Cloning of PoAIL6 Gene Related to Somatic Embryogenesis in Paeonia ostii ‘Fengdan’
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. PoAIL6 Screening and Cloning
2.2. Basic Physicochemical Properties of the PoAIL6 Protein
2.3. Prediction of PoAIL6’s Secondary Structure, Transmembrane Structure, and Signal Peptide
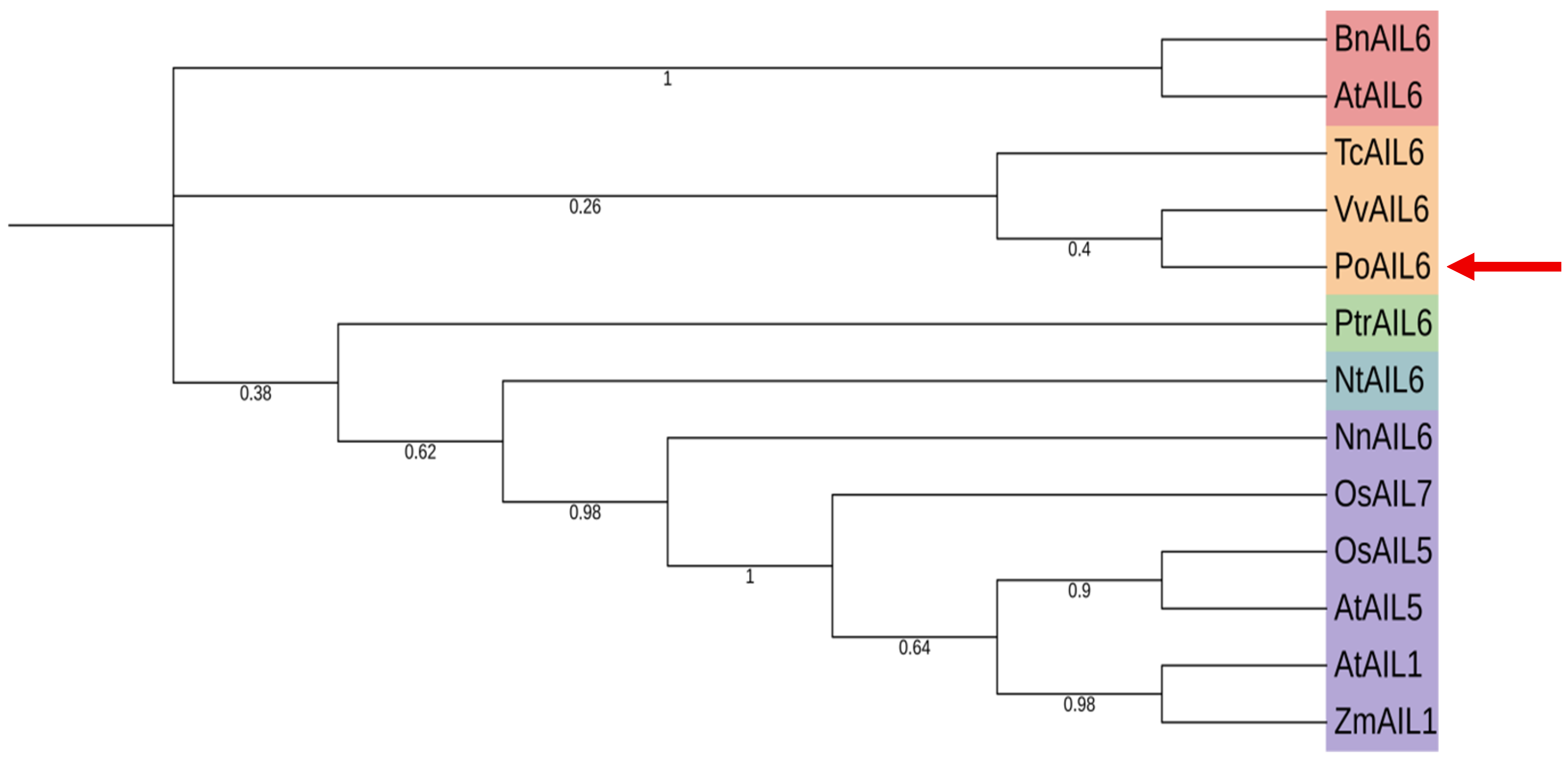
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of the PoAIL6 Amino Acid Sequence
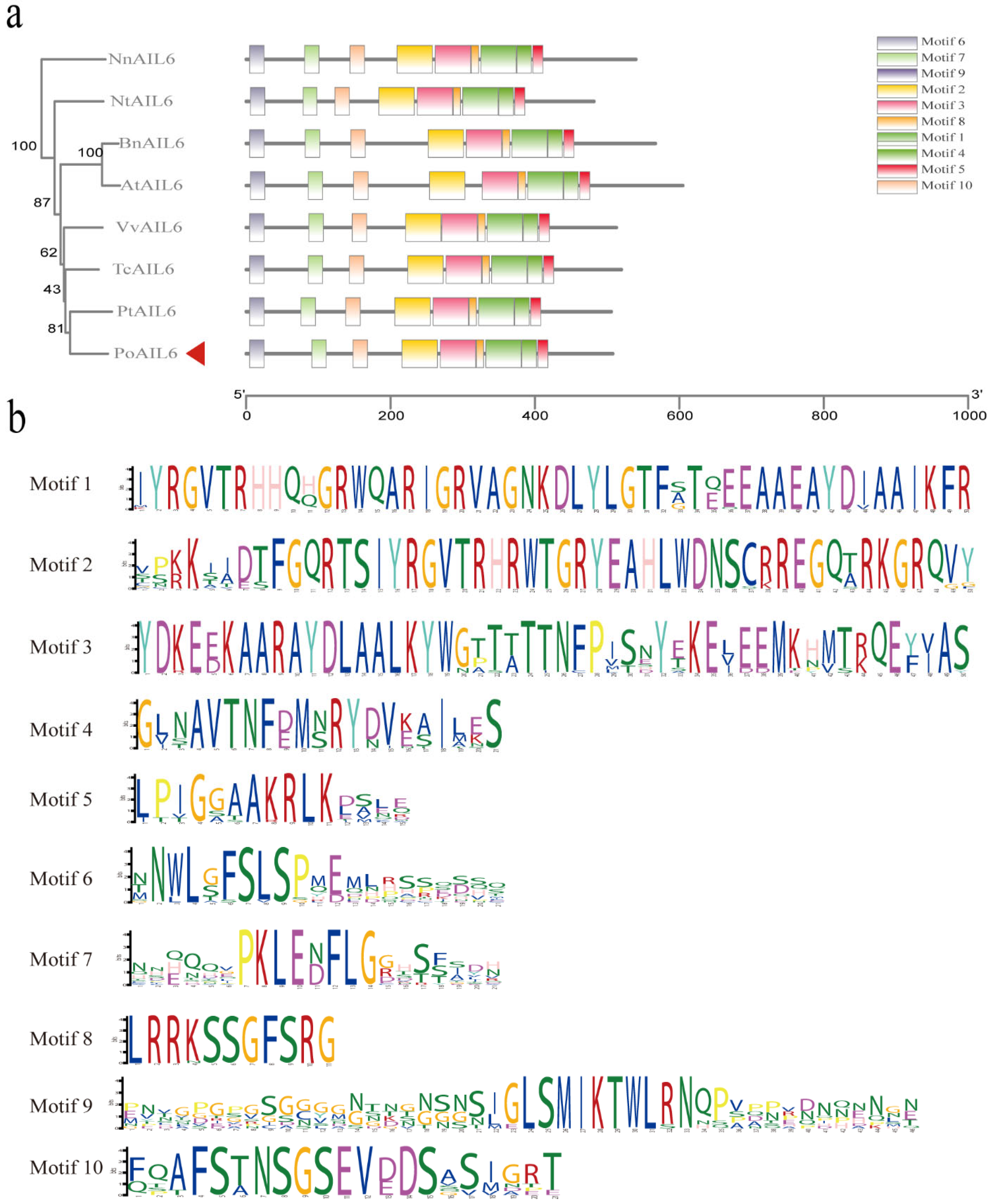
2.5. Conserved Feature and Sequence Alignment of PoAIL6
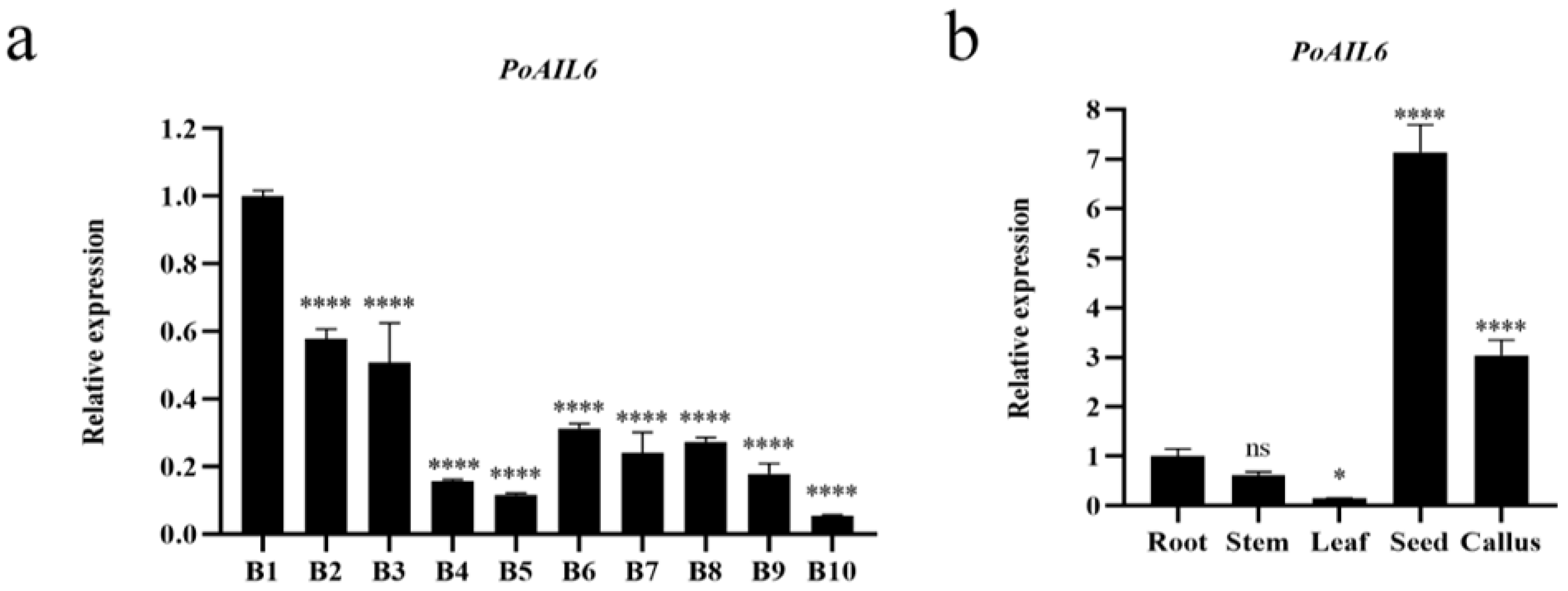
2.6. Expression Pattern Analysis of the PoAIL6 Gene in Peony
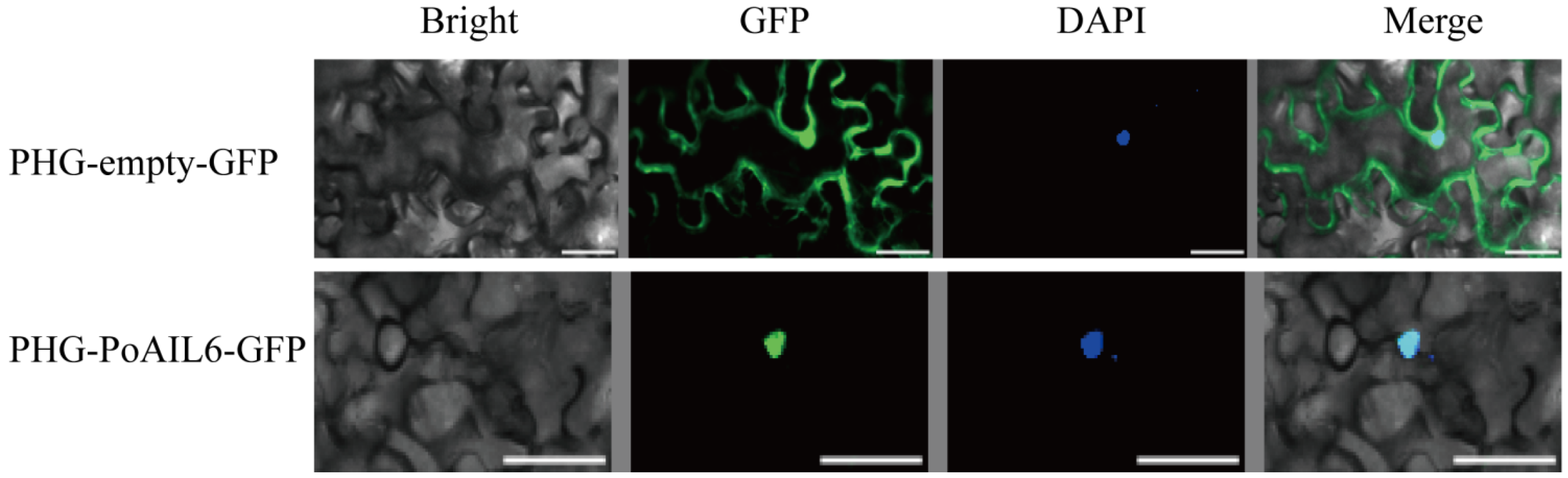
2.7. PoAIL6’s Subcellular Localization
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Materials
4.2. Identification of the PoAIL6 Gene
4.3. Protein Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.4. Gene Cloning
4.5. qRT-PCR
4.6. Subcellular Localization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, J.; Xue, J.; Xue, Y.; Liu, R.; Ren, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X. Transcriptome sequencing and identification of key callus browning-related genes from petiole callus of tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa cv. Kao) cultured on media with three browning inhibitors. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Niu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, M.; Ji, D.; Zhang, X. Pollen Sources Influence the Traits of Seed and Seed Oil in Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’. HortScience 2017, 52, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz-Figueroa, F.R.; Rojas-Herrera, R.; Galaz-Avalos, R.M.; Loyola-Vargas, V.M. Embryo production through somatic embryogenesis can be used to study cell differentiation in plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2006, 86, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cheng, F.; Zhong, Y. Induction of direct somatic embryogenesis and shoot organogenesis and histological study in tree peony (Paeonia sect. Moutan). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2020, 141, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xue, Y.; Ci, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X. Establishment of highly efficient plant regeneration of Paeonia ostii ‘Fengdan’ through optimization of callus, adventitious shoot, and rooting induction. Hortic. Plant J. 2022, 8, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesami, M.; Pepe, M.; de Ronne, M.; Yoosefzadeh-Najafabadi, M.; Adamek, K.; Torkamaneh, D.; Jones, A.M.P. Transcriptomic Profiling of Embryogenic and Non-Embryogenic Callus Provides New Insight into the Nature of Recalcitrance in Cannabis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, C.; Nie, J.; Yang, H.; Ji, W.; Xu, G.; Zhu, H.; Jin, S.; Zhu, X. The Effect of Anti-browning Agent Activated Carbon and Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone on the Rooting of Embryo Seedlings of “FengDan” and Its Transcriptome Analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 832619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, T.; Ohto, M.; Yee, K.M.; West, M.A.; Lo, R.; Kwong, R.W.; Yamagishi, K.; Fischer, R.L.; Goldberg, R.B.; Harada, J.J. Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON1 is sufficient to induce embryo development in vegetative cells. Cell 1998, 93, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, K.F.; Schoof, H.; Haecker, A.; Lenhard, M.; Jürgens, G.; Laux, T. Role of WUSCHEL in regulating stem cell fate in the Arabidopsis shoot meristem. Cell 1998, 95, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.; Kumar, V. BABY BOOM (BBM): A candidate transcription factor gene in plant biotechnology. Biotechnol. Lett. 2018, 40, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.P.; Sun, X.M.; Han, H.; Zhang, S.G. Isolation, characterization and expression analysis of the BABY BOOM (BBM) gene from Larix kaempferi × L. olgensis during adventitious rooting. Gene 2014, 551, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kareem, A.; Durgaprasad, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Du, Y.; Pulianmackal, A.J.; Trivedi, Z.B.; Abhayadev, P.V.; Pinon, V.; Meyerowitz, E.M.; Scheres, B.; et al. PLETHORA Genes Control Regeneration by a Two-Step Mechanism. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, M.; Harada, J.J. Embryogenesis in Higher Plants: An Overview. Plant Cell 1993, 5, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Liu, K.; Yuan, G.; He, S.; Cong, P.; Zhang, C. Genome-wide identification and characterization of AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE (AIL) family genes in apple (Malus domestica Borkh.). Genomics 2022, 114, 110313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.Y.; Kagale, S.; Ferrie, A.M.R. Multifaceted roles of transcription factors during plant embryogenesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1322728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutilier, K.; Offringa, R.; Sharma, V.K.; Kieft, H.; Ouellet, T.; Zhang, L.; Hattori, J.; Liu, C.M.; van Lammeren, A.A.; Miki, B.L.; et al. Ectopic expression of BABY BOOM triggers a conversion from vegetative to embryonic growth. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, K.; Wu, E.; Wang, N.; Hoerster, G.; Hastings, C.; Cho, M.J.; Scelonge, C.; Lenderts, B.; Chamberlin, M.; Cushatt, J.; et al. Morphogenic Regulators Baby boom and Wuschel Improve Monocot Transformation. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 1998–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, C.; Liu, Z.; Heidmann, I.; Supena, E.D.; Fukuoka, H.; Joosen, R.; Lambalk, J.; Angenent, G.; Scorza, R.; Custers, J.B.; et al. Heterologous expression of the BABY BOOM AP2/ERF transcription factor enhances the regeneration capacity of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Planta 2007, 225, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, A.; Bemer, M.; Boutilier, K. A transcriptional view on somatic embryogenesis. Regeneration 2017, 4, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.L.; Kwong, L.W.; Yee, K.M.; Pelletier, J.; Lepiniec, L.; Fischer, R.L.; Goldberg, R.B.; Harada, J.J. LEAFY COTYLEDON2 encodes a B3 domain transcription factor that induces embryo development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11806–11811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licausi, F.