First In Silico Study of Two Echinococcus granulosus Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Isoenzymes Recognized by Liver Cystic Echinococcosis Human Sera
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of EgGAPDH
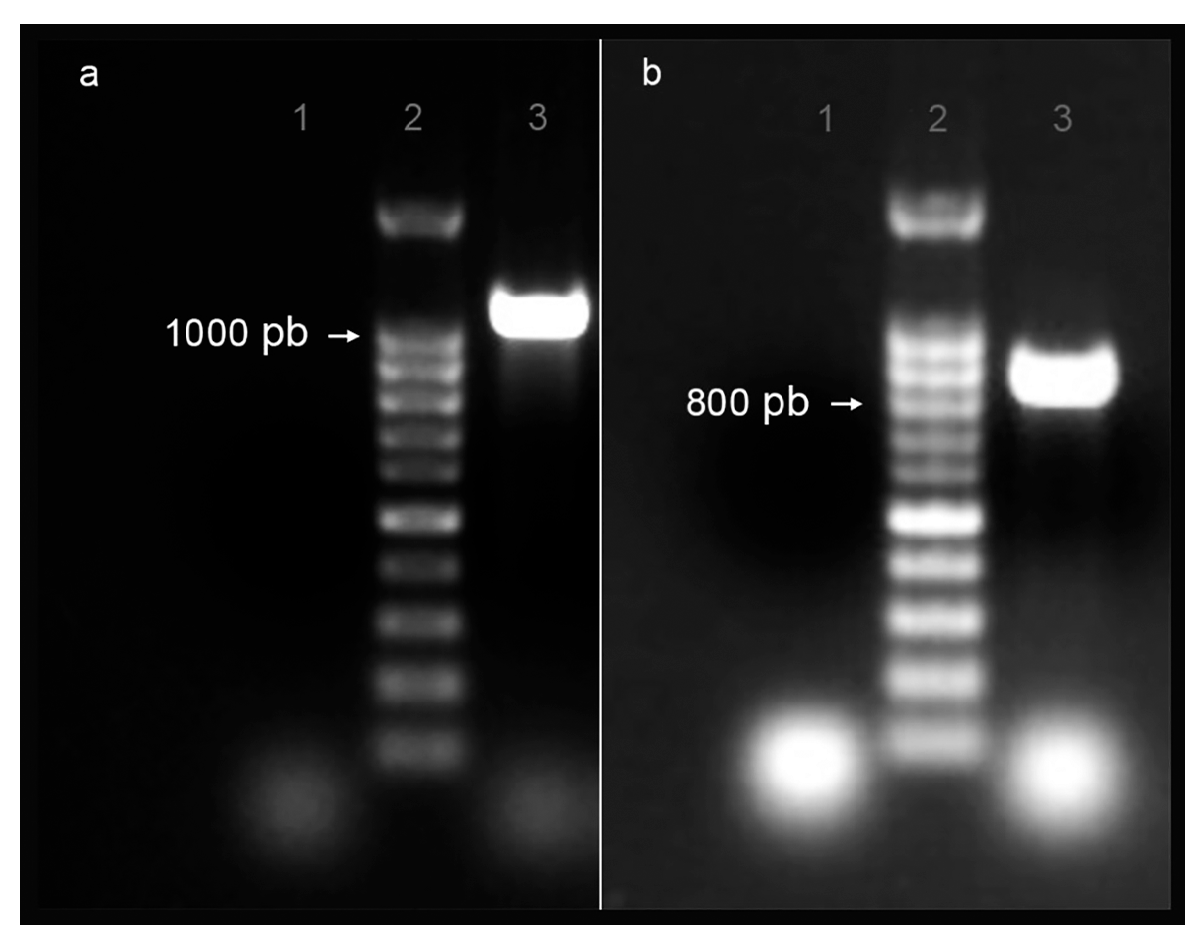
2.1.1. Genomic Sequences Identification
2.1.2. Amino Acid Sequence’s Identity
2.1.3. Physicochemical Characterization
2.2. EgGAPDH Secondary and Tertiary Structure Stability
2.2.1. Secondary Structure
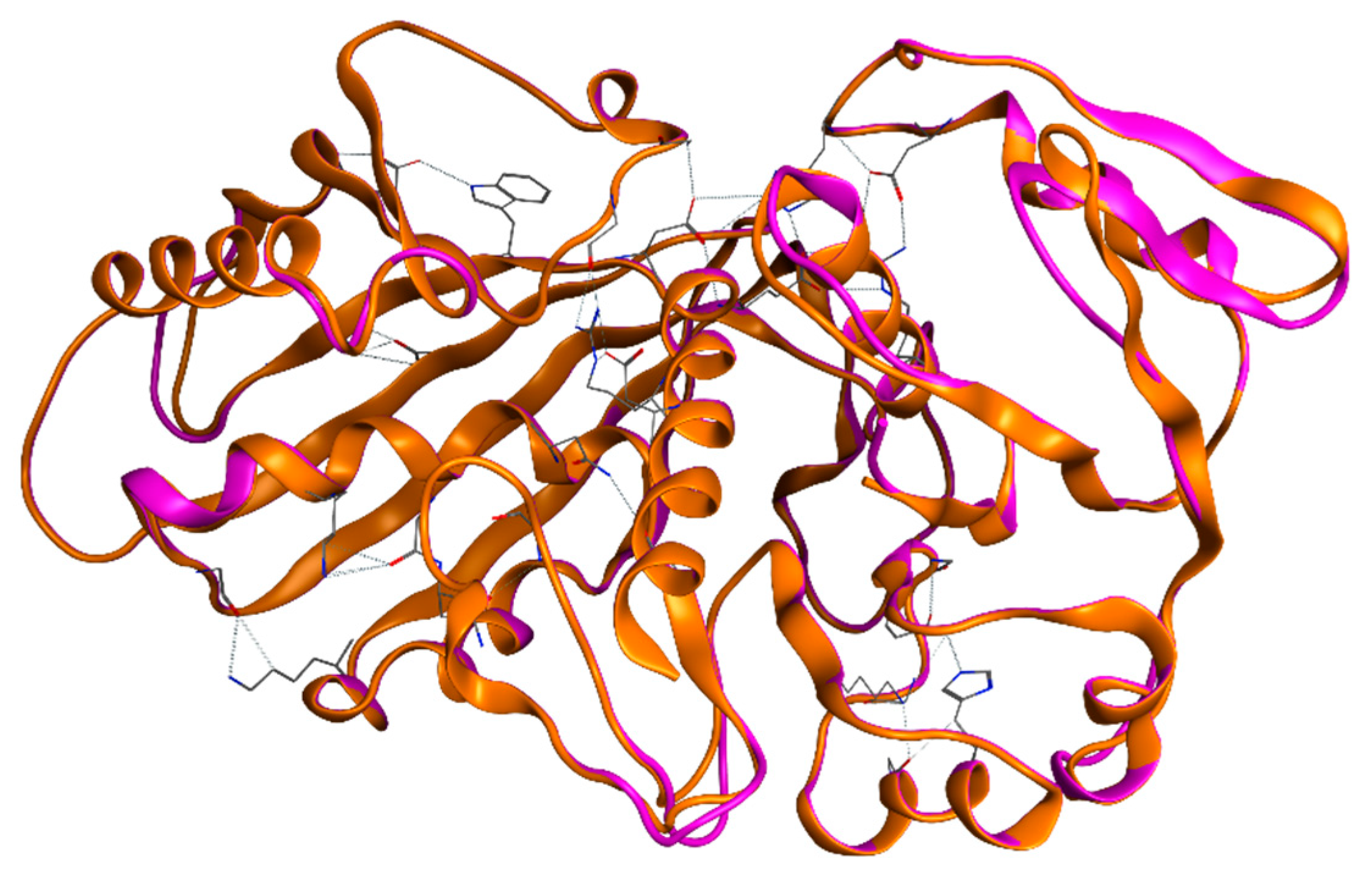
2.2.2. Tertiary Structure of EgGAPDH Isoenzymes Stability
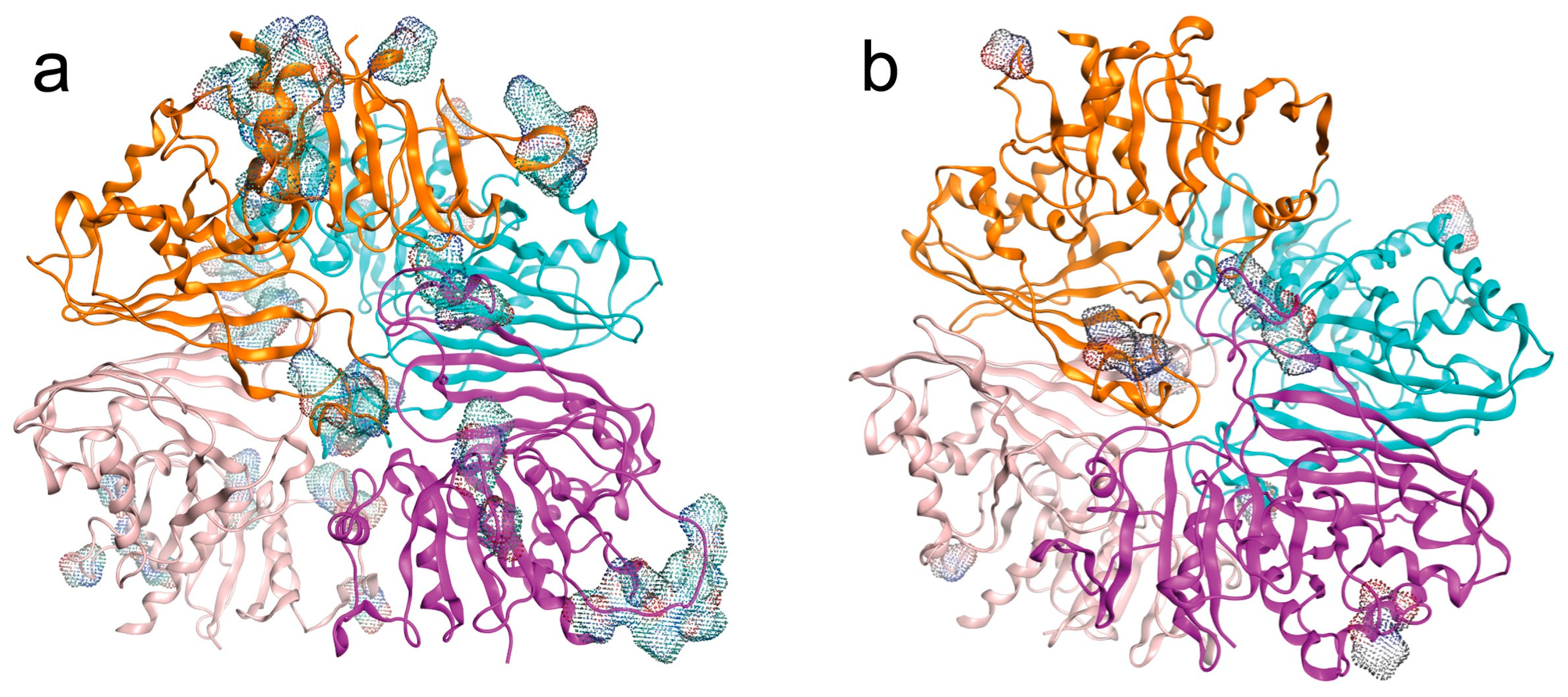
2.2.3. Quaternary Structures and LEP of Isoenzymes
