Antifungal Activities of Multi-Halogenated Indoles Against Drug-Resistant Candida Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
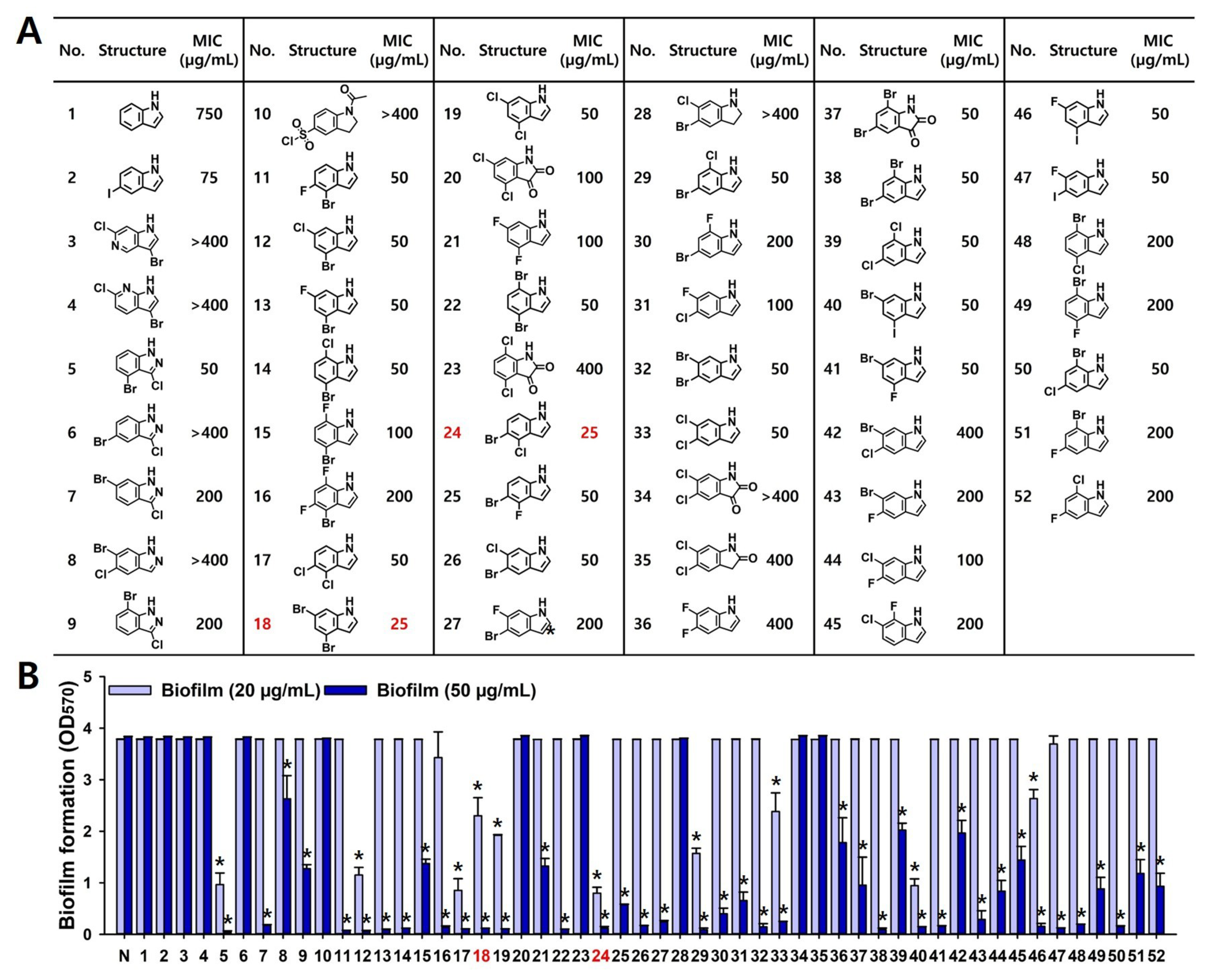
2.1. Antifungal and Antibiofilm Activities of Multi-Halogenated Indoles
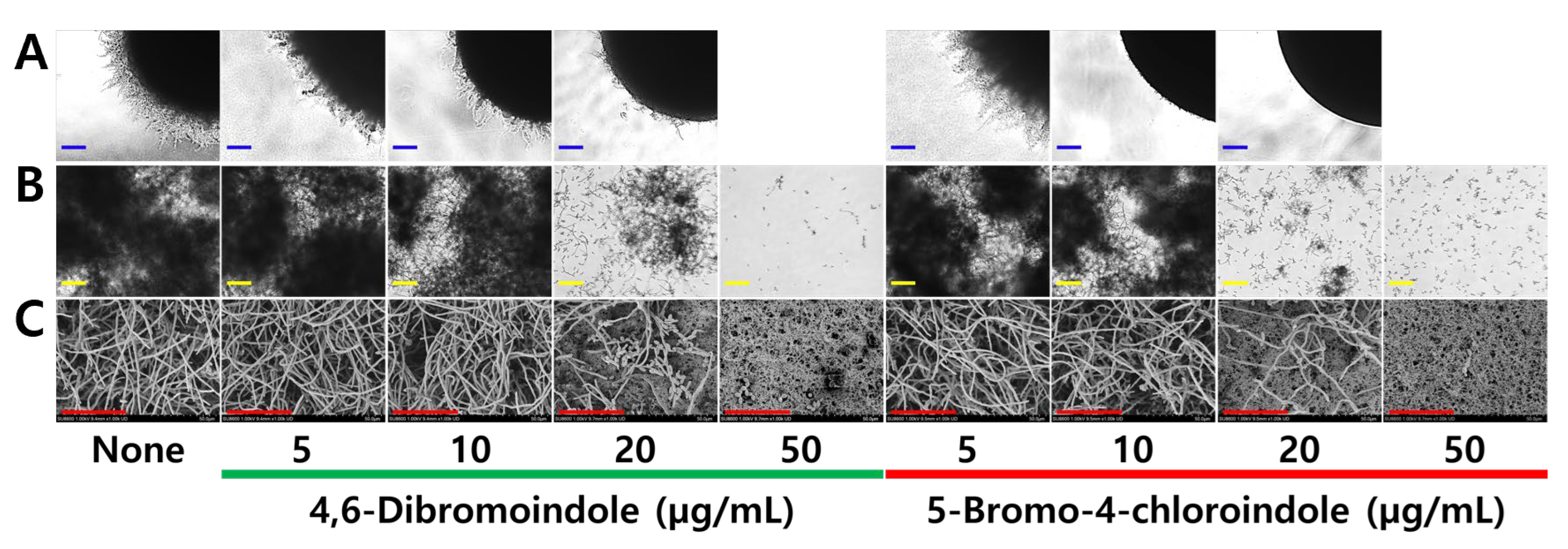
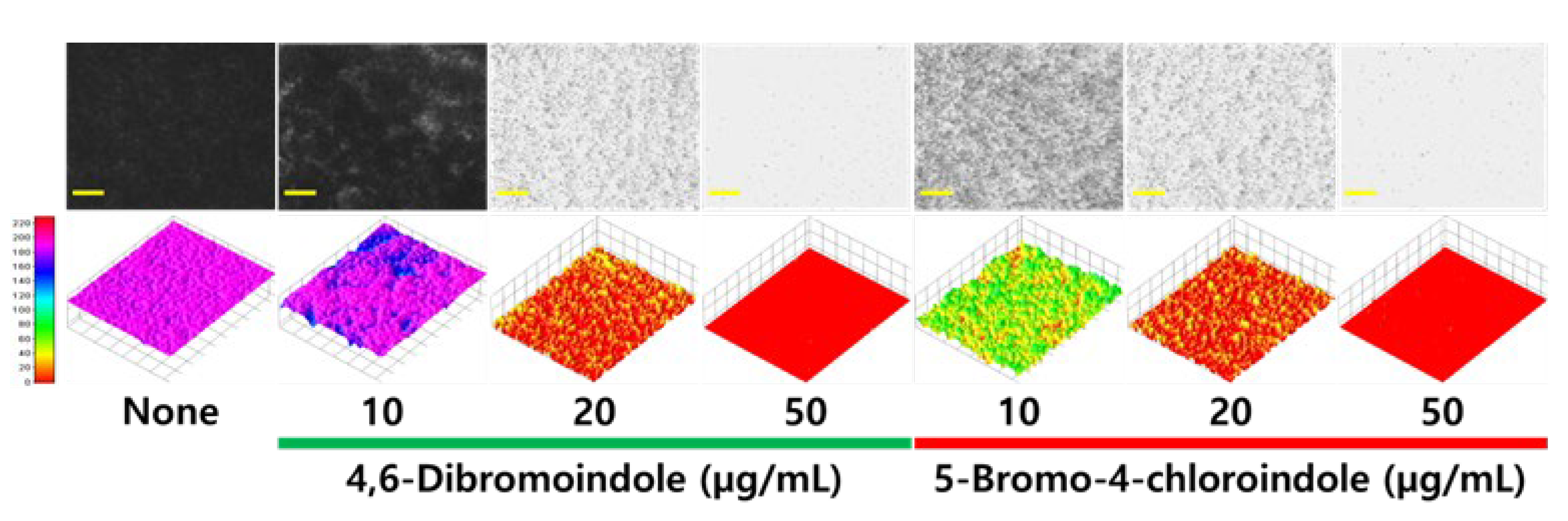
2.2. Antibiofilm and Anti-Hyphal Activities of Active Di-Halogenated Indoles
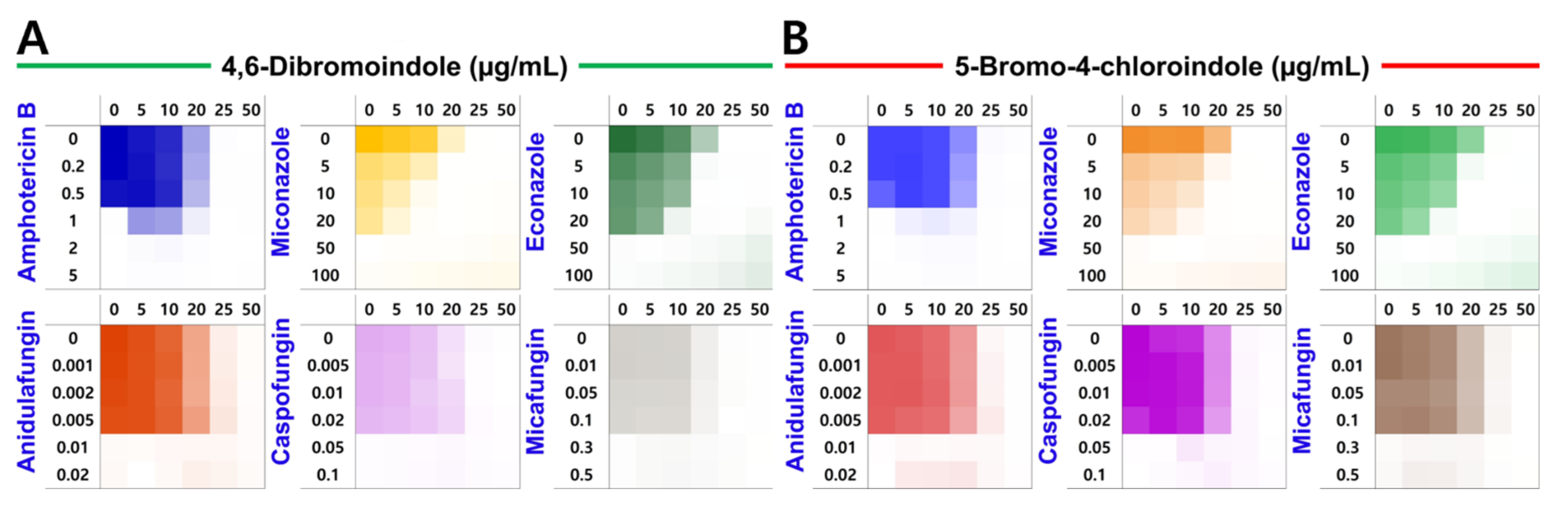
2.3. Induction of ROS Production and Combinatorial Assay
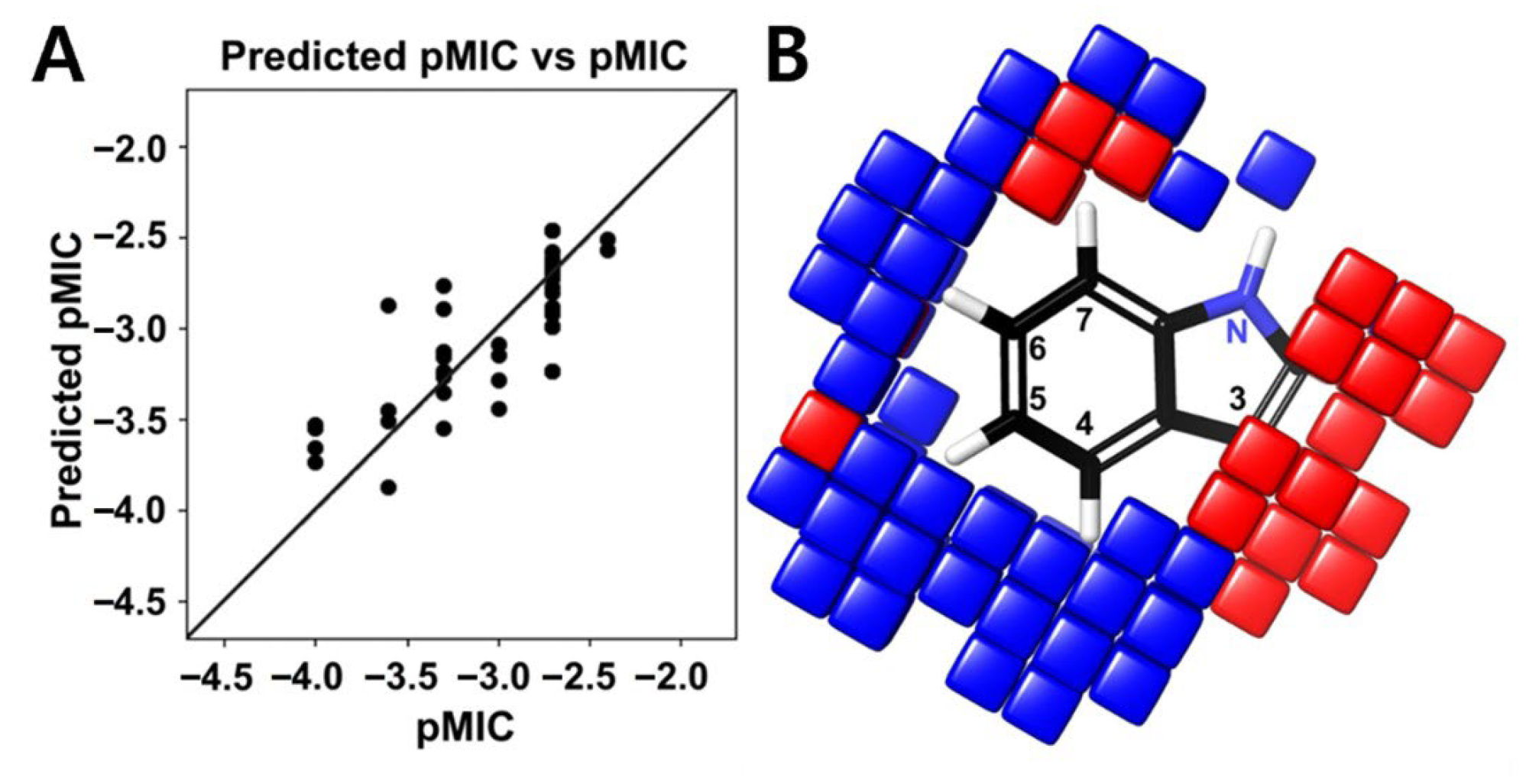
2.4. Structure–Activity Relationship of Halogenated Indoles
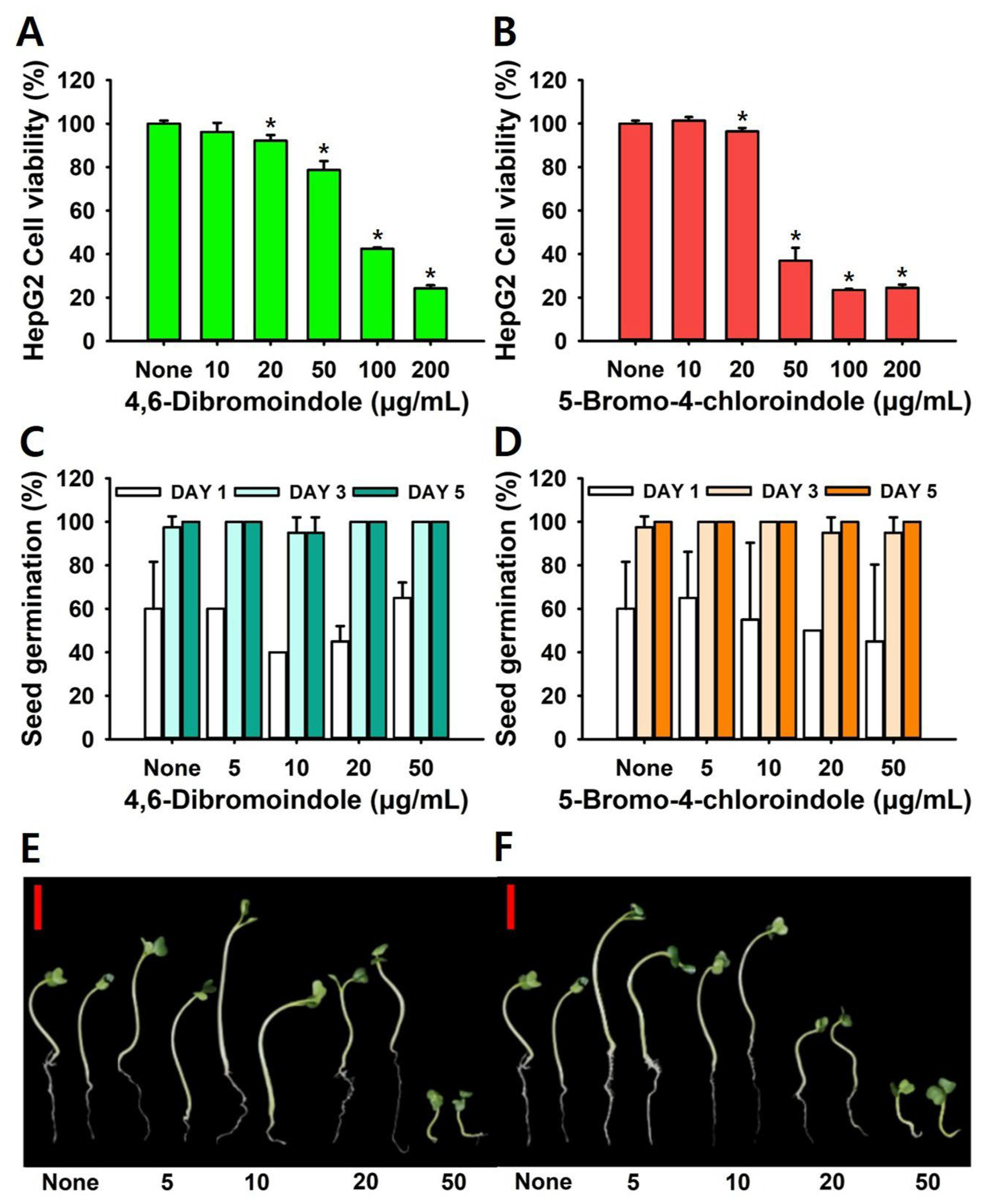
2.5. Toxicity Assay in HepG2 Cells and a Plant Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Microbial Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Antifungal Assay
4.3. Biofilm Assay
4.4. Microscopic Observation of Candida Biofilms
4.5. Hyphal Morphogenesis Analyses
4.6. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
4.7. Combinatorial Assay with Antifungal Drugs
4.8. QSAR Modeling
4.9. Cytotoxicity Assays in HepG2 Cells and a Plant Model
4.10. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliva, A.; De Rosa, F.G.; Mikulska, M.; Pea, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Tascini, C.; Venditti, M. Invasive Candida infection: Epidemiology, clinical and therapeutic aspects of an evolving disease and the role of rezafungin. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2023, 21, 957–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, J.M.; Cuomo, C.A.; Rogers, P.D. The molecular and genetic basis of antifungal resistance in the emerging fungal pathogen Candida auris. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2022, 70, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrpasopoulou, A.; Zarras, C.; Mouloudi, E.; Vakalis, G.; Ftergioti, A.; Kouroupis, D.; Papathanasiou, A.I.; Iosifidis, E.; Goumperi, S.; Lampada, C.; et al. Changing epidemiology of Candida spp. causing bloodstream infections in a tertiary hospital in northern greece: Appearance of Candida auris. Pathogens 2025, 14, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atriwal, T.; Azeem, K.; Husain, F.M.; Hussain, A.; Khan, M.N.; Alajmi, M.F.; Abid, M. Mechanistic understanding of Candida albicans biofilm formation and approaches for its inhibition. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 638609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Price-Whelan, A.; Dietrich, L.E.P. Gradients and consequences of heterogeneity in biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitzler, S.U.J.; Fernandez-Fernandez, C.; Gunther, K.; Dietschmann, A.; Hovhannisyan, H.; Moslinger, A.; Austermeier, S.; Cristovao, B.; Vascelli, G.; Zelante, T.; et al. Host albumin redirects Candida albicans metabolism to engage an alternative pathogenicity pathway. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Bamunuarachchi, N.I.; Pham, D.T.N.; Tabassum, N.; Khan, M.S.A.; Kim, Y.M. Mixed biofilms of pathogenic Candida-bacteria: Regulation mechanisms and treatment strategies. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 47, 699–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evivie, S.E.; Li, B.; Ding, X.; Meng, Y.; Yu, S.; Du, J.; Xu, M.; Li, W.; Jin, D.; Huo, G.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Streptococcus thermophilus KLDS 3.1003, a strain with high antimicrobial potential against foodborne and vaginal pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, C.J.; Johnson, A.D. Candida albicans biofilms and human disease. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Solis, N.V.; Marshall, M.; Yao, Q.; Garleb, R.; Yang, M.; Pearlman, E.; Filler, S.G.; Liu, H. Hyphal Als proteins act as CR3 ligands to promote immune responses against Candida albicans. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Araújo, D.; Rodrigues, M.E.; Henriques, M. Candida species biofilms’ antifungal resistance. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Nobile, C.J. Antifungal drug-resistance mechanisms in Candida biofilms. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2023, 71, 102237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Tabassum, N.; Jeong, G.J.; Jung, W.K.; Kim, Y.M. Inhibition of mixed biofilms of Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus by beta-caryophyllene-gold nanoparticles. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faleye, O.S.; Boya, B.R.; Lee, J.-H.; Choi, I.; Lee, J. Halogenated antimicrobial agents to combat drug-resistant pathogens. Pharmacol. Rev. 2023, 76, 90–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallo, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Milani, R.; Pilati, T.; Priimagi, A.; Resnati, G.; Terraneo, G. The halogen bond. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2478–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfi, F.; D’Acierno, F.; Bortolami, M.; De Vita, D.; Gallo, F.; De Meo, A.; Di Santo, R.; Costi, R.; Simonetti, G.; Scipione, L. Searching for new agents active against Candida albicans biofilm: A series of indole derivatives, design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 165, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Pan, M.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Mao, Z. New azole derivatives linked to indole/indoline moieties combined with FLC against drug-resistant Candida albicans. RSC Med. Chem. 2024, 15, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, Z. Synthesis and antifungal evaluation of new azole derivatives against Candida albicans. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Bamunuarachchi, N.I.; Tabassum, N.; Jo, D.M.; Khan, M.M.; Kim, Y.M. Suppression of hyphal formation and virulence of Candida albicans by natural and synthetic compounds. Biofouling 2021, 37, 626–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, B.S.; Victoria, A.E.; Deboh, E.D. Preparation and antifungal properties of chalcone and halogenated derivatives. Saudi J. Med. Pharm Sci. 2020, 6, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malefo, M.S.; Ramadwa, T.E.; Famuyide, I.M.; McGaw, L.J.; Eloff, J.N.; Sonopo, M.S.; Selepe, M.A. Synthesis and antifungal activity of chromones and benzoxepines from the leaves of Ptaeroxylon obliquum. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2508–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Burgain, A.; Chaillot, J.; Pic, É.; Khemiri, I.; Sellam, A. A phenotypic small-molecule screen identifies halogenated salicylanilides as inhibitors of fungal morphogenesis, biofilm formation and host cell invasion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, H.; Bayrak, N.; Yıldız, M.; Yılmaz, F.N.; Mataracı-Kara, E.; Shilkar, D.; Jayaprakash, V.; TuYuN, A.F. Highly active small aminated quinolinequinones against drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans. Molecules 2022, 27, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-G.; Jeon, H.; Boya, B.R.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Targeting biofilm formation in Candida albicans with halogenated pyrrolopyrimidine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 290, 117528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Tang, J. Intestinal infection of Candida albicans: Preventing the formation of biofilm by C. albicans and protecting the intestinal epithelial barrier. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 783010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Indole as an intercellular signal in microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, X.; Rao, D.P.; Kaur, K.; Hassan, R.; Abdel-Samea, A.S.; Farhan, S.M.; Bräse, S.; Hashem, H. Indole derivatives: A versatile scaffold in modern drug discovery—An updated review on their multifaceted therapeutic applications (2020–2024). Molecules 2024, 29, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathada, B.S.; Somappa, S.B. An insight into the recent developments in anti-infective potential of indole and associated hybrids. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1261, 132808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, A.; Sharma, R.; Singh, R.K. Target-based anticancer indole derivatives and insight into structure-activity relationship: A mechanistic review update (2018–2021). Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3006–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalola, B.A.; Malik, M.; Olowokere, O.; Adebesin, A.; Sharma, L. Indoles in drug design and medicinal chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2025, 13, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, K.R.; Li, S.C.; Revie, N.M.; Lou, J.W.; Duncan, D.; Fallah, S.; Sanchez, H.; Skulska, I.; Ušaj, M.M.; Safizadeh, H.; et al. Identification of triazenyl indoles as inhibitors of fungal fatty acid biosynthesis with broad-spectrum activity. Cell Chem. Biol. 2023, 30, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fan, L.; Pan, Z.; Fan, S.; Shi, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Wu, L.; Yang, G.; Xu, C. Synthesis of novel indole schiff base compounds and their antifungal activities. Molecules 2022, 27, 6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-G.; Gwon, G.; Wood, T.K.; Lee, J. Halogenated indoles eradicate bacterial persister cells and biofilms. AMB Express 2016, 6, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raorane, C.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Rapid killing and biofilm inhibition of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains and other microbes by iodoindoles. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethupathy, S.; Sathiyamoorthi, E.; Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Antibiofilm and antivirulence properties of indoles against Serratia marcescens. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 584812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoharan, R.K.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Efficacy of 7-benzyloxyindole and other halogenated indoles to inhibit Candida albicans biofilm and hyphal formation. Microb. Biotechnol. 2018, 11, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-G.; Gupta, V.K.; Manoharan, R.K.; Lee, J. Suppression of fluconazole resistant Candida albicans biofilm formation and filamentation by methylindole derivatives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdiero, E.; de Alteriis, E.; De Natale, A.; D’Alterio, A.; Siciliano, A.; Guida, M.; Lombardi, L.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S. Eradication of Candida albicans persister cell biofilm by the membranotropic peptide gH625. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, M.J.; Fillinger, R.J.; Anderson, L.M.; Anderson, M.Z. Automated quantification of Candida albicans biofilm-related phenotypes reveals additive contributions to biofilm production. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boya, B.R.; Lee, J.-H.; Choi, J.-M.; Lee, J. Impact of halogenation on scaffold toxicity assessed using HD-GEM machine learning model. Brief. Bioinform. 2025, 26, bbaf347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirinzadeh, H.; Suzen, S.; Altanlar, N.; Westwell, A.D. Antimicrobial activities of new indole derivatives containing 1,2,4-triazole, 1,3,4-thiadiazole and carbothioamide. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 15, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Q.; Defoirdt, T. Halogenated indoles decrease the virulence of Vibrio campbellii in a gnotobiotic brine shrimp model. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0268922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, M.; Nobile, C.J. Candida albicans biofilms: Development, regulation, and molecular mechanisms. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Robbins, N.; Cowen, L.E. Molecular mechanisms governing antifungal drug resistance. npj Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshnia, F.; de Almeida Júnior, J.N.; Ilkit, M.; Lombardi, L.; Perry, A.M.; Gao, M.; Nobile, C.J.; Egger, M.; Perlin, D.S.; Zhai, B.; et al. Worldwide emergence of fluconazole-resistant Candida parapsilosis: Current framework and future research roadmap. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e470–e480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakhshan, A.; Rahmati Kamel, B.; Saffaei, A.; Tavakoli-Ardakani, M. Hepatotoxicity induced by azole antifungal agents: A review study. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2023, 22, e130336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Boya, B.R.; Kim, G.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Inhibitory effects of bromoindoles on Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilms. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2024, 29, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boya, B.R.