Relationship Between Insulin Resistance Indicators and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Romania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Anamnestic, Socio-Demographic, and Lifestyle Data
4.3. Clinical and Biochemical Data
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADA | American Diabetes Association |
| AUROC | area under the receiver operating characteristic |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CHG | cholesterol, HDL, glucose |
| CHG–BMI | CHG–body mass index |
| CHG–NC | CHG–neck circumference |
| CHG–NHtR | CHG–neck-circumference-to-height ratio |
| CHG–WC | CHG–waist circumference |
| CHG–WHtR | CHG–waist-to-height ratio |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| DBP | diastolic blood pressure |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| FPG | fasting plasma glucose |
| FFA | free fatty acids |
| GCP | good clinical practice |
| HbA1c | glycated hemoglobin |
| HDL-c | high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HOMA-IR | homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance |
| ICH | International Conference on Harmonization |
| IDF | International Diabetes Federation |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| IR | insulin resistance |
| LDL-c | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| MASLD | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| MetS | metabolic syndrome |
| METS-IR | metabolic score for insulin resistance |
| NC | neck circumference |
| NHtR | neck-circumference-to-height ratio |
| OGTT | oral glucose tolerance test |
| OR | odds ratio |
| PREDATORR | PREvalence of DiAbeTes mellitus, pre diabetes, overweight, Obesity, dyslipidemia, hyperuricemia and chronic kidney disease in Romania |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| SBP | systolic blood pressure |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SPSS | statistical package for the social sciences |
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| TC | total cholesterol |
| TG | triglycerides |
| TG/HDL-c | triglyceride to high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol |
| TyG | triglyceride-glucose |
| TyG–BMI | TyG–body mass index |
| TyG–NC | TyG–neck circumference |
| TyG–NHtR | TyG–neck-circumference-to-height ratio |
| TyG–WC | TyG–waist circumference |
| TyG–WHtR | TyG–waist-to-height ratio |
| WC | waist circumference |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WHtR | waist-to-height ratio |
References
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Introduction and Methodology: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, S1–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 11th Edition. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/media/uploads/sites/3/2025/04/IDF_Atlas_11th_Edition_2025.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in diabetes prevalence and treatment from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 1108 population-representative studies with 141 million participants. Lancet 2024, 404, 2077–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, M.; Popa, S.G.; Mota, E.; Mitrea, A.; Catrinoiu, D.; Cheta, D.M.; Guja, C.; Hancu, N.; Ionescu-Tirgoviste, C.; Lichiardopol, R.; et al. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and prediabetes in the adult Romanian population: PREDATORR study. J. Diabetes 2016, 8, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, S27–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Ferrannini, E.; Groop, L.; Henry, R.R.; Herman, W.H.; Holst, J.J.; Hu, F.B.; Kahn, C.R.; Raz, I.