CAR-T Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Kidney Diseases: Where Do We Stand Now?
Abstract
1. Introduction
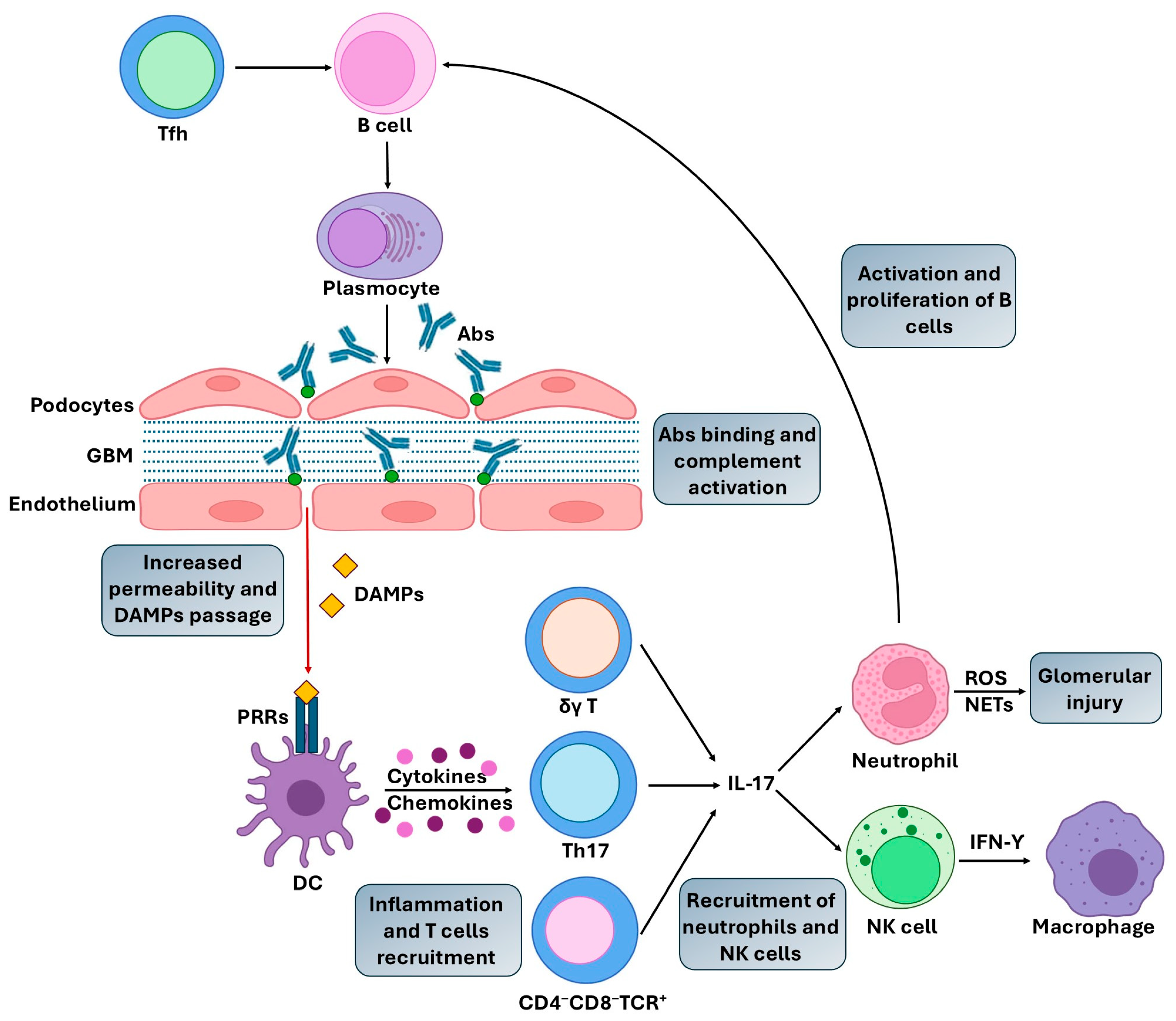
2. Pathogenic Mechanisms in AIKDs
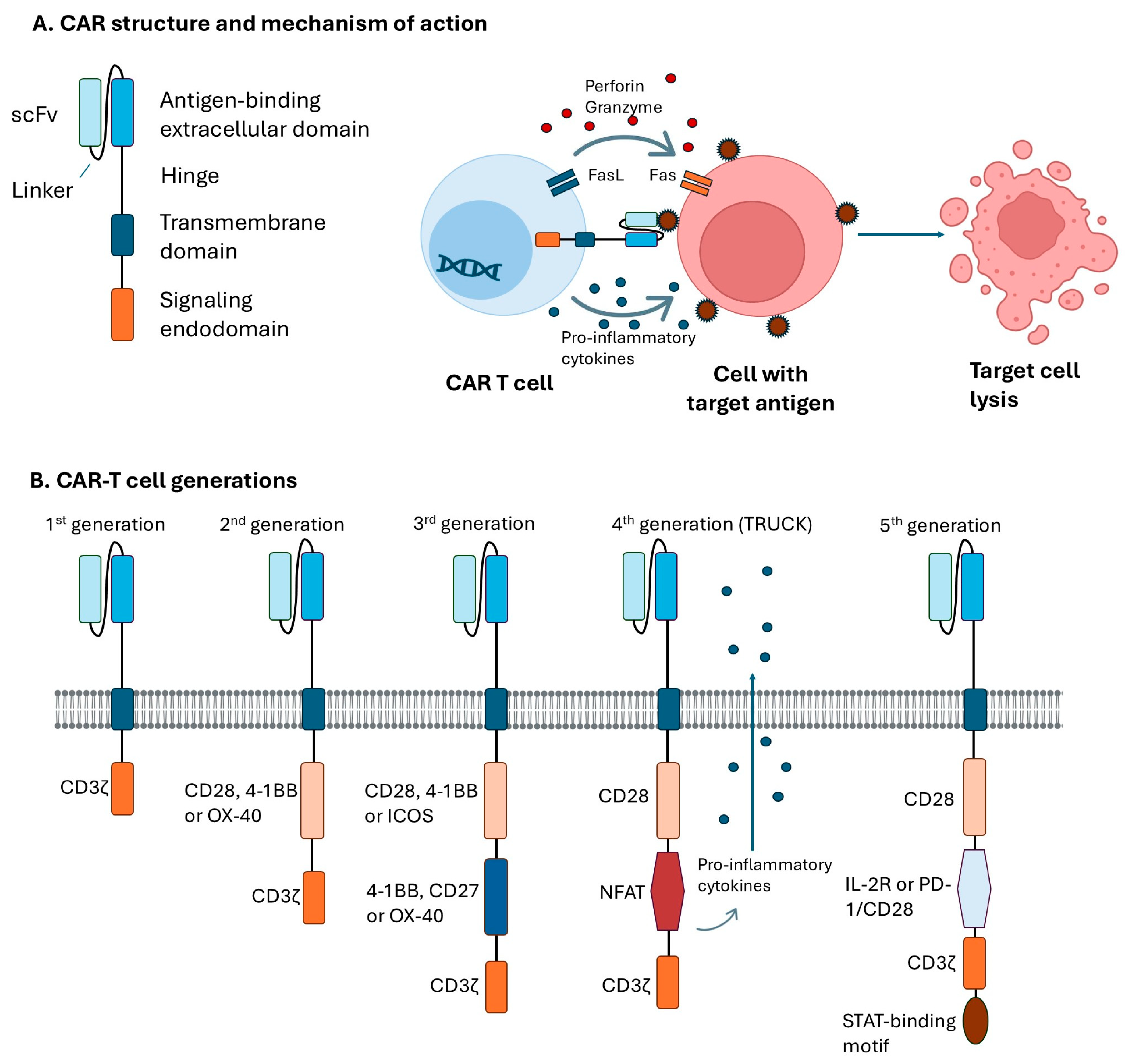
3. CAR Structure and Generations
4. Current B-Cell Therapy for AIKDs
5. CAR-Based Therapy for AIKDs
5.1. Studies Conducted on Animal Models
5.2. Pre-Clinical and Clinical Investigations
6. Challenges of CAR-T Therapy in AIKDs
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abs | Antibodies |
| ACT | Adoptive cell therapy |
| AIKDs | Autoimmune kidney diseases |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| ANCA | Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody |
| APRIL | A proliferation-inducing ligand |
| AVV | ANCA-associated vasculitis |
| BAFF | B-cell activating factor |
| CAR | Chimeric antigen receptor |
| CRS | Cytokine release syndrome |
| DAMPs | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| DC | Dendritic cell |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FSGS | Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis |
| GBM | Glomerular basement membrane |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor |
| ICANs | Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IgAN | Immunoglobulin A nephropathy |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LN | Lupus nephritis |
| MCD | Minimal Change disease |
| MN | Membranous nephropathy |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| NETs | Neutrophil extracellular traps |
| NFAT | Nuclear factor of activated T cells |
| NK | Natural killer |
| PD-1 | Programmed death receptor 1 |
| PRR | Pattern recognition receptor |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| scFv | Single-chain variable fragment |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| TACI | Transmembrane activator and calcium-modulator and cytophilin ligand interactor |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| Tfh | T follicular helper |
| Th | T helper |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TRUCKs | T-cells redirected for antigen-unrestricted cytokine-initiated killing |
References
- Sogkas, G.; Atschekzei, F.; Adriawan, I.R.; Dubrowinskaja, N.; Witte, T.; Schmidt, R.E. Cellular and molecular mechanisms breaking immune tolerance in inborn errors of immunity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1122–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.U.; Kulatunge, O.; O’Sullivan, K.M. Deciphering the Genetic Code of Autoimmune Kidney Diseases. Genes 2023, 14, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, N.; Misra, S.; Verbakel, J.Y.; Verbeke, G.; Molenberghs, G.; Taylor, P.N.; Mason, J.; Sattar, N.; McMurray, J.J.V.; McInnes, I.B.; et al. Incidence, prevalence, and co-occurrence of autoimmune disorders over time and by age, sex, and socioeconomic status: A population-based cohort study of 22 million individuals in the UK. Lancet 2023, 401, 1878–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaglio, A.; Gattorno, M.; McAdoo, S.; Obici, L.P.; Ghiggeri, G.M. Editorial: The kidney in auto-immune and auto-inflammatory processes: Definitions, mechanisms, and biomarkers. Front. Med. 2023, 9, 1129021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Yang, Z.; Miao, H.; Xing, S.; Wang, S.; Li, N. Recent advances in universal chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2025, 18, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappell, K.M.; Kochenderfer, J.N. Long-term outcomes following CAR T cell therapy: What we know so far. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecklenborg, J.; Clayton, D.; Siebert, S.; Coley, S.M. The role of the immune system in kidney disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 192, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.E.; Jones, N. Nephrin Signaling in the Podocyte: An Updated View of Signal Regulation at the Slit Diaphragm and Beyond. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruschi, M.; Angeletti, A.; Ghiggeri, G.M. Autoantibodies Targeting Nephrin in Podocytopathies. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Fueyo, A.; Bradley, S.J.; Klatzmann, D.; Tsokos, G.C. T cells and autoimmune kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, S.; Kronbichler, A.; Sharma, P.; Geetha, D. Advances in Understanding of Pathogenesis and Treatment of Immune-Mediated Kidney Disease: A Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 79, 582–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellier, J.; Nutt, S.L. Plasma cells: The programming of an antibody-secreting machine. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWolf, S.E.; Kasimsetty, S.G.; Hawkes, A.A.; Stocks, L.M.; Kurian, S.M.; McKay, D.B. DAMPs Released From Injured Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells Activate Innate Immune Signals in Healthy Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Transplantation 2022, 106, 1589–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shou, S.; Jin, H. The role of IL-17 in acute kidney injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 119, 110307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayadas, T.N.; Rosetti, F.; Ernandez, T.; Sethi, S. Neutrophils: Game changers in glomerulonephritis? Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.E.; Rickassel, C.; Healy, H.; Kassianos, A.J. Natural Killer Cells in Kidney Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hupperetz, C.; Lah, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, C.H. CAR T Cell Immunotherapy Beyond Haematological Malignancy. Immune Netw. 2022, 22, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schett, G.; Mackensen, A.; Mougiakakos, D. CAR T-cell therapy in autoimmune diseases. Lancet 2023, 402, 2034–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.J.; Harapan, B.N. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) immunotherapy: Basic principles, current advances, and future prospects in neuro-oncology. Immunol. Res. 2021, 69, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Śledź, M.; Wojciechowska, A.; Zagożdżon, R.; Kaleta, B. In Situ Programming of CAR-T Cells: A Pressing Need in Modern Immunotherapy. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2023, 71, 18. Erratum in Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2023, 71, 22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-023-00687-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, D. Fine-Tuning through Generations: Advances in Structure and Production of CAR-T Therapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiltensperger, M.; Krackhardt, A.M. Current and future concepts for the generation and application of genetically engineered CAR-T and TCR-T cells. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1121030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoedler, L.; Herfeld, K.; Schaefer, D.A.; Diatta, F.; Clune, J.; Evans, B.; Seu, M.; Kim, B.S.; Alfertshofer, M.; Schaschinger, T.; et al. CAR-T cell therapy and reconstructive oncologic surgery in peripheral solid tumors-A narrative review. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 102240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyco Vera, D.; Waghela, H.; Nuh, M.; Pan, J.; Lulla, P. Approved CAR-T therapies have reproducible efficacy and safety in clinical practice. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2024, 20, 2378543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Yan, H.; Xiong, J. Research advances on targeted-Treg therapies on immune-mediated kidney diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysler, E.F.; Spindler, A.J.; Guzman, R.; Bijl, M.; Jayne, D.; Furie, R.A.; Houssiau, F.A.; Drappa, J.; Close, D.; Maciuca, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ocrelizumab in active proliferative lupus nephritis: Results from a randomized, double-blind, phase III study. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2368–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.A.; Rovin, B.H.; Garg, J.P.; Santiago, M.B.; Aroca-Martínez, G.; Zuta Santillán, A.E.; Alvarez, D.; Navarro Sandoval, C.; Lila, A.M.; Tumlin, J.A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Obinutuzumab in Active Lupus Nephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivioli, G.; Peyronel, F.; Vaglio, A. The new generation of B cell-targeting therapies for the treatment of autoimmune kidney diseases. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, Q.; Shou, Z. Application of CD38 monoclonal antibody in kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1382977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, M.; Suzuki, H.; Suzuki, Y. New Insights and Future Perspectives of APRIL in IgA Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Budhathoki, P.; Adhikari, Y.; Marasini, A.; Bhandari, S.; Mir, W.A.Y.; Shrestha, D.B. Belimumab in Lupus Nephritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2021, 13, e20440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayne, D.; Blockmans, D.; Luqmani, R.; Moiseev, S.; Ji, B.; Green, Y.; Hall, L.; Roth, D.; Henderson, R.B.; Merkel, P.A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab and Azathioprine for Maintenance of Remission in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.K.; Barratt, J.; Lafayette, R.; Liew, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Tesař, V.; Trimarchi, H.; Wong, M.G.; Zhang, H.; Rizk, D.V. Targeting APRIL in the treatment of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 2024, 106, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, M.; Barratt, J.; Suzuki, Y. Phase 2 Trial of Sibeprenlimab in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1245–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampotas, A.; Richter, J.; Isenberg, D.; Roddie, C. CAR-T cell therapy embarks on autoimmune disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2025, 60, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholler, J.; Brady, T.L.; Binder-Scholl, G.; Hwang, W.T.; Plesa, G.; Hege, K.M.; Vogel, A.N.; Kalos, M.; Riley, J.L.; Deeks, S.G.; et al. Decade-long safety and function of retroviral-modified chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 132ra53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulsipher, M.A. Are CAR T cells better than antibody or HCT therapy in B-ALL? Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2018, 2018, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.D.; Aggen, D.H.; Schietinger, A.; Schreiber, H.; Kranz, D.M. A sensitivity scale for targeting T cells with chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) and bispecific T-cell Engagers (BiTEs). Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Terakura, S.; Martens, A.C.; van Meerten, T.; Uchiyama, S.; Imai, M.; Sakemura, R.; Goto, T.; Hanajiri, R.; Imahashi, N.; et al. Target antigen density governs the efficacy of anti-CD20-CD28-CD3 ζ chimeric antigen receptor-modified effector CD8+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansal, R.; Richardson, N.; Neeli, I.; Khawaja, S.; Chamberlain, D.; Ghani, M.; Ghani, Q.U.; Balazs, L.; Beranova-Giorgianni, S.; Giorgianni, F.; et al. Sustained B cell depletion by CD19-targeted CAR T cells is a highly effective treatment for murine lupus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Xu, Q.; Pu, C.; Zhu, K.; Lu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Han, Y.; Lu, L. Therapeutic efficacy of anti-CD19 CAR-T cells in a mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodka, D.; Zschummel, M.; Bunse, M.; Rousselle, A.; Sonnemann, J.; Kettritz, R.; Höpken, U.E.; Schreiber, A. CD19-targeting CAR T cells protect from ANCA-induced acute kidney injury. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougiakakos, D.; Krönke, G.; Völkl, S.; Kretschmann, S.; Aigner, M.; Kharboutli, S.; Böltz, S.; Manger, B.; Mackensen, A.; Schett, G. CD19-Targeted CAR T Cells in Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackensen, A.; Müller, F.; Mougiakakos, D.; Böltz, S.; Wilhelm, A.; Aigner, M.; Völkl, S.; Simon, D.; Kleyer, A.; Munoz, L.; et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2124–2132. Erratum in Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2956. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-02091-9. [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.; Taubmann, J.; Bucci, L.; Wilhelm, A.; Bergmann, C.; Völkl, S.; Aigner, M.; Rothe, T.; Minopoulou, I.; Tur, C.; et al. CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy in Autoimmune Disease—A Case Series with Follow-up. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krickau, T.; Naumann-Bartsch, N.; Aigner, M.; Kharboutli, S.; Kretschmann, S.; Spoerl, S.; Vasova, I.; Völkl, S.; Woelfle, J.; Mackensen, A.; et al. CAR T-cell therapy rescues adolescent with rapidly progressive lupus nephritis from haemodialysis. Lancet 2024, 403, 1627–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, Q.; Zheng, C.; Shen, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, D.; et al. Treatment of two pediatric patients with refractory systemic lupus erythematosus using CD19-targeted CAR T-cells. Autoimmun. Rev. 2025, 24, 103692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, W. Management of Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) following CAR T-cell therapy: A comprehensive review. Clin. Cancer Bull. 2025, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, K.; Merkle, F.; Dimitrov, M.; Merkle, S.; Hoover, A.; Bachanova, V. Major Adverse Events with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy: Presentation, Diagnosis, and Resuscitation. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, M. Latest updates on pathogenesis mechanisms and management strategies for cytokine release syndrome, neurotoxicity, and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis related to CAR-T cell therapies. Ann. Hematol. 