Evaluation and Modulation of Gut Microbiome Dysfunction in Chronically Critically Ill Patients: A Prospective Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
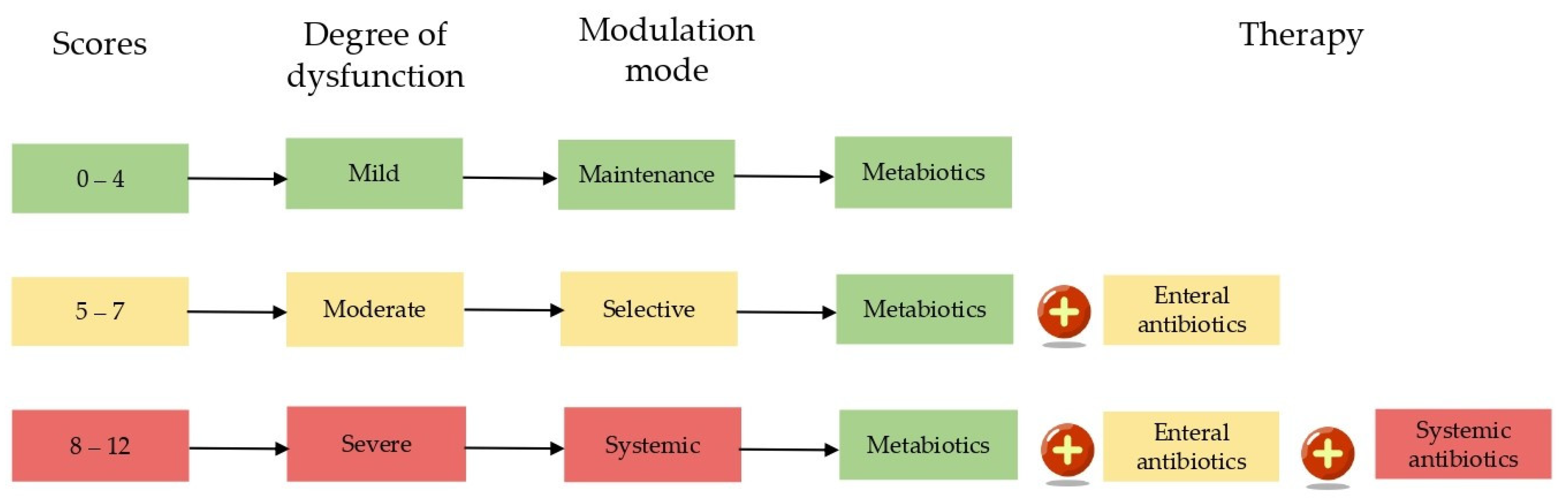
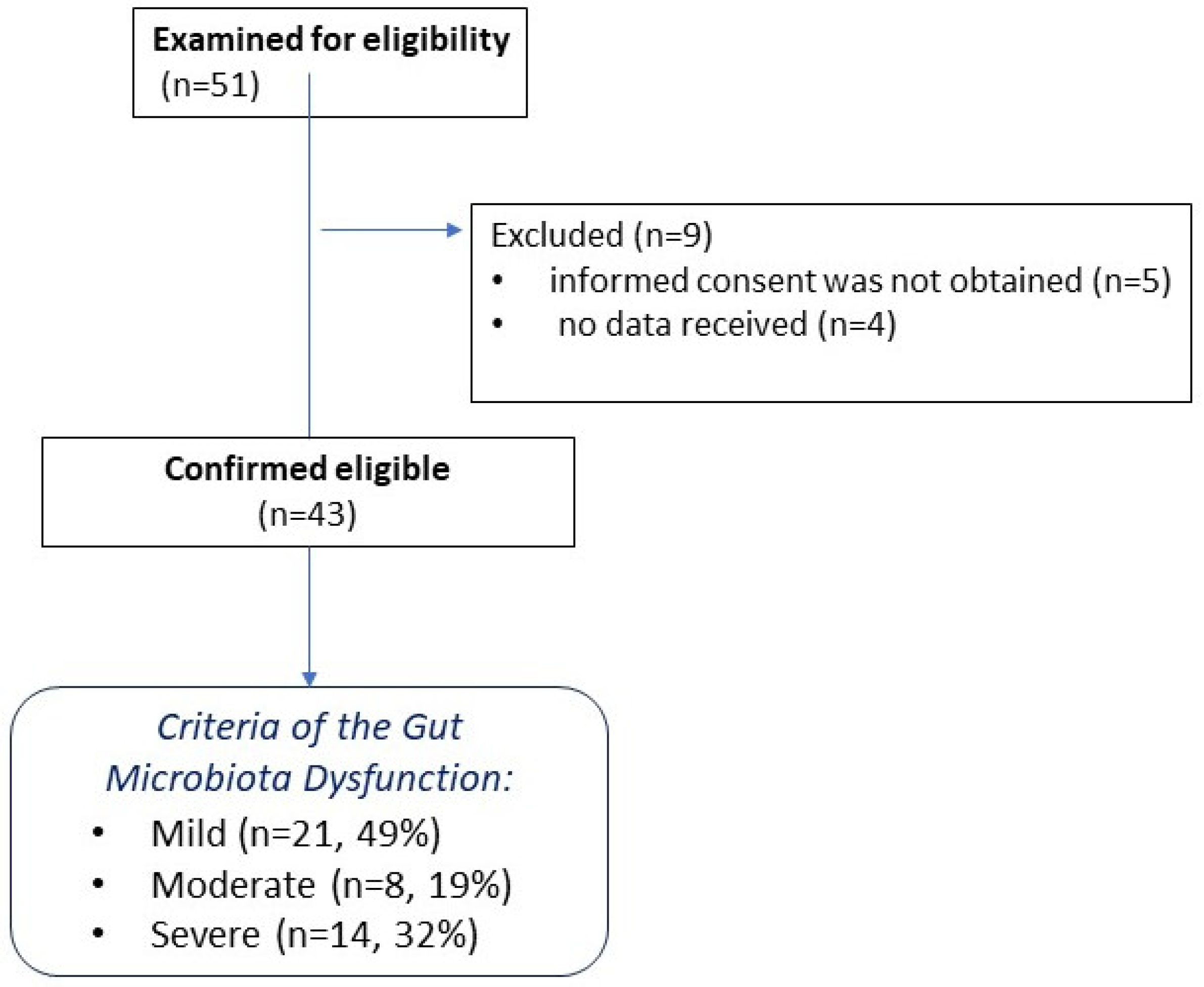
2.1. Classification of Microbiota Dysfunctions
2.2. Patient Characteristics
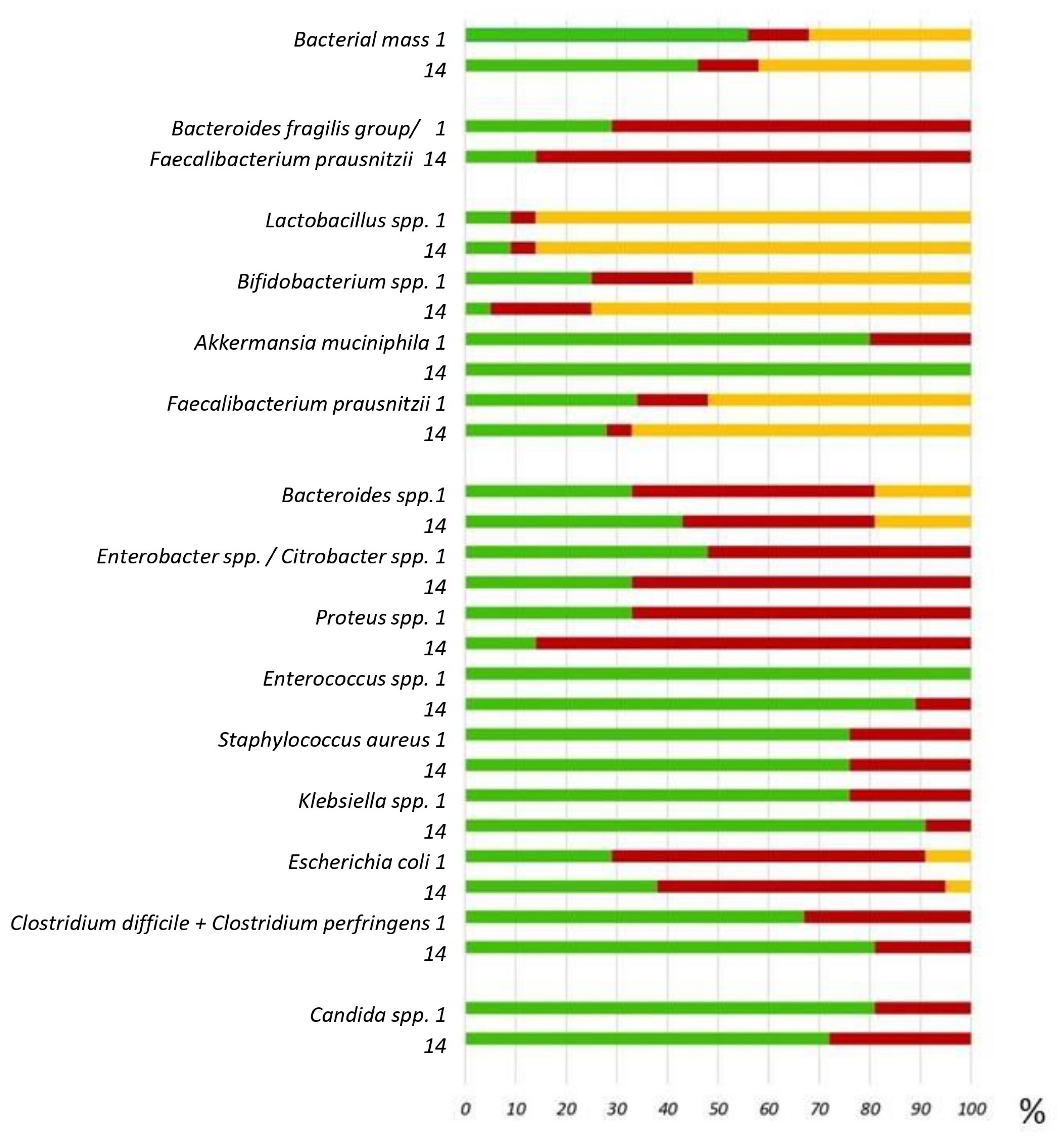
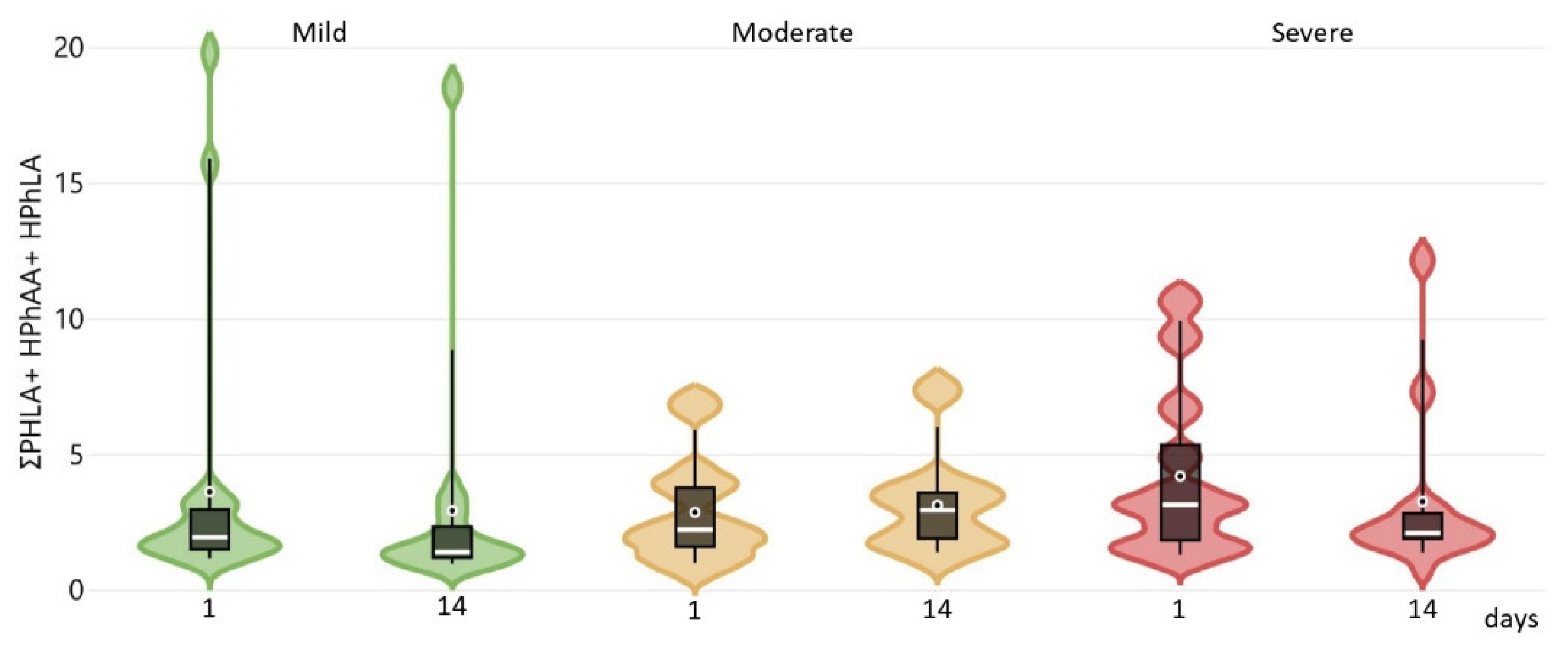
2.3. Changes in Parameters Compared to Baseline
