Nanostructured Ni-Zeolite Y and Carbon Nanohorns Electrode for Sensitive Electrochemical Determination of B-Group Vitamins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Electrode Modifiers
2.2. Electrochemical Characterization of Modified Electrodes
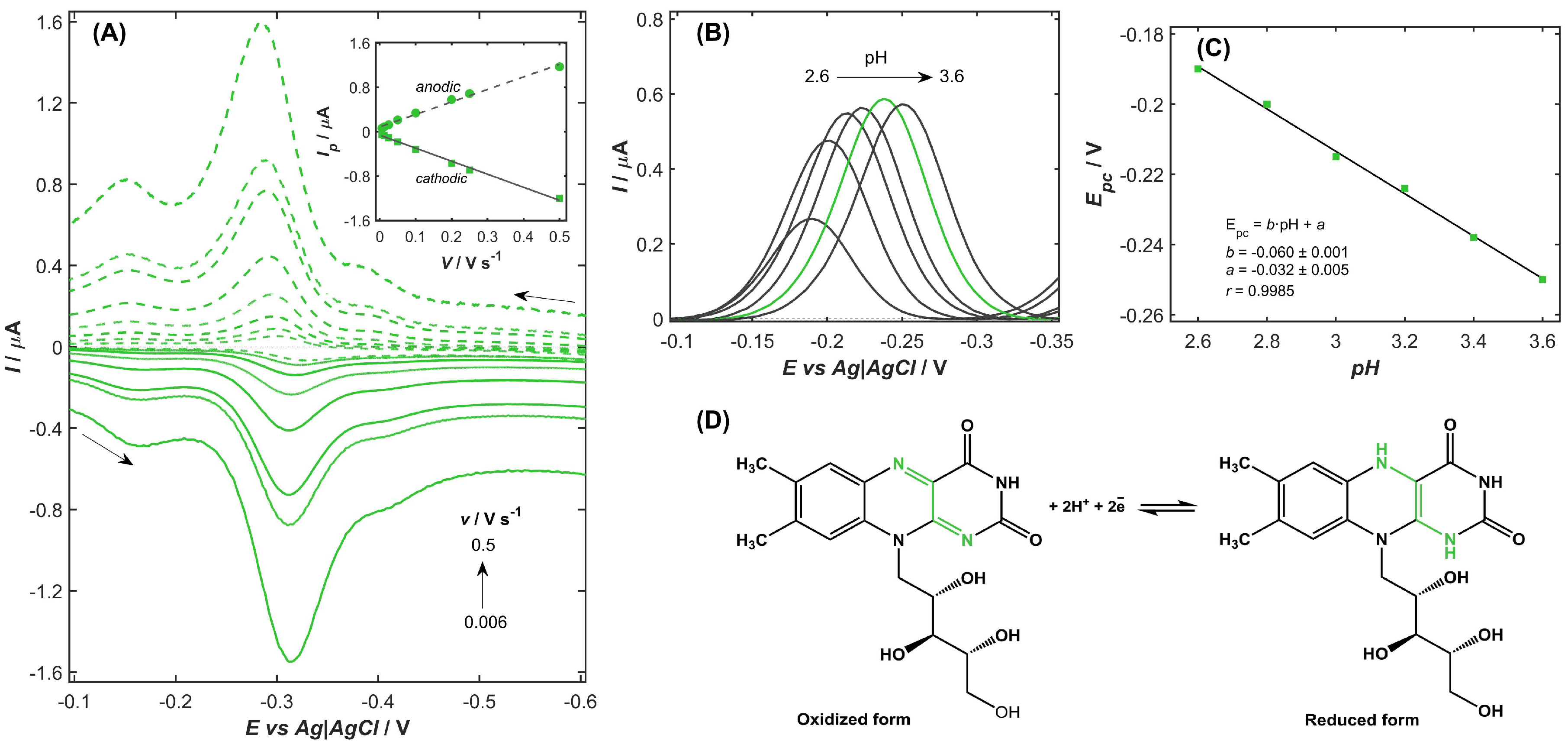
2.3. Investigation of the Redox Behavior of VB2 on the NiZY/CNHs-GCE
2.4. Optimization of the Experimental Conditions
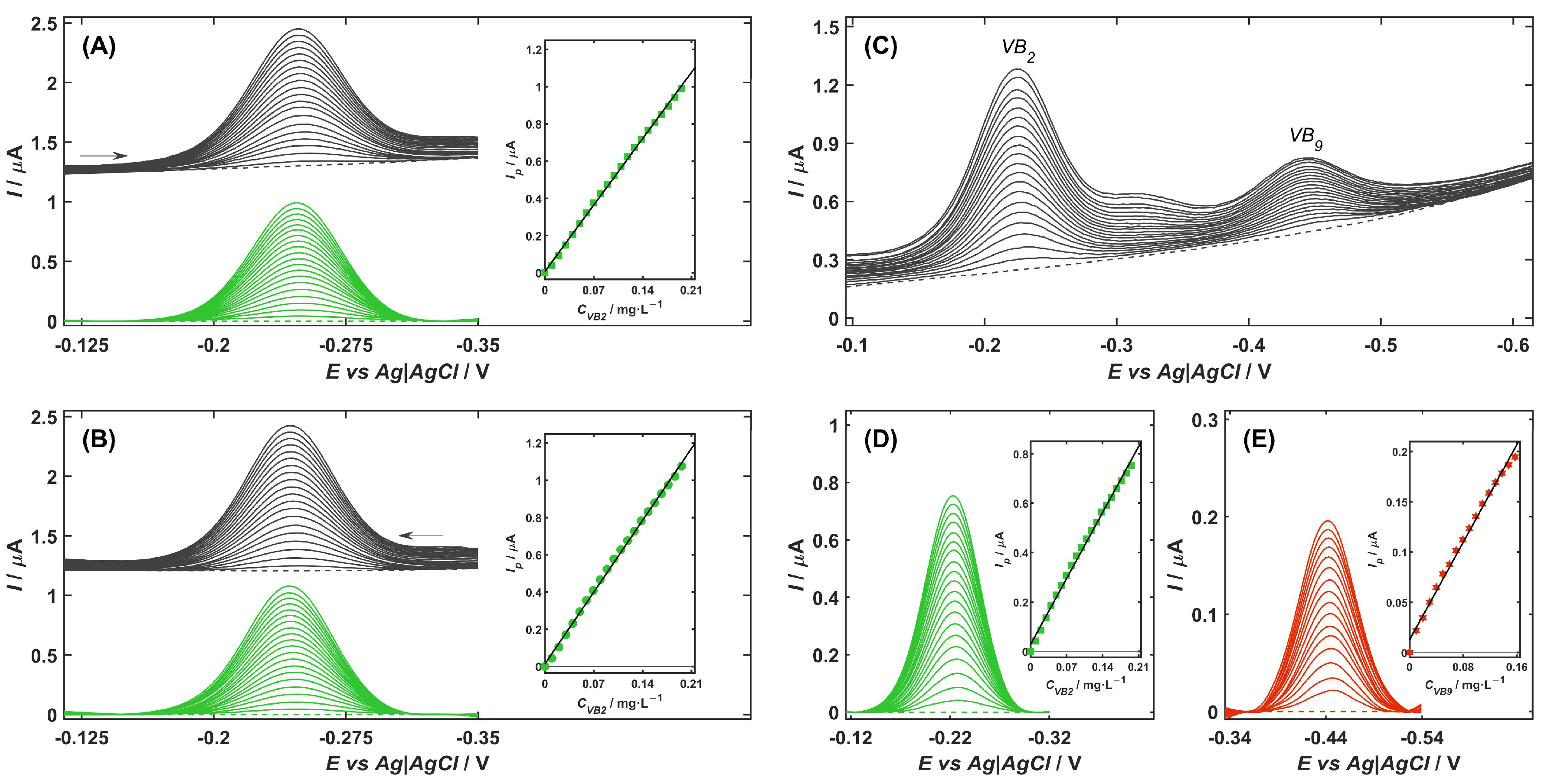
2.5. Analytical Performance
2.6. Selectivity
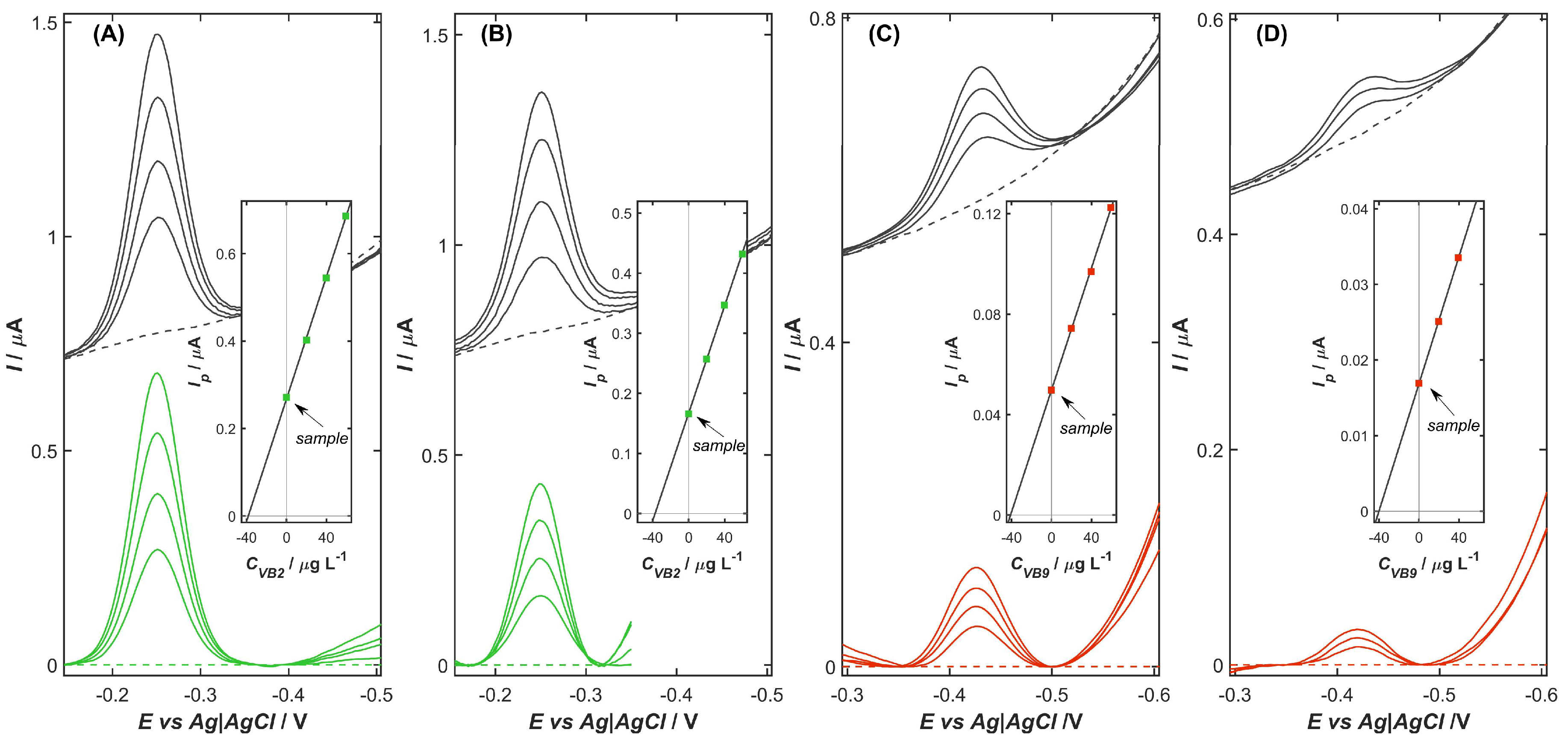
2.7. Analytical Application
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Solutions
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Procedures
3.3.1. Zeolite Y Modification and NiZY/CNHs Electrode Fabrication
3.3.2. Sample Preparation and Analysis
3.3.3. Standard Electrochemical Procedure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Powers, H.J. Riboflavin (Vitamin B-2) and Health. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, K.; Tomar, S.K.; Singh, A.K.; Mandal, S.; Arora, S. Riboflavin and Health: A Review of Recent Human Research. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3650–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Zhang, L.L.; Luo, H.J.; Chen, Y.; Long, L.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, P.T.; Li, E.M.; Xu, L.Y. Dietary Riboflavin Deficiency Induces Ariboflavinosis and Esophageal Epithelial Atrophy in Association with Modification of Gut Microbiota in Rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duyvis, M.G.; Hilhorst, R.; Laane, C.; Evans, D.J.; Schmedding, D.J.M. Role of Riboflavin in Beer Flavor Instability: Determination of Levels of Riboflavin and Its Origin in Beer by Fluorometric Apoprotein Titration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1548–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajicek, J.L.; Tillitt, D.E.; Brown, S.B.; Brown, L.R.; Honeyfield, D.C.; Fitzsimons, J.D. A Rapid Solid-Phase Extraction Fluorometric Method for Thiamine and Riboflavin in Salmonid Eggs. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2005, 17, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, U.; Zamora, A.; Liu, J.; Saldo, J.; Castillo, M. Rapid Quantification of Riboflavin in Milk by Front-Face Fluorescence Spectroscopy: A Preliminary Study. Foods 2020, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, J.; Abbasi, B.; Niazi, A.; Nadaf, E.; Mordai, A. Simultaneous Spectrophotometric Multicomponent Determination of Folic Acid, Thiamine, Riboflavin, and Pyridoxal by Using Double Divisor-Ratio Spectra Derivative-Zero Crossing Method. Anal. Lett. 2004, 37, 2609–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-de-Alba, P.L.; López-Martínez, L.; Cerdá, V.; Amador-Hernández, J. Simultaneous Determination and Classification of Riboflavin, Thiamine, Nicotinamide and Pyridoxine in Pharmaceutical Formulations, by UV-Visible Spectrophotometry and Multivariate Analysis. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2006, 17, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartzatt, R.; Wol, T. Detection and Assay of Vitamin B-2 (Riboflavin) in Alkaline Borate Buffer with UV/Visible Spectrophotometry. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 453085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capo-Chichi, C.D.; Guéant, J.L.; Feillet, F.; Namour, F.; Vidailhet, M. Analysis of Riboflavin and Riboflavin Cofactor Levels in Plasma by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2000, 739, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, C.C.; Herivel, T.R.; Hernandez, S.C.; Ruane, P.H.; Goodrich, R.P. Separation, Identification and Quantification of Riboflavin and Its Photoproducts in Blood Products Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection: A Method to Support Pathogen Reduction Technology. Photochem. Photobiol. 2004, 80, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viñas, P.; Balsalobre, N.; López-Erroz, C.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Liquid Chromatographic Analysis of Riboflavin Vitamers in Foods Using Fluorescence Detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldi, T.R.I.; Nardiello, D.; Carrara, V.; Ciriello, R.; De Benedetto, G.E. Assessment of Riboflavin and Flavin Content in Common Food Samples by Capillary Electrophoresis with Laser-Induced Fluorescence Detection. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, G.; Venkatesh, Y.P. Immunoassays for Riboflavin and Flavin Mononucleotide Using Antibodies Specific to D-Ribitol and D-Ribitol-5-Phosphate. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 445, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovander, M.D.; Lyon, J.D.; Parr, D.L.; Wang, J.; Parke, B.; Leddy, J. Critical Review—Electrochemical Properties of 13 Vitamins: A Critical Review and Assessment. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, G18–G49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Pouladsaz, P. Voltammetric Determination of Riboflavin Based on Electrocatalytic Oxidation at Zeolite-Modified Carbon Paste Electrodes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2146–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaloo, S.S.; Mozaffari, S.; Alimohammadi, P.; Kargar, H.; Ordookhanian, J. Sensitive and Selective Determination of Riboflavin in Food and Pharmaceutical Samples Using Manganese (III) Tetraphenylporphyrin Modified Carbon Paste Electrode. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 2272–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mehmeti, E.; Stanković, D.M.; Chaiyo, S.; Švorc, Ľ.; Kalcher, K. Manganese Dioxide-Modified Carbon Paste Electrode for Voltammetric Determination of Riboflavin. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bártová, M.; Bartoš, M.; Švancara, I.; Sýs, M. Shungite Paste Electrodes: Basic Characterization and Initial Examples of Applicability in Electroanalysis. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hareesha, N.; Manjunatha, J.G. Elevated and Rapid Voltammetric Sensing of Riboflavin at Poly(Helianthin Dye) Blended Carbon Paste Electrode with Heterogeneous Rate Constant Elucidation. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2020, 17, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varun, D.N.; Manjunatha, J.G.; Hareesha, N.; Sandeep, S.; Mallu, P.; Karthik, C.S.; Prinith, N.S.; Sreeharsha, N.; Asdaq, S.M.B. Simple and Sensitive Electrochemical Analysis of Riboflavin at Functionalized Carbon Nanofiber Modified Carbon Nanotube Sensor. Monatshefte Fur Chem. 2021, 152, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, É.S.; Da Silva, P.S.; Jost, C.L.; Spinelli, A. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Bismuth-Film Electrode for Voltammetric Studies on Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhuvilakku, R.; Alagar, S.; Mariappan, R.; Piraman, S. Green One-Pot Synthesis of Flowers-like Fe3O4/RGO Hybrid Nanocomposites for Effective Electrochemical Detection of Riboflavin and Low-Cost Supercapacitor Applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 253, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriramprabha, R.; Divagar, M.; Ponpandian, N.; Viswanathan, C. Tin Oxide/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Riboflavin. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, B498–B507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan, S.; Suganthi, A.; Rajarajan, M. A Facile Synthesis of ZnO/Manganese Hexacyanoferrate Nanocomposite Modified Electrode for the Electrocatalytic Sensing of Riboflavin. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 121, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, M.; Shamspur, T.; Molaakbari, E.; Mostafavi, A.; Saljooqi, A. Fabrication of a Novel Electrochemical Sensor for Determination of Riboflavin in Different Drink Real Samples. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2020, 56, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesu Amalraj, A.J.; Wang, S.F. An Effective Morphology Controlled Hydrothermal Synthesis of Bi2WO6 and Its Application in Riboflavin Electrochemical Sensor. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Sun, J.J.; Lin, Z.B.; Wu, A.H.; Zeng, Y.M.; Guo, L.; Zhang, D.F.; Dai, H.M.; Chen, G.N. Adsorptive Stripping Analysis of Riboflavin at Electrically Heated Graphite Cylindrical Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 2251–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Heydari-Bafrooei, E.; Amini, M. DNA-Functionalized Biosensor for Riboflavin Based Electrochemical Interaction on Pretreated Pencil Graphite Electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.; Vairamuthu, R. Electrochemical Detection of Riboflavin Using Tin-Chitosan Modified