2025, 104, 3129–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Seethapathy, H.; Strohbehn, I.A.; Frigault, M.J.; O’Donnell, E.K.; Jacobson, C.A.; Motwani, S.S.; Parikh, S.M.; Curhan, G.C.; Reynolds, K.L.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury and Electrolyte Abnormalities After Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell (CAR-T) Therapy for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.D.; Strohbehn, I.A.; Seethapathy, H.S.; Rusibamayila, N.; Casey, K.S.; Gupta, S.; Leaf, D.E.; Frigault, M.J.; Sise, M.E. Acute Kidney Injury After the CAR-T Therapy Tisagenlecleucel. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 990–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbay, M.; Mizrak, B.; Alper, E.N.; Copur, S.; Ortiz, A. Acute kidney injury following CAR-T cell therapy: A nephrologist’s perspective. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 18, sfae359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.C.; Sterner, R.M. CAR-T cell therapy: Current limitations and potential strategies. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppin, V.; Gibbons, H.; Troje, M.; Feinberg, D.; Webber, B.R.; Moriarity, B.S.; Parameswaran, R. CAR-T cell targeting three receptors on autoreactive B cells for systemic lupus erythematosus therapy. J. Autoimmun. 2025, 151, 103369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Tang, L.; Kong, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhu, X.; You, Y. Strategies for Reducing Toxicity and Enhancing Efficacy of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Hematological Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clinical Trial ID | Target Disease | Study Design | Cell Source and Type | Status | Duration | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD19 | ||||||
| NCT05938725 | LN * | Phase I/II N = 32 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2022–2029 | No |
| NCT05930314 | LN | Phase I N = 12 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Enrolling by invitation | 2023–2025 | No |
| NCT05798117 | LN | Phase I/II N = 24 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Not yet recruiting | 2023–2026 | No |
| NCT06121297 | LN | Phase I/II N = 12 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2027 | No |
| NCT06581198 | LN | Phase II N = 144 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2033 | No |
| NCT06585514 | LN | Phase I/II N = 18 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2025 | No |
| NCT06152172 | LN and AVV | Phase I N = 24 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Not yet recruiting | 2024–2026 | No |
| NCT06544330 | LN | Phase I N = 48 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2025–2041 | No |
| NCT06294236 | LN and AVV | Phase I N = 36 | Allogeneic anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2028 | No |
| NCT06557265 | LN | Phase I N = 48 | Allogeneic anti-CD19 CAR-NK cell | Recruiting | 2024–2027 | No |
| NCT05859997 | AVV | Not Applicable N = 15 | Allogeneic anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Enrolling by invitation | 2023–2025 | No |
| NCT06056921 | AVV | Phase I N = 24 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2023–2026 | No |
| NCT06685042 | AVV | Phase I/II N = 8 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2025 | No |
| NCT06508346 | AVV | Observational N = 12 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2027 | No |
