Platelet Releasate Reprograms Synovial Macrophages In Vitro: A New Approach in the Treatment of Hemophilic Synovitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
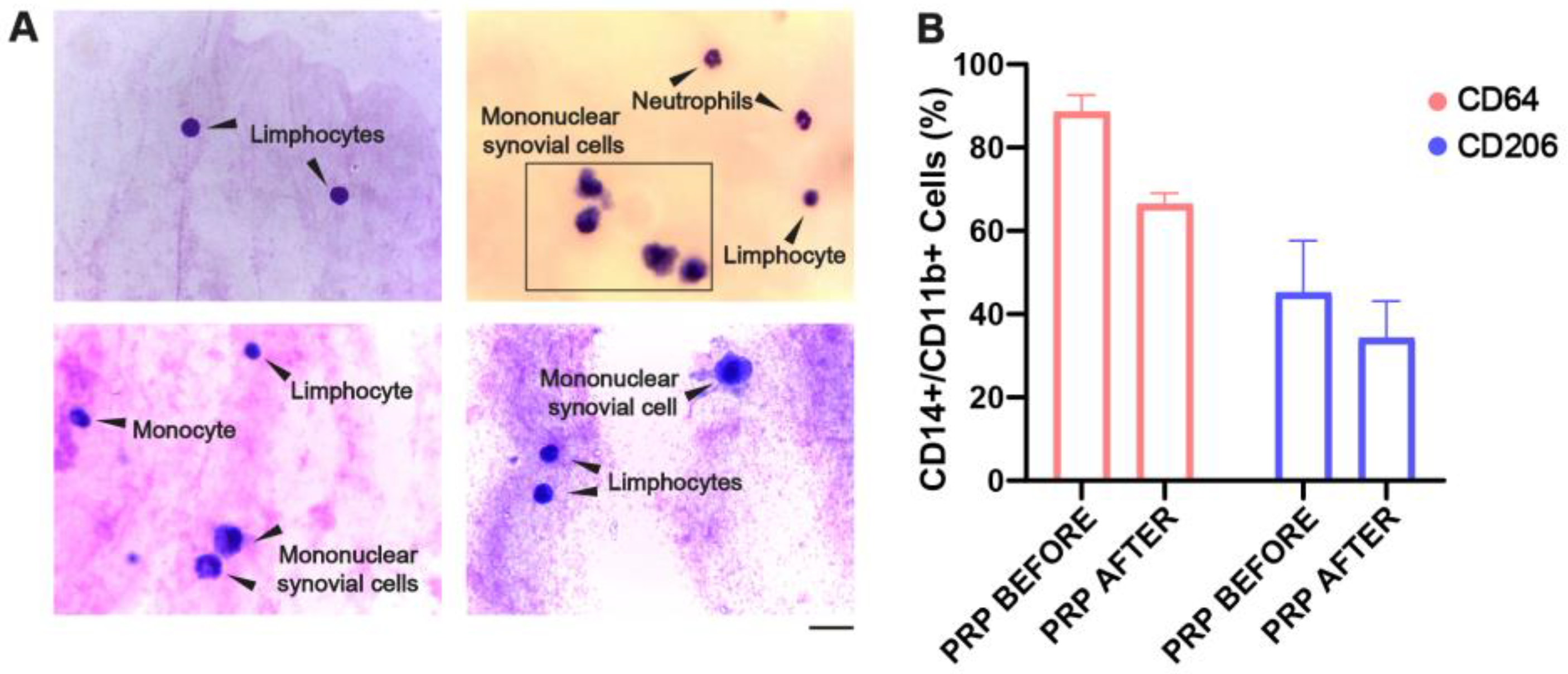
2.1. Hemosiderin Deposits and CD64+ Macrophages Characterize the Inflammatory Environment of SF of Patients with CHS
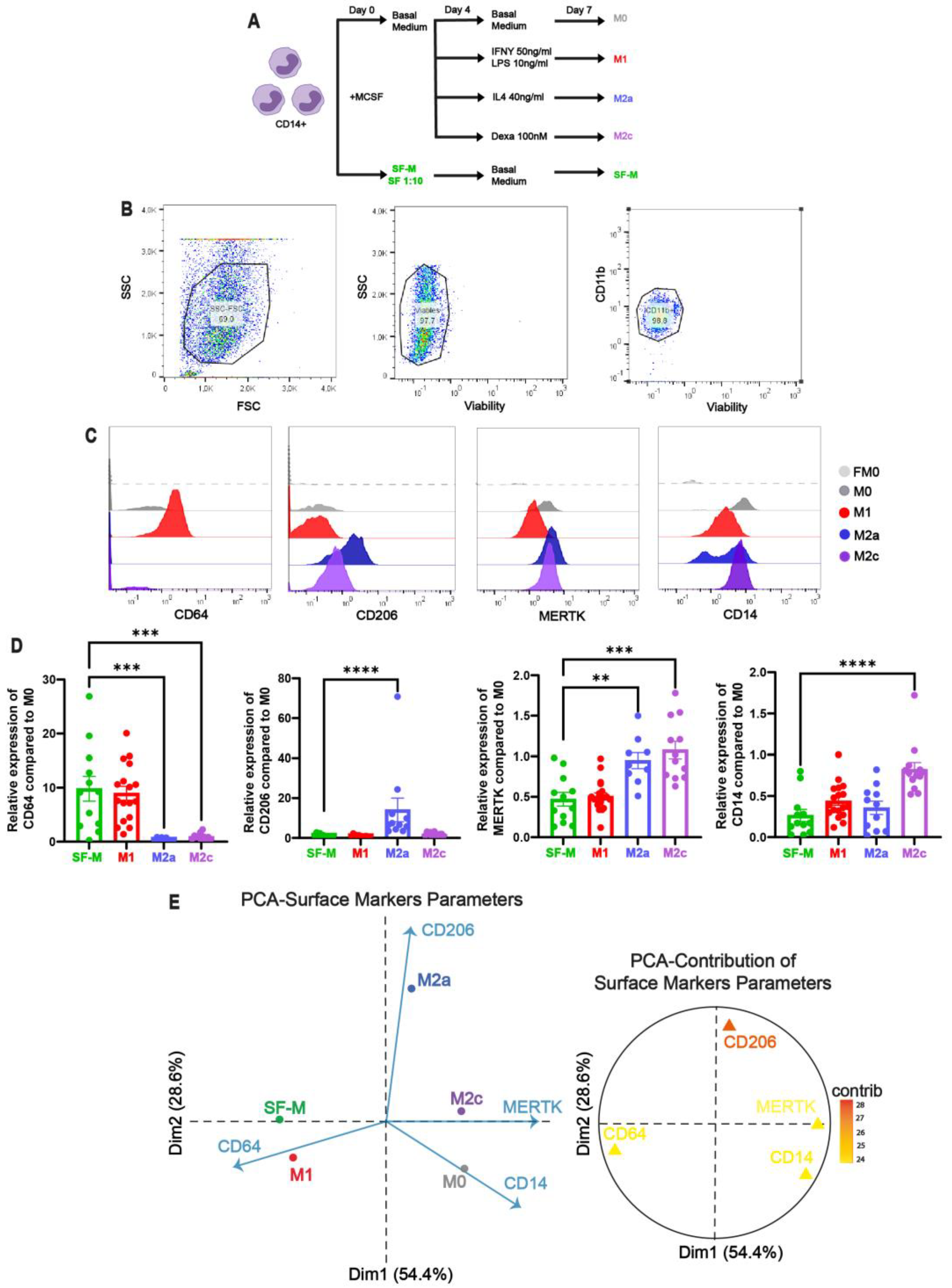
2.2. The Induction of Pro-Inflammatory MDM by SF of Patients with CHS In Vitro
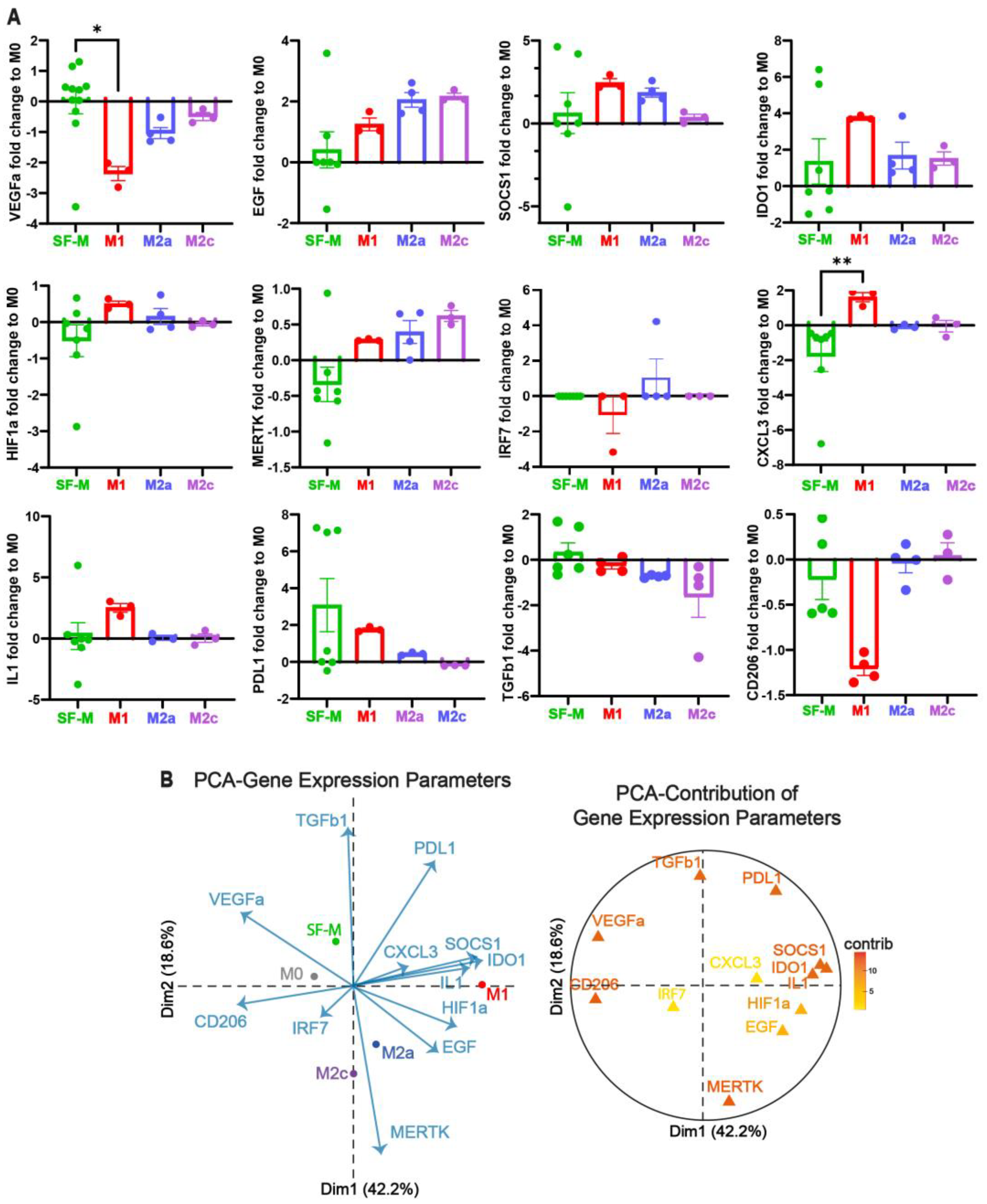
2.3. The Gene Program Profile Induced in SF-M Is Distinctive from Other Polarized MDMs
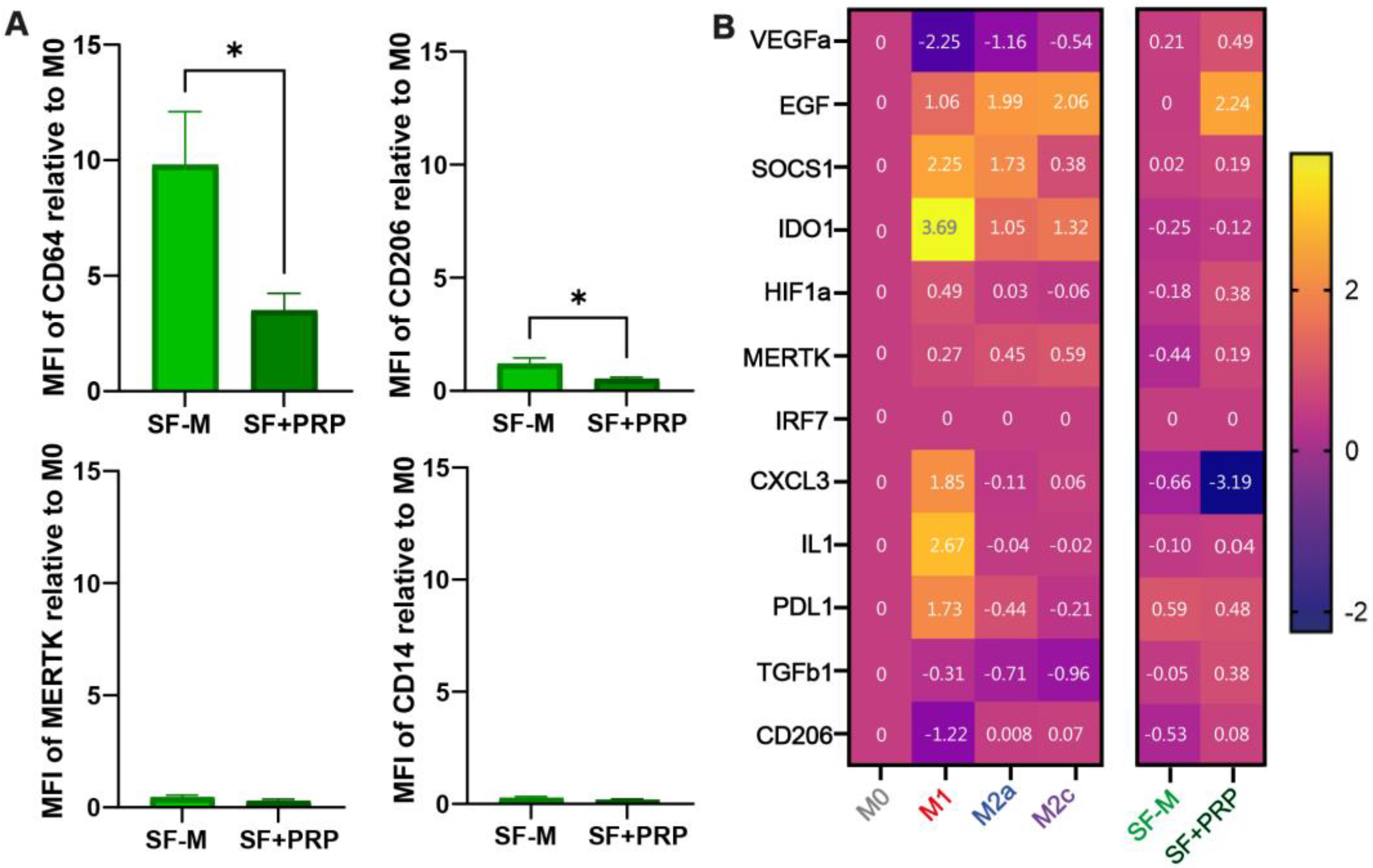
2.4. Addition of PRP Is Able to Dampen the Inflammatory Signature of SF-Ms
2.5. Cellular Reconstitution of and Reduction in CD64 Macrophage After PRP Treatment in the SF of CHS Patients
2.6. SF-Ms Treated with PRP Generate Multinuclear Giant Cells When Challenged with NETs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Considerations
4.2. Patients, Treatment, and Obtention of Synovial Fluid (SF)
4.3. Synovial Fluid (SF) Processing
4.4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Isolation for In Vitro Assays
4.5. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Isolation
4.6. CD14 Purification and In Vitro Monocyte-Derived Macrophage (MDM) Differentiation
4.7. Neutrophil Isolation and Purification
4.8. Surface Staining and Flow Cytometry
4.9. ELISA
4.10. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.11. Comparison of SF-Ms and SF + PRP Gene Profiles in the MoMacverse Framework
4.12. In Vitro ET Formation Induced by Synovial Fluid from Patients with CHS
4.13. Co-Culture of NETs with MDMs, SF-Ms, and SF + PRP–Macrophages to Analyze ET Clearance
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Limitations of the Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CHS | Chronic Hemophilic Synovitis |
| ETs | Extracellular Traps |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| FMO | Fluorescence Minus One |
| HJHS | Hemophilia Joint Health Score |
| MDM | Monocyte-Derived Macrophage |
| NETs | Neutrophil Extracellular Traps |
| OA | Osteoarthritis |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PBMC | Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PRP | Platelet-Rich Plasma |
| RA | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| SF | Synovial Fluid |
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
References
- Melchiorre, D.; Manetti, M.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Pathophysiology of Hemophilic Arthropathy. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooiveld, M.J.J.; Roosendaal, G.; van den Berg, H.M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G. Haemoglobin-derived iron-dependent hydroxyl radical formation in blood-induced joint damage: An in vitro study. Rheumatology 2003, 42, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojdasiewicz, P.; Poniatowski, Ł.A.; Nauman, P.; Mandat, T.; Paradowska-Gorycka, A.; Romanowska-Próchnicka, K.; Szukiewicz, D.; Kotela, A.; Kubaszewski, Ł.; Kotela, I.; et al. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of hemophilic arthropathy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 39, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwenhuizen, L.; Schutgens, R.E.G.; Coeleveld, K.; Mastbergen, S.C.; Roosendaal, G.; Biesma, D.H.