- Post-translational LEP modifications.
2.3. Isoenzymes Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation
2.3.1. Isoenzymes Docking
- Isoenzymes potential energy
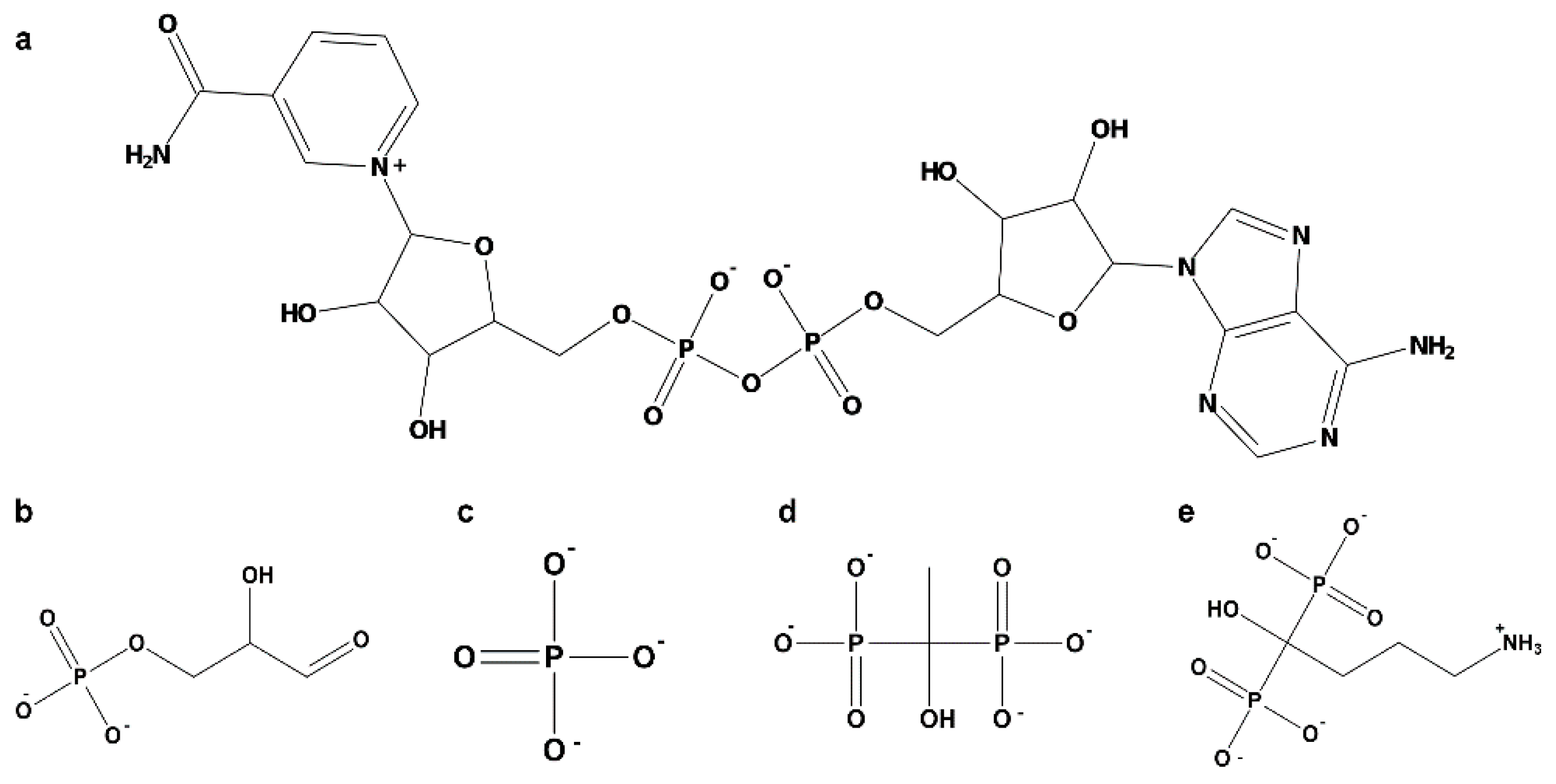
2.3.2. Amino Acids of EgGAPDH Involved in Substrate, Pi, and NAD+ Binding During Dynamics Simulation
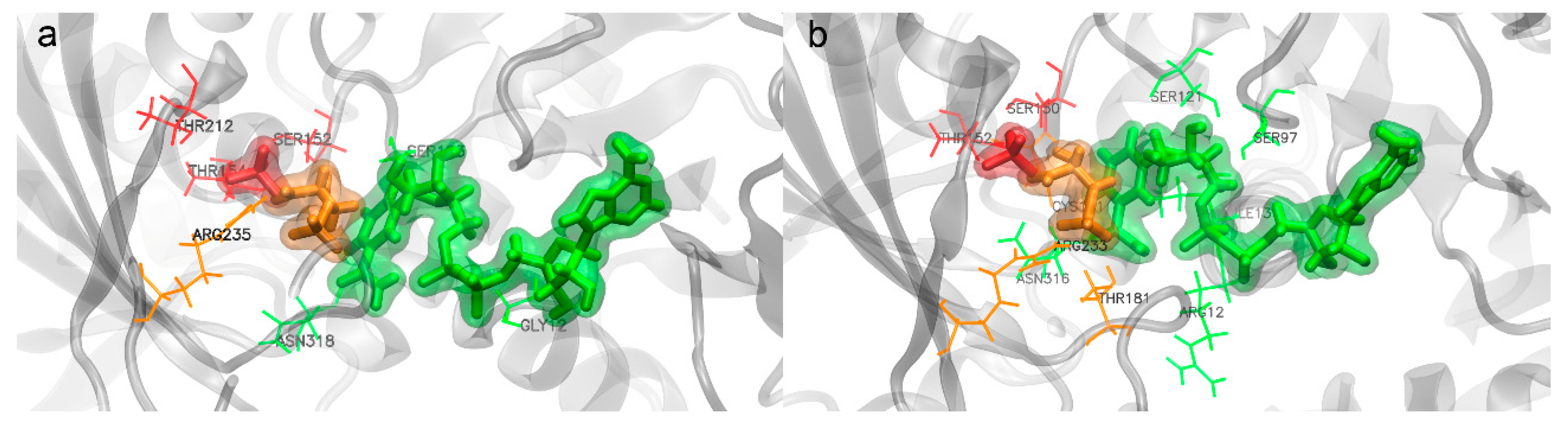
- Substrate binding
- Inorganic phosphorus binding
- NAD+ binding
2.3.3. Binding Free Energy (∆G) for Substrate, Pi, and NAD+
2.4. Interaction of BP with Both EgGAPDH Isoenzymes
2.4.1. Docking Affinity
- EHDP increased Pi docking
- AL increased NAD+ docking
2.4.2. BP Effect on the Isoenzyme Substrate Affinity Studied by Molecular Dynamics
