Molecular Diagnostics Supporting a ≥35% Diffuse Peritubular Capillaritis Extent Threshold for Diagnosis of AMR—A Retrospective Dual Center Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics and Biopsy Findings
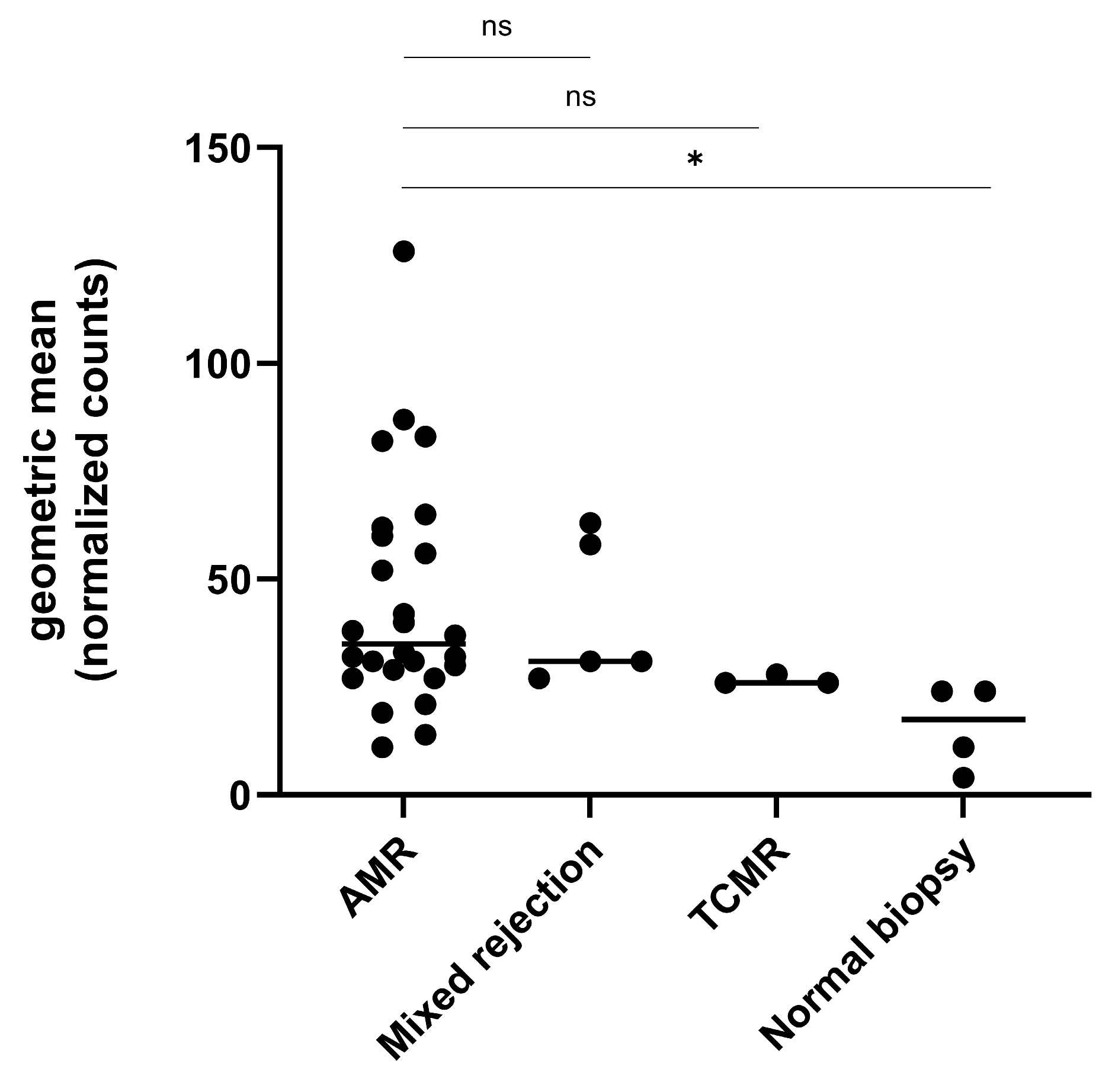
2.2. Gene Expression Analysis in the Exploratory Cohort
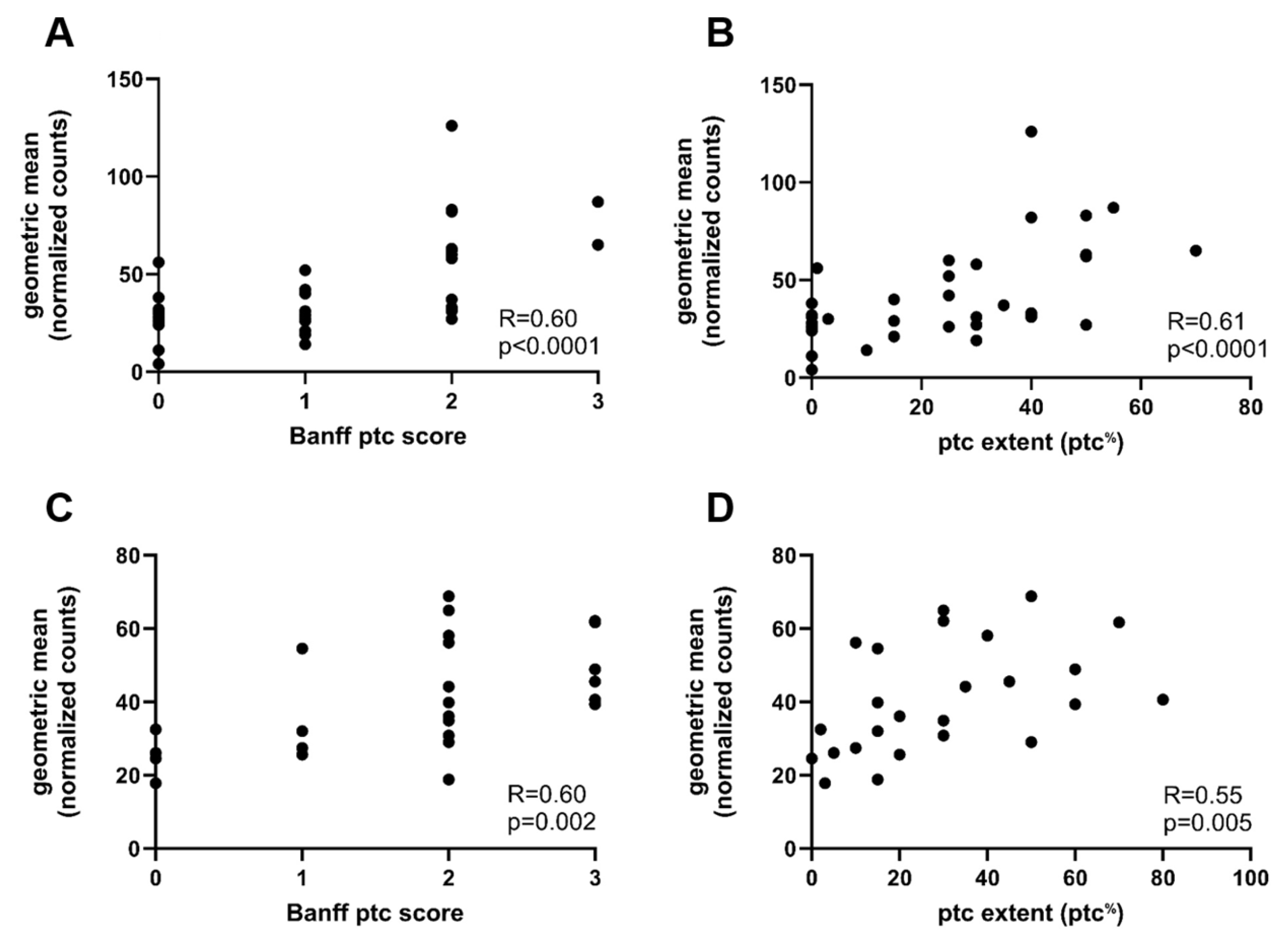
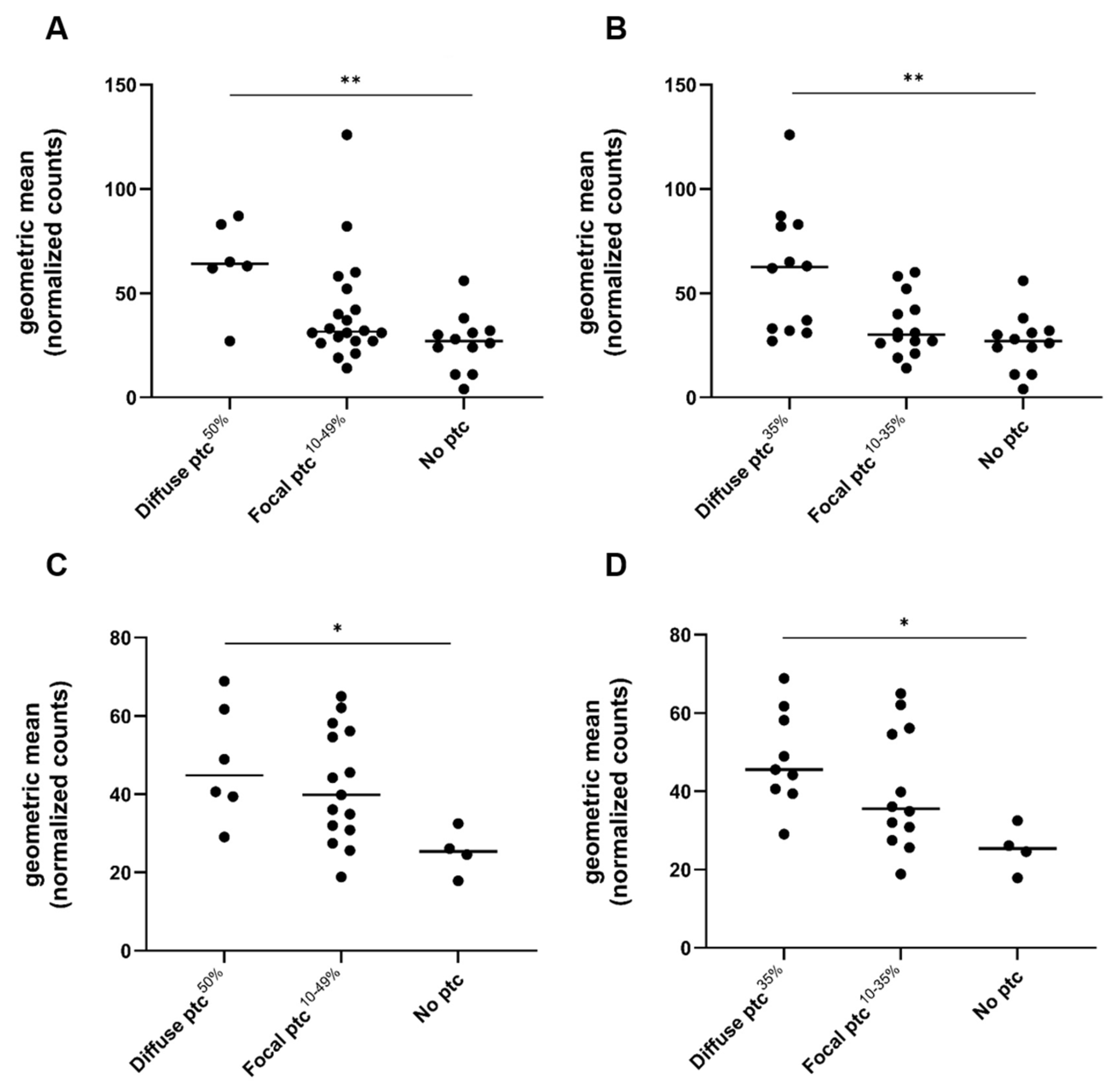
2.3. Gene Expression Analysis in Relation to Ptc and Other Banff Single Lesions
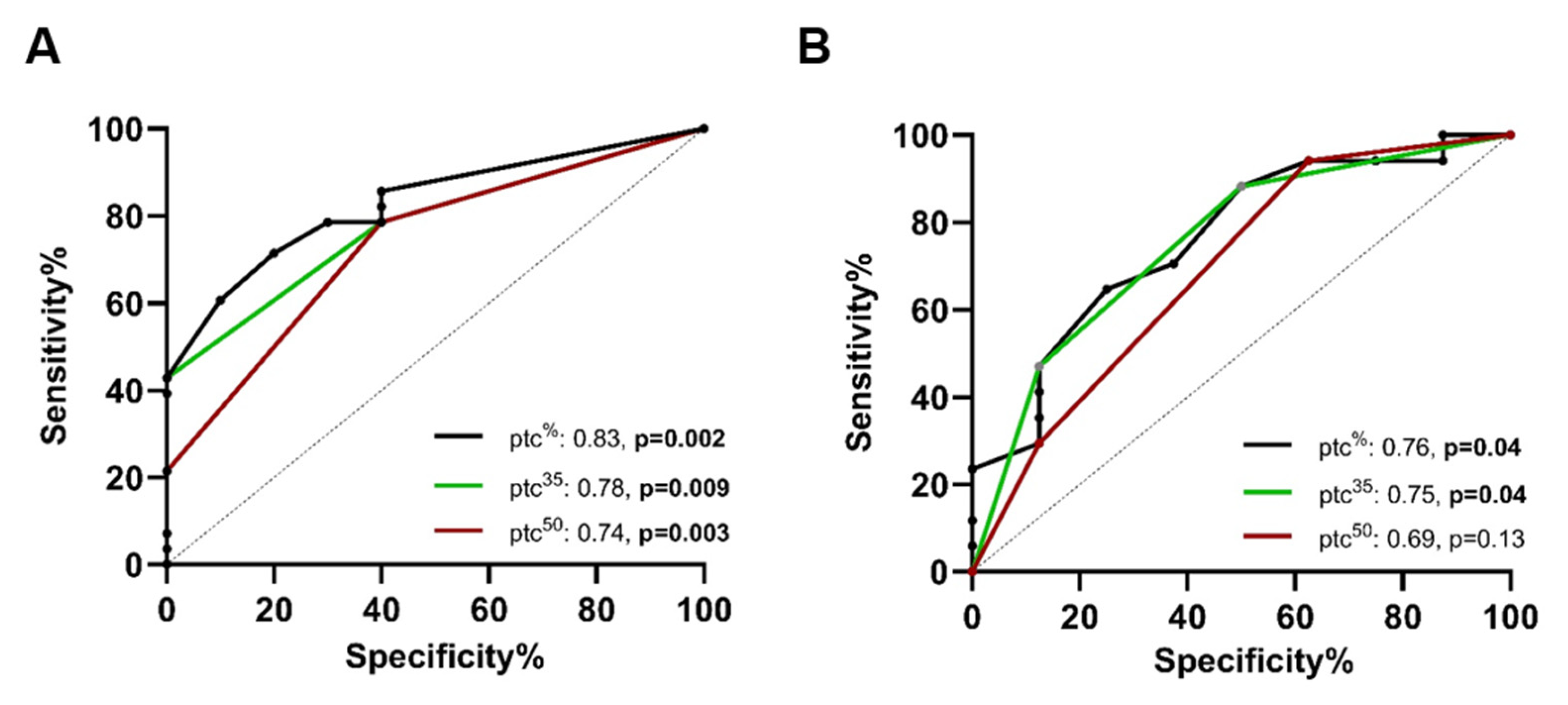
2.4. ROC Analysis for the Prediction of AMRQ>1
2.5. Comparison of Biopsies with and Without Transplant Glomerulopathy (cg > 0)
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis in the Validation Cohort
2.7. ROC Analysis for the Prediction of AMRQ>1 in the Validation Cohort
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Inclusion Criteria
4.2. Exploratory Cohort and Intragraft Gene Expression
4.3. Validation Cohort and Intragraft Gene Expression
4.4. Statistics
4.5. Ethics Committee
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ah | Banff score arteriolar hyalinosis |
| AMR | antibody-mediated rejection |
| AMRQ>1 | AMR-associated gene expression above the 1st quartile |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| cAMR | chronic antibody-mediated rejection |
| caAMR | chronic active antibody-mediated rejection |
| cg | Banff score chronic glomerulopathy |
| ci | Banff score interstitial fibrosis |
| CI | confidence interval |
| ct | Banff score tubular atrophy |
| cv | Banff score vascular fibrous intimal thickening |
| DSA | donor-specific antibodies |