Pencil Graphite Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 891, 115235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedhu, N.; Jagadeesh Kumar, J.; Sivaguru, P.; Raj, V. Electrochemical Detection of Riboflavin in Pharmaceutical and Food Samples Using in Situ Electropolymerized Glycine Coated Pencil Graphite Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 928, 117037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadara, R.O.; Haggett, B.G.D.; Birch, B.J. Disposable Sensor for Measurement of Vitamin B2 in Nutritional Premix, Cereal, and Milk Powder. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 4921–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riman, D.; Avgeropoulos, A.; Hrbac, J.; Prodromidis, M.I. Sparked-Bismuth Oxide Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Determination of Riboflavin in the Sub-Nanomolar Range in Non-Deoxygenated Solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 165, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusankar, G.; Rajkumar, C.; Chen, S.M.; Karkuzhali, R.; Gopu, G.; Sangili, A.; Sengottuvelan, N.; Sankar, R. Sonochemical Driven Simple Preparation of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots/SnO2 Nanocomposite: A Novel Electrocatalyst for Sensitive Voltammetric Determination of Riboflavin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavasileiou, A.V.; Hoder, T.; Medek, T.; Prodromidis, M.I.; Hrbac, J. Sensitive Riboflavin Sensing Using Silver Nanoparticles Deposited onto Screen-Printed Electrodes via Controlled-Energy Spark Discharges. Talanta 2023, 258, 124409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ndamanisha, J.C.; Liu, L.; Yang, L.; Guo, L. Voltammetric Detection of Riboflavin Based on Ordered Mesoporous Carbon Modified Electrode. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2010, 14, 2251–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkar, P.K.; Ganesan, V.; Sen Gupta, S.K.; Yadav, D.K.; Gupta, R.; Yadav, M. Highly Dispersed Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Coupled Manganese Salen Nanostructure for Simultaneous Electrochemical Sensing of Vitamin B2 and B6. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 807, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangili, A.; Veerakumar, P.; Chen, S.M.; Rajkumar, C.; Lin, K.C. Voltammetric Determination of Vitamin B 2 by Using a Highly Porous Carbon Electrode Modified with Palladium-Copper Nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, M.; Meydan, I.; Seckin, H. Electrochemical Characterization of Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) at Ag Nanoparticles Synthesized by Green Chemistry Dispersed on Reduced Graphene Oxide. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 135, 109875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes-Junior, P.C.; de Lima Augusto, K.K.; Longatto, G.P.; de Oliveira Gonçalves, R.; Silva, T.A.; Cavalheiro, É.T.G.