- Substrate affinity.
- Pi affinity
- NAD+ affinity
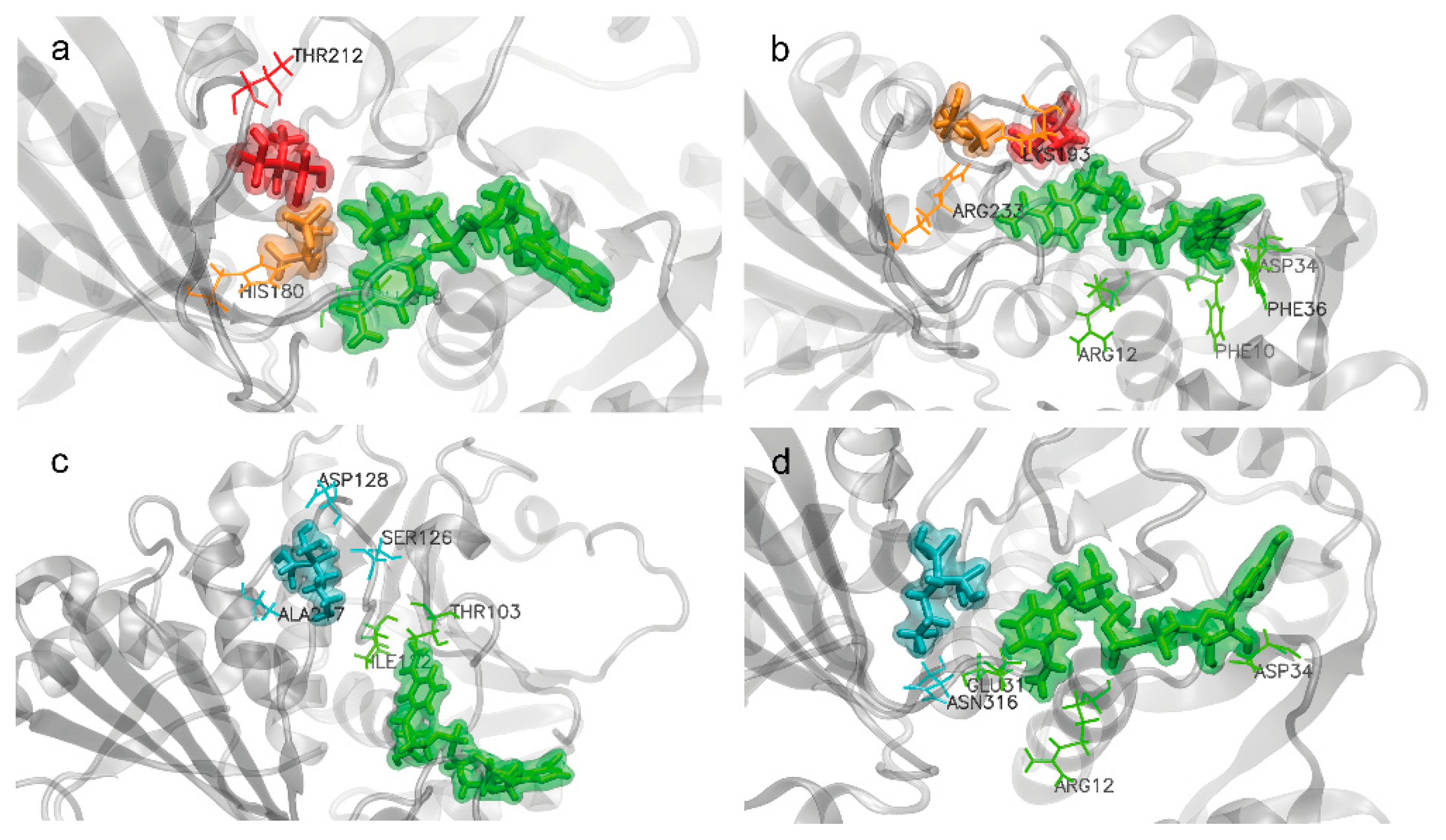
2.4.3. Amino Acids Involved in BP Interactions
- EHDP and AL interactions with EgGAPDH W6UJ19 and W6V1T8
2.5. CEP and Its Modification by the BP Interactions
CEPs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement and Serum Samples
4.2. Characterization of EgGAPDH
4.2.1. EGPE Cell Culture, Protein Extracts, and Supernatant
4.2.2. Protein Identification
4.2.3. EgGAPDH Genomic Sequence
4.2.4. Amino Acid Sequence, Protein Structure, and Physicochemical Analysis
4.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
Native Interactions of GAPD
- Free energy binding estimation.
