Improved Iron Overload with Pegcetacoplan in Eculizumab-Experienced Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria †
Abstract
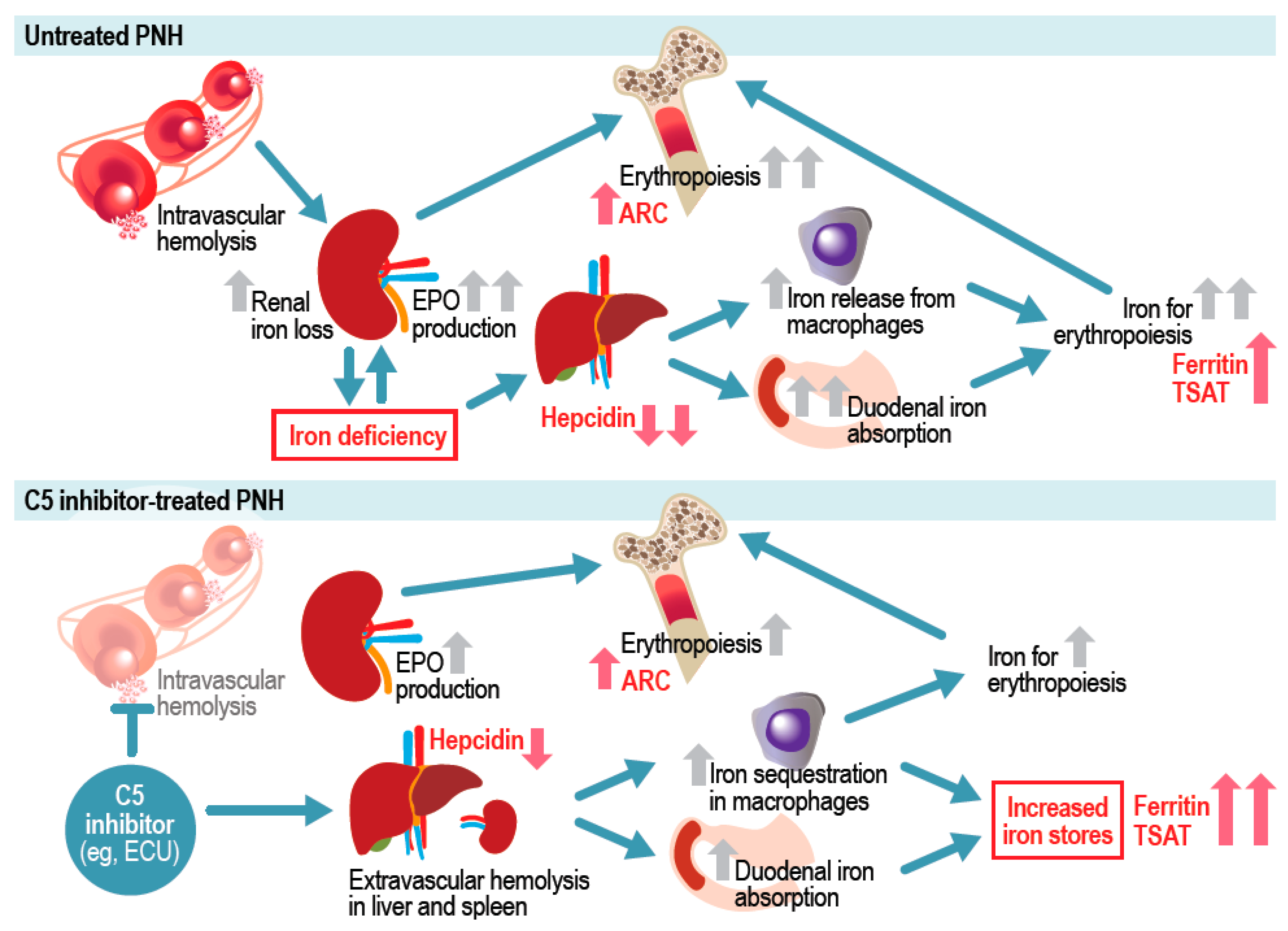
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics
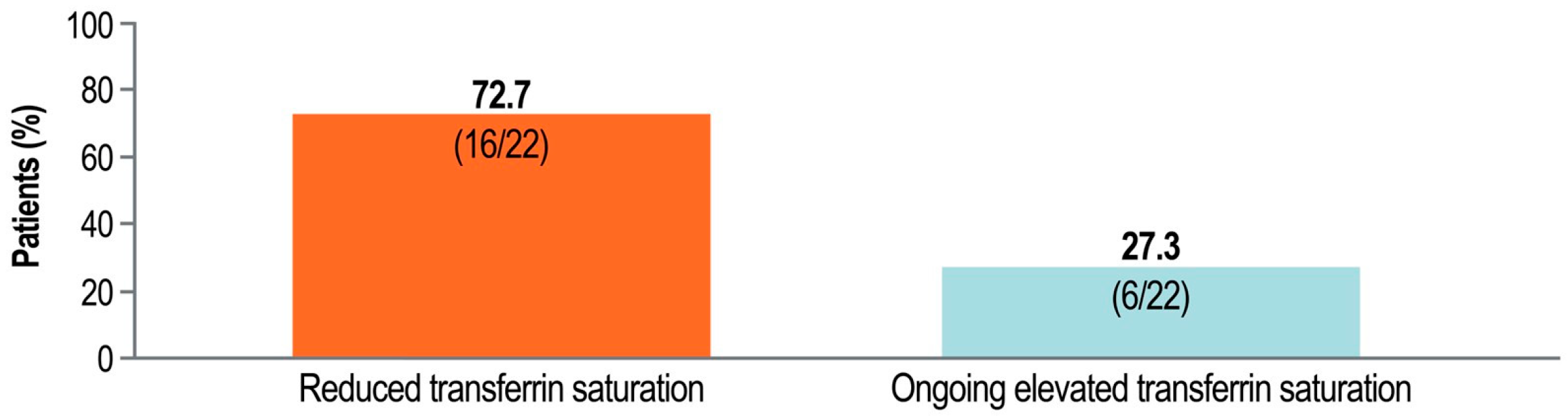
2.2. Resolution of Iron Overload with Pegcetacoplan
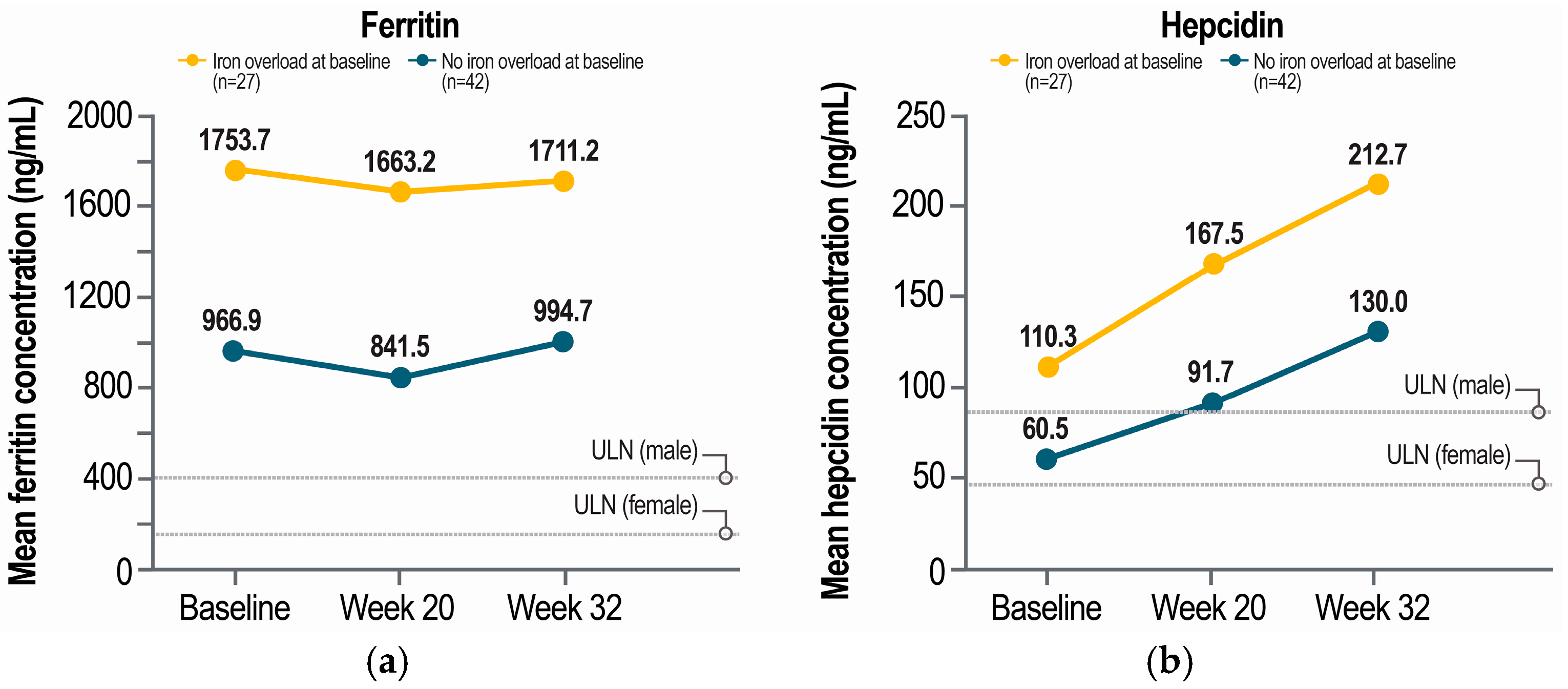
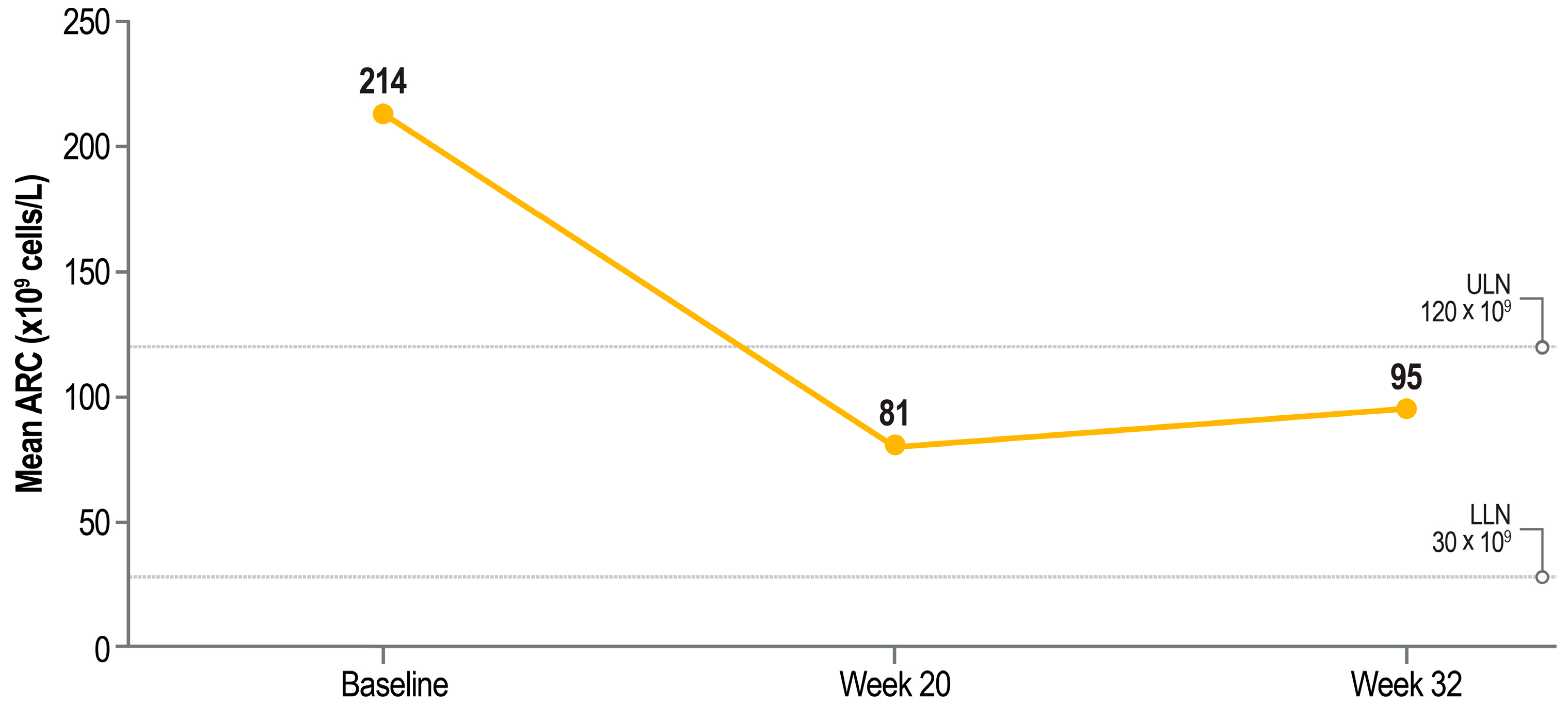
2.3. Iron Markers by Baseline Iron Overload Status
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
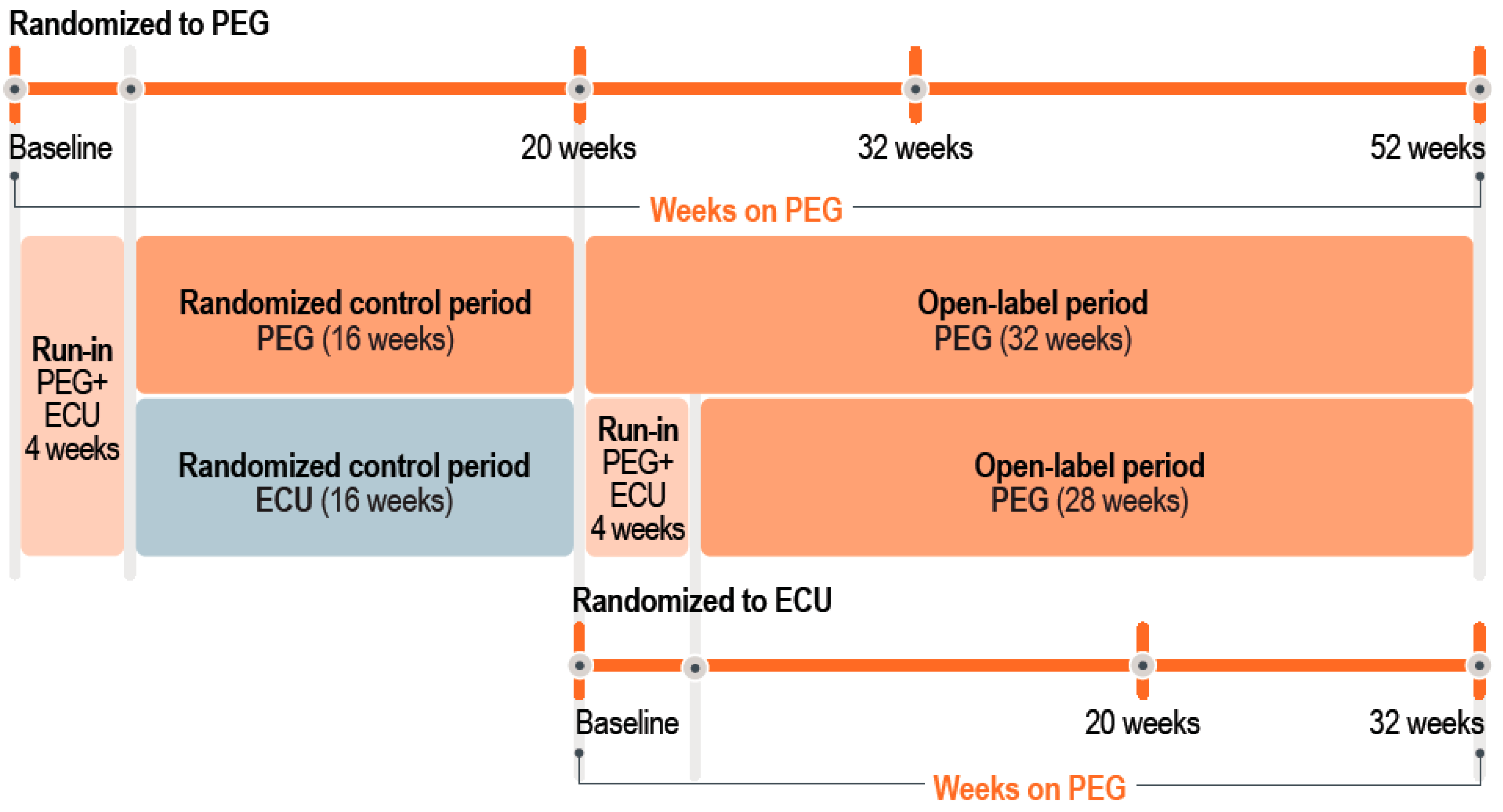
4.1. Patients and Study Design
4.2. Post Hoc Analysis
4.3. Outcomes
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Ethics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARC | Absolute reticulocyte count |
| C3 | Complement factor 3 |
| C5 | Complement factor 5 |
| EVH | Extravascular hemolysis |
| IVH | Intravascular hemolysis |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| PNH | Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria |
References
- Hill, A.; DeZern, A.E.; Kinoshita, T.; Brodsky, R.A. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versino, F.; Fattizzo, B. Complement inhibition in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: From biology to therapy. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2024, 46, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.J.; Hill, A.; Arnold, L.M.; Brooksbank, G.L.; Richards, S.J.; Cullen, M.; Mitchell, L.D.; Cohen, D.R.; Gregory, W.M.; Hillmen, P. Long-term treatment with eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Sustained efficacy and improved survival. Blood 2011, 117, 6786–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waheed, A.; Shammo, J.; Dingli, D. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Review of the patient experience and treatment landscape. Blood Rev. 2024, 64, 101158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulasekararaj, A.G.; Brodsky, R.A.; Nishimura, J.-I.; Patriquin, C.J.; Schrezenmeier, H. The importance of terminal complement inhibition in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2022, 13, 20406207221091046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodsky, R.A. How I treat paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2021, 137, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, R.A.; Young, N.S.; Antonioli, E.; Risitano, A.M.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Schubert, J.; Gaya, A.; Coyle, L.; de Castro, C.; Fu, C.L.; et al. Multicenter phase 3 study of the complement inhibitor eculizumab for the treatment of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2008, 111, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulasekararaj, A.G.; Hill, A.; Rottinghaus, S.T.; Langemeijer, S.; Wells, R.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, F.A.; Gaya, A.; Lee, J.W.; Gutierrez, E.O.; Piatek, C.I.; et al. Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) vs eculizumab in C5-inhibitor-experienced adult patients with PNH: The 302 study. Blood 2019, 133, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risitano, A.M.; Peffault de Latour, R. How we (’ll) treat paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria: Diving into the future. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 196, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notaro, R.; Luzzatto, L. Breakthrough hemolysis in PNH with proximal or terminal complement inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risitano, A.M.; Rotoli, B. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Pathophysiology, natural history and treatment options in the era of biological agents. Biologics 2008, 2, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellini, W.; Fattizzo, B. Clinical applications of hemolytic markers in the differential diagnosis and management of hemolytic anemia. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 635670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risitano, A.M.; Notaro, R.; Marando, L.; Serio, B.; Ranaldi, D.; Seneca, E.; Ricci, P.; Alfinito, F.; Camera, A.; Gianfaldoni, G.; et al. Complement fraction 3 binding on erythrocytes as additional mechanism of disease in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria patients treated by eculizumab. Blood 2009, 113, 4094–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmen, P.; Szer, J.; Weitz, I.; Röth, A.; Höchsmann, B.; Panse, J.; Usuki, K.; Griffin, M.; Kiladjian, J.J.; de Castro, C.; et al. Pegcetacoplan versus eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1028–1037, Erratum in N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Latour, R.P.; Szer, J.; Weitz, I.C.; Röth, A.; Höchsmann, B.; Panse, J.; Usuki, K.; Griffin, M.; Kiladjian, J.J.; de