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Martínez, M.; González-González, M.; Martagón, A.J.; Hlavinka, V.; Willson, R.C.; Rito-Palomares, M. Recent Developments in Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Screening of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2022, 22, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ca, J.; Joshi, A.; Ishaq, M.; Adoor, G.; V, M.; Jampugumpula, H.; R, K.; Sanjay, B.G.; Bhupathiraju, P.K. Triglyceride-Fasting Glucose Index and Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance as Predictors of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in South Indians with Normal Body Mass Index. Cureus 2024, 16, e62742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castorani, V.; Polidori, N.; Giannini, C.; Blasetti, A.; Chiarelli, F. Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes in children. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 25, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagi, V.M.; Giannini, C.; Chiarelli, F. Insulin Resistance in Children. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czech, M.P. Insulin action and resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, A.; Nosrati, M.; Dorchin, M.; Mohammadyari, F.; Derakhshan-Nezhad, E.; Ferns, G.; Esmaily, H.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M. A novel index for diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Cholesterol, High density lipoprotein, and Glucose (CHG) index. J. Diabetes Investig. 2025, 16, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, C.J.; Prentki, M. Insulin resistance and insulin hypersecretion in the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: Time for a conceptual framework shift. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2019, 16, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.D.; Corkey, B.E.; Istfan, N.W.; Apovian, C.M. Hyperinsulinemia: An Early Indicator of Metabolic Dysfunction. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 1727–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Gao, T. Triglyceride-glucose index in predicting the risk of new-onset diabetes in the general population aged 45 years and older: A national prospective cohort study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2025, 25, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.C.; Wei, J.N.; Chen, S.C.; Fan, K.C.; Lin, C.H.; Yang, C.Y.; Lin, M.S.; Shih, S.R.; Hua, C.H.; Hsein, Y.C.; et al. Progression of insulin resistance: A link between risk factors and the incidence of diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 161, 108050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Tobin, J.D.; Andres, R. Glucose clamp technique: A method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am. J. Physiol. 1979, 237, E214–E223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, T.M.; Levy, J.C.; Matthews, D.R. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.; Caldas, A.P.S.; Rocha, D.M.U.P.; Bressan, J. Triglyceride-glucose index predicts independently type 2 diabetes mellitus risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Prim. Care Diabetes 2020, 14, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Zhao, M.; Song, T.; Tang, J.; Kuang, M.; Liu, H.; Zhong, S. Role of Triglyceride-Glucose Index in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 3325–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawan, L.B. Triglyceride-Glucose Index As A Biomarker Of Insulin Resistance, Diabetes Mellitus, Metabolic Syndrome, And Cardiovascular Disease: A Review. EJIFCC 2024, 35, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Hu, H.; Li, Q.; Dengm, Z.; Liu, D. Triglyceride glucose-body mass index and the risk of progression to diabetes from prediabetes: A 5-year cohort study in Chinese adults. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1028461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; Liu, D.; Zhong, J.; Luo, H.; Zhang, X. Impacts of Triglyceride Glucose-Waist to Height Ratio on Diabetes Incidence: A Secondary Analysis of A Population-Based Longitudinal Data. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 949831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.A.; Maturu, A.; Lorenzo, C.; Langefeld, C.D.