4.4. Docking and Enzymatic Dynamic Interaction with BP
4.4.1. Docking
4.4.2. Molecular Dynamics Interaction
4.5. Searching for Epitopes
4.5.1. B-Cell LEP
4.5.2. B-Cell CEP and BP
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vuitton, D.A.; McManus, D.P.; Rogan, M.T.; Romig, T.; Gottstein, B.; Naidich, A.; Tuxun, T.; Wen, H.; da Silva, A.M.; World Association of Echinococcosis. International consensus on terminology to be used in the field of echinococcoses. Parasite 2020, 27, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucher, M.A.; Macchiaroli, N.; Baldi, G.; Camicia, F.; Prada, L.; Maldonado, L.; Avila, H.G.; Fox, A.; Gutiérrez, A.; Negro, P.; et al. Cystic echinococcosis in South America: Systematic review of species and genotypes of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato in humans and natural domestic hosts. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2016, 21, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Equinococosis. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/echinococcosis (accessed on 19 April 2023).
- Avila, H.G.; Maglioco, A.; Getiser, M.L.; Ferreyra, M.P.; Ferrari, F.; Klinger, E.; Barbery Venturi, M.S.; Agüero, F.A.; Fuchs, A.G.; Jensen, O. First report of Cystic echinococcosis caused by Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto/G1 in Felix catus from the Patagonian region of Argentina. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercero Gutiérrez, M.J.; Olala Herbosa, R. Hidatidosis una zoonosis de distribución mundial. ofFARM 2008, 27, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Tévez Craise, L.; Daiana Vaccaro, R.; De Luca, P.A.; Vásquez Guillén, M.E.; Calaramo, O.A.; Logioco, F. Hydatidosis: Clinical-imaging classification according to Gharbi and the World Health Organization. Rev. Argent. Radiol. 2022, 86, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Tamarozzi, F.; Silva, R.; Fittipaldo, V.A.; Buonfrate, D.; Gottstein, B.; Siles Lucas, M. Serology for the diagnosis of human hepatic cystic echinococcosis and its relation with cyst staging: A systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittini, A.; Martínez Acosta, Y.E.; Casaravilla, C.; Seoane, P.I.; Rückerl, D.; Quijano, C.; Allen, J.E.; Díaz, A. Particles from the Echinococcus granulosus laminated layer Inhibit CD40 upregulation in dendritic cells by interfering with Akt activation. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e0064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Fernández, V.; González, G.; Luaces, V.M.; Nieto, A. Diagnostic evaluation of a synthetic peptide derived from a novel antigen B subunit as related to other available peptides and native antigens used for serology of cystic hydatidosis. Parasite Immunol. 1998, 20, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadjjadi, S.F.; Tahereh Mohammadzadeh, T.; Fatemeh Hafezi, F.; Sadjjadi, S.M. Evaluation of the ability of antigen B originated from Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto and E. Canadensis for the diagnosis of confirmed human cystic echinococcosis using ELISA. Iran J. Parasitol. 2022, 17, 358–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverría, C.I.; Isolabella, D.M.; Prieto Gonzalez, E.A.; Leonardelli, A.; Prada, L.; Perrone, A.; Fuchs, A.G. Morphological and biological characterization of cell line developed from bovine Echinococcus granulosus. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2010, 46, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglioco, A.; Gentile, J.; Barbery Venturi, M.S.; Jensen, O.; Hernández, C.; Gertiser, M.L.; Poggio, V.; Canziani, G.; Fuchs, A.G. Detection of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato infection by using extracts derived from a protoscoleces G1 cell line. Parasite Immunol. 2019, 41, e12674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maglioco, M.; Agüero, F.A.; Valacco, M.P.; Juàrez Valdez, A.; Paulino, M.; Fuchs, A.G. Characterization of the B-Cell Epitopes of Echinococcus granulosus histones H4 and H2A recognized by sera from patients with liver cysts. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 901994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muronetz, V.I.; Kuravsky, M.L.; Barinova, K.V.; Schmalhausen, E.V. Sperm-specific glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase—An evolutionary acquisition of mammals. Biochemistry 2015, 80, 1672–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.S.; Kim, J.G.; Bae, Y.A.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, J.H.; Yang, Y.; Kang, I.; Kong, Y. Fasciclin-calcareous corpuscle binary complex mediated protein-protein interactions in Taenia solium metacestode. Parasit. Vectors. 2017, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, G.H.; Mendes, C.C.; Kuan, W.L.; Speciale, A.A.; Conceição, M.; Gorgens, A.; Uliyakina, I.; Lobo, M.J.; Lim, W.F.; EL Andaloussi, S.; et al. GAPDH controls extracellular vesicle biogenesis and enhances the therapeutic potential of EV mediated siRNA delivery to the brain. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6666, Erratum in Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Mao, L.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Hou, J.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, X. Identification and molecular characterization of exosome-like vesicles derived from the Taenia asiatica adult worm. Acta Trop. 2019, 198, 105036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quail, E.A.; Yeoh, G.C. The effect of iron status on glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase expression in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1995, 359, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alvarez, R.A.; Blaylock, M.W.; Baseman, J.B. Surface localized glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase of Mycoplasma genitalium binds mucin. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.Y.; Huang, P.J.; Ku, F.M.; Lin, R.; Alderete, J.F.; Tang, P. Comparative transcriptomic and proteomic analyze of Trichomonas vaginalis following adherence to fibronectin. Infect. Immun. 