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Perata, P. APETALA2/Ethylene Responsive Factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors: Mediators of stress responses and developmental programs. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, A.; Willemsen, V.; Boutilier, K.; Heidstra, R. AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE proteins: Hubs in a plethora of networks. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuwamoto, R.; Yokoi, S.; Takahata, Y. Arabidopsis EMBRYOMAKER encoding an AP2 domain transcription factor plays a key role in developmental change from vegetative to embryonic phase. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 73, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudunkothge, J.S.; Krizek, B.A. Three Arabidopsis AIL/PLT genes act in combination to regulate shoot apical meristem function. Plant J. 2012, 71, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Jin, X.; Lan, L.; Yang, B.; Yu, K.; Ni, X.; Li, N.; et al. Draft genome of the famous ornamental plant Paeonia suffruticosa. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 4518–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Jiang, S.; Jian, J.; Liu, M.; Yue, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, C.; Lin, L.; Jing, Y.; et al. Genomic basis of the giga-chromosomes and giga-genome of tree peony Paeonia ostii. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Zhang, W.; Chang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Deng, Y.; Fan, K.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, T. A Preliminary Investigation on the Functional Validation and Interactions of PoWOX Genes in Peony (Paeonia ostii). Horticulturae 2022, 8, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Chang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, N.; Bai, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, T. Cloning, Characterization, and Expression Pattern Analysis of the BBM Gene in Tree Peony (Paeonia ostii). Forests 2023, 15, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, T.; Chang, Y.; Xia, M.; Ma, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, W. Overexpression