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G. Hemarthrosis in hemophilic mice results in alterations in M1-M2 monocyte/macrophage polarization. Thromb. Res. 2014, 133, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oneto, P.; Landro, M.E.; Daffunchio, C.; Douglas Price, A.L.; Carrera Silva, E.A.; Caviglia, H.; Etulain, J. DNA extracellular traps as potential biomarker of chronic haemophilic synovitis and therapeutic perspective in patients treated with PRP: A pilot study. Haemophilia 2022, 28, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz Wilczyñski, J.M.; Mena, H.A.; Ledesma, M.M.; Olexen, C.M.; Podaza, E.; Schattner, M.; Negrotto, S.; Errasti, A.E.; Carrera Silva, E.A. The synthetic phospholipid C8-C1P determines pro-angiogenic and pro-reparative features in human macrophages restraining the proinflammatory M1-like phenotype. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1162671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Sheng, J.; Gu, N. Modulation of macrophage polarization by iron-based nanoparticles. Med. Rev. 2023, 3, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamilos, A.; Winter, L.; Schmitt, V.H.; Barsch, F.; Grevenstein, D.; Wagner, W.; Babel, M.; Keller, K.; Schmitt, C.; Gürtler. Macrophages: From Simple Phagocyte to an Integrative Regulatory Cell for Inflammation and Tissue Regeneration—A Review of the Literature. Cells 2023, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.J. Macrophage Polarization. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 541–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, D.; Baxter, B.; Campbell, B.C.V.; Carpenter, J.S.; Cognard, C.; Dippel, D.; Eesa, M.; Fischer, U.; Hausegger, K.; Hirsch, J.A. Multisociety Consensus Quality Improvement Revised Consensus Statement for Endovascular Therapy of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Stroke Off. J. Int. Stroke Soc. 2018, 13, 612–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Biswas, S.K.; Fisher, E.A.; Gilroy, D.W.; Goerdt, S.; Gordon, S.; Hamilton, J.A.; Ivanshkiv, L.B.; Lawrence, T. Macrophage Activation and Polarization: Nomenclature and Experimental Guidelines. Immunity 2014, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strizova, Z.; Benesova, I.; Bartolini, R.; Novysedlak, R.; Cecrdlova, E.; Foley, L.K.; Striz, I. M1/M2 macrophages and their overlaps—Myth or reality? Clin Sci. 2023, 137, 1067–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Ma, L.; Deng, D.; Zhang, T.; Han, L.; Xu, F.; Huang, S.; Ding, Y.; Chen, X. M2 macrophage polarization: A potential target in pain relief. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1243149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Plüddemann, A. Tissue macrophages: Heterogeneity and functions. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, N.; Ding, M.; Yang, H.; Zhong, Q.; Zheng, L.; Luo, D.; Yao, Y. Iron overload causes macrophages to produce a pro-inflammatory phenotype in the synovium of hemophiliac arthritis via the acetyl-p53 pathway. Haemophilia 2024, 30, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroner, A.; Greenhalgh, A.D.; Zarruk, J.G.; Passos dos Santos, R.; Gaestel, M.; David, S. TNF and Increased Intracellular Iron Alter Macrophage Polarization to a Detrimental M1 Phenotype in the Injured Spinal Cord. Neuron 2014, 83, 1098–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Jiang, D.; Yang, M.; Tao, J.; Hu, X.; Yang, X.; Zeng, Y. Emerging Roles of Macrophage Polarization in Osteoarthritis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Orthop. Surg. 2024, 16, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuci, A.; Dargaud, Y. Blood-Induced Arthropathy: A Major Disabling Complication of Haemophilia. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 13, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, E.J.; Joseph, B.C.; Nasamran, C.A.; Fisch, K.M.; von Drygalski, A. Maladaptive lymphangiogenesis is associated with synovial iron accumulation and delayed clearance in factor VIII–deficient mice after induced hemarthrosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 21, 2390–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Xiang, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, H. Crosstalk between lymphatic system and synovial inflammatory cells in osteoarthritis: Molecular mechanisms and potential cell-based therapies. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Merchan, E.C.; Valentino, L.A. Safety of radiation exposure after radiosynovectomy in paediatric patients with haemophilia. Haemophilia 2015, 21, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtierotti, R.; Solimeno, L.P.; Peyvandi, F. Hemophilic arthropathy: Current knowledge and future perspectives. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 2112–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Ding, Q.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, W. Impact of autologous platelet-rich plasma therapy vs. hyaluronic acid on synovial fluid biomarkers in knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1258727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piramoon, S.; Tahoori, M.T.; Owlia, M.B.; Royaei, M.R. PRP as a modulator of inflammation in FLS of RA patients by regulation of galectins and TGF-β1. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Liang, Q.; Ge, X.; Xu, J. Allogeneic platelet-rich plasma inhibits ferroptosis in promoting wound repair of type 2 diabetic ulcers. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 215, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, F.; Jia, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, X. Platelet-rich plasma alleviates knee arthritis in rats by inhibiting p65. Cell Tissue Bank 2024, 25, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graca, F.A.; Stephan, A.; Minden-Birkenmaier, B.A.; Shirinifard, A.; Wang, Y.D.; Demontis, F.; Labelle, M. Platelet-derived chemokines promote skeletal muscle regeneration by guiding neutrophil recruitment to injured muscles. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Ferreira, A.F.; Soares, M.; Santos, S.; Tomé, P.; Machado-Simões, J.; Pais, A.S.; Sousa, A.P.; Paiva, A.; Almeida-Santos, T. Optimization of Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation for Regenerative Medicine: Comparison of Different Anticoagulants and Resuspension Media. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oneto, P.; Etulain, J. PRP in wound healing applications. Platelets 2021, 32, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopelliti, F.; Caterina, C.; Valentina, D.; Gianfranco, C.; Concetta, M.; Andrea, C. Platelet lysate converts M (IFNγ+LPS) macrophages in CD206+TGF-β+arginase+ M2-like macrophages that affect fibroblast activity and T lymphocyte migration. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 15, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, R.; Toyoda, E.; Maehara, M.; Wasai, S.; Omura, H.; Watanabe, M.; Sato, M. Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, H.; Dehghani, B.; Yuan, X.; Chinenov, Y.; Kim, C.; Burge, A.; Banghari, R.; Nemirov, D.; Fava, P.; Moley, P.; et al. In vitro responses to platelet-rich-plasma are associated with variable clinical outcomes in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, G.; Escobar, A.; Ascui, G.; Tempio, F.I.; Ortiz, M.C.; Pérez, C.A.; López, M.N. Pure Platelet-Rich Plasma and Supernatant of Calcium-Activated P-PRP Induce Different Phenotypes of Human Macrophages. Regen. Med. 2018, 13, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviglia, H.; Landro, M.E.; Daffunchio, C.; Galatro, G.; Douglas Price, A.L.; Salgado, P.; Neme, D. Platelet Rich Plasma for Chronic Synovitis Treatment in Patients with Haemophilia. Haemophilia 2017, 23, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, I.; Lu, L.; Lin, K.; Yu, L.H.; Yang, S.; Tsai, M.; Tsai, T.; Yeh, C.; Hong, Y.; Yu, M. Combined intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid and platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of haemophilic arthropathy: A case series study. Haemophilia 2021, 27, E291–E294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Cheng, S.; Pan, R.; Chen, Y. An exploratory comparison of single intra-articular injection of platelet-rich plasma vs hyaluronic acid in treatment of haemophilic arthropathy of the knee. Haemophilia 2019, 25, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teyssler, P.; Kolostova, K.; Bobek, V. The impact of platelet-rich plasma on chronic synovitis in hemophilia. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2014, 80, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Landro, M.E. Platelet Rich Plasma Intra Articular Injection for Chronic Synovitis Treatment in Patients with Haemophilia One Year Follow Up. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2019, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviglia, H.; Daffunchio, C.; Galatro, G.; Cambiaggi, G.; Oneto, P.; Douglas Price, A.L.; Landro, M.E.; Etulain, J. Inhibition of Fenton reaction is a novel mechanism to explain the therapeutic effect of intra-articular injection of PRP in patients with chronic haemophilic synovitis. Haemophilia 2020, 26, E187–E193. [Google Scholar]
- Santocki, M.; Kolaczkowska, E. On Neutrophil Extracellular Trap (NET) Removal: What We Know Thus Far and Why So Little. Cells 2020, 9, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Choi, S.J.; Ahn, S.M.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, C.K.; Yoo, B.; Hong, S. Neutrophil extracellular trap clearance by synovial macrophages in gout. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demkow, U. Molecular Mechanisms of Neutrophil Extracellular Trap (NETs) Degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, W.; Grendas, L.N.; Sanmarco, L.M.; Estecho, I.G.; Arena, Á.R.; Eberhardt, N.; Rodante, D.E.; Aoiki, M.P.; Daray, F.M.; Carrera Silva, E.A.; et al. Pro-inflammatory monocyte profile in patients with major depressive disorder and suicide behaviour and how ketamine induces anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages by NMDAR and mTOR. EBioMedicine 2019, 50, 290–305, Erratum in EBioMedicine 2021, 66, 103295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera Silva, E.A.; Errasti, A.E. Reprograming Model of Human Monocyte-derived Macrophages for In-vitro Assays. J. Vis. Exp. 2025, 218, e67651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, M.B.; Vurundhur, D.; Mallam, K.K.; Gulabi, M. Analysis of