Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Molecular Mechanisms, Actions and Clinical Applications in Human Body
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods of Literature Review
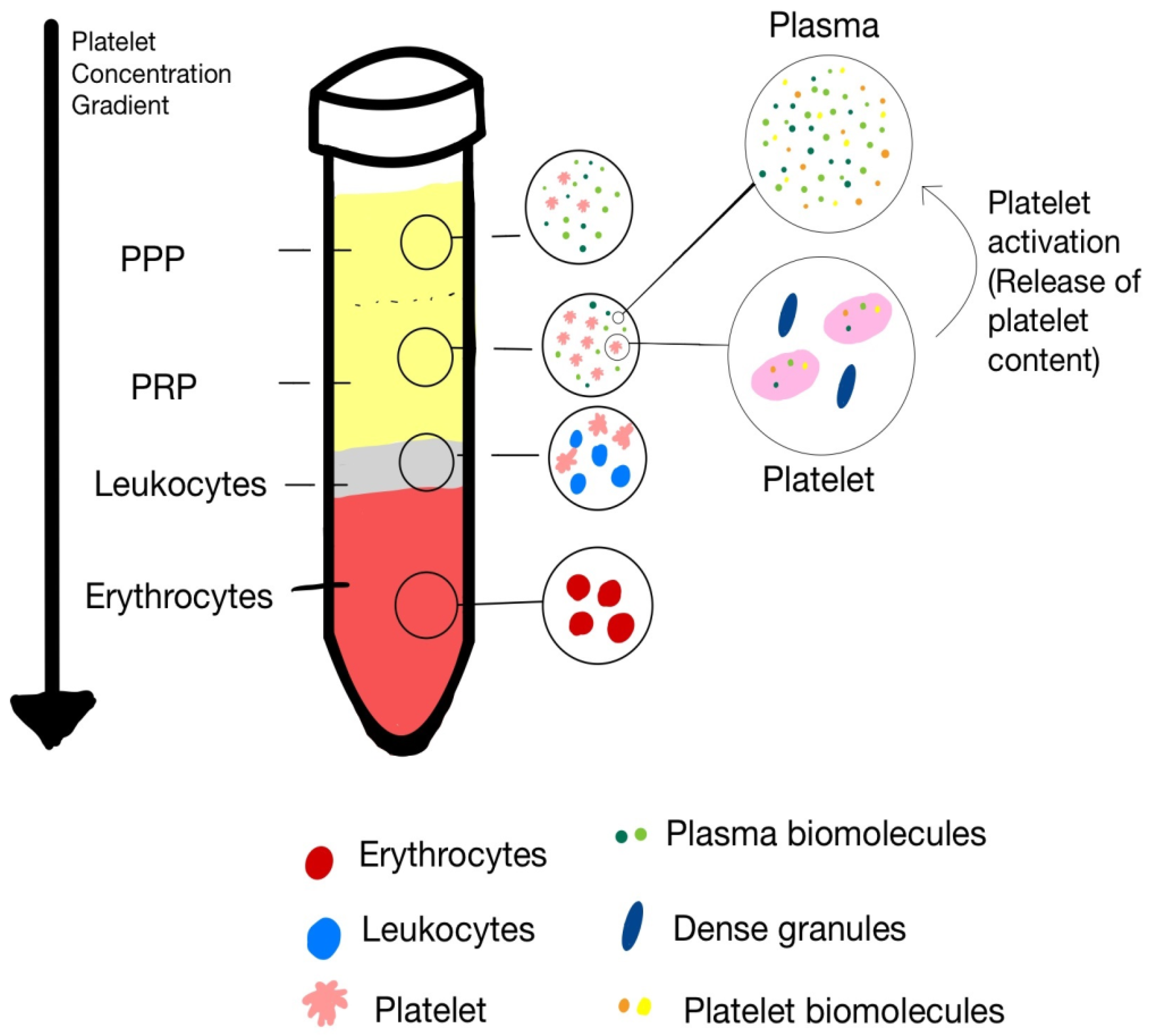
3. Preparation Methods of PRP
3.1. Double-Spin Method [11]
3.2. Buffy Coat Method [12]
4. Components of PRP
4.1. Platelets
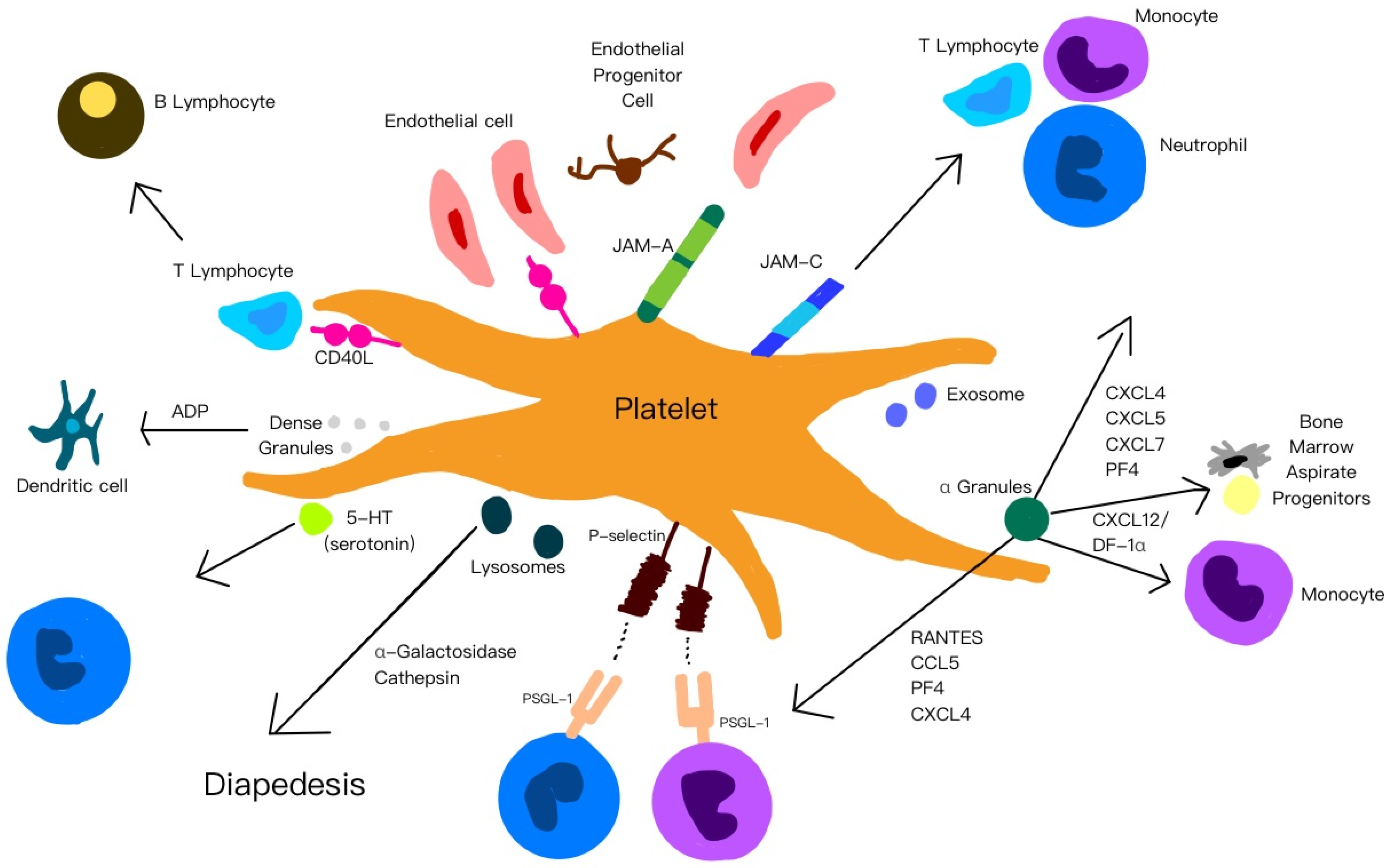
4.1.1. α-Granules
4.1.2. Platelet-Derived Exosomes
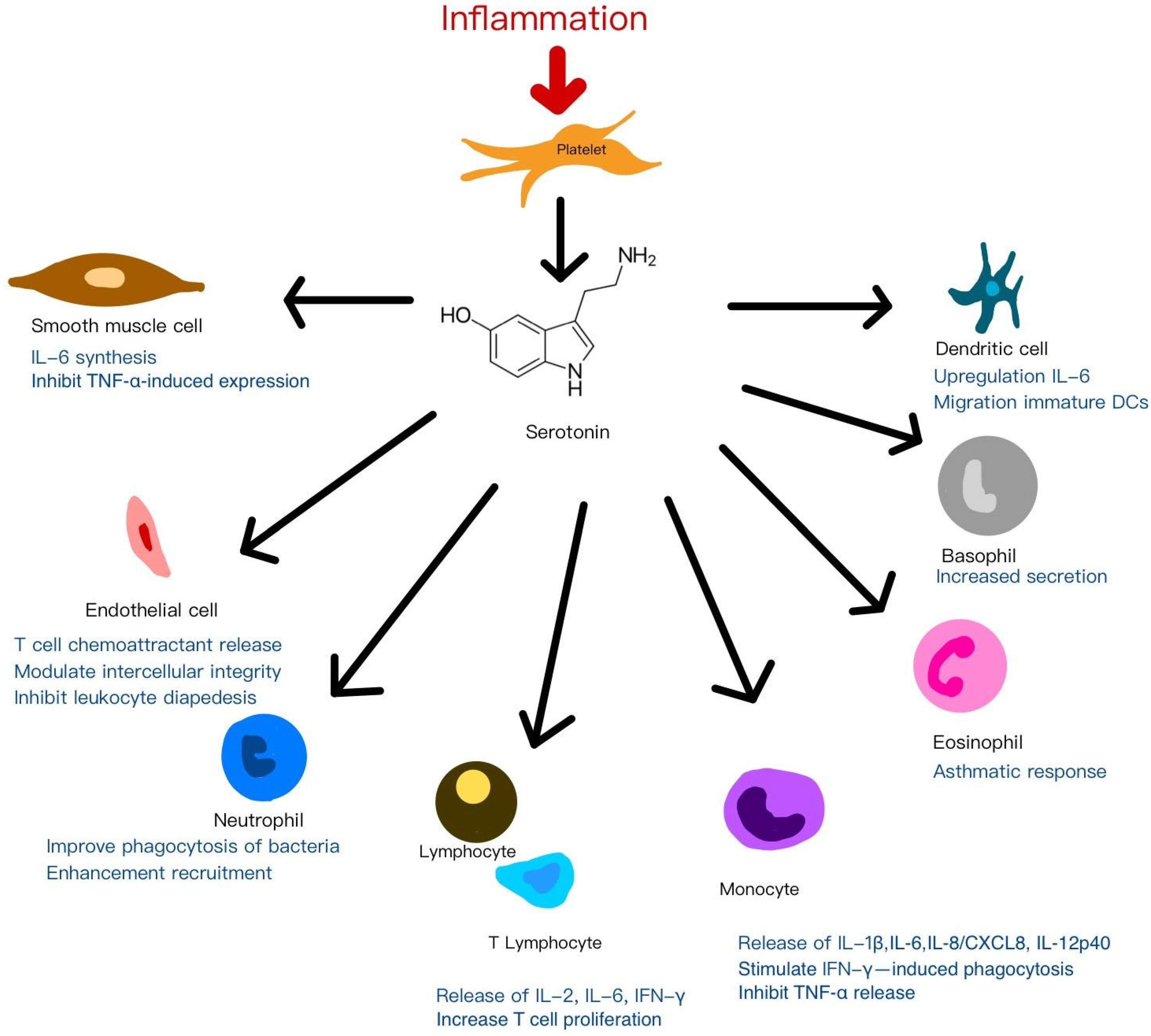
4.1.3. Dense Granules (δ-Granules)
4.1.4. Lysosomes
4.2. Leukocytes
4.2.1. Neutrophils
4.2.2. Monocytes
4.2.3. Lymphocytes
4.3. Red Blood Cells
4.4. Plasma
5. Tissue Repair and Regeneration Provoked by PRP
5.1. Platelet Adhesion Molecules
5.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
5.3. Immunomodulation
5.4. Angiogenesis
5.5. Analgesic Effects
6. The Applications of PRP
6.1. Wound Healing
6.2. The Application of PRP in Gynecology
6.2.1. Ovary
6.2.2. Endometrium
6.2.3. Urogynecology
6.2.4. Vaginal Atrophy
6.3. The Application of PRP in Dermatology
6.3.1. Hair Disorders
6.3.2. Pigmentary Disorders
Melasma
Vitiligo
6.3.3. Rejuvenation and Scars
6.3.4. Lichen Sclerosus and Other Inflammatory Disorders
6.4. The Application of PRP in Orthopedics
6.4.1. Bone Fracture Healing
6.4.2. Ligament, Muscle, and Tendon Injury
6.4.3. Peripheral Nerve Injury
6.4.4. Articular Cartilage Lesions and Osteoarthritis (OA)
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ehrenfest, D.M.D.; Rasmusson, L.; Albrektsson, T. Classification of Platelet Concentrates: From Pure Platelet-Rich Plasma (P-PRP) to Leucocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, J.M.; Russell, R.P.; Mazzocca, A.D. Platelet-Rich Plasma: The PAW Classification System. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. Off. Publ. Arthrosc. Assoc. N. Am. Int. Arthrosc. Assoc. 2012, 28, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mautner, K.; Malanga, G.A.; Smith, J.; Shiple, B.; Ibrahim, V.; Sampson, S.; Bowen, J.E. A Call for a Standard Classification System for Future Biologic Research: The Rationale for New PRP Nomenclature. PM&R 2015, 7 (Suppl. S4), S53–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalon, J.; Chateau, A.L.; Bertrand, B.; Louis, M.L.; Silvestre, A.; Giraudo, L.; Veran, J.; Sabatier, F. DEPA Classification: A Proposal for Standardising PRP Use and a Retrospective Application of Available Devices. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2016, 2, e000060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lana, J.F.S.D.; Purita, J.; Paulus, C.; Huber, S.C.; Rodrigues, B.L.; Rodrigues, A.A.; Santana, M.H.; Madureira, J.L.; Malheiros Luzo, Â.C.; Belangero, W.D.; et al. Contributions for Classification of Platelet Rich Plasma—Proposal of a New Classification: MARSPILL. Regen. Med. 2017, 12, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, E.; Di Matteo, B.; Delgado, D.; Cole, B.J.; Dorotei, A.; Dragoo, J.L.; Filardo, G.; Fortier, L.A.; Giuffrida, A.; Jo, C.H.; et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: An Expert Opinion and Proposal for a Novel Classification and Coding System. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 1447–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, T.N.; Pouliot, M.A.; Kim, H.J.; Dragoo, J.L. Comparison of Growth Factor and Platelet Concentration From Commercial Platelet-Rich Plasma Separation Systems. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, S.G.; Cole, B.J.; Sundman, E.A.; Karas, V.; Fortier, L.A. Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Milieu of Bioactive Factors. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2012, 28, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhurat, R.; Sukesh, M.S. Principles and Methods of Preparation of Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Review and Author’s Perspective. J. Cutan. Aesthetic Surg. 2014, 7, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A. Blood Components: Collection, Processing, and Storage. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1995, 25, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashore, S.; Chouhan, K.; Nanda, S.; Sharma, A. Preparation of Platelet-Rich Plasma: National IADVL PRP Taskforce Recommendations. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2021, 12 (Suppl. S1), S12–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meer, P.F.; Reesink, H.W.; de Korte, D.; Loos, J.A.; Klei, T.R.L. The History of Buffy Coat Platelet Concentrates: The Dutch Story. Vox Sang. 2022, 117, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, S.S.; Tobalem, M.; Vigato, E.; Heit, Y.; Modarressi, A.; Hinz, B.; Pittet, B.; Pietramaggiori, G. Nonactivated versus Thrombin-Activated Platelets on Wound Healing and Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Differentiation In Vivo and In Vitro. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 46e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshdeep; Kumaran, M.S. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Dermatology: Boon or a Bane? Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2014, 80, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, K.; Bhattacharyya, M. Overview of Platelet Physiology: Its Hemostatic and Nonhemostatic Role in Disease Pathogenesis. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 781857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Beitia, M.; Pompei, O.; Jorquera, C.; Sánchez, P.; Knörr, J.; Soldado, F.; López, L.; Oraa, J.; Bilbao, A.M.; et al. Isolation, Activation, and Mechanism of Action of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Its Applications for Joint Repair. In Regenerative Medicine; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machlus, K.R.; Italiano, J.E. The Incredible Journey: From Megakaryocyte Development to Platelet Formation. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 201, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalker, T.J.; Newman, D.K.; Ma, P.; Wannemacher, K.M.; Brass, L.F. Platelet Signaling. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2012, 210, 59–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ciciliano, J.; Myers, D.R.; Tran, R.; Lam, W.A. Platelets and Physics: How Platelets “Feel” and Respond to Their Mechanical Microenvironment. Blood Rev. 2015, 29, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.E.; Puskas, B.L.; Mandelbaum, B.R.; Gerhardt, M.B.; Rodeo, S.A. Platelet-Rich Plasma: From Basic Science to Clinical Applications. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 2259–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markopoulou, C.E.; Markopoulos, P.; Dereka, X.E.; Pepelassi, E.; Vrotsos, I.A. Effect of Homologous PRP on Proliferation of Human Periodontally Affected Osteoblasts. In Vitro Preliminary Study. Report of a Case. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2009, 9, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- McCarrel, T.; Fortier, L. Temporal Growth Factor Release from Platelet-Rich Plasma, Trehalose Lyophilized Platelets, and Bone Marrow Aspirate and Their Effect on Tendon and Ligament Gene Expression. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 2009, 27, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Terashima, H.; Yoneyama, S.; Tadano, S.; Ohkohchi, N. Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Intestinal Anastomotic Healing in Rats: PRP Concentration Is a Key Factor. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 173, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumbaut, R.E.; Thiagarajan, P. Platelet-Vessel Wall Interactions in Hemostasis and Thrombosis; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, P.; Flaumenhaft, R. Platelet Alpha-Granules: Basic Biology and Clinical Correlates. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, S.; Yuan, Y.; Du, C.; Song, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Armstrong, D.G.; Deng, W.; Li, L. Comparison and Investigation of Exosomes Derived from Platelet-Rich Plasma Activated by Different Agonists. Cell Transpl. 2021, 30, 9636897211017833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.-C.; Tao, S.-C.; Yin, W.-J.; Qi, X.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, C.