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Ultrasmall Platinum Nanoparticles Synthesized in Reline Deep Eutectic Solvent Explored towards the Voltammetric Sensing of Riboflavin in Beverages and Biological Fluids. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 395, 134489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian, A.; Rafati, A.A.; Afraz, A.; Najafi, M. Electrosynthesis of High-Density Polythiophene Nanotube Arrays and Their Application for Sensing of Riboflavin. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 199, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha, J.G.; Raril, C.; Hareesha, N.; Charithra, M.M.; Pushpanjali, P.A.; Tigari, G.; Ravishankar, D.; Mallappaji, S.C.; Gowda, J. Electrochemical Fabrication of Poly (Niacin) Modified Graphite Paste Electrode and Its Application for the Detection of Riboflavin. Open Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 14, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhayashri Kamath, K.; Manjunatha, J.G.; Girish, T.; Sillanpää, M.; TIGHEZZA, A.M.; Albaqami, M.D. Sensitive Electrochemical Determination of Riboflavin at Simple and Low-Cost Poly (Valine) Modified Graphite Paste Electrode. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 143, 109811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSuhaimi, A.O.; Althumayri, K.; Alessa, H.; Sayqal, A.; Mogharbel, A.T.; Alsehli, B.R.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Zeolite Integrated Carbon Paste Sensors for Sensitive and Selective Differential Pulse Voltammetric Determination of Carprofen. Microchem. J. 2023, 195, 109525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatikayala, D.; Noori, M.T.; Min, B. Zeolite-Modified Electrodes for Electrochemical Sensing of Heavy Metal Ions–Progress and Future Directions. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 29, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, H.S.; Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Karimi-Shamsabadi, M. A Novel Cysteine Sensor Based on Modification of Carbon Paste Electrode by Fe(II)-Exchanged Zeolite X Nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.J.; Zhuang, T.T.; Cao, Y.; Yun, Z.Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, J.H. Capturing Nitrosamines by Zeolite A: Molecular Recognition in Subnanometer Space. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 6740–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupulescu, A.I.; Kumar, M.; Rimer, J.D. A Facile Strategy to Design Zeolite L Crystals with Tunable Morphology and Surface Architecture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 6608–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porada, R.; Fendrych, K.; Baś, B. The Mn-Zeolite/Graphite Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode: Fabrication, Characterization and Analytical Applications. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 1208–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, S.; Saraswathi, R. Electrochemical Sensing of Cadmium and Lead Ions at Zeolite-Modified Electrodes: Optimization and Field Measurements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 141, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawde, A.; Ismail, A.; Al-Betar, A.R.; Muraza, O. Novel Ce-Incorporated Zeolite Modified-Carbon Paste Electrode for Simultaneous Trace Electroanalysis of Lead and Cadmium. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 243, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porada, R.; Fendrych, K.; Baś, B. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Ni-Exchanged Natural Zeolite/Carbon Black Hybrid Nanocomposite for Determination of Vitamin B6. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendrych, K.; Porada, R.; Baś, B. Ultrasensitive and Highly Selective Electrochemical Determination of Mesalazine in Pharmaceutical, Biological and Environmental Samples with the Use of Co-Mordenite/Mesoporous Carbon Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 468, 143209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendrych, K.; Porada, R.; Baś, B. A Novel Voltammetric Strategy of Furazidin Determination with the Use of Co-Ferrierite/Mesoporous Carbon Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. Soc. 2025, 172, 017523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porada, R.; Wenninger, N.; Bernhart, C.; Fendrych, K.; Kochana, J.; Baś, B.; Kalcher, K.; Ortner, A. Targeted Modification of the Carbon Paste Electrode by Natural Zeolite and Graphene Oxide for the Enhanced Analysis of Paracetamol. Microchem. J. 2023, 187, 108455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekrya, A.M.; Abdel-Gawad, S.A.; Azab, S.M.; Walcarius, A. A Sensitive Electrochemical Sensor for Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride Based on Nafion/Graphene Oxide/Zeolite Modified Carbon Paste Electrode. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaduk, J.A.; Faber, J. Crystal Structure of Zeolite Y as a Functon of Ion Exchange. Ridaku J. 1995, 12, 14–34. [Google Scholar]
- Król, M.; Mozgawa, W.; Jastrzbski, W.; Barczyk, K. Application of IR Spectra in the Studies of Zeolites from D4R and D6R Structural Groups. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 156, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, M.; Mozgawa, W.; Barczyk, K.; Bajda, T.; Kozanecki, M. Changes in the Vibrational Spectra of Zeolites Due to Sorption of Heavy Metal Cations. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2013, 80, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagona, G.; Mountrichas, G.; Rotas, G.; Karousis, N.; Pispas, S.; Tagmatarchis, N. Properties, Applications and Functionalisation of Carbon Nanohorns. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2009, 6, 176–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 9780387331508. [Google Scholar]