2012, 8, 3900–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.H.M.; Shao, D.; Tsukahara, Y.; Pimentel, D.R.; Weisbrod, R.M.; Hamburg, M.N.; McComb, M.E.; Matsui, R.; Bachschmid, M.M. Oxidized GAPDH transfers S-glutathionylation to a nuclear protein Sirtuin-1 leading to apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 174, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lama, A.; Kucknoor, A.; Mundodi, V.; Alderete, J.F. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is a surface-associated, fibronectin-binding protein of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2703–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sun, S.T.; McKenna, C.E. Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase modulators: A patent review (2006–2010). Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 2011, 21, 1433–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docampo, R.; Moreno, S.N.J. Acidocalcisomes. Cell Calcium. 2011, 50, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docampo, R.; de Souza, W.; Miranda, K.; Rohloff, P.; Moreno, S.N.J. Acidocalcisomes—Conserved from bacteria to man. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doggett, J.S.; Schultz, T.; Miller, A.J.; Bruzual, I.; Pou, S.; Winter, R.; Dodean, R.; Zakharov, L.N.; Nilsen, A.; Riscoe, M.K. Orally bioavailable endochin-like quinolone carbonate ester prodrug reduces Toxoplasma gondii brain cysts. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00535-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.H.; Poropat, E.; Pravia, C.; Landoni, M.; Couto, A.S.; Rojo, F.G.; Fuchs, A.G.; Lukeš, J. Solanesyl diphosphate synthase, an enzyme of the ubiquinone synthetic pathway, is required throughout the life cycle of Trypanosoma brucei. Eukaryot. Cell 2014, 13, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleda, M.A.; Li, Z.H.; Behera, R.; Baierna, B.; Li, C.; Jumpathong, J.; Malwal, S.R.; Kawamukai, M.; Oldfield, E.; Moreno, S.N.J. The heptaprenyl diphosphate synthase (Coq1) is the target of a lipophilic bisphosphonate that protects mice against Toxoplasma gondii Infection. mBio 2022, 13, e0196622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleda, M.A.; Pitafi, Z.F.; Song, W.; Oldfield, E.; Moreno, S.N.J. Lipophilic bisphosphonates reduced cyst burden and ameliorated hyperactivity of mice chronically infected with Toxoplasma gondii. mBio 2024, 15, e0175624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenti, M.T.; Bertoldo, F.; Dalle Carbonare, L.; Azzarello, G.; Zenari, S.; Zanatta, M.; Balducci, E.; Vinante, O.; Lo Cascio, V. The effect of bisphosphonates on gene expression: GAPDH as a housekeeping or a new target gene? BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, A.G.; Echeverría, C.I.; Pérez Rojo, F.G.; Prieto González, E.A.; Roldán, E.J. Proline modulates the effect of bisphosphonate on calcium levels and adenosine triphosphate production in cell lines derived from bovine Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces. J. Helminthol. 2014, 88, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrulli, M.; Pérez Rojo, F.G.; Granada Herrera, L.A.; Maglioco, A.F.; Roldán, E.A.J.; Fuchs, A.G. Effect of etidronate and ibandronate on cytosolic Ca2+ in HT29 and parasite cell line from Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato. Open Parasitol. J. 2019, 7, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebetino, F.H.; Hogan, A.M.; Sun, S.; Tsoumpra, M.K.; Duan, X.; Triffitt, J.T.; Kwaasi, A.A.; Dunford, J.E.; Barnett, B.L.; Oppermann, U.; et al. The relationship between the chemistry and biological activity of the bisphosphonates. Bone 2011, 49, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.Q.; Xiao, S.H.; Guo, H.F.; Jiao, P.Y.; Mei, J.Y.; Yao, M.Y. Effect of mebendazole and praziquantel on glucosephosphate isomerase and glyceraldehydephosphate dehydrogenase in Echinococcus granulosus cyst wall harbored in mice. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao 1997, 18, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Mülle Schollenberger, V.; Beyer, W.; Schnitzler, P.; Merckelbach, A.; Roth, S.; Kalinna, B.H.; Lucius, R. Immunisation with Salmonella typhimurium-delivered glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase protects mice against challenge infection with Echinococcus multilocularis eggs. Int. J. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, I.R.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Minuk, G.Y. Proliferative and nutritional dependent regulation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase expression in the rat liver. Cell Prolif. 2002, 35, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzfeld, J.; Schlesinger, P.A. Analysis of the allosteric basis for positive and negative co-operativity and half-of-the-sites reactivity in yeast and rabbit muscle glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J. Mol. Biol. 1975, 87, 483–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, A.R.; Ward, R.D.; Oliver, C. A mutation in glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase alters endocytosis in CHO cells. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 130, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, K.; Shibukawa, Y.; Yamazaki, N.; Wada, Y. Transglutaminase 2-dependent deamidation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promotes trophoblastic cell fusion. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Hirano, Y.; Inomata, A.; Yokota, S.; Miyachi, K.; Kaneda, M.; Umeda, M.; Furukawa, K.; Omata, S.; Horigome, T. Participation of a fusogenic protein, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, in nuclear membrane assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20395–20404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.; Dong, W.; Xu, J.; Ma, L.; You, C. Role of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) in autophagy activation following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 371, 114577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan’shina, P.V.; Schmalhausen, E.V.; Arutiunov, D.Y.; Pleten’, A.P.; Muronetz, V.I. Acceleration of glycolysis in the presence of the non-phosphorylating and the oxidized phosphorylating glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases. Biochemistry 2003, 68, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararajj, K.P.; Wood‡, R.E.; Ponnusamy, S.; Salas, A.M.; Szulc, Z.; Bielawska, A.; Obeid, L.M.; Hannun, Y.A.; Ogretmen, B. Rapid shortening of telomere length in response to ceramide involves the inhibition of telomere binding activity of nuclear glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 6152–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.R.; Khan, M.M.; Deredge, D.; Ross, C.R.; Quintyn, R.; Zucconi, B.E.; Wysocki, V.H.; Wintrode, P.L.; Wilson, G.M.; Garcin, E.D. A dimer interface mutation in glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase regulates its binding to AU-rich RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1770–1785, Erratum in J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Mukherjee, A.; Adak, S. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase present in extracellular vesicles from Leishmania major suppresses host TNF-alpha expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 01198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglioco, A.; Miana, V.; Valacco, M.P.; Agüero, F.A.; Gertiser, M.L.; Avila, H.G.; Barbery Venturi, M.S.; Jensen, O.; Juárez Valdez, A.Y.; Prieto González, E.A.; et al. First comparative proteomic and in vitro behavioral study of Echinococcus granulosus metacestodes in Felis catus. Front. Veter-Sci. 2025, 12, 1546420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Pan, L.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zubair, M.; Wei, Y.; Pillay, B.; Olaniran, A.O.; et al. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) moonlights as an adhesin in Mycoplasma hyorhinis adhesion to epithelial cells as well as a plasminogen receptor mediating extracellular matrix degradation. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.S.; Báo, S.N.; Andreotti, P.F.; de Faria, F.P.; Felipe, M.S.; dos Santos Feitosa, L.; Mendes-Giannini, M.J.; Soares, C.M. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis is a cell surface protein involved in fungal adhesion to extracellular matrix proteins and interaction with cells. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.G. Bisphosphonates: Mode of action and pharmacology. Pediatrics 2007, 2, S150–S162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duff, S.M.; Moorhead, G.B.; Lefebvre, D.D.; Plaxton, W.C. Phosphate starvation inducible; bypasses’ of adenylate and phosphate dependent glycolytic enzymes in Brassica nigra suspension cells. Plant Physiol. 1989, 90, 1275–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.K.; Boggaram, J.; Byers, L.D. Alkylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase with haloacetylphosphonates. An unusual pH-dependence. Biochem. J. 1991, 275, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, R.; Fast, D.K.; Sallis, J.D.; Fleisch, H. Effect of diphosphonates on glycogen content of rabbit ear cartilage cells in culture. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1980, 30, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, R.; Fleisch, H. Effect of diphosphonates on ATP and Pi content, Pi uptake and energy charge of cultured calvaria cells. Experientia 1982, 8, 644–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancela, M.; Paes, J.A.; Moura, H.; Barr, J.R.; Zaha, A.; Ferreira, H.B. Unraveling oxidative stress response in the cestode parasite Echinococcus granulosus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleisch, H. Bisphosphonates in Bone Disease: From the Laboratory to the Patients, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, R.G.G.; Wats, N.B.; Ebetino, F.H.; Rogers, M.J. Mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates: Similarities and differences and their potential influence on clinical efficacy. Osteoporos. Int. 2007, 19, 733–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, P.; Yang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Yang, W.; Tan, J.; Zhang, C.; Sun, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Guo, S.; et al. LL-37 and bisphosphonate co-delivery 3D-scaffold with antimicrobial and antiresorptive activities for bone regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yu, Z.; Xiao, H.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, M.; Li, L.; et al. The mevalonate pathway is a druggable target for vaccine adjuvant discovery. Cell 2018, 175, 1059–1073.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb?query=%22Glyceraldehyde%203-phosphate%20dehydrogenase%22%20AND%20(taxonomy_id:6210) (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 3, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 12, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combet, C.; Blanchet, C.; Geourjon, C.; Deléage, G. NPS@: Network protein sequence analysis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; Thanki, N.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paysan Lafosse, T.; Blum, M.; Chuguransky, S.; Grego, T.; Pinto, B.L.; Salazar, G.A.; Bileschi, M.L.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Colwell, L.; et al. InterPro in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D418–D427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döpner, P.; Kemnitz, S.; Doerr, M.; Schulig, L. af3cli: Streamlining AlphaFold3 Input Preparation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2025, 5, 3886–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiederstein, M.; Sippl, M.J. ProSA-web: Interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W407–W410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labute, P. Protonate3D: Assignment of ionization states and hydrogen coordinates to macromolecular structures. Proteins 2009, 75, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Hardy, D.J.; Maia, J.D.C.; Stone, J.E.; Ribeiro, J.V.; Bernardi, R.C.; Buch, R.; Fiorin, G.; Hénin, J.; Jiang, W.; et al. Scalable molecular dynamics on CPU and GPU architectures with NAMD. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 044130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molecular Operating Environment. Available online: https://www.chemcomp.com/en/Products.htm (accessed on 26 October 2025).