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Chen, Y.I.; Taylor, K.D.; Rotter, J.I.; Norris, J.M.; Rasouli, N. The triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio as a predictor of insulin resistance, β-cell function, and diabetes in Hispanics and African Americans. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2019, 33, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; He, S.; Yu, C.; Yang, R.; Kuang, M.; Sheng, G.; Zou, Y. Assessing the validity of METS-IR for predicting the future onset of diabetes: An analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2024, 24, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Yan, G.; Wang, D.; Tang, C. Relationship between indices of insulin resistance and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese adults. Endocrine 2024, 85, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Li, R.; Xu, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Jiang, W.; Meng, Y.; Han, J. Association of METS-IR index with Type 2 Diabetes: A cross-sectional analysis of national health and nutrition examination survey data from 2009 to 2018. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0308597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ştefan, A.G.; Clenciu, D.; Mitrea, A.; Vladu, I.M.; Protasiewicz-Timofticiuc, D.C.; Roşu, M.M.; Maria, D.T.; Dinu, I.R.; Gheonea, T.C.; Vladu, B.E.; et al. Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance in Romania. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirr, M.; Skrypnik, D.; Bogdański, P.; Owecki, M. Newly proposed insulin resistance indexes called TyG-NC and TyG-NHtR show efficacy in diagnosing the metabolic syndrome. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 2831–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Yang, C.; Shen, R.; Wei, X.; Gong, J.; Pan, Y.; Lv, Y.; Xu, Y. Association Between the Triglyceride-Glucose Index and the Incidence of Diabetes in People with Different Phenotypes of Obesity: A Retrospective Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 784616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.M.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.H. The triglyceride-glucose index is a more powerful surrogate marker for predicting the prevalence and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus than the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 180, 109042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, P.; Wu, X.; Xu, M.; Feng, J.; Xu, H.; Gan, Y.; Wang, C.; Deng, Z.; Liu, X.; Fu, W.; et al. Comparison of obesity indices and triglyceride glucose-related parameters to predict type 2 diabetes mellitus among normal-weight elderly in China. Eat Weight Disord. 2022, 27, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Tong, J.; Wang, R.; Ma, S.; Wei, L.; Zhao, W. Gender differences in triglyceride glucose index predictive power for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Chinese cohort study. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2025, 45, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Gao, Y.; Han, J.; Li, L.; Wang, M.; Peng, H.; Liao, J.; Wan, H.; Xiang, G.; Han, Y. Comparison of longitudinal changes in four surrogate insulin resistance indexes for incident T2DM in middle-aged and elderly Chinese. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1046223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikaiakou, E.; Vlachopapadopoulou, E.A.; Paschou, S.A.; Athanasouli, F.; Panagiotopoulos, Ι.; Kafetzi, M.; Fotinou, A.; Michalacos, S. Triglycerides-glucose (TyG) index is a sensitive marker of insulin resistance in Greek children and adolescents. Endocrine 2020, 70, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.E.; Park, C.Y.; Oh, K.W.; Park, S.W.; Rhee, E.J.; Lee, W.Y. Predictive Value of Triglyceride Glucose Index for the Risk of Incident Diabetes: A 4-Year Retrospective Longitudinal Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H. Stronger Associations of TyG Index with Diabetes Than TyG-Obesity-Related Parameters: More Pronounced in Young, Middle-Aged, and Women. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 3795–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Cumulative increased risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus with increasing triglyceride glucose index in normal-weight people: The Rural Chinese Cohort Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrea, A.; Vladu, I.M.; Roşu, M.M.; Clenciu, D.; Mota, E.; Mota, M. Paradigm of Insulin Resistance, Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity, Fatty Liver and Atherosclerosis in Metabolic Syndrome. In Type 2 Diabetes in 2024—From Early Suspicion to Effective Management; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudish, L.I.; Reusch, J.E.; Sussel, L. β Cell dysfunction during progression of metabolic syndrome to type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4001–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Li, T.; Wu, X.; Nice, E.C.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y. Oxidative stress and diabetes: Antioxidative strategies. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Boas, E.A.; Almeida, D.C.; Roma, L.P.; Ortis, F.; Carpinelli, A.R. Lipotoxicity and β-Cell Failure in Type 2 Diabetes: Oxidative Stress Linked to NADPH Oxidase and ER Stress. Cells 2021, 10, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytrivi, M.; Castell, A.L.; Poitout, V.; Cnop, M. Recent Insights Into Mechanisms of β-Cell Lipo- and Glucolipotoxicity in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 1514–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, S.S.; Kuriyakose, D.; Polisetty, L.D.; Patil, A.A.; Ameen, D.; Bonu, R.; Shetty, S.P.; Biswas, P.; Ulrich, M.T.; Letafatkar, N.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of triglyceride glucose index: A comprehensive evaluation of meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitroi Sakizlian, D.D.; Boldeanu, L.; Mitrea, A.; Clenciu, D.; Vladu, I.M.; Ciobanu Plasiciuc, A.E.; Șarla, A.V.; Siloși, I.; Boldeanu, M.V.; Assani, M.-Z.; et al. The Interplay of Cardiometabolic Syndrome Phenotypes and Cardiovascular Risk Indices in Patients Diagnosed with Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efrem, I.C.; Moța, M.; Vladu, I.M.; Mitrea, A.; Clenciu, D.; Timofticiuc, D.C.P.; Diaconu, I.-D.; Turcu, A.; Crișan, A.E.; Geormăneanu, C.; et al. A Study of Biomarkers Associated with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, H.R.; Shim, Y.S.; Kang, M.J.; Hwang, I.T. Triglyceride glucose index is superior biomarker for predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Endocr. J. 2022, 69, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laohabut, I.; Udol, K.; Phisalprapa, P.; Srivanichakorn, W.; Chaisathaphol, T.; Washirasaksiri, C.; Sitasuwan, T.; Chouriyagune, affiC.; Auesomwang, C. Neck circumference as a predictor of metabolic syndrome: A cross-sectional study. Prim. Care Diabetes 2020, 14, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.R.; Dye, T.D.; Zand, M.S.; Fogg, T.T.; Yuan, S.Y.; Yang, J.K.; Li, D. Association Between Neck Circumference and Coronary Heart Disease: A Meta-analysis. Asian Pac. Isl. Nurs. J. 2019, 4, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidi, M.; Baghbani-Oskouei, A.; Ahanchi, N.S.; Azizi, F.; Hadaegh, F. Fasting plasma glucose is a stronger predictor of diabetes than triglyceride-glucose index, triglycerides/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kwon, H.S.; Park, Y.M.; Ha, H.S.; Jeong, S.H.; Yang, H.K.; Lee, J.H.; Yim, H.W.; Kang, M.I.; Lee, W.C.; et al. Predicting the development of diabetes using the product of triglycerides and glucose: The Chungju Metabolic Disease Cohort (CMC) study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Chavolla, O.Y.; Almeda-Valdes, P.; Gomez-Velasco, D.; Viveros-Ruiz, T.; Cruz-Bautista, I.; Romo-Romo, A.; Sánchez-Lázaro, D.; Meza-Oviedo, D.; Vargas-Vázquez, A.; Campos, O.A.; et al. METS-IR, a novel score to evaluate insulin sensitivity, is predictive of visceral adiposity and incident type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, D.; Qin, P.