Challenges in Applying DNA-Binding Protein Predictors to Biological Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of DNA-Binding Prediction Tools
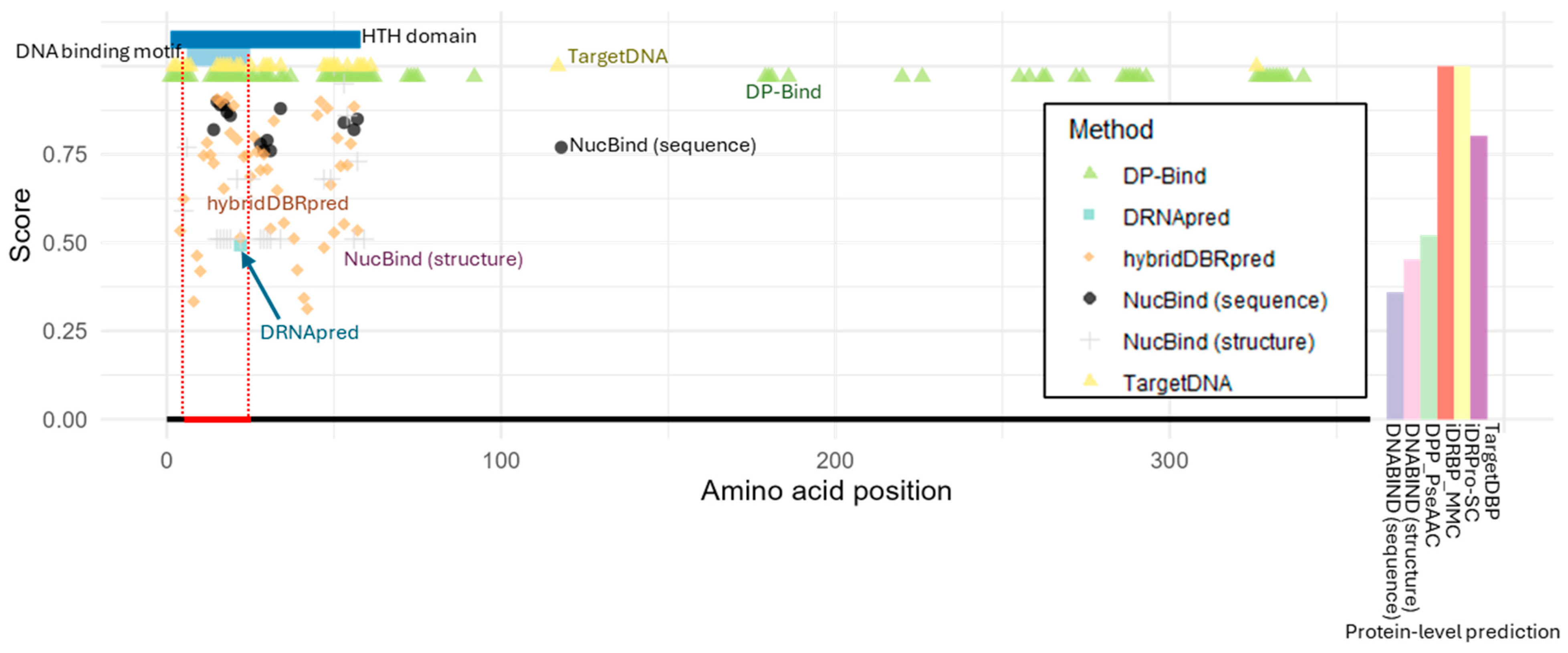
2.2. Case Study 1: Prediction of DNA-Binding in the Escherichia coli Lactose Operon Repressor
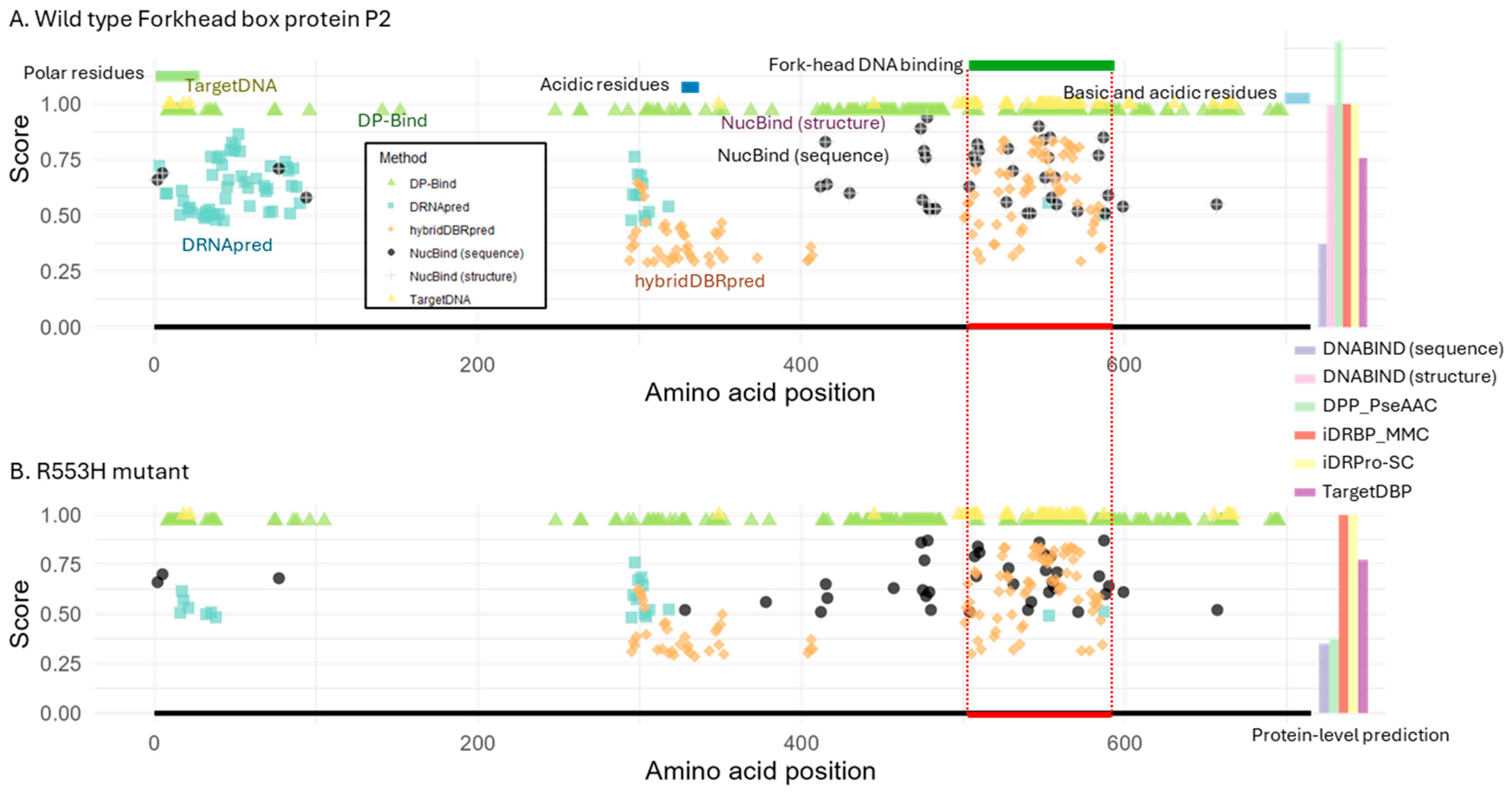
2.3. Case Study 2: Prediction of DNA-Binding Ability in Mutant Proteins
2.3.1. Forkhead Box P2 (FOXP2)
2.3.2. p53
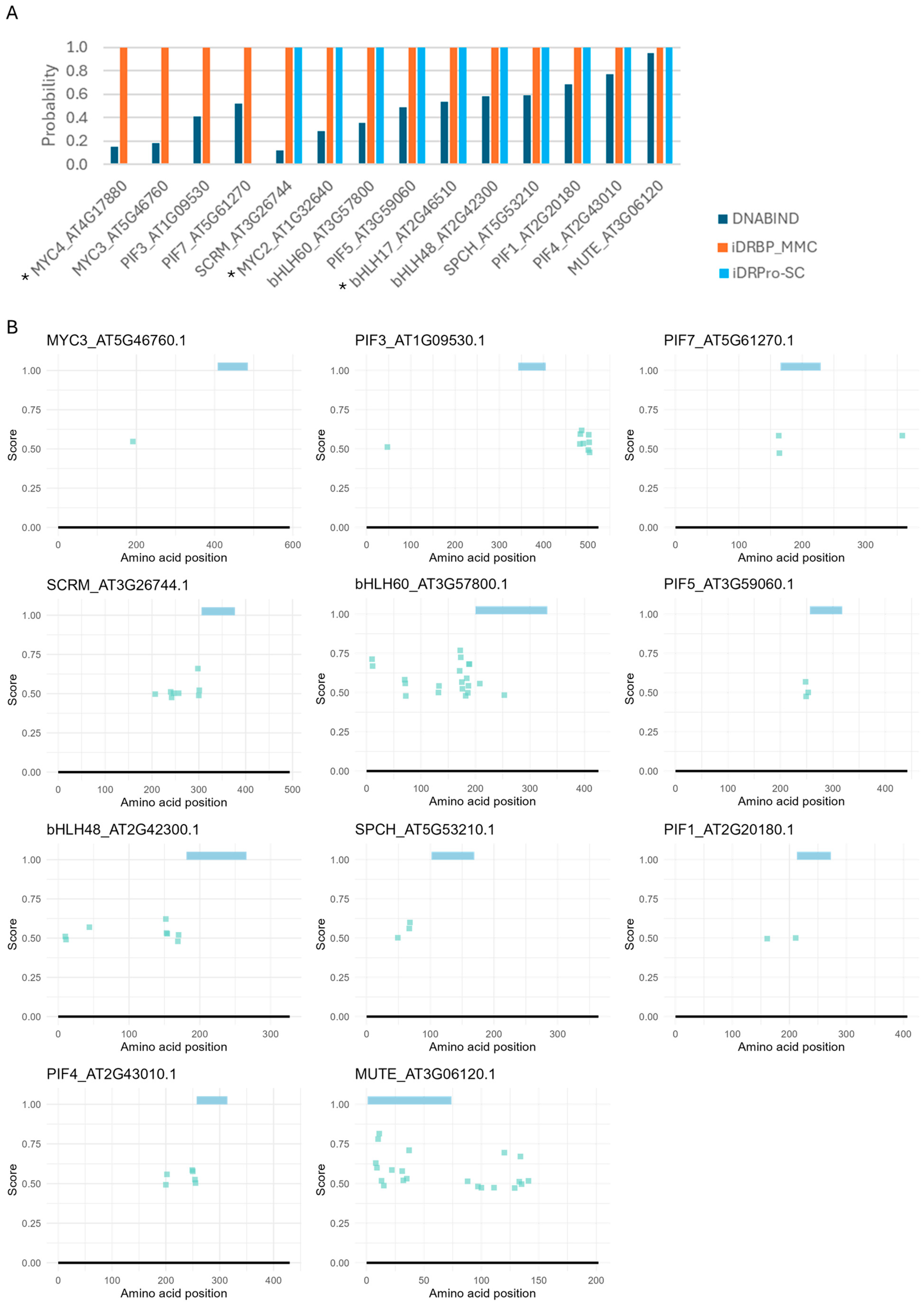
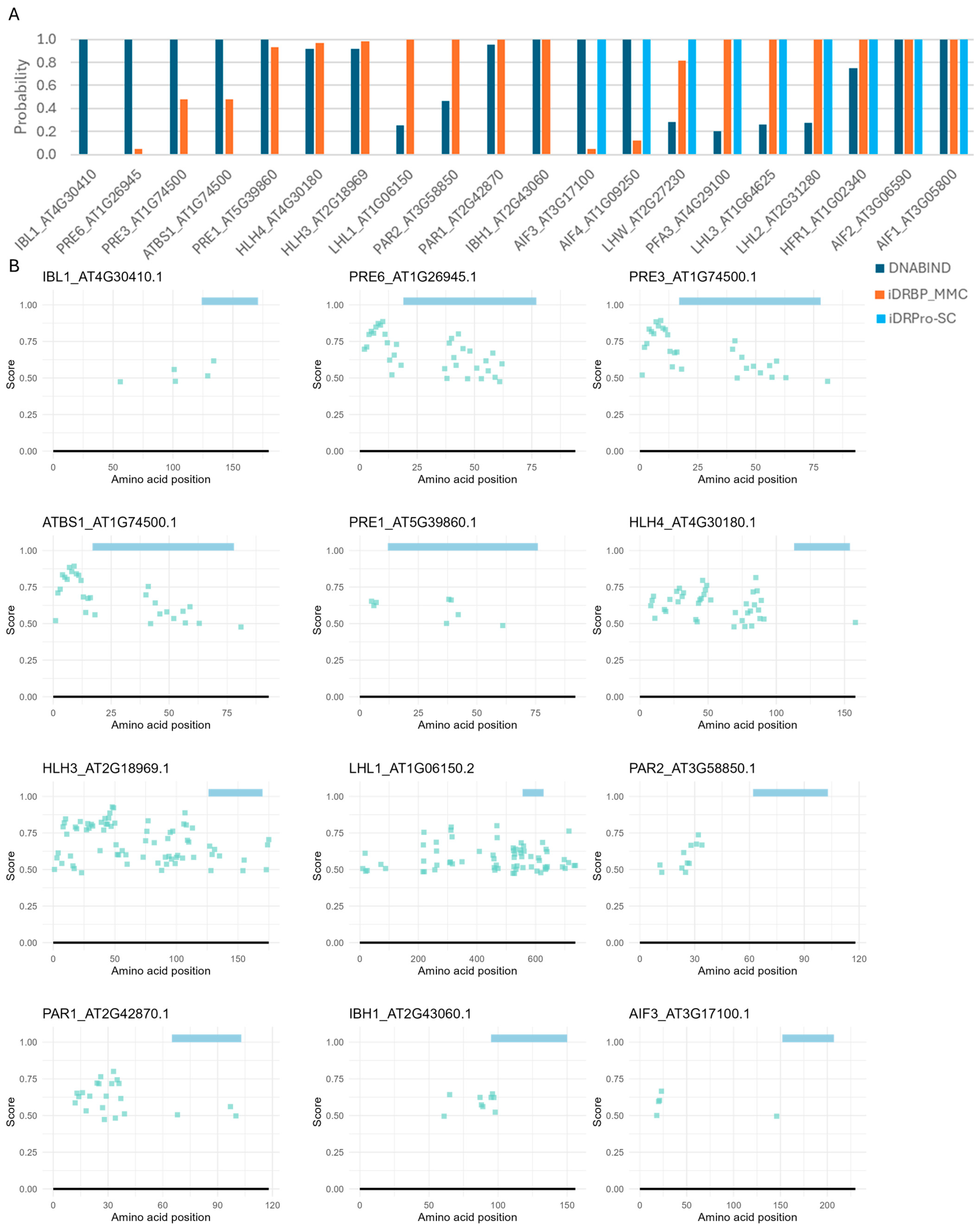
2.4. Case Study 3: Applicability to Evolutionary Genomics Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Assembly
4.2. Selection of Tools and Data Analysis
4.3. Assessments of Prediction Tools
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graur, D.; Li, W.-H. Fundamentals of Molecular Evolution; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D609–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, K.-Y.; Travers, A. DNA-Binding Proteins. In Brenner’s Encyclopedia of Genetics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 345–347. ISBN 9780080961569. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, M.K.; Rawls, A.; Wilson-Rawls, J.; Roalson, E.H. Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor Gene Family Phylogenetics and Nomenclature. Differentiation 2010, 80, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchley, W.R.; Fitch, W.M. A Natural Classification of the Basic Helix–Loop–Helix Class of Transcription Factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5172–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, M.A.; Jakoby, M.; Werber, M.; Martin, C.; Weisshaar, B.; Bailey, P.C. The Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor Family in Plants: A Genome-Wide Study of Protein Structure and Functional Diversity. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Dubos, C. The Arabidopsis BHLH Transcription Factor Family. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.; Dolan, L. Origin and Diversification of Basic-Helix-Loop-Helix Proteins in Plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.S.; Ramos, H.; Inga, A.; Sousa, E.; Saraiva, L. Structural and Drug Targeting Insights on Mutant P53. Cancers 2021, 13, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.; Fisher, S.E.; Scheffer, I.; Hildebrand, M. FOXP2-Related Speech and Language Disorder. In GeneReviews; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Szilágyi, A.; Skolnick, J. Efficient Prediction of Nucleic Acid Binding Function from Low-Resolution Protein Structures. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 358, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Kurgan, L. DRNApred, Fast Sequence-Based Method That Accurately Predicts and Discriminates DNA- and RNA-Binding Residues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Shatabda, S.; Saha, S.; Kaykobad, M.; Rahman, M.S. DPP-PseAAC: A DNA-Binding Protein Prediction Model Using Chou’s General PseAAC. J. Theor. Biol. 2018, 452, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Gou, Z.; Kuznetsov, I.B. DP-Bind: A Web Server for Sequence-Based Prediction of DNA-Binding Residues in DNA-Binding Proteins. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Basu, S.; Kurgan, L. HybridDBRpred: Improved Sequence-Based Prediction of DNA-Binding Amino Acids Using Annotations from Structured Complexes and Disordered Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, B. IDRBP_MMC: Identifying DNA-Binding Proteins and RNA-Binding Proteins Based on Multi-Label Learning Model and Motif-Based Convolutional Neural Network. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 5860–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Shen, H.-B.; Yu, D.-J. Predicting Protein-DNA Binding Residues by Weightedly Combining Sequence-Based Features and Boosting Multiple SVMs. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2017, 14, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Liu, M.; Sun, S.; Peng, Z.; Yang, J. Improving the Prediction of Protein-Nucleic Acids Binding Residues via Multiple Sequence Profiles and the Consensus of Complementary Methods. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhou, X.-G.; Zhu, Y.-H.; Yu, D.-J.; Zhang, G.-J. TargetDBP: Accurate DNA-Binding Protein Prediction via Sequence-Based Multi-View Feature Learning. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2020, 17, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Feng, J.; Huang, J.; Wu, H. IDRPro-SC: Identifying DNA-Binding Proteins and RNA-Binding Proteins Based on Subfunction Classifiers. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, K.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J. Sann: Solvent Accessibility Prediction of Proteins by Nearest Neighbor Method. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2012, 80, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.W.; Beck, J.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Chan, J.; Connor, R.; Feldgarden, M.; Fine, A.M.; Funk, K.; Hoffman, J.; et al. Database Resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D20–D29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; O’Neill, K.R.; Haft, D.H.; DiCuccio, M.; Chetvernin, V.; Badretdin, A.; Coulouris, G.