- Narmaeva, G.; Aronbaev, S.; Aronbaev, D. Achievements and Problems of Electrode Modification for Voltammetry. Int. J. Res.-Granthaalayah 2018, 6, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
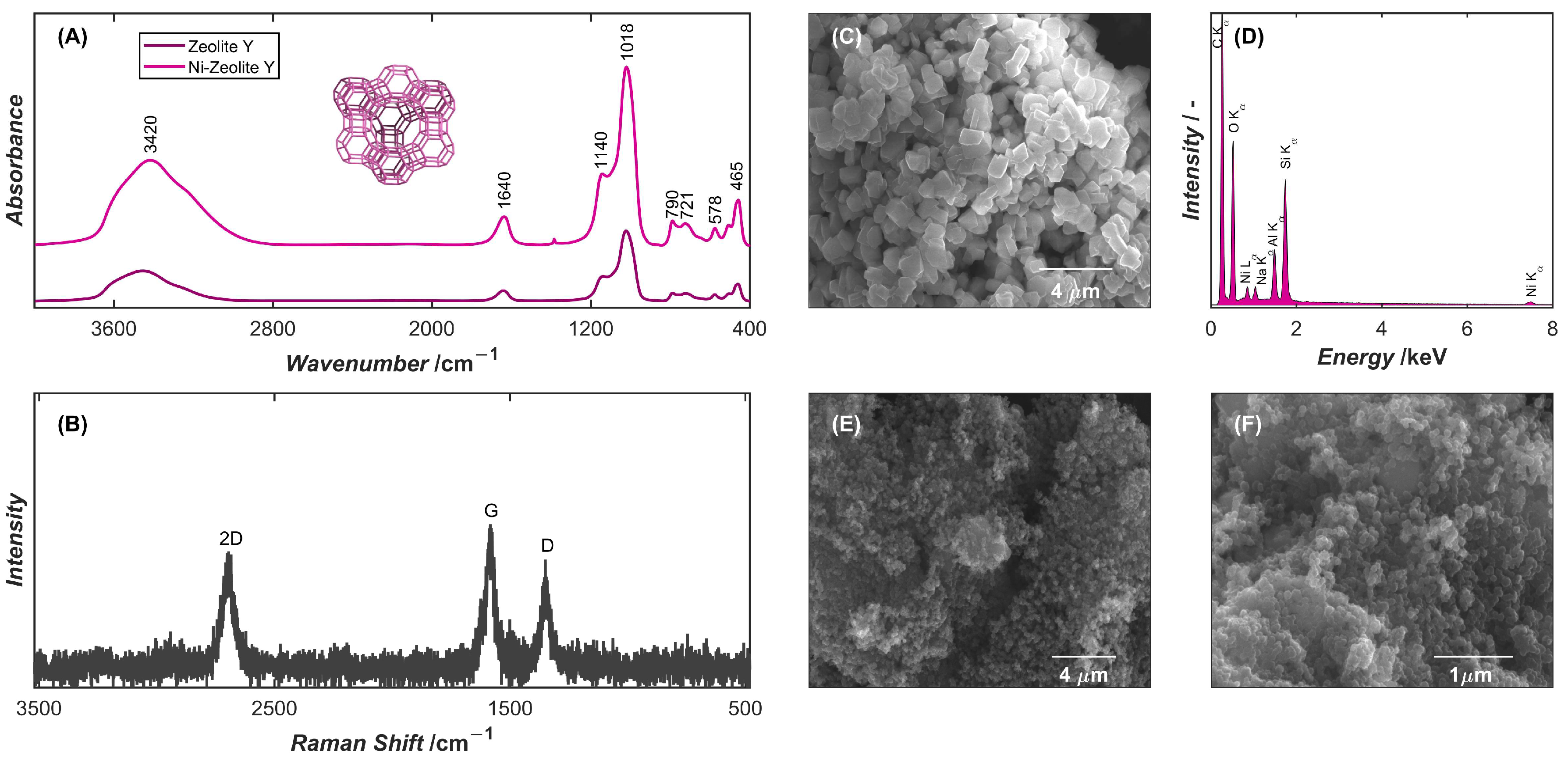

| Material | Surface Area [m2 g−1] | Pore Volume [cm3 g−1] | Average Pore Diameter [nm] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBET | Smicro | Sext | Vmicro+mezo | Vmicro | ||
| Zeolite Y | 1001.81 | 992.65 | 9.16 | 0.511 | 0.461 | 1.95 |
| Carbon nanohorns | 460.65 | 176.27 | 284.38 | 0.152 | 0.075 | 0.14 |
| Parameter | Unit | Working Electrode | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCE | NiZY-GCE | CNHs-GCE | NiZY/CNHs-GCE | ||
| Formal potential, Ef | mV | 138 | 164 | 152 | 160 |
| Peak separation, ∆E | mV | 72 | 261 | 360 | 536 |
| Anodic peak current, Ipa | µA | 9.6 | 1.0 | 21.0 | 9.8 |
| Anodic to cathodic peak current, Ipa/Ipc | - | 0.99 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.4 |
| Charge-transfer resistance, Rct | kΩ | 1.4 | 70.7 | 12.2 | 48.0 |
| Warburg coefficient, σ | kΩ s−1/2 | 3.15 | 6.70 | 2.90 | 2.80 |
| Electroactive surface area, Ael | mm2 | 8.9 | 4.2 | 9.7 | 10.0 |
| Double-layer capacitance, Cdl | µF cm−2 | 24.7 | 15.7 | 6.3 | 4.2 |
| Heterogeneous rate constant, ks | m s−1 | 4.3 × 10−5 | 1.6 × 10−6 | 4.5 × 10−6 | 1.4 × 10−6 |
| Parameter | Unit | VB2 | VB2 in the Presence of VB9 | VB9 in the Presence of VB2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cathodic | Anodic | ||||
| Linear range | mg L−1 | 0.01–0.2 | 0.01–0.2 | 0.01–0.2 | 0.01–0.16 |
| Intercept a | µA | 0.008 ± 0.005 | 0.014 ± 0.006 | 0.027 ± 0.006 | 0.012 ± 0.002 |
| Slope b | µA L mg−1 | 5.10 ± 0.04 | 5.51 ± 0.05 | 3.82 ± 0.06 | 1.21 ± 0.03 |
| r | - | 0.9993 | 0.9991 | 0.9979 | 0.9964 |
| LOD | µg L−1 (nM) | 3.2 (8.6) | 3.6 (9.5) | 5.2 (13.8) | 5.4 (12.3) |
| LOQ | µg L−1 (nM) | 9.8 (26.1) | 10.9 (28.9) | 15.7 (41.8) | 16.5 (37.3) |
| Figure | (A) | (B) | (D) | (E) | |
| Electrode | Technique | Linear Range [µmol L−1] | LOD [nmol L−1] | Samples | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Co2+-Y/CPE | CV | 1.7–34 | 710 | Multivitamin tablet | [16] |
| 2 MnTPP/CPE | DPV | 0.01–10 | 8.0 | Food, pharmaceuticals | [17] |
| 3 MnO2/CPE | DPV | 0.02–9 | 15 | Tablet | [18] |
| 4 ShPE/MnO2 | DPV | 0.1–10.0 | 27.4 | - | [19] |
| 5 PHLD- MCPE | CV | 60–150 | 40.2 | Pharmaceutical | [20] |
| 6 FCNF/CNTPE | DPV | 5.0–60.0 | 15.35 | B-complex capsule | [21] |
| 7 BiFE | SWAdSV | 0.3–0.8 | 100 | Oral solution, syrup, tablets | [22] |
| 1.0–9.0 | |||||
| 8 Fe3O4/rGO/GCE | DPV | 0.030–1 | 89 | Pharmaceutical, nutrition products | [23] |
| 1–100 | |||||
| 9 SnO2/RGO/GCE | SWV | 0.1–150 | 34 | Pharmaceutical, energy drink | [24] |
| 10 ZnO/MnHCNF/GCE | DPV | 0.2–3.0 | 0.0101 | Pharmaceutical, milk powder | [25] |