| FFPE | formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| g | Banff score glomerulitis |
| i | Banff score interstitial inflammation |
| MVI | microvascular inflammation |
| ptc | peritubular capillaritis |
| ptc% | ptc quantified as % |
| ptc35% | diffuse ptc extent cut-off defined as ≥35% |
| ptc50% | diffuse ptc extent cut-off defined as ≥50% |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| t | Banff score tubulitis |
| ti | Banff score total inflammation |
| TCMR | T-cell-mediated rejection |
| v | Banff score intimal arteritis |
References
- Aubert, O.; Loupy, A.; Hidalgo, L.; Duong van Huyen, J.P.; Higgins, S.; Viglietti, D.; Jouven, X.; Glotz, D.; Legendre, C.; Lefaucheur, C.; et al. Antibody-Mediated Rejection Due to Preexisting versus De Novo Donor-Specific Antibodies in Kidney Allograft Recipients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayrdorfer, M.; Liefeldt, L.; Wu, K.; Rudolph, B.; Zhang, Q.; Friedersdorff, F.; Lachmann, N.; Schmidt, D.; Osmanodja, B.; Naik, M.G.; et al. Exploring the Complexity of Death-Censored Kidney Allograft Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhmig, G.A.; Naesens, M.; Viklicky, O.; Thaunat, O.; Diebold, M.; Rostaing, L.; Budde, K. Antibody-mediated rejection—Treatment standard. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2025, 40, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roufosse, C.; Simmonds, N.; Clahsen-van Groningen, M.; Haas, M.; Henriksen, K.J.; Horsfield, C.; Loupy, A.; Mengel, M.; Perkowska-Ptasińska, A.; Rabant, M.; et al. A 2018 Reference Guide to the Banff Classification of Renal Allograft Pathology. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1795–1814, Erratum in Transplantation 2018, 102, e497. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000002519; Erratum in Transplantation 2022, 106, e528. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000004409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varol, H.; Wagenmakers, A.; Hoeft, K.; Callemeyn, J.; Bodewes, R.; Bramer, W.; Stubbs, A.; Kramann, R.; Naesens, M.; Clahsen-Van Groningen, M.C. Expanding the Scope of Microvascular Inflammation: Unveiling Its Presence Beyond Antibody-Mediated Rejection Into T-Cell Mediated Contexts. Transplant. Int. 2024, 37, 13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omić, H.; Eder, M.; Schrag, T.A.; Kozakowski, N.; Kläger, J.; Bond, G.; Kikić, Ž. Peritubular and Tubulointerstitial Inflammation as Predictors of Impaired Viral Clearance in Polyomavirus Nephropathy. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakowski, N.; Herkner, H.; Eskandary, F.; Eder, M.; Winnicki, W.; Kläger, J.; Bond, G.; Kikic, Ž. An integrative approach for the assessment of peritubular capillaritis extent and score in low-grade microvascular inflammation-associations with transplant glomerulopathy and graft loss. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakowski, N.; Herkner, H.; Böhmig, G.A.; Regele, H.; Kornauth, C.; Bond, G.; Kikić, Ž. The diffuse extent of peritubular capillaritis in renal allograft rejection is an independent risk factor for graft loss. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loupy, A.; Haas, M.; Roufosse, C.; Naesens, M.; Adam, B.; Afrouzian, M.; Akalin, E.; Alachkar, N.; Bagnasco, S.; Becker, J.U.; et al. The Banff 2019 Kidney Meeting Report (I): Updates on and clarification of criteria for T cell- and antibody-mediated rejection. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 2318–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, M.; Loupy, A.; Lefaucheur, C.; Roufosse, C.; Glotz, D.; Seron, D.; Nankivell, B.J.; Halloran, P.F.; Colvin, R.B.; Akalin, E.; et al. The Banff 2017 Kidney Meeting Report: Revised diagnostic criteria for chronic active T cell–mediated rejection, antibody-mediated rejection, and prospects for integrative endpoints for next-generation clinical trials. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, M.; Sis, B.; Racusen, L.C.; Solez, K.; Glotz, D.; Colvin, R.B.; Castro, M.C.R.; David, D.S.R.; David-Neto, E.; Bagnasco, S.M.; et al. Banff 2013 Meeting Report: Inclusion of C4d-Negative Antibody-Mediated Rejection and Antibody-Associated Arterial Lesions. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 272–283, Erratum in Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 2784. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.13517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, B.A.; Kikic, Z.; Wagner, S.; Bouatou, Y.; Gueguen, J.; Drieux, F.; Reid, G.; Du, K.; Bräsen, J.H.; D’Agati, V.D.; et al. Intragraft gene expression in native kidney BK virus nephropathy versus T cell-mediated rejection: Prospects for molecular diagnosis and risk prediction. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 3486–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, B.A.; Murakami, N.; Reid, G.; Du, K.; Jasim, R.; Boils, C.L.; Bu, L.; Hill, P.D.; Murray, A.G.; Renaudin, K.; et al. Gene expression profiling in kidney transplants with immune checkpoint inhibitor–associated adverse events. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikić, Ž.; Adam, B.A.; Buxeda, A.; Lefaucheur, C.; Loupy, A.; Regele, H.; Cejka, D.; Haas, M.; Colvin, R.B.; Mengel, M. Quantitative scoring of progression in transplant glomerulopathy using digital pathology may be superior to Banff cg scoring. Kidney Int. 2023, 103, 365–377, Erratum in Kidney Int. 2024, 106, 763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2024.07.016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohmig, G.A.; Loupy, A.; Sablik, M.; Naesens, M. Microvascular inflammation in kidney allografts: New directions for patient management. Am. J. Transplant. 2025, 25, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naesens, M.; Roufosse, C.; Haas, M.; Lefaucheur, C.; Mannon, R.B.; Adam, B.A.; Aubert, O.; Bohmig, G.A.; Callemeyn, J.; Clahsen-van Groningen, M.; et al. The Banff 2022 Kidney Meeting Report: Reappraisal of microvascular inflammation and the role of biopsy-based transcript diagnostics. Am. J. Transplant. 2024, 24, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sablik, M.; Sannier, A.; Raynaud, M.; Goutaudier, V.; Divard, G.; Astor, B.C.; Weng, P.; Smith, J.; Garro, R.; Warady, B.A.; et al. Microvascular Inflammation of Kidney Allografts and Clinical Outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouatou, Y.; Viglietti, D.; Pievani, D.; Louis, K.; Duong Van Huyen, J.P.; Rabant, M.; Aubert, O.; Taupin, J.L.; Glotz, D.; Legendre, C.; et al. Response to treatment and long-term outcomes in kidney transplant recipients with acute T cell-mediated rejection. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 1972–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.Y.; Paek, J.H.; Jin, K.; Park, S.B.; Choe, M.; Han, S. Differences in Pathologic Features and Graft Outcomes of Rejection on Kidney Transplant. Transplant. Proc. 2019, 51, 2655–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kort, H.; Willicombe, M.; Brookes, P.; Dominy, K.M.; Santos-Nunez, E.; Galliford, J.W.; Chan, K.; Taube, D.; McLean, A.G.; Cook, H.T.; et al. Microcirculation inflammation associates with outcome in renal transplant patients with de novo donor-specific antibodies. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Schmidt, D.; López del Moral, C.; Osmanodja, B.; Lachmann, N.; Halleck, F.; Choi, M.; Bachmann, F.; Ronicke, S.; Duettmann, W.; et al. Poor Outcomes in Patients with Transplant Glomerulopathy Independent of Banff Categorization or Therapeutic Interventions. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 889648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutani, A.; Guevara-Pineda, D.; Lerner, G.B.; Menon, M.C. Re-Evaluating the Transplant Glomerulopathy Lesion—Beyond Donor-Specific Antibodies. Transplant. Int. 2024, 37, 13365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengel, M.; Loupy, A.; Haas, M.; Roufosse, C.; Naesens, M.; Akalin, E.; Clahsen-van Groningen, M.C.; Dagobert, J.; Demetris, A.J.; Duong van Huyen, J.-P.; et al. Banff 2019 Meeting Report: Molecular diagnostics in solid organ transplantation–Consensus for the Banff Human Organ Transplant (B-HOT) gene panel and open source multicenter validation. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 2305–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, K.A.; Schrezenmeier, E.; Diebold, M.; Halloran, P.F.; Schatzl, M.; Schranz, S.; Haindl, S.; Kasbohm, S.; Kainz, A.; Eskandary, F.; et al. A Randomized Phase 2 Trial of Felzartamab in Antibody-Mediated Rejection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lye, W.-C.; Loh, H.-L. Anti-CD38 Daratumumab Treatment of Chronic Active Antibody-Mediated Kidney Allograft Rejection. Kidney Int. Rep. 2025, 10, 3506–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, G.; Wahrmann, M.; Exner, M.; Regele, H.; Huttary, N.; Schillinger, M.; Kormoczi, G.F.; Horl, W.H.; Bohmig, G.A. In vitro detection of C4d-fixing HLA alloantibodies: Associations with capillary C4d deposition in kidney allografts. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristoferi, I.; Varol, H.; van Baardwijk, M.; Rahiem, L.; Lila, K.A.; van den Bosch, T.P.P.; Baan, C.C.; Hesselink, D.A.; Kramann, R.; Minnee, R.C.; et al. Multiomic profiling of transplant glomerulopathy reveals a novel T-cell dominant subclass. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, H.; Ernst, A.; Cristoferi, I.; Arns, W.; Baan, C.C.; van Baardwijk, M.; van den Bosch, T.; Eckhoff, J.; Harth, A.; Hesselink, D.A.; et al. Feasibility and Potential of Transcriptomic Analysis Using the NanoString nCounter Technology to Aid the Classification of Rejection in Kidney Transplant Biopsies. Transplantation 2023, 107, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MedCalc Software Ltd. Comparison of AUC of Independent ROC Curves, MedCalc Software Ltd.: Ostend, Belgium, 2025.
