3-Gene-TB-SCORE Accuracy for Tuberculosis Disease Diagnosis Is Not Affected by Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Disease Comorbidity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Population
2.2. Patients with TB Disease Have a Significantly Lower TB-SCORE Compared to TBI and HD Individuals
2.3. IMID Status Does Not Influence TB-SCORE Assessment Within the TBI Cohort
2.4. Accuracy of TB-SCORE to Detect TB Cases
2.5. Antigen-Specific Immune Response of Individuals with TB Disease, TBI, and TBI-IMID
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Chest X-Ray Evaluation
4.3. PBMC Isolation and RNA Isolation
4.4. TB-Score Generation
4.5. Stimulation and Reagents
4.6. Intracellular Staining Assay and Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TB | Tuberculosis |
| TBI | Tuberculosis infection |
| IMID | immune-mediated inflammatory diseases |
| Mtb | Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
References
- WHO. WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-programme-on-tuberculosis-and-lung-health/tb-reports/global-tuberculosis-report-2024 (accessed on 2 November 2025).
- Houben, R.M.G.J.; Dodd, P.J. The Global Burden of Latent Tuberculosis Infection: A Re-Estimation Using Mathematical Modelling. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, A.K.; Zaidi, S.M.A.; Allwood, B.W.; Dewan, P.K.; Gray, G.; Kohli, M.; Kredo, T.; Marais, B.J.; Marks, G.B.; Martinez, L.; et al. Classification of Early Tuberculosis States to Guide Research for Improved Care and Prevention: An International Delphi Consensus Exercise. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 12, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantini, F.; Niccoli, L.; Capone, A.; Petrone, L.; Goletti, D. Risk of Tuberculosis Reactivation Associated with Traditional Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs and Non-Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Biologics in Patients with Rheumatic Disorders and Suggestion for Clinical Practice. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2019, 18, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, E.; Bonelli, M.; Duftner, C.; Gruber, J.; Mandl, P.; Moazedi-Furst, F.; Pieringer, H.; Puchner, R.; Flick, H.; Salzer, H.J.F.; et al. National Consensus Statement by the Austrian Societies for Rheumatology, Pulmonology, Infectiology, Dermatology and Gastroenterology Regarding the Management of Latent Tuberculosis and the Associated Utilization of Biologic and Targeted Synthetic Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs). Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2022, 134, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, T.; Brembilla, N.C.; Langley, R.G.; Warren, R.B.; Thaçi, D.; Kolios, A.G.A.; Prinz, J.C.; Londono-Garcia, A.; Nast, A.; Santin, M.; et al. Treatment of Psoriasis with Biologic and Non-Biologic Targeted Therapies in Patients with Latent Tuberculosis Infection or at Risk for Tuberculosis Disease Progression: Recommendations from a SPIN-FRT Expert Consensus. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. JEADV 2025, 39, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picchianti-Diamanti, A.; Aiello, A.; De Lorenzo, C.; Migliori, G.B.; Goletti, D. Management of Tuberculosis Risk, Screening and Preventive Therapy in Patients with Chronic Autoimmune Arthritis Undergoing Biotechnological and Targeted Immunosuppressive Agents. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1494283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. High Priority Target Product Profiles for New Tuberculosis Diagnostics: Report of a Consensus Meeting 2014. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-HTM-TB-2014.18 (accessed on 2 November 2025).
- Matteelli, A.; Churchyard, G.; Cirillo, D.; den Boon, S.; Falzon, D.; Hamada, Y.; Houben, R.M.G.J.; Kanchar, A.; Kritski, A.; Kumar, B.; et al. Optimizing the Cascade of Prevention to Protect People from Tuberculosis: A Potential Game Changer for Reducing Global Tuberculosis Incidence. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2024, 4, e0003306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteelli, A.; Lovatti, S.; Sforza, A.; Rossi, L. Programmatic Management of Tuberculosis Preventive Therapy: Past, Present, Future. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 130 (Suppl. S1), S43–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Consensus Meeting Report: Development of a Target Product Profile (TPP) and a Framework for Evaluation for a Test for Predicting Progression from Tuberculosis Infection to Active Disease. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-HTM-TB-2017.18 (accessed on 2 November 2025).