IL-6 marker in synovial fluid of the knee joint in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis before and after platelet-rich plasma administration. J. Res. Appl. Basic Med. Sci. 2024, 10, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nees, T.A.; Rosshirt, N.; Zhang, J.A.; Reiner, T.; Sorbi, R.; Tripel, E.; Walker, T.; Schiltenwolf, M.; Hagmann, S.; Moradi, B. Synovial Cytokines Significantly Correlate with Osteoarthritis-Related Knee Pain and Disability: Inflammatory Mediators of Potential Clinical Relevance. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehan, R.T.; Regan, E.A.; Hoffman, E.D.; Wolf, M.L.; Gill, M.T.; Crooks, J.L.; Parmar, P.J.; Scheuring, R.A.; Hill, J.C.; Pachecho, K.A.; et al. Synovial Fluid Cytokines, Chemokines and MMP Levels in Osteoarthritis Patients with Knee Pain Display a Profile Similar to Many Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luukkonen, J.; Huhtakangas, J.; Palosaari, S.; Tuukkanen, J.; Vuolteenaho, O.; Lehenkari, P. Preliminary Report: Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fluid Increased Osteoclastogenesis In Vitro by Monocyte Differentiation Pathway Regulating Cytokines. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 2606916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.L.; Min, S.Y.; Chang, S.H.; Kim, K.W.; Heo, S.B.; Lee, S.H.; Park, S.H.; Cho, C.S.; Kim, H.Y. Transforming growth factor beta 1(TGF-β1) down-regulates TNFα-induced RANTES production in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts through NF-κB-mediated transcriptional repression. Immunol. Lett. 2006, 105, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Hsieh, S.C.; Chen, W.Y.; Li, K.J.; Wu, C.H.; Wu, P.C.; Tsai, C.Y.; Yu, C.L. Spontaneous resolution of acute gouty arthritis is associated with rapid induction of the anti-inflammatory factors TGFβ1, IL-10 and soluble TNF receptors and the intracellular cytokine negative regulators CIS and SOCS3. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, K.; Patel, A.A.; Kong, W.T.; Piot, C.; Halitzki, E.; Dunsmore, G.; Khalilnezhad, S.; Irac, S.E.; Dubuisson, A.; Chevrier, M.; et al. Cross-tissue single-cell landscape of human monocytes and macrophages in health and disease. Immunity 2021, 54, 1883–1900.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambari, L.; Grassi, F.; Roseti, L.; Grigolo, B.; Desando, G. Learning from Monocyte-Macrophage Fusion and Multinucleation: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Osteoporosis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Putten, S.M.; Ploeger, D.T.A.; Popa, E.R.; Bank, R.A. Macrophage phenotypes in the collagen-induced foreign body reaction in rats. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6502–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.; Su, X.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, L.; Giannoudis, P.V.; Gou, J.J. No Benefit to Platelet-rich Plasma Over Placebo Injections in Terms of Pain or Function in Patients with Hemophilic Knee Arthritis: A Randomized Trial. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2022, 480, 2361–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannabouathong, C.; Del Fabbro, G.; Sales, B.; Smith, C.; Li, C.S.; Yardley, D.; Bhandari, M.; Petrisor, B. Intra-articular Injections in the Treatment of Symptoms from Ankle Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Foot Ankle Int. 2018, 39, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auroux, M.; Debionne, T.; Mainbourg, S.; Chapurlat, R. Efficacy of intra-articular platelet-rich plasma compared with placebo in knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Jt. Bone Spine 2025, 92, 105947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Merchan, E.C. Intra-articular injection of platelet-rich plasma in patients with hemophilia and painful knee joint cartilage degeneration. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2023, 16, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtierotti, R.; Suffritti, C.; Pescia, C.; Giachi, A.; Spena, S.; Molfino, F.; Lavorato, S.; Semproni, E.; Truma, A.; Arcudi, S.; et al. The Histopathological Landscape of Synovitis in Hemophilic Arthropathy. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuizen, L.; Schutgens, R.E.G.; van Asbeck, B.S.; Wenting, M.J.; van Veghel, K.; Roosendaal, G.; Biesma, D.H.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G. Identification and expression of iron regulators in human synovium: Evidence for upregulation in haemophilic arthropathy compared to rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and healthy controls. Haemophilia 2013, 19, e218–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zheng, L.; Luo, D.; Pang, N.; Yao, Y. Ferroptosis: A new target for iron overload-induced hemophilic arthropathy synovitis. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.Z.; Chengwei, W.; Zhu, J.; Yangyang, G. Deferoxamine in the Treatment of Hemophilic Synovitis by Inhibiting Macrophage Iron Overload. Res. Sq. 2024. preprints. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chi, R.; Xu, J.; Guo, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hou, L.; Zheng, Z.; Lu, F.; Xu, T.; et al. DMT1-mediated iron overload accelerates cartilage degeneration in Hemophilic Arthropathy through the mtDNA-cGAS-STING axis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcaterra, I.; Iannuzzo, G.; Dell’Aquila, F.; Di Minno, M.N.D. Pathophysiological Role of Synovitis in Hemophilic Arthropathy Development: A Two-Hit Hypothesis. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, E.; Zhou, J.; Wyseure, T.; Joshi, S.; Bhat, V.; Durden, D.; Mosnier, L.O.; von Drygalski, A. Vascular Permeability and Remodelling Coincide with Inflammatory and Reparative Processes after Joint Bleeding in Factor VIII-Deficient Mice. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1036–1047, Erratum in Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 1546–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, S.S.; Kaplan, R.N.; Macdonald, D.; Fabiyi, O.T.; DiMichele, D.; Lyden, D. Neoangiogenesis contributes to the development of hemophilic synovitis. Blood 2011, 117, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.S.; Cui, L.; Wang, G.D. miR-155-5p regulates macrophage M1 polarization and apoptosis in the synovial fluid of patients with knee osteoarthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 21, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menarim, B.C.; Gillis, K.H.; Oliver, A.; Mason, C.; Werre, S.R.; Luo, X.; Byron, C.R.; Kalbfleish, T.S.; MacLeod, J.N.; Dahlgren, L.A. Inflamed synovial fluid induces a homeostatic response in bone marrow mononuclear cells in vitro: Implications for joint therapy. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 4430–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopa, S.; Leijs, M.J.C.; Moretti, M.; Lubberts, E.; van Osch, G.J.V.M.; Bastiaansen-Jenniskens, Y.M. Arthritic and non-arthritic synovial fluids modulate IL10 and IL1RA gene expression in differentially activated primary human monocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1853–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.; Srivastava, V.; Tootsi, K.; Electricwala, A.; Kharat, A.; Bhonde, R.; Koks, S.; Martson, A.; Harsulkar, A. Synovial Fluid in Knee Osteoarthritis Extends Proinflammatory Niche for Macrophage Polarization. Cells 2022, 11, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Shi, W.; Yi, S.-J.; Chen, H.; Groffen, J.; Heisterkamp, N. TGFβ signaling plays a critical role in promoting alternative macrophage activation. BMC Immunol. 2012, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Jiang, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Fang, R.; Bu, X.; Cai, S.; et al. TGF-β induces M2-like macrophage polarization via SNAIL-mediated suppression of a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52294–52306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, E.; Massagué, J. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling in Immunity and Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 924–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Troya, M.; Alkhraisat, M.H. Immunoregulatory role of platelet derivatives in the macrophage-mediated immune response. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1399130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Xu, J.J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, T.T.; Xu, Y.B.; Shan, G.Q.; Zhou, M. Platelet-rich Plasma Induces M2 Macrophage Polarization via Regulating AMPK Singling Pathway. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2023, 31, 1486–1491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, B.; Tian, Y.; Guan, M.; Han, W.; Yi, W.; Li, K.; Yang, X.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Teng, P.; et al. Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma alleviate synovial inflammation by enhancing synovial lymphatic function. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akgül, A.; Cirak, M.; Birinci, T. Applications of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Lymphedema. Lymphat. Res Biol. 2016, 14, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, T.W.; Brzoska, T.; Tutuncuoglu, E.; Ragni, M.V.; Sundd, P. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote Joint Injury in Hemophilia. Blood 2021, 138 (Suppl. 1), 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, Z.; Brooks, P.; Barzilay, O.; Fine, N.; Glogauer, M. Macrophages, Foreign Body Giant Cells and Their Response to Implantable Biomaterials. Materials 2015, 8, 5671–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, A.K.; Anderson, J.M. Macrophage Fusion and Multinucleated Giant Cells of Inflammation. In Cell Fusion in Health and Disease; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 97–111. [Google Scholar]
