microRNAs as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introductions
2. MicroRNAs
3. The Effect of miR in Synovial Cells on Key Cellular Processes Involved in the Pathogenesis of RA
3.1. Dysregulation of Molecular Pathways in Synoviocytes and Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes
3.1.1. NF-κB
3.1.2. Apoptosis and Cell Cycle
3.1.3. PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway
3.1.4. Cytokines
3.1.5. Wnt
3.1.6. Osteogenesis
3.2. Dysregulation of miRs in PBMCs of RA Patients
4. Therapeutic Potential of miRNA in the Treatment of RA
| miRNA | Effect | Comment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-106a-5p, miR-148b-3p and miR-199a-5p, miR-143-5p and miR-346 | Serum levels of miR-106a-5p, miR-148b-3p and miR-199a-5p were decreased whereas serum miR-143-5p and miR-346 levels were increased in patients with RA compared to healthy individuals | RA vs. healthy individuals | [106] |
| miR-223 | miR-223 discriminated RA patients from controls with AUC = 0.85 | RA vs. healthy individuals | [107] |
| miR-146a, miR-155 and miR-16 | miR-223 in treatment naïve ERA correlated with disease activity, while miR-16 and miR-223 are possible predictors for disease outcome in ERA (correlated with DAS28) | Early RA vs. late RA. neither miR-16 nor miR-223 could distinguish ERA from HC | [102] |
| miR-22 | miR-22 is associated with progression from systemic autoimmunity to RA inflammation | Pre-clinical vs. early-stage RA | [108] |
| miR-126-3p, let-7d-5p, miR-431-3p, miR-221-3p, miR-24-3p, miR-130a-3p, miR-339-5p, let-7i-5p, and miR-17-5p | miR-126-3p, let-7d-5p, miR-431-3p, miR-221-3p, miR-24-3p, miR-130a-3p, miR-339-5p, let-7i-5p were significantly elevated in RA serum compared to HC (all p < 0.01) and 1 miRNA (miR-17-5p) was significantly lower in RA | RA patients vs. healthy controls | [109] |
| miR-103a-3p, miR-155, miR-146a-5p, miR-26b-3p, miR-346 | miR-103a-3p, miR-155, miR-146a-5p, and miR-26b-3p was significantly upregulated, whereas miR-346 was significantly downregulated in RA patients in comparison with healthy controls | RA patients, first-degree relatives, and healthy controls | [84] |
| miR-15a-5p, miR-24-3p, miR-26a-5p, miR-125a-5p, miR-146a-5p, miR-155-5p, and miR-223-3p | miR-15a-5p, miR-24-3p, miR-26a-5p, miR-125a-5p, miR-146a-5p, miR-155-5p, and miR-223-3p were significantly increased in patients with RA. The highest accuracy for diagnosis of RA was identified for the combination of miR-24-3p, miR-26a-5p, and miR-125a-5p | RA vs. healthy controls | [103] |
| miR-223-3p, miR-16-5p | miR-223-3p and miR-16-5p, were significantly lower in the sera from early RA patients than in those from established RA patients and healthy controls. miR-16-5p was higher in patients with established RA than in healthy control samples | Early RA vs. long-standing RA vs. healthy controls | [110] |
| miR-4634, miR-181d, miR-4764-5p, miR-342-3p, miR-3926, miR-3925-3p, miR-122-3p, miR-9-5p and miR-219-2-3p | miR-4634, miR-181d and miR-4764-5p expression levels were increased, whereas miR-342-3p, miR-3926, miR-3925-3p, miR-122-3p, miR-9-5p and miR-219-2-3p expression levels were decreased in RA patients vs. controls. miR-4764-5p, miR-4634, miR-9-5p and miR-219-2-3p exhibited significant correlations with either plasma cytokine and chemokine levels or clinical features | RA vs. healthy controls | [111] |
| miR-24, miR-125a-5p | miR-24, miR-125a-5p, were higher in patients with RA, ACPA-negative | RA vs. healthy controls vs. OA/SLE | [112] |
| miR-132, miR-16, miR-146a | miR-132 was higher in HCs and differentiated them from patients with RA or OA. miR-16 and miR-146a concentration correlated with disease activity | RA vs. OA vs. healthy controls | [113] |
| miR-210, miR-155 | MiR-210 was lower in RA compared to controls correlated inversely with disease activity and laboratory variables. MiR-155 expression was increased in RA compared and correlated with laboratory values of cytokines | RA vs. healthy controls | [12] |
| Target | Agent (Mimic/Inhibitor) | Model | Delivery System & Route/Dose | Efficacy | Safety | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-15a | Mimic | Auto-antibody arthritis mice | Double-stranded miR-15a-atellocollagen complex intraarticular injection | Induction of apoptosis by silencing the expression of Bcl-2 | Potential off-target risk in the liver | [104] |
| miR-140-3p | Mimic | Collagen-induced arthritis and collagen antibody-induced arthritis mice | Lentiviral-mediated transfection of pre-miR-140 precursor molecules | Increased cell apoptosis, reduced proliferation and migration rate and production of cytokines through reduction of Sirtuin 1 expression. Lower clinical arthritis scores. | Late injections fail to achieve therapeutic responses | [47] |
| miR-140-5p | Mimic | Collagen-induced arthritis and collagen antibody-induced arthritis mice | Lentiviral-mediated transfection of pre-miR-140 precursor molecules | Increased cell apoptosis, reduced proliferation and migration rate and production of cytokines. Lower clinical arthritis scores. | Late injections fail to achieve therapeutic responses | [47] |
| miR-150-5p exosomes | Mimic | Collagen-induced arthritis mice | Mesenchymal stem cell -derived miR-150-5p exosomes | Decreased migration and invasion in RA FLS. Reduced joint destruction by inhibiting synoviocyte hyperplasia and angiogenesis. Lower clinical arthritis scores. | No safety profile data | [114] |
