Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Niclosamide Enhances Sunitinib Efficacy via DNA Repair and Cell Cycle Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Niclosamide and Sunitinib Individually Exhibit Anticancer Effect in RCC
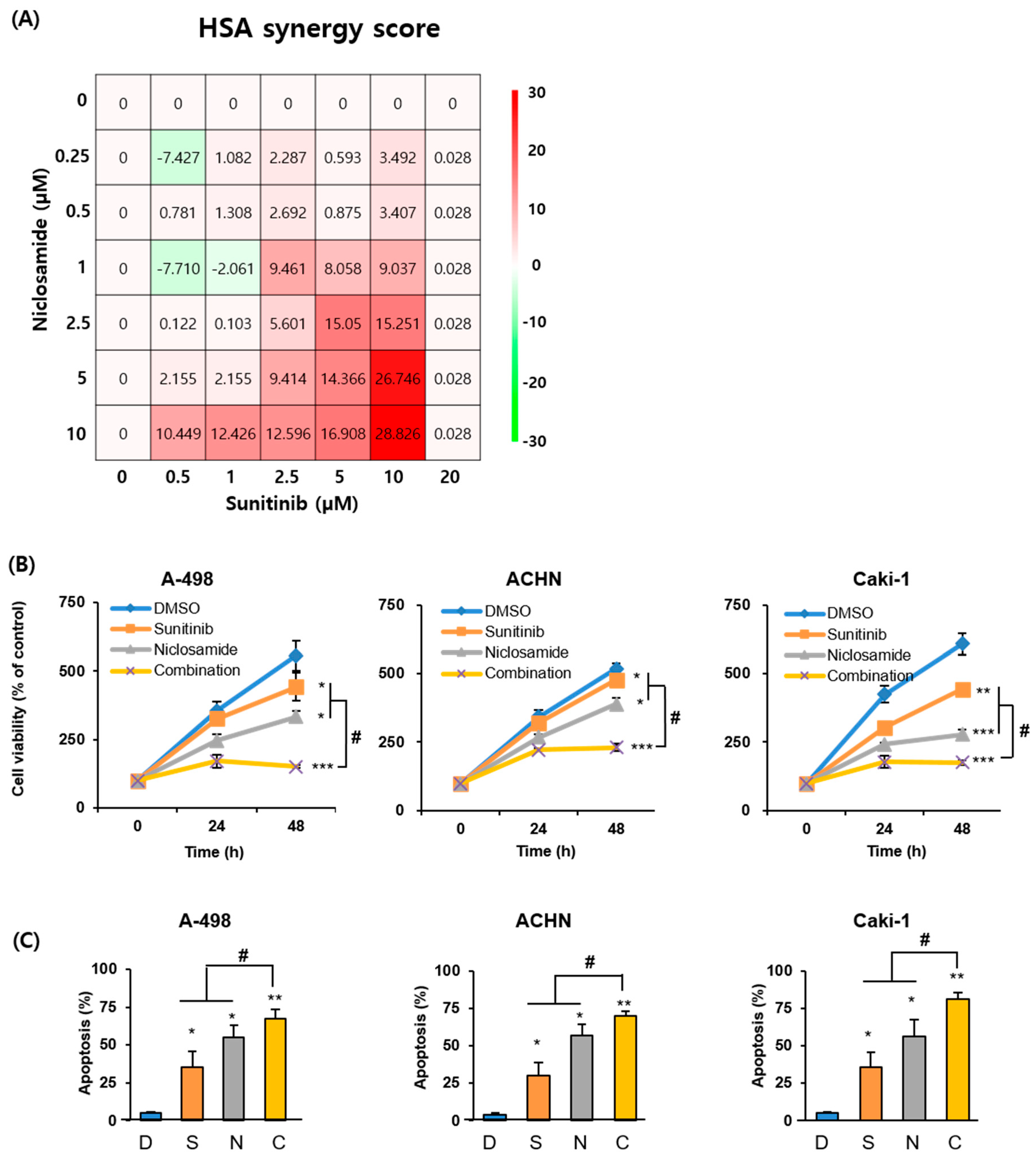
2.2. Combination of Sunitinib and Niclosamide Exerts Synergistic Anticancer Effects In Vitro
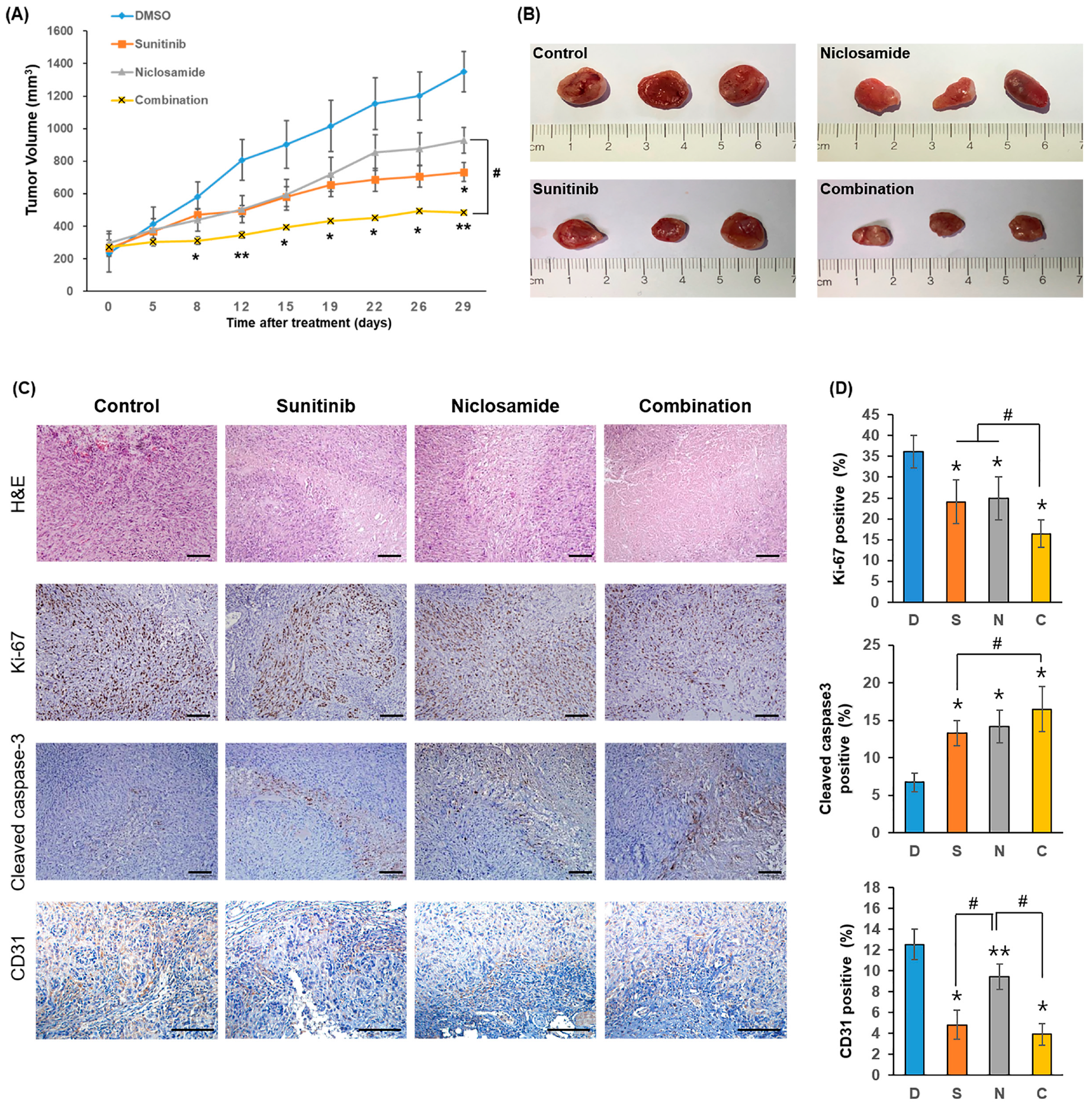
2.3. Combination Therapy Significantly Suppresses Tumor Growth In Vivo
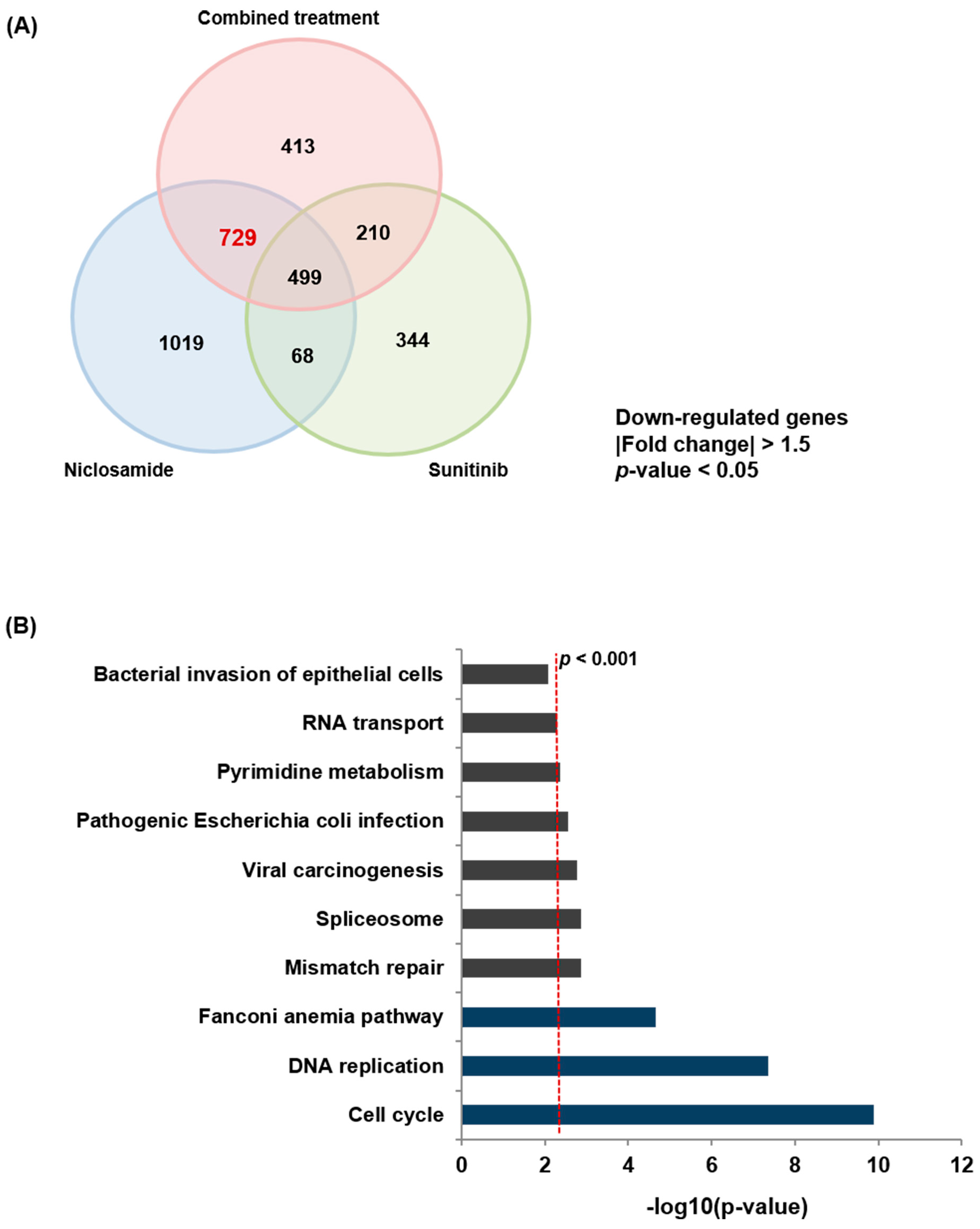
2.4. Niclosamide Induces Transcriptomic Alterations in RCC
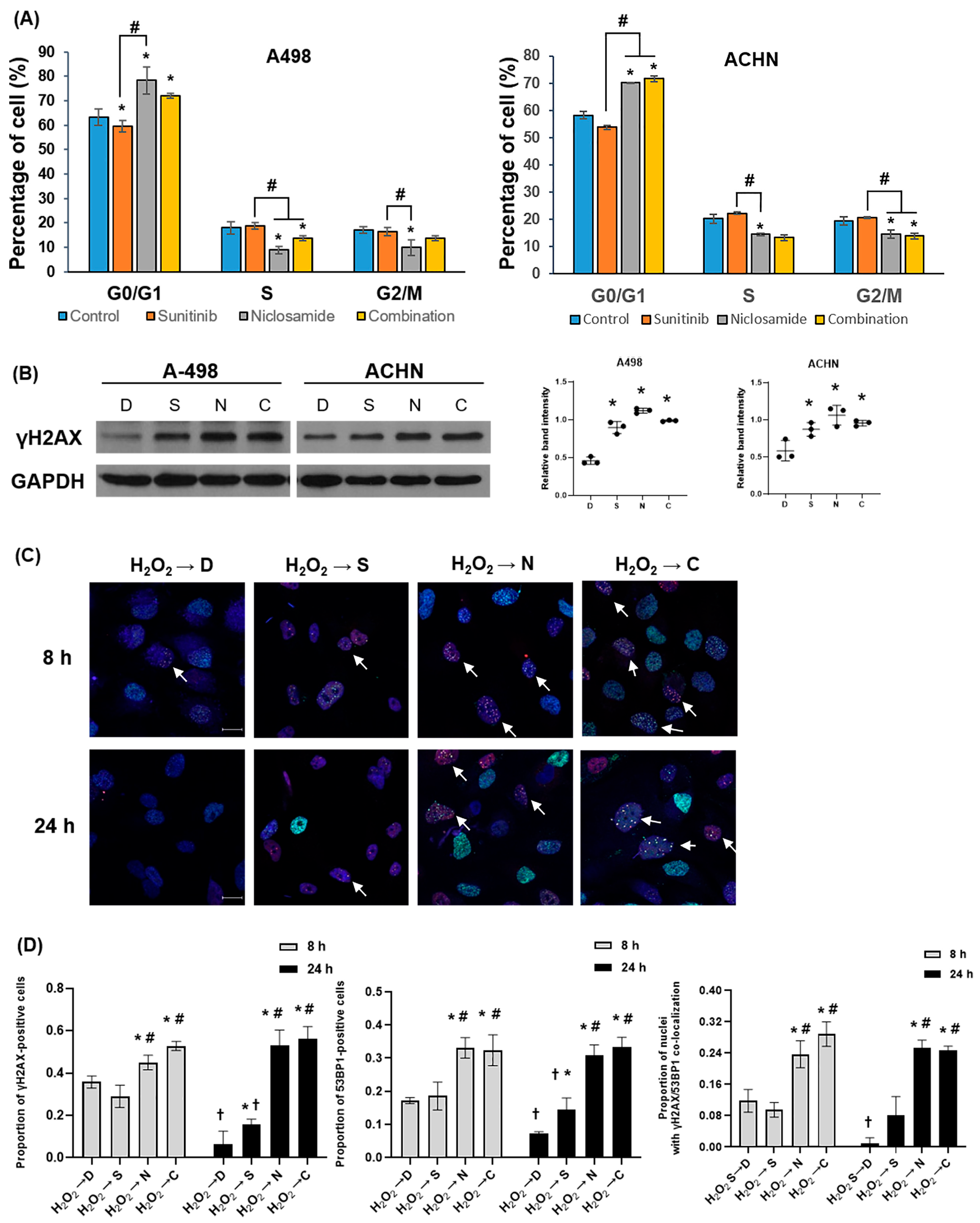
2.5. Niclosamide Induces Go/G1 Arrest and Activates DDR
2.6. Niclosamide Down-Regulates Key Regulators of the DNA Repair and the Cell Cycle Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Cell Cultures
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Apoptosis Assay
4.4. Wound Healing Assay and Invasion Assay
4.5. Drug Interaction and Synergy Analysis
4.6. In Vivo Study
4.7. Histological Analyses and Immunohistochemistry
4.8. mRNA Sequencing and Pathway Analysis
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Cell Cycle Assay
4.11. Immunocytochemistry
4.12. TCGA Dataset
4.13. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCC | Renal cell carcinoma |
| TKIs | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| VEGFR | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor |
| PDGFR | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor |
| FA | Fanconi anemia |
| DSBs | DNA double-strand breaks |
| DDR | DNA damage response |
| DEG | Differentially expressed gene |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SEM | standard error of the mean |
| ANOVA | A one-way analysis of variance |
| NT | Normal Tissue |
| TP | Primary Tumor Tissue |
References
- Capitanio, U.; Bensalah, K.; Bex, A.; Boorjian, S.A.; Bray, F.; Coleman, J.; Gore, J.L.; Sun, M.; Wood, C.; Russo, P. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.J.; Purdue, M.P.; Signoretti, S.; Swanton, C.; Albiges, L.; Schmidinger, M.; Heng, D.Y.; Larkin, J.; Ficarra, V. Renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Kaelin, W.G., Jr. The VHL/HIF axis in clear cell renal carcinoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013, 23, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivre, S.; Demetri, G.; Sargent, W.; Raymond, E. Molecular basis for sunitinib efficacy and future clinical development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, C. Sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma. J. Kidney Cancer VHL 2014, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.J.; Lee, C.H.; Heng, D. New approaches to first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 17588359211034708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, D.; Vale, N. Evaluation of synergism in drug combinations and reference models for future orientations in oncology. Curr. Res. Pharmacol. Drug Discov. 2022, 3, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weth, F.R.; Hoggarth, G.B.; Weth, A.F.; Paterson, E.; White, M.P.J.; Tan, S.T.; Peng, L.; Gray, C. Unlocking hidden potential: Advancements, approaches, and obstacles in repurposing drugs for cancer therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 130, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, P.K.; Roberts, M.J.; Arend, R.C.; Samant, R.S.; Buchsbaum, D.J. Multi-targeted therapy of cancer by niclosamide: A new application for an old drug. Cancer Lett. 2014, 349, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Krause, M.; Samoylenko, A.; Vainio, S. Wnt Signaling in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2016, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.Y.; Jung, A.R.; Shin, D.; Kwon, H.; Cho, H.J.; Ha, U.S.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Park, Y.H. Niclosamide exerts anticancer effects through inhibition of the FOXM1-mediated DNA damage response in prostate cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 2944–2959. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Liu, F.; Zeng, L.; He, F.; Zhang, R.; Yan, S.; Zeng, Z.; Shu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wu, X.; et al. Niclosamide Exhibits Potent Anticancer Activity and Synergizes with Sorafenib in Human Renal Cell Cancer Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; He, Q.; Gong, Z.; Chen, S.; Cui, L. Niclosamide suppresses renal cell carcinoma by inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin and inducing mitochondrial dysfunctions. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 2.0: Visual analytics of multi-drug combination synergies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W488–W493, Erratum in Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwertman, P.; Bekker-Jensen, S.; Mailand, N. Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifiers. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogakou, E.P.; Pilch, D.R.; Orr, A.H.; Ivanova, V.S.; Bonner, W.M. DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 5858–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Capetillo, O.; Chen, H.T.; Celeste, A.; Ward, I.; Romanienko, P.J.; Morales, J.C.; Naka, K.; Xia, Z.F.; Camerini-Otero, R.D.; Motoyama, N.; et al. DNA damage-induced G-M checkpoint activation by histone H2AX and 53BP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michl, J.; Zimmer, J.; Tarsounas, M. Interplay between Fanconi anemia and homologous recombination pathways in genome integrity. Embo J. 2016, 35, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.E.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, H.S.; Fang, S.; Lee, B.E.; Lee, K.J.; Yoo, J.; et al. Combination therapy of niclosamide with gemcitabine inhibited cell proliferation and apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin/c-Myc signaling pathway by inducing β-catenin ubiquitination in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2023, 24, 2272334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Wang, T.T.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Xie, Y.M.; Li, S.Q.; An, Z.M.; Ye, T.H. Niclosamide induces apoptosis through mitochondrial intrinsic pathway and inhibits migration and invasion in human thyroid cancer in vitro. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Z.; Zhou, X.Q.; Xu, H.J.; Shi, X.Q.; Zhao, J.F.; Yang, M.Y.; Zhang, L.H.; Jin, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Niclosamide Inhibits Cell Growth and Enhances Drug Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via STAT3 Signaling Pathway. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 4150–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zio, D.; Cianfanelli, V.; Cecconi, F. New Insights into the Link Between DNA Damage and Apoptosis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.C.; Nagaya, N.; Rha, K.H.; Han, W.K.; Kim, I.Y. DNA Damage Response Pathway Alteration in Locally Advanced Clear-Cell Renal-Cell Carcinoma Is Associated With a Poor Outcome. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2019, 17, 299–305.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, E.; Wu, C.; Ming, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Hu, G. The Clinical Significance of DNA Damage Repair Signatures in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 593039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Wu, X.; Jin, X.; Kanematsu, A.; Nojima, M.; Kakehi, Y.; Yamamoto, S. Apigenin inhibits renal cell carcinoma cell proliferation through G2/M phase cell cycle arrest. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 47, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Dang, Q.; Xu, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wu, K.; Zeng, J.; Long, Q.; Wang, X.; He, D.; et al. Kaempferol induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma through EGFR/p38 signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Yang, W.; Lv, W.; He, D.; Guo, P.; Li, L. 6-Gingerol induces cell-cycle G1-phase arrest through AKT-GSK 3β-cyclin D1 pathway in renal-cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2020, 85, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ren, Y.; Qiu, J. Dauricine inhibits viability and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in renal cell carcinoma cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7403–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassy, E.; Flippot, R.; Albiges, L. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immunotherapy combinations in renal cell carcinoma. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920907504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palovcak, A.; Liu, W.J.; Yuan, F.H.; Zhang, Y.B. Maintenance of genome stability by Fanconi anemia proteins. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlikowska, P.; Delestre, L.; Gregoricchio, S.; Oppezzo, A.; Esposito, M.; Diop, M.B.; Rosselli, F.; Guillouf, C. FANCA deficiency promotes leukaemic progression by allowing the emergence of cells carrying oncogenic driver mutations. Oncogene 2023, 42, 2764–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Navas, S.; Yanez, L.; Romon, I.; Pipaon, C. Elevated FANCA expression determines a worse prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and interferes with p53 function. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 10477–10489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouhtit, A.; Gupta, I.; Shaikh, Z. BRIP1, a potential candidate gene in development of non-BRCA1/2 breast cancer. Front. Biosci. 2016, 8, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; Ouhtit, A.; Al-Ajmi, A.; Rizvi, S.G.A.; Al-Riyami, H.; Al-Riyami, M.; Tamimi, Y. BRIP1 overexpression is correlated with clinical features and survival outcome of luminal breast cancer subtypes. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voutsadakis, I.A. Landscape of BRIP1 molecular lesions in gastrointestinal cancers from published genomic studies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimova, D.K.; Dyson, N.J. The E2F transcriptional network: Old acquaintances with new faces. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2810–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.F.; Song, C.Z.; Li, J.J.; Liu, M.; Fu, L.Y.; Jiang, J.L.; Zeng, Z.R.; Zhu, H.T. E2F2 enhances the chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer to gemcitabine by regulating the cell cycle and upregulating the expression of RRM2. Med. Oncol. 2022, 39, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X. Clinical performance of E2Fs 1-3 in kidney clear cell renal cancer, evidence from bioinformatics analysis. Genes Cancer 2017, 8, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, M.; Liu, C.; Wu, C.Y.; Evans, C.P.; Dall’Era, M.; Robles, D.; Lara, P.N.; Agarwal, N.; Gao, A.C.; Pan, C.X. Phase Ib trial of reformulated niclosamide with abiraterone/prednisone