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Durkin, A.S.; et al. RefSeq: Expanding the Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline Reach with Protein Family Model Curation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1020–D1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.S.; Hewitt, M.N.; Gulati, J.S.; Cruz, M.A.; Zhan, H.; Liu, S.; Matthews, K.S. Lactose Repressor Hinge Domain Independently Binds DNA. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernes, S.C.; Nicod, J.; Elahi, F.M.; Coventry, J.A.; Kenny, N.; Coupe, A.-M.; Bird, L.E.; Davies, K.E.; Fisher, S.E. Functional Genetic Analysis of Mutations Implicated in a Human Speech and Language Disorder. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 3154–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, A.; Matsuzaki, A.; Momoi, M.Y.; Fujita, E.; Tanabe, Y.; Momoi, T. Intracellular Distribution of a Speech/Language Disorder Associated FOXP2 Mutant. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 353, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joerger, A.C.; Fersht, A.R. Structure–Function–Rescue: The Diverse Nature of Common P53 Cancer Mutants. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2226–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, A.; Shi, H.; Tepperman, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Quail, P.H. Combinatorial Complexity in a Transcriptionally Centered Signaling Hub in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1598–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mayba, O.; Pfeiffer, A.; Shi, H.; Tepperman, J.M.; Speed, T.P.; Quail, P.H. A Quartet of PIF BHLH Factors Provides a Transcriptionally Centered Signaling Hub That Regulates Seedling Morphogenesis through Differential Expression-Patterning of Shared Target Genes in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornitschek, P.; Kohnen, M.V.; Lorrain, S.; Rougemont, J.; Ljung, K.; López-Vidriero, I.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Solano, R.; Trevisan, M.; Pradervand, S.; et al. Phytochrome Interacting Factors 4 and 5 Control Seedling Growth in Changing Light Conditions by Directly Controlling Auxin Signaling. Plant J. 2012, 71, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.Y.W.; Balcerowicz, M.; Di Antonio, M.; Jaeger, K.E.; Geng, F.; Franaszek, K.; Marriott, P.; Brierley, I.; Firth, A.E.; Wigge, P.A. An RNA Thermoswitch Regulates Daytime Growth in Arabidopsis. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, O.S.; Davies, K.A.; Chang, J.; Adrian, J.; Rowe, M.H.; Ballenger, C.E.; Bergmann, D.C. Direct Roles of SPEECHLESS in the Specification of Stomatal Self-Renewing Cells. Science 2014, 345, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-K.; Qi, X.; Sugihara, K.; Dang, J.H.; Endo, T.A.; Miller, K.L.; Kim, E.-D.; Miura, T.; Torii, K.U. MUTE Directly Orchestrates Cell-State Switch and the Single Symmetric Division to Create Stomata. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 303–315.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Zhao, L.; Ren, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhu, J.-K.; Zhao, C. The Transcription Factor ICE1 Functions in Cold Stress Response by Binding to the Promoters of CBF and COR Genes. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Huang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, C.; Ma, Q.; Pruneda-Paz, J.; Kay, S.A.; Li, L. Two BHLH Transcription Factors, BHLH48 and BHLH60, Associate with Phytochrome Interacting Factor 7 to Regulate Hypocotyl Elongation in Arabidopsis. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vidriero, I.; Godoy, M.; Grau, J.; Peñuelas, M.; Solano, R.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M. DNA Features beyond the Transcription Factor Binding Site Specify Target Recognition by Plant MYC2-Related BHLH Proteins. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, C.D.; Schumaker, M.A.; Quail, P.H. HFR1 Encodes an Atypical BHLH Protein That Acts in Phytochrome A Signal Transduction. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2377–2391. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.-Y.; Bai, M.-Y.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X.; et al. Antagonistic HLH/BHLH Transcription Factors Mediate Brassinosteroid Regulation of Cell Elongation and Plant Development in Rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3767–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelain, M.; Le Hir, R.; Bellini, C. The Non-DNA-Binding BHLH Transcription Factor PRE3/BHLH135/ATBS1/TMO7 Is Involved in the Regulation of Light Signaling Pathway in Arabidopsis. Physiol. Plant. 2012, 145, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Jia, Q.; Wang, X.; Hou, C.; Chen, J.-G.; Wang, S. Involvement of PACLOBUTRAZOL RESISTANCE6/KIDARI, an Atypical BHLH Transcription Factor, in Auxin Responses in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roig-Villanova, I.; Bou-Torrent, J.; Galstyan, A.; Carretero-Paulet, L.; Portolés, S.; Rodríguez-Concepción, M.; Martínez-García, J.F. Interaction of Shade Avoidance and Auxin Responses: A Role for Two Novel Atypical BHLH Proteins. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 4756–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galstyan, A.; Cifuentes-Esquivel, N.; Bou-Torrent, J.; Martinez-Garcia, J.F. The Shade Avoidance Syndrome in Arabidopsis: A Fundamental Role for Atypical Basic Helix–Loop–Helix Proteins as Transcriptional Cofactors. Plant J. 2011, 66, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhao, W.; Lu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Hu, B.; Yan, T.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chao, N.; et al. Overexpression of HLH4 Inhibits Cell Elongation and Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Cells 2022, 11, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Fujioka, S.; Asami, T.; Li, J.; Li, J. Regulation of Arabidopsis Brassinosteroid Signaling by Atypical Basic Helix–Loop–Helix Proteins. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3781–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Fujiwara, S.; Mitsuda, N.; Ohme-Takagi, M. A Triantagonistic Basic Helix-Loop-Helix System Regulates Cell Elongation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4483–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiponova, M.K.; Morohashi, K.; Vanhoutte, I.; Machemer-Noonan, K.; Revalska, M.; Van Montagu, M.; Grotewold, E.; Russinova, E. Helix–Loop–Helix/Basic Helix–Loop–Helix Transcription Factor Network Represses Cell Elongation in Arabidopsis through an Apparent Incoherent Feed-Forward Loop. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2824–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi-Ito, K.; Matsukawa, M.; Fukuda, H. An Atypical BHLH Transcription Factor Regulates Early Xylem Development Downstream of Auxin. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodsky, S.; Jana, T.; Barkai, N. Order through Disorder: The Role of Intrinsically Disordered Regions in Transcription Factor Binding Specificity. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2021, 71, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodsky, S.; Jana, T.; Mittelman, K.; Chapal, M.; Kumar, D.K.; Carmi, M.; Barkai, N. Intrinsically Disordered Regions Direct Transcription Factor in Vivo Binding Specificity. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 459–471.