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, M.; Qie, R.; et al. Association of metabolic score for insulin resistance and its 6-year change with incident type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes 2021, 13, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.T.; Jia, Z.; Wang, J.J.; Xie, Y.J.; Hernandez, J.; Wang, H.H.X.; Wu, H.F. Association between METS-IR and Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Subjects in China: A Large-Scale Population-Based Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 2004, 363, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, M.; Gibson, S. Waist-to-height ratio as an indicator of ‘early health risk’: Simpler and more predictive than using a ‘matrix’ based on BMI and waist circumference. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Waist Circumference and Waist–Hip Ratio: Report of a WHO Expert Consultation, Geneva, 8–11 December 2008. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/44583/9789241501491_eng.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. The product of fasting glucose and triglycerides as surrogate for identifying insulin resistance in apparently healthy subjects. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2008, 6, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, L.K.; Wu, S.; Chou, H.H.; Hsu, L.A.; Teng, M.S.; Sun, Y.C.; Ko, Y.L. Triglyceride Glucose-Body Mass Index Is a Simple and Clinically Useful Surrogate Marker for Insulin Resistance in Nondiabetic Individuals. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lim, J.; Kim, J.; Koo, S.H.; Kwon, G.C. Comparison of triglyceride glucose index, and related parameters to predict insulin resistance in Korean adults: An analysis of the 2007-2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, T.; Abbasi, F.; Cheal, K.; Chu, J.; Lamendola, C.; Reaven, G. Use of metabolic markers to identify overweight individuals who are insulin resistant. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Male Group | Female Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2DM (+) | T2DM (−) | p Value | T2DM (+) | T2DM (−) | p Value | |
| Participants, no. | 214 | 777 | 183 | 906 | ||
| Age (years) | 63 (12) | 55 (23) | <0.001 | 64 (12) | 54 (22) | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 30.6 (6.3) | 27.1 (5.3) | <0.001 | 31.6 (7.1) | 26.5 (7.9) | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 110 (15) | 100 (15) | <0.001 | 104 (15) | 90 (20) | <0.001 |
| WHtR | 0.62 (0.10) | 0.57 (0.08) | <0.001 | 0.65 ± 0.07 | 0.56 ± 0.09 | <0.001 |
| NC (cm) | 42 (4) | 40 (4) | <0.001 | 37 (4) | 35 (5) | <0.001 |
| NHtR | 0.24 (0.03) | 0.22 (0.03) | <0.001 | 0.23 (0.03) | 0.21 (0.03) | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 147 (30) | 136 (26) | <0.001 | 140 (31) | 130 (27) | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 81 (16) | 80 (17) | 0.137 | 80 (16) | 79 (16) | 0.168 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 121.5 (47) | 82.0 (17) | <0.001 | 123 (45) | 80 (15) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.73 (1.7) | 5.30 (0.4) | <0.001 | 6.7 (1.2) | 5.3 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 185.5 (60) | 202.0 (57) | <0.001 | 208 (72) | 206 (62) | 0.368 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 44.0 (15) | 48.6 (18) | <0.001 | 51.6 (18) | 58.0 (19) | <0.001 |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 111.1 (50) | 124.0 (51) | <0.001 | 124 (68) | 127 (53) | 0.196 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 136.5 (113) | 119.0 (84) | <0.001 | 138.4 (74) | 101.0 (67) | <0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.83 (3.68) | 1.68 (1.67) | <0.001 | 4.10 (3.53) | 1.62 (1.36) | <0.001 |
