Neurobiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Binge Eating Disorder: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. GLP-1 Therapeutic Opportunity in Eating Disorders
3. The Neurobiological and Molecular Basis of GLP-1 Action
3.1. GLP-1 Receptor Biology
3.2. Mechanisms of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Action on Feeding Behavior
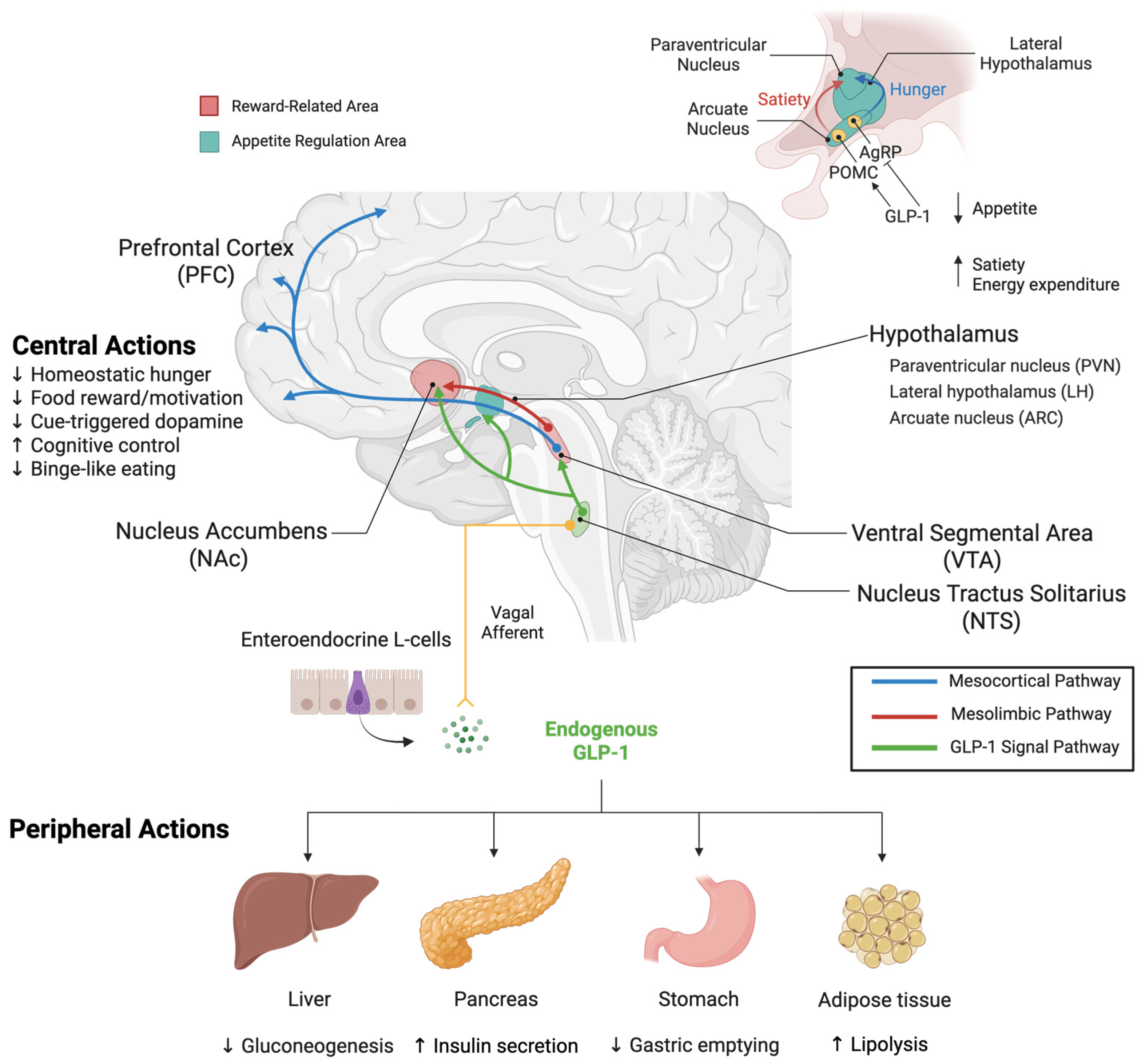
3.2.1. Peripheral Mechanisms of Action
3.2.2. Central Mechanisms of Action
4. Therapeutic Potential of GLP-1R Agonists for Binge-Eating Disorder
4.1. Preclinical Models and Baseline Findings for Binge Eating Research
4.2. Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists on Eating Behavior and Reward
4.2.1. Exendin-4
4.2.2. Semaglutide
4.2.3. Liraglutide
4.2.4. Dulaglutide
4.3. Region-Specific GLP-1 Receptor Activation and Behavioral Outcomes
4.4. Limitations of Current Research and Clinical Translation
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Adenylyl Cyclase |
| ACC | Anterior Cingulate Cortex |
| AgRP | Agouti-Related Peptide |
| AMPA/KAR | AMPA/Kainate Receptors |
| AN | Anorexia Nervosa |
| AOM | Anti-Obesity Medications |
| AP | Area Postrema |
| ARC | Arcuate Nucleus |
| BE | Binge Eating |
| BED | Binge Eating Disorder |
| BES | Binge-Eating Scale |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BN | Bulimia Nervosa |
| cAMP | Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate |
| CBT | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy |
| CCK | Cholecystokinin |
| CPP | Conditioned Place Preference |
| CVO | Circumventricular Organs |
| D1-MSN | Dopamine D1 Receptor-expressing Medium Spiny Neuron |
| D2-MSN | Dopamine D2 Receptor-expressing Medium Spiny Neuron |
| DAG | Diacylglycerol |
| DSM-5 | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition |
| EDE-Q | Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire |
| Ex-4 | Exendin-4 |
| FEDs | Feeding and Eating Disorders |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 |
| GLP-1R | GLP-1 Receptor |
| GLP-1RA | GLP-1 Receptor Agonist |
| GPCR | G-Protein Coupled Receptor |
| ICD-11 | International Classification of Diseases, 11th Revision |
| IPT | Interpersonal Therapy |
| LDX | Lisdexamfetamine |
| LH | Lateral Hypothalamus |
| mPFC | Medial Prefrontal Cortex |
| MSN | Medium Spiny Neuron |
| NAc | Nucleus Accumbens |
| NPY | Neuropeptide Y |
| NTS | Nucleus Tractus Solitarius |
| OFC | Orbitofrontal Cortex |
| PFC | Prefrontal Cortex |
| PKA | Protein Kinase A |
| PKC | Protein Kinase C |
| PLC | Phospholipase C |
| POMC | Proopiomelanocortin |
| PR | Progressive Ratio |
| PVN | Paraventricular Nucleus |
| PYY | Peptide YY |
| SCFA | Short-Chain Fatty Acid |
| vmPFC | Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex |
| VTA | Ventral Tegmental Area |
References
- Feng, B.; Harms, J.; Chen, E.; Gao, P.; Xu, P.; He, Y. Current Discoveries and Future Implications of Eating Disorders. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcelus, J.; Mitchell, A.J.; Wales, J.; Nielsen, S. Mortality rates in patients with anorexia nervosa and other eating disorders. A meta-analysis of 36 studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, H.; Wan, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, D. An update on the prevalence of eating disorders in the general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eat. Weight Disord. 2022, 27, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambleton, A.; Pepin, G.; Le, A.; Maloney, D.; Touyz, S.; Maguire, S. Psychiatric and medical comorbidities of eating disorders: Findings from a rapid review of the literature. J. Eat. Disord. 2022, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First, M.B. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edition, and clinical utility. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2013, 201, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, S.; McLean, S.A.; Bryant, E.; Le, A.; Marks, P.; Touyz, S.; Maguire, S. Risk factors for eating disorders: Findings from a rapid review. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treasure, J.; Claudino, A.M.; Zucker, N. Eating disorders. Lancet 2010, 375, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treasure, J.; Duarte, T.A.; Schmidt, U. Eating disorders. Lancet 2020, 395, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmiche, M.; Déchelotte, P.; Lambert, G.; Tavolacci, M.P. Prevalence of eating disorders over the 2000-2018 period: A systematic literature review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silén, Y.; Keski-Rahkonen, A. Worldwide prevalence of DSM-5 eating disorders among young people. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2022, 35, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smink, F.R.; van Hoeken, D.; Hoek, H.W. Epidemiology of eating disorders: Incidence, prevalence and mortality rates. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2012, 14, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfred, S.A.; Becker, C.B.; Kanzler, K.E.; Musi, N.; Espinoza, S.E.; Kilpela, L.S. Binge eating among older women: Prevalence rates and health correlates across three independent samples. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpela, L.S.; Marshall, V.B.; Keel, P.K.; LaCroix, A.Z.; Espinoza, S.E.; Hooper, S.C.; Musi, N. The clinical significance of binge eating among older adult women: An investigation into health correlates, psychological wellbeing, and quality of life. J. Eat. Disord. 2022, 10, 97, Erratum in J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C.; Berglund, P.A.; Chiu, W.T.; Deitz, A.C.; Hudson, J.I.; Shahly, V.; Aguilar-Gaxiola, S.; Alonso, J.; Angermeyer, M.C.; Benjet, C.; et al. The prevalence and correlates of binge eating disorder in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Giacomo, E.; Aliberti, F.; Pescatore, F.; Santorelli, M.; Pessina, R.; Placenti, V.; Colmegna, F.; Clerici, M. Disentangling binge eating disorder and food addiction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eat. Weight Disord. 2022, 27, 1963–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, Z.; Almahmood, H.O.; Alghasra, R.R.; Alherz, Z.A.S.; Alsharifa, H.A.G.; Qamber, S.J.; Alomar, N.A.; Almajed, F.E.; Almahroos, T.R.; Alnajjas, Z.A.; et al. Prevalence and associated factors of binge eating disorder among Bahraini youth and young adults: A cross-sectional study in a self-selected convenience sample. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmerich, H.; Kan, C.; Au, K.; Treasure, J. Pharmacological treatment of eating disorders, comorbid mental health problems, malnutrition and physical health consequences. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 217, 107667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalewska, E.; Bzowska, M.; Engel, J.; Lew-Starowicz, M. Comorbidity of binge eating disorder and other psychiatric disorders: A systematic review. BMC Psychiatry 2024, 24, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.; Straebler, S.; Cooper, Z.; Fairburn, C.G. Cognitive behavioral therapy for eating disorders. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 33, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debar, L.L.; Wilson, G.T.; Yarborough, B.J.; Burns, B.; Oyler, B.; Hildebrandt, T.; Clarke, G.N.; Dickerson, J.; Striegel, R.H. Cognitive Behavioral Treatment for Recurrent Binge Eating in Adolescent Girls: A Pilot Trial. Cogn. Behav. Pract. 