- Hamada, Y.; Penn-Nicholson, A.; Krishnan, S.; Cirillo, D.M.; Matteelli, A.; Wyss, R.; Denkinger, C.M.; Rangaka, M.X.; Ruhwald, M.; Schumacher, S.G. Are mRNA Based Transcriptomic Signatures Ready for Diagnosing Tuberculosis in the Clinic?—A Review of Evidence and the Technological Landscape. eBioMedicine 2022, 82, 104174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scriba, T.J.; Fiore-Gartland, A.; Penn-Nicholson, A.; Mulenga, H.; Kimbung Mbandi, S.; Borate, B.; Mendelsohn, S.C.; Hadley, K.; Hikuam, C.; Kaskar, M.; et al. Biomarker-Guided Tuberculosis Preventive Therapy (CORTIS): A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, S.C.; Andrade, B.B.; Mbandi, S.K.; Andrade, A.M.S.; Muwanga, V.M.; Figueiredo, M.C.; Erasmus, M.; Rolla, V.C.; Thami, P.K.; Cordeiro-Santos, M.; et al. Transcriptomic Signatures of Progression to Tuberculosis Disease Among Close Contacts in Brazil. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 230, e1355–e1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, D.E.; Penn-Nicholson, A.; Scriba, T.J.; Thompson, E.; Suliman, S.; Amon, L.M.; Mahomed, H.; Erasmus, M.; Whatney, W.; Hussey, G.D.; et al. A Blood RNA Signature for Tuberculosis Disease Risk: A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2016, 387, 2312–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, S.; Thompson, E.G.; Sutherland, J.; Weiner, J.; Ota, M.O.C.; Shankar, S.; Penn-Nicholson, A.; Thiel, B.; Erasmus, M.; Maertzdorf, J.; et al. Four-Gene Pan-African Blood Signature Predicts Progression to Tuberculosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelsohn, S.C.; Fiore-Gartland, A.; Penn-Nicholson, A.; Mulenga, H.; Mbandi, S.K.; Borate, B.; Hadley, K.; Hikuam, C.; Musvosvi, M.; Bilek, N.; et al. Validation of a Host Blood Transcriptomic Biomarker for Pulmonary Tuberculosis in People Living with HIV: A Prospective Diagnostic and Prognostic Accuracy Study. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e841–e853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penn-Nicholson, A.; Mbandi, S.K.; Thompson, E.; Mendelsohn, S.C.; Suliman, S.; Chegou, N.N.; Malherbe, S.T.; Darboe, F.; Erasmus, M.; Hanekom, W.A.; et al. RISK6, a 6-Gene Transcriptomic Signature of TB Disease Risk, Diagnosis and Treatment Response. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, S.C.; Mbandi, S.K.; Fiore-Gartland, A.; Penn-Nicholson, A.; Musvosvi, M.; Mulenga, H.; Fisher, M.; Hadley, K.; Erasmus, M.; Nombida, O.; et al. Prospective Multicentre Head-to-Head Validation of Host Blood Transcriptomic Biomarkers for Pulmonary Tuberculosis by Real-Time PCR. Commun. Med. 2022, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsinske, H.C.; Rao, A.M.; Moreira, F.M.F.; Santos, P.C.P.; Liu, A.B.; Scott, M.; Malherbe, S.T.; Ronacher, K.; Walzl, G.; Winter, J.; et al. Assessment of Validity of a Blood-Based 3-Gene Signature Score for Progression and Diagnosis of Tuberculosis, Disease Severity, and Treatment Response. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e183779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muwanga, V.M.; Mendelsohn, S.C.; Leukes, V.; Stanley, K.; Mbandi, S.K.; Erasmus, M.; Flinn, M.; Fisher, T.-L.; Raphela, R.; Bilek, N.; et al. Blood Transcriptomic Signatures for Symptomatic Tuberculosis in an African Multicohort Study. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 64, 2400153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, T.E.; Braviak, L.; Tato, C.M.; Khatri, P. Genome-Wide Expression for Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis: A Multicohort Analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, J.S.; van der Spuy, G.; Gindeh, A.; Thuong, N.T.T.; Namuganga, A.; Owolabi, O.; Mayanja-Kizza, H.; Nsereko, M.; Thwaites, G.; Winter, J.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of the Cepheid 3-Gene Host Response Fingerstick Blood Test in a Prospective, Multi-Site Study: Interim Results. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2022, 74, 2136–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Cao, Z.; Wang, L.; Wan, Y.; Peng, N.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y. Inducible GBP5 Mediates the Antiviral Response via Interferon-Related Pathways during Influenza A Virus Infection. J. Innate Immun. 