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bigman, L.S.; Greenblatt, H.M.; Yu, B.; Levy, Y.; Iwahara, J. Negatively Charged, Intrinsically Disordered Regions Can Accelerate Target Search by DNA-Binding Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 4701–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François-Moutal, L.; Perez-Miller, S.; Scott, D.D.; Miranda, V.G.; Mollasalehi, N.; Khanna, M. Structural Insights Into TDP-43 and Effects of Post-translational Modifications. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, E.; Baralle, F.E. TDP-43: Gumming up neurons through protein–protein and protein–RNA interactions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.H.; Wu, F.; Harrich, D.; García-Martínez, L.F.; Gaynor, R.B. Cloning and characterization of a novel cellular protein, TDP-43, that binds to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TAR DNA sequence motifs. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3584–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, C.C.; Klausner, R.D.; A Rouault, T. The bifunctional iron-responsive element binding protein/cytosolic aconitase: The role of active-site residues in ligand binding and regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 7321–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siggers, T.; Gordân, R. Protein-DNA Binding: Complexities and Multi-Protein Codes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 2099–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohs, R.; Jin, X.; West, S.M.; Joshi, R.; Honig, B.; Mann, R.S. Origins of Specificity in Protein-DNA Recognition. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 233–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoutzias, G.D.; Robertson, D.L.; Van de Peer, Y.; Oliver, S.G. Choose Your Partners: Dimerization in Eukaryotic Transcription Factors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, B.; Liu, S.; Song, W.; Qiao, J.; Ruan, H. Types of Nuclear Localization Signals and Mechanisms of Protein Import into the Nucleus. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Qu, L.; Li, J.; Chen, Y. Toward a Mechanistic Understanding of DNA Binding by Forkhead Transcription Factors and Its Perturbation by Pathogenic Mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 10235–10249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M.; Chang, H.-Y.; Chuguransky, S.; Grego, T.; Kandasaamy, S.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Qureshi, M.; Raj, S.; et al. The InterPro Protein Families and Domains Database: 20 Years On. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D344–D354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Lu, S.; Anderson, J.B.