| Smoking (%) | ||||||
| Daily smokers | 12.9 | 24.3 | <0.001 | 8.7 | 16.1 | 0.004 |
| Occasional smokers | 1.4 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 3.0 | ||
| Former smokers | 47.9 | 37.4 | 23.4 | 16.4 | ||
| Non-smokers | 37.8 | 33.8 | 67.4 | 64.5 | ||
| Alcohol consumption (%) | 66.4 | 82.0 | <0.001 | 29.9 | 36.0 | 0.115 |
| Reduced sleep duration (%) | 28.6 | 27.1 | 0.667 | 42.7 | 34.1 | 0.026 |
| Marital status (%) | ||||||
| Married | 85.3 | 81.5 | 0.002 | 61.4 | 67.2 | <0.001 |
| Single | 2.8 | 10.2 | 5.4 | 8.5 | ||
| Divorced | 5.5 | 4.7 | 4.3 | 8.1 | ||
| Widowed | 6.5 | 3.6 | 28.8 | 16.2 | ||
| High educational level (%) | 57.9 | 61.4 | 0.354 | 50.8 | 67.5 | <0.001 |
| IR Indicators | Male Group | Female Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2DM (+) | T2DM (−) | p Value | T2DM (+) | T2DM (−) | p Value | |
| TyG | 9.11 (0.95) | 8.49 (0.76) | <0.001 | 9.05 (0.71) | 8.30 (0.70) | <0.001 |
| TyG–BMI | 284.83 (73.39) | 230.78 (53.87) | <0.001 | 286.16 (68.54) | 223.17 (76.22) | <0.001 |
| TyG–WC | 999.36 (211.54) | 853.76 (171.75) | <0.001 | 945.11 ± 138.12 | 759.66 ± 148.10 | <0.001 |
| TyG–WHtR | 5.84 (1.27) | 4.86 (0.97) | <0.001 | 5.92 (1.01) | 4.68 (1.31) | <0.001 |
| TyG–NC | 388.24 (75.08) | 343.33 (60.41) | <0.001 | 339.21 (59.49) | 290.88 (55.38) | <0.001 |
| TyG–NHtR | 2.25 (0.45) | 1.96 (0.34) | <0.001 | 2.11 (0.34) | 1.79 (0.36) | <0.001 |
| TG/HDL-c | 3.45 (4.01) | 2.43 (2.46) | <0.001 | 2.71 (2.22) | 1.73 (1.57) | <0.001 |
| MetS-IR | 49.93 (14.09) | 39.71 (11.13) | <0.001 | 48.12 (11.86) | 36.93 (13.48) | <0.001 |
| CHG | 5.61 (0.69) | 5.12 (0.52) | <0.001 | 5.46 (0.61) | 4.94 (0.48) | <0.001 |
| CHG–BMI | 171.85 (47.13) | 139.20 (34.07) | <0.001 | 174.05 (46.81) | 134.11 (45.77) | <0.001 |
| CHG–WC | 611.01 (135.58) | 512.32 (106.83) | <0.001 | 573.58 (110.58) | 450.39 (128.17) | <0.001 |
| CHG–WHtR | 3.55 (0.88) | 2.92 (0.59) | <0.001 | 3.62 (0.71) | 2.79 (0.79) | <0.001 |
| CHG–NC | 236.70 (48.05) | 206.29 (36.13) | <0.001 | 207.54 (38.01) | 173.40 (34.90) | <0.001 |
| CHG–NHtR | 1.37 (0.26) | 1.17 (0.20) | <0.001 | 1.29 (0.21) | 1.07 (0.22) | <0.001 |
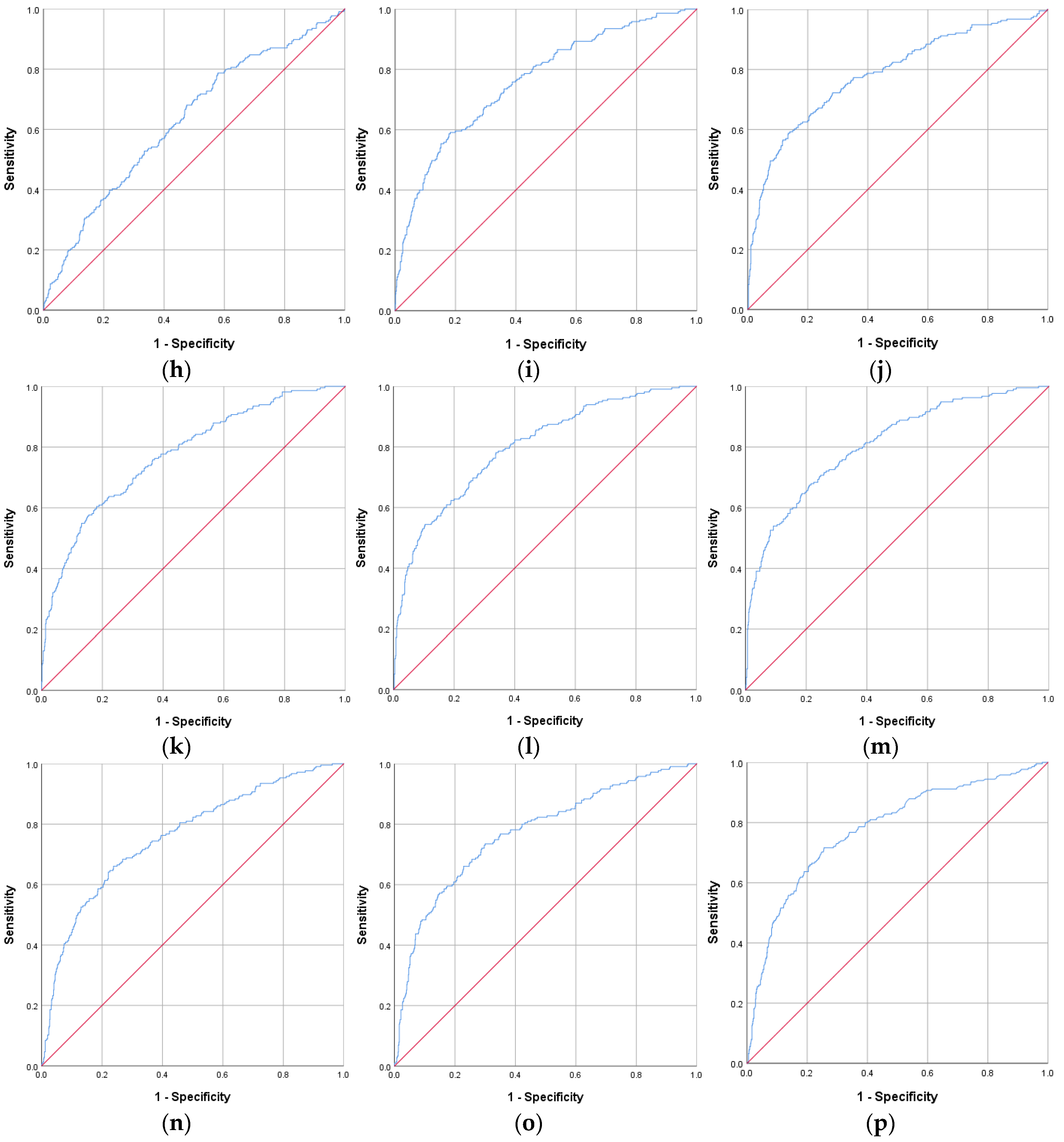
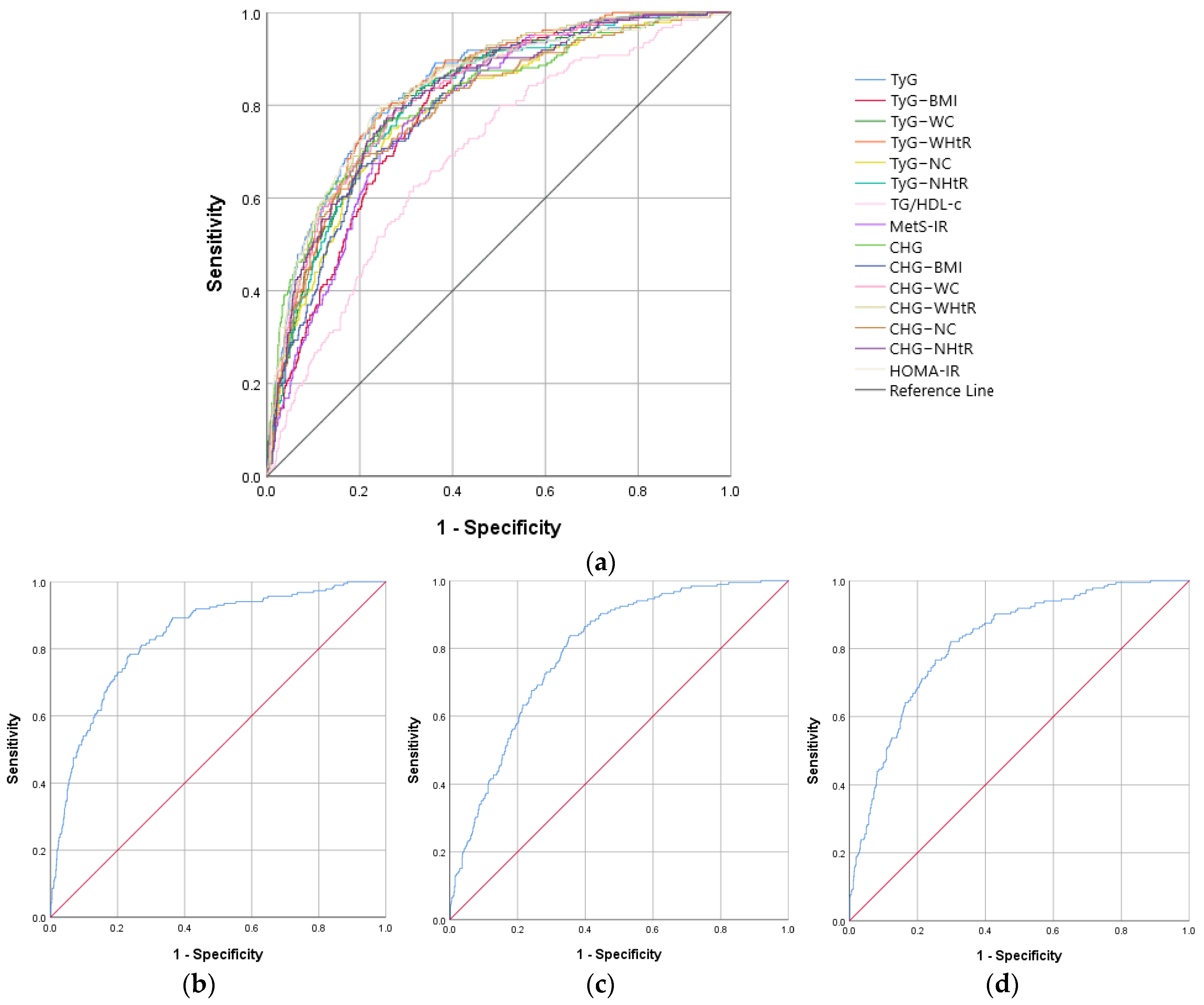
| IR Indicators | AUROC Curve | Standard Error | 95% CI | p Value | Cut-Off Value | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHG–WHtR | 0.809 | 0.017 | 0.775–0.842 | <0.001 | 3.22 | 70.7 | 75.3 |
| CHG–WC | 0.799 | 0.017 | 0.765–0.833 | <0.001 | 560.59 | 69.8 | 73.8 |
| TyG–WHtR | 0.791 | 0.018 | 0.756–0.826 | <0.001 | 5.37 | 69.3 | 75.8 |
| CHG | 0.784 | 0.019 | 0.746–0.821 | <0.001 | 5.32 | 72.2 | 71.7 |
| TyG–WC | 0.782 | 0.018 | 0.747–0.818 | <0.001 | 932.31 | 69.3 | 74.3 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.779 | 0.019 | 0.742–0.816 | <0.001 | 2.63 | 71.6 | 74.4 |
| CHG–BMI | 0.776 | 0.018 | 0.740–0.812 | <0.001 | 158.77 | 63.7 | 77.9 |
| CHG–NHtR | 0.771 | 0.019 | 0.734–0.809 | <0.001 | 1.25 | 73.5 | 70.0 |
| TyG–BMI | 0.762 | 0.019 | 0.725–0.799 | <0.001 | 261.03 | 64.2 | 76.0 |
| MetS-IR | 0.762 | 0.019 | 0.725–0.799 | <0.001 | 44.60 | 67.4 | 70.4 |
| CHG–NC | 0.760 | 0.019 | 0.722–0.798 | <0.001 | 223.84 | 66.0 | 76.2 |
| TyG | 0.751 | 0.020 | 0.713–0.790 | <0.001 | 8.92 | 65.7 | 76.1 |
| TyG–NHtR | 0.744 | 0.020 | 0.705–0.783 | <0.001 | 2.07 | 71.6 | 69.0 |
| TyG–NC | 0.735 | 0.020 | 0.696–0.774 | <0.001 | 368.23 | 65.1 | 72.0 |
| TG/HDL-c | 0.629 | 0.022 | 0.587–0.672 | <0.001 | 2.52 | 68.1 | 52.5 |
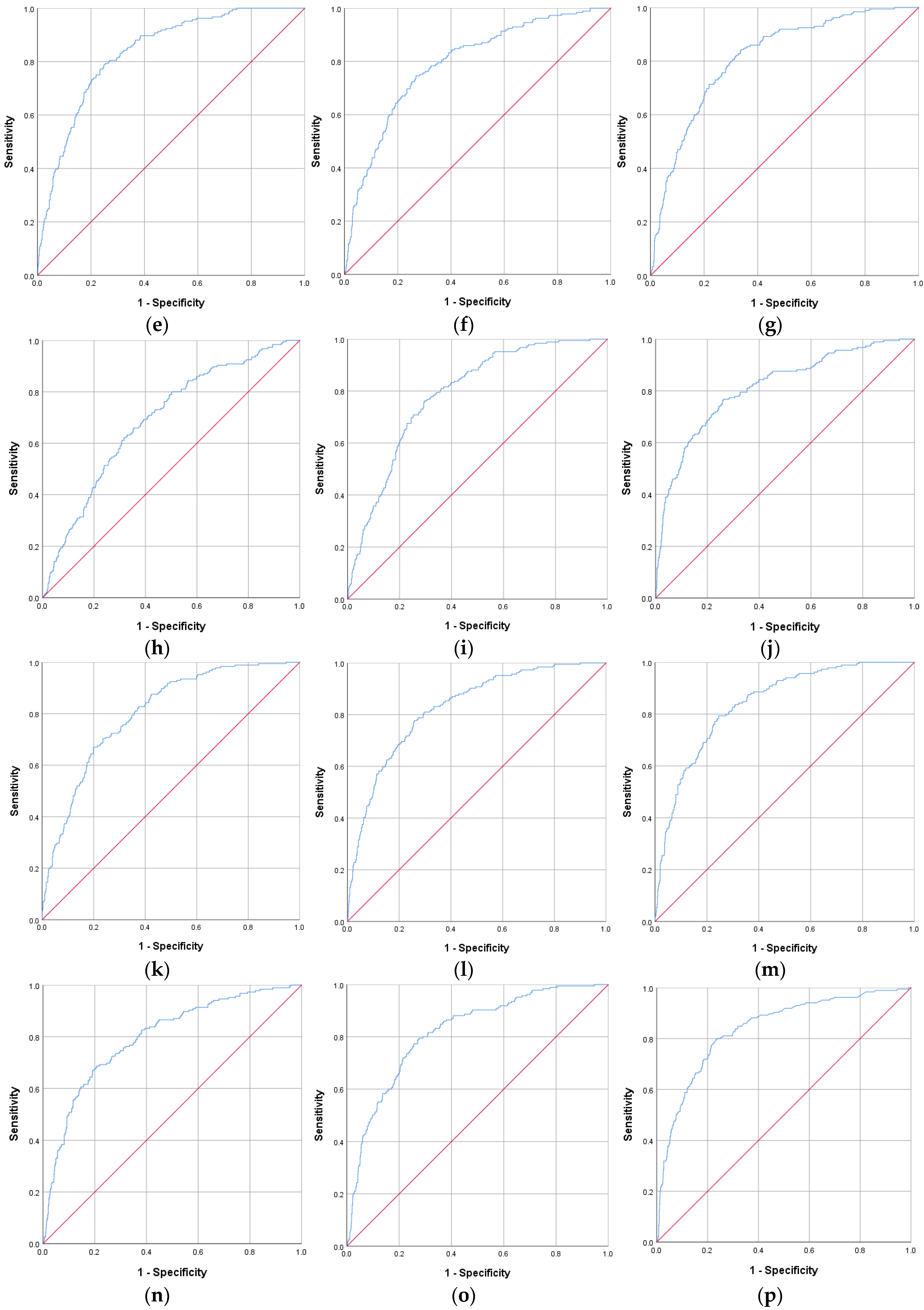
| IR Indicators | AUROC Curve | Standard Error | 95% CI | p Value | Cut-Off Value | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHG–WHtR | 0.840 | 0.015 | 0.811–0.869 | <0.001 | 3.20 | 79.3 | 75.5 |
