Functional Roles of the Complement Immune System in Cardiac Inflammation and Hypertrophy
Abstract
1. Introduction
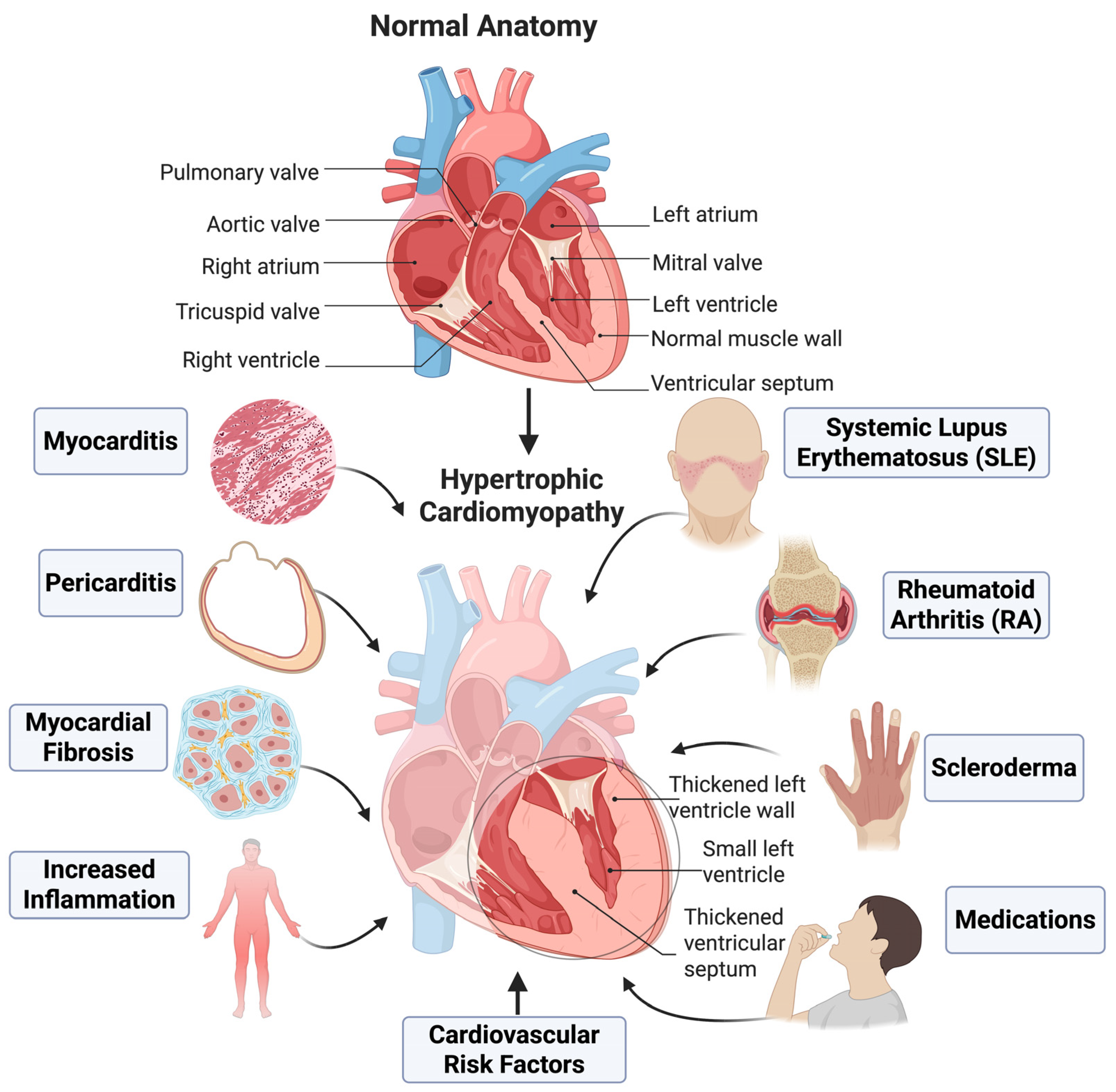
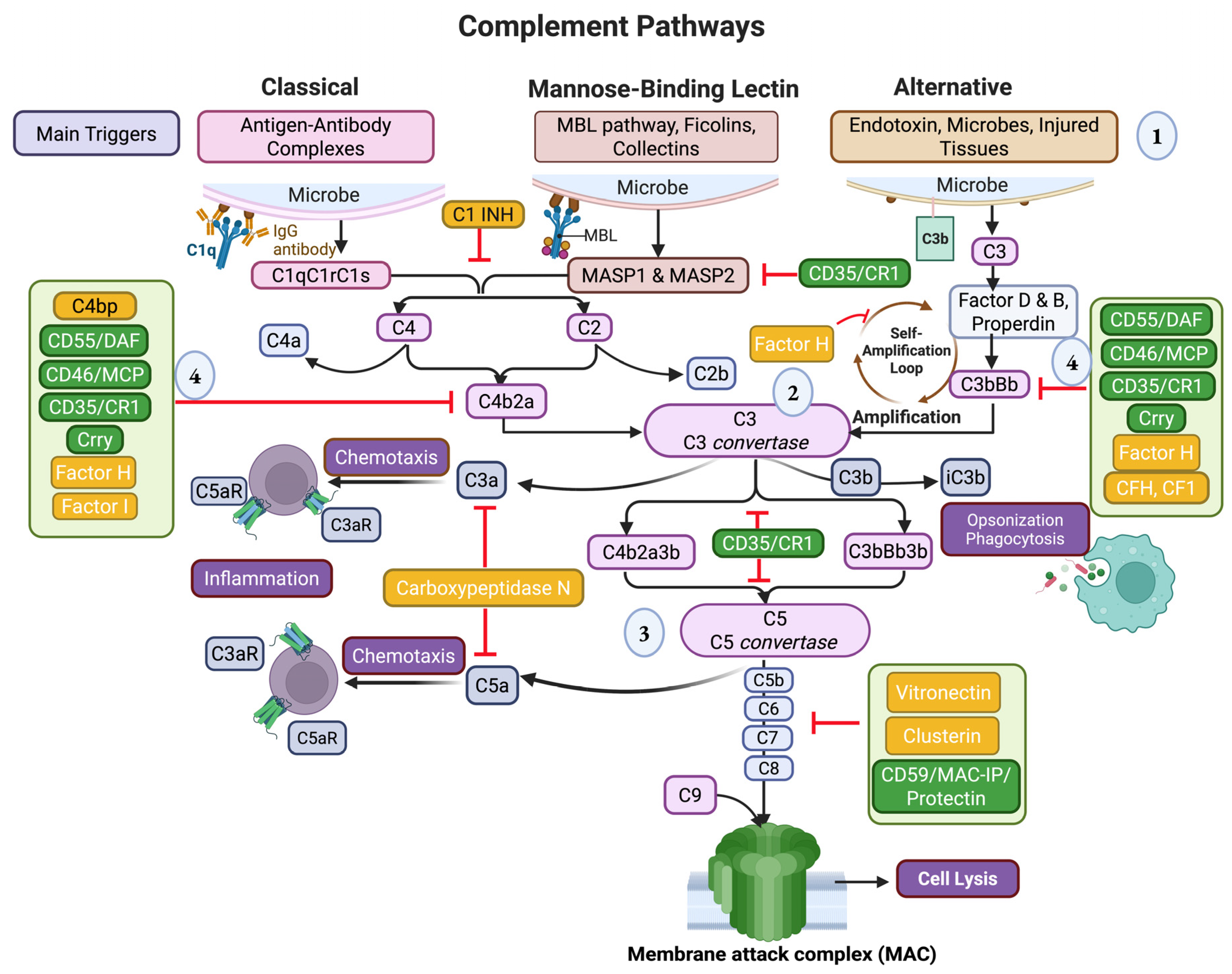
2. The Role of Complement Factors in Cardiac Inflammation and Hypertrophy
2.1. Classical Pathway
2.2. Lectin Pathway
2.3. Converging Point: C3
2.4. Alternative Pathway
2.5. Membrane Attack Complex
3. Regulators of Complement Activation
3.1. Soluble Regulators
3.2. Membrane-Bound Regulators
4. Genetic Variations in Complement Genes and Cardiac Consequences
4.1. Complement Component 2
4.2. Complement Factor H
4.3. Collectin-11 and MBL-Associated Serine Proteases (MASPs)
4.4. C5a Receptor 1
4.5. Genetic Dysregulation Affecting the Alternative Pathway in Cardiovascular Diseases
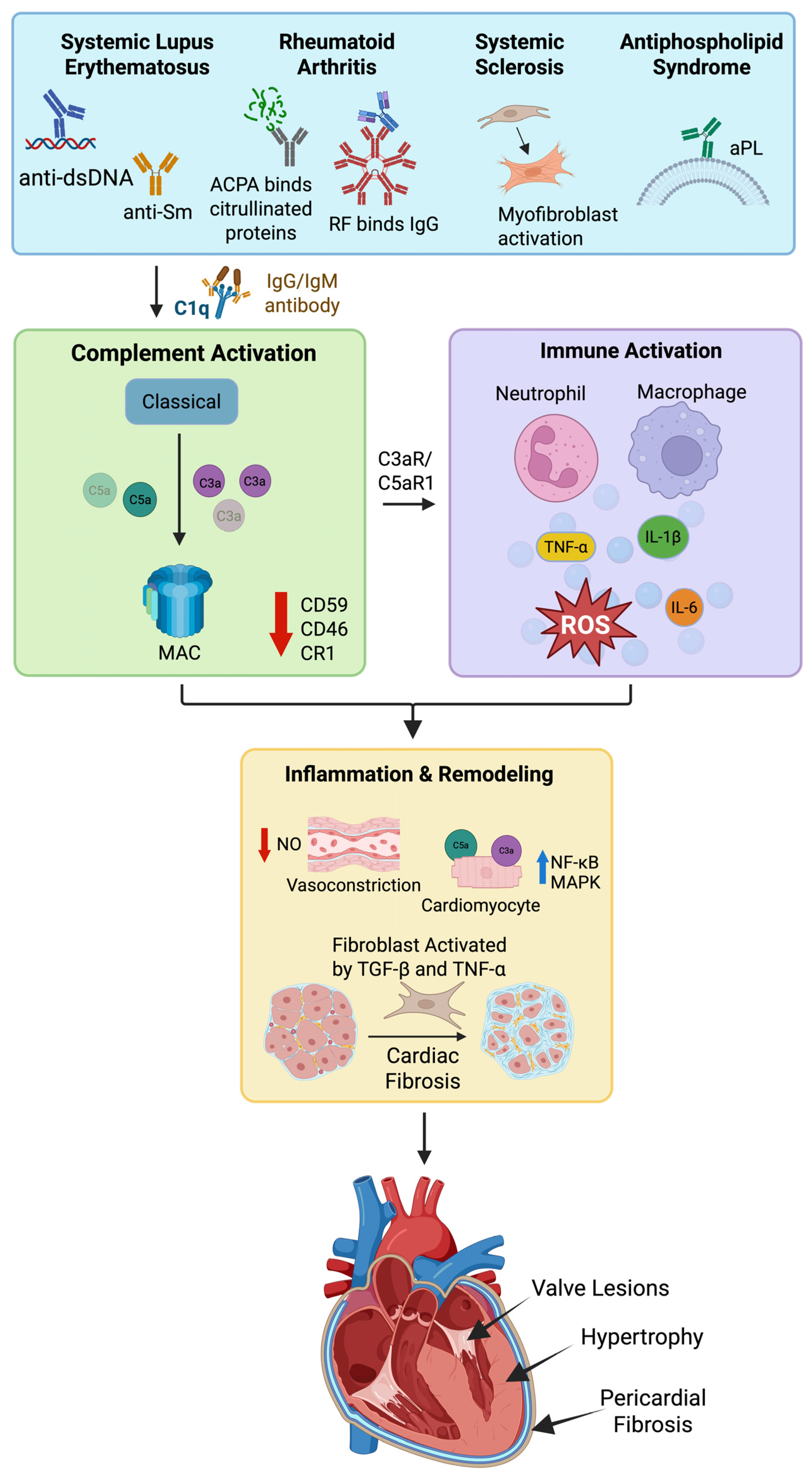
5. Autoimmune Diseases, Complement Activation, and Cardiac Consequences
5.1. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
5.2. Systemic Sclerosis
5.3. Rheumatoid Arthritis
5.4. Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome
6. Infectious Diseases, Complement Activation, and Cardiac Consequences
6.1. Rheumatic Heart Disease
6.2. Infective Endocarditis
6.3. Coxsackie B Virus
6.4. Chagas Disease
6.5. Septic Cardiomyopathy
7. Noninfectious Diseases, Complement Activation, and Cardiac Consequences
7.1. Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus
7.2. Dyslipidemias
7.3. Systemic Hypertension
7.4. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
7.5. Myocardial Infarction, Ischemia, and Reperfusion
7.6. Crosstalk Between Coagulation Cascade and Complement in Cardiovascular Events
8. Treatments and Clinical Trials for Cardiac Inflammation and Hypertrophy
| No. | Study Title | Conditions | Interventions | Clinical Trial Number | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pexelizumab in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting with cardiopulmonary bypass (PRIMO-CABG II) | Coronary Artery Bypass | Pexelizumab | NCT00088179 | Completed [215] |
| 2 | Effect of Pexelizumab on all-cause mortality and myocardial Infarction in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass | Coronary Artery Bypass | Pexelizumab | NCT00048308 | Completed [216] |
| 3 | Pexelizumab in conjunction with Angioplasty in acute myocardial infarction (APEX-AMI) | Myocardial infarction | Pexelizumab | NCT00091637 | Completed [217] |
| 4 | A study to assess the effect of Avacopan at therapeutic and Supratherapeutic doses on the QT/QTc interval in healthy participants | NA | Avacopan | NCT05988034 | Completed [220] |
| 5 | Safety and Efficacy of TP-10, a complement inhibitor, in adult women undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass surgery | Cardiopulmonary Bypass Surgery | TP-10 | NCT00082121 | Completed [221,222] |
| 6 | Effect of subcutaneous ACTEMRA on inflamed atherosclerotic plaques in patients with rheumatoid arthritis | RA, Atherosclerosis | Tocilizumab | NCT02659150 | Terminated [223,224] |
| 7 | Efficacy study of p38 kinase inhibitor to treat patients with atherosclerosis | Atherosclerosis | BMS-582949 | NCT00570752 | Completed [227,228] |
| 8 | Phase 2 study in vascular inflammation on patients after an acute coronary syndrome event | Acute coronary syndrome | VIA-2291 | NCT00552188 | Completed [233] |
| 9 | Effect of VIA-2291 on atherosclerotic vascular inflammation in patients undergoing elective carotid endarterectomy | Carotid stenosis, Atherosclerosis | VIA-2291 | NCT00352417 | Completed [233] |
| 10 | The stabilization of atherosclerotic plaque by initiation of Darapladib | Atherosclerosis, CAD | Darapladib | NCT00799903 | Completed [237] |
| 11 | A study of how MK-0736 affects arterial plaque | Atherosclerosis, PAD | MK-0736 | NCT00679055 | Terminated [238] |
| 12 | Complement and cardiovascular risk in adolescents (CCRIA) | Cardiovascular Risk | NA | NCT02821104 | Completed [239,240] |
| 13 | The complement lectin pathway after cardiac arrest | Cardiac Arrest | NA | NCT02826057 | Unknown [240] |
| 14 | Vilobelimab therapy for invasively mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 (PANAMO) | Critical COVID-19 | Vilobelimab | NCT04333420 | Completed [243] |
| 15 | Efficacy of the C5aR1 inhibitor avdoralimab (FORCE) | Critical COVID-19 | Avdoralimab | NCT04371367 | Completed [244] |
9. General Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakamura, M.; Sadoshima, J. Mechanisms of physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 387–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazgir, F.; Nau, J.; Nakhaei-Rad, S.; Amin, E.; Wolf, M.J.; Saucerman, J.J.; Lorenz, K.; Ahmadian, M.R. The Microenvironment of the Pathogenesis of Cardiac Hypertrophy. Cells 2023, 12, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M.J. The complement system and innate immunity. In Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease, 5th ed.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dunkelberger, J.R.; Song, W.C. Complement and its role in innate and adaptive immune responses. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monach, P.A. Complement. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyllouriotis, P.; Skyllouriotis-Lazarou, M.; Natter, S.; Steiner, R.; Spitzauer, S.; Kapiotis, S.; Valent, P.; Hirschl, A.M.; Guber, S.E.; Laufer, G.; et al. IgG subclass reactivity to human cardiac myosin in cardiomyopathy patients is indicative of a Th1-like autoimmune disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1999, 115, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, Y.; Marullo, S.; Hoyer, S.; Waagstein, F.; Andersson, B.; Vahlne, A.; Guillet, J.G.; Strosberg, A.D.; Hjalmarson, A.; Hoebeke, J. Mapping of a functional autoimmune epitope on the beta 1-adrenergic receptor in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 1658–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, T.; Bongartz, M.; Dlugonska, H.; Hess, H.; Schmitt, E.; Kolbe, L.; Kolsch, E.; Podlaski, F.J.; Gately, M.K.; Rude, E. Interleukin-12 profoundly up-regulates the synthesis of antigen-specific complement-fixing IgG2a, IgG2b and IgG3 antibody subclasses in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Hoogen, P.; de Jager, S.C.A.; Huibers, M.M.H.; Schoneveld, A.H.; Puspitasari, Y.M.; Valstar, G.B.; Oerlemans, M.; de Weger, R.A.; Doevendans, P.A.; den Ruijter, H.M.; et al. Increased circulating IgG levels, myocardial immune cells and IgG deposits support a role for an immune response in pre- and end-stage heart failure. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7505–7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Cui, W.; Miwa, T.; Sato, S.; Li, H.; Song, W.C.; Du, J. Complement 5a receptor mediates angiotensin II-induced cardiac inflammation and remodeling. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.L. The emerging role of innate immunity in the heart and vascular system: For whom the cell tolls. Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajic, G.; Degn, S.E.; Thiel, S.; Andersen, G.R. Complement activation, regulation, and molecular basis for complement-related diseases. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 2735–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.; McConnell, I.; Gorick, B.; Hughes-Jones, N.C. Antibody-independent activation of the classical pathway of complement by Epstein-Barr virus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1987, 67, 531–536. [Google Scholar]