| miR-26a | Mimic | Pristane induced arthritis rats | Intraperitoneal administration of miR-26a mimic | Results in decreased cytokine expression and ameliorates the disease severity assessed by arthritis severity scores | Potential off-target risk in the spleen | [115] |
| miR-223 | Inhibitor | Collagen-induced arthritis mice | Intraperitoneal injection of lentiviral vectors expressing miR-223 target sequence | Treatment reduced the arthritis score and less severe bone erosion in histopathologic slides | Widespread biodistribution of the vector. No histopathological assessment of off-target activity was performed | [116] |
| miR-106b | Inhibitor | Collagen-induced arthritis mice | Orbital injection with lentiviral-mediated miR-106b inhibitor | decreased arthritis incidence and attenuated bone destruction and histological severity | No safety profile data | [117] |
| miR-34a | Inhibitor | Collagen-induced arthritis mice | Intravenous treatment with chemically modified miR-34a inhibitor | Decreased arthritis scores, alleviation of joint swelling, suppressed bone loss | Low tissue selectivity of miR-34a | [101] |
| miR-708-5p | Mimic | Collagen-induced arthritis rat | Intravenous injection of miR-708-5p mimics | Restoration of miR-708-5p levels improves arthritis index | No safety profile data | [102] |
| miR-146a | Mimic | Collagen-induced arthritis mice | Intravenous injection of miR-146a | Administration of miR-146a partly prevented joint destruction (histological evidence). No differences in joint swelling. | Potential for off-target adverse effects in liver, spleen, and kidney | [118] |
| miR-141-3p | Mimic | Collagen-induced arthritis rats | Intra-articular injection of miR-141-3p mimic | miR-141-3p injection results in lower arthritis scores and reduced ankle joint swelling | miR-141-3p was expressed in target tissue 7 days post-injection. | [105] |
| miR-124 | Mimic | Adjuvant-induced arthritis rats | Intra-articular injection of precursor miR-124 | miR-124 suppressed arthritis, as demonstrated by decreased arthritis score and histopathological assessment | Evidence of systemic distribution | [119] |
5. miRs as Diagnostic Tools and Predictors of Disease Course
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S. Diagnosis and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review. JAMA 2018, 320, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, H.M.; Therneau, T.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Is the incidence of rheumatoid arthritis rising?: Results from Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1955–2007. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.E. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2001, 27, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038, Erratum in Lancet 2016, 388, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581, Erratum in Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Fu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liang, C. Promising Therapeutic Targets for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 686155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylenko, D.S.; Nemtsova, M.V.; Bure, I.V.; Kuznetsova, E.B.; Alekseeva, E.A.; Tarasov, V.V.; Lukashev, A.N.; Beloukhova, M.I.; Deviatkin, A.A.; Zamyatnin, A.A., Jr. Genetic Polymorphisms Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Development and Antirheumatic Therapy Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnowski, M.; Paradowska-Gorycka, A.; Dąbrowska-Zamojcin, E.; Czerewaty, M.; Słuczanowska-Głąbowska, S.; Pawlik, A. The effect of gene polymorphisms on patient responses to rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2016, 12, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelatos, G.; Fragoulis, G.E.; Koulouri, V.; Lambrou, G.I. MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: From pathogenesis to clinical impact. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Ge, G.; Peng, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Bai, J.; Geng, D. Comprehensive overview of microRNA function in rheumatoid arthritis. Bone Res. 2023, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Maksoud, R.S.; Sediq, A.M.; Kattaia, A.; Elsayed, W.; Ezzeldin, N.; Abdel Galil, S.M.; Ibrahem, R.A. Serum miR-210 and miR-155 expression levels as novel biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 74, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.X.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Kitai, H.; Suzuki, H.I. Network Regulation of microRNA Biogenesis and Target Interaction. Cells 2023, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhai, H.; Zhao, M. MicroRNAs regulate immune system via multiple targets. Discov. Med. 2014, 18, 237–247. [Google Scholar]
