 108444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez-Angeles, M.; Morales-Lázaro, S.L.; Juárez-González, E.; Rosenbaum, T. TRPV1: Structure, Endogenous Agonists, and Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, F.; Aono, H. Role of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 in Inflammation and Autoimmune Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Liao, Q.; Chen, C.; Yang, X.; Xie, R.; Xu, J. The Role of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 in Common Diseases of the Digestive Tract and the Cardiovascular and Respiratory System. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.d.M.; Jo, Y.-Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, C.-K. Current insights and therapeutic strategies for targeting TRPV1 in neuropathic pain management. Life Sci. 2024, 355, 122954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, H.A.; Chen, A.; Kravatz, N.L.; Chavan, S.S.; Chang, E.H. Involvement of Neural Transient Receptor Potential Channels in Peripheral Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 590261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Domínguez, M. Injury-Driven Structural and Molecular Modifications in Nociceptors. Biology 2025, 14, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.-X.; Zhai, M.-N.; Zhu, M.; He, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.-J. Inflammation in pathogenesis of chronic pain: Foe and friend. Mol. Pain 2023, 19, 17448069231178176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, P.; Holzer-Petsche, U. Pharmacology of Inflammatory Pain: Local Alteration in Receptors and Mediators. Dig. Dis. 2009, 27, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-I.; Hwang, S.W. Depolarizing Effectors of Bradykinin Signaling in Nociceptor Excitation in Pain Perception. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Huh, Y.; Ji, R.-R. Roles of inflammation, neurogenic inflammation, and neuroinflammation in pain. J. Anesth. 2019, 33, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciotti, E.; FitzGerald, G.A. Prostaglandins and Inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schaible, H.-G.; Ebersberger, A.; Natura, G. Update on peripheral mechanisms of pain: Beyond prostaglandins and cytokines. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscella, A.; Cossa, L.G.; Vetrugno, C.; Marsigliante, S. Bradykinin stimulates prostaglandin E2 release in human skeletal muscular fibroblasts. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2020, 507, 110771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkhaleq, L.A.; Assi, M.A.; Abdullah, R.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Hezmee, M.N.M. The crucial roles of inflammatory mediators in inflammation: A review. Vet. World 2018, 11, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogi, A.; Banderali, U.; Moreno, M.J.; Martina, M. Preclinical Animal Models to Investigate the Role of Nav1.7 Ion Channels in Pain. Life 2025, 15, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, Y.; Derouiche, S.; Maruyama, K.; Tominaga, M. Emerging Perspectives on Pain Management by Modulation of TRP Channels and ANO1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya-Rodriguez, C.A.; Carvajal-Zamorano, K.; Bustos, D.; Alegría-Arcos, M.; Castillo, K. A journey from molecule to physiology and in silico tools for drug discovery targeting the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channel. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1251061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.A.; Yu, J.; Cheung, C.W. Immune Actions on the Peripheral Nervous System in Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, H.R.; Espinoza-Navarro, O.; Arriaza, C.; Traipi, L.A. Emerging Role of Mast Cells as Biological Markers in the Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases and their Projection in Health Emergencies. Int. J. Morphol. 2024, 42, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, H.; Zheng, J.; Wong, D.; Waserman, S.; Sussman, G.L. Pathophysiology of bradykinin and histamine mediated angioedema. Front. Allergy 2023, 4, 1263432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.; Liu, Q.; Huang, F.; He, H.; Fan, W. Involvement of Mast Cells in the Pathophysiology of Pain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 665066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-T.; Jiang, B.-Y.; Chen, C.-C. Ion Channels Involved in Substance P-Mediated Nociception and Antinociception. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linhart, O.; Obreja, O.; Kress, M. The inflammatory mediators serotonin, prostaglandin e2 and bradykinin evoke calcium influx in rat sensory neurons. Neuroscience 2003, 118, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, A.E.; Minhas, D.; Clauw, D.J.; Lee, Y.C. Identifying and Managing Nociplastic Pain in Individuals with Rheumatic Diseases: A Narrative Review. Arthritis Care Res. 2023, 75, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.