- Mihlan, M.; Blom, A.M.; Kupreishvili, K.; Lauer, N.; Stelzner, K.; Bergstrom, F.; Niessen, H.W.; Zipfel, P.F. Monomeric C-reactive protein modulates classic complement activation on necrotic cells. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 4198–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVaughn, H.; Rich, H.E.; Shadid, A.; Vaidya, P.K.; Doursout, M.F.; Shivshankar, P. Complement Immune System in Pulmonary Hypertension-Cooperating Roles of Circadian Rhythmicity in Complement-Mediated Vascular Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Ohama, T.; Kawase, R.; Chang, J.; Inui, H.; Kanno, K.; Okada, T.; Masuda, D.; Koseki, M.; Nishida, M.; et al. Progranulin deficiency leads to enhanced age-related cardiac hypertrophy through complement C1q-induced beta-catenin activation. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2020, 138, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.D.; Nguyen, T.A.; Cenik, B.; Yu, G.; Herz, J.; Walther, T.C.; Davidson, W.S.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Secreted progranulin is a homodimer and is not a component of high density lipoproteins (HDL). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 8627–8635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder-Nascimento, A.; Awata, W.M.C.; Alves, J.V.; Singh, S.; Costa, R.M.; Bruder-Nascimento, T. Progranulin Maintains Blood Pressure and Vascular Tone Dependent on EphrinA2 and Sortilin1 Receptors and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Activation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e030353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawase, R.; Ohama, T.; Matsuyama, A.; Matsuwaki, T.; Okada, T.; Yamashita, T.; Yuasa-Kawase, M.; Nakaoka, H.; Nakatani, K.; Inagaki, M.; et al. Deletion of progranulin exacerbates atherosclerosis in ApoE knockout mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 100, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobo, J.; Kocsis, A.; Farkas, B.; Demeter, F.; Cervenak, L.; Gal, P. The Lectin Pathway of the Complement System-Activation, Regulation, Disease Connections and Interplay with Other (Proteolytic) Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, K.; Ajjan, R.; Phoenix, F.; Dobo, J.; Gal, P.; Schroeder, V. Effects of MASP-1 of the complement system on activation of coagulation factors and plasma clot formation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frauenknecht, V.; Thiel, S.; Storm, L.; Meier, N.; Arnold, M.; Schmid, J.P.; Saner, H.; Schroeder, V. Plasma levels of mannan-binding lectin (MBL)-associated serine proteases (MASPs) and MBL-associated protein in cardio- and cerebrovascular diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 173, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaeble, W.J.; Lynch, N.J.; Clark, J.E.; Marber, M.; Samani, N.J.; Ali, Y.M.; Dudler, T.; Parent, B.; Lhotta, K.; Wallis, R.; et al. Targeting of mannan-binding lectin-associated serine protease-2 confers protection from myocardial and gastrointestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7523–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degn, S.E.; Hansen, A.G.; Steffensen, R.; Jacobsen, C.; Jensenius, J.C.; Thiel, S. MAp44, a human protein associated with pattern recognition molecules of the complement system and regulating the lectin pathway of complement activation. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7371–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leanca, S.A.; Crisu, D.; Petris, A.O.; Afrasanie, I.; Genes, A.; Costache, A.D.; Tesloianu, D.N.; Costache, I.I. Left Ventricular Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction: From Physiopathology to Treatment. Life 2022, 12, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Meng, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Du, H.; Shi, H.; Xia, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Elevated serum complement C3 levels are associated with prehypertension in an adult population. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2017, 39, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norgaard, I.; Nielsen, S.F.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Complement C3 and High Risk of Venous Thromboembolism: 80517 Individuals from the Copenhagen General Population Study. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Balzo, U.H.; Levi, R.; Polley, M.J. Cardiac dysfunction caused by purified human C3a anaphylatoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombos, T.; Forhecz, Z.; Pozsonyi, Z.; Szeplaki, G.; Kunde, J.; Fust, G.; Janoskuti, L.; Karadi, I.; Prohaszka, Z. Complement anaphylatoxin C3a as a novel independent prognostic marker in heart failure. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2012, 101, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzelt, J.; Mueller, K.A.; Breuning, S.; Karathanos, A.; Schleicher, R.; Seizer, P.; Gawaz, M.; Langer, H.F.; Geisler, T. Expression of anaphylatoxin receptors on platelets in patients with coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis 2015, 238, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Hashimoto, H.; Yamakawa, H.; Kusumoto, D.; Akiba, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Momoi, M.; Komuro, J.; Katsuki, T.; Kimura, M.; et al. The complement C3-complement factor D-C3a receptor signalling axis regulates cardiac remodelling in right ventricular failure. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louwe, M.C.; Gialeli, C.; Michelsen, A.E.; Holm, S.; Edsfeldt, A.; Skagen, K.; Lekva, T.; Olsen, M.B.; Bjerkeli, V.; Schjorlien, T.; et al. Alternative Complement Pathway in Carotid Atherosclerosis: Low Plasma Properdin Levels Associate with Long-Term Cardiovascular Mortality. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2025, 14, e038316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, M.G.; Binder, C.J. The multifaceted impact of complement on atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2022, 351, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, M.F.; Michelsen, A.E.; Shahini, N.; Bjorkelund, E.; Bendz, C.H.; Massey, R.J.; Schjalm, C.; Halvorsen, B.; Broch, K.; Ueland, T.; et al. The Alternative Complement Pathway Is Activated Without a Corresponding Terminal Pathway Activation in Patients With Heart Failure. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 800978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahini, N.; Michelsen, A.E.; Nilsson, P.H.; Ekholt, K.; Gullestad, L.; Broch, K.; Dahl, C.P.; Aukrust, P.; Ueland, T.; Mollnes, T.E.; et al. The alternative complement pathway is dysregulated in patients with chronic heart failure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.B.; Jane-Wit, D.; Pober, J.S. Complement Membrane Attack Complex: New Roles, Mechanisms of Action, and Therapeutic Targets. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.B.; Jiang, B.; Qin, L.; Tellides, G.; Kirkiles-Smith, N.C.; Jane-Wit, D.; Pober, J.S. Complement-activated interferon-gamma-primed human endothelium transpresents interleukin-15 to CD8+ T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3437–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Arguelles, A.; Llorente, L. The role of complement regulatory proteins (CD55 and CD59) in the pathogenesis of autoimmune hemocytopenias. Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 6, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, G.H.; Brann, C.N.; Becker, K.; Thohan, V.; Koerner, M.M.; Loebe, M.; Noon, G.P.; Torre-Amione, G. Dynamic expression of the membrane attack complex (MAC) of the complement system in failing human myocardium. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 1626–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viedt, C.; Hansch, G.M.; Brandes, R.P.; Kubler, W.; Kreuzer, J. The terminal complement complex C5b-9 stimulates interleukin-6 production in human smooth muscle cells through activation of transcription factors NF-kappa B and AP-1. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 2370–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaka, T.P.; Manolov, D.; Ozdemir, C.; Marx, N.; Kaya, Z.; Kochs, M.; Hoher, M.; Hombach, V.; Torzewski, J. Complement and dilated cardiomyopathy: A role of sublytic terminal complement complex-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha synthesis in cardiac myocytes. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.J.; Acker, M.A.; Atluri, P. Left Ventricular Assist Devices. Circulation 2018, 138, 2841–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noris, M.; Remuzzi, G. Overview of complement activation and regulation. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Weitz, I. Complement Factor D as a Strategic Target for Regulating the Alternative Complement Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 712572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdei, A.; Isaak, A.; Torok, K.; Sandor, N.; Kremlitzka, M.; Prechl, J.; Bajtay, Z. Expression and role of CR1 and CR2 on B and T lymphocytes under physiological and autoimmune conditions. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 2767–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.D.; Song, W.C. Membrane complement regulatory proteins. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, I.; Baranyi, L.; Ishikawa, Y.; Okada, N.; Bohata, C.; Budai, D.; Fukuda, A.; Imai, M.; Okada, H. CD59 blocks not only the insertion of C9 into MAC but inhibits ion channel formation by homologous C5b-8 as well as C5b-9. J. Physiol. 2002, 539, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardhan, M.; Kaushik, R. Physiology, Complement Cascade. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.A.; Densen, P.; Hurford, R.K., Jr.; Colten, H.R.; Wetsel, R.A. Type I human complement C2 deficiency. A 28-base pair gene deletion causes skipping of exon 6 during RNA splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 9347–9353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, G.; Truedsson, L.; Sturfelt, G.; Oxelius, V.A.; Braconier, J.H.; Sjoholm, A.G. Hereditary C2 deficiency in Sweden: Frequent occurrence of invasive infection, atherosclerosis, and rheumatic disease. Medicine 2005, 84, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, M.A.; Trompet, S.; Mooijaart, S.P.; Smit, R.A.; Bohringer, S.; Castro Cabezas, M.; Jukema, J.W. Complement receptor 1 gene polymorphisms are associated with cardiovascular risk. Atherosclerosis 2017, 257, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.E.; Goodship, T.H.; Zipfel, P.F.; Perkins, S.J. An interactive web database of factor H-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome mutations: Insights into the structural consequences of disease-associated mutations. Hum. Mutat. 2006, 27, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokki, A.I.; Ren, Z.; Triebwasser, M.; Daly, E.; Finnpec; Perola, M.; Auro, K.; Burwick, R.; Salmon, J.E.; Daly, M.; et al. Identification of complement factor H variants that predispose to pre-eclampsia: A genetic and functional study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2023, 130, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, M.; Jarva, H.; Seitsonen, S.; Haapasalo, K.; Lehtinen, M.J.; Lindeman, N.; Anderson, D.H.; Johnson, P.T.; Jarvela, I.; Jokiranta, T.S.; et al. Y402H polymorphism of complement factor H affects binding affinity to C-reactive protein. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 3831–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jylhava, J.; Eklund, C.; Jylha, M.; Hervonen, A.; Lehtimaki, T.; Karhunen, P.; Hurme, M. Complement factor H 402His variant confers an increased mortality risk in Finnish nonagenarians: The Vitality 90+ study. Exp. Gerontol. 2009, 44, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jylhava, J.; Eklund, C.; Pessi, T.; Raitakari, O.T.; Juonala, M.; Kahonen, M.; Viikari, J.S.; Lehtimaki, T.; Hurme, M. Genetics of C-reactive protein and complement factor H have an epistatic effect on carotid artery compliance: The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 155, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardys, I.; Klaver, C.C.; Despriet, D.D.; Bergen, A.A.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Hofman, A.; Oostra, B.A.; Van Duijn, C.M.; de Jong, P.T.; Witteman, J.C. A common polymorphism in the complement factor H gene is associated with increased risk of myocardial infarction: The Rotterdam Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeijvoets, K.C.; Mooijaart, S.P.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Defesche, J.C.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Westendorp, R.G.; Kastelein, J.J.; van Hagen, P.M.; Sijbrands, E.J. Complement factor H Y402H decreases cardiovascular disease risk in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia. Eur. Heart J. 2009, 30, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ma, Y.J.; Skjoedt, M.O.; Garred, P. Collectin-11/MASP complex formation triggers activation of the lectin complement pathway--the fifth lectin pathway initiation complex. J. Innate Immun. 2013, 5, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, T.L.; Andrade, F.A.; Lidani, K.C.F.; Einig, E.; Boldt, A.B.W.; Mordmuller, B.; Esen, M.; Messias-Reason, I.J. Human collectin-11 (COLEC11) and its synergic genetic interaction with MASP2 are associated with the pathophysiology of Chagas Disease. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.X.; Cao, B.; Ma, N.; Wu, K.Y.; Chen, W.B.; Wu, W.; Dong, X.; Liu, C.F.; Gao, Y.F.; Diao, T.Y.; et al. Collectin-11 promotes cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e159452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajek, G.; Swierzko, A.S.; Cedzynski, M. Association of Polymorphisms of MASP1/3, COLEC10, and COLEC11 Genes with 3MC Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooryck, C.; Diaz-Font, A.; Osborn, D.P.; Chabchoub, E.; Hernandez-Hernandez, V.; Shamseldin, H.; Kenny, J.; Waters, A.; Jenkins, D.; Kaissi, A.A.; et al. Mutations in lectin complement pathway genes COLEC11 and MASP1 cause 3MC syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, N.; Abbas, Y.; Bryant, D.M.; Gonzalez-Rosa, J.M.; Sharpe, M.; Uygur, A.; Cocco-Delgado, L.H.; Ho, N.N.; Gerard, N.P.; Gerard, C.J.; et al. Complement Receptor C5aR1 Plays an Evolutionarily Conserved Role in Successful Cardiac Regeneration. Circulation 2018, 137, 2152–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Y.; Xie, X.; Ma, Y.T.; Yang, Y.N.; Fu, Z.Y.; Li, X.M.; Pan, S.; Adi, D.; Chen, B.D.; Liu, F. Association of C5aR1genetic polymorphisms with coronary artery disease in a Han population in Xinjiang, China. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Guo, F.; Liu, J.; Liang, X.; Xing, Z.; Cao, C. Association of acylation-stimulating protein and receptor gene polymorphisms with coronary heart disease in Han and Hui populations. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 18779–18785. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wysoczynski, M.; Solanki, M.; Borkowska, S.; van Hoose, P.; Brittian, K.R.; Prabhu, S.D.; Ratajczak, M.Z.; Rokosh, G. Complement component 3 is necessary to preserve myocardium and myocardial function in chronic myocardial infarction. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 2502–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprong, T.; Roos, D.; Weemaes, C.; Neeleman, C.; Geesing, C.L.; Mollnes, T.E.; van Deuren, M. Deficient alternative complement pathway activation due to factor D deficiency by 2 novel mutations in the complement factor D gene in a family with meningococcal infections. Blood 2006, 107, 4865–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taldir, G.; Parize, P.; Arvis, P.; Faisy, C. Acute right-sided heart failure caused by Neisseria meningitidis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferluga, J.; Kouser, L.; Murugaiah, V.; Sim, R.B.; Kishore, U. Potential influences of complement factor H in autoimmune inflammatory and thrombotic disorders. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 84, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichloo, A.; Chugh, S.S.; Gupta, S.; Pandav, J.; Chander, P. Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Presenting as Acute Heart Failure-A Rare Presentation: Diagnosis Supported by Skin Biopsy. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2019, 7, 2324709619842905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goicoechea de Jorge, E.; Lopez Lera, A.; Bayarri-Olmos, R.; Yebenes, H.; Lopez-Trascasa, M.; Rodriguez de Cordoba, S. Common and rare genetic variants of complement components in human disease. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 102, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez de Cordoba, S. Genetic variability shapes the alternative pathway complement activity and predisposition to complement-related diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 313, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroidis, M.; Davos, C.H.; Psarras, S.; Varela, A.; Athanasiadis, N.C.; Katsimpoulas, M.; Kostavasili, I.; Maasch, C.; Vater, A.; van Tintelen, J.P.; et al. Complement system modulation as a target for treatment of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2015, 110, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Tsilafakis, K.; Chen, L.; Lekkos, K.; Kostavasili, I.; Varela, A.; Cokkinos, D.V.; Davos, C.H.; Sun, X.; Song, J.; et al. Crosstalk between coagulation and complement activation promotes cardiac dysfunction in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5939–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagelbaum Ward, N.K.; Linares-Koloffon, C.; Posligua, A.; Gandrabur, L.; Kim, W.Y.; Sperber, K.; Wasserman, A.; Ash, J. Cardiac Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematous: An Overview of the Incidence, Risk Factors, Diagnostic Criteria, Pathophysiology and Treatment Options. Cardiol. Rev. 2022, 30, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Halushka, M.K. Cardiac pathology of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 62, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.; Smolag, K.I.; Bjork, A.; Gullstrand, B.; Okroj, M.; Leffler, J.; Jonsen, A.; Bengtsson, A.A.; Blom, A.M. Plasma C4d as marker for lupus nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhu, V.; Quan, M. SLE and Serum Complement: Causative, Concomitant or Coincidental? Open Rheumatol. J. 2017, 11, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Biswas, B.; Khera, R. Membrane-bound complement regulatory proteins as biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for SLE. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 735, 55–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manderson, A.P.; Pickering, M.C.; Botto, M.; Walport, M.J.; Parish, C.R. Continual low-level activation of the classical complement pathway. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coss, S.L.; Zhou, D.; Chua, G.T.; Aziz, R.A.; Hoffman, R.P.; Wu, Y.L.; Ardoin, S.P.; Atkinson, J.P.; Yu, C.Y. The complement system and human autoimmune diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2023, 137, 102979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selzer, F.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K.; Fitzgerald, S.G.; Pratt, J.E.; Tracy, R.P.; Kuller, L.H.; Manzi, S. Comparison of risk factors for vascular disease in the carotid artery and aorta in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botto, M.; Dell’Agnola, C.; Bygrave, A.E.; Thompson, E.M.; Cook, H.T.; Petry, F.; Loos, M.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Walport, M.J. Homozygous C1q deficiency causes glomerulonephritis associated with multiple apoptotic bodies. Nat. Genet. 1998, 19, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Gadban, M.M.; German, J.; Truman, J.P.; Soodavar, F.; Riemer, E.C.; Twal, W.O.; Smith, K.J.; Heller, D.; Hofbauer, A.F.; Oates, J.C.; et al. Lack of nitric oxide synthases increases lipoprotein immune complex deposition in the aorta and elevates plasma sphingolipid levels in lupus. Cell. Immunol. 2012, 276, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Andreasson, K.; Smith, V. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2023, 401, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meune, C.; Avouac, J.; Wahbi, K.; Cabanes, L.; Wipff, J.; Mouthon, L.; Guillevin, L.; Kahan, A.; Allanore, Y. Cardiac involvement in systemic sclerosis assessed by tissue-doppler echocardiography during routine care: A controlled study of 100 consecutive patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhai, M.; Meune, C.; Avouac, J.; Kahan, A.; Allanore, Y. Trends in mortality in patients with systemic sclerosis over 40 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, Y.; Takehara, K. Anti-nuclear autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis: News and perspectives. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2018, 3, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chepy, A.; Collet, A.; Launay, D.; Dubucquoi, S.; Sobanski, V. Autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis: From disease bystanders to pathogenic players. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2025, 10, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.T.; Reveille, J.D. The clinical relevance of autoantibodies in scleroderma. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2003, 5, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulkley, B.H.; Ridolfi, R.L.; Salyer, W.R.; Hutchins, G.M. Myocardial lesions of progressive systemic sclerosis. A cause of cardiac dysfunction. Circulation 1976, 53, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridolfi, R.L.; Bulkley, B.H.; Hutchins, G.M. The cardiac conduction system in progressive systemic sclerosis. Clinical and pathologic features of 35 patients. Am. J. Med. 1976, 61, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, L.Y.; Wang, X.D.; Zhang, T.; Xue, J. Cardiac complications in systemic sclerosis: Early diagnosis and treatment. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2019, 132, 2865–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicano, C.; Miglionico, M.; Romaggioli, L.; Colalillo, A.; Vantaggio, L.; Napodano, C.; Calla, C.; Gulli, F.; Marino, M.; Basile, U.; et al. Increased Complement Activation in Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Skin and Lung Fibrosis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okroj, M.; Johansson, M.; Saxne, T.; Blom, A.M.; Hesselstrand, R. Analysis of complement biomarkers in systemic sclerosis indicates a distinct pattern in scleroderma renal crisis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scambi, C.; Ugolini, S.; Jokiranta, T.S.; De Franceschi, L.; Bortolami, O.; La Verde, V.; Guarini, P.; Caramaschi, P.; Ravagnani, V.; Martignoni, G.; et al. The local complement activation on vascular bed of patients with systemic sclerosis: A hypothesis-generating study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0114856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Diaz, M.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, D.; Heras-Recuero, E.; Gomez-Bernal, F.; Quevedo-Abeledo, J.C.; Gonzalez-Rivero, A.F.; Gonzalez-Lopez, E.; Ocejo-Vinyals, J.G.; Jimenez-Sosa, A.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; et al. The Relationship between the complement system and subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Kwon, E.J.; Lee, J.J. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielen, M.M.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Reesink, H.W.; van de Stadt, R.J.; van der Horst-Bruinsma, I.E.; de Koning, M.H.; Habibuw, M.R.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Dijkmans, B.A. Specific autoantibodies precede the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis: A study of serial measurements in blood donors. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holers, V.M.; Banda, N.K. Complement in the Initiation and Evolution of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okroj, M.; Heinegard, D.; Holmdahl, R.; Blom, A.M. Rheumatoid arthritis and the complement system. Ann. Med. 2007, 39, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouw, L.A.; Haisma, E.M.; Levarht, E.W.; van der Woude, D.; Ioan-Facsinay, A.; Daha, M.R.; Huizinga, T.W.; Toes, R.E. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies from rheumatoid arthritis patients activate complement via both the classical and alternative pathways. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anquetil, F.; Clavel, C.; Offer, G.; Serre, G.; Sebbag, M. IgM and IgA rheumatoid factors purified from rheumatoid arthritis sera boost the Fc receptor- and complement-dependent effector functions of the disease-specific anti-citrullinated protein autoantibodies. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 3664–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias de la Rosa, I.; Font, P.; Escudero-Contreras, A.; Lopez-Montilla, M.D.; Perez-Sanchez, C.; Abalos-Aguilera, M.C.; Ladehesa-Pineda, L.; Ibanez-Costa, A.; Torres-Granados, C.; Jimenez-Gomez, Y.; et al. Complement component 3 as biomarker of disease activity and cardiometabolic risk factor in rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2020, 11, 2040622320965067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.P.; Hokstad, I.; Fagerland, M.W.; Mollnes, T.E.; Hollan, I.; Feinberg, M.W.; Hjeltnes, G.; Eilertsen, G.O.; Mikkelsen, K.; Agewall, S. Antirheumatic therapy is associated with reduced complement activation in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvirnik, N.; Belley-Cote, E.P.; Hanif, H.; Devereaux, P.J.; Lamy, A.; Dieleman, J.M.; Vincent, J.; Whitlock, R.P. Steroids in cardiac surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawla, P. Cardiac and vascular complications in rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatologia 2019, 57, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlers, M.J.; Lowery, B.D.; Farber-Eger, E.; Wang, T.J.; Bradham, W.; Ormseth, M.J.; Chung, C.P.; Stein, C.M.; Gupta, D.K. Heart Failure Risk Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis-Related Chronic Inflammation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezus, E.; Macovei, L.A.; Burlui, A.M.; Cardoneanu, A.; Rezus, C. Ischemic Heart Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis-Two Conditions, the Same Background. Life 2021, 11, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.T.; Damm, D.; Hancock, N.; Rosen, B.S.; Lowell, B.B.; Usher, P.; Flier, J.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Human adipsin is identical to complement factor D and is expressed at high levels in adipose tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 9210–9213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianflone, K.; Maslowska, M.; Sniderman, A.D. Acylation stimulating protein (ASP), an adipocyte autocrine: New directions. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999, 10, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilski, J.; Schramm-Luc, A.; Szczepanik, M.; Mazur-Bialy, A.I.; Bonior, J.; Luc, K.; Zawojska, K.; Szklarczyk, J. Adipokines in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Emerging Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phieler, J.