2013, 20, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilo, C.M.; Juarascio, A. Binge-Eating Disorder Interventions: Review, Current Status, and Implications. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Jin, J.; Zheng, Z. The effect of CBT and its modifications for relapse prevention in major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2018, 18, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moberg, L.T.; Solvang, B.; Sæle, R.G.; Myrvang, A.D. Effects of cognitive-behavioral and psychodynamic-interpersonal treatments for eating disorders: A meta-analytic inquiry into the role of patient characteristics and change in eating disorder-specific and general psychopathology in remission. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boswell, R.G.; Potenza, M.N.; Grilo, C.M. The Neurobiology of Binge-eating Disorder Compared with Obesity: Implications for Differential Therapeutics. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.M.; James, M.H. Binge eating, overeating and food addiction: Approaches for examining food overconsumption in laboratory rodents. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 123, 110717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren-Yazicioglu, C.Y.; Yigit, A.; Dogruoz, R.E.; Yapici-Eser, H. Can GLP-1 Be a Target for Reward System Related Disorders? A Qualitative Synthesis and Systematic Review Analysis of Studies on Palatable Food, Drugs of Abuse, and Alcohol. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 614884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badulescu, S.; Tabassum, A.; Le, G.H.; Wong, S.; Phan, L.; Gill, H.; Llach, C.D.; McIntyre, R.S.; Rosenblat, J.; Mansur, R. Glucagon-like peptide 1 agonist and effects on reward behaviour: A systematic review. Physiol. Behav. 2024, 283, 114622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, J.E.; Anderberg, R.H.; Göteson, A.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F.; Skibicka, K.P. Activation of the GLP-1 receptors in the nucleus of the solitary tract reduces food reward behavior and targets the mesolimbic system. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.E.; Galli, A.; Thomsen, M.; Jensen, K.L.; Thomsen, G.K.; Klausen, M.K.; Vilsbøll, T.; Christensen, M.B.; Holst, J.J.; Owens, A.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor regulation of basal dopamine transporter activity is species-dependent. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 138, 104772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diz-Chaves, Y.; Herrera-Pérez, S.; González-Matías, L.C.; Lamas, J.A.; Mallo, F. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) in the Integration of Neural and Endocrine Responses to Stress. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorli, C.; Harashima, S.I.; Tsoukas, G.M.; Unger, J.; Karsbøl, J.D.; Hansen, T.; Bain, S.C. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide monotherapy versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 1): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multinational, multicentre phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, A.; Henry, R.; Ratner, R.; Garcia-Hernandez, P.A.; Rodriguez-Pattzi, H.; Olvera-Alvarez, I.; Hale, P.M.; Zdravkovic, M.; Bode, B. Liraglutide versus glimepiride monotherapy for type 2 diabetes (LEAD-3 Mono): A randomised, 52-week, phase III, double-blind, parallel-treatment trial. Lancet 2009, 373, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi-Sunyer, X.; Astrup, A.; Fujioka, K.; Greenway, F.; Halpern, A.; Krempf, M.; Lau, D.C.; le Roux, C.W.; Violante Ortiz, R.; Jensen, C.B.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of 3.0 mg of Liraglutide in Weight Management. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.D.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Victoza (Liraglutide) Injection: Approval Letter. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2010/022341s000ltr.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Saxenda (Liraglutide) Injection: Approval Letter. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2014/206321Orig1s000ltr.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Ozempic (Semaglutide) Injection: Approval Letter. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2017/209637Orig1s000ltr.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Approves New Medication for Chronic Weight Management. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-medication-chronic-weight-management (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Wegovy (Semaglutide) Injection: Approval Letter. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2021/215256Orig1s000ltr.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Chao, A.M.; Wadden, T.A.; Walsh, O.A.; Gruber, K.A.; Alamuddin, N.; Berkowitz, R.I.; Tronieri, J.S. Effects of Liraglutide and Behavioral Weight Loss on Food Cravings, Eating Behaviors, and Eating Disorder Psychopathology. Obesity 2019, 27, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettadapura, S.; Dowling, K.; Jablon, K.; Al-Humadi, A.W.; le Roux, C.W. Changes in food preferences and ingestive behaviors after glucagon-like peptide-1 analog treatment: Techniques and opportunities. Int. J. Obes. 2025, 49, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hironaka, J.; Ushigome, E.; Kondo, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Osaka, T.; Majima, S.; Nakanishi, N.; Okada, H.; Senmaru, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; et al. Changes in food preferences after oral semaglutide administration in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: KAMOGAWA-DM cohort. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2025, 22, 14791641251318309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoun, L.; Almardini, S.; Saliba, F.; Haddadin, F.; Mourad, O.; Jdaidani, J.; Morcos, Z.; Al Saidi, I.; Bou Sanayeh, E.; Saliba, S.; et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists: A novel pharmacotherapy for binge eating (Binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa)? A systematic review. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2024, 35, 100333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, S.E.; Bulik, C.M. Environmental and genetic risk factors for eating disorders: What the clinician needs to know. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 18, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klump, K.L.; Suisman, J.L.; Burt, S.A.; McGue, M.; Iacono, W.G. Genetic and environmental influences on disordered eating: An adoption study. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2009, 118, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.J.; Perrini, A.A.; Eckel, L.A. The Role of the Gut Microbiome, Immunity, and Neuroinflammation in the Pathophysiology of Eating Disorders. Nutrients 2021, 13, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutter, M.; Nestler, E.J. Homeostatic and hedonic signals interact in the regulation of food intake. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, J. Food intake and addictive-like eating behaviors: Time to think about the circadian clock(s). Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 106, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerdjikova, A.I.; O’Melia, A.M.; Mori, N.; McCoy, J.; McElroy, S.L. Binge eating disorder in elderly individuals. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2012, 45, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, E.M.; Gomes, F.V.S.; Vaz, A.R.; Pinto-Bastos, A.; Machado, P.P.P. Prevalence of eating disorders and picking/nibbling in elderly women. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2017, 50, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeberger, M.; Gomis, R.; Claret, M. Hypothalamic and brainstem neuronal circuits controlling homeostatic energy balance. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 220, T25–T46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterson, M.J.; Horvath, T.L. Neuronal Regulation of Energy Homeostasis: Beyond the Hypothalamus and Feeding. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouret, S.G. Development of Hypothalamic Circuits That Control Food Intake and Energy Balance. In Appetite and Food Intake: Central Control; Harris, R.B.S., Ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 135–154. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Fu, S.; Wan, Y.; Mao, J.; Cui, K.; Jiang, H. The Integrated Function of the Lateral Hypothalamus in Energy Homeostasis. Cells 2025, 14, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joly-Amado, A.; Cansell, C.; Denis, R.G.; Delbes, A.S.; Castel, J.; Martinez, S.; Luquet, S. The hypothalamic arcuate nucleus and the control of peripheral substrates. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, M.S.; Benchoula, K.; Serpell, C.J.; Hwa, W.E. AgRP/NPY and POMC neurons in the arcuate nucleus and their potential role in treatment of obesity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 915, 174611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, K.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Mayer, E.A. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: From Motility to Mood. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, J.A.; Layden, B.T.; Dugas, L.R. Signalling cognition: The gut microbiota and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1130689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashique, S.; Mohanto, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; Mishra, N.; Garg, A.; Chellappan, D.K.; Omara, T.; Iqbal, S.; Kahwa, I. Gut-brain axis: A cutting-edge approach to target neurological disorders and potential synbiotic application. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, G.J.; Meek, T.H.; Schwartz, M.W. Neurobiology of food intake in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wren, A.M.; Bloom, S.R. Gut hormones and appetite control. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2116–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, R.; Sternini, C.; De Giorgio, R.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B. Enteroendocrine cells: A review of their role in brain-gut communication. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yu, B.; Chen, D. The effects of gut microbiota on appetite regulation and the underlying mechanisms. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2414796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.D.; Xu, Q.J.; Chang, R.B. Vagal sensory neurons and gut-brain signaling. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2020, 62, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Wang, B.; Gao, H.; He, C.; Hua, R.; Liang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xin, S.; Xu, J. Vagus Nerve and Underlying Impact on the Gut Microbiota-Brain Axis in Behavior and Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 6213–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammons, M.; Popescu, M.C.; Chi, J.; Liberles, S.D.; Gogolla, N.; Rolls, A. Brain-body physiology: Local, reflex, and central communication. Cell 2024, 187, 5877–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, H.B.; Hashimoto, K. The vagus nerve: An old but new player in brain-body communication. Brain Behav. Immun. 2025, 124, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burcelin, R.; Da Costa, A.; Drucker, D.; Thorens, B. Glucose competence of the hepatoportal vein sensor requires the presence of an activated glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.A.; Brierley, D.I. GLP-1 and the Neurobiology of Eating Control: Recent Advances. Endocrinology 2025, 166, bqae167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulloch, A.J.; Murray, S.; Vaicekonyte, R.; Avena, N.M. Neural responses to macronutrients: Hedonic and homeostatic mechanisms. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunigan, A.I.; Roseberry, A.G. Actions of feeding-related peptides on the mesolimbic dopamine system in regulation of natural and drug rewards. Addict. Neurosci. 2022, 2, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yapici, N. Eating regulation: How diet impacts food cognition. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, R153–R156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haber, S.N.; Knutson, B. The reward circuit: Linking primate anatomy and human imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 4–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, C.C.; Bower, J.E.; Eisenberger, N.I.; Irwin, M.R. Stress to inflammation and anhedonia: Mechanistic insights from preclinical and clinical models. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 152, 105307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Hao, M.; Duan, J.; Han, M.H. The Formation and Function of the VTA Dopamine System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Santiago, A.M.; Thomas, M.P.; Routh, V.H. Metabolic regulation of lateral hypothalamic glucose-inhibited orexin neurons may influence midbrain reward neurocircuitry. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 62, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Bonilla, P.; Santiago-Colon, K.; Leinninger, G.M. Lateral hypothalamic area neuropeptides modulate ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons and feeding. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 223, 112986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Alonso, M.; Woods, S.C.; Pelchat, M.; Grigson, P.S.; Stice, E.; Farooqi, S.; Khoo, C.S.; Mattes, R.D.; Beauchamp, G.K. Food reward system: Current perspectives and future research needs. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, J.H.; Ung, R.L.; Resendez, S.L.; Stamatakis, A.M.; Taylor, J.G.; Huang, J.; Veleta, K.; Kantak, P.A.; Aita, M.; Shilling-Scrivo, K.; et al. Visualizing hypothalamic network dynamics for appetitive and consummatory behaviors. Cell 2015, 160, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieh, E.H.; Matthews, G.A.; Allsop, S.A.; Presbrey, K.N.; Leppla, C.A.; Wichmann, R.; Neve, R.; Wildes, C.P.; Tye, K.M. Decoding neural circuits that control compulsive sucrose seeking. Cell 2015, 160, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbano, M.F.; Wang, H.L.; Morales, M.; Wise, R.A. Feeding and Reward Are Differentially Induced by Activating GABAergic Lateral Hypothalamic Projections to VTA. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 2975–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timper, K.; Brüning, J.C. Hypothalamic circuits regulating appetite and energy homeostasis: Pathways to obesity. Dis. Model. Mech. 2017, 10, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avena, N.M.; Bocarsly, M.E. Dysregulation of brain reward systems in eating disorders: Neurochemical information from animal models of binge eating, bulimia nervosa, and anorexia nervosa. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.; Port, J.D.; Acosta, A. Integrative Hedonic and Homeostatic Food Intake Regulation by the Central Nervous System: Insights from Neuroimaging. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, K.C.; Robinson, T.E. Liking, wanting, and the incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Am. Psychol. 2016, 71, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Naffziger, E.E.; Berridge, K.C. Positive Affect: Nature and brain bases of liking and wanting. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2021, 39, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, K.C.; Robinson, T.E.; Aldridge, J.W. Dissecting components of reward: ‘liking’, ‘wanting’, and learning. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.R.; Berridge, K.C.; Mahler, S.V. Endocannabinoid-Enhanced “Liking” in Nucleus Accumbens Shell Hedonic Hotspot Requires Endogenous Opioid Signals. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2018, 3, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, I.; Berridge, K.C. ‘Liking’ and ‘wanting’ in eating and food reward: Brain mechanisms and clinical implications. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 227, 113152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandhakrishnan, A.; Korbonits, M. Glucagon-like peptide 1 in the pathophysiology and pharmacotherapy of clinical obesity. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 572–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secher, A.; Jelsing, J.; Baquero, A.F.; Hecksher-Sørensen, J.; Cowley, M.A.; Dalbøge, L.S.; Hansen, G.; Grove, K.L.; Pyke, C.; Raun, K.; et al. The arcuate nucleus mediates GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide-dependent weight loss. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4473–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. The GLP-1 journey: From discovery science to therapeutic impact. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e175634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, R.; Hernandez, N.S.; Weir, V.; Zhang, Y.; Caffrey, A.; Rich, M.T.; Crist, R.C.; Reiner, B.C.; Schmidt, H.D. An endogenous GLP-1 circuit engages VTA GABA neurons to regulate mesolimbic dopamine neurons and attenuate cocaine seeking. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadr5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Irizarry, C.S.; Swanson, C.J.; Kelley, A.E. Glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens shell control feeding behavior via the lateral hypothalamus. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 6779–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, F.; Monteleone, P.; Maj, M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in bulimia nervosa. Psychiatry Res. 2009, 169, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.R.; Moran, T.H. Gastrointestinal peptides in eating-related disorders. Physiol. Behav. 2021, 238, 113456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balantekin, K.N.; Kretz, M.J.; Mietlicki-Baase, E.G. The emerging role of glucagon-like peptide 1 in binge eating. J. Endocrinol. 2024, 262, e230405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor: Mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Huang, N.; Wang, M.; Huang, W.; Luo, Y.; Huang, J. GLP-1R in diabetes mellitus: From basic discovery to therapeutics development. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1610512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, C.R.; Garibay, P.; Knudsen, L.B.; Hastrup, S.; Peters, G.H.; Rudolph, R.; Reedtz-Runge, S. Crystal structure of glucagon-like peptide-1 in complex with the extracellular domain of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; de Graaf, C.; Yang, L.; Song, G.; Dai, A.; Cai, X.; Feng, Y.; Reedtz-Runge, S.; Hanson, M.A.; Yang, H.; et al. Structural Determinants of Binding the Seven-transmembrane Domain of the Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor (GLP-1R). J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 12991–13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graaf, C.; Donnelly, D.; Wootten, D.; Lau, J.; Sexton, P.M.; Miller, L.J.; Ahn, J.M.; Liao, J.; Fletcher, M.M.; Yang, D.; et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Its Class B G Protein-Coupled Receptors: A Long March to Therapeutic Successes. Pharmacol. Rev. 2016, 68, 954–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Clydesdale, L.; Dai, A.; Cai, X.; Feng, Y.; Yang, D.; Liang, Y.L.; Koole, C.; Zhao, P.; Coudrat, T.; et al. Two distinct domains of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor control peptide-mediated biased agonism. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 9370–9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Chai, W.; Wang, W.; Zhao, L.; Fu, Z.; Cao, W.; Liu, Z. Protein kinase A mediates glucagon-like peptide 1-induced nitric oxide production and muscle microvascular recruitment. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, E222–E228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Noshokaty, T.M.; Abdelhamid, R.; Abdelmaksoud, N.M.; Khaled, A.; Hossam, M.; Ahmed, R.; Saber, T.; Khaled, S.; Elshaer, S.S.; Abulsoud, A.I. Unlocking the multifaceted roles of GLP-1: Physiological functions and therapeutic potential. Toxicol. Rep. 2025, 14, 101895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeto, M.; Ramracheya, R.; Tarasov, A.I.; Cha, C.Y.; Chibalina, M.V.; Hastoy, B.; Philippaert, K.; Reinbothe, T.; Rorsman, N.; Salehi, A.; et al. GLP-1 stimulates insulin secretion by PKC-dependent TRPM4 and TRPM5 activation. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 4714–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeto, M.; Cha, C.Y.; Rorsman, P.; Kaku, K. A role of PLC/PKC-dependent pathway in GLP-1-stimulated insulin secretion. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, J.; Heng, J.; Newsholme, P.; Carlessi, R. Pleiotropic Effects of GLP-1 and Analogs on Cell Signaling, Metabolism, and Function. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, M.M.; Halls, M.L.; Zhao, P.; Clydesdale, L.; Christopoulos, A.; Sexton, P.M.; Wootten, D. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor internalisation controls spatiotemporal signalling mediated by biased agonists. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 156, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moo, E.V.; Møller, T.C.; Sørensen, F.A.; Inoue, A.; Bräuner-Osborne, H. Arrestin-independent internalization of the GLP-1 receptor is facilitated by a GRK, clathrin, and caveolae-dependent mechanism. FEBS J. 2025, 292, 1675–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.J. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1409–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, L.L.; Yusta, B.; Mulvihill, E.E.; Cao, X.; Streutker, C.J.; Butany, J.; Cappola, T.P.; Margulies, K.B.; Drucker, D.J. GLP-1 Receptor Expression Within the Human Heart. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 1570–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J.; Andersen, D.B.; Grunddal, K.V. Actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor ligands in the gut. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, G.R.; Hovind, P.; Asmar, A. The GLP-1-mediated gut-kidney cross talk in humans: Mechanistic insight. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2024, 326, C567–C572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, J.P.; Daniels, D.; Lee, S.; Mastitskaya, S.; Langhans, W. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Links Ingestion, Homeostasis, and the Heart. Compr. Physiol. 2025, 15, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, I.; Wang, L.; Xia, B.; Liu, J.; Tahiri, A.; El Ouaamari, A.; Wheeler, M.B.; Pang, Z.P. Activation of arcuate nucleus glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor-expressing neurons suppresses food intake. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsurada, K.; Nakata, M.; Saito, T.; Zhang, B.; Maejima, Y.; Nandi, S.S.; Sharma, N.M.; Patel, K.P.; Kario, K.; Yada, T. Central Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Signaling via Brainstem Catecholamine Neurons Counteracts Hypertension in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, R.H.; Dickson, S.L.; Skibicka, K.P. Gut peptide GLP-1 and its analogue, Exendin-4, decrease alcohol intake and reward. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, E.; Szilvásy-Szabó, A.; Ruska, Y.; Sinkó, R.; Rasch, M.G.; Egebjerg, T.; Pyke, C.; Gereben, B.; Knudsen, L.B.; Fekete, C. Distribution and ultrastructural localization of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) in the rat brain. Brain Struct. Funct. 2021, 226, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.M.; Hahn, J.D.; Konanur, V.R.; Lam, A.; Kanoski, S.E. Hippocampal GLP-1 receptors influence food intake, meal size, and effort-based responding for food through volume transmission. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Bloom, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Fritsche, A.; Gribble, F.; Grill, H.J.; Habener, J.F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 72–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolhurst, G.; Heffron, H.; Lam, Y.S.; Parker, H.E.; Habib, A.M.; Diakogiannaki, E.; Cameron, J.; Grosse, J.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Short-chain fatty acids stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion via the G-protein-coupled receptor FFAR2. Diabetes 2012, 61, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, T.U.; Bäckhed, F. Microbial regulation of GLP-1 and L-cell biology. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puddu, A.; Sanguineti, R.; Montecucco, F.; Viviani, G.L. Evidence for the gut microbiota short-chain fatty acids as key pathophysiological molecules improving diabetes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 162021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, C.B.; Gabe, M.B.N.; Svendsen, B.; Dragsted, L.O.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Holst, J.J. The impact of short-chain fatty acids on GLP-1 and PYY secretion from the isolated perfused rat colon. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G53–G65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.M.; Sun, Y.S.; Zhao, L.Q.; Chen, T.T.; Fan, M.N.; Jiao, H.C.; Zhao, J.P.; Wang, X.J.; Li, F.C.; Li, H.F.; et al. SCFAs-Induced GLP-1 Secretion Links the Regulation of Gut Microbiome on Hepatic Lipogenesis in Chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinnen, D. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists for Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Müller, T.D. Incretin hormones and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1780–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, N.; Husain, M.; Lehrke, M.; Verma, S.; Sattar, N. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for the Reduction of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Circulation 2022, 146, 1882–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantea, I.; Repanovici, A.; Andreescu, O. The Influence of GLP1 on Body Weight and Glycemic Management in Patients with Diabetes—A Scientometric Investigation and Visualization Study. Medicina 2024, 60, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriyotha, S.; Anothaisintawee, T.; Looareesuwan, P.; Nimitphong, H.; McKay, G.; Attia, J.; Thakkinstian, A. Effectiveness of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for reduction of body mass index and blood glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity: A retrospective cohort study and difference-in-difference analysis. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e086424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Marso, S.P.; Neeland, I.J. Liraglutide for weight management: A critical review of the evidence. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2017, 3, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, N.C.; Davies, M.J.; Lingvay, I.; Knop, F.K. Semaglutide for the treatment of overweight and obesity: A review. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, G.E.; Shu, I.; Rometo, D.; Arnold, J.; Korytkowski, M.; Luo, J. Real-world weight-loss effectiveness of glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists among patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study. Obesity 2023, 31, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brierley, D.I.; de Lartigue, G. Reappraising the role of the vagus nerve in GLP-1-mediated regulation of eating. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiz, A.; Filion, K.B.; Tsoukas, M.A.; Yu, O.H.; Peters, T.M.; Eisenberg, M.J. Mechanisms of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist-Induced Weight Loss: A Review of Central and Peripheral Pathways in Appetite and Energy Regulation. Am. J. Med. 2025, 138, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.R.; Mietlicki-Baase, E.G.; Kanoski, S.E.; De Jonghe, B.C. Incretins and amylin: Neuroendocrine communication between the gut, pancreas, and brain in control of food intake and blood glucose. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2014, 34, 237–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Hua, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Long, X.; Bai, Y.; Cheng, N. Efficacy and safety of GLP-1 agonists in the treatment of T2DM: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 24103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buller, S.; Blouet, C. Brain access of incretins and incretin receptor agonists to their central targets relevant for appetite suppression and weight loss. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 326, E472–E480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipa, R.O.; Balan, D.G.; Georgescu, M.T.; Ignat, L.A.; Vacaroiu, I.A.; Georgescu, D.E.; Raducu, L.; Mihai, D.A.; Chiperi, L.V.; Balcangiu-Stroescu, A.E. A Systematic Review of Semaglutide’s Influence on Cognitive Function in Preclinical Animal Models and Cell-Line Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crunkhorn, S. Understanding semaglutide action in the brain. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2025, 24, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Nakata, M.; Zhang, B.Y.; Otgon-Uul, Z.; Yada, T. GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide exerts central action to induce β-cell proliferation through medulla to vagal pathway in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabery, S.; Salinas, C.G.; Paulsen, S.J.; Ahnfelt-Rønne, J.; Alanentalo, T.; Baquero, A.F.; Buckley, S.T.; Farkas, E.; Fekete, C.; Frederiksen, K.S.; et al. Semaglutide lowers body weight in rodents via distributed neural pathways. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e133429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankir, M.K.; Lutz, T.A. Novel neural pathways targeted by GLP-1R agonists and bariatric surgery. Pflugers Arch-Eur. J. Physiol. 2025, 477, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lieu, L.; Afrin, S.; Cao, J.; Michael, N.J.; Dong, Y.; Sun, J.; Guo, H.; Williams, K.W. Direct and indirect effects of liraglutide on hypothalamic POMC and NPY/AgRP neurons–Implications for energy balance and glucose control. Mol. Metab. 2019, 28, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deem, J.D.; Faber, C.L.; Morton, G.J. AgRP neurons: Regulators of feeding, energy expenditure, and behavior. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 2362–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Carty, J.; Goldstein, N.; He, Z.; Hwang, E.; Chau, D.; Wallace, B.; Kabahizi, A.; Lieu, L.; Peng, Y.; et al. Time and metabolic state-dependent effects of GLP-1R agonists on NPY/AgRP and POMC neuronal activity in vivo. Mol. Metab. 2021, 54, 101352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto-Vianna, A.R.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-de-Lacerda, C.A. Effects of liraglutide in hypothalamic arcuate nucleus of obese mice. Obesity 2016, 24, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, S.J.; Nestler, E.J. The brain reward circuitry in mood disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 609–625, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Kwon, H.; Song, Y.; Yun, B.; Lee, Y.; Cho, Y.; Joo, A.; Han, P.L. A Group of Descending Glutamatergic Neurons Activated by Stress in Corticolimbic Regions Project to the Nucleus Accumbens. Exp. Neurobiol. 2018, 27, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Meneses, J.D.; Olaya-Bonilla, S.A.; Barrera-Carreño, S.; Tibaduiza-Arévalo, L.C.; Forero-Cárdenas, S.; Carrillo-Vaca, L.; Rojas-Rodríguez, L.C.; Calderon-Ospina, C.A.; Rodríguez-Quintana, J. GLP-1 Analogues in the Neurobiology of Addiction: Translational Insights and Therapeutic Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupa, A.J. Curbing the appetites and restoring the capacity for satisfaction: The impact of GLP-1 agonists on the reward circuitry. Neurosci. Appl. 2025, 4, 105512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindvall Dahlgren, C.; Wisting, L.; Rø, Ø. Feeding and eating disorders in the DSM-5 era: A systematic review of prevalence rates in non-clinical male and female samples. J. Eat. Disord. 2017, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, H.W.; van Elburg, A.A. Feeding and eating disorders in the DSM-5. Tijdschr. Psychiatr. 2014, 56, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.F. Animal models of eating disorders. Neuroscience 2012, 211, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corwin, R.L.; Babbs, R.K. Rodent models of binge eating: Are they models of addiction? ILAR J. 2012, 53, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, K.D.; Murdaugh, D.L.; King, V.L.; Boggiano, M.M. Motivation for palatable food despite consequences in an animal model of binge eating. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2011, 44, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyzyk, T.A.; Sahr, A.E.; Statnick, M.A. A model of binge-like eating behavior in mice that does not require food deprivation or stress. Obesity 2010, 18, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petković, A.; Chaudhury, D. Encore: Behavioural animal models of stress, depression and mood disorders. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 931964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzoli, M.; Sanghez, V.; Bartolomucci, A. Chronic subordination stress induces hyperphagia and disrupts eating behavior in mice modeling binge-eating-like disorder. Front. Nutr. 2015, 1, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, A.L.; Calvin, D.C.; Silver, R.I.; Peppas, D.S.; Docimo, S.G. Immunohistochemical description of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in human clitoris. J. Urol. 1997, 158, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, S.P.; Goddard, S.; Brammer, R.J.; Hutson, P.H.; Heal, D.J. Investigation of impulsivity in binge-eating rats in a delay-discounting task and its prevention by the d-amphetamine prodrug, lisdexamfetamine. J. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 31, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquale, E.K.; Boyar, A.M.; Boutelle, K.N. Reward and Inhibitory Control as Mechanisms and Treatment Targets for Binge Eating Disorder. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2024, 26, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sclafani, A.; Ackroff, K. Reinforcement value of sucrose measured by progressive ratio operant licking in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 2003, 79, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Sánchez, C.; Santos, J.W.; Smith, K.L.; Ferragud, A.; Sabino, V.; Cottone, P. Seeking behavior, place conditioning, and resistance to conditioned suppression of feeding in rats intermittently exposed to palatable food. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 129, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astur, R.S.; Palmisano, A.N.; Hudd, E.C.; Carew, A.W.; Deaton, B.E.; Kuhney, F.S.; Niezrecki, R.N.; Santos, M. Pavlovian conditioning to food reward as a function of eating disorder risk. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 291, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercante, F.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, E.; Pucci, M.; Botticelli, L.; Cifani, C.; D’Addario, C.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V. Repeated binge-like eating episodes in female rats alter adenosine A2A and dopamine D2 receptor genes regulation in the brain reward system. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2024, 57, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, B.A.; Sinclair, E.B.; Sisk, C.L.; Klump, K.L. Exploring reward system responsivity in the nucleus accumbens across chronicity of binge eating in female rats. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2018, 51, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, J.H. Dopamine signaling in reward-related behaviors. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenaerts, N.; Jongen, D.; Ceccarini, J.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Vrieze, E. The neurobiological reward system and binge eating: A critical systematic review of neuroimaging studies. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2022, 55, 1421–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanoski, S.E.; Fortin, S.M.; Arnold, M.; Grill, H.J.; Hayes, M.R. Peripheral and central GLP-1 receptor populations mediate the anorectic effects of peripherally administered GLP-1 receptor agonists, liraglutide and exendin-4. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3103–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Dou, G.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K. In vitro metabolic stability of exendin-4: Pharmacokinetics and identification of cleavage products. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, S.L.; Shirazi, R.H.; Hansson, C.; Bergquist, F.; Nissbrandt, H.; Skibicka, K.P. The glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) analogue, exendin-4, decreases the rewarding value of food: A new role for mesolimbic GLP-1 receptors. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 4812–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ferreras, L.; Richard, J.E.; Noble, E.E.; Eerola, K.; Anderberg, R.H.; Olandersson, K.; Taing, L.; Kanoski, S.E.; Hayes, M.R.; Skibicka, K.P. Lateral hypothalamic GLP-1 receptors are critical for the control of food reinforcement, ingestive behavior and body weight. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konanur, V.R.; Hsu, T.M.; Kanoski, S.E.; Hayes, M.R.; Roitman, M.F. Phasic dopamine responses to a food-predictive cue are suppressed by the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist Exendin-4. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 215, 112771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce-Messick, Z.; Pratt, W.E. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors modulate the binge-like feeding induced by µ-opioid receptor stimulation of the nucleus accumbens in the rat. Neuroreport 2020, 31, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mietlicki-Baase, E.G.; Ortinski, P.I.; Reiner, D.J.; Sinon, C.G.; McCutcheon, J.E.; Pierce, R.C.; Roitman, M.F.; Hayes, M.R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation in the nucleus accumbens core suppresses feeding by increasing glutamatergic AMPA/kainate signaling. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 6985–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, C.; Blundell, J.; Tetens Hoff, S.; Dahl, K.; Bauer, R.; Baekdal, T. Effects of oral semaglutide on energy intake, food preference, appetite, control of eating and body weight in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichsen, M.; Breitschaft, A.; Tadayon, S.; Wizert, A.; Skovgaard, D. The effect of semaglutide 2.4 mg once weekly on energy intake, appetite, control of eating, and gastric emptying in adults with obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooij, K.L.; Koster, D.I.; Eeltink, E.; Luijendijk, M.; Drost, L.; Ducrocq, F.; Adan, R.A.H. GLP-1 receptor agonist semaglutide reduces appetite while increasing dopamine reward signaling. Neurosci. Appl. 2024, 3, 103925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, J.; Bang, N.; Ratliff, E.L.; Paszkowiak, M.A.; Khorgami, Z.; Khalsa, S.S.; Simmons, W.K. Successful treatment of binge eating disorder with the GLP-1 agonist semaglutide: A retrospective cohort study. Obes. Pillars 2023, 7, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzoulis, P.; Batavanis, M.; Baldeweg, S. A Real-World Study of the Effectiveness and Safety of Semaglutide for Weight Loss. Cureus 2024, 16, e59558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, N.J.; Kanoski, S.E.; Hayes, M.R.; Daniels, D. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists suppress water intake independent of effects on food intake. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 301, R1755–R1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, S.M.; Lipsky, R.K.; Lhamo, R.; Chen, J.; Kim, E.; Borner, T.; Schmidt, H.D.; Hayes, M.R. GABA neurons in the nucleus tractus solitarius express GLP-1 receptors and mediate anorectic effects of liraglutide in rats. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaay8071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, H.J.; Olson, D.; Mayfield, D.; Wright, P.; Nian, H.; Mashayekhi, M.; Koethe, J.R.; Niswender, K.D.; Luther, J.M.; Brown, N.J. Effect of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist liraglutide, compared to caloric restriction, on appetite, dietary intake, body fat distribution and cardiometabolic biomarkers: A randomized trial in adults with obesity and prediabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 2340–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Sample, C.H.; Davidson, T.L. The effects of a GLP-1 analog liraglutide on reward value and the learned inhibition of appetitive behavior in male and female rats. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1875–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Pang, M.; Yu, Y.; Gou, X.; Si, P.; Zhawatibai, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Guo, T.; Yi, X.; et al. The neuroprotection of liraglutide on diabetic cognitive deficits is associated with improved hippocampal synapses and inhibited neuronal apoptosis. Life Sci. 2019, 231, 116566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, R.; Rigoux, L.; Kuzmanovic, B.; Iglesias, S.; Kretschmer, A.C.; Schlamann, M.; Albus, K.; Edwin Thanarajah, S.; Sitnikow, T.; Melzer, C.; et al. Liraglutide restores impaired associative learning in individuals with obesity. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, M.R.; Schmidt, H.D. GLP-1 influences food and drug reward. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2016, 9, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, S.A.; Rohana, A.G.; Shah, S.A.; Chinna, K.; Wan Mohamud, W.N.; Kamaruddin, N.A. Improvement in binge eating in non-diabetic obese individuals after 3 months of treatment with liraglutide–A pilot study. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 9, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, K.C.; Chao, A.M.; Bruzas, M.B.; McCuen-Wurst, C.; Jones, E.; McAllister, C.; Gruber, K.; Berkowitz, R.I.; Wadden, T.A.; Tronieri, J.S. A pilot randomized controlled trial of liraglutide 3.0 mg for binge eating disorder. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2023, 9, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Porto, A.; Casarsa, V.; Colussi, G.; Catena, C.; Cavarape, A.; Sechi, L. Dulaglutide reduces binge episodes in type 2 diabetic patients with binge eating disorder: A pilot study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierret, A.C.S.; Benton, M.; Sen Gupta, P.; Ismail, K. A qualitative study of the mental health outcomes in people being treated for obesity and type 2 diabetes with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. Acta Diabetol. 2025, 62, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, J.R.; Skibicka, K.P.; Dickson, S.L.; Leng, G. Neural substrates underlying interactions between appetite stress and reward. Obes. Facts 2012, 5, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffino, F.L.; Siemian, J.N.; Petrella, M.; Laing, B.T.; Sarsfield, S.; Borja, C.B.; Gajendiran, A.; Zuccoli, M.L.; Aponte, Y. Activation of a lateral hypothalamic-ventral tegmental circuit gates motivation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadeff, A.L.; Grill, H.J. Hindbrain nucleus tractus solitarius glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signaling reduces appetitive and motivational aspects of feeding. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 307, R465–R470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Merrer, J.; Becker, J.A.; Befort, K.; Kieffer, B.L. Reward processing by the opioid system in the brain. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 1379–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikemoto, S. Brain reward circuitry beyond the mesolimbic dopamine system: A neurobiological theory. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 35, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, H.; Takenoya, F.; Guan, J.L.; Kageyama, H.; Yada, T.; Shioda, S. Hypothalamic neuronal networks and feeding-related peptides involved in the regulation of feeding. Anat. Sci. Int. 2003, 78, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börchers, S.; Skibicka, K.P. GLP-1 and Its Analogs: Does Sex Matter? Endocrinology 2025, 166, bqae165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outeiriño-Iglesias, V.; Romaní-Pérez, M.; González-Matías, L.C.; Vigo, E.; Mallo, F. GLP-1 Increases Preovulatory LH Source and the Number of Mature Follicles, As Well As Synchronizing the Onset of Puberty in Female Rats. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 4226–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, H.; Wolf, S.; Rabasa, C.; Rodriguez-Pacheco, F.; Babaei, C.S.; Stöber, F.; Goldschmidt, J.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Finan, B.; Tschöp, M.H.; et al. GLP-1 and estrogen conjugate acts in the supramammillary nucleus to reduce food-reward and body weight. Neuropharmacology 2016, 110, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadeff, A.L.; Rupprecht, L.E.; Hayes, M.R. GLP-1 neurons in the nucleus of the solitary tract project directly to the ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens to control for food intake. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, T.; Sun, Z.; Pan, Y.; Deng, X.; Yuan, G. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: New Regulator in Lipid Metabolism. Diabetes Metab. J. 2024, 48, 354–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderberg, R.H.; Anefors, C.; Bergquist, F.; Nissbrandt, H.; Skibicka, K.P. Dopamine signaling in the amygdala, increased by food ingestion and GLP-1, regulates feeding behavior. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 136, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, C.P. The role of D2-autoreceptors in regulating dopamine neuron activity and transmission. Neuroscience 2014, 282, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, B.; Zweifel, L.S. Disinhibitory feedback loops for reward and aversion. Cell Res. 2022, 32, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derman, R.C.; Bryda, E.C.; Ferrario, C.R. Role of nucleus accumbens D1-type medium spiny neurons in the expression and extinction of sign-tracking. Behav. Brain Res. 2024, 459, 114768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egecioglu, E.; Engel, J.A.; Jerlhag, E. The glucagon-like peptide 1 analogue Exendin-4 attenuates the nicotine-induced locomotor stimulation, accumbal dopamine release, conditioned place preference as well as the expression of locomotor sensitization in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erreger, K.; Davis, A.R.; Poe, A.M.; Greig, N.H.; Stanwood, G.D.; Galli, A. Exendin-4 decreases amphetamine-induced locomotor activity. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 106, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egecioglu, E.; Engel, J.A.; Jerlhag, E. The glucagon-like peptide 1 analogue, exendin-4, attenuates the rewarding properties of psychostimulant drugs in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossat, A.M.; Lilly, N.; Kay, K.; Williams, D.L. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptors in nucleus accumbens affect food intake. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 14453–14457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranäs, C.; Edvardsson, C.E.; Shevchouk, O.T.; Zhang, Q.; Witley, S.; Blid Sköldheden, S.; Zentveld, L.; Vallöf, D.; Tufvesson-Alm, M.; Jerlhag, E. Semaglutide reduces alcohol intake and relapse-like drinking in male and female rats. eBioMedicine 2023, 93, 104642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. From metabolism to mind: The expanding role of the GLP-1 receptor in neurotherapeutics. Neurotherapeutics 2025, 22, e00712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, J.N.; Belknap, J.K.; Collins, A.; Crabbe, J.C.; Frankel, W.; Henderson, N.; Hitzemann, R.J.; Maxson, S.C.; Miner, L.L.; Silva, A.J.; et al. Behavioral phenotypes of inbred mouse strains: Implications and recommendations for molecular studies. Psychopharmacology 1997, 132, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton, É.; Juster, R.P.; Booij, L. Gender and sex in eating disorders: A narrative review of the current state of knowledge, research gaps, and recommendations. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, J.; Fonseca, L.M. How sample size influences research outcomes. Dental Press. J. Orthod. 2014, 19, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, C.; Pinto-Gouveia, J.; Ferreira, C. Expanding binge eating assessment: Validity and screening value of the Binge Eating Scale in women from the general population. Eat. Behav. 2015, 18, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilo, C.M.; Ivezaj, V.; Yurkow, S.; Tek, C.; Wiedemann, A.A.; Gueorguieva, R. Lisdexamfetamine maintenance treatment for binge-eating disorder following successful treatments: Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Psychol. Med. 2024, 54, 3334–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Drug/Dosage/ Administration Route | Model | Key Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
Exendin-4
| Rats |
| [176] |
Exendin-4
| Male and female rats |
| [174] |
Exendin-4
| Rats |
| [175] |
Exendin-4
| Rats |
| [28] |
Semaglutide
| Diet-induced obese mice and Rats fed a high-fat diet |
| [143] |
Semaglutide
| Pitx3-cre mice with cre-dependent GCaMP6s virus into the VTA |
| [180] |
| Liraglutide 10 μg/kg
| Male and female rats |
| [186] |
| Drug/Dosage/ Administration Route | Subject/ Study Design | Key Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semaglutide | BED Open-label retrospective cohort study (N = 98) |
| [181] |
Liraglutide
| Non-diabetic obesity with subclinical binge eating Randomized controlled trial (N = 44; 12 weeks) |
| [190] |
Liraglutide
| BMI ≥ 27 kg/m2 and BED Double-blind, randomized controlled trial (N = 27; 17 weeks) |
| [191] |
Liraglutide
| Obesity Randomized controlled trial with exploratory analysis (N = 150; 52 weeks) |
| [40] |
Dulaglutide
| Type 2 diabetes with BED Pilot open label, prospective controlled study (12 weeks) |
| [192] |
| Multiple GLP-1RAs Various Doses: Liraglutide
| Obesity and/or type 2 diabetes Qualitative, individual, semi-structured interviews (N = 9; 12–16 weeks) |
| [193] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tongta, S.; Sungkaworn, T.; Pathomthongtaweechai, N. Neurobiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Binge Eating Disorder: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210974
Tongta S, Sungkaworn T, Pathomthongtaweechai N. Neurobiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Binge Eating Disorder: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210974
Chicago/Turabian StyleTongta, Sujitra, Titiwat Sungkaworn, and Nutthapoom Pathomthongtaweechai. 2025. "Neurobiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Binge Eating Disorder: A Narrative Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210974
APA StyleTongta, S., Sungkaworn, T., & Pathomthongtaweechai, N. (2025). Neurobiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Binge Eating Disorder: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210974