Castro, C.M.; et al. Pegcetacoplan versus eculizumab in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria (PEGASUS): 48-week follow-up of a randomised, open-label, phase 3, active-comparator, controlled trial. Lancet Haematol. 2022, 9, e648–e659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peffault de Latour, R.; Röth, A.; Kulasekararaj, A.G.; Han, B.; Scheinberg, P.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Ueda, Y.; de Castro, C.M.; Di Bona, E.; Fu, R.; et al. Oral iptacopan monotherapy in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 994–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Griffin, M.; Kim, J.S.; Lee Lee, L.W.; Piatek, C.; Nishimura, J.I.; Carrillo Infante, C.; Jain, D.; Liu, P.; Filippov, G.; et al. Addition of danicopan to ravulizumab or eculizumab in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria and clinically significant extravascular haemolysis (ALPHA): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2023, 10, e955–e965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, A.; Nai, A.; Silvestri, L.; Camaschella, C. Hepcidin and anemia: A tight relationship. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Kuter, D.J. Iron overload after complement inhibitor treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, E235–E237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaap, C.C.M.; Schols, S.E.M.; Preijers, F.W.M.B.; de Jonge, E.; Laarakkers, C.M.M.; Jansen, J.H.; Blijlevens, N.M.A.; Swinkels, D.W.; Langemeijer, S.M.C. Effect