in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, W.M.; Zhang, Z.F.; Snider, J.; VandenBeldt, K.; Qian, C.N.; Teh, B.T. Sunitinib Acts Primarily on Tumor Endothelium rather than Tumor Cells to Inhibit the Growth of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, P.; Kulkarni, P.; Majid, S.; Shahryari, V.; Hashimoto, Y.; Bhat, N.S.; Shiina, M.; Deng, G.R.; Saini, S.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; et al. MicroRNA-203 Inhibits Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR and Regulates Tumorigenesis through Epithelial-to-mesenchymal Transition Pathway in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Pachter, L.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.C.; Colaprico, A.; Olsen, C.; D’Angelo, F.; Bontempi, G.; Ceccarelli, M.; Noushmehr, H. TCGA Workflow: Analyze cancer genomics and epigenomics data using Bioconductor packages. F1000Res 2016, 5, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, A.R.; Kim, G.E.; Kim, M.Y.; Rhew, S.A.; Shin, D.; Ha, U.-S.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Park, Y.H. Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Niclosamide Enhances Sunitinib Efficacy via DNA Repair and Cell Cycle Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210922
Jung AR, Kim GE, Kim MY, Rhew SA, Shin D, Ha U-S, Hong S-H, Lee JY, Kim SW, Park YH. Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Niclosamide Enhances Sunitinib Efficacy via DNA Repair and Cell Cycle Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210922
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Ae Ryang, Ga Eun Kim, Mee Young Kim, Seung Ah Rhew, Dongho Shin, U-Syn Ha, Sung-Hoo Hong, Ji Youl Lee, Sae Woong Kim, and Yong Hyun Park. 2025. "Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Niclosamide Enhances Sunitinib Efficacy via DNA Repair and Cell Cycle Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210922
APA StyleJung, A. R., Kim, G. E., Kim, M. Y., Rhew, S. A., Shin, D., Ha, U.-S., Hong, S.-H., Lee, J. Y., Kim, S. W., & Park, Y. H. (2025). Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Niclosamide Enhances Sunitinib Efficacy via DNA Repair and Cell Cycle Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210922