-M.; Kim, K.-H. Current understanding of nociplastic pain. Korean J. Pain. 2024, 37, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bułdyś, K.; Górnicki, T.; Kałka, D.; Szuster, E.; Biernikiewicz, M.; Markuszewski, L.; Sobieszczańska, M. What Do We Know about Nociplastic Pain? Healthcare 2023, 11, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campen, R.; Mankin, H.; Louis, D.N.; Hirano, M.; MacCollin, M. Familial occurrence of adiposis dolorosa. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 44, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía Granados, D.M.; de Baptista, M.B.; Bonadia, L.C.; Bertuzzo, C.S.; Steiner, C.E. Clinical and Molecular Investigation of Familial Multiple Lipomatosis: Variants in the HMGA2 Gene. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadlou, R.; Pandian, G.N.; Hafner, J.; Akdis, C.A.; Stingl, G.; Maverakis, E.; Brüggen, M. Subcutaneous adipose tissue: Implications in dermatological diseases and beyond. Allergy 2024, 79, 3310–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.C.; Kang, S. Epigenetic regulation of inflammatory factors in adipose tissue. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 159019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, A.L.; Munger, C.J.; Ringel, A.E. Emerging insights into the impact of systemic metabolic changes on tumor-immune interactions. Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 115234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Mao, C.; Liu, S.; Tao, Y.; Xiao, D. Epigenetic modifications in obesity-associated diseases. MedComm 2024, 5, e496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhou, B. Epigenetics in obesity: Mechanisms and advances in therapies based on natural products. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2024, 12, e1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Dhar, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, P. Contribution of environmental, genetic and epigenetic factors to obesity-related metabolic syndrome. Nucleus 2023, 66, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofides, E.A.; Gonzalez-Campoy, J.M. Adiposopathy. In Bariatric Endocrinology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.C.; Gross, G.P. Adiposis Dolorosa; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Abriola, S.T.; Oliver, J.B.; Hurley, R.W. Clinical perspectives: Navigating buprenorphine formulations for pain treatment and opioid use disorder—A case-based approach. Pain Med. 2025, pnaf094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.P.; Bhatia, A.; Buvanendran, A.; Schwenk, E.S.; Wasan, A.D.; Hurley, R.W.; Viscusi, E.R.; Narouze, S.; Davis, F.N.; Ritchie, E.C.; et al. Consensus Guidelines on the Use of Intravenous Ketamine Infusions for Chronic Pain from the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, the American Academy of Pain Medicine, and the American Society of Anesthesiologists. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2018, 43, 521–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, K.C.; Crowley, E.L.; Kadlubowska, D.; Gooderham, M.J. Uncommon Adverse Effects of Deoxycholic Acid Injection for Submental Fullness: Beyond the Clinical Trials. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2020, 24, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, G.A.; Cherubini, K.; de Figueiredo, M.A.Z.; Salum, F.G. Deoxycholic acid in the submental fat reduction: A review of properties, adverse effects, and complications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, M.; Eekema, A.; Ussery, C.; Neuhardt, D.; Garby, K.; Herbst, K.L. Subcutaneous adipose tissue therapy reduces fat by dual X-ray absorptiometry scan and improves tissue structure by ultrasound in women with lipoedema and Dercum disease. Clin. Obes. 2018, 8, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A. A review of the literature relating to liposuction in women with lipoedema and Dercum’s Disease. J. Lymphoedema 2019, 14, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Martinenghi, S.; Caretto, A.; Losio, C.; Scavini, M.; Bosi, E. Successful Treatment of Dercum’s Disease by Transcutaneous Electrical Stimulation. Medicine 2015, 94, e950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.L.; Cordova, M.J.; Dedert, E.A. Cognitive behavioral therapy for chronic pain in veterans: Evidence for clinical effectiveness in a model program. Psychol. Serv. 2022, 19, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.W.; Van Dyke, B.P.; Newman, A.K.; Morais, C.A.; Thorn, B.E. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and pain education for people with chronic pain: Tests of treatment mechanisms. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2020, 88, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volcheck, M.M.; Graham, S.M.; Fleming, K.C.; Mohabbat, A.B.; Luedtke, C.A. Central sensitization, chronic pain, and other symptoms: Better understanding, better management. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2023, 90, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeidan, F.; Baumgartner, J.N.; Coghill, R.C. The neural mechanisms of mindfulness-based pain relief: A functional magnetic resonance imaging-based review and primer. Pain Rep. 2019, 4, e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asdourian, M.S.; Shah, N.; Jacoby, T.V.; Tiao, J.; Fedeles, F. Dercum’s disease: A retrospective cohort study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 88, 738–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, R.; Bittar, K.; Aziz, M. Infliximab; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- McKay, C.E.; Batish, I.; Arami, S. Infliximab-Induced Improvement in Dercum’s Disease. Cureus 2024, 16, e61499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, T.; Kawakami, A. Interleukin-6 inhibition in the treatment of autoinflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 956795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, R.M.L.; Yim, C.W. Role of Interleukin 6 Inhibitors in the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis. JCR J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, e516–e524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronstein, B.N.; Aune, T.M. Methotrexate and its mechanisms of action in inflammatory arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.d.M.; Jo, H.J.; Park, C.-K.; Kim, Y.H. Diosgenin Exerts Analgesic Effects by Antagonizing the Selective Inhibition of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 in a Mouse Model of Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.A. Modulation of TRPV1 channel function by natural products in the treatment of pain. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 330, 109178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, V.; Li, T.; Kumari, S.; Wang, S.; Asgar, J.; Chung, M.-K. Capsaicin-induced depolymerization of axonal microtubules mediates analgesia for trigeminal neuropathic pain. Pain 2022, 163, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canseco, J.A.; Levy, H.A.; Karamian, B.A.; Blaber, O.; Chang, M.; Patel, N.; Curran, J.; Hilibrand, A.S.; Schroeder, G.D.; Vaccaro, A.R.; et al. Inhibition of Neurogenic Inflammatory Pathways Associated with the Reduction in Discogenic Back Pain. Asian Spine J. 2023, 17, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodick, D.W. CGRP ligand and receptor monoclonal antibodies for migraine prevention: Evidence review and clinical implications. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 445–458, Erratum in Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.C.; Allen, P.; Bacsi, A.; Bosco, J.J.; Chen, L.; Eller, M.; Kua, H.; Lim, L.L.; Matharu, M.S.; Monif, M.; et al. Inflammatory complications of CGRP monoclonal antibodies: A case series. J. Headache Pain. 2021, 22, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, F.A.; King, R.; Smillie, S.-J.; Kodji, X.; Brain, S.D. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1099–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-A.; Kwon, J.; Kim, H.J.; Woo, S.-Y. Mast Cells Promote Macrophage Polarization to M1-like Phenotype through a Tryptase-dependent Process. J. Bacteriol. Virol. 2025, 55, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, D.; Heger, K.; Giansanti, P.; Iuliano, C.; Meissner, F.; Mann, M.; Böttcher, J.; Öllinger, R.; Rad, R.; Tammer, F.; et al. Mast cells modulate macrophage biology through release of prestored CSF1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2025, 156, 1260–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holter, D.B.; Zahalka, S.; Brösamlen, J.; Radhouani, M.; Watzenboeck, M.L.; Artner, T.J.; Farhat, A.; Gawish, R.; Lakovits, K.; Hladik, A.; et al. Mast cells activated in vitro can modulate macrophage polarization and antibacterial responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2025, 156, 754–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, A. Mechanism of Action of Ropeginterferon Alfa-2b in Polycythemia Vera Treatment. Clin. Ther. 2024, 46, 439–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-L.; Tao, M.-H.; Li, R.-H.; Ge, S.-H.; Xiao, W. Metformin and Adipose Tissue: A Multifaceted Regulator in Metabolism, Inflammation, and Regeneration. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 40, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, N. The anti-inflammatory effect of metformin: The molecular targets. Genes Cells 2024, 29, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, S.H. Anti-inflammatory role of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and its clinical implications. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 15, 20420188231222367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, W.; Kong, W.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Zeng, T. The effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists on circulating inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27, 3607–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freuer, D.; Linseisen, J.; Schmitz, T.; Thorand, B.; Peters, A.; Petrera, A.; Heier, M.; Meisinger, C. Pleiotropic effects between statin intake and inflammation parameters in two distinct population-based studies. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Ma, J.; Wu, P.; Yan, R.; Bian, Y.; Jia, S.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, X. PCSK9 inhibition mitigates vulnerable plaque formation induced by hyperhomocysteinemia through regulating lipid metabolism and inflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2025, 239, 117031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reytor-González, C.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Jiménez-Flores, E.; Campuzano-Donoso, M.; Carella, A.M.; Coppola, L.; Marchetti, M.; Zambrano-Villacres, R.; Sarno, G. Oesophageal adenocarcinoma, obesity, and cancer: The role of nutrition in prevention and management. Food Agric. Immunol. 2025, 36, 2510951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simancas-Racines, D.; Annunziata, G.; Verde, L.; Fascì-Spurio, F.; Reytor-González, C.; Muscogiuri, G.; Frias-Toral, E.; Barrea, L. Nutritional Strategies for Battling Obesity-Linked Liver Disease: The Role of Medical Nutritional Therapy in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Management. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2025, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Verde, L.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Zambrano, A.K.; Frias-Toral, E.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S.; Muscogiuri, G. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet as a possible additional tool to be used for screening the metabolically unhealthy obesity (MUO) phenotype. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.; Tarmaster, A.; Bodemer, A.; Sivamani, R.K. The Influence of a Plant-Based Diet on Skin Health: Inflammatory Skin Diseases, Skin Healing, and Plant-Based Sources of Micro- and Macro-Nutrients. Life 2024, 14, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reytor-González, C.; Zambrano, A.K.; Frias-Toral, E.; Campuzano-Donoso, M.; Simancas-Racines, D. Mediterranean diet and breast cancer: A narrative review. Medwave 2025, 25, e3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsigalou, C.; Konstantinidis, T.; Paraschaki, A.; Stavropoulou, E.; Voidarou, C.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Mediterranean Diet as a Tool to Combat Inflammation and Chronic Diseases. Overv. Biomed. 2020, 8, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reytor-González, C.; Zambrano, A.K.; Montalvan, M.; Frias-Toral, E.; Simancas-Racines, A.; Simancas-Racines, D. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and its association with gastric cancer: Health benefits from a Planeterranean perspective. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalupahana, N.S.; Goonapienuwala, B.L.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Adipose Tissue: Inflammation and Browning. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2020, 40, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrani, C.; Verde, L.; Colao, A.; Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G. The Mediterranean Diet: Effects on Insulin Resistance and Secretion in Individuals with Overweight or Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colao, A.; Vetrani, C.; Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Tricopoulou, A.; Soldati, L.; Piscitelli, P. “Planeterranean” Diet: Extending worldwide the health benefits of Mediterranean Diet based on nutritional properties of locally available foods. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simancas-Racines, D.; Román-Galeano, N.M.; Verde, L.; Annunziata, G.; Marchetti, M.; Matos, A.; Campuzano-Donoso, M.; Reytor-González, C.; Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; et al. Targeting Cytokine Dysregulation in Psoriasis: The Role of Dietary Interventions in Modulating the Immune Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, A.K.; Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Frias-Toral, E.; Simancas-Racines, D. Impact of fundamental components of the Mediterranean diet on the microbiota composition in blood pressure regulation. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Frias-Toral, E.; Laudisio, D.; Pugliese, G.; Castellucci, B.; Garcia-Velasquez, E.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. Nutrition and immune system: From the Mediterranean diet to dietary supplementary through the microbiota. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3066–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Frias-Toral, E.; Zambrano, A.K. Effect of diet on the microbiota and immune system in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Food Agric. Immunol. 2024, 35, 2434475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simancas-Racines, D.; Reytor-González, C.; Parise-Vasco, J.M.; Angamarca-Iguago, J.; Garcia-Velasquez, E.; Cuzco-Macias, A.C.; Frias-Toral, E.; Schiavo, L. Effectiveness and Safety of Preoperative Nutritional Interventions on Surgical Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, J.; Jabakhanji, A.; Biemann, R.; Mai, K.; Abraham, K.; Weikert, C. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the associations of vegan and vegetarian diets with inflammatory biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingkapairoj, K.; Chularojanamontri, L.; Chaiyabutr, C.; Silpa-archa, N.; Wongpraparut, C.; Bunyaratavej, S. Dietary habits and perceptions of psoriatic patients: Mediterranean versus Asian diets. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godos, J.; Guglielmetti, M.; Ferraris, C.; Frias-Toral, E.; Azpíroz, I.D.; Lipari, V.; Di Mauro, A.; Furnari, F.; Castellano, S.; Galvano, F.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Quality of Life in Adults: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finicelli, M.; Di Salle, A.; Galderisi, U.; Peluso, G. The Mediterranean Diet: An Update of the Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Caprio, M.; Tuccinardi, D.; Moriconi, E.; Di Renzo, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S.; on behalf of the Obesity Programs of nutrition, Education, Research and Assessment (OPERA) group. Could ketogenic diet “starve” cancer? Emerging evidence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1800–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Verde, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; Reytor-González, C.; Annunziata, G.; Proganò, M.; Savastano, S.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Colao, A.; Barrea, L. Weight loss, changes in body composition and inflammatory status after a very low-energy ketogenic therapy (VLEKT): Does gender matter? J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Megna, M.; Caiazzo, G.; Potestio, L.; Maisto, M.; Tenore, G.C.; Colao, A.; et al. Very low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD): A therapeutic nutritional tool for acne? J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapela, S.P.; Simancas-Racines, A.; Ceriani, F.; Martinuzzi, A.L.N.; Russo, M.P.; Zambrano, A.K.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Verde, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Katsanos, C.S.; et al. Obesity and Obesity-Related Thyroid Dysfunction: Any Potential Role for the Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD)? Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2024, 13, 194–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Megna, M.; Verde, L.; Marasca, C.; Vono, R.; Camajani, E.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S.; Fabbrocini, G.; et al. The effect of the ketogenic diet on Acne: Could it be a therapeutic tool? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 6850–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Y.; Seo, D.S.; Jang, Y. Metabolic Effects of Ketogenic Diets: Exploring Whole-Body Metabolism in Connection with Adipose Tissue and Other Metabolic Organs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak, D.; Kasperek, K.; Rękawek, P.; Piątkowska-Chmiel, I. The Therapeutic Role of Ketogenic Diet in Neurological Disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarar-Fisher, C.; Li, J.; Womack, E.D.; Alharbi, A.; Seira, O.; Kolehmainen, K.L.; Plunet, W.T.; Alaeiilkhchi, N.; Tetzlaff, W. Ketogenic regimens for acute neurotraumatic events. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 70, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Caprio, M.; Grassi, D.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Bagnato, C.; Paolini, B.; Muscogiuri, G. A New Nomenclature for the Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD): Very Low-Energy Ketogenic Therapy (VLEKT). Ketodiets and Nutraceuticals Expert Panels: “KetoNut”, Italian Society of Nutraceuticals (SINut) and the Italian Association of Dietetics and Clinical Nutrition (ADI). Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2024, 13, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simancas-Racines, D.; Reytor-González, C.; Zambrano, A.K.; Annunziata, G.; Carella, A.M.; Verde, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; Guerra, C.V.; Hidalgo, R. Unlocking the potential: Very-low-energy ketogenic therapy in obesity-related disorders. Food Agric. Immunol. 2025, 36, 2442368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; El Ghoch, M.; Colao, A.; Hassapidou, M.; Yumuk, V.; Busetto, L. European Guidelines for Obesity Management in Adults with a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Facts 2021, 14, 222–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, M.; Moriconi, E.; Armani, A.; Fabbri, A.; Mantovani, G.; Mariani, S.; Lubrano, C.; Poggiogalle, E.; Migliaccio, S.; Donini, L.M.; et al. Very-low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD) in the management of metabolic diseases: Systematic review and consensus statement from the Italian Society of Endocrinology (SIE). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 1365–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Laudisio, D.; Pugliese, G.; Salzano, C.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. The management of very low-calorie ketogenic diet in obesity outpatient clinic: A practical guide. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Caprio, M.; Camajani, E.; Verde, L.; Perrini, S.; Cignarelli, A.; Prodam, F.; Gambineri, A.; Isidori, A.M.; Colao, A.; et al. Ketogenic nutritional therapy (KeNuT)—A multi-step dietary model with meal replacements for the management of obesity and its related metabolic disorders: A consensus statement from the working group of the Club of the Italian Society of Endocrinology (SIE)—Diet therapies in endocrinology and metabolism. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2024, 47, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, G.; Capó, X.; Muscogiuri, G.; Colao, A.; Barrea, L. Intermittent fasting: A new trend or a valid approach for the treatment of obesity? Minerva Endocrinol. 2023, 48, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, R.; Chapela, S.; Llobera, N.D.; Montalván, M.; Vásquez, C.A.; Martinuzzi, A.L.N.; Katsanos, C.S.; Verde, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; Barrea, L.; et al. Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet: What Effects on Lipid Metabolism? Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2024, 13, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvie, M.; Howell, A. Potential Benefits and Harms of Intermittent Energy Restriction and Intermittent Fasting Amongst Obese, Overweight and Normal Weight Subjects—A Narrative Review of Human and Animal Evidence. Behav. Sci. 2017, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Zambrano-Villacres, R.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Zambrano, A.K. The effect of intermittent fasting on microbiota as a therapeutic approach in obesity. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1393292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savencu, C.E.; Linţa, A.; Farcaş, G.; Bînă, A.M.; Creţu, O.M.; Maliţa, D.C.; Muntean, D.M.; Sturza, A. Impact of Dietary Restriction Regimens on Mitochondria, Heart, and Endothelial Function: A Brief Overview. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 768383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasim, I.; Majeed, C.N.; DeBoer, M.D. Intermittent Fasting and Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guevara-Cruz, M.; Hernández-Gómez, K.G.; Condado-Huerta, C.; González-Salazar, L.E.; Peña-Flores, A.K.; Pichardo-Ontiveros, E.; Serralde-Zúñiga, A.E.; Sánchez-Tapia, M.; Maya, O.; Medina-Vera, I.; et al. Intermittent fasting, calorie restriction, and a ketogenic diet improve mitochondrial function by reducing lipopolysaccharide signaling in monocytes during obesity: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1914–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-Villegas, L.; Hernández-Gómez, K.; Pichardo-Ontiveros, E.; López-Barradas, A.; Condado-Huerta, M.; Sánchez-Tapia, M.; González-Salazar, L.; León-Hernández, V.; Serralde-Zúñiga, A.; Medina-Vera, I.; et al. Intermittent fasting, caloric restriction, and ketogenic diet increase bioenergetic health index in monocytes and improve metabolic outcome in subjects with obesity via changes in gut microbiota. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 58, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedner, M.; Aghajanzadeh, D.; Richter, D.F. Differential diagnoses and treatment of lipedema. Plast. Aesthetic Res. 2020, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollands, M.; Wee, C.; Breidahl, W.; Xu, D. Presentation of multiple painful subcutaneous nodules: Dercum’s disease, a rare variant of lipoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2023, 16, e254263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, L.; Cinelli, G.; Romano, L.; Zomparelli, S.; De Santis, G.L.; Nocerino, P.; Bigioni, G.; Arsini, L.; Cenname, G.; Pujia, A.; et al. Potential Effects of a Modified Mediterranean Diet on Body Composition in Lipoedema. Nutrients 2021, 13, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, L.; Seo, C.; Rowsemitt, C.; Pfeffer, M.; Wahi, M.; Staggs, M.; Dudek, J.; Gower, B.; Carmody, M. Ketogenic diet as a potential intervention for lipedema. Med. Hypotheses 2021, 146, 110435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannataro, R.; Michelini, S.; Ricolfi, L.; Caroleo, M.C.; Gallelli, L.; De Sarro, G.; Onorato, A.; Cione, E. Management of Lipedema with Ketogenic Diet: 22-Month Follow-Up. Life 2021, 11, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørlie, V.; De Soysa, A.K.; Hyldmo, A.A.; Retterstøl, K.; Martins, C.; Nymo, S. Effect of a ketogenic diet on pain and quality of life in patients with lipedema: The LIPODIET pilot study. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2022, 8, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verde, L.; Camajani, E.; Annunziata, G.; Sojat, A.; Marina, L.V.; Colao, A.; Caprio, M.; Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L. Ketogenic Diet: A Nutritional Therapeutic Tool for Lipedema? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeziorek, M.; Chachaj, A.; Sowicz, M.; Adaszyńska, A.; Truszyński, A.; Putek, J.; Kujawa, K.; Szuba, A. The Benefits of Low-Carbohydrate, High-Fat (LCHF) Diet on Body Composition, Leg Volume, and Pain in Women with Lipedema. J. Obes. 2023, 2023, 5826630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundanes, J.; Sandnes, F.; Gjeilo, K.H.; Hansson, P.; Salater, S.; Martins, C.; Nymo, S. Effect of a low-carbohydrate diet on pain and quality of life in female patients with lipedema: A randomized controlled trial. Obesity 2024, 32, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Quintana, Y. Challenges to Global Standardization of Outcome Measures. AMIA Jt. Summits Transl. Sci. Proc. 2021, 2021, 404–409. [Google Scholar]
- Alarcón Garavito, G.A.; Moniz, T.; Déom, N.; Redin, F.; Pichini, A.; Vindrola-Padros, C. The implementation of large-scale genomic screening or diagnostic programmes: A rapid evidence review. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 31, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallifant, J.; Kistler, E.A.; Nakayama, L.F.; Zera, C.; Kripalani, S.; Ntatin, A.; Fernandez, L.; Bates, D.; Dankwa-Mullan, I.; Celi, L.A. Disparity dashboards: An evaluation of the literature and framework for health equity improvement. Lancet Digit. Health 2023, 5, e831–e839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richesson, R.L.; Rozenblit, L.; Vehik, K.; Tcheng, J.E. Patient Registries for Clinical Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rached, S.; Patino, C.M.; Ferreira, J. Using data from patient registries to answer important research questions. J. Bras. De Pneumol. 2024, 50, e20240216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.; Tchuvatkina, O.; Tulloch-Reid, M.K.; McKenzie, J.; Younger-Coleman, N.; Hambleton, I.; Ashing, K.; Ragin, C. Harmonization and integration of data from prospective cohort studies across the Region of the Americas. Rev. Panam. de Salud Pública 2025, 49, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuvana, D. Innovations in Molecular Biology-Cutting-Edge Breakthroughs in Molecular Genetics. Ann. Exp. Mol. Biol. 2024, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M.; Snyder, M. Multi-Omics Profiling for Health. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2023, 22, 100561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboktakin Rizi, S.; Stamenkovic, A.; Ravandi, A. Integrative Omics Approaches in Cardiovascular Disease Research: Current Trends and Future Directions. Can. J. Cardiol. 2025, 41, 1642–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguita-Ruiz, A.; Bustos-Aibar, M.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Mendez-Gutierrez, A.; Alcalá-Fdez, J.; Aguilera, C.M.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J. Omics Approaches in Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle Addressing the Role of Extracellular Matrix in Obesity and Metabolic Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañé, H.; Jiménez-Franco, A.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Martínez-Navidad, C.; Cambra-Cortés, V.; Onoiu, A.-I.; Jiménez-Aguilar, J.M.; París, M.; Hernández, M.; Parada, D.; et al. Multi-omics profiling reveals altered mitochondrial metabolism in adipose tissue from patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. EBioMedicine 2025, 111, 105532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, K.; Ebright, B.; Chow, K.; Dave, P.; Mead, A.; Poblete, R.; Louie, S.G.; Asante, I. Lipidomics in Understanding Pathophysiology and Pharmacologic Effects in Inflammatory Diseases: Considerations for Drug Development. Metabolites 2022, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovayo, A.; Toledo, E.; Razquin, C. Lipidome and inflammation interplay: The role of diet in this relationship. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2024, 35, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rocco, G.; Trivisonno, A.; Trivisonno, G.; Toietta, G. Dissecting human adipose tissue heterogeneity using single-cell omics technologies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, M.A.; Mcheick, H.; Adda, M. From Data Silos to Health Records Without Borders: A Systematic Survey on Patient-Centered Data Interoperability. Information 2025, 16, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, L.M.; Bynum, J.P.W.; Pincus, H.A. Care Fragmentation, Care Continuity, and Care Coordination—How They Differ and Why It Matters. JAMA Intern. Med. 2024, 184, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J.L.; Warren, J.S. The Case for Understanding Interdisciplinary Relationships in Health Care. Ochsner J. 2023, 23, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.; Koksal, C.; Montel, L.; Le Gouais, A.; Barnfield, A.; Bates, G.; Kwon, H.R. Developing shared understanding through online interdisciplinary collaboration: Reflections from a research project on better integration of health outcomes in future urban development practice. Futures 2023, 150, 103176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reytor-González, C.; Jiménez-Flores, E.; González, N.; Simancas-Racines, D. Redefining Chemoresistance: Natural Bioactives as Molecular Modulators at the Cancer–Tumor Microenvironment Interface. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Fan, R.; Zhang, N.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y. Advances in Integrated Multi-omics Analysis for Drug-Target Identification. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogeser, M.; Bendt, A.K. From research cohorts to the patient—A role for “omics” in diagnostics and laboratory medicine? Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. CCLM 2023, 61, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakus, D. The Impact of Patient Advocacy Groups on Clinical Trial Design and Imple-mentation. Ashdin Publ. J. Evol. Med. 2024, 12, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ciupek, A.; Chichester, L.-A.; Acharya, R.; Schofield, E.; Criswell, A.; Shelley, D.; King, J.C.; Ostroff, J.S. Utilizing a patient advocacy-led clinical network to engage diverse, community-based sites in implementation-effectiveness research. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2024, 24, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Subtype | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| I | Generalized diffuse | Diffuse pain originating from fatty tissue, with tiny fat deposits that can be felt in different areas of the body, although discomfort may also be present in regions where no noticeable lumps are found [8,11,19]. |
| II | Generalized nodular | Multiple localized areas throughout the body exhibit nodular formations, with pain occurring both within and surrounding the lipomas [8,11,19]. |
| III | Localized nodular | Localized lipomas associated with pain in specific areas of the body [8,11,19]. |
| IV | Juxta-articular | Painful fat folds situated within or adjacent to major joints such as the knee, hip, or elbow [8,11,19]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reytor-González, C.; Jiménez-Flores, E.; Toral-Noristz, M.; Campuzano-Donoso, M.; Román-Galeano, N.M.; Simancas-Racines, D. The Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Dercum’s Disease: Exploring the Intersection of Obesity, Pain, and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211130
Reytor-González C, Jiménez-Flores E, Toral-Noristz M, Campuzano-Donoso M, Román-Galeano NM, Simancas-Racines D. The Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Dercum’s Disease: Exploring the Intersection of Obesity, Pain, and Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211130
Chicago/Turabian StyleReytor-González, Claudia, Emilia Jiménez-Flores, Melannie Toral-Noristz, Martín Campuzano-Donoso, Náthaly Mercedes Román-Galeano, and Daniel Simancas-Racines. 2025. "The Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Dercum’s Disease: Exploring the Intersection of Obesity, Pain, and Inflammation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211130
APA StyleReytor-González, C., Jiménez-Flores, E., Toral-Noristz, M., Campuzano-Donoso, M., Román-Galeano, N. M., & Simancas-Racines, D. (2025). The Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Dercum’s Disease: Exploring the Intersection of Obesity, Pain, and Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211130






