Portulaca oleracea Extract Modulates Diet-Dependent Neuroplasticity in a Murine Model of MCD-Induced NAFLD and Depression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical and Behavioral Assessments
2.1.1. Methionine- and Choline-Deficient Diet Induces Weight Loss and Increases Vulnerability to Anhedonia-like Behavior, While Methionine- and Choline-Controlled Diet Promotes Weight Gain and Confers Protection Against Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Induced Anhedonia
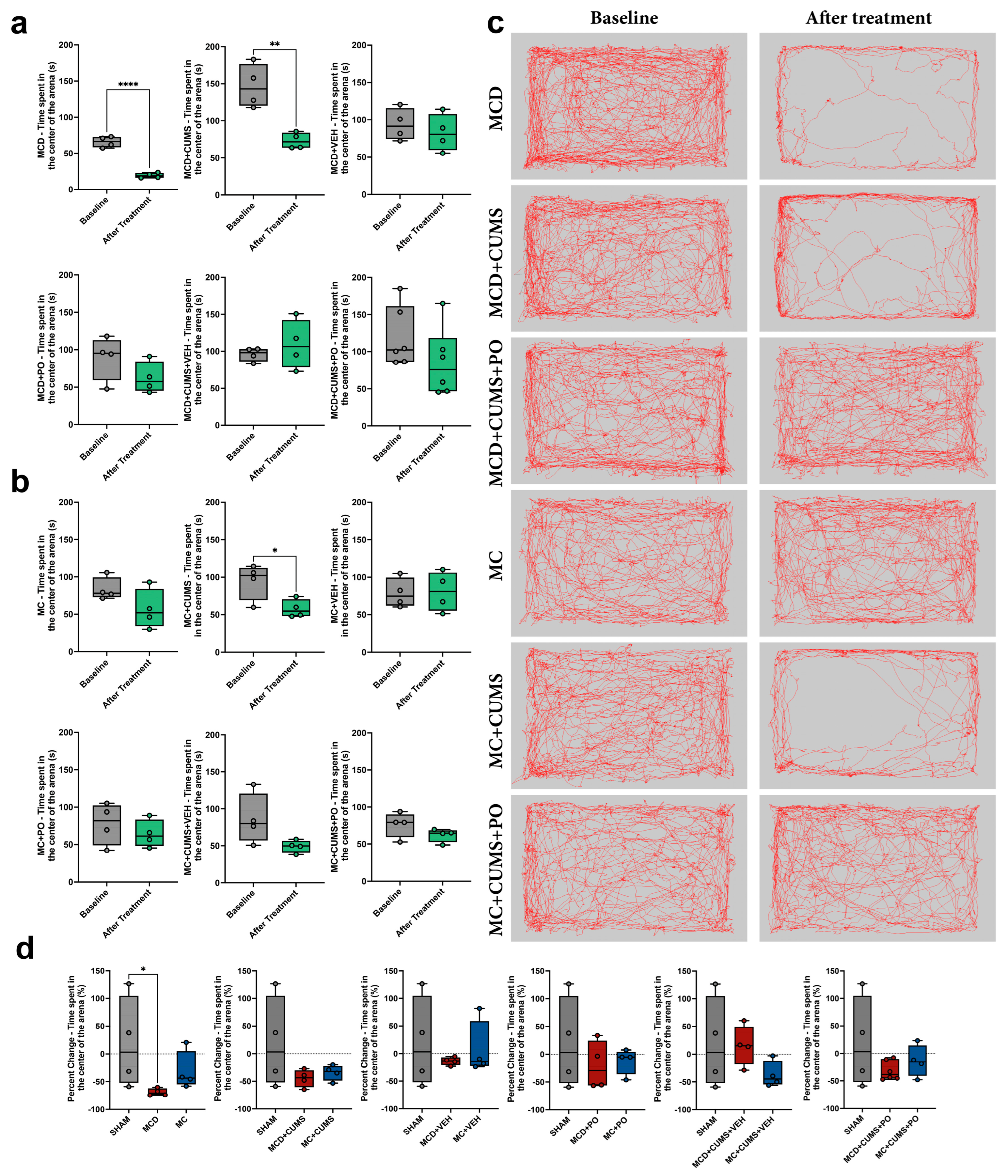
2.1.2. Anxiety-like Behavior Is Induced by the MCD Diet Alone, While MC Diet Induces Anxiety Only Under Chronic Stress Conditions
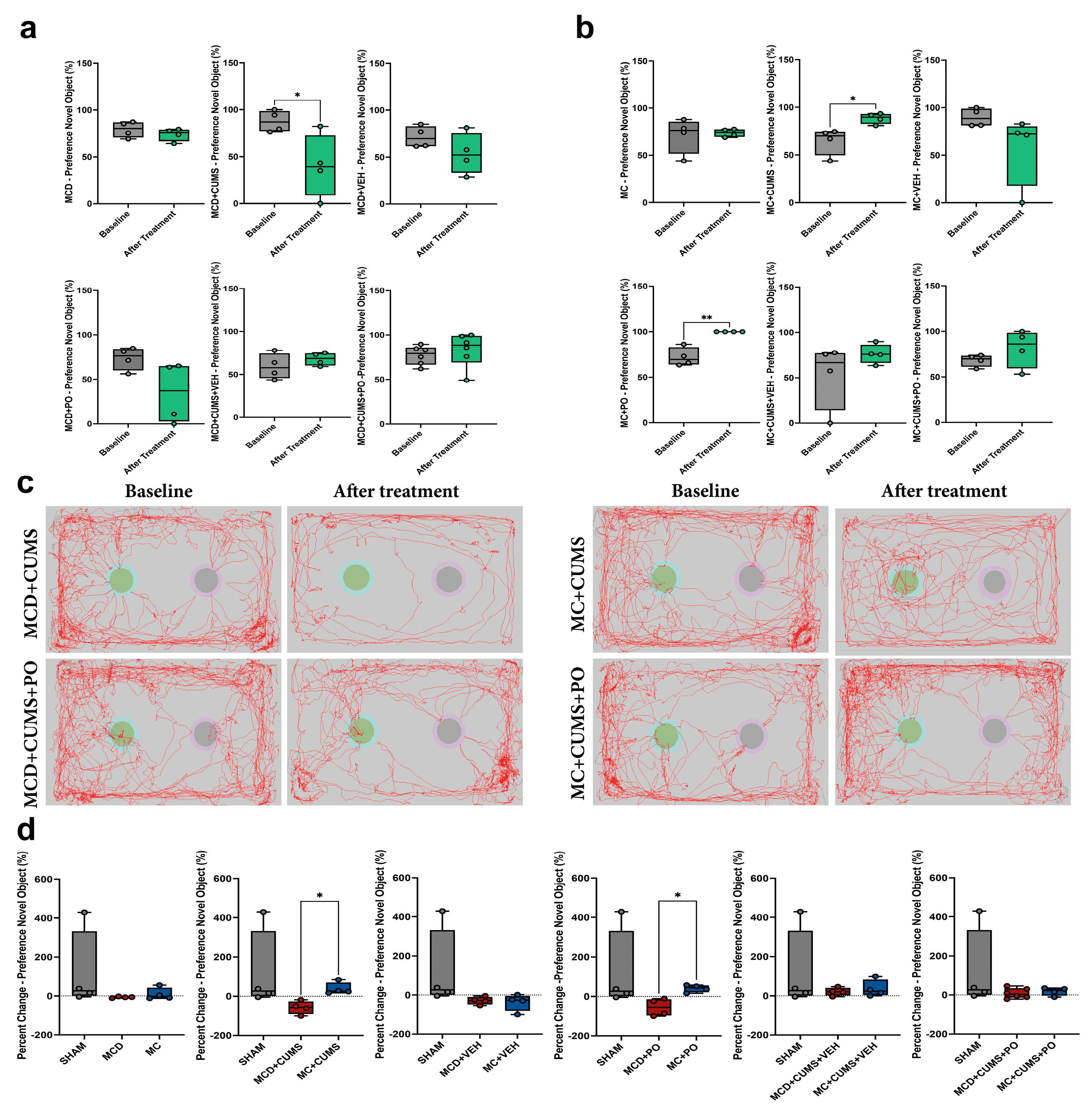
2.1.3. The MCD Diet Impairs Recognition Memory in Chronically Stressed Mice, While the MC Diet Increases Preference for the Novel Object
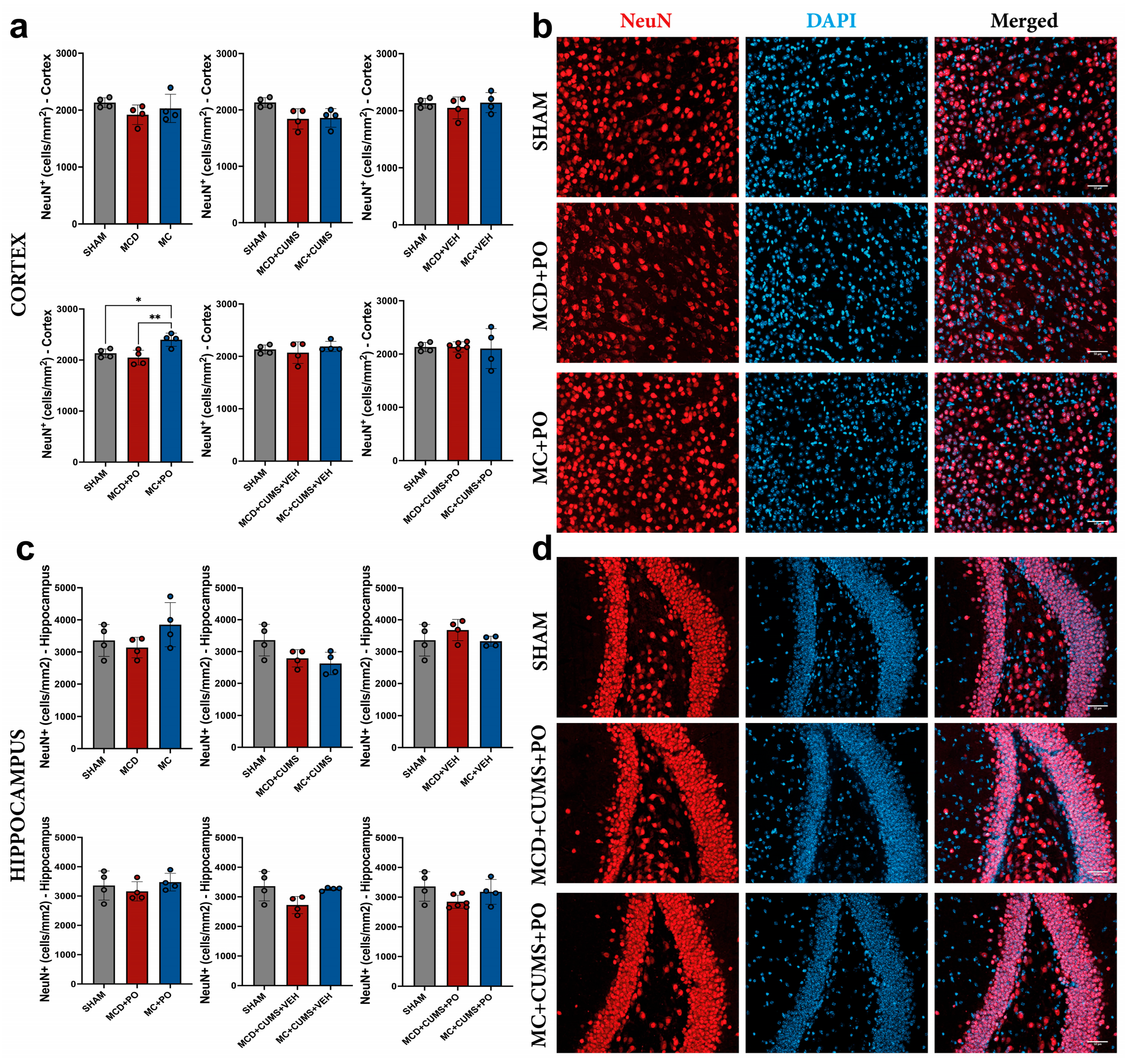
2.2. Immunofluorescent Assessment of Neural and Glial Markers
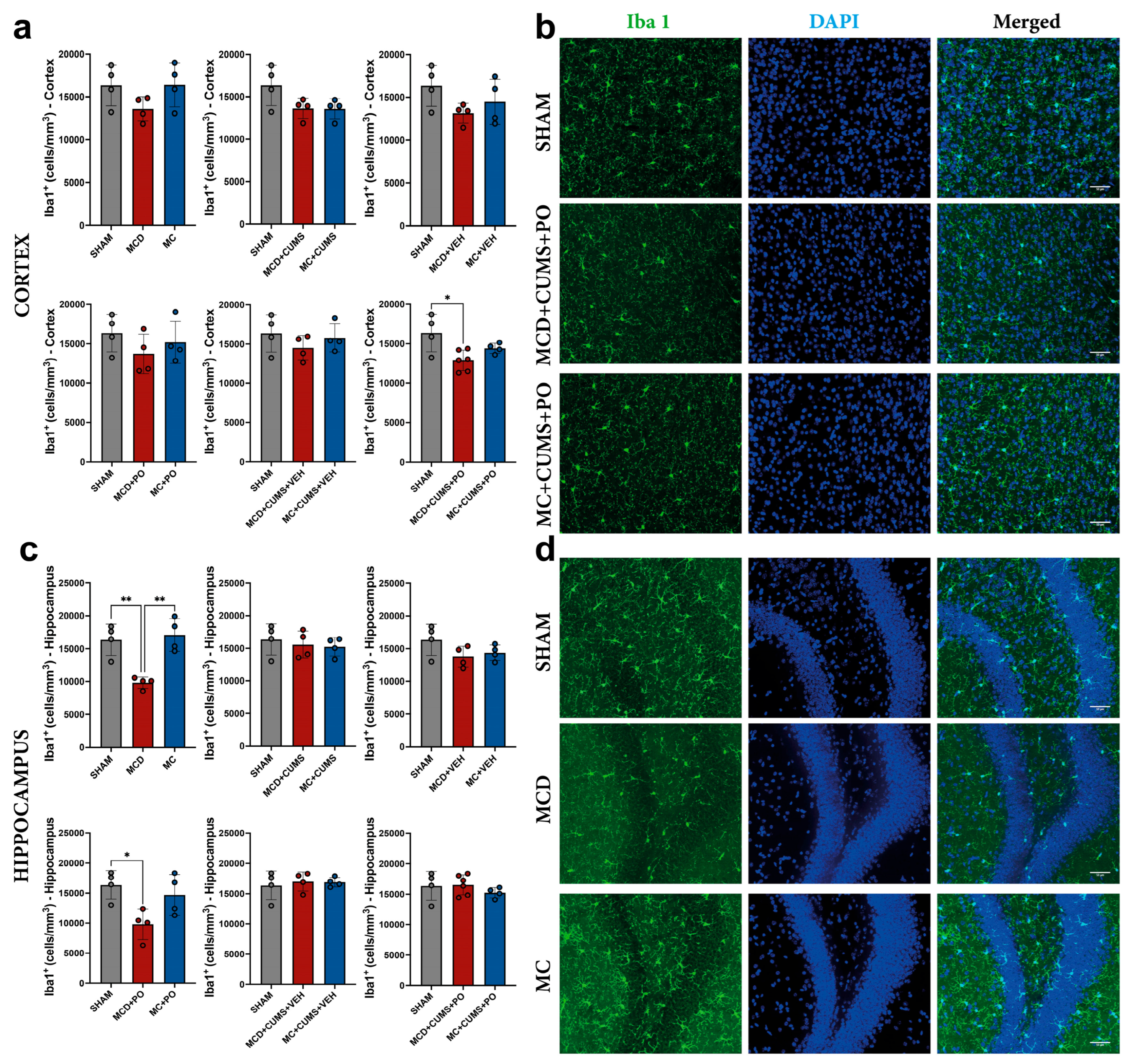
2.2.1. Portulaca oleracea Treatment Fails to Reverse the Microglial Inhibition Induced by the MCD Diet in the Hippocampus
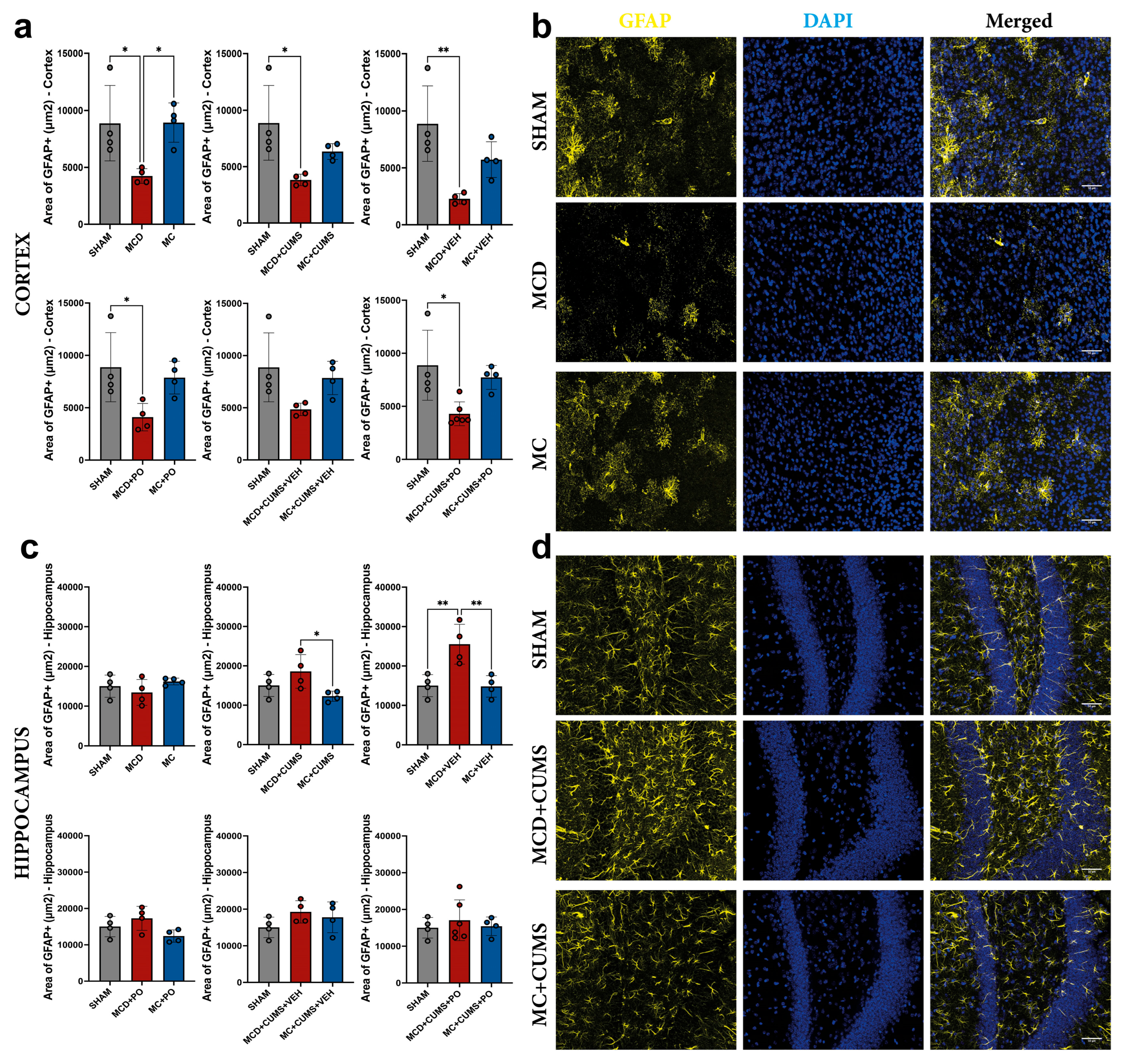
2.2.2. The MCD Diet Induces Astrocyte Dysfunction in the Cortex Regardless of Treatment, as Evidenced by Decreased Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Expression
2.2.3. The MC Diet Combined with PO Can Increase Cortical Neurogenesis, but This Effect Is Not Observed Under Chronic Stress Conditions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Plant Material
4.3. Experimental Animals
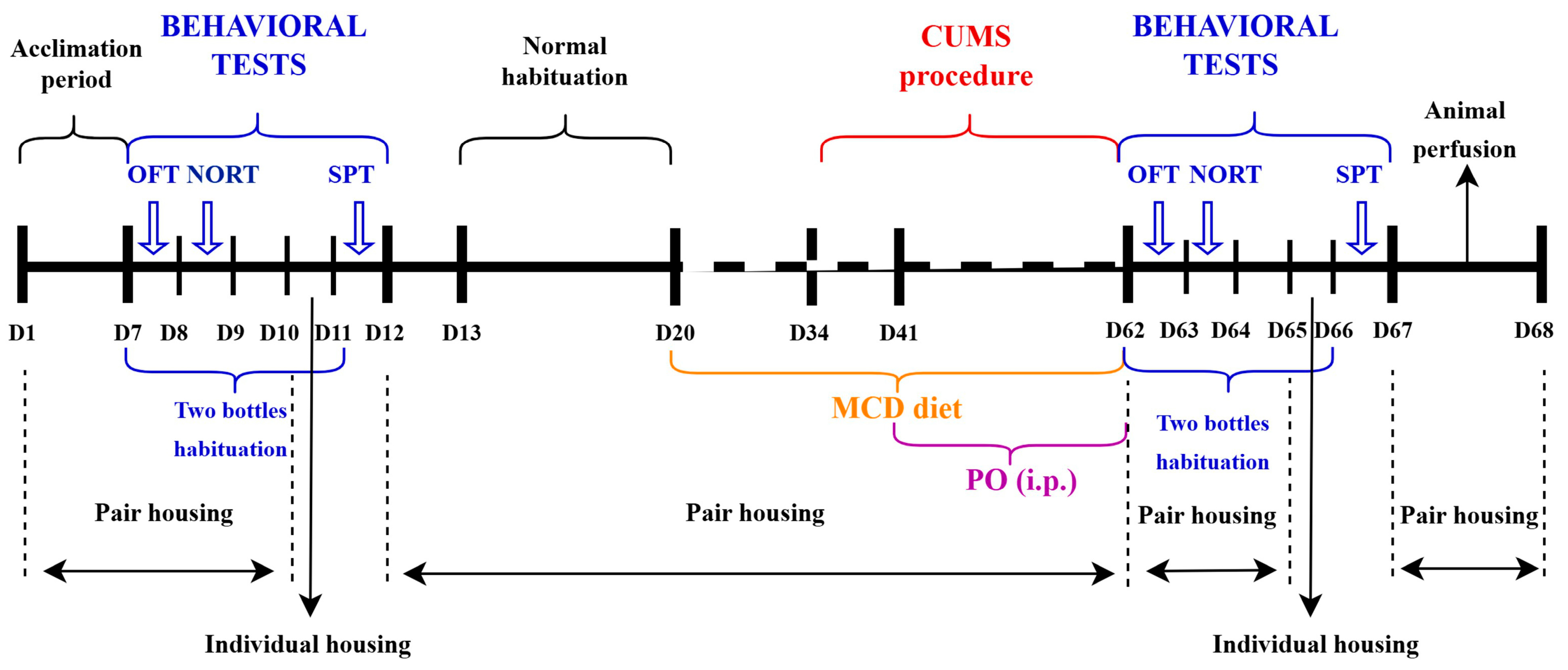
4.4. Depressive-like Behavior and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis and CUMS Induction
4.5. Portulaca oleracea Extract Preparation and Administration
4.5.1. Sample Preparation: Extraction, Hydrolysis, and Derivatization
4.5.2. UHPLC–MS/PDA Analysis
4.5.3. Treatment Administration
4.6. Clinical Evaluation and Behavior Testing
4.7. Immunofluorescent Staining of Paraformaldehyde-Fixed Brain Tissue
4.8. Image Acquisition and Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| CUMS | Chronic unpredictable mild stress |
| D | Day |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| EPO | Erythropoietin |
| FMOC | Fluorenylmethyl chloroformate |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| HCl | Hydrochloric acid |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| Iba1 | Ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| MC | Methionine- and choline-controlled diet |
| MCD | Methionine- and choline-deficient diet |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| MW | Molecular weight |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NeuN | Neuronal nuclei |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NORT | Novel object recognition test |
| NT-3 | Neurotrophin-3 |
| OFT | Open field test |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PDA | Photodiode array |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PO | Portulaca oleracea |
| RT | Room temperature |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SIR | Single ion recording |
| SPT | Sucrose preference test |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| tR | Retention time |
| UAE | Ultrasound-assisted extraction |
| UHPLC | Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography |
| VEH | Vehicle |
| wwPTFE | Water-wettable polytetrafluoroethene |
References
- Whalley, S.; Puvanachandra, P.; Desai, A.; Kennedy, H. Hepatology outpatient service provision in secondary care: A study of liver disease incidence and resource costs. Clin. Med. 2007, 7, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.; Chan, W.K.; Chitturi, S.; Chawla, Y.; Dan, Y.Y.; Duseja, A.; Fan, J.; Goh, K.L.; Hamaguchi, M.; Hashimoto, E.; et al. Asia-Pacific Working Party on Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease guidelines 2017-Part 1: Definition, risk factors and assessment. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Rafiq, N.; Makhlouf, H.; Younoszai, Z.; Agrawal, R.; Goodman, Z. Pathologic criteria for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Interprotocol agreement and ability to predict liver-related mortality. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Sanyal, A.J. Management of NAFLD: A stage-based approach. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.A.; Sanderson, S.; Lindor, K.D.; Angulo, P. The histological course of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A longitudinal study of 103 patients with sequential liver biopsies. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, D.-W.; Yan, H.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhao, S.-H.; Wang, B. Obesity is an independent risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Evidence from a meta-analysis of 21 cohort studies. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-Y.; Chung, T.-H.; Lim, K.-M.; Park, H.-J.; Jang, J.-M. The impact of weight changes on nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease in adult men with normal weight. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2014, 35, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, Y.; Cho, Y.J.; Nam, G.E. Recent Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 31, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Tabibian, J.H.; Ekstedt, M.; Kechagias, S.; Hamaguchi, M.; Hultcrantz, R.; Hagström, H.; Yoon, S.K.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; et al. Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Hashimoto, N.; Kikuchi, T.; Takahashi, H.; Uchiyama, M. The relationship between fatty liver and hyperinsulinemia in obese Japanese children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1997, 24, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Shanab, A.; Quigley, E.M.M. The role of the gut microbiota in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miele, L.; Valenza, V.; La Torre, G.; Montalto, M.; Cammarota, G.; Ricci, R.; Mascianà, R.; Forgione, A.; Gabrieli, M.L.; Perotti, G.; et al. Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosato, V.; Masarone, M.; Dallio, M.; Federico, A.; Aglitti, A.; Persico, M. NAFLD and Extra-Hepatic Comorbidities: Current Evidence on a Multi-Organ Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.W.; Gottesman, R.F.; Clark, J.M.; Hernaez, R.; Chang, Y.; Kim, C.; Ha, K.H.; Guallar, E.; Lazo, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with cognitive function in adults. Neurology 2016, 86, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Lange, S.M.M. Metabolic syndrome in psychiatric patients: Overview, mechanisms, and implications. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muşat, M.I.; Mitran, S.I.; Udriştoiu, I.; Albu, C.V.; Cătălin, B. The impact of stress on the behavior of C57BL/6 mice with liver injury: A comparative study. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1358964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.H.; Xiao, J.; Chew, N.W.S.; Chin, Y.H.; Chan, K.E.; Quek, J.; Lim, W.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Loke, R.W.K.; Tan, C.; et al. Depression in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an increased risk of complications and mortality. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 985803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipović, B.; Marković, O.; Đurić, V.; Filipović, B. Cognitive Changes and Brain Volume Reduction in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 9638797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjihambi, A. Cerebrovascular alterations in NAFLD: Is it increasing our risk of Alzheimer’s disease? Anal. Biochem. 2022, 636, 114387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marušić, M.; Paić, M.; Knobloch, M.; Liberati Pršo, A.-M. NAFLD, Insulin Resistance, and Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 2021, 6613827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, A.A.; Kaplan, G.G.; Sharkey, K.A.; Lethebe, B.C.; Swain, M.G. Impact of major depression and antidepressant use on alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A population-based study. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2308–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, P.A.; Thomas, A.B.; Chopada, V.M.; Bokaria, P.V.; Deokate, S.B.; Chougule, P.S.; Chavan, P.N.; Chitlange, S.S. Correlation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and neurodegenerative disorders. Egypt. Liver J. 2024, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Srivastava, V.; Singh, A. Multipurpose Benefits of an Underexplored Species Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.): A Critical Review. Environ. Manag. 