Monomeric and Oligomeric Decorsins of the Asian Medicinal Leech Hirudinaria manillensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Putative Decorsin Genes
2.2. Calculation of Putative Decorsin Diversity
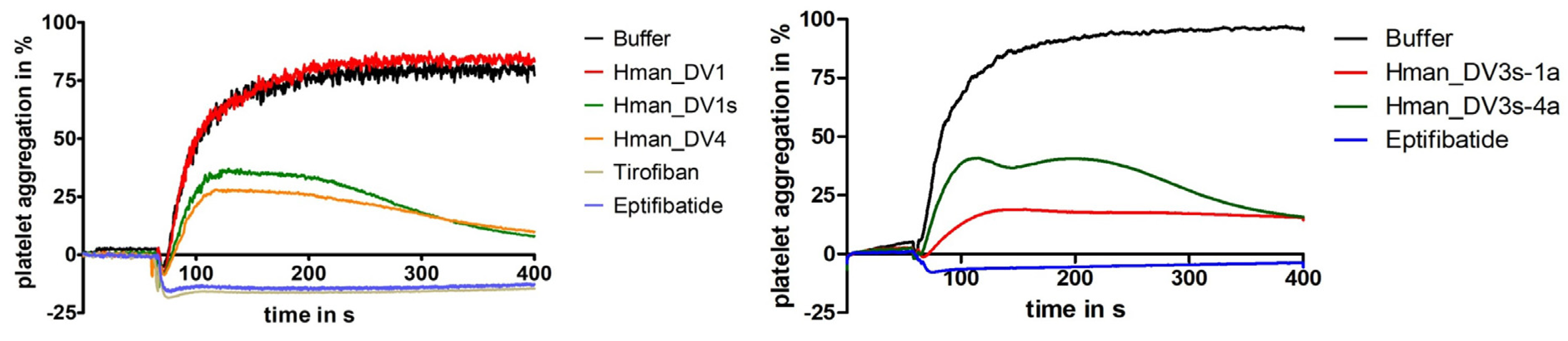
2.3. Functional Characterization of Putative Decorsins
3. Discussion
- (1)
- (2)
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genome and Transcriptome Data
4.2. Bioinformatics and Graphical Tools
4.3. Gene Synthesis
4.4. Amplification and Cloning of Putative Monomeric and Oligomeric Decorsin cDNAs
4.5. Expression, Purification, Processing, and Quantification of Putative Decorsins
4.6. Platelet Aggregation Assays
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phillips, A.J.; Siddall, M.E. Poly-paraphyly of Hirudinidae: Many lineages of medicinal leeches. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiranuntskul, P.; Boonporn, A.; Kongrit, C.; Panha, S.; Jeratthitikul, E. Biodiversity of the buffalo leeches genus Hirudinaria (Arhynchobdellida, Hirudinidae) in Southern Thailand revealed from DNA barcoding. Zool. Stud. 2022, 61, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.T.; Hechtel, F.O.P.; Hagy, J.W.; Scacheri, E. A study in medical history: Introduction of medicinal leeches into the West Indies in the nineteenth century. Zoosystema 1998, 20, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.M.; Kutschera, U. Medicinal leeches: Historical use, ecology, genetics and conservation. Freshw. Rev. 2011, 4, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.J. Phylogenetic placement of a new species of Asian buffalo leech (Arhynchobdellida: Hirudinidae), and confirmation of human mediated dispersal of a congener to the Caribbean. Invertebr. Syst. 2012, 26, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeratthitikul, E.; Jiranuntskul, P.; Nakano, T.; Sutcharit, C.; Panha, S. A new species of buffalo leech in the genus Hirudinaria Whitman, 1886 (Arhynchobdellida, Hirudinidae) from Thailand. Zookeys 2020, 933, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubtimon, J.; Jeratthitikul, E.; Sutcharit, C.; Kongim, B.; Panha, S. Systematics of the freshwater leech genus Hirudinaria Whitman, 1886 (Arhynchobdellida, Hirudinidae) from northeastern Thailand. Zookeys 2014, 452, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdualkader, A.M.; Merzouk, A.M.A.; Ghawi, A.M.; Alaama, M. Some biological activities of Malaysian leech saliva extract. IIUM Eng. J. 2011, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, K.D.; Lineaweaver, W.C.; Follansbee, S.; Feibel, R.; Jackson, R.; Buncke, H.J. Intestinal flora of the medicinal leech Hirudinaria manillensis. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 1994, 10, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, H.K.R.; Ahmad, N.W.; Lee, H.L.; Ahmad, N.; Othamn, S.; Mokhtar, N.S.H.M.; Chong, S.S.Y. Hirudotherapy in wound healing. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2022, 21, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutschera, U.; Roth, M. Notes on the ecology of the Asian medicinal leech Hirudinaria manillensis (Hirudinea: Hirudinidae). Lauterbornia 2006, 56, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wannapat, N. Harnessing the benefits of breeding the Asian medicinal leech. Fish People 2019, 17, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, V.; Knecht, R.; Gruetter, M.; Raschdorf, F.; Gassmann, E.; Maschler, R. Isolation and purification of novel hirudins from the leech Hirudinaria manillensis by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 1990, 530, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, V.; Knecht, R.; Börnsen, K.O.; Gassmann, E.; Stone, S.R.; Raschdorf, F.; Schlaeppi, J.M.; Maschler, R. Primary structure and function of novel O-glycosylated hirudins from the leech Hirudinaria manillensis. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 2294–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scacheri, E.; Nitti, G.; Valsasina, B.; Orsini, G.; Visco, C.; Ferrera, M.; Sawyer, R.T.; Sarmientos, P. Novel hirudin variants from the leech Hirudinaria manillensis. Amino acid sequence, cDNA cloning and genomic organization. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 214, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Wang, G.; Du, C.; Ombati, R.; Lai, R.; Long, C.; Li, H. Purification and characterization of a novel Kazal-type trypsin inhibitor from the leech of Hirudinaria manillensis. Toxins 2016, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.-M.; Tang, X.-P.; Long, A.-L.; Mwangi, J.; Lai, R.; Sun, R.-P.; Long, C.-B.; Zhang, Z.-Q. Purification and characterization of a novel anti-coagulant from the leech Hirudinaria manillensis. Zool. Res. 2019, 40, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Haase, M.; Lemke, S.; Hildebrandt, J.-P. Hirudins and hirudin-like factors in Hirudinidae: Implications for function and phylogenetic relationships. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, P.; Wolf, R.; Rauch, B.H.; Hildebrandt, J.-P.; Müller, C. Hirudins of the Asian medicinal leech, Hirudinaria manillensis: Same same, but different. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2223–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, P.; Melikian, G.; Hildebrandt, J.-P.; Müller, C. Make it double: Identification and characterization of a Tandem-Hirudin from the Asian medicinal leech Hirudinaria manillensis. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 2995–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, S.; Asmamaw, D.; Mwangi, J.; Chen, Q.; Tadese, D.A.; Michira, B.B.; Yang, J.; Lv, Q.; et al. The derivatives of hirudin-like peptides from the Poecilobdella manillensis exhibit antithrombotic and anti-ischemic stroke effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 307 Pt 3, 141950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.L.; Henzel, W.J.; Nevins, B.; Stults, J.T.; Lazarus, R.A. Decorsin. A potent glycoprotein IIb-IIIa antagonist and platelet aggregation inhibitor from the leech Macrobdella decora. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 10143–10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, P.; Henzel, W.J.; Seymour, J.L.; Lazarus, R.A. Ornatins: Potent glycoprotein IIb-IIIa antagonists and platelet aggregation inhibitors from the leech Placobdella ornata. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 202, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.; Sponholz, D.; Tolksdorf, C.; Rauch, B.H.; Kvist, S. Identification and functional characterization of multiple haemadins and an oligomeric decorsin in the Asian land leech Haemadipsa interrupta. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodt, J.; Seemüller, U.; Maschler, R.; Fritz, H. The complete covalent structure of hirudin. Localization of the disulfide bonds. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1985, 366, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Mescke, K.; Liebig, S.; Mahfoud, H.; Lemke, S.; Hildebrandt, J.-P. More than just one: Multiplicity of Hirudins and Hirudin-like Factors in the Medicinal Leech, Hirudo medicinalis. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, C.C. Exons encode protein functional units. Nature 1979, 277, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traut, T.W. Do exons code for structural or functional units in proteins? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2944–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, R.E.; Tessler, M.; Siddall, M.E.; Kvist, S. The origin and evolution of antistasin-like proteins in leeches (Hirudinida, Clitellata). Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 13, evaa242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerhoff, C.P.; Söllner, C.; Mentele, R.; Piechottka, G.P.; Auerswald, E.A.; Fritz, H. A Kazal-type inhibitor of human mast cell tryptase: Isolation from the medical leech Hirudo medicinalis, characterization, and sequence analysis. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1994, 375, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, F.; Huang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Meng, R.; Lin, Y.; Qi, H.; Lin, G. Revisiting the Asian buffalo leech (Hirudinaria manillensis) genome: Focus on antithrombotic genes and their corresponding proteins. Genes 2023, 14, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, C.S.; Krafft, B.; Frech, M.; Hofmann, U.R.; Papendieck, A.; Dahlems, U.; Gellissen, G.; Hoylaerts, M.F. Production and characterization of saratin, an inhibitor of von Willebrand factor-dependent platelet adhesion to collagen. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2001, 27, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronwald, W.; Bomke, J.; Maurer, T.; Domogalla, B.; Huber, F.; Schumann, F.; Kremer, W.; Fink, F.; Rysiok, T.; Frech, M.; et al. Structure of the leech protein saratin and characterization of its binding to collagen. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 381, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Müller, C.; Zhou, B. Chromosome-level genome assembly and anticoagulant protein annotation of the buffalo leech Hirudinaria bpling (Hirudinea: Hirudinidae). BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, V.; Palfree, R.G.; Bateman, A. Isolation and sequence of the granulin precursor cDNA from human bone marrow reveals tandem cysteine-rich granulin domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palfree, R.G.E.; Bennett, H.P.J.; Bateman, A. The evolution of the secreted regulatory protein progranulin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.J.; Kang, K.W. Purification of granulin-like polypeptide from the blood-sucking leech, Hirudo nipponia. Protein Expr. Purif. 1999, 16, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, D.L. Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 291–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Liu, J.; Zang, E.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, L. Exploring a hirudin variant from nonhematophagous leeches: Unraveling full-length sequence, alternative splicing, function, and potential as a novel anticoagulant polypeptide. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 330, 118257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, R.E. Diversification and Evolution of Leech (Hirudinida) Anticoagulants with Emphasis on Antistasin-like Proteins. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, USA, 2022. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/1807/110805 (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Simakov, O.; Marletaz, F.; Cho, S.-J.; Edsinger-Gonzales, E.; Havlak, P.; Hellsten, U.; Kuo, D.