2017, 9, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krapp, C.; Hotter, D.; Gawanbacht, A.; McLaren, P.J.; Kluge, S.F.; Stürzel, C.M.; Mack, K.; Reith, E.; Engelhart, S.; Ciuffi, A.; et al. Guanylate Binding Protein (GBP) 5 Is an Interferon-Inducible Inhibitor of HIV-1 Infectivity. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Dejager, L.; Amand, M.; Theatre, E.; Vandereyken, M.; Zurashvili, T.; Singh, M.; Mack, M.; Timmermans, S.; Musumeci, L.; et al. DUSP3 Genetic Deletion Confers M2-like Macrophage-Dependent Tolerance to Septic Shock. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2015, 194, 4951–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, H.; Kumar, A.; Lin, Z.; Patino, W.D.; Hwang, P.M.; Feinberg, M.W.; Majumder, P.K.; Jain, M.K. Kruppel-like Factor 2 (KLF2) Regulates Proinflammatory Activation of Monocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6653–6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Södersten, E.; Ongarello, S.; Mantsoki, A.; Wyss, R.; Persing, D.H.; Banderby, S.; Strömqvist Meuzelaar, L.; Prieto, J.; Gnanashanmugam, D.; Khatri, P.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy Study of a Novel Blood-Based Assay for Identification of Tuberculosis in People Living with HIV. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e01643-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.M.F.; Verma, R.; Pereira Dos Santos, P.C.; Leite, A.; da Silva Santos, A.; de Araujo, R.C.P.; da Silva, B.O.; de Sá Queiroz, J.H.F.; Persing, D.H.; Södersten, E.; et al. Blood-Based Host Biomarker Diagnostics in Active Case Finding for Pulmonary Tuberculosis: A Diagnostic Case-Control Study. eClinicalMedicine 2021, 33, 100776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinsohn, D.A.; Lewinsohn, D.M.; Scriba, T.J. Polyfunctional CD4+ T Cells As Targets for Tuberculosis Vaccination. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, F. Characterizing the Immune Response to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: A Comprehensive Narrative Review and Implications in Disease Relapse. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1437901, Erratum in Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1560113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, D.; Rani, G.; Arora, A.; Sharma, V.; Rathore, I.; Mubeen, S.A.; Singh, A. Tuberculosis and T Cells: Impact of T Cell Diversity in Tuberculosis Infection. Tuberc. Edinb. Scotl. 