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; DeWeese-Scott, C.; Fong, J.H.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; et al. CDD: A Conserved Domain Database for the Functional Annotation of Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D225–D229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henikoff, S.; Henikoff, J.G. Amino Acid Substitution Matrices from Protein Blocks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 10915–10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ghadermarzi, S.; Katuwawala, A.; Kurgan, L. DNAgenie: Accurate Prediction of DNA-Type-Specific Binding Residues in Protein Sequences. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-H.; Hu, J.; Song, X.-N.; Yu, D.-J. DNAPred: Accurate Identification of DNA-Binding Sites from Protein Sequence by Ensembled Hyperplane-Distance-Based Support Vector Machines. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 3057–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Kurgan, L. High-Throughput Prediction of RNA, DNA and Protein Binding Regions Mediated by Intrinsic Disorder. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.-C. Some Remarks on Protein Attribute Prediction and Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 273, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Residue | Protein | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | DP-Bind | TargetDNA | HybridDBRpred | DRNApred + | NucBind *+ | DNABIND * | DPP-PseAAC | TargetDBP | iDRBP-MMC + | iDRPro-SC + |
| Link | https://lcg.rit.albany.edu/dp-bind/ (accessed on 8 September 2025) | https://csbioinformatics.njust.edu.cn/TargetDNA/ (accessed on 8 September 2025) | https://biomine.cs.vcu.edu/servers/hybridDBRpred/ (accessed on 8 September 2025) | https://biomine.cs.vcu.edu/servers/DRNApred/ (accessed on 8 September 2025) | https://yanglab.qd.sdu.edu.cn/NucBind/ (accessed on 8 September 2025) | https://dnabind.szialab.org/ (accessed on 8 September 2025) | http://77.68.43.135:8080/DPP-PseAAC/ (accessed on 8 September 2025) | https://csbioinformatics.njust.edu.cn/targetdbp/ (accessed on 8 September 2025) | http://bliulab.net/iDRBP_MMC/server (accessed on 8 September 2025) | http://bliulab.net/iDRPro-SC/server (accessed on 8 September 2025) |
| Publication year | 2007 | 2017 | 2024 | 2017 | 2019 | 2006 | 2018 | 2020 | 2020 | 2023 |