-H.; Larsson, T.; Lv, J.; Arendt, D.; et al. Insights into bilaterian evolution from three spiralian genomes. Nature 2013, 493, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvist, S.; Manzano-Marín, A.; de Carle, D.; Trontelj, P.; Siddall, M.E. Draft genome of the European medicinal leech Hirudo medicinalis (Annelida, Clitellata, Hirudiniformes) with emphasis on anticoagulants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babenko, V.V.; Podgorny, O.V.; Manuvera, V.A.; Kasianov, A.S.; Manolov, A.I.; Grafskaia, E.N.; Shirokov, D.A.; Kurdyumov, A.S.; Vinogradov, D.V.; Nikitina, A.S.; et al. Draft genome sequences of Hirudo medicinalis and salivary transcriptome of three closely related medicinal leeches. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.-L.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.-K.; Li, Y.; Mi, D.; Ma, L.-B.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Xu, S.-Q.; Qiu, Q. Draft genome of the Asian buffalo leech Hirudinaria manillensis. Front. Genet. 2020, 10, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Dai, S.-X.; Kong, D.-J.; Yang, P.-P.; Tong, X.; Tong, X.-R.; Bi, X.-X.; Su, Y.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Liu, Z.-C. The genome of medicinal leech (Whitmania pigra) and comparative genomic study for exploration of bioactive ingredients. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Yan, X.; Shan, H.; Ma, X.; Zhou, W.; Xu, W.; Lu, L.; et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying hematophagia revealed by comparative analyses of leech genomes. Gigascience 2023, 12, giad023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Guan, D.; Yang, L.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, L.; Khan, M.S.; Xu, S.-Q. Chromosome-level genome assembly of the cave leech Sinospelaeobdella cavatuses (Hirudinea: Haemadipsidae). Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Huang, Z.; He, B.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Lin, G. Comparative genomics of two Asian medicinal leeches Hirudo nipponia and Hirudo tianjinensis: With emphasis on antithrombotic genes and their corresponding proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270 Pt 1, 132278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredi, S.K.; Appy, R.; Martín-Durán, J.M.; Oatley, G.; Sinclair, E.; Aunin, E.; Gettle, N.; Santos, C.; Paulini, M.; Niu, H.; et al. The chromosomal genome sequence of the marine leech, Branchellion lobata Moore, 1952 and its associated microbial metagenome sequences. Wellcome Open Res. 2025, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Huang, Z.; Tang, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Lin, G. Comparative genomics of three non-hematophagous leeches (Whitmania spp.) with emphasis on antithrombotic biomolecules. Front. Genet. 2025, 16, 1548006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskova, I.P.; Zavalova, L.L.; Basanova, A.V.; Moshkovskii, S.A.; Zgoda, V.G. Protein profiling of the medicinal leech salivary gland secretion by proteomic analytical methods. Biochemistry 2004, 69, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanes, O.; Villanueva, J.; Querol, E.; Aviles, F.X. Functional screening of serine protease inhibitors in the medical leech Hirudo medicinalis monitored by intensity fading MALDI-TOF MS. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2005, 4, 1602–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, L.; Hu, H.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jia, M.; Zhang, X.; Jia, M.; Li, C.; Wu, Z. Tips for improving genome annotation quality. Genom. Commun. 