of Peony PoWOX1 Promotes Callus Induction and Root Development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 2025, 14, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizek, B.A.; Bantle, A.T.; Heflin, J.M.; Han, H.; Freese, N.H.; Loraine, A.E. AINTEGUMENTA and AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE6 directly regulate floral homeotic, growth, and vascular development genes in young Arabidopsis flowers. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 5478–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizek, B.A. AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE genes have partly overlapping functions with AINTEGUMENTA but make distinct contributions to Arabidopsis thaliana flower development. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 4537–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizek, B. AINTEGUMENTA and AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE6 act redundantly to regulate Arabidopsis floral growth and patterning. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1916–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, O.; Rahimi, A.; Mak, P.; Horstman, A.; Boutilier, K.; Compier, M.; van der Zaal, B.; Offringa, R. An Arabidopsis AT-hook motif nuclear protein mediates somatic embryogenesis and coinciding genome duplication. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Fischer, R.L.; Goldberg, R.B.; Harada, J.J. Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON1 represents a functionally specialized subunit of the CCAAT binding transcription factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2152–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tomes, S.; Gleave, A.P.; Hall, W.; Luo, Z.; Xu, J.; Yao, J.L. Significant improvement of apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) transgenic plant production by pre-transformation with a Baby boom transcription factor. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhab014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Jin, X.; Han, L.; Chen, H.; Shao, C.; Shi, G.; Bao, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE genes regulate reproductive growth and bud dormancy in Platanus acerifolia. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar]
