Therapeutic Promise and Biotechnological Prospects of Dendroaspis polylepis Venom Proteins: Mambalgins, Fasciculins, and Dendrotoxins
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Toxin | Structure/Type | Protein Size | Mechanism of Action | Molecular Target | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mambalgin Mambalgin-1 | Three-finger toxin (3FTx) family peptide | ~57 amino acids ~7 kDa | Blocks acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs); produces strong analgesic effects comparable to morphine | ASIC1a and ASIC1b channels, “thumb” domain, electrostatic, hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds | [19] |
| Amino acid sequence: LKCYQHGKVVTCHRDMKFCYHNTGMPFRNLKLILQGCSSSCSETENNKCCSTDRCNK | |||||
Fasciculin Fasciculin-1 | Three-finger toxin (3FTx) family peptide | ~61 amino acids ~7 kDa | Inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase; prolongs the action of acetylcholine at synapses | AChE enzyme, peripheral anionic site (PAS), hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic, ionic interactions | [15,16] |
| Amino acid sequence: TMCYSHTTTSRAILTNCGENSCYRKSRRHPPKMVLGRGCGCPPGDDYLEVKCCTSPDKCNY | |||||
Dendrotoxin (I/K) Dendrotoxin-K | Kunitz-type peptide (protease inhibitor-like) | ~57 amino acids ~7 kDa (6.8 kDa) | Selectively blocks voltage-gated potassium channels (Kv1) | Kv1 potassium channels (Kv1.1, Kv1.2, Kv1.6), electrostatic, hydrophobic interactions | [17] |
| Amino acid sequence: AAKYCKLPLRIGPCKRKIPSFYYKWKAKQCLPFDYSGCGGNANRFKTIEECRRTCVG | |||||
 Dendrotoxin-I Dendrotoxin-I | Kunitz-type peptide (protease inhibitor-like) | ~60 amino acids ~7 kDa (6.8 kDa) | Selectively blocks voltage-gated potassium channels (Kv1) | Kv1 potassium channels (Kv1.1, Kv1.2, Kv1.6), electrostatic, hydrophobic interactions | [17] |
| Amino acid sequence: QPLRKLCILHRNPGRCYQKIPAFYYNQKKKQCEGFTWSGCGGNSNRFKTIEECRRTCIRK | |||||
2. Study Design
3. Therapeutic Applications of Animal-Derived Protein Toxins: From Molecular Targets to Clinical Tools
4. Biotechnology and Recombinant Proteins in Medicine
5. Characteristics of Dendroaspis polylepis
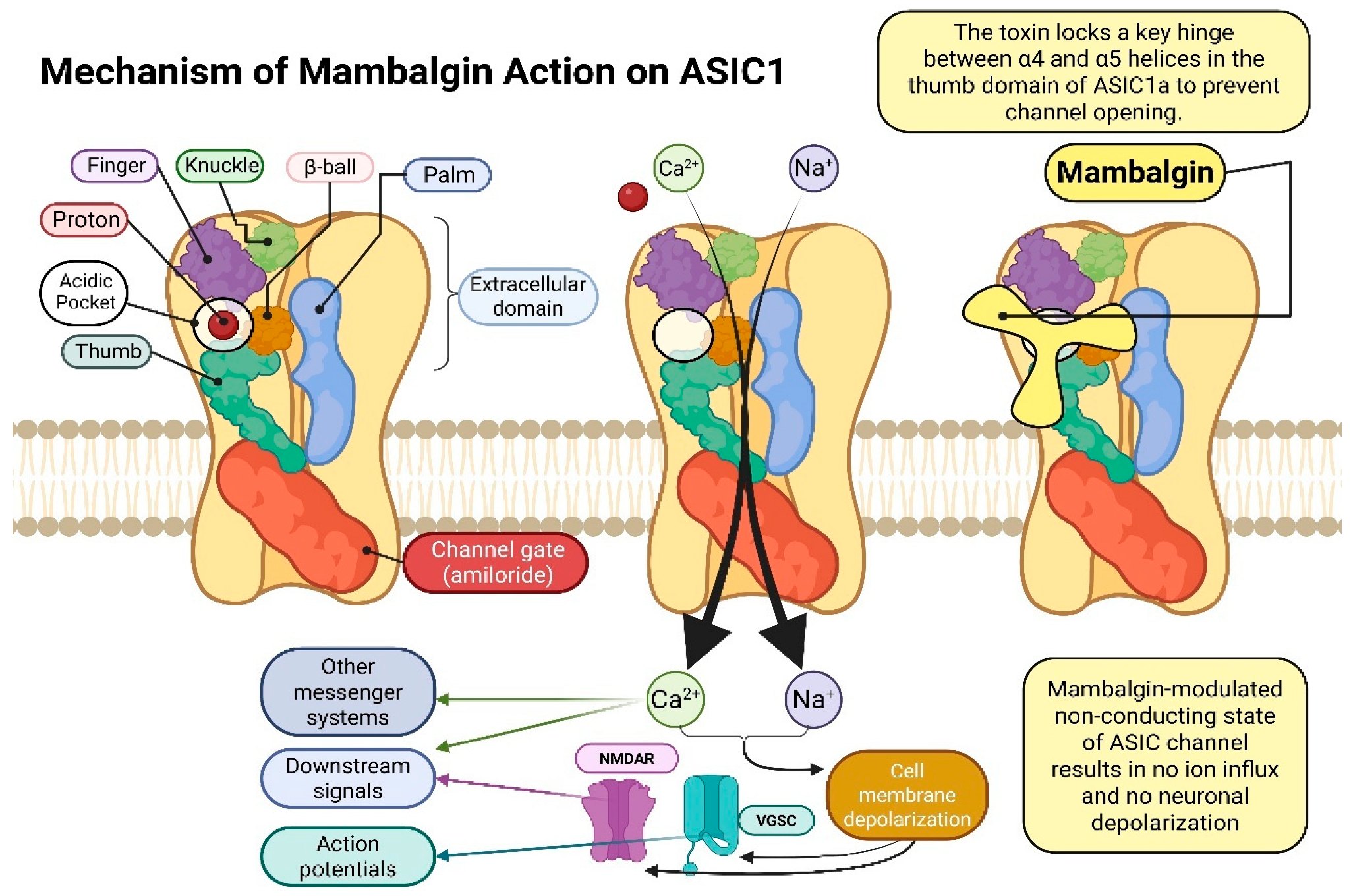
6. Mambalgins
6.1. Characteristics of Mambalgins
6.2. Acid-Sensing Ion Channels (ASICS)—Structure, Function, and Biological Significance
7. Genetic Recombination Techniques for the Mambalgin Protein as a Selective ASIC1a Channel Blocker: From Expression to Anticancer Applications
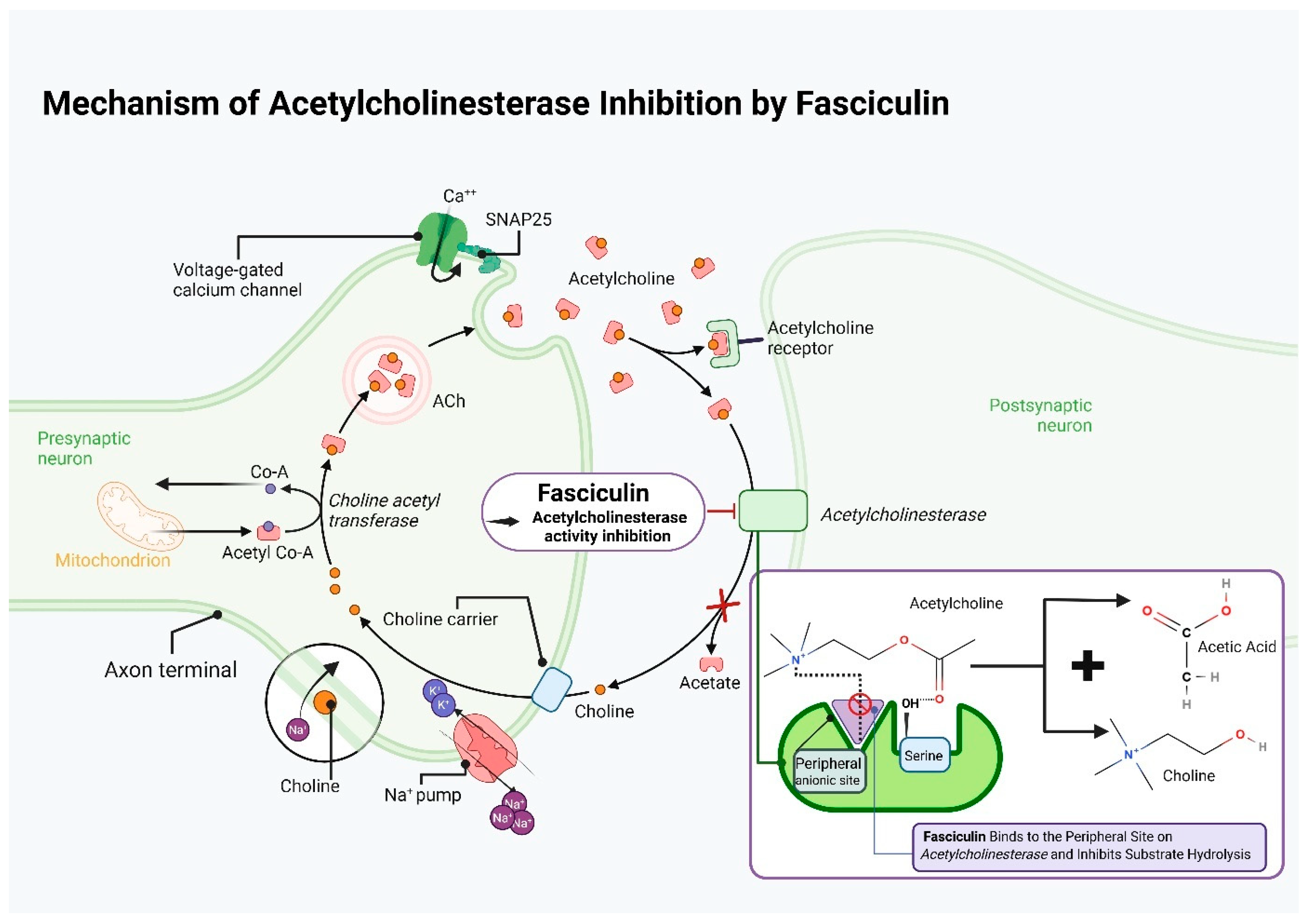
8. Fasciculin
8.1. Characteristics of Fasciculins
8.2. Mechanism of Fasciculin Action
8.3. The Use of Fasciculin in Medical Research
9. Dendrotoxin
9.1. Characteristics of Dendrotoxins
9.2. Structure of Dendrotoxins
9.3. Mechanism of Dendrotoxin Action
9.4. The Use of Dendrotoxin-K in Medical Research
9.5. The Use of Dendrotoxin-I in Medical Research
10. Conclusions, Limitations and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borzelleca, J.F. Paracelsus: Herald of modern toxicology. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 53, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandjean, P. Paracelsus revisited: The dose concept in a complex world. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 119, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantenbein, U.L. Poison and its dose: Paracelsus on toxicology. In Toxicology in the Middle Ages and Renaissance; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, S.D.; Norton, R.S. Conotoxin gene superfamilies. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 6058–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.H.; Muttenthaler, M.; Dutertre, S.; Himaya, S.W.A.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Conotoxins: Chemistry and biology. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 11510–11549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, T.C.; Yamashita, K.M.; Barbaro, K.C.; Saiki, M.; Santoro, M.L. Comparative analysis of newborn and adult Bothrops jararaca snake venoms. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1443–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, S.M.; Oliveira, A.K.; Menezes, M.C.; Zelanis, A. The proteinase-rich proteome of Bothrops jararaca venom. Toxin Rev. 2014, 33, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, F.J.; Strydom, D.J. Snake venom. The amino acid sequence of protein A from Dendroaspis polylepis polylepis (black mamba) venom. Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 1980, 361, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spawls, S.; Branch, B. The Dangerous Snakes of Africa; Blandford: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Management of Snakebites, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Waheed, H.; Moin, S.F.; Choudhary, M.I. Snake Venom: From Deadly Toxins to Life-saving Therapeutics. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1874–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petras, D.; Heiss, P.; Harrison, R.A.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Calvete, J.J. Top-down venomics of the East African green mamba, Dendroaspis angusticeps, and the black mamba, Dendroaspis polylepis, highlight the complexity of their toxin arsenals. J. Proteom. 2016, 146, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Xu, T.L. Acidosis, acid-sensing ion channels, and neuronal cell death. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 44, 350–358, S2CID 15169653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diochot, S.; Baron, A.; Salinas, M.; Douguet, D.; Scarzello, S.; Dabert-Gay, A.S.; Debayle, D.; Friend, V.; Alloui, A.; Lazdunski, M.; et al. Black mamba venom peptides target acid-sensing ion channels to abolish pain. Nature 2012, 490, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.L.; Anderson, A.J.; Mbugua, P.M.; Karlsson, E. Toxins from mamba venoms that facilitate neuroiluscular transmission. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 1984, 3, 91–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadón, A.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Valerio, L.G. Onchidal and fasciculins. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 455–466. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, A.L. Recent studies on dendrotoxins and potassium ion channels. Gen. Pharmacol. 1997, 28, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterholzner, S.J.; Poppenberger, B.; Rozhon, W. Toxin–antitoxin systems: Biology, identification, and application. Mob. Genet. Elem. 2013, 3, e26219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, A.; Waldmann, R.; Lazdunski, M. ASIC-like, proton-activated currents in rat hippocampal neurons. J. Physiol. 2002, 539, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalliedde, L. Animal toxins. Br. J. Anaesth. 1995, 74, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro Figueiredo Bordon, K.; Cologna, C.T.; Fornari-Baldo, E.C.; Pinheiro-Júnior, E.L.; Cerni, F.A.; Amorim, F.G.; Anjolette, F.A.P.; Cordeiro, F.A.; Wiezel, G.A.; Cardoso, I.A.; et al. From animal poisons and venoms to medicines: Achievements, challenges and perspectives in drug discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.J.; Herzig, V.; King, G.F.; Alewood, P.F. The insecticidal potential of venom peptides. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3665–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelsen, D.R.; Nisani, Z.; Cooper, A.M.; Fox, G.A.; Gren, E.C.; Corbit, A.G.; Hayes, W.K. Poisons, toxungens, and venoms: Redefining and classifying toxic biological secretions and the organisms that employ them. Biol. Rev. 2014, 89, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.C.; Armugam, A.; Jeyaseelan, K. Snake venom components and their applications in biomedicine. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 3030–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wüster, W.; Vonk, F.J.; Harrison, R.A.; Fry, B.G. Complex cocktails: The evolutionary novelty of venoms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Roelants, K.; Champagne, D.E.; Scheib, H.; Tyndall, J.D.; King, G.F.; Nevalainen, T.J.; Norman, J.A.; Lewis, R.J.; Norton, R.S.; et al. The toxicogenomic multiverse: Convergent recruitment of proteins into animal venoms. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 483–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondetti, M.A.; Rubin, B.; Cushman, D.W. Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme: New class of orally active antihypertensive agents. Science 1977, 196, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, J. From snake venom to ACE inhibitor-The discovery and rise of captopril. Pharm. J. 2009, 282, 455. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, A.C.; Ianzer, D.; Guerreiro, J.R.; Serrano, S.M. Bradykinin-potentiating peptides: Beyond captopril. Toxicon 2012, 59, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangieh, J.; Rima, M.; Fajloun, Z.; Henrion, D.; Sabatier, J.M.; Legros, C.; Mattei, C. Snake venom components: Tools and cures to target cardiovascular diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawgood, B.J. Maurício Rocha e Silva MD: Snake venom, bradykinin and the rise of autopharmacology. Toxicon 1997, 35, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housley, D.M.; Housley, G.D.; Liddell, M.J.; Jennings, E.A. Scorpion toxin peptide action at the ion channel subunit level. Neuropharmacology 2017, 127, 46–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavya, J.; Francois, N.N.; More, V.S.; More, S.S. Scorpion Toxin Polyptides as Therapeutic Agents: An Overview. Protein Pept. Lett. 2016, 23, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiseh, M.; Gabikian, P.; Bahrami, S.B.; Veiseh, O.; Zhang, M.; Hackman, R.C.; Ravanpay, A.C.; Stroud, M.R.; Kusuma, Y.; Hansen, S.J.; et al. Tumor paint: A chlorotoxin:Cy5.5 bioconjugate for intraoperative visualization of cancer foci. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6882–6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Asmari, A.K.; Islam, M.; Al-Zahrani, A.M. In vitro analysis of the anticancer properties of scorpion venom in colorectal and breast cancer cell lines. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.L.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Miller, K.; Strong, P.N. Antimicrobial peptides from scorpion venoms. Toxicon 2014, 88, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Larios, A.; Gurrola, G.B.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Possani, L.D. Hadrurin, a new antimicrobial peptide from the venom of the scorpion Hadrurus aztecus. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5023–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’Gouemo, P.; Rittenhouse, A.R. Biophysical and pharmacological characterization of voltage-sensitive calcium currents in neonatal rat inferior colliculus neurons. Neuroscience 2000, 96, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, A.H.; Ferreira, J.; Cordeiro, M.D.N.; Vieira, L.B.; De Castro, C.J.; Trevisan, G.; Reis, H.; Souza, I.A.; Richardson, M.; Prado, M.A.; et al. Analgesic effect in rodents of native and recombinant Phα1β toxin, a high-voltage-activated calcium channel blocker isolated from armed spider venom. Pain 2008, 140, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigo, F.K.; Trevisan, G.; Rosa, F.; Dalmolin, G.D.; Otuki, M.F.; Cueto, A.P.; de Castro Junior, C.J.; Romano-Silva, M.A.; Cordeiro, M.d.N.; Richardson, M.; et al. Spider peptide Phα1β induces analgesic effect in a model of cancer pain. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 1226–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Adams, M.E. Lycotoxins, antimicrobial peptides from venom of the wolf spider Lycosa carolinensis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 2059–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, J.; Feng, W.; Bao, N.; Song, D.; Zhu, B.C. Pharmacological characterisation of spider antimicrobial peptides. Protein Pept. Lett. 2005, 12, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aridoss, G.; Kim, D.M.; Kim, J.I.; Kang, J.E. Ziconotide (ω-conotoxin MVIIA)—Efficient solid-phase synthesis of a linear precursor peptide and its strategic native folding. Pept. Sci. 2021, 113, e24223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljanich, G.P. Ziconotide: Neuronal calcium channel blocker for treating severe chronic pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 3029–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A.; Day, M.; Heavner, J.E. Ziconotide: An update and review. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2008, 9, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safavi-Hemami, H.; Brogan, S.E.; Olivera, B.M. Pain therapeutics from cone snail venoms: From Ziconotide to novel non-opioid pathways. J. Proteom. 2019, 190, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rady, I.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Rady, M.; Mukhtar, H. Melittin, a major peptide component of bee venom, and its conjugates in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2017, 402, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-C.; Hao, D.-J.; Zhang, Q.; An, J.; Zhao, J.-J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, L.-L.; Yang, H. Application of bee venom and its main constituent melittin for cancer treatment. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 1113–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.M.; Tao, W.H.; Diao, Y.L.; Fang, P.H.; Wang, J.J.; Bo, P.; Qian, F. Melittin induces human gastric cancer cell apoptosis via activation of mitochondrial pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.; Park, M.H.; Kollipara, P.S.; An, B.J.; Song, H.S.; Han, S.B.; Kim, J.H.; Song, M.J.; Hong, J.T. Anti-cancer effect of bee venom toxin and melittin in ovarian cancer cells through induction of death receptors and inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 258, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, M.; He, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wang, F.; Song, C.; Sun, S.; Ling, C.; Xu, Z. Melittin prevents liver cancer cell metastasis through inhibition of the Rac1-dependent pathway. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.F.; Chen, Z. Melittin exerts an antitumor effect on non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3581–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.-J.; Choi, Y.; Shin, J.-M.; Cho, H.-J.; Kang, J.-H.; Park, K.-K.; Choe, J.-Y.; Bae, Y.-S.; Han, S.-M.; Kim, C.-H.; et al. Melittin suppresses EGF-induced cell motility and invasion by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eze, O.B.; Nwodo, O.F.; Ogugua, V.N. Therapeutic effect of honey bee venom. Proteins (Enzym.) 2016, 1, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kokot, Z.J.; Matysiak, J.; Kłs, J.; Kędzia, B.; Hołderna-Kędzia, E. Application of Principal Component Analysis for evaluation of chemical and antimicrobial properties of honey bee (Apis mellifera) venom. J. Apic. Res. 2009, 48, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.S.; Gwee, M.C.; Yuen, R.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Khoo, H.E. Stonustoxin: Effects on neuromuscular function in vitro and in vivo. Toxicon 1994, 32, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadessy, F.J.; Chen, D.; Kini, R.M.; Chung, M.M.