| Physicochemical property | NA | SA (SANN) | AA (polarizability, charge, hydrophilicity, propensity for intrinsic disorder), SA (ASAquick) | SA (PROFphd, NETASA, and RVP-net) | NA | Proportion of Arg, Lys, Asp, Ala, and Gly | AA (frequency) | AA (frequency), pseSA (SANN) | Protein motif | Protein subfunction (bi-LSTM) |
| Protein structure | NA | NA | Disorder (IUPred3) | SS (PSIPRED), Disorder (IUPred and Espritz) | SS (PSIPRED), SM (HHblits) | Spatial asymmetry of Arg, Gly, Asn, and Ser; Dipole moment | NA | NA | Protein structual motif | NA |
| Evolutionary information | PSSM (PSI-BLAST) | PSSM (PSI-BLAST) | NA | EP (HHblits) | PSSM (PSI-BLAST) | NA | NA | psePSSM (PSI-BLAST) | PSSM (PSI-BLAST) | PSSM (PSI-BLAST) |
| DBR prediction of other methods | NA | NA | DNAPred, DNAgenie, and DisoRDPbind | NA | SVMnuc and COACH-D | NA | NA | TargetDNA | NA | NA |
| Maximum number of proteins per run | 1 | 1 | 1 | >=37 | 1 | >=37 | 1 | 5 | >=37 | >=37 |
| Protein | UniProID | PDB ID |
|---|---|---|
| DNA-binding protein | ||
| Lactose operon repressor (LacI) | P03023 | LACI_AF-P03023-F1-model_v4 |
| Forkhead box protein P2 (FOXP2) | O15409 | 2A07_AF-O15409-F1-model_v4 |
| p53 | P04637 | P53_AF-P04637-F1-model_v4 |
| TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) | Q13148 | 7Q3U_AF-Q13148-F1-model_v4 |
| Non-DNA-binding protein | ||
| Cytoplasmic aconitate hydratase (Aconitase) | P21399 | 2B3X_AF-P21399-F1-model_v4 |
| Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) | Q15910 | 4MI5_AF-Q15910-F1-model_v4 |
| Myoglobin | P02185 | 1MBN_AF-P02185-F1-model_v4 |
| Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | Q9C0B1 | 7CKK_AF-Q9C0B1-F1-model_v4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cowgill, G.; Strazza, S.A.; Wilson, S.; Odari, R.; Bristy, S.A.; Qiu, Y.; Miura, S. Challenges in Applying DNA-Binding Protein Predictors to Biological Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199785
Cowgill G, Strazza SA, Wilson S, Odari R, Bristy SA, Qiu Y, Miura S. Challenges in Applying DNA-Binding Protein Predictors to Biological Research. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199785
Chicago/Turabian StyleCowgill, Graydon, Steven Anthony Strazza, Savannah Wilson, Ranjeeta Odari, Sadia Afrin Bristy, Yongjian Qiu, and Sayaka Miura. 2025. "Challenges in Applying DNA-Binding Protein Predictors to Biological Research" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199785
APA StyleCowgill, G., Strazza, S. A., Wilson, S., Odari, R., Bristy, S. A., Qiu, Y., & Miura, S. (2025). Challenges in Applying DNA-Binding Protein Predictors to Biological Research. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199785