- Geourjon, C.; Deléage, G. SOPMA: Significant improvements in protein secondary structure prediction by consensus prediction from multiple alignments. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1995, 11, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Shen, H.B. Plant-mPLoc: A top-down strategy to augment the power for predicting plant protein subcellular localization. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Physical and Chemical Characteristics | PoAIL6 Gene |
|---|---|
| Open reading frame (bp) | 1 479 |
| Amino acid number | 493 |
| Molecular weight (Da) | 54,392.88 |
| Isoelectric point | 5.85 |
| II Instability coefficient | 45.88 |
| Aliphatic index | 61.81 |
| GRAVY | −0.582 |
| Prediction of the subcellular localization | nucleus |
| Primer Name | Primers Sequence | Application |
|---|---|---|
| PoAIL6-F | ATGGGTTCTATGAACAACTGGT | CDS amplification primers |
| PoAIL6-R | TTAAGTATCATTCCACACTGTGAAAGT | |
| Q-PoAIL6-F | GGTCCTCTGCTGCTTCTCCTCA | qRT-PCR primers |
| Q-PoAIL6-R | GTTTGGTGTTGGGTGTGGTGGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Y.; Hu, T.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, W. Cloning of PoAIL6 Gene Related to Somatic Embryogenesis in Paeonia ostii ‘Fengdan’. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211006
Chang Y, Zhang X, Deng Y, Hu T, Jiang Z, Zhang W. Cloning of PoAIL6 Gene Related to Somatic Embryogenesis in Paeonia ostii ‘Fengdan’. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211006
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Yanting, Xue Zhang, Yayun Deng, Tao Hu, Zehui Jiang, and Wenbo Zhang. 2025. "Cloning of PoAIL6 Gene Related to Somatic Embryogenesis in Paeonia ostii ‘Fengdan’" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211006
APA StyleChang, Y., Zhang, X., Deng, Y., Hu, T., Jiang, Z., & Zhang, W. (2025). Cloning of PoAIL6 Gene Related to Somatic Embryogenesis in Paeonia ostii ‘Fengdan’. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211006