-Q. Exosomes Derived from Platelet-Rich Plasma Promote the Re-Epithelization of Chronic Cutaneous Wounds via Activation of YAP in a Diabetic Rat Model. Theranostics 2017, 7, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Ostrowski, M.; Segura, E. Membrane Vesicles as Conveyors of Immune Responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, J. Synovial Fluid-Derived Exosomal lncRNA PCGEM1 as Biomarker for the Different Stages of Osteoarthritis. Int. Orthop. 2018, 42, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J.; Kolhe, R.; Hunter, M.; Isales, C.; Hamrick, M.; Fulzele, S. Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: A Potential Alternative Therapeutic Agent in Orthopaedics. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 5802529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, A.; Bajracharya, S.D.; Yuen, P.S.T.; Zhou, H.; Star, R.A.; Illei, G.G.; Alevizos, I. Exosomes from Human Saliva as a Source of microRNA Biomarkers. Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beit-Yannai, E.; Tabak, S.; Stamer, W.D. Physical Exosome:Exosome Interactions. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 2001–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, H.J.; Holvoet, P. Exosomes: Emerging Roles in Communication between Blood Cells and Vascular Tissues during Atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2015, 26, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arraud, N.; Linares, R.; Tan, S.; Gounou, C.; Pasquet, J.-M.; Mornet, S.; Brisson, A.R. Extracellular Vesicles from Blood Plasma: Determination of Their Morphology, Size, Phenotype and Concentration. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yuan, T.; Tschannen, M.; Sun, Z.; Jacob, H.; Du, M.; Liang, M.; Dittmar, R.L.; Liu, Y.; Liang, M.; et al. Characterization of Human Plasma-Derived Exosomal RNAs by Deep Sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torreggiani, E.; Perut, F.; Roncuzzi, L.; Zini, N.; Baglìo, S.R.; Baldini, N. Exosomes: Novel Effectors of Human Platelet Lysate Activity. Eur. Cell. Mater. 2014, 28, 137–151, discussion 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, D.S.; Chen, Y.; Sen, G.L. Progenitor Function in Self-Renewing Human Epidermis Is Maintained by the Exosome. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 11, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, G.-X.; Kazlauskas, A. Axl Is Essential for VEGF-A-Dependent Activation of PI3K/Akt. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 1692–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, D.J. Vesicle Vehicles of Genetic Information. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iberg, C.A.; Hawiger, D. Natural and Induced Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 1950 2020, 204, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganor, Y.; Besser, M.; Ben-Zakay, N.; Unger, T.; Levite, M. Human T Cells Express a Functional Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor GluR3, and Glutamate by Itself Triggers Integrin-Mediated Adhesion to Laminin and Fibronectin and Chemotactic Migration. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4362–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukasik, Z.M.; Makowski, M.; Makowska, J.S. From Blood Coagulation to Innate and Adaptive Immunity: The Role of Platelets in the Physiology and Pathology of Autoimmune Disorders. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, N.; Bode, C.; Duerschmied, D. The Effects of Serotonin in Immune Cells. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloëz-Tayarani, I.; Petit-Bertron, A.-F.; Venters, H.D.; Cavaillon, J.-M. Differential Effect of Serotonin on Cytokine Production in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Involvement of 5-hydroxytryptamine2A Receptors. Int. Immunol. 2003, 15, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciferri, S.; Emiliani, C.; Guglielmini, G.; Orlacchio, A.; Nenci, G.G.; Gresele, P. Platelets Release Their Lysosomal Content in Vivo in Humans upon Activation. Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 83, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, H.; van der Sluijs, P. Platelet Secretory Behaviour: As Diverse as the Granules … or Not? J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderli, S.L.; Blache, U.; Beretta Piccoli, A.; Niederöst, B.; Holenstein, C.N.; Passini, F.S.; Silván, U.; Bundgaard, L.; Auf dem Keller, U.; Snedeker, J.G. Tendon Response to Matrix Unloading Is Determined by the Patho-Physiological Niche. Matrix Biol. J. Int. Soc. Matrix Biol. 2020, 89, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendu, F.; Brohard-Bohn, B. The Platelet Release Reaction: Granules’ Constituents, Secretion and Functions. Platelets 2001, 12, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, V.L.; Abukabda, A.B.; Radio, N.M.; Witt-Enderby, P.A.; Clafshenkel, W.P.; Cairone, J.V.; Rutkowski, J.L. Platelet-Rich Preparations to Improve Healing. Part I: Workable Options for Every Size Practice. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 40, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoemann, C.D.; Chen, G.; Marchand, C.; Tran-Khanh, N.; Thibault, M.; Chevrier, A.; Sun, J.; Shive, M.S.; Fernandes, M.J.G.; Poubelle, P.E.; et al. Scaffold-Guided Subchondral Bone Repair: Implication of Neutrophils and Alternatively Activated Arginase-1+ Macrophages. Am. J. Sports Med. 2010, 38, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.-Q.; Yeaman, M.R.; Selsted, M.E. Antimicrobial Peptides from Human Platelets. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 6524–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipson, M.; Kubes, P. The Healing Power of Neutrophils. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, N.V.; Ksenofontov, A.L.; Serebryakova, M.V.; Stadnichuk, V.I.; Gaponova, T.V.; Baratova, L.A.; Sud’ina, G.F.; Galkina, S.I. Neutrophils Release Metalloproteinases during Adhesion in the Presence of Insulin, but Cathepsin G in the Presence of Glucagon. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1574928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borregaard, N. Neutrophils, from Marrow to Microbes. Immunity 2010, 33, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, L.C.; Sørensen, O.E.; Cowland, J.B.; Borregaard, N.; Theilgaard-Mönch, K. The Secretory Leukocyte Protease Inhibitor (SLPI) and the Secondary Granule Protein Lactoferrin Are Synthesized in Myelocytes, Colocalize in Subcellular Fractions of Neutrophils, and Are Coreleased by Activated Neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faurschou, M.; Borregaard, N. Neutrophil Granules and Secretory Vesicles in Inflammation. Microbes Infect. 2003, 5, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borregaard, N.; Cowland, J.B. Granules of the Human Neutrophilic Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte. Blood 1997, 89, 3503–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Vidriero, E.; Goulding, K.A.; Simon, D.A.; Sanchez, M.; Johnson, D.H. The Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Arthroscopy and Sports Medicine: Optimizing the Healing Environment. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2010, 26, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, J.; Vilcinskas, A. Antimicrobial Peptides: The Ancient Arm of the Human Immune System. Virulence 2010, 1, 440–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Sinha, M.; Datta, S.; Abas, M.; Chaffee, S.; Sen, C.K.; Roy, S. Monocyte and Macrophage Plasticity in Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 2596–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, C.J.; Leibovich, S.J. Regulation of Macrophage Polarization and Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2012, 1, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italiani, P.; Boraschi, D. From Monocytes to M1/M2 Macrophages: Phenotypical vs. Functional Differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubezio, G.; Ghio, M.; Contini, P.; Bertorello, R.; Marino, G.; Tomasini, A.; Tripodi, G. Bio-Modulators in Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Comparison of the Amounts in Products from Healthy Donors and Patients Produced with Three Different Techniques. Blood Transfus. 2014, 12 (Suppl. S1), s214–s220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooiveld, M.; Roosendaal, G.; Wenting, M.; van den Berg, M.; Bijlsma, J.; Lafeber, F. Short-Term Exposure of Cartilage to Blood Results in Chondrocyte Apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.L.; Anderson, N.G. The Human Plasma Proteome: History, Character, and Diagnostic Prospects. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2002, 1, 845–867, Erratum in Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2003, 2, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monastero, R.N.; Pentyala, S. Cytokines as Biomarkers and Their Respective Clinical Cutoff Levels. Int. J. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 4309485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, M.; Choi, J.; Hansson, S.; Storm, M.U.; Nilsson, L. Proteins and Antibodies in Serum, Plasma, and Whole Blood-Size Characterization Using Asymmetrical Flow Field-Flow Fractionation (AF4). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4867–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Quintela, A.; Alende, R.; Gude, F.; Campos, J.; Rey, J.; Meijide, L.M.; Fernandez-Merino, C.; Vidal, C. Serum Levels of Immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgM) in a General Adult Population and Their Relationship with Alcohol Consumption, Smoking and Common Metabolic Abnormalities. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 151, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibault, M.M.; Hoemann, C.D.; Buschmann, M.D. Fibronectin, Vitronectin, and Collagen I Induce Chemotaxis and Haptotaxis of Human and Rabbit Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Standardized Transmembrane Assay. Stem Cells Dev. 2007, 16, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, L.A.; van der Meulen, M.C.H.; Bertram, J.E.A.; Starrak, G.S.; Nixon, A.J. Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Improves Cellular and Molecular Aspects of Healing in a Collagenase-Induced Model of Flexor Tendinitis. J. Orthop. Res. 2002, 20, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, L.A.; Lust, G.; Mohammed, H.O.; Nixon, A.J. Coordinate Upregulation of Cartilage Matrix Synthesis in Fibrin Cultures Supplemented with Exogenous Insulin-like Growth Factor-I. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 1999, 17, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Deng, X.; Li, Y. Inhibition of Oxidative-Stress-Induced Platelet Aggregation by Androgen at Physiological Levels via Its Receptor Is Associated with the Reduction of Thromboxane A2 Release from Platelets. Steroids 2007, 72, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akarasereenont, P.; Tripatara, P.; Chotewuttakorn, S.; Palo, T.; Thaworn, A. The Effects of Estrone, Estradiol and Estriol on Platelet Aggregation Induced by Adrenaline and Adenosine Diphosphate. Platelets 2006, 17, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossaint, J.; Zarbock, A. Platelets in Leucocyte Recruitment and Function. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 107, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gils, J.M.; Zwaginga, J.J.; Hordijk, P.L. Molecular and Functional Interactions among Monocytes, Platelets, and Endothelial Cells and Their Relevance for Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 85, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, M.A.; Diacovo, T.G.; Emsley, J.; Liddington, R.; Handin, R.I. Mapping the Glycoprotein Ib-Binding Site in the von Willebrand Factor A1 Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 19098–19105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.S. Structure and Function of the Platelet Integrin alphaIIbbeta3. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3363–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Ley, K.; McEver, R.P.; Hidalgo, A. Leukocyte Ligands for Endothelial Selectins: Specialized Glycoconjugates That Mediate Rolling and Signaling under Flow. Blood 2011, 118, 6743–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Furie, B.C.; Furie, B. The Biology of P-Selectin Glycoprotein Ligand-1: Its Role as a Selectin Counterreceptor in Leukocyte-Endothelial and Leukocyte-Platelet Interaction. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 81, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, C.; Springer, T.A. Neutrophil Accumulation on Activated, Surface-Adherent Platelets in Flow Is Mediated by Interaction of Mac-1 with Fibrinogen Bound to alphaIIbbeta3 and Stimulated by Platelet-Activating Factor. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diacovo, T.G.; deFougerolles, A.R.; Bainton, D.F.; Springer, T.A. A Functional Integrin Ligand on the Surface of Platelets: Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-2. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.; Onishi, K.; Jayaram, P.; Lana, J.F.; Mautner, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejnek, M.; Moreira, H.; Płaczkowska, S.; Barg, E.; Reichert, P.; Królikowska, A. Leukocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma as an Effective Source of Molecules That Modulate Local Immune and Inflammatory Cell Responses. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8059622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurden, A.T. Platelets, Inflammation and Tissue Regeneration. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 105 (Suppl. S1), S13–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, R.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, M.; Luo, Y.; Hu, Z.; Mou, X.; Zhu, Y. Biologic Mechanisms of Macrophage Phenotypes Responding to Infection and the Novel Therapies to Moderate Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, R.; Zufferey, A.; Boilard, E.; Semple, J.W. Nouvelle Cuisine: Platelets Served with Inflammation. J. Immunol. 1950 2015, 194, 5579–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuerer, B.; Ernst, M.; Dürrbaum-Landmann, I.; Fleischer, J.; Grage-Griebenow, E.; Brandt, E.; Flad, H.D.; Petersen, F. The CXC-Chemokine Platelet Factor 4 Promotes Monocyte Survival and Induces Monocyte Differentiation into Macrophages. Blood 2000, 95, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muiños-López, E.; Delgado, D.; Sánchez, P.; Paiva, B.; Anitua, E.; Fiz, N.; Aizpurua, B.; Guadilla, J.; Padilla, S.; Granero-Moltó, F.; et al. Modulation of Synovial Fluid-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Intra-Articular and Intraosseous Platelet Rich Plasma Administration. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 1247950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodell-May, J.E.; Sommerfeld, S.D. Role of Inflammation and the Immune System in the Progression of Osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 2020, 38, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K.; Dixit, V.M. Signaling in Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a006049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognasse, F.; Laradi, S.; Berthelot, P.; Bourlet, T.; Marotte, H.; Mismetti, P.; Garraud, O.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H. Platelet Inflammatory Response to Stress. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, A.; Syvannarath, V.; Lamrani, L.; Ollivier, V.; Loyau, S.; Goerge, T.; Nieswandt, B.; Jandrot-Perrus, M.; Ho-Tin-Noé, B. Single Platelets Seal Neutrophil-Induced Vascular Breaches via GPVI during Immune-Complex-Mediated Inflammation in Mice. Blood 2015, 126, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.R.; Ma, A.C.; Tavener, S.A.; McDonald, B.; Goodarzi, Z.; Kelly, M.M.; Patel, K.D.; Chakrabarti, S.; McAvoy, E.; Sinclair, G.D.; et al. Platelet TLR4 Activates Neutrophil Extracellular Traps to Ensnare Bacteria in Septic Blood. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiko, G.E.; Horvat, J.C.; Beagley, K.W.; Hansbro, P.M. Immunological Decision-Making: How Does the Immune System Decide to Mount a Helper T-Cell Response? Immunology 2008, 123, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, V.; Slupsky, J.R.; Gräfe, M.