- Ribeiro, J.V.; Bernardi, R.C.; Rudack, T.; Stone, J.E.; Phillips, J.C.; Freddolino, P.L.; Schulten, K. QwikMD - Integrative Molecular Dynamics Toolkit for Novices and Experts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P. Prediction of continuous B-cell epitopes in an antigen using recurrent neural network. Proteins 2006, 65, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitam, R.; Blazeska, N.; Marrama, D.; IEDB Curation Team Members; Duesing, S.; Bennett, J.; Greenbaum, J.; De Almeida Mendes, M.; Mahita, J.; Wheeler, D.K.; et al. The Immune Epitope Database (IEDB): 2024 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D436–D443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, D.; Yuchi, J.; He, F.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, S.; Li, J.; Xu, D. MusiteDeep: A deep-learning based webserver for protein post-translational modification site prediction and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W140–W146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Ma, W.; Huang, J.; Cui, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zuo, Z.; et al. DeepNitro: Prediction of Protein Nitration and Nitrosylation Sites by Deep Learning. Genom. Proteom. Bioinf. 2018, 16, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| GAPDH Specie (UniProt) | Amino Acid Number / M.W. | Charge | Isoelectric Point | Protein Instability | Aliphatic Index | Gravy Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Echinococcus granulosus (W6UJ19) | 338 / 36.6 | +1 (R + K: 37; N + E: 36) | 7.56 | 24.45 | 86.55 | −0.100 |
| Echinococcus granulosus (W6V1T8) | 336 / 36.1 | +3 (R + K: 35; N + E: 32) | 8.44 | 21.82 | 85.89 | 0.004 |
| Echinococcus multilocularis (Q27652) | 336 / 36.4 | +7 (R + K: 39; N + E: 32) | 9.02 | 27.10 | 84.40 | −0.090 |
| Taenia solium (A8R8Q4) | 336 / 36.3 | +3 (R + K: 35; N + E: 32) | 8.44 | 19.73 | 86.19 | −0.029 |
| Fasciola hepatica (A0A068LJN3) | 338 / 36.9 | 0 (R + K: 37; N + E: 37) | 7.10 | 25.15 | 84.76 | −0.109 |
| Leishmania mexicana (Q27890) | 361 / 39.0 | +7 (R + K: 42; N + E: 35) | 9.05 | 27.63 | 83.96 | −0.115 |
| Homo sapiens (P04406) | 335 / 36.0 | +3 (R + K: 36; N + E: 33) | 8.57 | 15.04 | 85.55 | −0.112 |
| Bos taurus (P10096) | 333 / 35.9 | +3 (R + K: 36; N + E: 33) | 8.51 | 17.70 | 84.89 | −0.078 |
| Ovis aries (Q28554) | 322 / 34.7 | +1 (R + K: 34; N + E: 33) | 7.83 | 17.38 | 85.09 | −0.091 |
| GAPDH Isoenzyme | LEP | Residue | Predicted Modification(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| W6UJ19 | A82-EAIPWDKDGVYYVV-E97 | W87 | Nitration |
| K89 | Ubiquitination | ||
| D88-KDGVYYVVESTGVN-T103 | K89 | Ubiquitination | |
| S123-APSKDAPTFVVGVN-L138 | - | - | |
| K140-YDPSMTIVSNASCT-T155 | S149 | Phosphorylation | |
| N150 | Glycosylation | ||
| S152 | Phosphorylation | ||
| T154 | Phosphorylation | ||
| Q186-KLVDGPNPKGWRDG-R201 | K195 | Acetylation Methylation | |
| D282-VVSMDFRTSTASST-F297 | S285 | Phosphorylation | |
| F288-RTSTASSTFDANAG-I303 | - | - | |
| W6V1T8 | K138-YDPSMKVVSNASCT-T153 | S147 | Phosphorylation |
| N148 | Glycosylation | ||
| C151 | Nitrosylation | ||
| S150 | Phosphorylation | ||
| T152 | Phosphorylation | ||
| T153 | Phosphorylation | ||
| F286-LSTTCSSTFDARAG-I301 | - | - |
| GAPDH | Electrostatic | Van der Waals | Total Potential Energy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| W6UJ19 | MD | −498,905.11 | 484.6043 | 35,705.02 | 302.8204 | −433,534.22 | 357.6353 |
| W6V1T8 | MD | −500,354.14 | 483.1283 | 35,967.32 | 303.1194 | −435,622.22 | 344.5178 |
| Ligand | ∆G of Binding (kcal/mol) | |
|---|---|---|
| IC W6UJ19 | IC W6V1T8 | |
| Pi (system GAPDH: Pi, G3P, NAD+) | −2.136 ± 1.366 | −3.477 ± 0.098 |
| EHDP (system GAPDH: EHDP, G3P, NAD+) | −4.413 ± 0.313 | −4.363 ± 0.331 |
| Ligand | ∆G of Binding (kcal/mol) | |
|---|---|---|
| IC W6UJ19 | EC W6V1T8 | |
| NAD+ (system GAPDH: Pi, G3P, NAD+) | −7.727 ± 0.674 | −9.274 ± 0.419 |
| NAD+ (system GAPDH: AL, NAD+) | −9.418 ± 0.644 | −10.376 ± 0.771 |
| MMPBSA of EgGAPDH With and Without BP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CONTROL | W6UJ19 | W6V1T8 | |||||
| Subunit | Ligands | Mean | ±sd | ±CI 95% | Mean | ±sd | ±CI 95% |
| A | G3P | −10.6968 | 5.1229 | 1.005 | −4.724 | 3.2619 | 0.64 |
| B | 15.4506 | 5.1449 | 1.01 | 3.9659 | 4.4619 | 0.875 | |
| C | 16.4556 | 4.8065 | 0.945 | 44.9831 | 7.6067 | 1.49 | |
| D | 24.028 | 3.8583 | 0.755 | 6.2637 | 4.5538 | 0.895 | |
| A | NAD+ | 22.4688 | 6.7112 | 1.315 | 6.6577 | 5.4992 | 1.08 |
| B | 32.8592 | 7.3992 | 1.45 | −4.0176 | 3.6996 | 0.725 | |
| C | 13.5946 | 4.3631 | 0.855 | 23.7809 | 5.5271 | 1.08 | |
| D | 6.0962 | 4.2739 | 0.835 | −0.61 | 2.8136 | 0.55 | |
| A | Pi | 29.6458 | 6.7445 | 1.325 | 6.7074 | 3.0 | 0.59 |
| B | 39.1984 | 7.6647 | 1.5 | 1.2245 | 10.312 | 2.025 | |
| C | 22.235 | 6.1243 | 1.205 | 45.3445 | 5.9314 | 1.165 | |
| D | 37.2889 | 7.0652 | 1.385 | 2.1399 | 10.741 | 2.11 | |
| EHDP | |||||||
| A | G3P | −16.9965 | 4.7622 | 0.935 | −7.9112 | 3.9841 | 0.78 |
| B | 5.2706 | 3.8102 | 0.75 | −7.5877 | 3.8438 | 0.755 | |
| C | −5.1953 | 7.1869 | 1.405 | −7.9317 | 3.1745 | 0.62 | |
| D | −9.1029 | 5.5589 | 1.09 | −14.587 | 4.1819 | 0.82 | |
| A | NAD+ | 2.4725 | 10.0795 | 1.975 | 1.7223 | 5.9318 | 1.16 |
| B | 7.3854 | 4.7754 | 0.935 | 6.221 | 5.0763 | 0.995 | |
| C | 27.6537 | 8.7531 | 1.715 | −4.6031 | 3.9027 | 0.765 | |
| D | 28.9197 | 5.1906 | 1.02 | 4.4928 | 4.5107 | 0.885 | |
| A | EHDP | −6.6067 | 3.3539 | 0.655 | −4.0724 | 3.0422 | 0.595 |
| B | −7.1715 | 2.9301 | 0.575 | 0.5011 | 3.9765 | 0.78 | |
| C | 0.815 | 5.1088 | 1.005 | −11.8148 | 3.0683 | 0.605 | |
| D | 2.0767 | 4.4194 | 0.865 | −1.3616 | 3.2844 | 1.29 | |
| AL | |||||||
| A | NAD+ | 24.1947 | 7.3184 | 1.435 | 9.1407 | 6.0582 | 1.19 |
| B | 2.1941 | 4.4401 | 0.87 | 8.8646 | 5.4337 | 1.065 | |
| C | −3.7258 | 3.5832 | 0.705 | 5.2785 | 4.2828 | 0.84 | |
| D | −3.0283 | 2.003 | 0.39 | −3.2583 | 3.9806 | 0.78 | |
| A | AL | 19.1598 | 3.9525 | 0.77 | 7.624 | 3.2452 | 0.635 |
| B | −1.2968 | 2.2008 | 0.43 | 0.3786 | 2.3406 | 0.46 | |
| C | 4.3972 | 3.5114 | 0.685 | 6.9541 | 3.3836 | 0.665 | |