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Khoo, H.E.; Yuen, R. Stonustoxin is a novel lethal factor from stonefish (Synanceja horrida) venom: cDNA cloning and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 25575–25581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.S.; Gwee, M.E.; Yuen, R.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Khoo, H.E. Stonustoxin: A highly potent endothelium-dependent vasorelaxant in the rat. Toxicon 1993, 31, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, H.E.; Chen, D.; Yuen, R. Role of free thiol groups in the biological activities of stonustoxin, a lethal factor from stonefish (Synanceja horrida) venom. Toxicon 1998, 36, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Mishra, R.; Biswas, A.K.; Dasgupta, S.C.; Giri, B. Anticancer potential of animal venoms and toxins. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 48, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Gopal, G.J.; Kumar, A. Strategies for the production of recombinant protein in Escherichia coli. Protein J. 2013, 32, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, H.P.; Mortensen, K.K. Advanced genetic strategies for recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 115, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Anumanthan, A.; Gao, X.G.; Ilangovan, K.; Suzara, V.V.; Düzgüneş, N.; Renugopalakrishnan, V. Expression of recombinant proteins in Pichia pastoris. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2007, 142, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Schutter, K.; Lin, Y.-C.; Tiels, P.; Van Hecke, A.; Glinka, S.; Weber-Lehmann, J.; Rouzé, P.; Van de Peer, Y.; Callewaert, N. Genome sequence of the recombinant protein production host Pichia pastoris. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.A.; Echavarri-Erasun, C. Yeast biotechnology. In The Yeasts; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 21–44. [Google Scholar]
- O’Callaghan, P.M.; James, D.C. Systems biotechnology of mammalian cell factories. Brief. Funct. Genom. Proteom. 2008, 7, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targovnik, A.M.; Arregui, M.B.; Bracco, L.F.; Urtasun, N.; Baieli, M.F.; Segura, M.M.; Simonella, M.A.; Fogar, M.; Wolman, F.J.; Cascone, O.; et al. Insect larvae: A new platform to produce commercial recombinant proteins. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonomou, L.; Schneider, Y.J.; Agathos, S.N. Insect cell culture for industrial production of recombinant proteins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 62, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, M.J.; Burnett, A.C. Therapeutic recombinant protein production in plants: Challenges and opportunities. Plants People Planet 2020, 2, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egelkrout, E.; Rajan, V.; Howard, J.A. Overproduction of recombinant proteins in plants. Plant Sci. 2012, 184, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusnadi, A.R.; Nikolov, Z.L.; Howard, J.A. Production of recombinant proteins in transgenic plants: Practical considerations. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1997, 56, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, A.J.; Zhu, H.; Le, L.C.; Jevnikar, A.M.; Lee, B.H.; Brandle, J.E.; Menassa, R. Recombinant protein production in a variety of Nicotiana hosts: A comparative analysis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, G.M. CHO cells in biotechnology for production of recombinant proteins: Current state and further potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demain, A.L.; Vaishnav, P. Production of recombinant proteins by microbes and higher organisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, B.R.; Patten, C.L. Molecular Biotechnology: Principles and Applications of Recombinant DNA; John Wiley Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.A. Development of recombinant vaccines for botulinum neurotoxin. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.K.; Xie, G.; Foley, B.T.; Smith, T.J.; Munk, A.C.; Bruce, D.; A Smith, L.; Brettin, T.S.; Detter, J.C. Recombination and insertion events involving the botulinum neurotoxin complex genes in Clostridium botulinum types A, B, E and F and Clostridium butyricum type E strains. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, D.J.; Kreitman, R.; Wilson, W.; Squires, D.; Pastan, I. Recombinant immunotoxins for treating cancer. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 293, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, B.; Farajnia, S.; Ahdi Khosroshahi, S.; Safari, F.; Yousefi, M.; Dariushnejad, H.; Rahbarnia, L. Immunotoxins in cancer therapy: Review and update. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 36, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potala, S.; Sahoo, S.K.; Verma, R.S. Targeted therapy of cancer using diphtheria toxin-derived immunotoxins. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, F.; Aucoin, M.G.; Jahanian-Najafabadi, A. Targeted diphtheria toxin-based therapy: A review article. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Germana, S.; Huang, C.A.; Madsen, J.C.; Sachs, D.H.; Wang, Z. Diphtheria-toxin based anti-human CCR4 immunotoxin for targeting human CCR4+ cells in vivo. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1458–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litzinger, M.T.; Fernando, R.; Curiel, T.J.; Grosenbach, D.W.; Schlom, J.; Palena, C. IL-2 immunotoxin denileukin diftitox reduces regulatory T cells and enhances vaccine-mediated T-cell immunity. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2007, 110, 3192–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoukian, G.; Hagemeister, F. Denileukin diftitox: A novel immunotoxin. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2009, 9, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitman, R.J.; Pastan, I. Antibody fusion proteins: Anti-CD22 recombinant immunotoxin moxetumomab pasudotox. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6398–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reulen, H.J.; Suero Molina, E.; Zeidler, R.; Gildehaus, F.J.; Böning, G.; Gosewisch, A.; Stummer, W. Intracavitary radioimmunotherapy of high-grade gliomas: Present status and future developments. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 1109–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xie, J.; He, H.Y.; Huang, E.W.; Cao, Q.H.; Luo, L.; Liao, Y.S.; Guo, Y. Suppression of CLC-3 chloride channel reduces the aggressiveness of glioma through inhibiting nuclear factor-κB pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 63788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minea, R.; Swenson, S.; Costa, F.; Chen, T.C.; Markland, F.S. Development of a novel recombinant disintegrin, contortrostatin, as an effective anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic agent. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2005, 34, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, S.; Costa, F.; Ernst, W.; Fujii, G.; Markland, F.S. Contortrostatin, a snake venom disintegrin with anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activity. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2005, 34, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Lohse, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; McCafferty, J.; Rasmussen, A.R. Recombinant Antivenoms; University of Copenhagen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.S.; Jiang, B.R.; Hu, K.C.; Liu, C.H.; Hsieh, W.C.; Lin, M.H.; Sung, W.C. Development of a broad-spectrum antiserum against cobra venoms using recombinant three-finger toxins. Toxins 2021, 13, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jing, L.; Xu, K. A unique approach for high level expression and production of a recombinant cobra neurotoxin in Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 94, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkeaw, K.; Sakolvaree, Y.; Srimanote, P.; Tongtawe, P.; Maneewatch, S.; Sookrung, N.; Tungtrongchitr, A.; Tapchaisri, P.; Kurazono, H.; Chaicumpa, W. Human monoclonal ScFv neutralize lethal Thai cobra, Naja kaouthia, neurotoxin. J. Proteom. 2009, 72, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.; Oliveira, T.; Silveira, C.; Caporrino, M.; Rodriguez, D.; Moura-Da-Silva, A.; Ramos, O.; Rucavado, A.; Gutiérrez, J.; Magalhães, G.; et al. A neutralizing recombinant single chain antibody, scFv, against BaP1, A PI hemorrhagic metalloproteinase from Bothrops asper snake venom. Toxicon 2014, 87, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B.; Leon, G.; Angulo, Y.; Rucavado, A.; Nunez, V. Neutralization of Bothrops asper venom by antibodies, natural products and synthetic drugs: Contributions to understanding snakebite envenomings and their treatment. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1012–1028, Erratum in Toxicon 2010, 55, 1412–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logtenberg, T. Antibody cocktails: Next-generation biopharmaceuticals with improved potency. Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastan, I.; Hassan, R.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Kreitman, R.J. Immunotoxin therapy of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandaranayake, A.D.; Almo, S.C. Recent advances in mammalian protein production. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, K.A. Engineered toxins: New therapeutics. Toxicon 2009, 54, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalten, M.; Bakhuis, C.F.J.; Asaggau, I.; Wulfse, M.; van Binsbergen, M.F.; Arntz, E.R.A.N.; Troenokarso, M.F.; Oediet Doebe, J.L.R.; Mahamuud, U.; Belbachir, L.; et al. The clinical course and treatment of black mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis) envenomations: A narrative review. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, B.J.; Boyer, L.V.; Seifert, S.A. Non-native (exotic) snake envenomations in the US, 2005–2011. Toxins 2014, 6, 2899–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, P.S.; Davidson, T.M. Biology and treatment of the mamba snakebite. Wilderness Environ. Med. 1996, 7, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Geographic. Black Mamba, Facts and Photos; National Geographic Partners: Washington, DC, USA; Available online: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/reptiles/b/black-mamba/ (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Brittanica. Black Mamba; Encyclopeadia Brittanica: Chicago, IL, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.britannica.com/animal/black-mamba (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Guinness World Records Fastest Land Snake, Londyn: Guinness World Records. Available online: https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/70269-fastest-land-snake (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Spawls, S.; Spawls, S.; Howell, K.; Hinkel, H.; Menegon, M. Field Guide to East African Reptiles; Bloomsbury Publishing: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gulsevin, A.; Meiler, J. An Investigation of Three-Finger Toxin-nAChR Interactions through Rosetta Protein Docking. Toxins 2020, 12, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiremath, K.; Dodakallanavar, J.; Sampat, G.H.; Patil, V.S.; Harish, D.R.; Chavan, R.; Hegde, H.V.; Roy, S. Three finger toxins of elapids: Structure, function, clinical applications and its inhibitors. Mol. Divers. 2024, 28, 3409–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, S.V.; Valle, M.B.; Mackessy, S.P.; Menzies, S.K.; Casewell, N.R.; Ahmadi, S.; Burlet, N.J.; Muratspahić, E.; Sappington, I.; Overath, M.D.; et al. De novo designed proteins neutralize lethal snake venom toxins. Nature 2025, 639, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RCSB PDB Protein Data Bank. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/2MFA (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Diochot, S.; Baron, A.; Rash, L.D.; Deval, E.; Escoubas, P.; Scarzello, S.; Salinas, M.; Lazdunski, M. A new sea anemone peptide, APETx2, inhibits ASIC3, a major acid-sensitive channel in sensory neurons. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoubas, P.; De Weille, J.R.; Lecoq, A.; Diochot, S.; Waldmann, R.; Champigny, G.; Moinier, D.; Ménez, A.; Lazdunski, M. Isolation of a tarantula toxin specific for a class of proton-gated Na+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25116–25121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkov, M.; Shulepko, M.; Osmakov, D.; Andreev, Y.; Sudarikova, A.; Vasileva, V.; Pavlyukov, M.S.; Latyshev, Y.A.; Potapov, A.A.; Kirpichnikov, M.; et al. Mambalgin-2 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Glioma Cells via Interaction with ASIC1a. Cancers 2020, 12, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourier, G.; Salinas, M.; Kessler, P.; Stura, E.A.; Leblanc, M.; Tepshi, L.; Besson, T.; Diochot, S.; Baron, A.; Douguet, D.; et al. Mambalgin-1 Pain-relieving Peptide, Stepwise Solid-phase Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Functional Domain for Acid-sensing Ion Channel 1a Inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 291, 2616–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Rash, L.D. Acid-sensing ion channel (ASIC) structure and function: Insights from spider, snake and sea anemone venoms. Neuropharmacology 2017, 127, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingueglia, E.; de Weille, J.R.; Bassilana, F.; Heurteaux, C.; Sakai, H.; Waldmann, R.; Lazdunski, M. A modulatory subunit of acid sensing ion channels in brain and dorsal root ganglion cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29778–29783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasti, J.; Furukawa, H.; Gonzales, E.B.; Gouaux, E. Structure of acid-sensing ion channel 1 at 1.9 A resolution and low pH. Nature 2007, 449, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gründer, S.; Pusch, M. Biophysical properties of acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs). Neuropharmacology 2015, 94, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, R.; Champigny, G.; Bassilana, F.; Heurteaux, C.; Lazdunski, M. A proton-gated cation channel involved in acid-sensing. Nature 1997, 386, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, D.M.; Soto, E. Editorial: ASICs: Structure, Function, and Pharmacology. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 831830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanukoglu, I. ASIC and ENaC type sodium channels: Conformational states and the structures of the ion selectivity filters. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, T.W.; Frey, E.N.; Askwith, C.C. Structure and activity of the acid-sensing ion channels. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012, 303, C699–C710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Osmakov, D.I.; Andreev, Y.A.; Kozlov, S.A. Acid-sensing ion channels and their modulators. Biochem. Biokhimiia 2014, 79, 152845, S2CID 14874830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkhatib, W.; Yanez-Guerra, L.A.; Mayorova, T.D.; Currie, M.A.; Singh, A.; Perera, M.; Gauberg, J.; Senatore, A. Function and phylogeny support the independent evolution of an ASIC-like Deg/ENaC channel in the Placozoa. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluka, K.A.; Winter, O.C.; Wemmie, J.A. Acid-sensing ion channels: A new target for pain and CNS diseases. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2009, 12, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zha, X.M. Acid-sensing ion channels: Trafficking and synaptic function. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xiong, Z.G.; Pignataro, G.; Li, M.; Chang, S.Y.; Simon, R.P. Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) as pharmacological targets for neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Baron, A.; Lingueglia, E. Pharmacology of acid-sensing ion channels—Physiological and therapeutical perspectives. Neuropharmacology 2015, 94, 19–35, S2CID 25550294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voilley, N. Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs): New targets for the analgesic effects of non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2004, 3, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynagh, T.; Romero-Rojo, J.L.; Lund, C.; Pless, S.A. Molecular Basis for Allosteric Inhibition of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a by Ibuprofen. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 8192–8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, T.D.; Si, H.F.; Li, J.; Yang, T.; Zhu, M.; Wang, B.; Simon, R.P.; Xiong, Z.G. Amiloride Analogs as ASIC1a Inhibitors. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezri, G.; Baghban Kohneh Rouz, B.; Ofoghi, H.; Davarpanah, S.J. Heterologous expression of biologically active Mambalgin-1 peptide as a new potential anticancer, using a PVX-based viral vector in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2020, 142, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodin, M.M.; Zaitlin, D.; Naidu, R.A.; Lommel, S.A. Nicotiana benthamiana: Its History and Future as a Model for Plant-Pathogen Interactions. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2015, 2015, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurotani, K.I.; Hirakawa, H.; Shirasawa, K.; Tanizawa, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Isobe, S.; Notaguchi, M. Genome Sequence and Analysis of Nicotiana benthamiana, the Model Plant for Interactions between Organisms. Plant Cell Physiol. 2023, 64, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, E.D.; Rajniak, J.; Sattely, E.S. Multiplicity of the Agrobacterium Infection of Nicotiana benthamiana for Transient DNA Delivery. ACS Synth. Biol. 2023, 12, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norkunas, K.; Harding, R.; Dale, J.; Dugdale, B. Improving agroinfiltration-based transient gene expression in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Aziz, N.; Tan, B.C.; Rejab, N.A.; Othman, R.Y.; Khalid, N. A New Plant Expression System for Producing Pharmaceutical Proteins. Mol. Biotechnol. 2020, 62, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P.D. Analysis of Cell Viability by the MTT Assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018, 2018, pdb-prot095505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grela, E.; Kozłowska, J.; Grabowiecka, A. Current methodology of MTT assay in bacteria—A review. Acta Histochem. 2018, 120, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkov, M.L.; Kirichenko, A.V.; Shulepko, M.A.; Mikhaylova, I.N.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Lyukmanova, E.N. Mambalgin-2 Inhibits Growth, Migration, and Invasion of Metastatic Melanoma Cells by Targeting the Channels Containing an ASIC1a Subunit Whose Up-Regulation Correlates with Poor Survival Prognosis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Zaguilán, R.; Seftor, E.A.; Seftor, R.E.; Chu, Y.W.; Gillies, R.J.; Hendrix, M.J. Acidic pH enhances the invasive behavior of human melanoma cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1996, 14, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhme, I.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Acidic tumor microenvironment in human melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramonov, A.S.; Kocharovskaya, M.V.; Tsarev, A.V.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Loktyushov, E.V.; Shulepko, M.A.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shenkarev, Z.O. Structural Diversity and Dynamics of Human Three-Finger Proteins Acting on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idalia, V.M.N.; Bernardo, F. Escherichia coli as a model organism and its application in biotechnology. Recent Adv. Physiol. Pathog. Biotechnol. Appl. 2017, 13, 253–274. [Google Scholar]
- Pouresmaeil, M.; Azizi-Dargahlou, S. Factors involved in heterologous expression of proteins in E. coli host. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmakov, D.I.; Koshelev, S.G.; Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shulepko, M.A.; Andreev, Y.A.; Illes, P.; Kozlov, S.A. Multiple Modulation of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a by the Alkaloid Daurisoline. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulepko, M.A.; Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Dubovskii, P.V.; Astapova, M.V.; Feofanov, A.V.; Arseniev, A.S.; Utkin, Y.N.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Dolgikh, D.A. Towards universal approach for bacterial production of three-finger Ly6/uPAR proteins: Case study of cytotoxin I from cobra N. oxiana. Protein Expr. Purif. 2017, 130, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuiderweg, E.R. Mapping protein—Protein interactions in solution by NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, B.K.; Peng, H.B. Xenopus laevis: Practical Uses in Cell and Molecular Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992; Volume 36. [Google Scholar]
- Bychkov, M.L.; Shulepko, M.A.; Vasileva, V.Y.; Sudarikova, A.V.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Lyukmanova, E.N. ASIC1a Inhibitor mambalgin-2 Suppresses the Growth of Leukemia Cells by Cell Cycle Arrest. Acta Naturae 2020, 12, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudarikova, A.V.; Bychkov, M.L.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin, V.I.; Shlepova, O.V.; Shulepko, M.A.; Koshelev, S.G.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Lyukmanova, E.N. Mambalgin-2 Inhibits Lung Adenocarcinoma Growth and Migration by Selective Interaction with ASIC1/α-ENaC/γ-ENaC Heterotrimer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 904742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Lomonte, B.; Lohse, B.; Fernández, J.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Unveiling the nature of black mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis) venom through venomics and antivenom immunoprofiling: Identification of key toxin targets for antivenom development. J. Proteom. 2015, 119, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ithurralde, D.; Silveira, R.; Barbeito, L.; Dajas, F. Fasciculin, a powerful anticholinesterase polypeptide from Dendroaspis angusticeps venom. Neurochem. Int. 1983, 5, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarch, V.; Brander, L.; Cioccari, L. An Unexpected Case of Black Mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis) Bite in Switzerland. Case Rep. Crit. Care 2017, 2017, 5021924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, B.W.; Preston, H.S.; Sato, A.; Rosen, L.S.; Searl, J.E.; Rudko, A.D.; Richardson, J.S. Three dimensional structure of erabutoxin b neurotoxic protein: Inhibitor of acetylcholine receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 2991–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.K.S.; Jayaraman, G.; Lee, C.S.; Arunkumar, A.I.; Sivaraman, T.; Samuel, D.; Yu, C. Snake venom cardiotoxins-structure, dynamics, function and folding. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1997, 15, 431–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- le Du, M.; Marchot, P.; Bougis, P.; Fontecilla-Camps, J. 1.9-A resolution structure of fasciculin 1, an anti-acetylcholinesterase toxin from green mamba snake venom. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 22122–22130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protein Data Bank. 2025. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1FSC (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Larréché, S.; Mion, G.; Clapson, P.; Debien, B.; Wybrecht, D.; Goyffon, M. Neurotoxines ophidiennes. Ann. Françaises D’Anesthésie Réanimation 2008, 27, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, R.; Cerveñansky, C.; Dajas, F.; Tipton, K.F. Fasciculin inhibition of acetylcholinesterase is prevented by chemical modification of the enzyme at a peripheral site. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1201, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chippaux, J.P.; Goyffon, M. Envenimations et intoxications par les animaux venimeux ou vénéneux—I. Généralitś [Venomous and poisonous animals—I. Overview]. Med. Trop. Rev. Corps Sante Colon. 2006, 66, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, P. Anticholinesterase agents. Goodman Gilman’s Pharmacol. Basis Ther. 2006, 11, 201–216. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, E.; Mbugua, P.M.; Rodriguez-Ithurralde, D. Fasciculins, anticholinesterase toxins from the venom of the green mamba Dendroaspis angusticeps. J. Physiol. 1984, 79, 232–240. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry, T.L.; Rabl, C.R.; Neumann, E. Binding of the neurotoxin fasciculin 2 to the acetylcholinesterase peripheral site drastically reduces the association and dissociation rate constants for N-methylacridinium binding to the active site. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van denBorn, H.K.; Radić, Z.; Marchot, P.; Taylor, P.; Tsigelny, I. Theoretical analysis of the structure of the peptide fasciculin and its docking to acetylcholinesterase. Protein Sci. 1995, 4, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchot, P. L’interaction fasciculine-acétylcholinestérase [The fasciculin-acetylcholinesterase interaction]. J. Soc. Biol. 1999, 193, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvir, H.; Silman, I.; Harel, M.; Rosenberry, T.L.; Sussman, J.L. Acetylcholinesterase: From 3D structure to function. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 187, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radić, Z.; Quinn, D.M.; Vellom, D.C.; Camp, S.; Taylor, P. Allosteric control of acetylcholinesterase catalysis by fasciculin. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 20391–20399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolucci, C.; Stojan, J.; Yu, Q.S.; Greig, N.H.; Lamba, D. Kinetics of Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase inhibition by bisnorcymserine and crystal structure of the complex with its leaving group. Biochem. J. 2012, 444, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radić, Z.; Duran, R.; Vellom, D.C.; Li, Y.; Cervenansky, C.; Taylor, P. Site of fasciculin interaction with acetylcholinesterase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 11233–11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, M.; Kleywegt, G.J.; Ravelli, R.B.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. Crystal structure of an acetylcholinesterase-fasciculin complex: Interaction of a three-fingered toxin from snake venom with its target. Structure 1995, 3, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.; Wilson, E.J.; Cerveñansky, C.; Rosenberry, T.L. Fasciculin 2 binds to the peripheral site on acetylcholinesterase and inhibits substrate hydrolysis by slowing a step involving proton transfer during enzyme acylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 19694–19701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, Y.; Taylor, P.; Marchot, P. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition by fasciculin: Crystal structure of the complex. Cell 1995, 83, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerveñansky, C.; Durán, R.; Karlsson, E. Fasciculin: Modification of carboxyl groups and discussion of structure-activity relationship. Toxicon 1996, 34, 718–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, K.; Shen, T.; Henchman, R.H.; Bourne, Y.; Marchot, P.; McCammon, J.A. Mechanism of acetylcholinesterase inhibition by fasciculin: A 5-ns molecular dynamics simulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6153–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharabi, O.; Peleg, Y.; Mashiach, E.; Vardy, E.; Ashani, Y.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L.; Shifman, J.M. Design, expression and characterization of mutants of fasciculin optimized for interaction with its target, acetylcholinesterase. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2009, 22, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafurke, U.; Erijman, A.; Aizner, Y.; Shifman, J.M.; Eichler, J. Synthetic peptides mimicking the binding site of human acetylcholinesterase for its inhibitor fasciculin 2. J. Pept. Sci. 2015, 21, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchot, P.; Bougis, P.E. Elapidae Toxins: The Fasciculins, and their Interaction with Acetylcholinesterase. In Animal Toxins; Rochat, H., Martin-Eauclaire, M.F., Eds.; Methods and Tools in Biosciences and Medicine; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toiber, D.; Berson, A.; Greenberg, D.; Melamed-Book, N.; Diamant, S.; Soreq, H. N-acetylcholinesterase-induced apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Gray, N.W.; Brimijoin, S. Amyloid-beta alters trafficking of internalized acetylcholinesterase and dextran. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 1, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nachon, F.; Carletti, E.; Ronco, C.; Trovaslet, M.; Nicolet, Y.; Jean, L.; Renard, P.Y. Crystal structures of human cholinesterases in complex with huprine W and tacrine: Elements of specificity for anti-Alzheimer’s drugs targeting acetyl- and butyryl-cholinesterase. Biochem. J. 2013, 453, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waqar, M.; Batool, S. In silico analysis of binding of neurotoxic venom ligands with acetylcholinesterase for therapeutic use in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 372, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, R.D.; Campos, F.O.; Dajas, F.; Inestrosa, N.C. Developmental regulation of mouse brain monomeric acetylcholinesterase. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 1998, 16, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajas, F.; Silveira, R.; Costa, G.; Castello, M.E.; Jerusalinsky, D.; Medina, J.; Levesque, D.; Greenfield, S. Differential cholinergic and non-cholinergic actions of acetylcholinesterase in the substantia nigra revealed by fasciculin-induced inhibition. Brain Res. 1993, 616, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, A.J.; Harvey, A.L.; Mbugua, P.M. Effects of fasciculin 2, an anticholinesterase polypeptide from green mamba venom, on neuromuscular transmission in mouse diaphragm preparations. Neurosci. Lett. 1985, 54, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/ (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, C.; Gauthier, S.; Corbett, A.; Brayne, C.; Aarsland, D.; Jones, E. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2011, 377, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzman, R. Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 314, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; Blennow, K.; Breteler, M.M.; De Strooper, B.; Frisoni, G.B.; Salloway, S.; Van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2016, 388, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, D.G.; Feldman, H. Causes of Alzheimer’s disease. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2000, 162, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, S.M. The new cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease, Part 2: Illustrating their mechanisms of action. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2000, 61, 813–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, R.; Garcia, A.G.; Marco-Contelles, J. Recent advances in the multitarget-directed ligands approach for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Res. Rev. 2013, 33, 139–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oset-Gasque, M.J.; Marco-Contelles, J. Alzheimer’s disease, the “one-molecule, one-target” paradigm, and the multitarget directed ligand approach. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasina, M.F.; Faria, A.C.; Gardino, P.F.; Hokoc, J.N.; Almeida, O.M.; de Mello, F.G.; Arruti, C.; Dajas, F. Evidence for a noncholinergic function of acetylcholinesterase during development of chicken retina as shown by fasciculin. Cell Tissue Res. 2000, 299, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchot, P.; Bourne, Y.; Prowse, C.N.; Bougis, P.E.; Taylor, P. Inhibition of mouse acetylcholinesterase by fasciculin: Crystal structure of the complex and mutagenesis of fasciculin. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.d.S.; França, T.C.C.; de Oliveira, O.V. Computational studies of acetylcholinesterase complexed with fullerene derivatives: A new insight for Alzheimer disease treatment. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.J.; Harvey, A.L.; Rowan, E.G.; Strong, P.N. Effects of charybdotoxin, a blocker of Ca2+-activated K+ channels, on motor nerve terminals. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 95, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, F.J.; Taljaard, N. The amino acid sequence of two proteinase inhibitor homologues from Dendroaspis angusticeps venom. Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 1980, 361, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benishin, C.G.; Sorensen, R.G.; Brown, W.E.; Krueger, B.K.; Blaustein, M.P. Four polypeptide components of green mamba venom selectively block certain potassium channels in rat brain synaptosomes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988, 34, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Závada, J.; Valenta, J.; Kopecký, O.; Stach, Z.; Leden, P. Black mamba Dendroaspis polylepis bite: A case report. Prague Med. Rep. 2011, 112, 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, P.A.; Anderson, C.G. Observations on Dendroaspis venoms. In Animals’ Toxins; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Protein Data Bank. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/3d-view/1DTK (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Protein Data Bank. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1DEM (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Oltersdorf, T.; Fritz, L.C.; Schenk, D.B.; Lieberburg, I.; Johnson-Wood, K.L.; Beattie, E.C.; Ward, P.J.; Blacher, R.W.; Dovey, H.F.; Sinha, S. The secreted form of the Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein with the Kunitz domain is protease nexin-II. Nature 1989, 341, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.C.; Sprecher, C.A.; Foster, D.C.; Blumberg, H.; Hamamoto, T.; Kisiel, W. Inhibitory properties of a novel human Kunitz-type protease inhibitor homologous to tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.H.; He, Q.Y.; Peng, K.; Diao, J.B.; Jiang, L.P.; Tang, X.; Liang, S.P. Discovery of a distinct superfamily of Kunitz-type toxin (KTT) from tarantulas. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3414, Erratum in PLoS ONE 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendre, A.D.; Ramasamy, S.; Suresh, C.G. Analysis of Kunitz inhibitors from plants for comprehensive structural and functional insights. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, M. Evolutionary aspects of the structural convergence and functional diversification of Kunitz-domain inhibitors. J. Mol. Evol. 2020, 88, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.L.; Rowan, E.G. Dendrotoxins and BPTI-like Proteins. In Animal Toxins; Rochat, H., Martin-Eauclaire, M.F., Eds.; Methods and Tools in Biosciences and Medicine; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L.; Robertson, B. Dendrotoxins: Structure-activity relationships and effects on potassium ion channels. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, P.; Hariharan, M.; Murali, R.; Singh, C.U. Molecular structure, conformational analysis, and structure-activity studies of Dendrotoxin and its homologues using molecular mechanics and molecular dynamics techniques. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 2141–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imredy, J.P.; MacKinnon, R. Energetic and structural interactions between delta-dendrotoxin and a voltage-gated potassium channel. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 296, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, E.; Nishio, H.; Inui, T.; Nishiuchi, Y.; Kimura, T.; Sakakibara, S.; Yamazaki, T. Structural basis for the biological activity of dendrotoxin-I, a potent potassium channel blocker. Biopolym. Orig. Res. Biomol. 2000, 54, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufton, M.J.; Harvey, A.L. Dendrotoxins: How does structure determine function? J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 1998, 17, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallement, G.; Fosbraey, P.; Baille-Le-Crom, V.; Tattersall, J.E.H.; Blanchet, G.; Wetherell, J.R.; Rice, P.; Passingham, S.L.; Sentenac-Roumanou, H. Compared toxicity of the potassium channel blockers, apamin and dendrotoxin. Toxicology 1995, 104, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, J.V.; Othman, I.B.; Pelchen-Matthews, A.; Dolly, J.O. Central action of dendrotoxin: Selective reduction of a transient K conductance in hippocampus and binding to localized acceptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbs, G.R.; Dolly, J.O.; Nicholls, D.G. Dendrotoxin, 4-aminopyridine, and β-bungarotoxin act at common loci but by two distinct mechanisms to induce Ca2+-dependent release of glutamate from guinea-pig cerebrocortical synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 1989, 52, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, W.I.; Ryu, P.D.; Lee, S.Y. Effects of voltage-gated K+ channel blockers in gefitinib-resistant H460 non-small cell lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 5279–5284. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Ryu, P.D.; Lee, S.Y. Anti-proliferative effect of Kv1.3 blockers in A549 human lung adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 651, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellerhoff-Losch, B.; Korol, S.V.; Ganor, Y.; Gu, S.; Cooper, I.; Eilam, R.; Besser, M.; Goldfinger, M.; Chowers, Y.; Wank, R.; et al. Normal human CD4+ helper T cells express Kv1.1 voltage-gated K+ channels, and selective Kv1.1 block in T cells induces by itself robust TNFα production and secretion and activation of the NFκB non-canonical pathway. J. Neural Transm. 