2023, 72, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segneanu, A.-E.; Vlase, G.; Marin, C.N.; Vlase, T.; Sicoe, C.; Herea, D.D.; Ciocîlteu, M.V.; Bejenaru, L.-E.; Minuti, A.E.; Zară, C.-M.; et al. Wild grown Portulaca oleracea as a novel magnetite based carrier with in vitro antioxidant and cytotoxicity potential. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, D.G.; Lee, H.S. Anti-TNF-α activity of Portulaca oleracea in vascular endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 5628–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, V.R.; Rezaee, S.A.; Abnous, K.; Iranshahi, M.; Boskabady, M.H. The influence of hydro-ethanolic extract of Portulaca oleracea L. on Th1/Th2 balance in isolated human lymphocytes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranshahy, M.; Javadi, B.; Iranshahi, M.; Jahanbakhsh, S.P.; Mahyari, S.; Hassani, F.V.; Karimi, G. A review of traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Portulaca oleracea L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 205, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, F.; Boskabady, M.H. A review of the relaxant effect of various medicinal plants on tracheal smooth muscle, their possible mechanism(s) and potency. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 175, 528–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.; Islam, M.W.; Kamil, M.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Zakaria, M.N.; Habibullah, M.; Attas, A. The analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of Portulaca oleracea L. subsp. sativa (Haw.) Celak. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 73, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Zang, X.; Ma, J.; Xu, G. Anti-Diabetic Effect of Portulaca oleracea L. Polysaccharide and its Mechanism in Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinou, E.; Pericleous, M.; Stefanova, I.; Kaur, V.; Angelidi, A.M. Diagnostic Modalities of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From Biochemical Biomarkers to Multi-Omics Non-Invasive Approaches. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Tao, B.; Chen, M. High-fat Fructose diet induces neuroinflammation and anxiety-like behaviors by modulating liver–brain axis communication. Psychopharmacology 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-G.; Krenz, A.; Toussaint, L.E.; Maurer, K.J.; Robinson, S.-A.; Yan, A.; Torres, L.; Bynoe, M.S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induces signs of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in wild-type mice and accelerates pathological signs of AD in an AD model. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, E.; Yılmaz, Y. Association of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease with Cognitive Impairment and All-Cause Dementia: A Comprehensive Review. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 35, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, A.P.; Knight-Scott, J.; Caillaud, M.; Gallagher, I.; Park, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Tanaka, H.; Browning, J.D. Low carbohydrate and low-calorie diets reduce liver fat and lower brain glutamate and myo-inositol levels in patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Metab. Brain Dis. 2025, 40, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.K.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J. Animal models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Current perspectives and recent advances. J. Pathol. 2017, 241, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soret, P.-A.; Magusto, J.; Housset, C.; Gautheron, J. In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Critical Appraisal. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Obata, A.; Kashiwagi, Y.; Rokugawa, T.; Matsushima, S.; Hamada, T.; Watabe, H.; Abe, K. Gd–EOB–DTPA-enhanced–MR imaging in the inflammation stage of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in mice. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 34, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcolin, E.; Forgiarini, L.F.; Tieppo, J.; Dias, A.S.; Freitas, L.A.R.; Marroni, N.P. Methionine- and choline-deficient diet induces hepatic changes characteristic of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2011, 48, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Hahn, K.R.; Yoo, D.Y.; Jung, H.Y.; Hwang, I.K.; Seong, J.K.; Yoon, Y.S. Methionine-Choline Deprivation Impairs Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in C57BL/6 Mice. J. Med. Food. 2019, 22, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelea, G.; Muşat, M.I.; Mitran, S.I.; Ciorbagiu, M.C.; Cătălin, B. Morphological Differences in Hippocampal Microglia in C57BL/6N Mice with Liver Injury and Depressive-Like Behavior. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2024, 50, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelea, G.; Muşat, M.I.; Buican-Chirea, A.C.; Ciorbagiu, M.C.; Cătălin, B. Depressive-Like Behavior and Liver Damage Generate Behavioral and Cortical Microglial Morphological Differences in Mice. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2024, 50, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelea, G.; Muşat, M.I.; Mitran, S.I.; Ciorbagiu, M.C.; Cătălin, B. Acute liver damage generates age independent microglia morphology changes in mice. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2024, 65, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.Y.; Chang, Y.; Sung, E.; Kang, J.-H.; Wild, S.H.; Byrne, C.D.; Shin, H.; Ryu, S. Depression and increased risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in individuals with obesity. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2021, 30, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, R.; Caruso, P.; Gazzin, S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and neurological defects. Ann. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.-X.; Xin, H.-L.; Rahman, K.; Wang, S.-J.; Peng, C.; Zhang, H. Portulaca oleracea L.: A review of phytochemistry and pharmacological effects. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 925631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-Q.; Zhou, Y.; Ping, J.; Xu, L.-M. Traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of liver diseases: Progress, challenges and opportunities. J. Integr. Med. 2014, 12, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Shen, Z.-Y.; Wu, B.; Xia, S.-J.; Huang, J.-H.; Chen, W.-H.; Ying, J. Study on changes of protein phosphorylation of p65, IκBα and IκBε in lymphocytes of rats in progress of aging and interventional effect of Epimedium flavonoids. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2008, 33, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, M.I. Effects of Portulaca oleracea L. seeds in treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus patients as adjunctive and alternative therapy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muşat, M.I.; Ifrim-Predoi, A.-M.; Mitran, S.I.; Osiac, E.; Cătălin, B. The Behavioral and Neuroinflammatory Impact of Ketamine in a Murine Model of Depression and Liver Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morega, S.; Gresita, A.; Mitran, S.I.; Musat, M.I.; Boboc, I.K.S.; Gheorman, V.; Udristoiu, I.; Albu, C.V.; Streba, C.T.; Catalin, B.; et al. Cerebrolysin Use in Patients with Liver Damage—A Translational Study. Life 2022, 12, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morega, S.; Cătălin, B.; Simionescu, C.E.; Sapalidis, K.; Rogoveanu, I. Cerebrolysin Prevents Brain Injury in a Mouse Model of Liver Damage. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Green, R.M. The methionine-choline deficient dietary model of steatohepatitis does not exhibit insulin resistance. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, H.H.; Feigh, M.; Veidal, S.S.; Rigbolt, K.T.; Vrang, N.; Fosgerau, K. Mouse models of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in preclinical drug development. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Elias, M.S.; Smolak, R.R.; Fu, T.; Borensztajn, J.; Green, R.M. Mechanisms of hepatic steatosis in mice fed a lipogenic methionine choline-deficient diet. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, F.H. Methionine and choline deficiency in the rat with special reference to the pregnant state. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1951, 32, 481–492. [Google Scholar]