2024, 149, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinian, K.; Gerami, A.; Bral, M.; Venketaraman, V. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection and the Role of T Cells in Protection. Vaccines 2024, 12, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinsohn, D.M.; Lewinsohn, D.A. The Missing Link in Correlates of Protective Tuberculosis Immunity: Recognizing the Infected Cell. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 869057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farroni, C.; Altera, A.M.G.; Salmi, A.; Vanini, V.; Cuzzi, G.; Lindestam Arlehamn, C.S.; Sette, A.; Delogu, G.; Palucci, I.; Sbarra, S.; et al. Specific Immune Response to M. Tuberculosis and Ability to in Vitro Control Mycobacterial Replication Are Not Impaired in Subjects with Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Disease and Tuberculosis Infection. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1484143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petruccioli, E.; Petrone, L.; Chiacchio, T.; Farroni, C.; Cuzzi, G.; Navarra, A.; Vanini, V.; Massafra, U.; Lo Pizzo, M.; Guggino, G.; et al. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Immune Response in Patients with Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 716857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallin, M.A.; Kauffman, K.D.; Riou, C.; Du Bruyn, E.; Foreman, T.W.; Sakai, S.; Hoft, S.G.; Myers, T.G.; Gardina, P.J.; Sher, A.; et al. Host Resistance to Pulmonary Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection Requires CD153 Expression. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpande, C.A.M.; Dintwe, O.B.; Musvosvi, M.; Mabwe, S.; Bilek, N.; Hatherill, M.; Nemes, E.; Scriba, T.J. SATVI Clinical Immunology Team Functional, Antigen-Specific Stem Cell Memory (TSCM) CD4+ T Cells Are Induced by Human Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpande, C.A.M.; Rozot, V.; Mosito, B.; Musvosvi, M.; Dintwe, O.B.; Bilek, N.; Hatherill, M.; Scriba, T.J.; Nemes, E. ACS Study Team Immune Profiling