2025, 2, e005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfordt, V.; Kalatehjari, P.; Tolksdorf, C.; Rauch, B.H.; Müller, C. Go West: Hirudins and decorsin/ornatin-like platelet aggregation inhibitors in two representatives of American hematophagous leeches. Parasitologia 2022, 2, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, R.A.; McDowell, R.S. Structural and functional aspects of RGD-containing protein antagonists of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1993, 4, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krezel, A.M.; Wagner, G.; Seymour-Ulmer, J.; Lazarus, R.A. Structure of the RGD protein decorsin: Conserved motif and distinct function in leech proteins that affect blood clotting. Science 1994, 264, 1944–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, P.; Wei, S.; Hu, C.; Miyoshi, M.; Okamoto, K.; Itoh, H.; Okuda, S.; Suzuki, M.; Kawakami, H.; et al. Refolding, crystallization, and crystal structure analysis of a scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain of human salivary agglutinin expressed in Escherichia coli. Protein J. 2024, 43, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Marco, A. Strategies for successful recombinant expression of disulfide bond-dependent proteins in Escherichia coli. Microb. Cell Factories 2009, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkmen, M. Production of disulfide-bonded proteins in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2012, 82, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krezel, A.M.; Ulmer, J.S.; Wagner, G.; Lazarus, R.A. Recombinant decorsin: Dynamics of the RGD recognition site. Protein Sci. 2000, 9, 1428–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javid, H.; Oryani, M.A.; Rezagholinejad, N.; Esparham, A.; Tajaldini, M.; Karimi-Shahri, M. RGD peptide in cancer targeting: Benefits, challenges, solutions, and possible integrin–RGD interactions. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintella, B.R.; Clemens, B.J.; Sutton, T.M.; Lança, M.J.; Madenjian, C.P.; Happel, A.; Harvey, C.J. At-sea feeding ecology of parasitic lampreys. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, S72–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Lu, Q.; Shao, F.; Li, W.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. rLj-RGD3, a novel three-RGD-motif-containing recombinant protein from Lampetra japonica, protects PC12 cells from injury induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6701249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemke, S.; Vilcinskas, A. European medicinal leeches—New roles in modern medicine. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl. Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, K.B.; Nicholas, H.B., Jr. GeneDoc: A Tool for Editing and Annotating Multiple Sequence Alignments; ScienceOpen: Lexington, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Teufel, F.; Armenteros, J.J.A.; Johansen, A.R.; Gíslason, M.H.; Pihl, S.I.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 6.0 predicts all five types of signal peptides using protein language models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Techniques for transformation of E. coli. In DNA Cloning: A Practical Approach; Glover, D.M., Ed.; IRL Press: Oxford, UK, 1985; Volume 1, pp. 109–135. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, S.C.; von Hippel, P.H. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 182, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, C.N.; Vajdos, F.; Fee, L.; Grimsley, G.; Gray, T. How to measure and predict the molar absorption coefficient of a protein. Protein Sci. 1995, 4, 2411–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Schmaier, A.H. Platelet aggregation testing in platelet rich plasma: Description of procedures with the aim to develop standards in the field. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 123, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