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Antibiofilm and antimicrobial activities of chloroindoles against uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 872943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Bian, Z.; Song, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. 4F-indole enhances the susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e04519-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudbery, P.E. Growth of Candida albicans hyphae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Lee, D.G. Indole propionic acid induced Ca2+-dependent apoptosis in Candida albicans. IUBMB Life 2022, 74, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.S.; Lee, D.G. In vitro antimicrobial activity and the mode of action of indole-3-carbinol against human pathogenic microorganisms. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, A.; Chen, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, T.; Ni, G.; Wang, R. Synthesis, structure-activity relationship and biological evaluation of indole derivatives as anti-Candida albicans agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 146, 107293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcken, R.; Zimmermann, M.O.; Lange, A.; Joerger, A.C.; Boeckler, F.M. Principles and applications of halogen bonding in medicinal chemistry and chemical biology. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1363–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeGroot, D.E.; Franks, D.G.; Higa, T.; Tanaka, J.; Hahn, M.E.; Denison, M.S. Naturally occurring marine brominated indoles are aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands/agonists. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.; Woolner, V.H.; Keyzers, R.A.; Rosengren, R.J. Characterization of marine-derived halogenated indoles as ligands of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidaud, A.L.; Schwarz, P.; Herbreteau, G.; Dannaoui, E. Techniques for the assessment of in vitro and in vivo antifungal combinations. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kang, K.; Kim, H.; Seo, M. In vitro toxicity screening of fifty complex mixtures in HepG2 cells. Toxics 2024, 12, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.; Kim, S.H.; Kwon, D.; Byun, M.R.; Chung, K.W.; Lee, J.; Jung, Y.S. Doxorubicin attenuates free fatty acid-induced lipid accumulation via stimulation of p53 in HepG2 cells. Biomol. Ther. 2024, 32, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Karthik, R.; Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, J. Antibiofilm and antifungal properties of SrWO4 microstructures against multi-azole-resistant Candida albicans and other microbes. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 514, 163091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| MIC (μg/mL) | 4,6-Dibromoindole | 5-Bromo-4-Chloroindole | Ketoconazole | Miconazole |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. albicans DAY 185 | 25 | 25 | >400 | 50 |
| C. albicans ATCC 10231 | 25 | 25 | >400 | 25 |
| C. auris KCTC 17809 | 25 | 25 | 50 | 10 |
| C. auris KCTC 17810 | 10 | 10 | 50 | 10 |
| C. glabrata ATCC 2001 | 25 | 25 | >400 | 25 |
| C. glabrata KCCM 12552 | 25 | 50 | >400 | 25 |
| C. glabrata KCCM 50701 | 25 | 25 | >400 | 25 |
| C. parapsilosis ATCC 7330 | 25 | 25 | >400 | 25 |
| C. parapsilosis ATCC 22019 | 10 | 10 | 25 | 10 |
| C. parapsilosis KCCM 50030 | 25 | 25 | >400 | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, H.; Boya, B.R.; Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Antifungal Activities of Multi-Halogenated Indoles Against Drug-Resistant Candida Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210836
Jeong H, Boya BR, Kim Y-G, Lee J-H, Lee J. Antifungal Activities of Multi-Halogenated Indoles Against Drug-Resistant Candida Species. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210836
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Hyeonwoo, Bharath Reddy Boya, Yong-Guy Kim, Jin-Hyung Lee, and Jintae Lee. 2025. "Antifungal Activities of Multi-Halogenated Indoles Against Drug-Resistant Candida Species" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210836
APA StyleJeong, H., Boya, B. R., Kim, Y.-G., Lee, J.-H., & Lee, J. (2025). Antifungal Activities of Multi-Halogenated Indoles Against Drug-Resistant Candida Species. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210836