| TyG | 0.837 | 0.016 | 0.805–0.868 | <0.001 | 8.70 | 77.7 | 76.9 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.837 | 0.016 | 0.805–0.870 | <0.001 | 2.52 | 79.5 | 76.9 |
| TyG–WHtR | 0.834 | 0.015 | 0.805–0.864 | <0.001 | 5.33 | 78.8 | 75.2 |
| CHG–WC | 0.826 | 0.016 | 0.794–0.857 | <0.001 | 510.35 | 77.7 | 74.2 |
| TyG–WC | 0.821 | 0.016 | 0.790–0.853 | <0.001 | 854.88 | 76.6 | 74.7 |
| CHG–NHtR | 0.818 | 0.017 | 0.786–0.851 | <0.001 | 1.17 | 77.3 | 74.4 |
| CHG | 0.813 | 0.018 | 0.777–0.848 | <0.001 | 5.19 | 76.8 | 73.8 |
| TyG–NHtR | 0.813 | 0.016 | 0.781–0.845 | <0.001 | 1.94 | 79.3 | 70.6 |
| CHG–BMI | 0.803 | 0.016 | 0.772–0.835 | <0.001 | 159.60 | 70.3 | 76.4 |
| CHG–NC | 0.797 | 0.018 | 0.761–0.833 | <0.001 | 193.66 | 68.6 | 79.2 |
| TyG–BMI | 0.793 | 0.016 | 0.762–0.825 | <0.001 | 245.02 | 83.2 | 64.9 |
| TyG–NC | 0.791 | 0.018 | 0.756–0.826 | <0.001 | 315.03 | 74.6 | 73.2 |
| MetS-IR | 0.787 | 0.017 | 0.754–0.819 | <0.001 | 42.72 | 76.2 | 70.3 |
| TG/HDL-c | 0.691 | 0.021 | 0.650–0.731 | <0.001 | 2.20 | 65.9 | 64.6 |
| Variables | Male Group | Female Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Age (years) | 1.058 | 1.044–1.072 | <0.001 | 1.073 | 1.057–1.090 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 1.181 | 1.139–1.224 | <0.001 | 1.146 | 1.114–1.179 | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 1.067 | 1.052–1.081 | <0.001 | 1.068 | 1.054–1.082 | <0.001 |
| WHtR (≥0.5995) | 4.641 | 3.366–6.400 | <0.001 | 5.439 | 3.816–7.752 | <0.001 |
| NC (cm) | 1.050 | 1.024–1.078 | <0.001 | 1.136 | 1.092–1.182 | <0.001 |
| NHtR (≥0.2305) | 2.908 | 2.092–4.040 | <0.001 | 3.591 | 2.593–4.972 | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 1.021 | 1.014–1.029 | <0.001 | 1.023 | 1.016–1.030 | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 1.010 | 0.997–1.022 | 0.122 | 1.009 | 0.996–1.023 | 0.176 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 1.073 | 1.061–1.084 | <0.001 | 1.097 | 1.083–1.112 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) * | 40.877 | 23.731–70.412 | <0.001 | 3.968 | 3.135–5.022 | <0.001 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 0.994 | 0.990–0.997 | <0.001 | 0.998 | 0.995–1.001 | 0.224 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 0.966 | 0.954–0.978 | <0.001 | 0.968 | 0.957–0.980 | <0.001 |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 0.990 | 0.986–0.994 | <0.001 | 0.997 | 0.993–1.001 | 0.127 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 1.003 | 1.002–1.004 | <0.001 | 1.005 | 1.003–1.007 | <0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.289 | 1.213–1.370 | <0.001 | 1.391 | 1.296–1.494 | <0.001 |
| TyG | 5.849 | 4.222–8.103 | <0.001 | 11.543 | 7.890–16.885 | <0.001 |
| TyG–BMI | 5.662 | 4.092–7.835 | <0.001 | 9.182 | 6.095–13.834 | <0.001 |
| TyG–WC | 6.540 | 4.690–9.121 | <0.001 | 9.705 | 6.679–14.102 | <0.001 |
| TyG–WHtR | 7.018 | 5.025–9.801 | <0.001 | 11.137 | 7.579–16.366 | <0.001 |
| TyG–NC | 4.799 | 3.477–6.623 | <0.001 | 8.003 | 5.567–11.505 | <0.001 |
| TyG–NHtR | 5.366 | 3.840–7.498 | <0.001 | 9.179 | 6.229–13.527 | <0.001 |
| TG/HDL-c | 2.342 | 1.701–3.223 | <0.001 | 3.442 | 2.466–4.805 | <0.001 |
| MetS-IR | 4.929 | 3.561–6.823 | <0.001 | 7.596 | 5.257–10.974 | <0.001 |
| CHG | 6.233 | 4.454–8.723 | <0.001 | 9.204 | 6.343–13.356 | <0.001 |
| CHG–BMI | 6.200 | 4.473–8.594 | <0.001 | 7.654 | 5.387–10.874 | <0.001 |
| CHG–WC | 6.506 | 4.663–9.076 | <0.001 | 10.008 | 6.856–14.610 | <0.001 |
| CHG–WHtR | 7.289 | 5.206–10.206 | <0.001 | 11.844 | 8.033–17.462 | <0.001 |
| CHG–NC | 6.233 | 4.491–8.652 | <0.001 | 8.344 | 5.879–11.844 | <0.001 |
| CHG–NHtR | 6.166 | 4.391–8.660 | <0.001 | 9.911 | 6.759–14.533 | <0.001 |
| Variables | Male Group | Female Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p Value | OR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| TyG | 2.994 | 1.656–5.412 | <0.001 | 8.170 | 3.779–17.665 | <0.001 |