- Rouas, R.; Fayyad-Kazan, H.; El Zein, N.; Lewalle, P.; Rothé, F.; Simion, A.; Akl, H.; Mourtada, M.; El Rifai, M.; Burny, A.; et al. Human natural Treg microRNA signature: Role of microRNA-31 and microRNA-21 in FOXP3 expression. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafari, P.; Yari, K.; Mostafaei, S.; Iranshahi, N.; Assar, S.; Fekri, A.; Taghadosi, M. Analysis of Helios gene expression and Foxp3 TSDR methylation in the newly diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis patients. Immunol. Investig. 2018, 47, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarilyo, G.; La Cava, A. miRNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 144, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wong, S.H.; Shen, J.; Chan, M.T.V.; Wu, W.K.K. The Role of MicroRNAS in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Medicine 2016, 95, e3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Steiner, G. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Koeller, M.; Weisman, M.H.; Emery, P. New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2007, 370, 1861–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaltskan, V.; Firestein, G.S. Targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 67, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ma, D.; Yang, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, G.; Xu, K.; Zhang, L. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: Surface markers and phenotypes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 93, 107392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottini, N.; Firestein, G.S. Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: Passive responders and imprinted aggressors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, N.; Kawakami, A. Recent findings regarding the effects of microRNAs on fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Med. 2019, 42, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, S.; Meier, F.M.; Neumann, E.; Muller-Ladner, U. Role of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xian, P.F.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.X. MicroRNA-21 Promotes Proliferation of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes through Mediation of NF-κB Nuclear Translocation in a Rat Model of Collagen-Induced Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9279078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkmann, M.; Brock, M.; Gay, R.E.; Michel, B.A.; Gay, S.; Huber, L.C. Tumor necrosis factor α-induced microRNA-18a activates rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts through a feedback loop in NF-κB signaling. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, N.; Gu, J.; Huang, T.; Zhang, C.; Shu, Z.; Li, M.; Hao, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; et al. A novel NF-κB/YY1/microRNA-10a regulatory circuit in fibroblast-like synoviocytes regulates inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, N.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, C.; Xu, J.; Geng, M.; Wu, X.; Hussain, S.; Wang, B.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Li, Y.; et al. Down-regulation of miR-10a-5p promotes proliferation and restricts apoptosis via targeting T-box transcription factor 5 in inflamed synoviocytes. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederer, F.; Trenkmann, M.; Ospelt, C.; Karouzakis, E.; Neidhart, M.; Stanczyk, J.; Kolling, C.; Gay, R.E.; Detmar, M.; Gay, S.; et al. Down-regulation of microRNA-34a* in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts promotes apoptosis resistance. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Y. miR-143-3p regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting IGF1R and IGFBP5 and regulating the Ras/p38 MAPK signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 3781–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.S.; Chen, S.Y.; Wu, C.L.; Chong, H.E.; Ding, Y.C.; Shiau, A.L.; Wang, C.R. Amelioration of Experimental Autoimmune Arthritis Through Targeting of Synovial Fibroblasts by Intraarticular Delivery of MicroRNAs 140-3p and 140-5p. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yang, Y. Downregulation of microRNA-221 decreases migration and invasion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 2395–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jin, Z.; Lu, X. MicroRNA-192 suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by downregulating caveolin 1. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2017, 432, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangyang, Y.; Yi, L.; Wang, T.; Feng, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, D.; Zheng, X. MiR-199a-3p inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via suppressing retinoblastoma 1. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Ding, H.; Jiang, H.; Bao, N.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, J. miR-338-5p Regulates the Viability, Proliferation, Apoptosis and Migration of Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes by Targeting NFAT5. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, S.; Nakamachi, Y. miR-124a as a key regulator of proliferation and MCP-1 secretion in synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70 (Suppl. 1), i88–i91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.Q.; Wang, W. miR-137 Modulates Human Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Migration by Targeting EZH2. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2022, 32, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, F.; Guo, J. miR-137 decreases proliferation, migration and invasion in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 3312–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablos, J.L.; Santiago, B.; Galindo, M.; Torres, C.; Brehmer, M.T.; Blanco, F.J.; García-Lázaro, F.J. Synoviocyte-derived CXCL12 is displayed on endothelium and induces angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, B.; Calonge, E.; Del Rey, M.J.; Gutierrez-Cañas, I.; Izquierdo, E.; Usategui, A.; Galindo, M.; Alcamí, J.; Pablos, J.L. CXCL12 gene expression is upregulated by hypoxia and growth arrest but not by inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Cytokine 2011, 53, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.L.; Shi, G.R.; Xie, J.; Du, X.Z.; Yang, H. MicroRNA-27a Inhibits Cell Migration and Invasion of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes by Targeting Follistatin-Like Protein 1 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.; Zhu, X.Y.; Xia, Y.F.; Dai, Y.; Wei, Z.F. Tetrandrine inhibits migration and invasion of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes through down-regulating the expressions of Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoA GTPases and activation of the PI3K/Akt and JNK signaling pathways. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 13, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Wu, J.; Deng, J.X.; Zhang, Y.P.; Liang, W.Y.; Jiang, Z.L.; Yu, Q.H.; Li, J. MicroRNA-126 affects rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast proliferation and apoptosis by targeting PIK3R2 and regulating PI3K-AKT signal pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 74217–74226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komai-Koma, M.; Jones, L.; Ogg, G.S.; Xu, D.; Liew, F.Y. TLR2 is expressed on activated T cells as a costimulatory receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3029–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Nascimento, L.; Massari, P.; Wetzler, L.M. The Role of TLR2 in Infection and Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, T.; Veale, D.J.; Gao, W.; Orr, C.; Fearon, U.; Connolly, M. Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) induces migration and invasive mechanisms in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Cai, J.; Cao, X. MiR-19 suppresses fibroblast-like synoviocytes cytokine release by targeting toll like receptor 2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 5512–5518. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collins, A.S.; McCoy, C.E.; Lloyd, A.T.; O’Farrelly, C.; Stevenson, N.J. miR-19a: An effective regulator of SOCS3 and enhancer of JAK-STAT signalling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, L.; Alsaleh, G.; Suffert, G.; Meyer, A.; Georgel, P.; Sibilia, J.; Wachsmann, D.; Pfeffer, S. TLR2 expression is regulated by microRNA miR-19 in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, L.; Alsaleh, G.; Pichot, A.; Ostermann, E.; Zuber, G.; Frisch, B.; Sibilia, J.; Pfeffer, S.; Bahram, S.; Wachsmann, D.; et al. MiR-20a regulates ASK1 expression and TLR4-dependent cytokine release in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldhoen, M. Interleukin 17 is a chief orchestrator of immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwa, M.A.; Emara, A.S.; Youssef, N.; Bayoumy, N.M. Serum concentration of IL-17, IL-23 and TNF-α among patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria: Association with disease activity and autologous serum skin test. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifle, R.; Rothe, T.; Ipseiz, N.; Scherer, H.U.; Culemann, S.; Harre, U.; Ackermann, J.A.; Seefried, M.; Kleyer, A.; Uderhardt, S.; et al. Regulation of autoantibody activity by the IL-23-T(H)17 axis determines the onset of autoimmune disease. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Kong, R.; Zhou, X.; Ji, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, D. Correction to: MiRNA-126 expression inhibits IL-23R mediated TNF-α or IFN-γ production in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in a mice model of collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis. Apoptosis 2019, 24, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, N.; Shibasaki, S.; Karasaki, M.; Iwasaki, T. The Impact of MicroRNA-223-3p on IL-17 Receptor D Expression in Synovial Cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Pan, W.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Shao, X.; Tang, Y.; Liang, D.; He, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; et al. The microRNA miR-23b suppresses IL-17-associated autoimmune inflammation by targeting TAB2, TAB3 and IKK-α. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, M.W.; Roth, S.J.; Luther, E.; Rose, S.S.; Springer, T.A. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 acts as a T-lymphocyte chemoattractant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3652–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamachi, Y.; Kawano, S.; Takenokuchi, M.; Nishimura, K.; Sakai, Y.; Chin, T.; Saura, R.; Kurosaka, M.; Kumagai, S. MicroRNA-124a is a key regulator of proliferation and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 secretion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleh, G.; Suffert, G.; Semaan, N.; Juncker, T.; Frenzel, L.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Sibilia, J.; Pfeffer, S.; Wachsmann, D. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is involved in miR-346-related regulation of IL-18 release by lipopolysaccharide-activated rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5088–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, F.; Schneider, P.; Rennert, P.; Browning, J. BAFF AND APRIL: A tutorial on B cell survival. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 231–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaleh, G.; François, A.; Knapp, A.M.; Schickel, J.N.; Sibilia, J.; Pasquali, J.L.