of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis-Specific T Cells in Recent and Remote Infection. eBioMedicine 2021, 64, 103233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, T.; Steigler, P.; Mpande, C.A.M.; Rozot, V.; Mosito, B.; Schreuder, C.; Reid, T.D.; Hatherill, M.; Scriba, T.J.; Little, F.; et al. Multidimensional Analysis of Immune Responses Identified Biomarkers of Recent Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpande, C.A.M.; Steigler, P.; Lloyd, T.; Rozot, V.; Mosito, B.; Schreuder, C.; Reid, T.D.; Bilek, N.; Ruhwald, M.; Andrews, J.R.; et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Specific T Cell Functional, Memory, and Activation Profiles in QuantiFERON-Reverters Are Consistent with Controlled Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 712480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qiu, Y.; Guo, M.; Qu, R.; Tian, F.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, S.; Takiff, H.; et al. Evaluation of the Cepheid 3-Gene Host Response Blood Test for Tuberculosis Diagnosis and Treatment Response Monitoring in a Primary-Level Clinic in Rural China. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2023, 61, e0091123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tan, G.; Ma, J.; Yang, J.; Guo, Y.; Lu, H.; Ke, H.; Li, M.; Tang, Y.-W.; Sha, W.; et al. Assessment of the Cepheid 3-Gene Host Response Fingerstick Blood Test (MTB-HR) on Rapid Diagnosis of Tuberculosis. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2261561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zheng, J.; Han, T.; Ma, J.; Gnanashanmugam, D.; Li, M.; Tang, Y.-W.; Deng, G. A Blood-Based 3-Gene Signature Score for Therapeutic Monitoring in Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Tuberc. Edinb. Scotl. 2024, 147, 102521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, A.J.; Schumacher, S.G.; Södersten, E.; Mantsoki, A.; Wyss, R.; Persing, D.H.; Banderby, S.; Strömqvist Meuzelaar, L.; Prieto, J.; Gnanashanmugam, D.; et al. A Novel Blood-Based Assay for Treatment Monitoring of Tuberculosis. BMC Res. Notes 2021, 14, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbrich, L.; Verghese, V.P.; Franckling-Smith, Z.; Sabi, I.; Ntinginya, N.E.; Mfinanga, A.; Banze, D.; Viegas, S.; Khosa, C.; Semphere, R.