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Förster, R.; Müller-Berghaus, G.; Kroczek, R.A. CD40 Ligand on Activated Platelets Triggers an Inflammatory Reaction of Endothelial Cells. Nature 1998, 391, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Ding, L.; Wang, D.; Han, J.; Gao, P. Serotonin: A Potent Immune Cell Modulator in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerschmied, D.; Suidan, G.L.; Demers, M.; Herr, N.; Carbo, C.; Brill, A.; Cifuni, S.M.; Mauler, M.; Cicko, S.; Bader, M.; et al. Platelet Serotonin Promotes the Recruitment of Neutrophils to Sites of Acute Inflammation in Mice. Blood 2013, 121, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire-Garabal, M.; Núñez, M.J.; Balboa, J.; López-Delgado, P.; Gallego, R.; García-Caballero, T.; Fernández-Roel, M.D.; Brenlla, J.; Rey-Méndez, M. Serotonin Upregulates the Activity of Phagocytosis Through 5-HT1A Receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, T.P.; Peters, M.C.; Ennett, A.B.; Mooney, D.J. Polymeric System for Dual Growth Factor Delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bir, S.C.; Esaki, J.; Marui, A.; Sakaguchi, H.; Kevil, C.G.; Ikeda, T.; Komeda, M.; Tabata, Y.; Sakata, R. Therapeutic Treatment with Sustained-Release Platelet-Rich Plasma Restores Blood Perfusion by Augmenting Ischemia-Induced Angiogenesis and Arteriogenesis in Diabetic Mice. J. Vasc. Res. 2011, 48, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marushima, A.; Nieminen, M.; Kremenetskaia, I.; Gianni-Barrera, R.; Woitzik, J.; von Degenfeld, G.; Banfi, A.; Vajkoczy, P.; Hecht, N. Balanced Single-Vector Co-Delivery of VEGF/PDGF-BB Improves Functional Collateralization in Chronic Cerebral Ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 40, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, I.; Rughetti, A.; D’Ascenzo, S.; Millimaggi, D.; Pavan, A.; Dell’Orso, L.; Dolo, V. Identification of an Optimal Concentration of Platelet Gel for Promoting Angiogenesis in Human Endothelial Cells. Transfusion 2009, 49, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.A.; Devilee, R.J.J.; Brown Mahoney, C.; van Erp, A.; Oosterbos, C.J.M.; Stellenboom, M.; Knape, J.T.A.; van Zundert, A. Exogenous Application of Platelet-Leukocyte Gel during Open Subacromial Decompression Contributes to Improved Patient Outcome. A Prospective Randomized Double-Blind Study. Eur. Surg. Res. Eur. Chir. Forsch. Rech. Chir. Eur. 2008, 40, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.A.M.; Knape, J.T.A.; Weibrich, G.; Schönberger, J.P.A.M.; Hoffmann, J.; Overdevest, E.P.; Box, H.A.M.; van Zundert, A. Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet Gel: A Review. J. Extra. Corpor. Technol. 2006, 38, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, R.; Small, J.; Dixon, A.K.; Spanswick, D.; Lee, K. Serotonin Receptor mRNA Expression in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 337, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-P.; Hao, J.-X.; Xu, X.-J.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z.; Koek, W.; Colpaert, F.C. The Very-High-Efficacy 5-HT1A Receptor Agonist, F 13640, Preempts the Development of Allodynia-like Behaviors in Rats with Spinal Cord Injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 478, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patetsos, E.; Horjales-Araujo, E. Treating Chronic Pain with SSRIs: What Do We Know? Pain. Res. Manag. 2016, 2016, 2020915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Funasaki, H.; Marumo, K. Efficacy of Autologous Leukocyte-Reduced Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy for Patellar Tendinopathy in a Rat Treadmill Model. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2016, 6, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.-J.; Sun, J.-B.; Bi, Z.-G.; Wang, X.-M.; Yang, C.-L. Evaluation of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Fibrin Matrix to Assist in Healing and Repair of Rotator Cuff Injuries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 31, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaegen, F.; Brys, P.; Debeer, P. Rotator Cuff Healing after Needling of a Calcific Deposit Using Platelet-Rich Plasma Augmentation: A Randomized, Prospective Clinical Trial. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016, 25, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urits, I.; Smoots, D.; Franscioni, H.; Patel, A.; Fackler, N.; Wiley, S.; Berger, A.A.; Kassem, H.; Urman, R.D.; Manchikanti, L.; et al. Injection Techniques for Common Chronic Pain Conditions of the Foot: A Comprehensive Review. Pain Ther. 2020, 9, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-T.; Wei, K.-C.; Wu, C.-H. Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffler, D.P. Platelet-Rich Plasma Promotes Axon Regeneration, Wound Healing, and Pain Reduction: Fact or Fiction. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 990–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johal, H.; Khan, M.; Yung, S.-H.P.; Dhillon, M.S.; Fu, F.H.; Bedi, A.; Bhandari, M. Impact of Platelet-Rich Plasma Use on Pain in Orthopaedic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Health 2019, 11, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Gonzalez, A.C.; Costa, T.F.; de Araújo Andrade, Z.; Medrado, A.R.A.P. Wound Healing—A Literature Review. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2016, 91, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, C.K. Human Wounds and Its Burden: An Updated Compendium of Estimates. Adv. Wound Care 2019, 8, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andia, I.; Abate, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Underlying Biology and Clinical Correlates. Regen. Med. 2013, 8, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacci, K.M.; Dardik, A. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Support for Its Use in Wound Healing. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2010, 83, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Babaei, V.; Afradi, H.; Gohardani, H.Z.; Nasseri, F.; Azarafza, M.; Teimourian, S. Management of Chronic Diabetic Foot Ulcers Using Platelet-Rich Plasma. J. Wound Care 2017, 26, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslik-Bielecka, A.; Skowroński, R.; Jędrusik-Pawłowska, M.; Pierchała, M. The Application of L-PRP in AIDS Patients with Crural Chronic Ulcers: A Pilot Study. Adv. Med. Sci. 2018, 63, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karayannopoulou, M.; Psalla, D.; Kazakos, G.; Loukopoulos, P.; Giannakas, N.; Savvas, I.; Kritsepi-Konstantinou, M.; Chantes, A.; Papazoglou, L.G. Effect of Locally Injected Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma on Second Intention Wound Healing of Acute Full-Thickness Skin Defects in Dogs. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. VCOT 2015, 28, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Yin, X.; Li, H.; Jia, L.; He, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, N.; Wan, K.; Li, X.; Lin, S. Synergistic Effect of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Platelet-Rich Plasma in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Ann. Dermatol. 2014, 26, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sills, E.S.; Wood, S.H. Autologous Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection into Adult Human Ovary Tissue: Molecular Mechanism, Analysis, and Discussion of Reproductive Response. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farimani, M.; Heshmati, S.; Poorolajal, J.; Bahmanzadeh, M. A Report on Three Live Births in Women with Poor Ovarian Response Following Intra-Ovarian Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharara, F.I.; Lelea, L.-L.; Rahman, S.; Klebanoff, J.S.; Moawad, G.N. A Narrative Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Reproductive Medicine. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2021, 38, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnashar, A.M. Intraovarian Platelet-Rich Plasma: Current Status. Middle East Fertil. Soc. J. 2021, 26, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, Y.A.R.; Woods, D.C.; Takai, Y.; Ishihara, O.; Seki, H.; Tilly, J.L. Oocyte Formation by Mitotically Active Germ Cells Purified from Ovaries of Reproductive-Age Women. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhartiya, D.; Sriraman, K.; Parte, S. Stem Cell Interaction with Somatic Niche May Hold the Key to Fertility Restoration in Cancer Patients. Obstet. Gynecol. Int. 2012, 2012, 921082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lew, R. Natural History of Ovarian Function Including Assessment of Ovarian Reserve and Premature Ovarian Failure. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2019, 55, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantos, K.; Simopoulou, M.; Pantou, A.; Rapani, A.; Tsioulou, P.; Nitsos, N.; Syrkos, S.; Pappas, A.; Koutsilieris, M.; Sfakianoudis, K. A Case Series on Natural Conceptions Resulting in Ongoing Pregnancies in Menopausal and Prematurely Menopausal Women Following Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment. Cell Transpl. 