| NCT06548607 | AVV | Phase I N = 20 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2027 | No |
| NCT06549296 | AVV | Phase I N = 12 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2027 | No |
| NCT06548620 | AVV | Phase I N = 18 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Not yet Recruiting | 2024–2027 | No |
| NCT06420154 | AVV | Phase I N = 9 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Not yet Recruiting | 2024–2027 | No |
| NCT06590545 | AVV | Phase I/II N = 8 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Not yet Recruiting | 2025–2027 | No |
| NCT06690359 | IgAN and MN | Phase I N = 12 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-T cell | Not yet Recruiting | 2024–2026 | No |
| NCT06469190 | Immune nephropathy | Phase I N = 36 | Autologous anti-CD19 CAR-NK cell | Recruiting | 2024–2026 | No |
| CD20 | ||||||
| NCT06375993 | LN | Phase I N = 180 | Allogeneic anti-CD20 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2027 | No |
| BCMA | ||||||
| NCT06277427 | LN and AVV | Not Applicable N = 24 | Autologous anti-BCMA CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2027 | No |
| NCT06497387 | LN | Phase I N = 30 | Autologous anti-BCMA CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2027 | No |
| CD19/CD20 | ||||||
| NCT06708845 | LN | Phase I N = 48 | Autologous anti-CD19/CD20 CAR-T cell | Not yet recruiting | 2025–2026 | No |
| NCT06462144 | AVV | Phase I N = 36 | Autologous anti-CD19/CD20 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2026 | No |
| CD19/BCMA | ||||||
| NCT06350110 | LN and AVV | Phase I/II N = 75 | Autologous anti-CD19/BCMA CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2025 | No |
| NCT06497361 | LN | Phase I N = 30 | Autologous anti-CD19/BCMA CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2028 | No |
| NCT06681337 | LN | Phase I N = 10 | Allogeneic anti-CD19/BCMA CAR-T cell | Not yet recruiting | 2024–2025 | No |
| NCT06285279 | LN, AVV and MN | Phase I N = 24 | Autologous anti-CD19/BCMA CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2028 | No |
| NCT05085418 | Immune nephropathy | Phase I N = 9 | Autologous anti-CD19/BCMA CAR-T cell | Unknown status | 2021–2024 | No |
| CD19/CD20/CD22 | ||||||
| NCT06653556 | LN | Phase I N = 34 | Autologous anti-CD19/CD20/CD22 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2025–2029 | No |
| CD19/CD3E | ||||||
| NCT06373081 | LN and AVV | Not Applicable N = 6 | Autologous anti-CD19/CD3E CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2026 | No |
| BCMA/CD70 | ||||||
| NCT06553898 | MDR-SRNS | Phase I N = 18 | Autologous anti-BCMA/CD70 CAR-T cell | Recruiting | 2024–2027 | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaleta, B. CAR-T Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Kidney Diseases: Where Do We Stand Now? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010070
Kaleta B. CAR-T Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Kidney Diseases: Where Do We Stand Now? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010070
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaleta, Beata. 2025. "CAR-T Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Kidney Diseases: Where Do We Stand Now?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010070
APA StyleKaleta, B. (2025). CAR-T Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Kidney Diseases: Where Do We Stand Now? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010070