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of a Three-Gene Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Host Response Cartridge Using Fingerstick Blood for Childhood Tuberculosis: A Multicentre Prospective Study in Low-Income and Middle-Income Countries. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STROBE. Available online: https://www.strobe-statement.org/ (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Lindestam Arlehamn, C.S.; McKinney, D.M.; Carpenter, C.; Paul, S.; Rozot, V.; Makgotlho, E.; Gregg, Y.; van Rooyen, M.; Ernst, J.D.; Hatherill, M.; et al. A Quantitative Analysis of Complexity of Human Pathogen-Specific CD4 T Cell Responses in Healthy M. Tuberculosis Infected South Africans. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
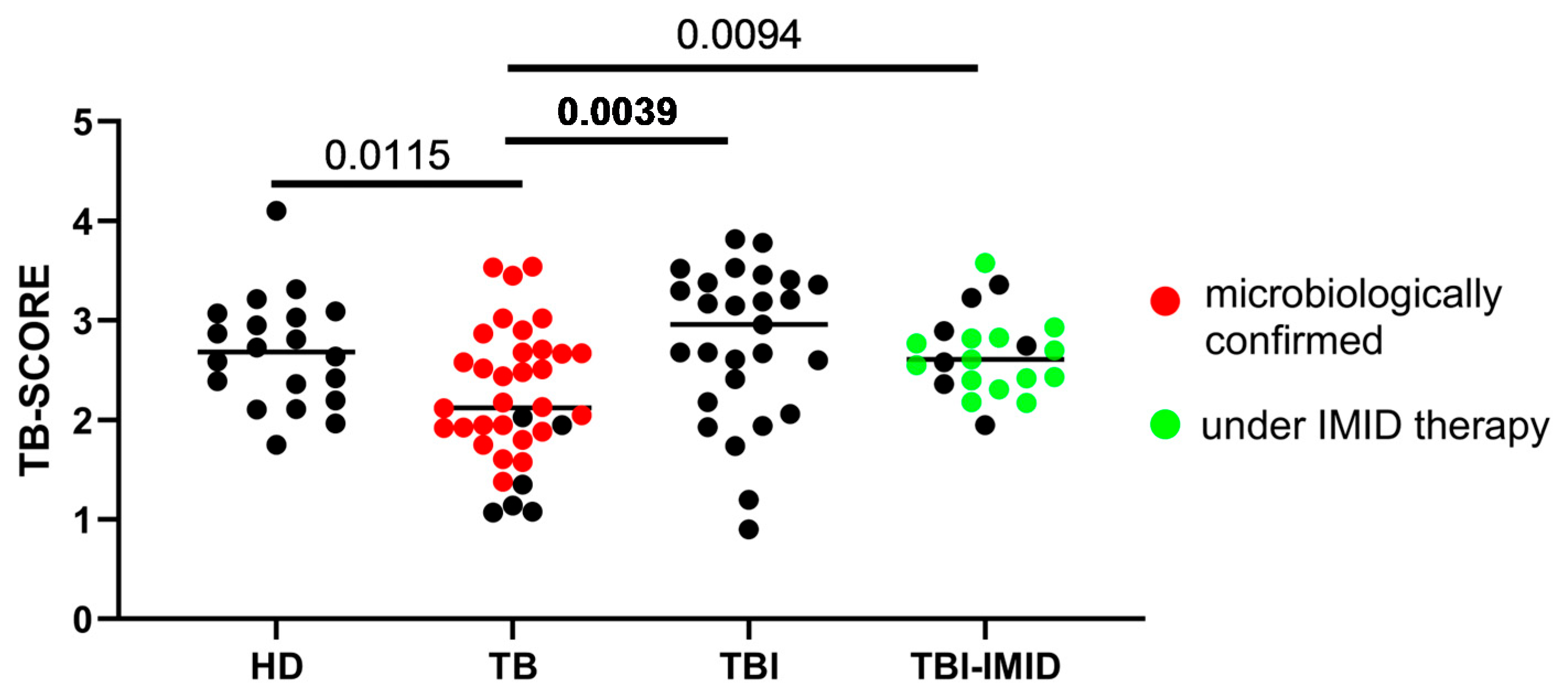
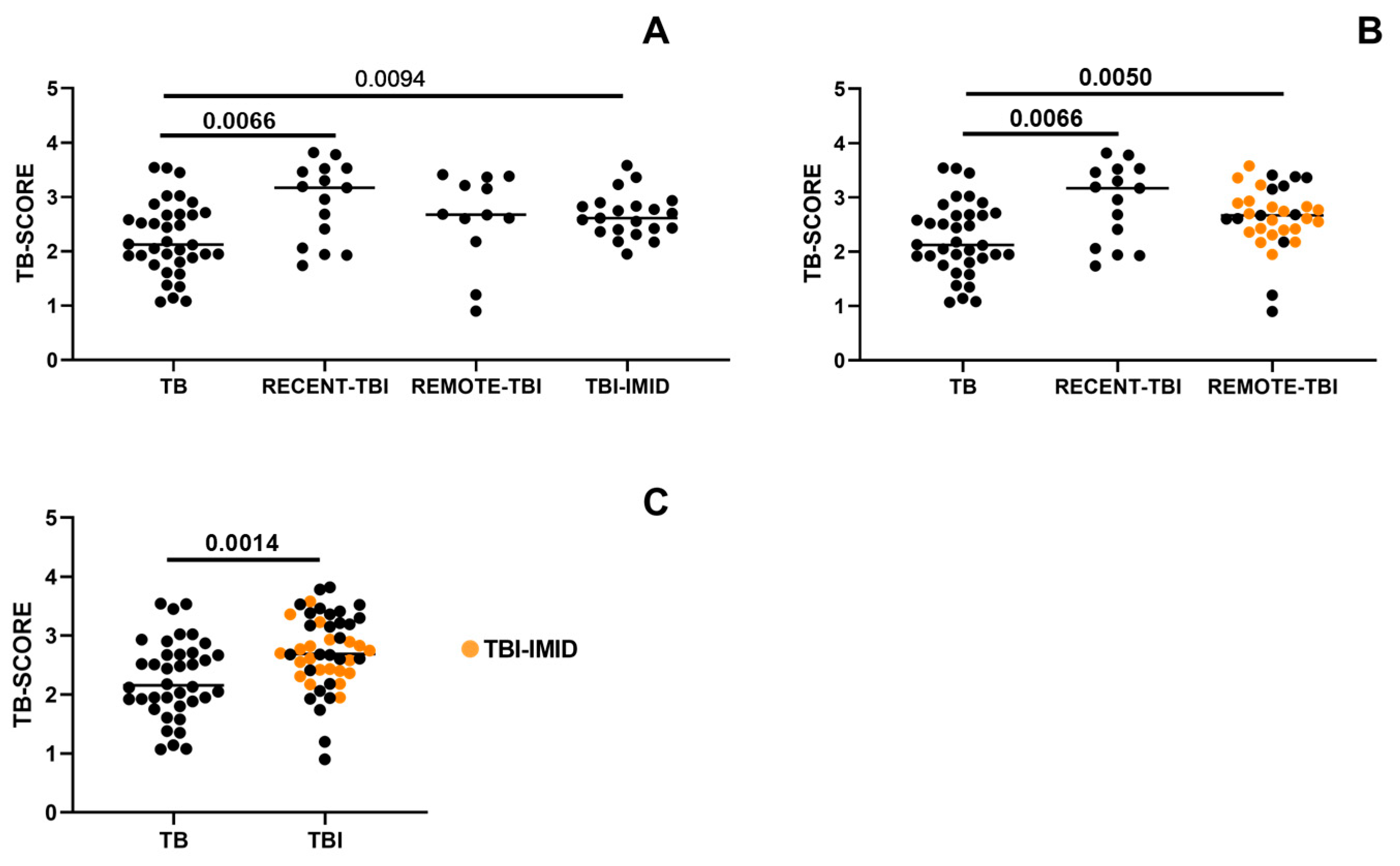
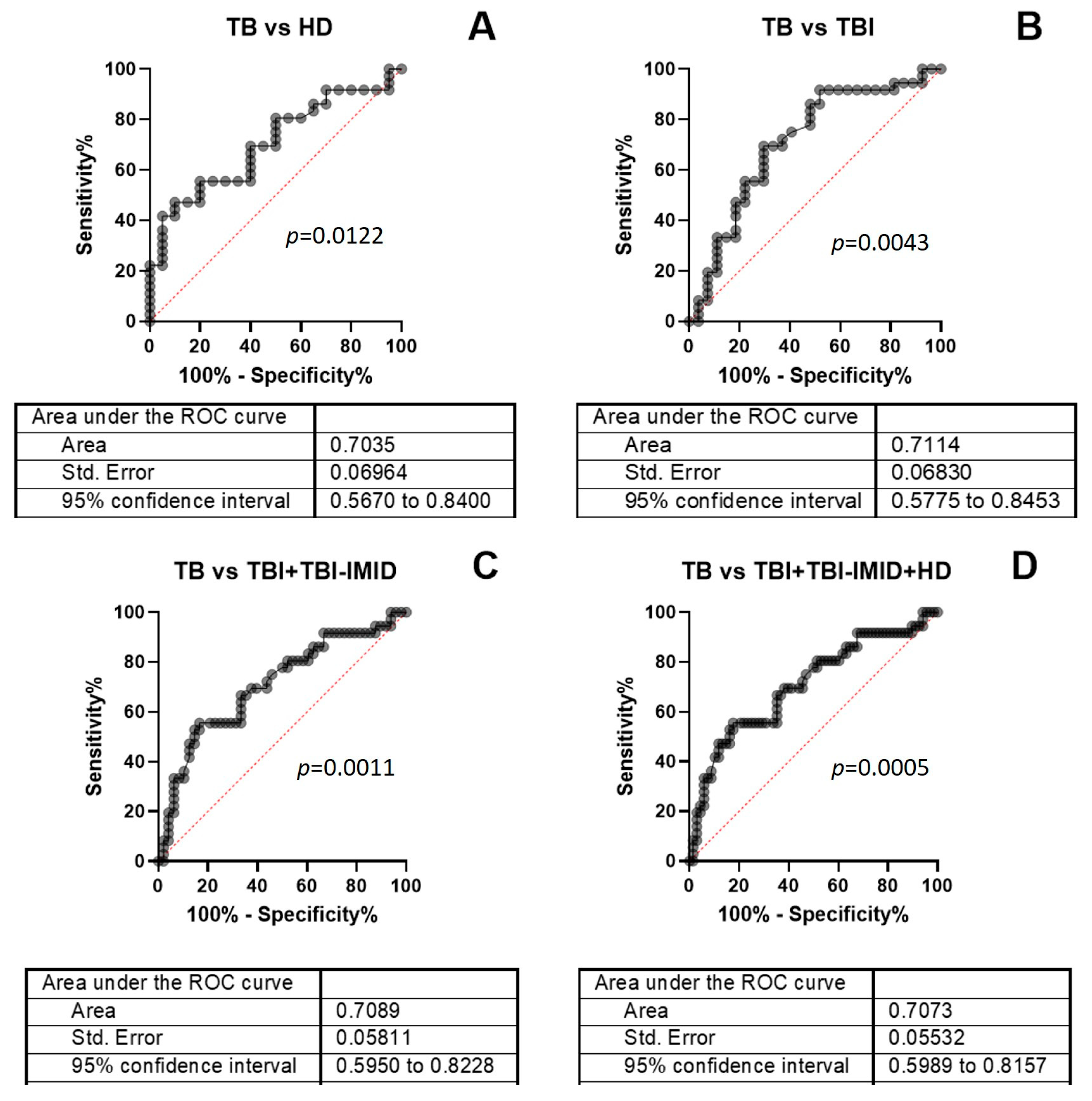
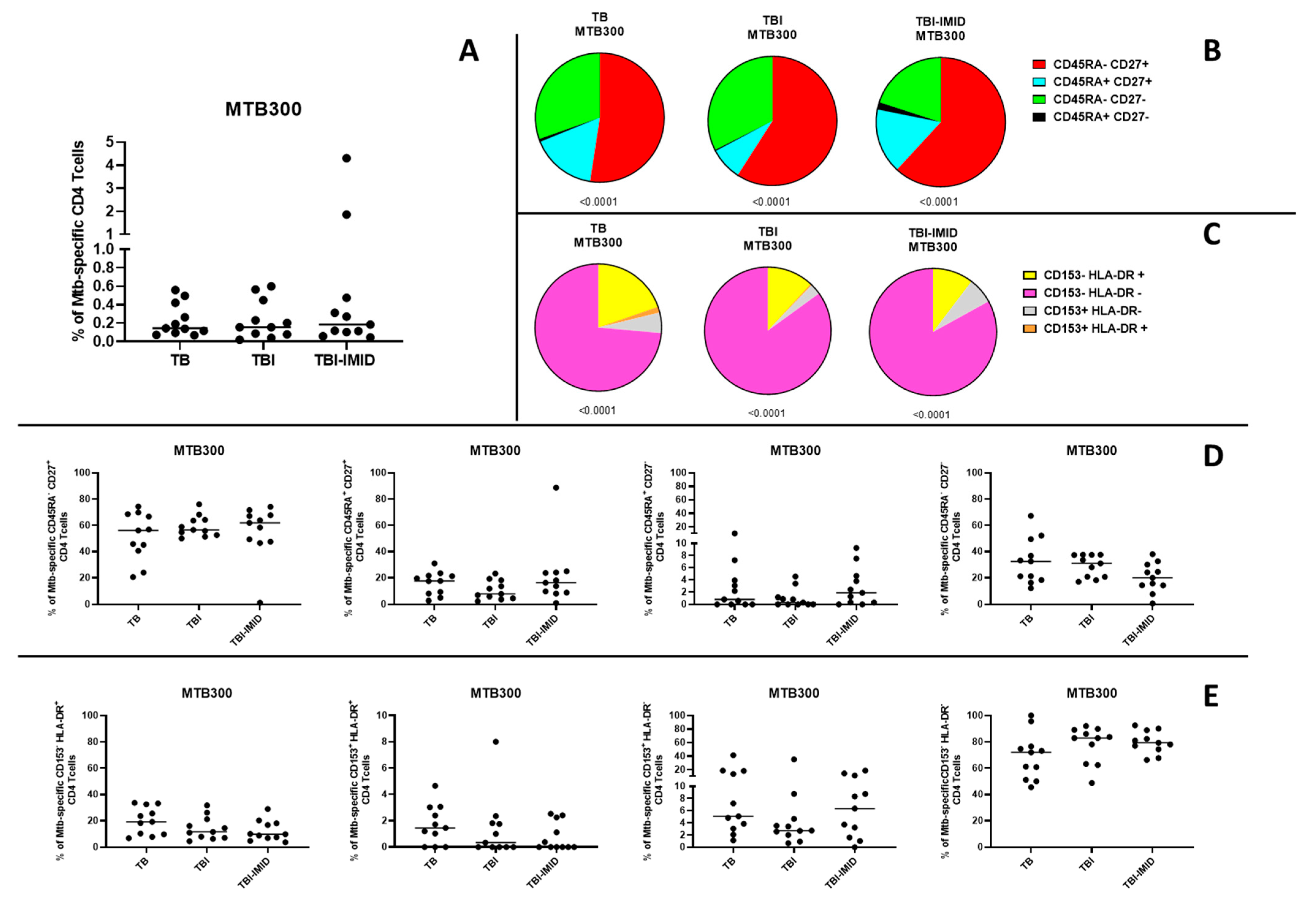
| HD N = 20 | TB N = 36 | TBI N = 27 | TBI-IMID N = 21 | TOTAL N = 104 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age median (IQR) | 46 (39–53) | 36 (28–49) | 37 (23–54) | 54 (48–66) | 45 (31–54) | 0.0014 * |
| Female N (%) | 12 | 17 | 13 | 14 | 0.443 # | |
| Origin N (%) | na | |||||
| West Europe | 20 (0) | 11 (31) | 13 (48) | 14 (67) | 58 (55.7) | |
| East Europe | 0 (0) | 13 (36) | 9 (33) | 4 (19) | 26 (25) | |
| Africa | 0 (0) | 2 (5) | 2 (8) | 0 (0) | 4 (4) | |
| Asia | 0 (0) | 6 (17) | 3 (11) | 1 (5) | 10 (9.6) | |
| South America | 0 (0) | 4 (11) | 0 (0) | 2 (9) | 6 (5.7) | |
| BCG vaccination (%) | 0 | 24 | 14 | 7 | 45 (43) | na |
| IMID N (%) | ||||||
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 10 (48) | 0.0019 # | ||||
| Psoriatic arthritis | 8 (38) | |||||
| Polymyalgia rheumatica | 1 (5) | |||||
| Psoriasis | 2 (9) | |||||
| under IMID therapy N (%) | 16 (76) | / | ||||
| IMID therapy N (%) | ||||||
| B | 5 (31) | |||||
| C | 3 (19) | na | ||||
| cDMARDs | 3 (19) | |||||
| cDMARDs + C | 5 (31) |
| Coefficient (95% CI) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | (per 10-year increment) | −0.01 (−0.12; 0.11) | 0.884 |