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Wachsmann, D.; Soulas-Sprauel, P. Synovial fibroblasts promote immunoglobulin class switching by a mechanism involving BAFF. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleh, G.; François, A.; Philippe, L.; Gong, Y.Z.; Bahram, S.; Cetin, S.; Pfeffer, S.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Wachsmann, D.; Georgel, P.; et al. MiR-30a-3p negatively regulates BAFF synthesis in systemic sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, J.; Cao, Q.; Xiao, L.; Wang, L.; He, D.; Ouyang, G.; Lin, J.; Shen, B.; Shi, Y.; et al. A critical role of Cyr61 in interleukin-17-dependent proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 3602–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Huo, R.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, X.; Xie, J.; Sun, S.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, Z.; et al. A novel p53/microRNA-22/Cyr61 axis in synovial cells regulates inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, E.H.; Panayi, G.S. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, F.M.; Chantry, D.; Jackson, A.; Maini, R.; Feldmann, M. Inhibitory effect of TNF alpha antibodies on synovial cell interleukin-1 production in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1989, 2, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, K.; Aono, H.; Hasunuma, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Mita, S.; Nishioka, K. Activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B in human synovial cells in response to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Singh, A.K.; Ahmed, S. MicroRNA-17 Suppresses TNF-α Signaling by Interfering with TRAF2 and cIAP2 Association in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 2219–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.K.; You, S.; Yoo, S.A.; Park, D.; Hwang, D.; Cho, C.S.; Kim, W.U. MicroRNA-143 and -145 modulate the phenotype of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.K.; Noss, E.H.; Chen, M.; Gu, Z.; Townsend, K.; Grenha, R.; Leon, L.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, D.M.; Brenner, M.B. Cadherin-11 regulates fibroblast inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8402–8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.Y.; Pan, Y.F.; Guo, X.H.; Wu, Y.Q.; Gu, J.R.; Cai, D.Z. Expression of β-catenin in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 40, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Ladner, U.; Kriegsmann, J.; Franklin, B.N.; Matsumoto, S.; Geiler, T.; Gay, R.E.; Gay, S. Synovial fibroblasts of patients with rheumatoid arthritis attach to and invade normal human cartilage when engrafted into SCID mice. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 149, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Pandis, I.; Ospelt, C.; Karagianni, N.; Denis, M.C.; Reczko, M.; Camps, C.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G.; Ragoussis, J.; Gay, S.; Kollias, G. Identification of microRNA-221/222 and microRNA-323-3p association with rheumatoid arthritis via predictions using the human tumour necrosis factor transgenic mouse model. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.G.; Qin, D.; Du, C.L.; Ye, H.; Shi, W.J.; Xiong, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Yu, H.; Dou, J.F.; Ma, S.T.; et al. DNMT1 activates the canonical Wnt signaling in rheumatoid arthritis model rats via a crucial functional crosstalk between miR-152 and the DNMT1, MeCP2. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanczyk, J.; Ospelt, C.; Gay, R.E.; Gay, S. Synovial cell activation. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2006, 18, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Ryu, C.J.; Choi, H.M.; Park, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.I.; Yang, H.I.; Yoo, M.C.; Kim, K.S. Effects of the pro-inflammatory milieu on the dedifferentiation of cultured fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, N.; Fukui, S.; Takatani, A.; Shimizu, T.; Umeda, M.; Nishino, A.; Igawa, T.; Koga, T.; Kawashiri, S.Y.; Ichinose, K.; et al. Osteogenic differentiation of fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis is induced by microRNA-218 through a ROBO/Slit pathway. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Farina, N.H.; Matzelle, M.M.; Fanning, P.J.; Lian, J.B.; Gravallese, E.M. Synovium-Derived MicroRNAs Regulate Bone Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaparti, V.; Smolik, I.; Meng, X.; Spicer, V.; Mookherjee, N.; El-Gabalawy, H. Whole blood microRNA expression pattern differentiates patients with rheumatoid arthritis, their seropositive first-degree relatives, and healthy unrelated control subjects. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauley, K.M.; Satoh, M.; Chan, A.L.; Bubb, M.R.; Reeves, W.H.; Chan, E.K. Upregulated miR-146a expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo ElAtta, A.S.; Ali, Y.B.M.; Bassyouni, I.H.; Talaat, R.M. Upregulation of miR-221/222 expression in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients: Correlation with disease activity. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 19, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruskova, V.; Jandova, R.; Vernerova, L.; Mann, H.; Pecha, O.; Prajzlerova, K.; Pavelka, K.; Vencovsky, J.; Filkova, M.; Senolt, L. MicroRNA-125b: Association with disease activity and the treatment response of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, N.S.; Yu, H.C.; Yu, C.L.; Koo, M.; Huang, H.B.; Lu, M.C. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies suppress let-7a expression in monocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and facilitate the inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, F.; Wang, F. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated microRNA-155 targets SOCS1 and upregulates TNF-α and IL-1β in PBMCs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 23910–23921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; Yu, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, R.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhou, B.; et al. Upregulated microRNA-155 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 296139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, S.E.; Hammaker, D.; Boyle, D.L.; Firestein, G.S. Regulation of c-Jun phosphorylation by the I kappa B kinase-epsilon complex in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6424–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, F.; Gao, G.; Yan, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Cai, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, J. MiR-548a-3p regulates inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Yin, K.; Zhu, H.; Tian, J.; Shen, D.; Yi, L.; Rui, K.; Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, S. Correlation Between the Expression of MicroRNA-301a-3p and the Proportion of Th17 Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammation 2016, 39, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Wang, X.; Tan, J.; Li, H.; Qian, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Tao, C.; et al. Decreased expression of microRNA-21 correlates with the imbalance of Th17 and Treg cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 2213–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, G.; Mao, H.; Qiu, Y. MicroRNA-26b inhibits cell proliferation and cytokine secretion in human RASF cells via the Wnt/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.; Yang, F.; Lei, H.; Liu, X.; Yan, M.; Huang, H.; Fan, X.; Li, Y. Inhibition of microRNA-34a ameliorates murine collagen-induced arthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 1633–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Fan, W.; Ma, L.; Geng, X. miR-708-5p promotes fibroblast-like synoviocytes’ cell apoptosis and ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis by the inhibition of Wnt3a/β-catenin pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 3439–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Csak, T.; Momen-Heravi, F.; Lippai, D.; Kodys, K.; Catalano, D.; Satishchandran, A.; Ambros, V.; Szabo, G. Biodistribution and function of extracellular miRNA-155 in mice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, Y.; Nakasa, T.; Mochizuki, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; Miyaki, S.; Shibuya, H.; Yamasaki, K.; Adachi, N.; Asahara, H.; Ochi, M. Induction of apoptosis in the synovium of mice with autoantibody-mediated arthritis by the intraarticular injection of double-stranded MicroRNA-15a. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2677–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chang, J.; Lu, M.; Gao, W.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Yin, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Identification of a novel microRNA-141-3p/Forkhead box C1/β-catenin axis associated with rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast function in vivo and in vitro. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5412–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, S.S.; Li, J.; Tao, S.S.; Wang, M.; Leng, R.X.; Pan, H.F.; Ye, D.Q. miR-210 expression in PBMCs from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 187, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filková, M.; Aradi, B.; Senolt, L.; Ospelt, C.; Vettori, S.; Mann, H.; Filer, A.; Raza, K.; Buckley, C.D.; Snow, M.; et al. Association of circulating miR-223 and miR-16 with disease activity in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormseth, M.J.; Solus, J.F.; Vickers, K.C.; Oeser, A.M.; Raggi, P.; Stein, C.M. Utility of Select Plasma MicroRNA for Disease and Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Shen, W.W.; Sun, Y.Y.; Li, W.X.; Sun, Z.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, L.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.M.; Li, J. MicroRNA-20a negatively regulates expression of NLRP3-inflammasome by targeting TXNIP in adjuvant-induced arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Jt. Bone Spine 2016, 83, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.R.; Wang, W.Y.; Fu, J.; Deng, R.; Li, F.; Dai, X.J.; Zhan, X. Novel anti-inflammatory target of geniposide: Inhibiting Itgβ1/Ras-Erk1/2 signal pathway via the miRNA-124a in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 65, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque-Tévar, M.; Perez-Sanchez, C.; Patiño-Trives, A.M.; Barbarroja, N.; Arias de la Rosa, I.; Abalos-Aguilera, M.C.; Marin-Sanz, J.A.; Ruiz-Vilchez, D.; Ortega-Castro, R.; Font, P.; et al. Integrative Clinical, Molecular, and Computational Analysis Identify Novel Biomarkers and Differential Profiles of Anti-TNF Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 631662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.; Shaker, O.G.; Abdelsalam, E.; Taha, N. Serum a proliferation-inducing ligand and MicroRNA-223 are associated with rheumatoid arthritis: Diagnostic and prognostic implications. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouboussad, L.; Hunt, L.; Hensor, E.M.A.; Nam, J.L.; Barnes, N.A.; Emery, P.; McDermott, M.F.; Buch, M.H. Profiling microRNAs in individuals at risk of progression to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.C.; Wade, S.; Floudas, A.; Orr, C.; McGarry, T.; Cregan, S.; Fearon, U.; Veale, D.J. Serum miRNA Signature in Rheumatoid Arthritis and “At-Risk Individuals”. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 633201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunaeva, M.; Blom, J.; Thurlings, R.; Pruijn, G.J.M. Circulating serum miR-223-3p and miR-16-5p as possible biomarkers of early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 193, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Duan, T.; Xu, Q.; Wang, R.; Lu, L.; Jiao, Z. Plasma microRNA expression profiles in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 42557–42568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, K.; Furu, M.; Yoshitomi, H.; Ishikawa, M.; Shibuya, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Imura, Y.; Fujii, T.; Ito, H.; Mimori, T.; et al. Comprehensive microRNA analysis identifies miR-24 and miR-125a-5p as plasma biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, K.; Yoshitomi, H.; Tanida, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Nishitani, K.; Ito, H.; Nakamura, T. Plasma and synovial fluid microRNAs as potential biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhou, X.L.; Kong, R.N.; Ji, L.M.; He, L.L.; Zhao, D.B. microRNA-126 targeting PIK3R2 promotes rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibro-blasts proliferation and resistance to apoptosis by regulating PI3K/AKT pathway. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2016, 100, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasa, T.; Miyaki, S.; Okubo, A.; Hashimoto, M.; Nishida, K.; Ochi, M.; Asahara, H. Expression of microRNA-146 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.G.; Yang, Y.Y.; He, X.; Huang, C.; Huang, Y.; Qin, D.; Du, C.L.; Li, J. MicroRNA-152 modulates the canonical Wnt pathway activation by targeting DNA methyltransferase 1 in arthritic rat model. Biochimie 2014, 106, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Xia, Y.; Yan, F.; Lu, Y. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Cell-Derived miRNA-150-5p-Expressing Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mediated by the Modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2472–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhu, W.; Xu, J.; Wang, B.; Hou, W.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, N.; Ning, Q.; Han, Y.; Yu, H.; et al. MicroRNA-26a negatively regulates toll-like receptor 3 expression of rat macrophages and ameliorates pristane induced arthritis in rats. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Chen, S.Y.; Wang, C.R.; Liu, M.F.; Lin, C.C.; Jou, I.M.; Shiau, A.L.; Wu, C.L. Brief report: Amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis in mice by lentivirus-mediated silencing of microRNA-223. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3240–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Shi, J.; Guo, X.; Zhou, W.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, H.; et al. Downregulation of miR-106b attenuates inflammatory responses and joint damage in collagen-induced arthritis. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1804–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasa, T.; Shibuya, H.; Nagata, Y.; Niimoto, T.; Ochi, M. The inhibitory effect of microRNA-146a expression on bone destruction in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamachi, Y.; Ohnuma, K.; Uto, K.; Noguchi, Y.; Saegusa, J.; Kawano, S. MicroRNA-124 inhibits the progression of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

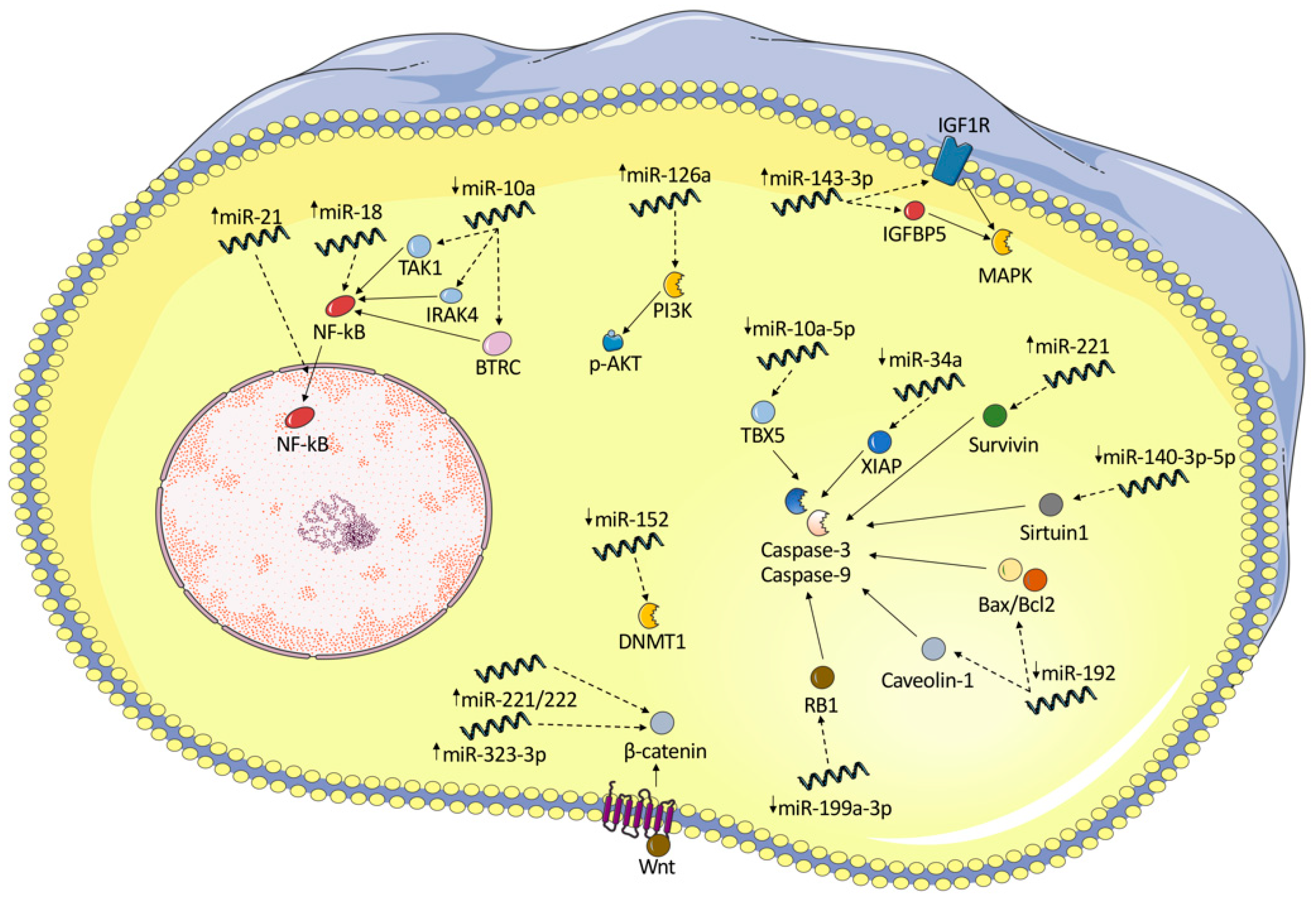
| miRNA | Up/Down | Evidence Type | Compartment | Affected Molecular Pathway | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-20a | Down | In vitro | FLS | ASK1/IL-6 | Associated with overexpression of ASK1 and subsequent release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6) | [25] |
| miR-30a-3p | Down | In vitro | Fibroblasts | BAFF | Strong decrease in BAFF synthesis and release, and thus B cell survival | [26] |
| miR-23b | Down | In vitro and animal model | FLS | IL-17 | Under normal conditions, miR-23b represses autoimmune inflammation. IL-17 downregulates miR-23b | [27] |
| miR-10a-5p | Down | In vitro | Synoviocytes | TBX-5 | Promotes proliferation and restricts apoptosis | [28] |
| miR-10a | Down | Human | FLS | NF-κB activation by targeting IRAK4, TAK1, and BTRC | promotes the excessive secretion of NF-κB-mediated inflammatory cytokines and the proliferation and migration of RA FLSs | [29] |
| miR-17 | Down | Animal | FLS | TRAF2, cIAP1, cIAP2, USP2, and PSMD13 | miR-17 acts as a negative regulator of TNF-α signaling | [30] |
| miR-18a | Up | Human | Synovial fibroblasts | TNFAIP-3 | Positive feedback loop in NF-κB signaling | [31] |
| miR-19 | Down | Human | FLS | TLR2 | increased TLR2 expression and enhanced cytokine release | [32] |