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Lambris, J.D.; Chavakis, T. The role of the complement system in metabolic organs and metabolic diseases. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghavi, N.; Ingrassia, J.P.; Korem, S.; Ash, J.; Pan, S.; Wasserman, A. Cardiovascular Manifestations in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cardiol. Rev. 2024, 32, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrao, S.; Messina, S.; Pistone, G.; Calvo, L.; Scaglione, R.; Licata, G. Heart involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, L.E.; Johnson, T.M.; England, B.R.; Wysham, K.D.; George, M.D.; Sauer, B.; Hamilton, B.C.; Hunter, C.D.; Duryee, M.J.; Thiele, G.M.; et al. Circulating Adipokines and Associations With Incident Cardiovascular Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2023, 75, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hok, K.D.; Li, Y.-D.; Mueller-Ortiz, S.; Domozhirov, A.Y.; Restrepo, M.I.; Shivshankar, P. Single-cell transcriptomic changes in mouse hearts during collagen-induced arthritic inflammation. Immunobiology 2025, 230, 153047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, I.; Song, J.A.; Suh, J.H.; Kim, S.; Son, J.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, S.Y.; Hwang, K.Y.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, S. EPRS1 Controls the TGF-beta Signaling Pathway via Interaction with TbetaRI in Hepatic Stellate Cell. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2023, 43, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Subbaiah, K.C.V.; Xie, L.H.; Jiang, F.; Khor, E.S.; Mickelsen, D.; Myers, J.R.; Tang, W.H.W.; Yao, P. Glutamyl-Prolyl-tRNA Synthetase Regulates Proline-Rich Pro-Fibrotic Protein Synthesis During Cardiac Fibrosis. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 827–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyakis, S.; Lockshin, M.D.; Atsumi, T.; Branch, D.W.; Brey, R.L.; Cervera, R.; Derksen, R.H.; De Groot, P.G.; Koike, T.; Meroni, P.L.; et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.H.; Park, C.Y. Lupus anticoagulant-hypoprothrombinemia in healthy adult. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2008, 23, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojnik, M.; George, J.; Ziporen, L.; Shoenfeld, Y. Heart valve involvement (Libman-Sacks endocarditis) in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Circulation 1996, 93, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolitz, T.; Shiber, S.; Sharabi, I.; Winder, A.; Zandman-Goddard, G. Cardiac Manifestations of Antiphospholipid Syndrome with Focus on Its Primary Form. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziporen, L.; Goldberg, I.; Arad, M.; Hojnik, M.; Ordi-Ros, J.; Afek, A.; Blank, M.; Sandbank, Y.; Vilardell-Tarres, M.; de Torres, I.; et al. Libman-Sacks endocarditis in the antiphospholipid syndrome: Immunopathologic findings in deformed heart valves. Lupus 1996, 5, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinis, C.; Biffi, S.; Garrovo, C.; Durigutto, P.; Lorenzon, A.; Bek, A.; Bulla, R.; Grossi, C.; Borghi, M.O.; Meroni, P.; et al. In vivo distribution of beta2 glycoprotein I under various pathophysiologic conditions. Blood 2011, 118, 4231–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrame, M.H.; Catarino, S.J.; Goeldner, I.; Boldt, A.B.; de Messias-Reason, I.J. The lectin pathway of complement and rheumatic heart disease. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fae, K.C.; da Silva, D.D.; Oshiro, S.E.; Tanaka, A.C.; Pomerantzeff, P.M.; Douay, C.; Charron, D.; Toubert, A.; Cunningham, M.W.; Kalil, J.; et al. Mimicry in recognition of cardiac myosin peptides by heart-intralesional T cell clones from rheumatic heart disease. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 5662–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.W.; Ho, T.K.; Hanson-Manful, P.; Tritscheller, S.; Raynes, J.M.; Whitcombe, A.L.; Tay, M.L.; McGregor, R.; Lorenz, N.; Oliver, J.R.; et al. Systems immunology reveals a linked IgG3-C4 response in patients with acute rheumatic fever. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2020, 98, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafranski, M.D.; Stier, A.; Nisihara, R.; Messias-Reason, I.J. Significantly increased levels of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) in rheumatic heart disease: A beneficial role for MBL deficiency. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 138, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. Editorial commentary: Myocardial fibrosis in genetic cardiomyopathies: A cause of dysfunction, or simply an epiphenomenon? Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 30, 362–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, V.I.; La Bonte, L.R.; Baldwin, W.M.; Markiewski, M.M.; Lambris, J.D.; Stahl, G.L. Absence of mannose-binding lectin prevents hyperglycemic cardiovascular complications. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjabi, S.; Zenewicz, L.A.; Kamanaka, M.; Flavell, R.A. Anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory roles of TGF-beta, IL-10, and IL-22 in immunity and autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontainhas, S.; Baptista, B.; Bertao, M.I.; Lima, B.; Gomes, R. Infective Endocarditis Caused by Streptococcus viridans in a Previously Healthy Man: A Case Report. Cureus 2025, 17, e76896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.R., 3rd; Jenks, J.D.; Baddley, J.W.; Lewis, J.S., 2nd; Egger, M.; Schwartz, I.S.; Boyer, J.; Patterson, T.F.; Chen, S.C.; Pappas, P.G.; et al. Fungal Endocarditis: Pathophysiology, Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 36, e0001923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleszewicz-Baranowska, J.; Ulewicz, F.J.; Lipska, B.S.; Balcerska, A.; Ereciński, J. Infectious Endocarditis. Pediatr. Pol. 2023, 82, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messias-Reason, I.J.; Hayashi, S.Y.; Nisihara, R.M.; Kirschfink, M. Complement activation in infective endocarditis: Correlation with extracardiac manifestations and prognosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 127, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, L.; Alobaidi, A.; Lytvak, I. Endocarditis-Associated C3-Dominant Glomerulonephritis in a Patient with a Solitary Kidney. Cureus 2022, 14, e27675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, I.; Varadarasa, S.; Swisher, J.; Gidda, H.; Schreiber, T. Dilated Cardiomyopathy as a Result of Coxsackie B Virus Myocarditis. Cureus 2023, 15, e35895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, N.; Kyriakopoulos, C. Group B Coxsackie Virus. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Fairweather, D.; Frisancho-Kiss, S.; Njoku, D.B.; Nyland, J.F.; Kaya, Z.; Yusung, S.A.; Davis, S.E.; Frisancho, J.A.; Barrett, M.A.; Rose, N.R. Complement receptor 1 and 2 deficiency increases coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis, dilated cardiomyopathy, and heart failure by increasing macrophages, IL-1beta, and immune complex deposition in the heart. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 3516–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.C.; Hwang, S.W.; Luo, H.; Mohamud, Y. Double-Edged Sword: Exploring the Mitochondria-Complement Bidirectional Connection in Cellular Response and Disease. Biology 2024, 13, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamud, Y.; Bahreyni, A.; Hwang, S.W.; Lin, J.C.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhang, J.; Luo, H. Mitochondrial injury and complement dysregulation are drivers of pathological inflammation in viral myocarditis. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e0180424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, B.; Spiller, O.B.; Choy, J.; Luo, H.; Cheung, P.; Zhang, H.M.; Goodfellow, I.G.; Evans, D.J.; Suarez, A.; Yang, D.; et al. Coxsackievirus B3-associated myocardial pathology and viral load reduced by recombinant soluble human decay-accelerating factor in mice. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, V.D.; Reis, M.M.; Benvenuti, L.A.; Higuchi Mde, L.; Ramires, J.A.; Halperin, J.A. A possible role for complement in the pathogenesis of chronic chagasic cardiomyopathy. J. Pathol. 2002, 197, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappegard, K.T.; Garred, P.; Jonasson, L.; Espevik, T.; Aukrust, P.; Yndestad, A.; Mollnes, T.E.; Hovland, A. A vital role for complement in heart disease. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 61, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samstad, E.O.; Niyonzima, N.; Nymo, S.; Aune, M.H.; Ryan, L.; Bakke, S.S.; Lappegard, K.T.; Brekke, O.L.; Lambris, J.D.; Damas, J.K.; et al. Cholesterol crystals induce complement-dependent inflammasome activation and cytokine release. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 2837–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cestari Idos, S.; Krarup, A.; Sim, R.B.; Inal, J.M.; Ramirez, M.I. Role of early lectin pathway activation in the complement-mediated killing of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 47, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonney, K.M.; Engman, D.M. Chagas heart disease pathogenesis: One mechanism or many? Curr. Mol. Med. 2008, 8, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, K.L.; Kono, H. The inflammatory response to cell death. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2008, 3, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.J.; Garred, P. Pentraxins in Complement Activation and Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, S.Y.; Sun, J.H.; Zhang, H.C.; Cai, Q.L.; Gao, C.; Li, L.; Cao, J.; Xu, F.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: Mechanisms, diagnosis and current treatment options. Mil. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Poll, T.; van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Scicluna, B.P.; Netea, M.G. The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, F.; Russell, M.W.; Malan, E.A.; Parlett, M.; Abe, E.; Zetoune, F.S.; Ward, P.A. Harmful Roles of TLR3 and TLR9 in Cardiac Dysfunction Developing during Polymicrobial Sepsis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4302726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankowski, R.T.; Yende, S.; Angus, D.C. Long-term impact of sepsis on cardiovascular health. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconi, M.; Evans, L.; Levy, M.; Rhodes, A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 2018, 392, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silasi-Mansat, R.; Zhu, H.; Popescu, N.I.; Peer, G.; Sfyroera, G.; Magotti, P.; Ivanciu, L.; Lupu, C.; Mollnes, T.E.; Taylor, F.B.; et al. Complement inhibition decreases the procoagulant response and confers organ protection in a baboon model of Escherichia coli sepsis. Blood 2010, 116, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizer, M.P.; Pouw, R.B.; Kamp, A.M.; Patiwael, S.; Marsman, G.; Hart, M.H.; Zeerleder, S.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Wouters, D. TFPI inhibits lectin pathway of complement activation by direct interaction with MASP-2. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, S.; Holzknecht, R.A.; Patte, C.P.; Stern, D.M.; Platt, J.L. Complement-mediated regulation of tissue factor activity in endothelium. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, S.; Platt, J.L. Transient perturbation of endothelial integrity induced by natural antibodies and complement. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 181, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atefi, G.; Zetoune, F.S.; Herron, T.J.; Jalife, J.; Bosmann, M.; Al-Aref, R.; Sarma, J.V.; Ward, P.A. Complement dependency of cardiomyocyte release of mediators during sepsis. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruh, S.M. Obesity: Risk factors, complications, and strategies for sustainable long-term weight management. J. Am. Assoc. Nurse Pract. 2017, 29, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, T.; Peppard, P.E.; Taheri, S. Excess weight and sleep-disordered breathing. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2005, 99, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellbin, L.G.; Bjerre, M.; Thiel, S.; Hansen, T.K. Complement activation and prognosis in patients with type 2 diabetes and myocardial infarction: A report from the DIGAMI 2 trial. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, H.S.; Samuel, C.S.; Lau, D.H.; Kelly, D.J.; Royce, S.G.; Alasady, M.; Mahajan, R.; Kuklik, P.; Zhang, Y.; Brooks, A.G.; et al. Obesity results in progressive atrial structural and electrical remodeling: Implications for atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2013, 10, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, M.A.; Karthikeyan, K.; Abdullah, O.; Ghadban, R. Obesity and Cardiac Remodeling in Adults: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 61, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.; Marwick, T.H. Alterations in myocardial characteristics associated with obesity: Detection, mechanisms, and implications. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suen, J.Y.; Gardiner, B.; Grimmond, S.; Fairlie, D.P. Profiling gene expression induced by protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) activation in human kidney cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitis, M.; Lowenstein, C.J. Dyslipidemia. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, ITC81–ITC96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berisha, H.; Hattab, R.; Comi, L.; Giglione, C.; Migliaccio, S.; Magni, P. Nutrition and Lifestyle Interventions in Managing Dyslipidemia and Cardiometabolic Risk. Nutrients 2025, 17, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, H.; Li, C. Dietary Regulation of Oxidative Stress in Chronic Metabolic Diseases. Foods 2021, 10, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, N.; Sanghvi, M.M.; Piechnik, S.K.; Neubauer, S.; Munroe, P.B.; Petersen, S.E. The Effect of Blood Lipids on the Left Ventricle: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Arguinzonis, M.; Diaz-Riera, E.; Pena, E.; Escate, R.; Juan-Babot, O.; Mata, P.; Badimon, L.; Padro, T. Alternative C3 Complement System: Lipids and Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alic, L.; Dendinovic, K.; Papac-Milicevic, N. The complement system in lipid-mediated pathologies. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1511886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nanda, V.; Direnzo, D.; Ye, J.; Xiao, S.; Kojima, Y.; Howe, K.L.; Jarr, K.U.; Flores, A.M.; Tsantilas, P.; et al. Clonally expanding smooth muscle cells promote atherosclerosis by escaping efferocytosis and activating the complement cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15818–15826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramoni, D.; Carbone, F.; Kraler, S.; Di Vece, D.; Montecucco, F.; Liberale, L. Inflammation-Driven Plaque Erosion in Atherosclerosis: A Focus on Complement System Pathways. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2025, 27, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebari-Benslaiman, S.; Galicia-Garcia, U.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Olaetxea, J.R.; Alloza, I.; Vandenbroeck, K.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Martin, C. Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlynarska, E.; Czarnik, W.; Fularski, P.; Hajdys, J.; Majchrowicz, G.; Stabrawa, M.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. From Atherosclerotic Plaque to Myocardial Infarction-The Leading Cause of Coronary Artery Occlusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, P.F.; Gawryl, M.S. Detection of the terminal complement complex in patient plasma following acute myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis 1988, 70, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasojima, K.; Kilgore, K.S.; Washington, R.A.; Lucchesi, B.R.; McGeer, P.L. Complement gene expression by rabbit heart: Upregulation by ischemia and reperfusion. Circ. Res. 1998, 82, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasojima, K.; Schwab, C.; McGeer, E.G.; McGeer, P.L. Human heart generates complement proteins that are upregulated and activated after myocardial infarction. Circ. Res. 1998, 83, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystel-Whittemore, M.; Dileepan, K.N.; Wood, J.G. Mast Cell: A Multi-Functional Master Cell. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, K.; Henz, B.M.; Kruger-Krasagakes, S.; Kohl, J.; Burger, R.; Guhl, S.; Haase, I.; Lippert, U.; Zuberbier, T. C3a and C5a stimulate chemotaxis of human mast cells. Blood 1997, 89, 2863–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seravalle, G.; Grassi, G. Essential Hypertension. In Primer on the Autonomic Nervous System; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 467–470. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, D.G.; Coffman, T.M.; Wilcox, C.S. Pathophysiology of Hypertension: The Mosaic Theory and Beyond. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cobb, A.; Leslie, S.W. Primary Hyperaldosteronism. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Tomek, J.; Bub, G. Hypertension-induced remodelling: On the interactions of cardiac risk factors. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 4027–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrom, G.; Hedblad, B.; Berglund, G.; Janzon, L.; Lindgarde, F. Plasma levels of complement C3 is associated with development of hypertension: A longitudinal cohort study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2007, 21, 276–282. [Google Scholar]