| TyG–BMI | 1.303 | 0.564–3.010 | 0.535 | 1.987 | 0.869–4.542 | 0.104 |
| TyG–WC | 2.221 | 1.031–4.787 | 0.042 | 0.818 | 0.318–2.099 | 0.676 |
| TyG–WHtR | 1.243 | 0.582–2.655 | 0.574 | 1.843 | 0.764–4.449 | 0.174 |
| TyG–NC | 0.529 | 0.234–1.198 | 0.127 | 1.085 | 0.480–2.449 | 0.845 |
| TyG–NHtR | 1.191 | 0.534–2.658 | 0.669 | 0.864 | 0.382–1.950 | 0.724 |
| TG/HDL-c | 0.371 | 0.201–0.683 | 0.001 | 0.176 | 0.085–0.364 | <0.001 |
| MetS-IR | 1.018 | 0.504–2.053 | 0.961 | 0.977 | 0.390–2.446 | 0.960 |
| CHG | 2.927 | 1.681–5.096 | <0.001 | 2.004 | 1.105–3.636 | 0.022 |
| CHG–BMI | 1.798 | 0.832–3.887 | 0.136 | 1.429 | 0.669–3.052 | 0.356 |
| CHG–WC | 0.617 | 0.284–1.339 | 0.222 | 0.818 | 0.318–2.107 | 0.678 |
| CHG–WHtR | 1.030 | 0.492–2.156 | 0.936 | 1.699 | 0.670–4.308 | 0.264 |
| CHG–NC | 2.734 | 1.334–5.601 | 0.006 | 1.675 | 0.779–3.599 | 0.186 |
| CHG–NHtR | 1.054 | 0.507–2.190 | 0.888 | 1.319 | 0.586–2.969 | 0.503 |
| Measure | Categorical Cut Points |
|---|---|
| FPG | ≥126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) |
| or | |
| 2 h plasma glucose during OGTT | ≥200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) |
| or | |
| HbA1c | ≥6.5% (48 mmol/mol) |
| or | |
| A random plasma glucose in an individual with classic symptoms of hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic crisis * | ≥200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) |
| Biomarker | Formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| HOMA-IR | (Fasting Insulin [µU/mL] × Fasting Glucose [mmol/L])/22.5 | [18] |
| TyG index | Ln [Fasting Triglycerides (mg/dL) × Fasting Glucose (mg/dL)/2] | [20,60] |
| TyG–BMI | TyG × BMI (kg/m2) | [61] |
| TyG–WC | TyG × WC | [61] |
| TyG–WHtR | TyG × WHtR | [62] |
| TyG–NC | TyG × NC | [30] |
| TyG–NHtR | TyG × NHtR | [30] |
| TG/HDL-c | Triglycerides (mg/dL)/HDL-C (mg/dL) | [63] |
| METS-IR | (Ln [2 × Fasting Glucose (mg/dL) + Fasting Triglycerides (mg/dL)]) × BMI/(Ln [HDL-C (mg/dL)]) | [53] |
| CHG index | Ln [Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) × Fasting Glucose (mg/dL)/HDL-C (mg/dL)] | [12] |
| CHG–BMI | CHG × BMI | [12] |
| CHG–WC | CHG × WC | [12] |
| CHG–WHtR | CHG × WHtR | Present study |
| CHG–NC | CHG × NC | Present study |
| CHG–NHtR | CHG × NHtR | Present study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ştefan, A.-G.; Clenciu, D.; Vladu, I.-M.; Mitrea, A.; Protasiewicz-Timofticiuc, D.-C.; Roşu, M.-M.; Gheonea, T.-C.; Vladu, B.-E.; Efrem, I.-C.; Pintilei, D.-V.R.; et al. Relationship Between Insulin Resistance Indicators and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Romania. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209888
Ştefan A-G, Clenciu D, Vladu I-M, Mitrea A, Protasiewicz-Timofticiuc D-C, Roşu M-M, Gheonea T-C, Vladu B-E, Efrem I-C, Pintilei D-VR, et al. Relationship Between Insulin Resistance Indicators and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Romania. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209888
Chicago/Turabian StyleŞtefan, Adela-Gabriela, Diana Clenciu, Ionela-Mihaela Vladu, Adina Mitrea, Diana-Cristina Protasiewicz-Timofticiuc, Maria-Magdalena Roşu, Theodora-Claudia Gheonea, Beatrice-Elena Vladu, Ion-Cristian Efrem, Delia-Viola Reurean Pintilei, and et al. 2025. "Relationship Between Insulin Resistance Indicators and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Romania" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209888
APA StyleŞtefan, A.-G., Clenciu, D., Vladu, I.-M., Mitrea, A., Protasiewicz-Timofticiuc, D.-C., Roşu, M.-M., Gheonea, T.-C., Vladu, B.-E., Efrem, I.-C., Pintilei, D.-V. R., Moţa, E., & Moţa, M. (2025). Relationship Between Insulin Resistance Indicators and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Romania. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209888