| miR-19b | Down | Human and in vitro | FLS | TLR2 | Controls TLR2 expression, miR-19b can act as negative regulator of inflammation | [33] |
| miR-20a | Down | In vitro | FLS | NLPR3 | Downregulation of miR-20a increases the expression of NLRP3-inflammasome and the secretion of IL-1β and MMP-1 | [34] |
| miR-22 | Down | Human | FLS | Cyr61 | P53 mediates overexpression of Cyr61 via miR-22, leading to joint inflammation | [35] |
| miR-27a | Down | Human | FLS | FSTL1 | Downregulation of miR-27a promotes cell migration and invasion of RA-FLS by targeting FSTL1 and upregulating the TLR4/NFκB pathway | [36] |
| miR-21 | Up | Animal | FLS | NF-κB | miR-21 overexpression results in increased NF-κB levels and cell proliferation rates | [37] |
| miR-34a | Down | Human | Synovial fibroblasts | XIAP | Decreased rate of FasL- and TRAIL-mediated apoptosis | [38] |
| miR-124a | Down | Human | Synoviocytes | CDK-2, MCP-1 | Induces cell proliferation through overexpression of CDK-2 and MCP-1 proteins | [39] |
| miR-124a | Down | Human | Synoviocytes | CDK-2, MCP-1 | Overexpression of CDK-2 and MCP-1 proteins | [40] |
| miR-124a | Down | In vitro | FLS | Itgβ1 | TNF-α-stimulated cell proliferation and activation of the Ras-Erk1/2 pathway | [41] |
| miR-126 | Down | Animal | FLS | TNF, IFN, IL-23R | TNF-α and IFN-γ production and IL-23R expression were significantly upregulated | [42] |
| miR-126 | Up | Human | RASF | PIK3R2 | Stimulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway, reduced apoptosis | [43] |
| miR-143 | Up | Human | FLS | IGFBP5 | Renders synoviocytes susceptible to TNF-α and VEGF165 stimuli | [44] |
| miR-145 | Up | Human | FLS | SEMA3A | Renders synoviocytes susceptible to TNF-α and VEGF165 stimuli | [44] |
| miR-137 | Down | Animal | FLS | CXCL12 | Increased proliferation, migration, and invasion, and expression of inflammatory cytokines | [45] |
| miR-143-3p | Up | Human and in vitro | Synovium | IGF1R, IGFBP5 | Regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by regulating the Ras/p38 MAPK signaling | [46] |
| miR-140 | Down | Human and animal | Synovial fibroblasts | Sirtuin1, SCDF1 | Decreased apoptosis, increased proliferation, and cell migration | [47] |
| miR-146a | Up | Human | Synovial tissue | Unknown | Unknown | [48] |
| miR-323-3p | Up | Animal | Synovial fibroblasts | Wnt/cadherin | enhances Wnt pathway activation and decreases the levels of its predicted target | [49] |
| miR-152 | Down | Animal | FLS | DNMT1, SFRP1, SFRP4 | Promotes the canonical Wnt signaling | [50,51] |
| miR-192 | Down | Human and in vitro | FLS | CAV1 | Increases cell proliferation and decreases apoptosis—decrease in caspase-3 activity and altered Bax/Bcl-2 ratio | [52] |
| miR-199a-3p | Down | In vitro | FLS | RB1 | Attenuation of apoptosis, decrease in caspase-3 activity and Bax/Bcl-2 ratio | [53] |
| miR-218-5p | Up/down | Human | FLS | ROBO1 | Promotes osteogenic differentiation of FLS | [54] |
| miR-221 | Up | Animal | Mouse synovial samples | Wnt, BMP | Promotes compensatory bone formation | [55] |
| miR-221 | Up | Human | FLS | MMP-3, MMP-9, survivin, XIAP | Promotes the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, increases FLS cell migration and invasion. Inhibits apoptosis | [56] |
| miR-223-3p | Up | Animal | Synovial cells | IL-17RD | downregulates the expression of IL-17RD and upregulates that of IL-6 in synovial cells | [57] |
| miR-338-5p | Up | Human | RAFLS | NFAT5 | promotes RAFLS’s viability and proliferation, migration by targeting NFAT5 | [58] |
| miR-346 | Up | Human | FLS | BTK | Modulates the inflammatory response | [59] |
| miRNA | Up/Down | Evidence Type | Compartment | Pathway | Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Let-7a | Down | Human | PBMCs | JNK, ERK1/2 | Increased expression of IL-1β | [60] |
| miR-146a | Up | Human | PBMCs | TRAF6, IRAK1 | Production of pro-inflammatory cytokines—IL-1 and TNF-α | [61] |
| miR-155 | Up | Human | PBMCs | Unknown | Production of pro-inflammatory cytokines—IL-1 and TNF-α | [61] |
| miR-132, | Up | Human | PBMCs | Unknown | Production of pro-inflammatory cytokines—IL-1 and TNF-α | [61] |
| miR-16 | Up | Human | PBMCs | Unknown | Production of pro-inflammatory cytokines—IL-1 and TNF-α | [61] |
| miR-155 | Up | Human | PBMCs | SOCS1 | Increased cytokine production | [62] |
| miR-155 | Up | Human | PBMCs | IKBKE | Attenuates inflammation | [63] |
| miR-301a-3p | Up | Human | PBMCs | PIAS3 | Positively correlates with Th17 frequency | [64] |
| miR-21 | Down | Human | PBMCs | STAT3, STAT5, Foxp3 | Dysregulation of Th17/Treg balance through feedback loop | [65] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Machaj, F.; Chmielewska-Jeznach, M.; Koryszewska-Bagińska, A.; Malinowski, D.; Pawlik, A.; Olędzka, G. microRNAs as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209950
Machaj F, Chmielewska-Jeznach M, Koryszewska-Bagińska A, Malinowski D, Pawlik A, Olędzka G. microRNAs as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209950
Chicago/Turabian StyleMachaj, Filip, Magdalena Chmielewska-Jeznach, Anna Koryszewska-Bagińska, Damian Malinowski, Andrzej Pawlik, and Gabriela Olędzka. 2025. "microRNAs as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Rheumatoid Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209950
APA StyleMachaj, F., Chmielewska-Jeznach, M., Koryszewska-Bagińska, A., Malinowski, D., Pawlik, A., & Olędzka, G. (2025). microRNAs as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209950