2019, 28, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchante, M.; Buigues, A.; Ramirez-Martin, N.; Martinez, J.; Pellicer, N.; Pellicer, A.; Herraiz, S. Single Intraovarian Dose of Stem Cell– and Platelet-Secreted Factors Mitigates Age-Related Ovarian Infertility in a Murine Model. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 228, 561.e1–561.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, A.; Sánchez, J.; Sánchez, W.; Vielma, V. Platelet-Rich Plasma as an Adjuvant in the Endometrial Preparation of Patients with Refractory Endometrium. JBRA Assist. Reprod. 2018, 22, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehraninejad, E.S.; Kashani, N.G.; Hosseini, A.; Tarafdari, A. Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Infusion Does Not Improve Pregnancy Outcomes in Frozen Embryo Transfer Cycles in Women with History of Repeated Implantation Failure without Thin Endometrium. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2021, 47, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, I.; Cicinelli, E.; Garcia-Grau, I.; Gonzalez-Monfort, M.; Bau, D.; Vilella, F.; De Ziegler, D.; Resta, L.; Valbuena, D.; Simon, C. The Diagnosis of Chronic Endometritis in Infertile Asymptomatic Women: A Comparative Study of Histology, Microbial Cultures, Hysteroscopy, and Molecular Microbiology. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 218, 602.e1–602.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, F.; Takebayashi, A.; Ishida, M.; Nakamura, A.; Kitazawa, J.; Morimune, A.; Hirata, K.; Takahashi, A.; Tsuji, S.; Takashima, A.; et al. Review: Chronic Endometritis and Its Effect on Reproduction. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2019, 45, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfakianoudis, K.; Simopoulou, M.; Nitsos, N.; Lazaros, L.; Rapani, A.; Pantou, A.; Koutsilieris, M.; Nikas, Y.; Pantos, K. Successful Implantation and Live Birth Following Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment for a Patient with Recurrent Implantation Failure and Chronic Endometritis. In Vivo 2019, 33, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, M.G.; Perrini, C.; Esposti, P.; Corradetti, B.; Bizzaro, D.; Riccaboni, P.; Fantinato, E.; Urbani, G.; Gelati, G.; Cremonesi, F.; et al. Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma in a Model of Bovine Endometrial Inflammation In Vitro. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. RBE 2016, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caley, M.P.; Martins, V.L.C.; O’Toole, E.A. Metalloproteinases and Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajanova, L.; Houshdaran, S.; Balayan, S.; Manvelyan, E.; Irwin, J.C.; Huddleston, H.G.; Giudice, L.C. In Vitro Evidence That Platelet-Rich Plasma Stimulates Cellular Processes Involved in Endometrial Regeneration. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2018, 35, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanova, L.; Sundaram, V.; Kao, C.-N.; Letourneau, J.M.; Manvelyan, E.; Cedars, M.I.; Huddleston, H.G. Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment for Moderate-Severe Asherman Syndrome: The First Experience. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2021, 38, 2955–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanova, L.; Cedars, M.I.; Huddleston, H.G. Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Management of Asherman Syndrome: Case Report. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2018, 35, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Mohamed Mahmoud Abd Elwahab Torky; Amer, M.I.M.; Ahmed, M.E.-S.; Kamal, R.M. The Value of Using Platelet Rich Plasma after Hysteroscopic Analysis of Severe Intrauterine Adhesions (A Randomized Controlled Trial). Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2018, 71, 2869–2874. [Google Scholar]
- Streit-Ciećkiewicz, D.; Futyma, K.; Miotła, P.; Grzybowska, M.E.; Rechberger, T. Platelet-Rich Plasma as Adjuvant Therapy for Recurrent Vesicovaginal Fistula: A Prospective Case Series. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atılgan, A.E.; Aydın, A. Cystocele Repair with Platelet-Rich Plasma. Indian J. Surg. 2021, 83, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlero, F.; Glorio, M.; Lorenzi, P.; Bruno-Franco, M.; Mazzei, C. New Approach in Vaginal Prolapse Repair: Mini-Invasive Surgery Associated with Application of Platelet-Rich Fibrin. Int. Urogynecology J. 2012, 23, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.-Y.; Lin, K.-L.; Shen, C.-R.; Ker, C.-R.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Loo, Z.-X.; Hsiao, H.-H.; Lee, Y.-C. A Pilot Study: Effectiveness of Local Injection of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma in Treating Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Man, K.-M.; Chen, W.-C.; Liu, P.-L.; Tsai, K.-S.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Wu, Y.-T.; Chen, H.-Y. Platelet-Rich Plasma Ameliorates Cyclophosphamide-Induced Acute Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome in a Rat Model. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, J.-F.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Ho, H.-C.; Birder, L.A.; Lin, T.-Y.; Kuo, H.-C. Improved Urothelial Cell Proliferation, Cytoskeleton and Barrier Function Protein Expression in the Patients With Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome After Intravesical Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection. Int. Neurourol. J. 2022, 26 (Suppl. S1), S57–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futyma, K.; Nowakowski, Ł.; Ziętek-Strobl, A.; Kamińska, A.; Taoussi, N.; Rechberger, T. Urine Proteomic Study in OAB Patients-Preliminary Report. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghe, T.; Acharya, N.; Karnik, M.; Mohammad, S.; Patel, N.A.; Gemnani, R. Role of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause. Cureus 2024, 16, e53316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinks, A.; Desai, D.D.; Kearney, C.A.; Needle, C.; Anyanwu, N.; Nohria, A.; Sikora, M.; Oh, C.S.; Shapiro, J.; Lo Sicco, K.I. Impact of Age on Response to Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siah, T.W.; Guo, H.; Chu, T.; Santos, L.; Nakamura, H.; Leung, G.; Shapiro, J.; McElwee, K.J. Growth Factor Concentrations in Platelet-Rich Plasma for Androgenetic Alopecia: An Intra-Subject, Randomized, Blinded, Placebo-Controlled, Pilot Study. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinks, A.; Desai, D.D.; Needle, C.; Kearney, C.A.; Nohria, A.; Sikora, M.; Oh, C.S.; Anyanwu, N.; Shapiro, J.; Lo Sicco, K.I. Evaluating the Accuracy of Patient-Reported Hair Outcomes versus Trichometric Measurements in PRP Therapy. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2025, 317, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.; Ho, A.; Sukhdeo, K.; Yin, L.; Lo Sicco, K. Evaluation of Platelet-Rich Plasma as a Treatment for Androgenetic Alopecia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.; Karim, M.; Kim, R.; Lo Sicco, K.; Shapiro, J. Reversible Hair Loss in Lichen Planopilaris: Regrowth With Low-Dose Naltrexone and Platelet-Rich Plasma. J. Drugs Dermatol. JDD 2022, 21, 671–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, A.J.; Pincelli, T.P.; Heckman, M.G.; Desmond, C.M.; Arthurs, J.R.; Diehl, N.N.; Douglass, E.J.; Bruce, C.J.; Shapiro, S.A. A Randomized, Controlled Pilot Trial Comparing Platelet-Rich Plasma to Topical Minoxidil Foam for Treatment of Androgenic Alopecia in Women. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. Al 2020, 46, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhasz, M.L.W.; Lo Sicco, K.; Shapiro, J. The Utility of Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Alopecia. J. Drugs Dermatol. JDD 2020, 19, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aristizabal, M.; Bruce, A.; Pincelli, T.; Arthurs, J.; Shapiro, S. An Academic Dermatology Center’s Structured Platelet-Rich Plasma Approach to Patients with Androgenetic Alopecia. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2024, 17 (Suppl. S1), S28–S30. [Google Scholar]