| D | 8.2511 | 4.1911 | 0.82 | −1.8823 | 13.8439 | 2.715 | |
| W6UJ19 Control | Initial | Final | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G3P | Pi | NAD+ | G3P | Pi | NAD+ | |
| Subunit A | R235(2) | T154 S152 T212 | G12(2) N318(2) S123(2) | R235(3) His180(2) T183 C153 | K195(3) R235(2) | S123 |
| Subunit B | C153 H180 T183 | C153(2) T154 H180 | G12 R13 D35 N318(2) | R235(2) H180(2) T183 | R235(3) K195(2) | R13 D35 D190 |
| Subunit C | R235(2) | T154 | R13 H180 EA319 K187 | T212(2) G213 | R235(2) H180(2) | E319(2) D190 N193 K187 |
| Subunit D | H180 | T154(2) H180 G213 | D35 S98 C153 | C153 | K195 R235 | D35 T99 |
| W6UJ19 EHDP | Initial | Final | ||||
| G3P | EHDP | NAD+ | G3P | EHDP | NAD+ | |
| Subunit A | R235(2) | T154(2) Q211 T212 G213 R235 | G12(2) S98 S123(2) N318(2) | T183 H180(3) | Q211 R235 | D337 |
| Subunit B | C153 H180 T183 | C153 T154 H180 | G12 R13 D35 N318(2) | C153 | D199(2) Q211(2) P209 | K195 |
| Subunit C | R235(2) | T154(2) T212 | R13 H180 K187 E319 | H180(2) | T212 | P192 E319 |
| Subunit D | C153 | T154 Q211 T212(2) G213 | D35 S98 C153 | S123 C153(2) H180(2) T183 N318 | Q211 T212 R235 | D35 E319 |
| W6UJ19 AL | Initial | Final | ||||
| AL | NAD+ | AL | NAD+ | |||
| Subunit A | T154(2) Q211 T212(2) G213 R235 | G12(2) S98 S123(2) N318(2) | S123 | A184 E319 K187 D190 | ||
| Subunit B | C153 T154 H180 | G12 R13 D35 N318(2) | I38 | - | ||
| Subunit C | T212 T154(2) | R13 H180 K187 E319 | S126 D128(2) A217 | T103(2) I122 K187 | ||
| Subunit D | T154 Q211 T212(2) G213 | D35 S98 C153 | A124 S149 S152 | - | ||
| W6V1T8 Control | Initial | Final | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G3P | Pi | NAD+ | G3P | Pi | NAD+ | |
| Subunit A | T181 C151 R233(2) | S150 C151(2) T152(2) | R12 I13 S97 S121(2) N316(2) | R233(3) K193(2) | - | R12(2) D34(2) T98 S121 E317 |
| Subunit B | C151 R233 | C151 T152(2) | R12(2) D34(2) S121 N316(2) | R233(2) K193(2) | - | G11 D34(2) |
| Subunit C | C151 | S150 C151(2) T152 T210 | R12 I13 S97(2) Y320 | R233 | R233(2) K233(3) | T181 A182 P237 |
| Subunit D | Cys151(2) | S150 C151 T152(2) | G11(2) R12 I13 | N101 K193 R233(3) | - | - |
| W6V1T8 EHDP | Initial | Final | ||||
| G3P | EHDP | NAD+ | G3P | EHDP | NAD+ | |
| Subunit A | C151 T181 R233 | T152(2) T210 | G11 R12 I13 S121(2) N316(2) | K193(2) R233(2) | - | F10 R12 D34(2) F36 |
| Subunit B | S150 C151 R233 | T152(2) | R12(2) D34 E78 S121 N316(2) E317 | K193(2) R233(2) | - | F10 R12 D34(2) S121 |
| Subunit C | C151 | C151(2) T152 H178 | R12 I13 P35 E78 S97(2) Y320 | K193(2) | G99 | G11 R12 D34(2) |
| Subunit D | C151 T183 | C151 T152 | G11 R12 I13 P123(2) | K193 R233(2) | T152 T210 | P35 S97 T98 S121 P123 T181 T183 K192 |
| W6V1T8 AL | Initial | Final | ||||
| AL | NAD+ | AL | NAD+ | |||
| Subunit A | C151 | G11 R12 I13 S121(2) D316(2) | T181 | F10 D34(2) F36 | ||
| Subunit B | C151 | R12 I13 D34 E78 C151 E317 | D165 N166 | G11 R12(2) I13 D34(2) | ||
| Subunit C | C151(2) E317 | R12 I13 S97(2) Y320 | N316 | R12 D34(2) E317 | ||
| Subunit D | C151(2) H178 | G11(2) R12 I13 D34 | - | P190 K185 K192 | ||
| Isoenzyme | System | Chain A | Chain B | Chain C | Chain D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W6UJ19 | Control | K63, D64, G65, K66, L80, K89, A106, K107, G109, A110, L112, K113, N114, N115, S144, N193, P194, K195 | L80, N81, E83, A108, G109, A110, H111, L112, K113, N114, N115, S144, N193, P194 | E79, L80, N81, A82, E83, K89, K113, S144, T185, N193, P194, K195, G200, D337 | I38, D39, D64, N81, A82, A106, G109, K113, S144, P192, N193, P194 |
| AL | D64, G65, K66, L80, N81, K89, A106, K107, G109, A110, L112, K113, N114, N115, S144, P192, N193, P194, K195 | L80, N81, A82, A84, I85, P86, W87, D88, K89, D90, A108, G109, A110, H111, L112, K113, N114, S144, N193, P194, K195 | L80, N81, A82, E83, K89, H111, S144, P192, N193, P194, K195, G200 | N81, A106, A110, K113, N114, N115, S144, T185, N193, P194, K195 | |
| EHDP | D39, K63, D64, G65, K66, K107, G109, A110, K113, N114, N115, S144, N193, P194, K195, G196, D337 | T41, L112, K113, S144, P192, N193, P194, K195 | L80, N81, A82, E83, A106, S144, N193, P194, K195 | N81, K107, A110, H111, K113, N114, N115, S144, P194, K195, G196, G200 | |
| Post-translational modifications | -CH3/-CH3CO | K66 and K195 | K195 | K195 | K195 |
| Ubiq | K89 | K89 | K89 | - | |
| Ph | - | - | - | T185 | |
| W6V1T8 | Control | S142, K192, K193 | P141, S142, K192, K193 | K192, D335 | S142, K192 |
| AL | P141, S142, K192 | S142, K192 | S142 | P141, K193 | |
| EHDP | K192 | S142, K192 | D38, K138, K192, K193 | P190, K192 | |
| Post-translational modifications | -CH3 | K192 | K192 | K192 | K192 |
| -CH3/-CH3CO | K193 | K193 | K193 | K193 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agüero, F.A.; Maglioco, A.; Valacco, M.P.; Juárez Valdez, A.Y.; Roldán, E.; Paulino, M.; Fuchs, A.G. First In Silico Study of Two Echinococcus granulosus Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Isoenzymes Recognized by Liver Cystic Echinococcosis Human Sera. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110622
Agüero FA, Maglioco A, Valacco MP, Juárez Valdez AY, Roldán E, Paulino M, Fuchs AG. First In Silico Study of Two Echinococcus granulosus Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Isoenzymes Recognized by Liver Cystic Echinococcosis Human Sera. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110622
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgüero, Facundo Ariel, Andrea Maglioco, María Pía Valacco, Alejandra Yaqueline Juárez Valdez, Emilio Roldán, Margot Paulino, and Alicia Graciela Fuchs. 2025. "First In Silico Study of Two Echinococcus granulosus Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Isoenzymes Recognized by Liver Cystic Echinococcosis Human Sera" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110622
APA StyleAgüero, F. A., Maglioco, A., Valacco, M. P., Juárez Valdez, A. Y., Roldán, E., Paulino, M., & Fuchs, A. G. (2025). First In Silico Study of Two Echinococcus granulosus Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Isoenzymes Recognized by Liver Cystic Echinococcosis Human Sera. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110622