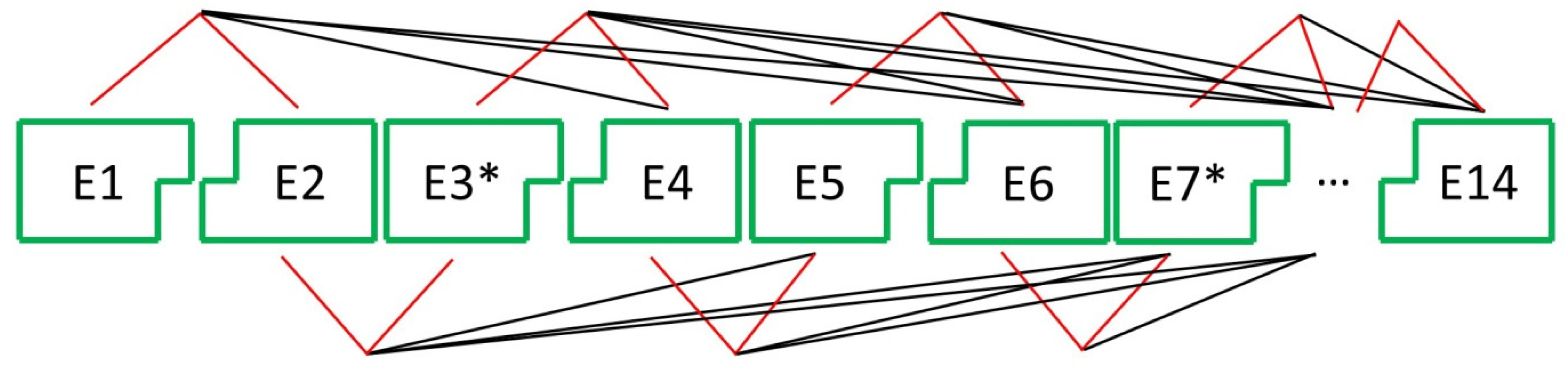
| Gene | Guan et al., 2020 contig00065 | Zheng et al., 2023 Chromosome 3 | Liu et al., 2023 Chromosome 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hman_DV1 | 1,441,956–1,445,508 re+co | 12,431,399–12,434,976 fw | 12,102,877–12,106,430 fw |
| Hman_DV2 | 1,437,246–1,439,788 re+co | 12,437,478–12,440,006 fw | 12,108,608–12,111,161 fw |
| Hman_DV3 | 1,432,730–1,436,010 re+co | 12,441,249–12,444,510 fw | 12,112,407–12,115,657 fw |
| Hman_DV4 | 1,431,197–1,432,077 re+co | 12,445,166–12,446,038 fw | 12,116,319–12,117,203 fw |
| Hman_DV5 | 1,426,608–1,430,176 re+co | 12,447,043–12,450,617 fw | 12,118,197–12,120,025 fw |
| total length: | 18,901 bp | 19,219 bp | 17,149 bp |
| gap: | 140,046 bp | 121,121 bp | 133,389 bp |
| Hman_HV1 | 1,283,961–1,284,564 fw | 12,587,203–12,587,806 re+co | 12,249,296–12,249,899 re+co |
| Hman_HV2 | 1,287,886–1,288,539 fw | 12,583,089–12,583,742 re+co | 12,245,322–12,245,958 re+co |
| Hman_HV3 | 1,289,984–1,290,638 fw | 12,580,970–12,581,635 re+co | 12,243,197–12,243,865 re+co |
| Hman_HV4 | 1,297,158–1,297,813 fw | 12,575,511–12,576,174 re+co | 12,240,038–12,240,688 re+co |
| Hman_TH | 1,300,423–1,301,910 fw | 12,571,738–12,572,909 re+co | 12,236,266–12,237,439 re+co |
| total length: | 17,950 bp | 16,069 bp | 13,634 bp |
| Factor | Length in aa | Repeats | Motifs | MW in kDa | pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hman_DV1 * | 257 | 6 | 1 (KGD) | 28.81 | 5.49 |
| Hman_DV2 | 171 | 4 | 1 (KGD) 4 (RGD) | 19.12 | 4.58 |
| Hman_DV3 * | 271 | 6 | 1 (RGD) 3 (RGD) | 30.69 | 8.26 |
| Hman_DV4 * | 45 | 1 | 1 (RGD) | 4.75 | 8.33 |
| Hman_DV5 | 268 | 6 | 1 (RGD) | 30.17 | 8.60 |
| Factor | Length in aa | MW in kDa | pI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hman_DV1s * | 63 | 7.29 | 4.50 |
| Hman_DV2s-1 | 51 | 5.66 | 6.05 |
| Hman_DV2s-2 | 47 | 5.19 | 5.53 |
| Hman_DV2s-3 | 39 | 4.30 | 4.54 |
| Hman_DV2s-4 | 47 | 5.23 | 4.72 |
| Hman_DV2s-5 | 40 | 4.46 | 4.08 |
| Hman_DV3s-1a * | 51 | 5.99 | 5.66 |
| Hman_DV3s-1b | 61 | 7.09 | 9.17 |
| Hman_DV3s-2a | 49 | 5.52 | 7.76 |
| Hman_DV3s-2b | 61 | 6.75 | 9.33 |
| Hman_DV3s-3a | 46 | 5.12 | 4.40 |
| Hman_DV3s-3b | 58 | 6.36 | 8.28 |
| Hman_DV3s-4a * | 51 | 5.58 | 4.21 |
| Hman_DV3s-4b | 63 | 6.82 | 7.21 |
| Hman_DV4 * | 45 | 4.75 | 8.33 |
| Hman_DV5sa | 61 | 6.94 | 7.51 |
| Hman_DV5sb | 58 | 6.61 | 8.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tolksdorf, C.; Wolf, R.; Rauch, B.H.; Jedlitschky, G.; Müller, C. Monomeric and Oligomeric Decorsins of the Asian Medicinal Leech Hirudinaria manillensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211017
Tolksdorf C, Wolf R, Rauch BH, Jedlitschky G, Müller C. Monomeric and Oligomeric Decorsins of the Asian Medicinal Leech Hirudinaria manillensis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211017
Chicago/Turabian StyleTolksdorf, Céline, Robert Wolf, Bernhard H. Rauch, Gabriele Jedlitschky, and Christian Müller. 2025. "Monomeric and Oligomeric Decorsins of the Asian Medicinal Leech Hirudinaria manillensis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211017
APA StyleTolksdorf, C., Wolf, R., Rauch, B. H., Jedlitschky, G., & Müller, C. (2025). Monomeric and Oligomeric Decorsins of the Asian Medicinal Leech Hirudinaria manillensis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211017