- Philpott, M.P.; Kealey, T. Effects of EGF on the Morphology and Patterns of DNA Synthesis in Isolated Human Hair Follicles. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1994, 102, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkini, M.-A.; Kouskoukis, A.-E.; Tripsianis, G.; Rigopoulos, D.; Kouskoukis, K. Study of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections in the Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia through an One-Year Period. J. Cutan. Aesthetic Surg. 2014, 7, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria-Angeliki, G.; Alexandros-Efstratios, K.; Dimitris, R.; Konstantinos, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma as a Potential Treatment for Noncicatricial Alopecias. Int. J. Trichology 2015, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, P.; Cole, J.P.; Cole, M.A.; Garcovich, S.; Bielli, A.; Scioli, M.G.; Orlandi, A.; Insalaco, C.; Cervelli, V. Evaluation of Not-Activated and Activated PRP in Hair Loss Treatment: Role of Growth Factor and Cytokine Concentrations Obtained by Different Collection Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, P.; Garcovich, S. Systematic Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma Use in Androgenetic Alopecia Compared with Minoxidil®, Finasteride®, and Adult Stem Cell-Based Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paichitrojjana, A.; Paichitrojjana, A. Platelet Rich Plasma and Its Use in Hair Regrowth: A Review. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2022, 16, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pixley, J.N.; Cook, M.K.; Singh, R.; Larrondo, J.; McMichael, A.J. A Comprehensive Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Dermatologic Disorders. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2023, 34, 2142035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, J.A.; Estharabadi, N.; Farah, R.S.; Hordinsky, M.K. Heterogeneity in Amount of Growth Factors Secreted by Platelets in Platelet-Rich Plasma Samples from Alopecia Patients. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofny, E.R.M.; Abdel-Motaleb, A.A.; Ghazally, A.; Ahmed, A.M.; Hussein, M.R.A. Platelet-Rich Plasma Is a Useful Therapeutic Option in Melasma. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2019, 30, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamea, M.M.; Kamal, D.A.; Donia, A.A.; Hegab, D.S. Comparative Study between Topical Tranexamic Acid Alone versus Its Combination with Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma for Treatment of Melasma. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Arámbula, A.; Torres-Álvarez, B.; Cortés-García, D.; Fuentes-Ahumada, C.; Castanedo-Cázares, J.P. CD4, IL-17, and COX-2 Are Associated with Subclinical Inflammation in Malar Melasma. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2015, 37, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, M.; Xiao, Q.; Zhou, R.; Li, Y.; Xiong, L.; Li, L. Efficacy and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Melasma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Liu, S.-X. Progress in the Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma to Treat Vitiligo and Melasma. Int. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 04, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Z.A.; El-Ashmawy, A.A.; El-Tatawy, R.A.; Sallam, F.A. The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on the Outcome of Short-Term Narrowband-Ultraviolet B Phototherapy in the Treatment of Vitiligo: A Pilot Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, H. Current Art of Combination Therapy with Autologous Platelet-rich Plasma for Stable Vitiligo: A Meta-analysis. Int. Wound J. 2020, 18, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghani, R.; Ahmed, N.A.; Darwish, H.M. Combined Treatment with Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser, Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma, and Narrow Band Ultraviolet B for Vitiligo in Different Body Sites: A Prospective, Randomized Comparative Trial. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.A.; Li, M.O. TGF-β: Guardian of T Cell Function. J. Immunol. 1950 2013, 191, 3973–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenberg, E.; Hattier, G.; Wang, J.V.; Saedi, N. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Facial Rejuvenation: An Early Examination. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 38, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, Z.; Alimohamadi, Y.; Janani, M.; Hejazi, P.; Kamali, M.; Goodarzi, A. Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Scars, to Suggest or Not to Suggest? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2022, 16, 875–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Lu, Y.; Bi, B.; Chen, L.; Yang, Q.; Yang, P.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, N.; Liu, T. Platelet-Rich Plasma Ameliorates Senescence-like Phenotypes in a Cellular Photoaging Model. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 3152–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devereaux, J.; Nurgali, K.; Kiatos, D.; Sakkal, S.; Apostolopoulos, V. Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Poor Plasma on Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Maturitas 2018, 117, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Xiang, L.-J.; Shi, H.-X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Cai, P.; Lin, Z.-L.; Lin, B.-B.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.-L.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factors Stimulate Hair Growth through β-Catenin and Shh Expression in C57BL/6 Mice. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 730139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, V.; Ciric, M.; Jovanovic, V.; Stojanovic, P. Platelet Rich Plasma: A Short Overview of Certain Bioactive Components. Open Med. 2016, 11, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Levy, F.M. Autologous Platelet Concentrates for Facial Rejuvenation. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2022, 30, e20220020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.-W.; Kim, S.-A.; Lee, K.-S. Platelet-Rich Plasma Induces Increased Expression of G1 Cell Cycle Regulators, Type I Collagen, and Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 in Human Skin Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.S.; Nouri, M.; Zarrabi, M.; Fatemi, M.J.; Shpichka, A.; Timashev, P.; Hassan, M.; Vosough, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Regenerative Medicine: Possible Applications in Management of Burns and Post-Burn Scars: A Review. Cell J. Yakhteh 2023, 25, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayzullin, A.; Ignatieva, N.; Zakharkina, O.; Tokarev, M.; Mudryak, D.; Khristidis, Y.; Balyasin, M.; Kurkov, A.; Churbanov, S.; Dyuzheva, T.; et al. Modeling of Old Scars: Histopathological, Biochemical and Thermal Analysis of the Scar Tissue Maturation. Biology 2021, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina Garrido, C.; Cano García, A.; de la Cruz Cea, L.; Oreja Cuesta, A.B. Mid-Term Symptomatic Relief after Platelet-Rich Plasma Infiltration in Vulvar Lichen Sclerosus. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2023, 315, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.A.; Tan, X.; Macri, C.J.; Goldstein, A.T.; Fu, S.W. Lichen Sclerosus: An Autoimmunopathogenic and Genomic Enigma with Emerging Genetic and Immune Targets. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlou, A.; Santegoets, L.A.M.; van der Meijden, W.I.; Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Swagemakers, S.M.A.; van der Spek, P.J.; Ewing, P.C.; van Beurden, M.; Helmerhorst, T.J.M.; Blok, L.J. An Autoimmune Phenotype in Vulvar Lichen Sclerosus and Lichen Planus: A Th1 Response and High Levels of MicroRNA-155. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlundt, C.; Bucher, C.H.; Tsitsilonis, S.; Schell, H.; Duda, G.N.; Schmidt-Bleek, K. Clinical and Research Approaches to Treat Non-Union Fracture. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabongi, R.G.; De Rizzo, L.A.L.M.; Fernandes, M.; Valente, S.G.; Gomes dos Santos, J.B.; Faloppa, F.; Leite, V.M. Nerve Regeneration: Is There an Alternative to Nervous Graft? J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2014, 30, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, J.P.; Ketzmar, A.