| 11 GO/Au/polyEAmVS/GCE | DPV | 1–100 | 7.2 | Non-alcoholic beverage, energy drink | [26] |
| 12 Bi2WO6(PVP + NaOH)/GCE | DPV | 0.03–457 | 3.65 | Almond milk, soymilk | [27] |
| 13 HGCE | SWV | 0.01–0.07 | 5 | Multivitamin tablets | [28] |
| 0.07–1.0 | |||||
| 14 DNA-PGE | DPV | 1.86–133 | 956.5 | Multivitamin tablets | [29] |
| 15 PPGE | ASDPV | 0.008–2.34 | 0.202 | Multivitamin tablets | [29] |
| 16 Sn/Cs/PGE | SWV | 0.01–1.2 | 5.56 | Tablets, milk powder | [30] |
| 17 PGl/PGE | SWV | 0.02–0.45 | 1.24 | Pharmaceutical, foods | [31] |
| 18 SPE | DPV | 2.66–61.1 | 2390 | Foods | [32] |
| 19 sparked-BiSPEs | SWV | 0.001–0.1 | 0.7 | Pharmaceutical | [33] |
| 20 N-CQD/SnO2/SPCE | DPV | 0.05–306 | 8 | Tablets, milk powder | [34] |
| 21 AgNP-SPE | DPV | 0.0019–0.1 | 0.56 | Pharmaceutical, energy drink | [35] |
| 22 OMC/GCE | CV | 0.4–1.0 | 20 | Vitamin tablets | [36] |
| 23 GC/MWCNTs-MnIIIsalen | DPV | 1.0–400 | 730 | Injection, tablet | [37] |
| 24 Pd-Cu@NSC/SPCE | DPV | 0.004–0.1 | 0.0076 | Tablets, milk powder | [38] |
| 0.02–9.0 | |||||
| 25 Ag/rGO/GCE | DPV | 0.002–2.2 | 0.6 | Pharmaceutical | [39] |
| 26 USPtNPs-DES/MWCNT/GCE | SWV | 0.02–1.2 | 1.8 | Energy drink, biological fluids | [40] |
| 27 PTN/GCE | DPV | 0.01–65 | 3 | Human plasma | [41] |
| 28 PNNMGPE | LSV | 5.0–65.0 | 782 | Tablets | [42] |
| 29 EP(VLN)MGPE | CV | 2.0–40.0 | 286.9 | Pharmaceutical | [43] |
| NiZY/CNHs-GCE | DPV | 0.027–0.53 | 8.6 | Dietary supplements | This work |
| Vitamin | Sample | Amount of VB2 [mg per Tablet] | RE [%] | RSD [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Declared | ± S | ||||
| VB2 | Apteo Witamina B2 | 3 | 2.90 ± 0.06 | −3.3 | 2.1 |
| Panawit Witamina B2 | 10 | 9.38 ± 0.12 | −6.2 | 1.3 | |
| VB9 | Olimp Labs Kwas foliowy | 0.4 | 0.411 ± 0.008 | 2.7 | 1.9 |
| ActiFolin | 0.8 | 0.813 ± 0.003 | 1.6 | 0.4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fendrych, K.; Nyrka, J.; Smajdor, J.; Piech, R.; Baś, B. Nanostructured Ni-Zeolite Y and Carbon Nanohorns Electrode for Sensitive Electrochemical Determination of B-Group Vitamins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110469
Fendrych K, Nyrka J, Smajdor J, Piech R, Baś B. Nanostructured Ni-Zeolite Y and Carbon Nanohorns Electrode for Sensitive Electrochemical Determination of B-Group Vitamins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110469
Chicago/Turabian StyleFendrych, Katarzyna, Justyna Nyrka, Joanna Smajdor, Robert Piech, and Bogusław Baś. 2025. "Nanostructured Ni-Zeolite Y and Carbon Nanohorns Electrode for Sensitive Electrochemical Determination of B-Group Vitamins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110469
APA StyleFendrych, K., Nyrka, J., Smajdor, J., Piech, R., & Baś, B. (2025). Nanostructured Ni-Zeolite Y and Carbon Nanohorns Electrode for Sensitive Electrochemical Determination of B-Group Vitamins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110469