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. A method of comparing the areas under receiver operating characteristic curves derived from the same cases. Radiology 1983, 148, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Biopsies (N = 38) |
|---|---|
| Findings at transplantation * | |
| Recipient age at transplantation, mean ± SD | 46.6 ± 16.0 |
| DSAs at transplantation, N (%) | 2 (5.3%) |
| Diagnosis | |
| No rejection/normal biopsy, N (%) | 4 (10.5) |
| AMR, N (%) | 26 (68.4) |
| Mixed rejection, N (%) | 5 (13.2) |
| TCMR, N (%) | 3 (7.9) |
| Findings at the time of biopsy | |
| DSAs detectable at biopsy, N (%) | 24 (66.7) |
| Months after Tx, median (IQR) | 4.2 (1.1–42.3) |
| Serum creatinine at 1st biopsy, mg/dL, median (IQR) * | 2.2 (1.9–2.8) |
| Serum creatinine at 2nd biopsy, mg/dL, median (IQR) * | 2.6 (2.1–4.7) |
| Banff lesion scores | |
| Peritubular capillaritis (ptc) extent (%) | 25 (0–40) |
| Peritubular capillaritis (ptc) score, median (IQR) | 1 (0–2) |
| Glomerulitis (g), median (IQR) | 2 (1–2.5) |
| MVI score (g + ptc), median (IQR) | 4 (1–4) |
| Chronic glomerulopathy (cg), median (IQR) | 1 (0–3) |
| Interstitial inflammation (i), median (IQR) | 0 (0–1) |
| Total inflammation (ti), median (IQR) | 1 (1–2) |
| Tubulitis (t), median (IQR) | 0 (0–1) |
| Intimal arteritis (v), median (IQR) | 1 (0–2) |
| Interstitial fibrosis (ci), median (IQR) | 1 (1–2) |
| Tubular atrophy (ct), median (IQR) | 1 (1–2) |
| Vascular fibrous intimal thickening (cv), median (IQR) | 0 (0–1) |
| Arteriolar hyalinosis (ah), median (IQR) | 0 (0–0) |
| Variable | Prediction of AMRQ>1 (AUC, 95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Exploratory Cohort | Validation Cohort | |
| PTC score | 0.81, CI: 0.67–0.93, p = 0.004 | 0.81, CI: 0.63–0.98, p = 0.02 |
| PTC extent (%) | 0.83, CI: 0.70–0.96, p = 0.002 | 0.76, CI: 0.56–0.96, p = 0.04 |
| PTC extent (50%) | 0.74, CI: 0.56–0.90, p = 0.03 | 0.69, CI: 0.46–0.93, p = 0.13 |
| PTC extent (35%) | 0.78, CI: 0.63–0.93, p = 0.009 | 0.75, CI: 0.54–0.96, p = 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eder, M.; Clahsen-van Groningen, M.C.; Mengel, M.; Omic, H.; Cejka, D.; Adam, B.; Kozakowski, N.; Kikić, Ž. Molecular Diagnostics Supporting a ≥35% Diffuse Peritubular Capillaritis Extent Threshold for Diagnosis of AMR—A Retrospective Dual Center Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10945. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210945
Eder M, Clahsen-van Groningen MC, Mengel M, Omic H, Cejka D, Adam B, Kozakowski N, Kikić Ž. Molecular Diagnostics Supporting a ≥35% Diffuse Peritubular Capillaritis Extent Threshold for Diagnosis of AMR—A Retrospective Dual Center Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10945. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210945
Chicago/Turabian StyleEder, Michael, Marian C. Clahsen-van Groningen, Michael Mengel, Haris Omic, Daniel Cejka, Benjamin Adam, Nicolas Kozakowski, and Željko Kikić. 2025. "Molecular Diagnostics Supporting a ≥35% Diffuse Peritubular Capillaritis Extent Threshold for Diagnosis of AMR—A Retrospective Dual Center Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10945. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210945
APA StyleEder, M., Clahsen-van Groningen, M. C., Mengel, M., Omic, H., Cejka, D., Adam, B., Kozakowski, N., & Kikić, Ž. (2025). Molecular Diagnostics Supporting a ≥35% Diffuse Peritubular Capillaritis Extent Threshold for Diagnosis of AMR—A Retrospective Dual Center Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10945. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210945