2016, 123, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Chen, S.R.; Li, D.P.; Pan, H.L. Kv1.1/1.2 channels are downstream effectors of nitric oxide on synaptic GABA release to preautonomic neurons in the paraventricular nucleus. Neuroscience 2007, 149, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianna-Jorge, R.; Oliveira, C.F.; Garcia, M.L.; Kaczorowski, G.J.; Suarez-Kurtz, G. Shaker-type Kv1 channel blockers increase the peristaltic activity of guinea-pig ileum by stimulating acetylcholine and tachykinins release by the enteric nervous system. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 138, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forootan, M.; Bagheri, N.; Darvishi, M. Chronic constipation: A review of literature. Medicine 2018, 97, e10631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatton, W.J.; Mason, H.S.; Carl, A.; Doherty, P.; Latten, M.J.; Kenyon, J.L.; Sanders, K.M.; Horowitz, B. Functional and molecular expression of a voltage-dependent K+ channel (Kv1.1) in interstitial cells of Cajal. J. Physiol. 2001, 533 Pt 2, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnegan, T.F.; Chen, S.R.; Pan, H.L. Mu opioid receptor activation inhibits GABAergic inputs to basolateral amygdala neurons through Kv1.1/1.2 channels. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 95, 2032–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.X.; Nicol, G.D. Manipulation of the potassium channel Kv1.1 and its effect on neuronal excitability in rat sensory neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 98, 2683–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Padilla, F.; Dandonneau, M.; Lavebratt, C.; Lesage, F.; Noël, J.; Delmas, P. Kv1.1 channels act as mechanical brake in the senses of touch and pain. Neuron 2013, 77, 899–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.; Trosclair, K.; Hamilton, K.A.; Glasscock, E. Genetic ablation or pharmacological inhibition of Kv1.1 potassium channel subunits impairs atrial repolarization in mice. Am. J. Physiology Cell Physiol. 2019, 316, C154–C161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Lavebratt, C.; Almgren, M.; Portwood, N.; Forsberg, L.E.; Bränström, R.; Berglund, E.; Falkmer, S.; Sundler, F.; Wierup, N.; et al. Evidence for presence and functional effects of Kv1.1 channels in β-cells: General survey and results from mceph/mceph mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.L.; Koh, D.S.; Tempel, B.L. Cyclic AMP regulates potassium channel expression in C6 glioma by destabilizing Kv1.1 mRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7693–7698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valsecchi, F.; Ramos-Espiritu, L.S.; Buck, J.; Levin, L.R.; Manfredi, G. cAMP and mitochondria. Physiology 2013, 28, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, D.; Moran, N. Modulation of small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in C6 glioma cells. J. Membr. Biol. 1994, 140, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strupp, M.; Staub, F.; Grafe, P. A Ca2+-and pH-Dependent K+ Channel of rat C6 glioma cells and its possible role in acidosis-induced cell swelling. Glia 1993, 9, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzaire-Dubois, B.; Milandri, J.B.; Bostel, S.; Dubois, J.M. Control of cell proliferation by cell volume alterations in rat C6 glioma cells. Pflügers Arch. 2000, 440, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Castle, N.A.; Wang, G.K. Identification of RBK1 potassium channels in C6 astrocytoma cells. Glia 1992, 5, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Yamawaki, Y.; Yamaoka, K.; Yoshida, T.; Okada, K.; Tan, W.; Yamasaki, M.; Matsumoto-Makidono, Y.; Kubo, R.; Nakayama, H.; et al. Spike firing attenuation of serotonin neurons in learned helplessness rats is reversed by ketamine. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriger, A.; Pickering, G. Ketamine and depression: A narrative review. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 3051–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, J.S.; Manis, P.B. Differential expression of three distinct potassium currents in the ventral cochlear nucleus. J. Neurophysiol. 2003, 89, 3070–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamlet, W.R.; Liu, Y.W.; Tang, Z.Q.; Lu, Y. Interplay between low threshold voltage-gated K+ channels and synaptic inhibition in neurons of the chicken nucleus laminaris along its frequency axis. Front. Neural Circuits 2014, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibukawa, Y.; Chilton, E.L.; Maccannell, K.A.; Clark, R.B.; Giles, W.R. K+ currents activated by depolarization in cardiac fibroblasts. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 3924–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeres, C.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Fibroblasts in the infarcted, remodeling, and failing heart. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2019, 4, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanzolini, K.L.; Ainsworth, S.; Bruyneel, B.; Herzig, V.; Seraus, M.G.L.; Somsen, G.W.; Casewell, N.R.; Cass, Q.B.; Kool, J. Rapid ligand fishing for identification of acetylcholinesterase-binding peptides in snake venom reveals new properties of dendrotoxins. Toxicon 2018, 152, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdoust, H.; Janahmadi, M.; Behzadi, G. Physiological role of dendrotoxin-sensitive K+ channels in the rat cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Physiol. Res. 2007, 56, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputi, A.; Melzer, S.; Michael, M.; Monyer, H. The long and short of GABAergic neurons. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, Y.; Puschhof, J.; Beumer, J.; Kerkkamp, H.M.; de Bakker, M.A.; Slagboom, J.; de Barbanson, B.; Wevers, N.R.; Spijkers, X.M.; Olivier, T.; et al. Snake Venom Gland Organoids. Cell 2020, 180, 233–247.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüddecke, T.; Paas, A.; Harris, R.J.; Talmann, L.; Kirchhoff, K.N.; Billion, A.; Hardes, K.; Steinbrink, A.; Gerlach, D.; Fry, B.G.; et al. Venom biotechnology: Casting light on nature’s deadliest weapons using synthetic biology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1166601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kowalczyk, T.; Muskała, M.; Piekarski, J.; Kowalski, M.; Staszewski, M.; Konuklugil, B.; Rijo, P.; Sitarek, P. Therapeutic Promise and Biotechnological Prospects of Dendroaspis polylepis Venom Proteins: Mambalgins, Fasciculins, and Dendrotoxins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209895
Kowalczyk T, Muskała M, Piekarski J, Kowalski M, Staszewski M, Konuklugil B, Rijo P, Sitarek P. Therapeutic Promise and Biotechnological Prospects of Dendroaspis polylepis Venom Proteins: Mambalgins, Fasciculins, and Dendrotoxins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209895
Chicago/Turabian StyleKowalczyk, Tomasz, Martyna Muskała, Janusz Piekarski, Maciej Kowalski, Marek Staszewski, Belma Konuklugil, Patricia Rijo, and Przemysław Sitarek. 2025. "Therapeutic Promise and Biotechnological Prospects of Dendroaspis polylepis Venom Proteins: Mambalgins, Fasciculins, and Dendrotoxins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209895
APA StyleKowalczyk, T., Muskała, M., Piekarski, J., Kowalski, M., Staszewski, M., Konuklugil, B., Rijo, P., & Sitarek, P. (2025). Therapeutic Promise and Biotechnological Prospects of Dendroaspis polylepis Venom Proteins: Mambalgins, Fasciculins, and Dendrotoxins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209895