| Sex | F vs. M | 0.19 (−0.09; 0.46) | 0.178 |
| Origin | Eastern Europe vs. Western Europe | −0.25 (−0.75; 0.24) | 0.308 |
| Asia vs. Western Europe vs. Western Europe | −0.09 (−0.83; 0.65) | 0.810 | |
| Africa vs. Western Europe | −0.49 (−1.49; 0.52) | 0.338 | |
| South America vs. Western Europe | −0.12 (−0.98; 0.75) | 0.791 | |
| All origins vs. Western Europe | −0.15 (−0.48; 0.18) | 0.384 | |
| Diagnosis | HD vs. TB | 0.60 (0.09; 1.10) | 0.021 |
| TBI vs. TB | 0.83 (0.21; 1.44) | 0.009 | |
| TBI-IMID vs. TB | 0.48 (0.05; 0.91) | 0.031 | |
| TBI/TBI-IMID vs. TB | 0.57 (0.14; 0.99) | 0.010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petruccioli, E.; Alonzi, T.; Navarra, A.; Altera, A.M.G.; Cuzzi, G.; Farroni, C.; Repele, F.; Gualano, G.; Lindestam Arlehamn, C.S.; Palmieri, F.; et al. 3-Gene-TB-SCORE Accuracy for Tuberculosis Disease Diagnosis Is Not Affected by Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Disease Comorbidity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210931
Petruccioli E, Alonzi T, Navarra A, Altera AMG, Cuzzi G, Farroni C, Repele F, Gualano G, Lindestam Arlehamn CS, Palmieri F, et al. 3-Gene-TB-SCORE Accuracy for Tuberculosis Disease Diagnosis Is Not Affected by Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Disease Comorbidity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210931
Chicago/Turabian StylePetruccioli, Elisa, Tonino Alonzi, Assunta Navarra, Anna Maria Gerarda Altera, Gilda Cuzzi, Chiara Farroni, Federica Repele, Gina Gualano, Cecilia S. Lindestam Arlehamn, Fabrizio Palmieri, and et al. 2025. "3-Gene-TB-SCORE Accuracy for Tuberculosis Disease Diagnosis Is Not Affected by Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Disease Comorbidity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210931
APA StylePetruccioli, E., Alonzi, T., Navarra, A., Altera, A. M. G., Cuzzi, G., Farroni, C., Repele, F., Gualano, G., Lindestam Arlehamn, C. S., Palmieri, F., Salmi, A., Vanini, V., & Goletti, D. (2025). 3-Gene-TB-SCORE Accuracy for Tuberculosis Disease Diagnosis Is Not Affected by Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Disease Comorbidity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210931