- Rizki, G.; Arnaboldi, L.; Gabrielli, B.; Yan, J.; Lee, G.S.; Ng, R.K.; Turner, S.M.; Badger, T.M.; Pitas, R.E.; Maher, J.J. Mice fed a lipogenic methionine-choline-deficient diet develop hypermetabolism coincident with hepatic suppression of SCD-1. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 2280–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, K.; Lu, K.; Chen, Q.; Guo, Z.; Du, X.; Riaz, F.; Feng, L.; Fu, Y.; Yin, C.; Zhang, F.; et al. Epigallocatechin Gallate Protects Mice against Methionine-Choline-Deficient-Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis by Improving Gut Microbiota to Attenuate Hepatic Injury and Regulate Metabolism. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20800–20809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Li, H.; Lu, B.; Guo, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, F.; Li, Q.; Xie, L.; Glaser, S.; Francis, H.; et al. Indole supplementation ameliorates MCD-induced NASH in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 107, 109041, Erratum in: J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 133, 109705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2024.109705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T.; Suzuki, S.; Sato, Y.; Itoh, T.; Umegaki, K. Evaluation of Methionine Content in a High-Fat and Choline-Deficient Diet on Body Weight Gain and the Development of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Hada, N.; Sakamaki, Y.; Uno, A.; Shiga, T.; Tanaka, C.; Ito, T.; Katsume, A.; Sudoh, M. An improved mouse model that rapidly develops fibrosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 94, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown-Borg, H.M. Reduced growth hormone signaling and methionine restriction: Interventions that improve metabolic health and extend life span. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1363, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.-G.; Kim, S.-U.; Wong, V.W.-S. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundi, M.S.; Velapati, S.; Patel, J.; Kellogg, T.A.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Hurt, R.T. Evolution of NAFLD and Its Management. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2020, 35, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, K.; Stelmach-Mardas, M.; Schlesinger, S. Obesity and Liver Cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2016, 208, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.-L.; Shen, J.-D.; Wang, B.-Y.; Lu, S.-F.; Ming, B.; Xu, E.-P.; Li, Y.-C.; Fang, X.-Y. Depressive-like behaviors are induced by chronic liver injury in male and female mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 718, 134750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, R.D.; Mueller, A.; Sisti, H.M.; Ogawa, S.; McEwen, B.S.; Brake, W.G. Anxiety and fear behaviors in adult male and female C57BL/6 mice are modulated by maternal separation. Horm. Behav. 2003, 43, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, J.L.; Stell, B.M.; Rafizadeh, M.; Mody, I. Ovarian cycle-linked changes in GABAA receptors mediating tonic inhibition alter seizure susceptibility and anxiety. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shansky, R.M. Are hormones a “female problem” for animal research? Science 2019, 364, 825–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, J.A.; Collins, F.S. Policy: NIH to balance sex in cell and animal studies. Nature 2014, 509, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beery, A.K. Inclusion of females does not increase variability in rodent research studies. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2018, 23, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meziane, H.; Ouagazzal, A.-M.; Aubert, L.; Wietrzych, M.; Krezel, W. Estrous cycle effects on behavior of C57BL/6J and BALB/cByJ female mice: Implications for phenotyping strategies. Genes Brain Behav. 2007, 6, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisbett, K.E.; Gonzalez, L.A.; Teruel, M.; Carter, C.S.; Vendruscolo, L.F.; Ragozzino, M.E.; Koob, G.F. Sex and hormonal status influence the anxiolytic-like effect of oxytocin in mice. Neurobiol. Stress 2023, 26, 100567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.-H.; Wu, K.-Y.; Su, N.C.; Edwards, A.; Huang, G.-J. The influence of sex difference on behavior and adult hippocampal neurogenesis in C57BL/6 mice. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Lee, C.-L.; Ma, Y.-K.; Kuo, T.-H. Minimal influence of estrous cycle on studies of female mouse behaviors. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1146109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Swain, M.G. Avenues within the gut–liver–brain axis linking chronic liver disease and symptoms. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1171253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Man, S.; Sun, B.; Ma, L.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Gut liver brain axis in diseases: The implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2023, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cól, J.P.; de Lima, E.P.; Pompeu, F.M.; Cressoni Araújo, A.; de Alvares Goulart, R.; Bechara, M.D.; Laurindo, L.F.; Méndez-Sánchez, N.; Barbalho, S.M. Underlying Mechanisms behind the Brain–Gut–Liver Axis and Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilen, M.; Ibrahim, P.; Barmo, N.; Abou Haidar, E.; Karnib, N.; El Hayek, L.; Khalifeh, M.; Jabre, V.; Houbeika, R.; Stephan, J.S.; et al. Methionine mediates resilience to chronic social defeat stress by epigenetic regulation of NMDA receptor subunit expression. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 3007–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisova, K.Y.; Gabova, A.V.; Fedosova, E.A.; Shatskova, A.B.; Narkevich, V.B.; Kudrin, V.S. Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Effects of L-Methionine in the WAG/Rij Rat Model of Depression Comorbid with Absence Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kang, X.; Zhang, L.; Luo, J.; Zhang, D. Dietary choline is inversely associated with depressive symptoms: A cross-sectional study of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2011 to 2018. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 301, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazeminejad, S.; Moradmand, Z.; Shahdadian, F.; Hajhashemy, Z.; Rouhani, P.; Saneei, P. Dietary choline and betaine intake in relation to psychological disorders in adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2025, 133, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekdash, R.A. Neuroprotective Effects of Choline and Other Methyl Donors. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, B.; Li, W.; He, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhong, Z.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Y. Effects of repeated drug administration on behaviors in normal mice and fluoxetine efficacy in chronic unpredictable mild stress mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 615, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Zakaria, M.N.; Islam, M.W.; Chen, H.B.; Kamil, M.; Chan, K.; Al-Attas, A. Neuropharmacological actions of Portulaca oleraceae L v. sativa (Hawk). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 76, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, O.; Okwuasaba, F.K.; Ejike, C. Skeletal muscle relaxant action of an aqueous extract of Portulaca oleracea in the rat. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1987, 19, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouzanfar, F.; Hosseinzadeh, H.; Khorrami, M.B.; Asgharzade, S.; Rakhshandeh, H. Attenuating Effect of Portulaca oleracea Extract on Chronic Constriction Injury Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats: An Evidence of Anti-oxidative and Anti-inflammatory Effects. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 18, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, V.B.; Ajam, F.; Rakhshandeh, H.; Askari, V.R. A Pharmacological Review on Portulaca oleracea L.: Focusing on Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Oxidant, Immuno-Modulatory and Antitumor Activities. J. Pharmacopunct. 2019, 22, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Moneim, A.E. The neuroprotective effects of purslane (Portulaca oleracea) on rotenone-induced biochemical changes and apoptosis in brain of rat. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanyin, W.; Liwei, D.; Lin, J.; Hailiang, X.; Changquan, L.; Min, L. Ethanol extract of Portulaca oleracea L. protects against hypoxia-induced neuro damage through modulating endogenous erythropoietin expression. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Q.; Yang, G.Q. Betacyanins from Portulaca oleracea L. ameliorate cognition deficits and attenuate oxidative damage induced by D-galactose in the brains of senescent mice. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ren, J.; Yang, M.; Li, S. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of the total alkaloid from traditional Chinese herbal medicine for treating Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groblewski, P.A.; Bax, L.S.; Cunningham, C.L. Reference-dose place conditioning with ethanol in mice: Empirical and theoretical analysis. Psychopharmacology 2008, 201, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Ma, H.; Li, M. Dyslipidemic Diet Induces Mobilization of Peripheral Neutrophils and Monocytes That Exacerbate Hemorrhagic Brain Injury and Neuroinflammation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockhurst, J.; Cheleuitte-Nieves, C.; Buckmaster, C.L.; Schatzberg, A.F.; Lyons, D.M. Stress inoculation modeled in mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.R.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, Q.; Glaser, S.; Francis, H.; Alpini, G.; Wu, C. Methionine- and Choline-Deficient Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Associated with Increased Intestinal Inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, J.; Aggarwal, H.; Kumari, D.; Gupta, S.K.; Kumar, Y.; Dikshit, M. A methionine-choline-deficient diet induces nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and alters the lipidome, metabolome, and gut microbiome profile in the C57BL/6J mouse. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Biol. Lipids 2024, 1869, 159545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Shu, J.; Shi, L.; Shi, Z. Interactive Effects of Methionine and Lead Intake on Cognitive Function among Chinese Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lail, H.; Mabb, A.M.; Parent, M.B.; Pinheiro, F.; Wanders, D. Effects of Dietary Methionine Restriction on Cognition in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Grune, T.; Shi, L.; Hou, M.; Liu, Z. Effects of methionine intake on cognitive function in mild cognitive impairment patients and APP/PS1 Alzheimer’s Disease model mice: Role of the cystathionine-β-synthase/H2S pathway. Redox Biol. 2023, 59, 102595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yao, J.; Liu, J.; Niu, Y.; Ying, X. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of a new skeleton alkaloid isolated from Portulaca oleracea L. Fitoterapia 2025, 185, 106760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiu, J.; Wei, W.; Yao, J.; He, F.; Ying, X. A new alkaloid and five known compounds from Portulaca oleracea L. and their anti-inflammatory activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2025, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gu, L.; Dong, L.; Wang, X.; Ling, C.; Li, M. Protective effect of Portulaca oleracea extracts on hypoxic nerve tissue and its mechanism. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, W.B.; Rodrigues, S.A.; Silva, H.K.; Dantas, C.G.; Júnior, W.L.; Filho, L.X.; Cardoso, J.C.; Gomes, M.Z. Neuroprotective effect of Portulaca oleracea extracts against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced lesion of dopaminergic neurons. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2016, 88, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itagaki, H.; Shimizu, K.; Morikawa, S.; Ogawa, K.; Ezaki, T. Morphological and functional characterization of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a methionine-choline-deficient diet in C57BL/6 mice. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 2683–2696. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-D.; Yang, G.; Bai, Y.; Feng, Y.-P.; Li, H. The behavioral study on the interactive aggravation between pruritus and depression. Brain Behav. 2018, 8, e00964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałucha-Poniewiera, A.; Podkowa, K.; Rafało-Ulińska, A. The group II mGlu receptor antagonist LY341495 induces a rapid antidepressant-like effect and enhances the effect of ketamine in the chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression in C57BL/6J mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 109, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herselman, M.F.; Bobrovskaya, L. The Effects of Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress and Semi-Pure Diets on the Brain, Gut and Adrenal Medulla in C57BL6 Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Sun, M.; Li, L.; He, W. Chrysin alleviated CUMS-induced depressive-like behaviors in mice via directly targeting Fyn. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 106, 105603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio-Mendoza, J.A.; Pokorski, P.; Aktaş, H.; Kurek, M.A. Rapid and efficient high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet determination of total amino acids in protein isolates by ultrasound-assisted acid hydrolysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 111, 107082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackaberry, E.A.; Wang, X.; Schweiger, M.; Messick, K.; Valle, N.; Dean, B.; Sambrone, A.; Bowman, T.; Xie, M. Solvent-based formulations for intravenous mouse pharmacokinetic studies: Tolerability and recommended solvent dose limits. Xenobiotica 2014, 44, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, J.; Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M. Ameliorative effects of Portulaca oleracea L. (purslane) and its active constituents on nervous system disorders: A review. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2023, 26, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, S.; Forouzanfar, F.; Rakhshandeh, H.; Arian, A. Hypnotic Effect of Portulaca oleracea on Pentobarbital-Induced Sleep in Mice. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2019, 16, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muşat, M.I.; Cătălin, B.; Hadjiargyrou, M.; Popa-Wagner, A.; Greşiţă, A. Advancing Post-Stroke Depression Research: Insights from Murine Models and Behavioral Analyses. Life 2024, 14, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boboc, I.K.S.; Cojocaru, A.; Nedelea, G.; Catalin, B.; Bogdan, M.; Calina, D. Chronic Administration of Ion Channel Blockers Impact Microglia Morphology and Function in a Murine Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cătălin, B.; Stopper, L.; Bălşeanu, T.-A.; Scheller, A. The in situ morphology of microglia is highly sensitive to the mode of tissue fixation. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2017, 86, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godeanu, S.; Muşat, M.I.; Scheller, A.; Osiac, E.; Cătălin, B. Minimal differences observed when comparing the morphological profiling of microglia obtained by confocal laser scanning and optical sectioning microscopy. Front. Neuroanat. 2025, 18, 1507140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godeanu, S.; Clarke, D.; Stopper, L.; Deftu, A.-F.; Popa-Wagner, A.; Bălşeanu, A.T.; Scheller, A.; Catalin, B. Microglial morphology in the somatosensory cortex across lifespan. A quantitative study. Dev. Dyn. 2023, 252, 1113–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | No. of Animals |
|---|---|
| SHAM | 4 |
| MCD | 4 |
| MC | 4 |
| MCD + CUMS | 4 |
| MC + CUMS | 4 |
| MCD + VEH | 4 |
| MC + VEH | 4 |
| MCD + PO | 4 |
| MC + PO | 4 |
| MCD + CUMS + VEH | 4 |
| MC + CUMS + VEH | 4 |
| MCD + CUMS + PO | 6 |
| MC + CUMS + PO | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitran, S.I.; Muşat, M.I.; Bejenaru, C.; Mogoşanu, G.D.; Boboc, I.K.Ş.; Tudoraşcu, R.-I.; Târtea, G.; Zlătian, O.M.; Blendea, A.; Biţă, A.; et al. Portulaca oleracea Extract Modulates Diet-Dependent Neuroplasticity in a Murine Model of MCD-Induced NAFLD and Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010050
Mitran SI, Muşat MI, Bejenaru C, Mogoşanu GD, Boboc IKŞ, Tudoraşcu R-I, Târtea G, Zlătian OM, Blendea A, Biţă A, et al. Portulaca oleracea Extract Modulates Diet-Dependent Neuroplasticity in a Murine Model of MCD-Induced NAFLD and Depression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010050
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitran, Smaranda Ioana, Mădălina Iuliana Muşat, Cornelia Bejenaru, George Dan Mogoşanu, Ianis Kevyn Ştefan Boboc, Robertina-Iulia Tudoraşcu, Georgică Târtea, Ovidiu Mircea Zlătian, Antonia Blendea, Andrei Biţă, and et al. 2025. "Portulaca oleracea Extract Modulates Diet-Dependent Neuroplasticity in a Murine Model of MCD-Induced NAFLD and Depression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010050
APA StyleMitran, S. I., Muşat, M. I., Bejenaru, C., Mogoşanu, G. D., Boboc, I. K. Ş., Tudoraşcu, R.-I., Târtea, G., Zlătian, O. M., Blendea, A., Biţă, A., Segneanu, A.-E., & Bejenaru, L. E. (2025). Portulaca oleracea Extract Modulates Diet-Dependent Neuroplasticity in a Murine Model of MCD-Induced NAFLD and Depression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010050