- Farrera, C.; Fadeel, B. Macrophage Clearance of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Is a Silent Process. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Lucci, F.; Schattner, M. Phosphatidylserine trapped in the net: A new therapeutic target for the ischemic stroke? EBioMedicine 2020, 54, 102713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Li, T.; Jin, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Sun, Q.; Tain, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; Ma, S.; et al. Interactions between neutrophil extracellular traps and activated platelets enhance procoagulant activity in acute stroke patients with ICA occlusion. EBioMedicine 2020, 53, 102671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carestia, A.; Mena, H.A.; Olexen, C.M.; Ortiz Wilczyñski, J.M.; Negrotto, S.; Errasti, A.E.; Gómez, R.M.; Jenne, G.N.; Carrera Silva, E.A.; Schattner, M. Platelets Promote Macrophage Polarization toward Pro-inflammatory Phenotype and Increase Survival of Septic Mice. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 896–908.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzaretto, B.; Fadeel, B. Intra- and Extracellular Degradation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps by Macrophages and Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 2276–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
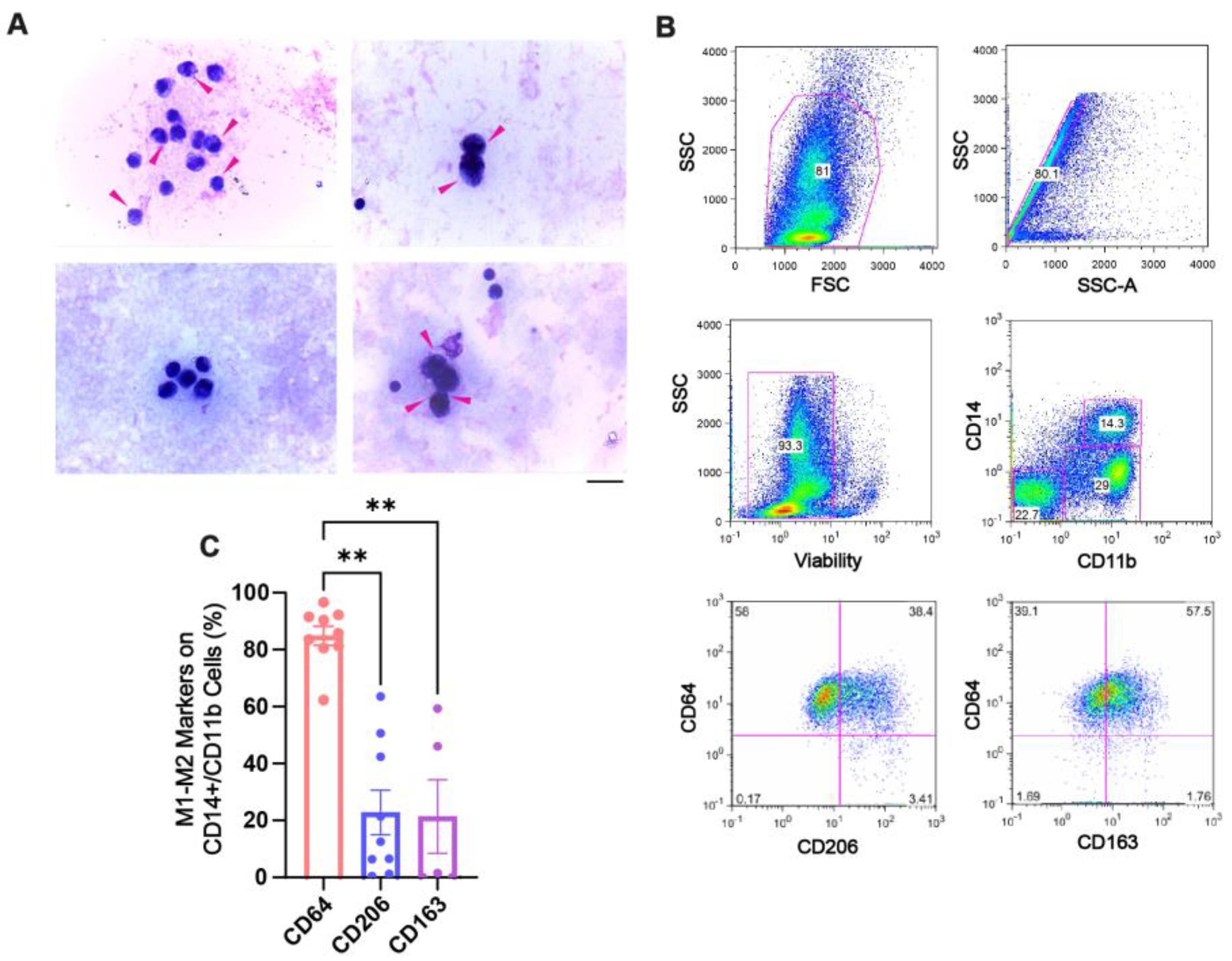

| Variable | Patients | Joints |
|---|---|---|
| N (Male) | 22 | 23 |
| Age in years | 28 (13:60) | |
| Severity and type of hemophilia | 20 severe and type A; 2 moderate and type B | |
| Joint | 22 knees; 1 ankle |
| Gene Name | 5′-3′ Forward Sequence | 5′-3′ Reverse Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Eef1A1 | TCGGGCAAGTCCACCACTAC | CCAAGACCCAGGCATACTTG |
| VEGF | ATGAGGACACCGGCTCTGACCA | AGGCTCCTGAATCTTCCAGGCA |
| EGF | CTTGGGAGCCTGAGCAGAAA | TGCACAAGTGTGACTGGAGG |
| SOCS1 | CACGCACTTCCGCACATTC | TAAGGGCGAAAAAGCAGTTCC |
| IDO1 | GATGTCCGTAAGGTCTTGCC | TCCAGTCTCCATCACGAAAT |
| HIF1α | ACTAGCCGAGGAAGAACTATGAA | TACCCACACTGAGGTTGGTTA |
| MERTK | CTCTGGCGTAGAGCTATCACT | AGGCTGGGTTGGTGAAAACA |
| IRF7 | CAGCGAGTGCTGTTTGGAGAC | AAGTTCGTACACCTTATGCGG |
| CXCL3 | CGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATAG | GCTCCCCTTGTTCAGTATCTTTT |
| IL1 | CTGAACTGCACGCTCCGGG | GCTTATCATCTTTCAACACGCAGG |
| PDL1 (CD274) | GCTTTTCAATGTGACCAGCA | GATGGCTCCCAGAATTACCA |
| TGFb1 | GGAAATTGAGGGCTTTCGCC | CCGGTAGTGAACCCGTTGAT |
| MRC1 (CD206) | AGCCAACACCAGCTCCTCAAGA | CAAAACGCTCGCGCATTGTCCA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oneto, P.; Landro, M.E.; Ledesma, M.M.; Etulain, J.; Daffunchio, C.; Cambiaggi, G.; Schattner, M.; Errasti, A.E.; Caviglia, H.; Carrera Silva, E.A. Platelet Releasate Reprograms Synovial Macrophages In Vitro: A New Approach in the Treatment of Hemophilic Synovitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110616
Oneto P, Landro ME, Ledesma MM, Etulain J, Daffunchio C, Cambiaggi G, Schattner M, Errasti AE, Caviglia H, Carrera Silva EA. Platelet Releasate Reprograms Synovial Macrophages In Vitro: A New Approach in the Treatment of Hemophilic Synovitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110616
Chicago/Turabian StyleOneto, Paula, María Eulalia Landro, Martin Manuel Ledesma, Julia Etulain, Carla Daffunchio, Guillermo Cambiaggi, Mirta Schattner, Andrea Emilse Errasti, Horacio Caviglia, and Eugenio Antonio Carrera Silva. 2025. "Platelet Releasate Reprograms Synovial Macrophages In Vitro: A New Approach in the Treatment of Hemophilic Synovitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110616
APA StyleOneto, P., Landro, M. E., Ledesma, M. M., Etulain, J., Daffunchio, C., Cambiaggi, G., Schattner, M., Errasti, A. E., Caviglia, H., & Carrera Silva, E. A. (2025). Platelet Releasate Reprograms Synovial Macrophages In Vitro: A New Approach in the Treatment of Hemophilic Synovitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110616