-K.; Endres, M.; Pruss, A.; Siclari, A.; Kaps, C. Human Platelet-Rich Plasma Induces Chondrogenic Differentiation of Subchondral Progenitor Cells in Polyglycolic Acid-Hyaluronan Scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yuan, X.; Fernandes, G.; Dziak, R.; Ionita, C.N.; Li, C.; Wang, C.; Yang, S. The Combination of Nano-Calcium Sulfate/Platelet Rich Plasma Gel Scaffold with BMP2 Gene-Modified Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes Bone Regeneration in Rat Critical-Sized Calvarial Defects. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, A.; Boerckel, J.D.; Saifzadeh, S.; Steck, R.; Ren, J.; Vaquette, C.; Zhang, J.Q.; Nerlich, M.; Guldberg, R.E.; Hutmacher, D.W.; et al. Biomimetic Tubular Nanofiber Mesh and Platelet Rich Plasma-Mediated Delivery of BMP-7 for Large Bone Defect Regeneration. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 347, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Pelletier, M.; Oliver, R.; Christou, C.; Walsh, W.R. Platelet-Rich Plasma and Bone Defect Healing. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 20, 2614–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, E.; Flückiger, L.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Sawada, K.; Sculean, A.; Schaller, B.; Miron, R.J. Comparative Release of Growth Factors from PRP, PRF, and Advanced-PRF. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 2353–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazem-Arki, M.; Kabiri, M.; Rad, I.; Roodbari, N.H.; Hosseinpoor, H.; Mirzaei, S.; Parivar, K.; Hanaee-Ahvaz, H. Enhancement of Osteogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells by PRP Modified Nanofibrous Scaffold. Cytotechnology 2018, 70, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Huang, A.-W.; Fan, J.J.; Wei, K.; Jin, D.; Chen, B.; Li, D.; Bi, L.; Wang, J.; Pei, G. The Potential Use of Allogeneic Platelet-Rich Plasma for Large Bone Defect Treatment: Immunogenicity and Defect Healing Efficacy. Cell Transpl. 2013, 22, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentini, F.; Ceglia, M.J.; Bettini, L.; Bianco, S.; Buzzi, R.; Campanacci, D.A. Induced Membrane Technique Using Enriched Bone Grafts for Treatment of Posttraumatic Segmental Long Bone Defects. J. Orthop. Traumatol. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Orthop. Traumatol. 2019, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebergall, M.; Schroeder, J.; Mosheiff, R.; Gazit, Z.; Yoram, Z.; Rasooly, L.; Daskal, A.; Khoury, A.; Weil, Y.; Beyth, S. Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Prevention of Delayed Fracture Union: A Randomized and Prospective Preliminary Study. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2013, 21, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashef-Saberi, M.S.; Hayati Roodbari, N.; Parivar, K.; Vakilian, S.; Hanaee-Ahvaz, H. Enhanced Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Electrospun Polyethersulfone/Poly(Vinyl) Alcohol/Platelet Rich Plasma Nanofibrous Scaffolds. ASAIO J. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1992 2018, 64, e115–e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Nie, D.; Williamson, K.; Rocha, J.L.; Hogan, M.V.; Wang, J.H.-C. Selectively Activated PRP Exerts Differential Effects on Tendon Stem/Progenitor Cells and Tendon Healing. J. Tissue Eng. 2019, 10, 2041731418820034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Song, D.H.; Park, J.W.; Park, S.; Kim, S.J. Effect of Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate-Platelet-Rich Plasma on Tendon-Derived Stem Cells and Rotator Cuff Tendon Tear. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Chang, P.; Bao, N.; Yang, C.; Ti, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, J. Harmful Effects of Leukocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma on Rabbit Tendon Stem Cells In Vitro. Am. J. Sports Med. 2016, 44, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornetti, P.; Nourissat, G.; Berenbaum, F.; Sellam, J.; Richette, P.; Chevalier, X.; under the aegis of the Osteoarthritis Section of the French Society for Rheumatology (Société Française de Rhumatologie, SFR). Does Platelet-Rich Plasma Have a Role in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis? Jt. Bone Spine 2016, 83, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Marumo, K. An Autologous Leukocyte-Reduced Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy for Chronic Injury of the Medial Collateral Ligament in the Knee: A Report of 3 Successful Cases. Clin. J. Sport Med. Off. J. Can. Acad. Sport Med. 2019, 29, e4–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podesta, L.; Crow, S.A.; Volkmer, D.; Bert, T.; Yocum, L.A. Treatment of Partial Ulnar Collateral Ligament Tears in the Elbow with Platelet-Rich Plasma. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallari, D.; Stagni, C.; Rani, N.; Sabbioni, G.; Pelotti, P.; Torricelli, P.; Tschon, M.; Giavaresi, G. Ultrasound-Guided Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid, Separately and in Combination, for Hip Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2016, 44, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.J.; Murphy, R.; Dakin, S.G.; Rombach, I.; Wheway, K.; Watkins, B.; Franklin, S.L. Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection With Arthroscopic Acromioplasty for Chronic Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 2891–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavolta, E.A.; Gracitelli, M.E.C.; Assunção, J.H.; Ferreira Neto, A.A.; Bordalo-Rodrigues, M.; de Camargo, O.P. Clinical and Structural Evaluations of Rotator Cuff Repair with and Without Added Platelet-Rich Plasma at 5-Year Follow-Up: A Prospective Randomized Study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 3134–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Garate, A.; Delgado, D.; Padilla, S. Platelet-Rich Plasma, an Adjuvant Biological Therapy to Assist Peripheral Nerve Repair. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, J.J.; McClendon, M.T.; Stephanopoulos, N.; Álvarez, Z.; Stupp, S.I.; Richter, C.-P. Electrophysiological Assessment of a Peptide Amphiphile Nanofiber Nerve Graft for Facial Nerve Repair. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; He, C.; Jiang, L.; Quan, D. Improved Peripheral Nerve Regeneration Using Acellular Nerve Allografts Loaded with Platelet-Rich Plasma. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 20, 3228–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, B.; Akdeniz, S.S.; Diker, N.; Helvacioğlu, F.; Erdem, S.R. Effects of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Membrane on Sciatic Nerve Regeneration. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2018, 29, e239–e243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, B.; Buncke, G. Autograft Substitutes: Conduits and Processed Nerve Allografts. Hand Clin. 2016, 32, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baklaushev, V.P.; Bogush, V.G.; Kalsin, V.A.; Sovetnikov, N.N.; Samoilova, E.M.; Revkova, V.A.; Sidoruk, K.V.; Konoplyannikov, M.A.; Timashev, P.S.; Kotova, S.L.; et al. Tissue Engineered Neural Constructs Composed of Neural Precursor Cells, Recombinant Spidroin and PRP for Neural Tissue Regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andarawis-Puri, N.; Philip, A.; Laudier, D.; Schaffler, M.B.; Flatow, E.L. Temporal Effect of in Vivo Tendon Fatigue Loading on the Apoptotic Response Explained in the Context of Number of Fatigue Loading Cycles and Initial Damage Parameters. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 2014, 32, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, M.; Naseri-Nosar, M.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S.; Nourani, M.; Khojasteh, A.; Farzamfar, S.; Mansouri, K.; Ai, J. Polyurethane/Gelatin Nanofibrils Neural Guidance Conduit Containing Platelet-Rich Plasma and Melatonin for Transplantation of Schwann Cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malahias, M.-A.; Nikolaou, V.S.; Johnson, E.O.; Kaseta, M.-K.; Kazas, S.-T.; Babis, G.C. Platelet-Rich Plasma Ultrasound-Guided Injection in the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, e1480–e1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenses, F.; Önder, M.E.; Koçyiğit, I.D.; Kul, O.; Aydin, G.; Inal, E.; Atil, F.; Tekin, U. Effect of Platelet-Rich Fibrin on Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2016, 27, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehranfar, S.; Abdi Rad, I.; Mostafav, E.; Akbarzadeh, A. The Use of Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF), Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) and Stem Cells in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis: An Overview of Clinical Trials. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Morgan, B.J.; Smith, R.; Fellows, C.R.; Thornton, C.; Snow, M.; Francis, L.W.; Khan, I.M. Platelet-Rich Plasma Induces Post-Natal Maturation of Immature Articular Cartilage and Correlates with LOXL1 Activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reurink, G.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; Tol, J.L. More on Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections in Acute Muscle Injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1264–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, W.-Y.; Cheng, J.-H.; Wang, C.-J.; Hsu, S.-L.; Chen, J.-H.; Huang, C.-Y. Shockwave Targeting on Subchondral Bone Is More Suitable than Articular Cartilage for Knee Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medvedeva, E.V.; Grebenik, E.A.; Gornostaeva, S.N.; Telpuhov, V.I.; Lychagin, A.V.; Timashev, P.S.; Chagin, A.S. Repair of Damaged Articular Cartilage: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterman, C.; McCarthy, M.B.R.; Cote, M.P.; Beitzel, K.; Bradley, J.; Polkowski, G.; Mazzocca, A.D. Platelet-Rich Plasma Increases Anti-Inflammatory Markers in a Human Coculture Model for Osteoarthritis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, K.; Trøstrup, H.; Christophersen, L.; Lundquist, R.; Høiby, N.; Moser, C. The Phagocytic Fitness of Leucopatches May Impact the Healing of Chronic Wounds. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 184, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filardo, G.; Di Matteo, B.; Di Martino, A.; Merli, M.L.; Cenacchi, A.; Fornasari, P.; Marcacci, M.; Kon, E. Platelet-Rich Plasma Intra-Articular Knee Injections Show No Superiority Versus Viscosupplementation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, B.J.; Karas, V.; Hussey, K.; Pilz, K.; Fortier, L.A. Hyaluronic Acid Versus Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Prospective, Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Clinical Outcomes and Effects on Intra-Articular Biology for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ren, M.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Hou, X. A Novel Collagen/Platelet-Rich Plasma (COL/PRP) Scaffold: Preparation and Growth Factor Release Analysis. Cell Tissue Bank. 2016, 17, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Niu, X.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L. An in Situ Photocrosslinkable Platelet Rich Plasma—Complexed Hydrogel Glue with Growth Factor Controlled Release Ability to Promote Cartilage Defect Repair. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, W.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Yuan, Z.; et al. Three Dimensional Printing-Based Strategies for Functional Cartilage Regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2019, 25, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, H.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H. Chondrogenic Progenitor Cells Exhibit Superiority Over Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Chondrocytes in Platelet-Rich Plasma Scaffold-Based Cartilage Regeneration. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 2200–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanasse, R.H.; De Lábio, R.W.; Marques, L.; Fukasawa, J.T.; Segato, R.; Kinoshita, A.; Matsumoto, M.A.; Felisbino, S.L.; Solano, B.; Dos Santos, R.R.; et al. Xenotransplantation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Full-Thickness Articular Cartilage Defects in a Rabbit Model. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 4344–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, N.-J.; Erdenekhuyag, Y.; Chou, P.-H.; Chu, C.-J.; Lin, C.-C.; Shie, M.-Y. Therapeutic Effects of the Addition of Platelet-Rich Plasma to Bioimplants and Early Rehabilitation Exercise on Articular Cartilage Repair. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 2232–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Classification System | Criteria | Subtypes/Levels | Definition and Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ehrenfest (2009) [1] | Leukocyte content and fibrin architecture |
|
|
| PAW Classification (2012) [2] | Platelet count, Activation status, WBC content |
| Provides quantitative platelet levels. Considers activation methods. Specifies WBC subtypes (neutrophils). |
| PLRA Classification (2015) [3] | Platelet concentration, Leukocyte content, RBC presence, Activation method | e.g., P3-L2-R1-A+ |
|
| DEPA Classification (2016) [4] | Dose, Efficiency, Purity, Activation |
|
|
| MARSPILL (2020) [5] | Method, Activation, RBCs, Spin, Platelet conc., Image guidance, Leukocytes, Light activation | Each letter is a reporting item |
|
| Six-Digit Coding System (2020) [6] | platelet composition, purity, and activation | N1–N6 |
|
| Component | Size/Structure | Key Contents | Primary Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-Granules | 300–500 nm membrane-bound vesicles; 50–60 per platelet | Growth factors (PDGF, TGF-β1, VEGF, bFGF, EGF), adhesive proteins, coagulation, fibrinolytic factors and others listed in Table 2. | Regulate tissue repair, hemostasis, angiogenesis, immune modulation |
| Platelet-Derived Exosomes | 30–150 nm vesicles derived from multivesicular bodies | Proteins, mRNA, miRNA, lipids; growth factors encapsulated (PDGF, VEGF, TGF-β1) | Mediators of intercellular communication and delivery of regenerative signals |
| Dense Granules (δ-granules) | 250–300 nm organelles | ADP, ATP, serotonin (5-HT), calcium, histamine, epinephrine, polyphosphates | Promote platelet activation, vasoconstriction, and immune signaling |
| Lysosomes (λ-granules) | 50 to 500 nm organelles | Acid hydrolases (collagenase, elastase, cathepsins), antimicrobial proteases | Contribute to ECM remodeling, fibrinolysis, antimicrobial defense |
| Structure | Key Content | Main Functions |
|---|---|---|
| α-granules | Growth Factors: PDGF (AA-BB-AB-CC), VEGF, TGF (α-β), FGF (a-b), EGF, CTGF | Cell proliferation, chemotaxis, angiogenesis, collagen synthesis, and tissue remodeling |
| Adhesive Proteins: Fibronectin, vitronectin, fibrinogen, vWF, P-selectin, integrins αIIbβ, Phosphatidylserine | Platelet aggregation, platelet–endothelial cell interaction, and thrombus formation. | |
| Coagulation Factors: Factors IV, XI, XIII, plasminogen, plasmin, antithrombin, tissue factor | Initiate and regulate clot formation, stabilize fibrin networks, and support clot breakdown to maintain hemostatic balance | |
| Angiogenic Regulators: IL8, thrombospondin, Angiostatin, PF-4, TIMP-1,4, MMP-1,2,9, Angiopoietin, Endostatin, SDF-1, PMP | Angiogenesis cascades, coordinate blood vessel formation, remodeling, and stabilization to restore tissue perfusion and support regenerative processes. | |
| Cytokines: IL1, IL4, IL6, TFNα, SDF-1 | Chemotaxis, inflammatory response modulation, and antimicrobial activity. | |
| Chemokines: RANTES, CXCL4, CXCL7, CCL2, CCL3, CCL5, β-TG | Inflammation, antimicrobial, and bactericidal activity. | |
| Complement Proteins: C3, C4 | Phagocytosis, chemotaxis, and platelet activation. | |
| Exosomes: mRNA, miRNA, CXCL4, CXCL7 | Cell adhesion, paracrine communication, regulation of cell fate, and promote tissue regeneration by delivering growth factors, RNAs, and signaling molecules to target cells. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.-S.; Chen, L.-R.; Chen, K.-H. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Molecular Mechanisms, Actions and Clinical Applications in Human Body. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110804
Wu W-S, Chen L-R, Chen K-H. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Molecular Mechanisms, Actions and Clinical Applications in Human Body. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110804
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wen-Shan, Li-Ru Chen, and Kuo-Hu Chen. 2025. "Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Molecular Mechanisms, Actions and Clinical Applications in Human Body" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110804
APA StyleWu, W.-S., Chen, L.-R., & Chen, K.-H. (2025). Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Molecular Mechanisms, Actions and Clinical Applications in Human Body. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110804