- Engstrom, G.; Hedblad, B.; Janzon, L.; Lindgarde, F. Complement C3 and C4 in plasma and incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke: A population-based cohort study. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2007, 14, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekassy, Z.D.; Kristoffersson, A.C.; Rebetz, J.; Tati, R.; Olin, A.I.; Karpman, D. Aliskiren inhibits renin-mediated complement activation. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, M.H.; Lamparello, N.A.; Logiurato, B. Renal Artery Stenosis. In Interventional Urology; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 421–439. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, S.D.; Gurley, S.B.; Herrera, M.J.; Ruiz, P.; Griffiths, R.; Kumar, A.P.; Kim, H.S.; Smithies, O.; Le, T.H.; Coffman, T.M. Angiotensin II causes hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy through its receptors in the kidney. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17985–17990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Fisher, A.J.; Mickler, E.A.; Duerson, F., 3rd; Cummings, O.W.; Peters-Golden, M.; Twigg, H.L., 3rd; Woodruff, T.M.; Wilkes, D.S.; Vittal, R. Contribution of the anaphylatoxin receptors, C3aR and C5aR, to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 2336–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Bundy, J.D.; Kelly, T.N.; Reed, J.E.; Kearney, P.M.; Reynolds, K.; Chen, J.; He, J. Global Disparities of Hypertension Prevalence and Control: A Systematic Analysis of Population-Based Studies From 90 Countries. Circulation 2016, 134, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiot, J.; Corhay, J.L.; Louis, R. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Rev. Med. Liege 2014, 69, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maron, B.A. Revised Definition of Pulmonary Hypertension and Approach to Management: A Clinical Primer. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e029024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratwatte, S.; Celermajer, D.S. The latest definition and classification of pulmonary hypertension. Int. J. Cardiol. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2024, 17, 100534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.J.; Archer, S.L. The right ventricle in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Disorders of metabolism, angiogenesis and adrenergic signaling in right ventricular failure. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frid, M.G.; Thurman, J.M.; Hansen, K.C.; Maron, B.A.; Stenmark, K.R. Inflammation, immunity, and vascular remodeling in pulmonary hypertension; Evidence for complement involvement? Glob. Cardiol. Sci. Pract. 2020, 2020, e202001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.J.; Wharton, J.; Ghataorhe, P.; Watson, G.; Girerd, B.; Howard, L.S.; Gibbs, J.S.R.; Condliffe, R.; Elliot, C.A.; Kiely, D.G.; et al. Plasma proteome analysis in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: An observational cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; He, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhong, X. A novel complement C3 inhibitor CP40-KK protects against experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension via an inflammasome NLRP3 associated pathway. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, K.E.; Langseth, M.S.; Andersen, G.O.; Halvorsen, S.; Opstad, T.B.; Arnesen, H.; Tonnessen, T.; Seljeflot, I.; Helseth, R. Complement activation in association with clinical outcomes in ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Am. Heart J. Plus 2022, 24, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, X.; Wu, H.; Li, G.; Chen, J.; Kang, L.; Wang, K. Proteomic evaluation of the thrombosis-inflammation interplay in STEMI with MVO. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2025, 25, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Fernandes, S.M.; Davis, A.E., 3rd. The effect of C1 inhibitor on myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2013, 22, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber-Lang, M.; Sarma, J.V.; Zetoune, F.S.; Rittirsch, D.; Neff, T.A.; McGuire, S.R.; Lambris, J.D.; Warner, R.L.; Flierl, M.A.; Hoesel, L.M.; et al. Generation of C5a in the absence of C3: A new complement activation pathway. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, H.I.; Boral, I.; Bevington, A. Complement-Coagulation Cross-Talk: A Potential Mediator of the Physiological Activation of Complement by Low pH. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saggu, G.; Cortes, C.; Emch, H.N.; Ramirez, G.; Worth, R.G.; Ferreira, V.P. Identification of a novel mode of complement activation on stimulated platelets mediated by properdin and C3(H2O). J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 6457–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Conde, I.; Cruz, M.A.; Zhang, H.; Lopez, J.A.; Afshar-Kharghan, V. Platelet activation leads to activation and propagation of the complement system. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Rao, M.; Zhang, N.N.; Chen, K.; Deng, H.; Song, J.P.; Hu, S.S. Comprehensive Myocardial Proteogenomics Profiling Reveals C/EBPalpha as the Key Factor in the Lipid Storage of ARVC. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 2863–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Long, B.; Xu, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, S. Identification of Crucial Genes and Pathways in Human Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy by Coexpression Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.H.; Tanaka, K.A. Inflammatory response to cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2003, 75, S715–S720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascione, R.; Lloyd, C.T.; Underwood, M.J.; Lotto, A.A.; Pitsis, A.A.; Angelini, G.D. Inflammatory response after coronary revascularization with or without cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2000, 69, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverich, A.; Shernan, S.K.; Levy, J.H.; Chen, J.C.; Carrier, M.; Taylor, K.M.; Van de Werf, F.; Newman, M.F.; Adams, P.X.; Todaro, T.G.; et al. Pexelizumab reduces death and myocardial infarction in higher risk cardiac surgical patients. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 82, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Investigators, A.A.; Armstrong, P.W.; Granger, C.B.; Adams, P.X.; Hamm, C.; Holmes, D., Jr.; O’Neill, W.W.; Todaro, T.G.; Vahanian, A.; Van de Werf, F. Pexelizumab for acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction in patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2007, 297, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, D.; Masuda, S.; Tomaru, U.; Ishizu, A. Pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions for ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muldur, S.; Vadysirisack, D.D.; Ragunathan, S.; Tang, Y.; Ricardo, A.; Sayegh, C.E.; Irimia, D. Human Neutrophils Respond to Complement Activation and Inhibition in Microfluidic Devices. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 777932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Staehr, P.; Tai, E.; Darpo, B.; Xue, H.; Armas, D.; Webster, K.; Oberoi, R.K. A phase I thorough QT/QTc study evaluating therapeutic and supratherapeutic doses of avacopan in healthy participants. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e13878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, H.L.; Bokesch, P.M.; van Lenta, F.; Fitzgerald, C.; Emmett, C.; Marsh, H.C., Jr.; Ryan, U.; OBE and the TP10 Cardiac Surgery Study Group. Soluble human complement receptor 1 limits ischemic damage in cardiac surgery patients at high risk requiring cardiopulmonary bypass. Circulation 2004, 110, II274–II279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, H.L.; Keilani, T.; Fitzgerald, C.A.; Shapira, O.M.; Hunter, C.T.; Shemin, R.J.; Marsh, H.C., Jr.; Ryan, U.S.; TP10 Cardiac Surgery Study Group. Beneficial effects of complement inhibition with soluble complement receptor 1 (TP10) during cardiac surgery: Is there a gender difference? Circulation 2007, 116, I83–I88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz-Amaro, I.; Santos-Concepcion, S.; Castro-Hernandez, J.; Hernandez-Hernandez, M.V.; Tejera Segura, B.; Luna, C.; Delgado-Frias, E.; Diaz-Gonzalez, F. Tocilizumab modulates the activity of the classical and alternative complement pathways in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1486588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, C.; Del Mastro, A.; Sellitto, A.; Solaro, E.; Esposito, S.; Cuomo, G. Tocilizumab reduces complement C3 and C4 serum levels in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Ye, D.; Wang, Z.; Pan, H.; Lu, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; et al. The Role of Interleukin-6 Family Members in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 818890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drosos, A.A.; Venetsanopoulou, A.A.; Pelechas, E.; Voulgari, P.V. Exploring Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 128, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, D.; Cheng, H.; Zhu, K. The selective p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor, SB203580, improves renal disease in MRL/lpr mouse model of systemic lupus. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canovas, B.; Nebreda, A.R. Diversity and versatility of p38 kinase signalling in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reustle, A.; Torzewski, M. Role of p38 MAPK in Atherosclerosis and Aortic Valve Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Becerra, R.; Mora, A.; Manieri, E.; Nikolic, I.; Santamans, A.M.; Montalvo-Romeral, V.; Cruz, F.M.; Rodriguez, E.; Leon, M.; Leiva-Vega, L.; et al. MKK6 deficiency promotes cardiac dysfunction through MKK3-p38gamma/delta-mTOR hyperactivation. Elife 2022, 11, e75250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccioni, G.; Zanasi, A.; Vitulano, N.; Mancini, B.; D’Orazio, N. Leukotrienes in atherosclerosis: New target insights and future therapy perspectives. Mediat. Inflamm. 2009, 2009, 737282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Eglite, S.; Pluss, K.; Dahinden, C.A. Requirements for C5a receptor-mediated IL-4 and IL-13 production and leukotriene C4 generation in human basophils. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaztanaga, J.; Farkouh, M.; Rudd, J.H.; Brotz, T.M.; Rosenbaum, D.; Mani, V.; Kerwin, T.C.; Taub, R.; Tardif, J.C.; Tawakol, A.; et al. A phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the effect of VIA-2291, a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, on vascular inflammation in patients after an acute coronary syndrome. Atherosclerosis 2015, 240, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Ehr, A.; Bode, C.; Hilgendorf, I. Macrophages in Atheromatous Plaque Developmental Stages. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 865367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baverel, V.; Garrido, C.; Kohli, E. Intracellular complement in monocytes and macrophages: Emerging roles. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2025, 96, 102629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhao, J.; Qi, X.M.; Wu, Y.G. Complement-mediated M2/M1 macrophage polarization may be involved in crescent formation in lupus nephritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Paik, D.C.; Barile, G.R. Bioactive lysophospholipids generated by hepatic lipase degradation of lipoproteins lead to complement activation via the classical pathway. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 6187–6193. [Google Scholar]
- Ignatova, I.D.; Kostadinova, R.M.; Goldring, C.E.; Nawrocki, A.R.; Frey, F.J.; Frey, B.M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha upregulates 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 expression by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-beta in HepG2 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E367–E377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Luo, L.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, H.; Huang, M.; Zhou, S. 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 amplifies inflammation in LPS-induced THP-1 cells. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2023, 26, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copenhaver, M.M.; Yu, C.Y.; Zhou, D.; Hoffman, R.P. Relationships of complement components C3 and C4 and their genetics to cardiometabolic risk in healthy, non-Hispanic white adolescents. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 87, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, H.; Tarantino, M.D.; Chaturvedi, S.; McCrae, K.R.; Roberts, J.C. Eculizumab for refractory thrombosis in antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulego-Erroz, I.; Martinez-Saenz de Jubera, J.; Ocana-Alcober, C.; Regueras-Santos, L.; Ferrero-De la Mano, L.; Martinez-Badas, J.P. Pediatric Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Successfully Treated with Eculizumab. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 640–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaar, A.P.J.; Witzenrath, M.; van Paassen, P.; Heunks, L.M.A.; Mourvillier, B.; de Bruin, S.; Lim, E.H.T.; Brouwer, M.C.; Tuinman, P.R.; Saraiva, J.F.K.; et al. Anti-C5a antibody (vilobelimab) therapy for critically ill, invasively mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 (PANAMO): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Carvelli, J.; Meziani, F.; Dellamonica, J.; Cordier, P.Y.; Allardet-Servent, J.; Fraisse, M.; Velly, L.; Barbar, S.D.; Lehingue, S.; Guervilly, C.; et al. Avdoralimab (Anti-C5aR1 mAb) Versus Placebo in Patients With Severe COVID-19: Results From a Randomized Controlled Trial (FOR COVID Elimination [FORCE]). Crit. Care Med. 2022, 50, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Hasturk, H.; Lambris, J.D.; Contributing, A. C3-targeted therapy in periodontal disease: Moving closer to the clinic. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasturk, H.; Hajishengallis, G.; The Forsyth Institute Center for Clinical and Translational Research Staff; Lambris, J.D.; Mastellos, D.C.; Yancopoulou, D. Phase IIa clinical trial of complement C3 inhibitor AMY-101 in adults with periodontal inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e152973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, S.K.; Claes, K.; Goh, Y.T.; Kwong, Y.L.; Leung, N.; Mendrek, W.; Nakamura, R.; Sathar, J.; Ng, E.; Nangia, N.; et al. Narsoplimab, a Mannan-Binding Lectin-Associated Serine Protease-2 Inhibitor, for the Treatment of Adult Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2447–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; de la Fuente, M.; Nieman, M.T. Complement factor C4a does not activate protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1) or PAR4 on human platelets. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 5, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ricklin, D.; Lambris, J.D. Complement-activation fragment C4a mediates effector functions by binding as untethered agonist to protease-activated receptors 1 and 4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10948–10953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe-Kusunoki, K.; Anders, H.J. Balancing efficacy and safety of complement inhibitors. J. Autoimmun. 2024, 145, 103216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebnasab, M.; Eriksson, O.; Persson, B.; Sandholm, K.; Mohlin, C.; Huber-Lang, M.; Keating, B.J.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Nilsson, B. Current and Future Approaches for Monitoring Responses to Anti-complement Therapeutics. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hok, K.D.; Rich, H.E.; Shadid, A.; Gunamalai, L.; Weng-Mills, T.; Thandavarayan, R.A.; Banda, N.K.; Doursout, M.-F.; Restrepo, M.I.; Shivshankar, P. Functional Roles of the Complement Immune System in Cardiac Inflammation and Hypertrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209931
Hok KD, Rich HE, Shadid A, Gunamalai L, Weng-Mills T, Thandavarayan RA, Banda NK, Doursout M-F, Restrepo MI, Shivshankar P. Functional Roles of the Complement Immune System in Cardiac Inflammation and Hypertrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209931
Chicago/Turabian StyleHok, Kathryn D., Haydn E. Rich, Anthony Shadid, Lavanya Gunamalai, Tingting Weng-Mills, Rajarajan A. Thandavarayan, Nirmal K. Banda, Marie-Francoise Doursout, Marcos I. Restrepo, and Pooja Shivshankar. 2025. "Functional Roles of the Complement Immune System in Cardiac Inflammation and Hypertrophy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209931
APA StyleHok, K. D., Rich, H. E., Shadid, A., Gunamalai, L., Weng-Mills, T., Thandavarayan, R. A., Banda, N. K., Doursout, M.-F., Restrepo, M. I., & Shivshankar, P. (2025). Functional Roles of the Complement Immune System in Cardiac Inflammation and Hypertrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209931







