The Clinical Significance of GRP78 in COVID-19 Pneumonia Across Two Regional Cohorts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| GRP78 | Glucose-regulated protein 78 |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
References
- Lamers, M.M.; Haagmans, B.L. SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonagle, D.; Sharif, K.; O’Regan, A.; Bridgewood, C. The Role of Cytokines including Interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced Pneumonia and Macrophage Activation Syndrome-Like Disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, J.; Zhong, W.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Tan, L.; Ding, L. Gender, age and comorbidities as the main prognostic factors in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 6537. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wu, X.; Pang, B.; Yang, F.; Zheng, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J. Comorbidities and complications of COVID-19 associated with disease severity, progression, and mortality in China with centralized isolation and hospitalization: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 923485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.H.; Tipih, T.; Makoah, N.A.; Vermeulen, J.G.; Goedhals, D.; Sempa, J.B.; Burt, F.J.; Taylor, A.; Mahalingam, S. Comorbidities in SARS-CoV-2 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. mBio 2021, 12, e03647-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzyrenko, A.; Jacobs, E.R.; Sun, Y.; Felix, J.C.; Sheinin, Y.; Ge, L.; Lai, S.; Dai, Q.; Gantner, B.N.; Nanchal, R. Pneumocytes are distinguished by highly elevated expression of the ER stress biomarker GRP78, a co-receptor for SARS-CoV-2, in COVID-19 autopsies. Cell Stress Chaperones 2021, 26, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köseler, A.; Sabirli, R.; Gören, T.; Türkçüer, I.; Kurt, Ö. Endoplasmic reticulum stress markers in SARS-CoV-2 infection and pneumonia: Case-control study. In Vivo 2020, 34, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assal, H.H.; Abdel-hamid, H.M.; Magdy, S.; Salah, M.; Ali, A.; Elkaffas, R.H.; Sabry, I.M. Predictors of severity and mortality in COVID-19 patients. Egypt. J. Bronchol. 2022, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Mittal, S.; Gollapudi, S.; Butzmann, A.; Kumar, J.; Ohgami, R.S. A meta-analysis of SARS-CoV-2 patients identifies the combinatorial significance of D-dimer, C-reactive protein, lymphocyte, and neutrophil values as a predictor of disease severity. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2020, 43, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariyanto, T.I.; Japar, K.V.; Kwenandar, F.; Damay, V.; Siregar, J.I.; Lugito, N.P.H.; Tjiang, M.M.; Kurniawan, A. Inflammatory and hematologic markers as predictors of severe outcomes in COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 41, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerushalmi, R.; Raiter, A.; Nalbandyan, K.; Hardy, B. Cell surface GRP78: A potential marker of good prognosis and response to chemotherapy in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, G.; Castagneto-Gissey, L.; Salinari, S.; Bertuzzi, A.; Anello, D.; Pradhan, M.; Zschätzsch, M.; Ritter, P.; Le Roux, C.W.; Rubino, F.; et al. Upper gut heat shock proteins HSP70 and GRP78 promote insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, E.; Causse, S.; Baverel, V.; Dubrez, L.; Borges-Bonan, N.; Demidov, O.; Garrido, C. Endoplasmic Reticulum Chaperones in Viral Infection: Therapeutic Perspectives. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e00035-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlos, A.J.; Ha, D.P.; Yeh, D.-W.; Van Krieken, R.; Tseng, C.-C.; Zhang, P.; Gill, P.; Machida, K.; Lee, A.S. The chaperone GRP78 is a host auxiliary factor for SARS-CoV-2 and GRP78 depleting antibody blocks viral entry and infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.P.; Shin, W.-J.; Hernandez, J.C.; Neamati, N.; Dubeau, L.; Machida, K.; Lee, A.S. GRP78 Inhibitor YUM70 Suppresses SARS-CoV-2 Viral Entry, Spike Protein Production and Ameliorates Lung Damage. Viruses 2023, 15, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Krad, D.; Stegmann, K.M.; Dickmanns, A.; Kumar, P.; Blaurock, C.; Mohl, B.-P.; Wille, S.J.; Breithaupt, A.; Britzke, T.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; et al. The protease inhibitor Nirmatrelvir synergizes with inhibitors of GRP78 to suppress SARS-CoV-2 replication. Antivir. Res. 2025, 241, 106247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altunok, E.S.; Alkan, M.; Kamat, S.; Demirok, B.; Satici, C.; Demirkol, M.A.; Gursoy, B.; Surmeli, C.D.; Cengel, F.; Calik, M.; et al. Clinical characteristics of adult patients hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 pneumonia. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostadinova, T.; Todorova, T.; Stoykova, Z.; Niyazi, D.; Bozhkova, M.; Bizheva, S.; Stoeva, T. Dynamics of COVID-19 and demographic characteristics as predisposing risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection: A hospital-based, one-center retrospective study. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2021, 35, 1869–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtay, T.; Bahadir, S.; Kabacaoglu, E.; Yetiz, O.; Demirci, M.F.; Genctoy, G. Prognosis of patients hospitalized with a diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia in a tertiary hospital in Turkey. Ann. Saudi. Med. 2021, 41, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.M.; Bai, P.; He, W.; Wu, F.; Liu, X.F.; Han, D.M.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.K. Gender differences in patients with COVID-19: Focus on severity and mortality. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, M.S.; Hung, M. Men and COVID-19: A Pathophysiologic Review. Am. J. Men’s Health 2020, 14, 1557988320954021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corica, B.; Tartaglia, F.; D’Amico, T.; Romiti, G.F.; Cangemi, R. Sex and gender differences in community-acquired pneumonia. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2022, 17, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortolan, A.; Lorenzin, M.; Felicetti, M.; Doria, A.; Ramonda, R. Does gender influence clinical expression and disease outcomes in COVID-19? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligi, D.; Della Franca, C.; Notarte, K.I.; Goldrich, N.; Kavteladze, D.; Henry, B.M.; Mannello, F. Platelet distribution width (PDW) as a significant correlate of COVID-19 infection severity and mortality. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2024, 62, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, A.; Lesichkova, S.; Atanasova, M.; Hristova, J.; Grigorova, V.; Gesheva, N.; Svinarov, D.; Velizarova, M.; Naumova, E. Dynamics of Immunological and Biochemical Markers Depends on the Severity and Time after Symptoms Onset of COVID-19 - Single Centre Analysis. Proc. Bulg. Acad. Sci. 2023, 76, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, V.; Dhaliwal, M.; Sharma, A.; Nair, D.; Kumar, H.M.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Sehgal, I.S.; Choudhary, H.; Panda, N.; Chakrabarti, A.; et al. Serum glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) levels in COVID-19-associated mucormycosis: Results of a case–control study. Mycopathologia 2022, 187, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Llanos, G.; Porras-Perales, Ó.; Escalante, S.; Vázquez-Calero, D.B.; Valiente, L.; Castillo, M.I.; Pérez-Tejeiro, J.M.; Baglietto-Vargas, D.; Becerra, J.; Reguera, J.M.; et al. Cellular stress modulates severity of the inflammatory response in lungs via cell surface BiP. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1054962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabirli, R.; Koseler, A.; Goren, T.; Turkcuer, I.; Kurt, O. High GRP78 levels in COVID-19 infection: A case-control study. Life Sci. 2021, 265, 118781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
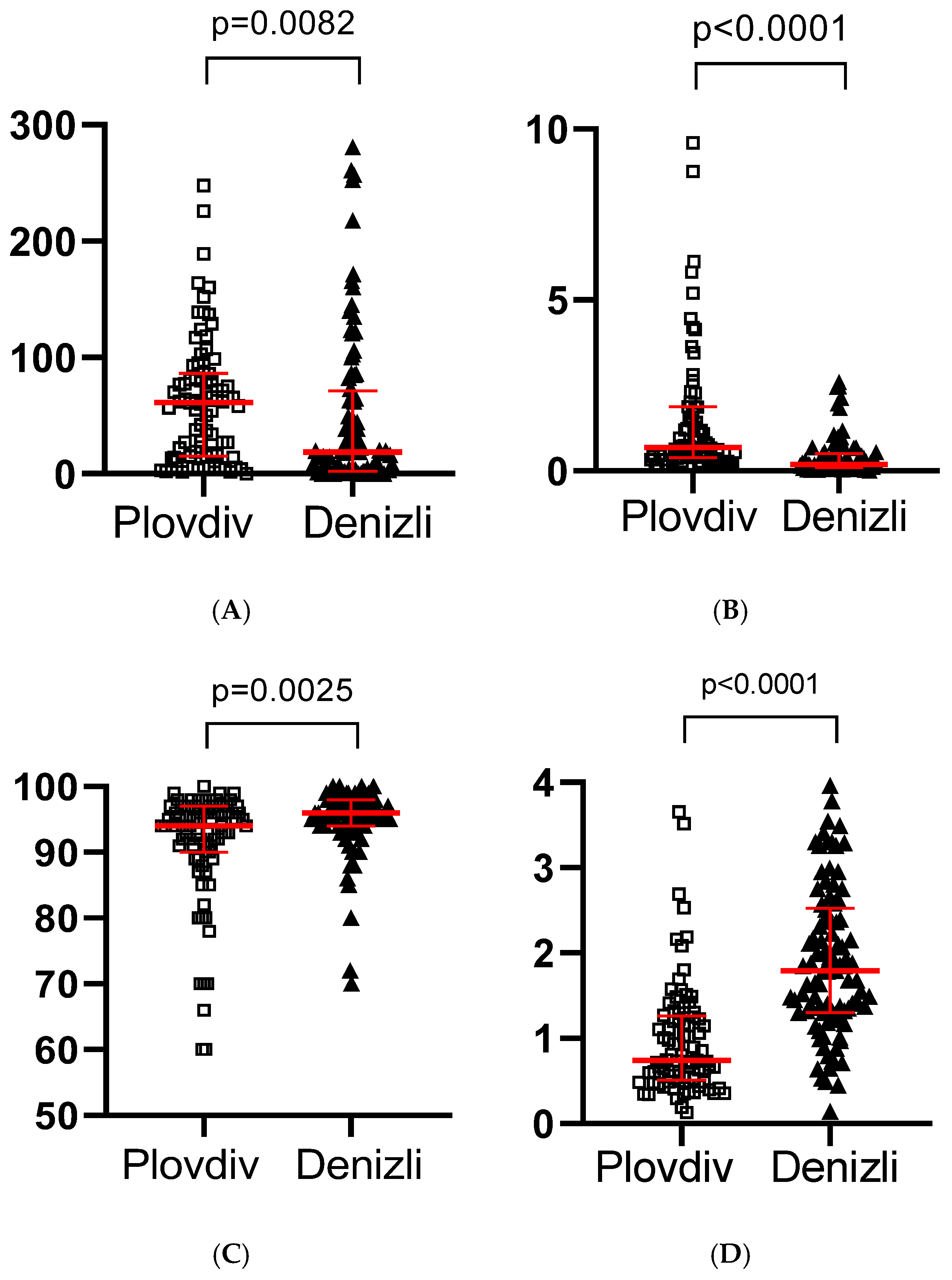
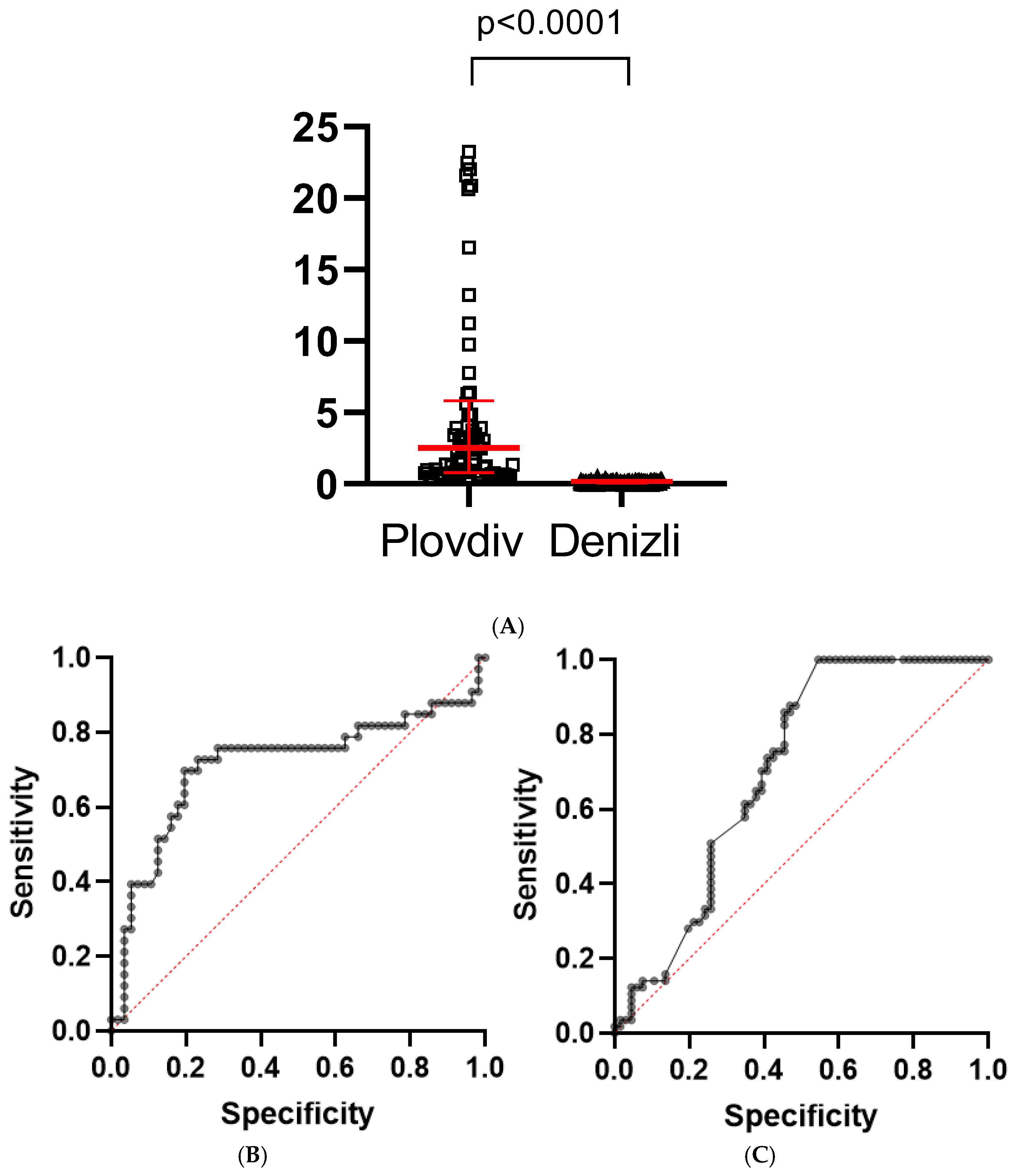

| Column1 | Plovdiv | Denizli | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (N) | 82 | 97 | |
| Males (N, %) | 42 (51.22%) | 58 (59.79%) | 0.2497 |
| Females (N, %) | 40 (48.78%) | 39 (40.20%) | 0.2497 |
| Age (Median, range) | 61 (32–86) | 48 (18–88) | 0.0012 |
| Pneumonia (N, %) | 40 (48.78%) | 57 (58.76%) | 0.1816 |
| Moderate COVID-19 (N, %) | 45 (54.88%) | 73 (75.26%) | 0.0042 |
| Severe COVID-19 (N, %) | 37 (45.12%) | 24 (24.74%) | 0.0042 |
| Hypertension (N, %) | 13 (15.85) | 16 (16.49) | |
| Diabetes mellitus (N, %) | 6 (7.31) | 15 (15.46) |
| Variable | Events per Variable Ratio | Coefficient (β) | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% CI | p-Value of Likelihood Ratio Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 13.3 | −0.0048 | 0.9952 | 0.96–1.032 | 0.797 |
| sex | 13.3 | −0.2345 | 0.791 | 0.277–2.259 | 0.6615 |
| Serum GRP78 levels | 13.3 | 0.0637 | 1.066 | 1.017–1.137 | 0.0055 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrov, S.; Bozhkova, M.; Popova-Belova, S.; Geneva-Popova, M.; Deneva, T.; Türkçüer, İ.; Köseler, A. The Clinical Significance of GRP78 in COVID-19 Pneumonia Across Two Regional Cohorts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110312
Petrov S, Bozhkova M, Popova-Belova S, Geneva-Popova M, Deneva T, Türkçüer İ, Köseler A. The Clinical Significance of GRP78 in COVID-19 Pneumonia Across Two Regional Cohorts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110312
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrov, Steliyan, Martina Bozhkova, Stanislava Popova-Belova, Mariela Geneva-Popova, Tanya Deneva, İbrahim Türkçüer, and Aylin Köseler. 2025. "The Clinical Significance of GRP78 in COVID-19 Pneumonia Across Two Regional Cohorts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110312
APA StylePetrov, S., Bozhkova, M., Popova-Belova, S., Geneva-Popova, M., Deneva, T., Türkçüer, İ., & Köseler, A. (2025). The Clinical Significance of GRP78 in COVID-19 Pneumonia Across Two Regional Cohorts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110312