of eculizumab on iron metabolism in transfusion-independent patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.; Hillmen, P.; Richards, S.J.; Elebute, D.; Marsh, J.C.; Chan, J.; Mojcik, C.F.; Rother, R.P. Sustained response and long-term safety of eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2005, 106, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.; Rother, R.P.; Arnold, L.; Kelly, R.; Cullen, M.J.; Richards, S.J.; Hillmen, P. Eculizumab prevents intravascular hemolysis in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and unmasks low-level extravascular hemolysis occurring through C3 opsonization. Haematologica 2010, 95, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.A.; Noori, M.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Karamzad, N.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Abdollahi, M.; Collins, G.S.; Kaufman, J.S.; et al. Burden of anemia and its underlying causes in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease study 2019. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.C. Diagnosis and management of transfusion iron overload: The role of imaging. Am. J. Hematol. 2007, 82, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Zeng, T.; Guo, X.; Li, X. Ferritin’s role in infectious diseases: Exploring pathogenic mechanisms and clinical implications. New Microbes New Infect. 2025, 65, 101582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines on haemochromatosis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 479–502, Erratum in J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1341.
| Baseline Characteristics | Patients with Baseline Iron Overload (n = 27) | Patients Without Baseline Iron Overload (n = 53) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean, years | 55.4 | 53.4 | NS |
| Male, n (%) | 16 (59.3) | 14 (26.4) | 0.006 |
| Hemoglobin concentration at baseline, a mean, g/dL | 8.6 | 8.7 | NS |
| Transfusions, mean, n | |||
| Before baseline | (n = 24) 10.8 | (n = 33) 6.4 | 0.02 |
| During the trial | (n = 19) 5.8 | (n = 27) 3.3 | NS |
| Volume transfused, mean, U | |||
| Before baseline | (n = 24) 18.1 | (n = 33) 12.1 | NS |
| During the trial | (n = 19) 11.5 | (n = 27) 6.4 | NS |
| Red blood cell transfusions in the past year, mean, n | 9.7 | 6.1 | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shammo, J.; Hillmen, P.; Blandino, P.; Abilash, V.; Kuter, D.J. Improved Iron Overload with Pegcetacoplan in Eculizumab-Experienced Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010019
Shammo J, Hillmen P, Blandino P, Abilash V, Kuter DJ. Improved Iron Overload with Pegcetacoplan in Eculizumab-Experienced Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleShammo, Jamile, Peter Hillmen, Peter Blandino, Vijay Abilash, and David J. Kuter. 2025. "Improved Iron Overload with Pegcetacoplan in Eculizumab-Experienced Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010019
APA StyleShammo, J., Hillmen, P., Blandino, P., Abilash, V., & Kuter, D. J. (2025). Improved Iron Overload with Pegcetacoplan in Eculizumab-Experienced Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010019