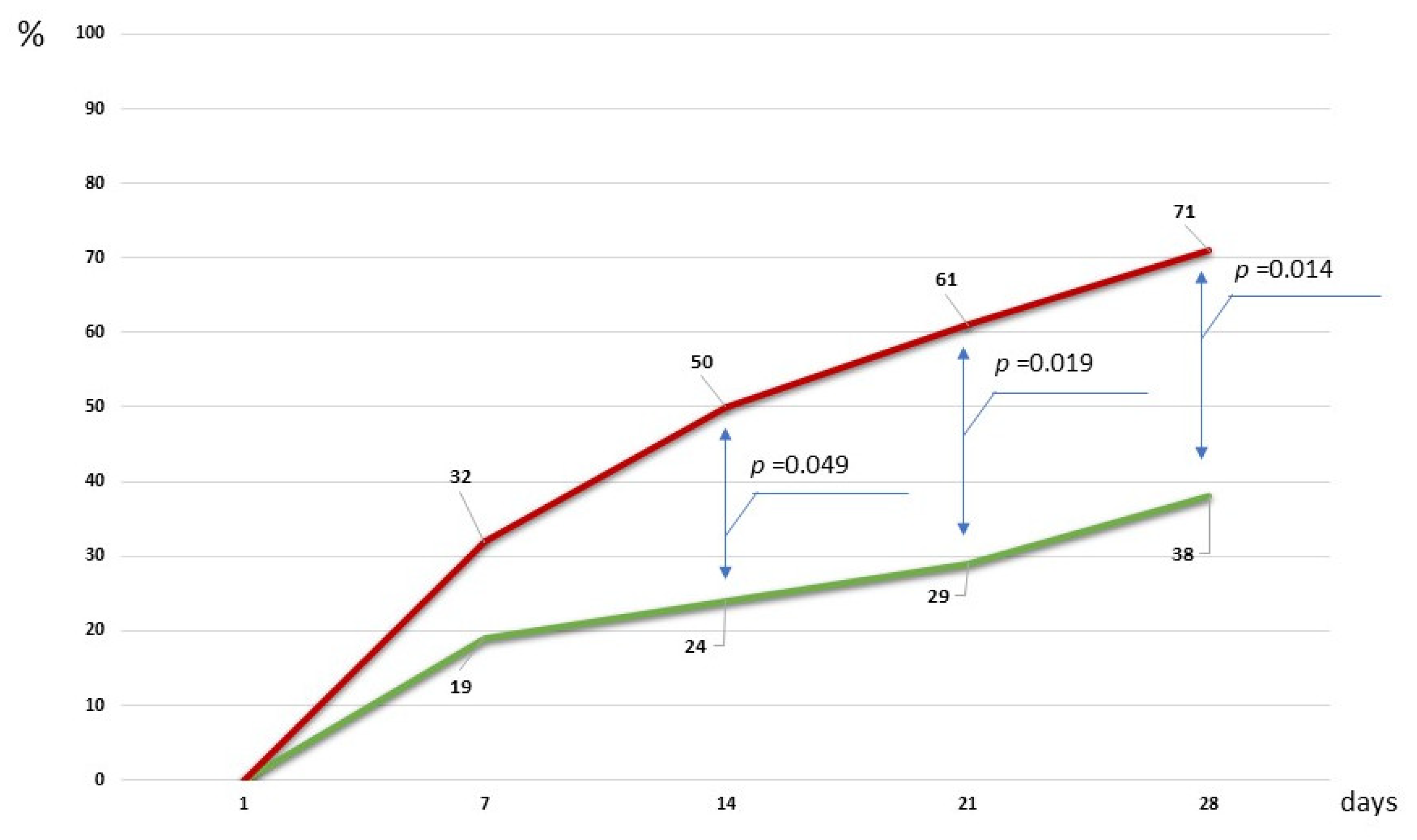
2.4. Clinical Efficacy of a Microbiota-Oriented Strategy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Sample Collection
4.3. Sample Analysis
4.3.1. GC–MS Analysis
4.3.2. Biomarker Analysis
4.3.3. Assessment of Disturbances of Intestinal Microbiota
4.3.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wozniak, H.; Beckmann, T.S.; Fröhlich, L.; Soccorsi, T.; Le Terrier, C.; de Watteville, A.; Schrenzel, J.; Heidegger, C.-P. The Central and Biodynamic Role of Gut Microbiota in Critically Ill Patients. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglini, D.; Torres, A. Gut Microbiota and Its Impact on Critical Illness. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2025, 31, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Ackermann, G.; Khailova, L.; Baird, C.; Heyland, D.; Kozar, R.; Lemieux, M.; Derenski, K.; King, J.; Vis-Kampen, C.; et al. Extreme Dysbiosis of the Microbiome in Critical Illness. mSphere 2016, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.A.; Strayer, K.; Dobson, B.; McDonald, B. Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Opportunities of Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis in Critical Illness. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2351478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Chen, X.; Hu, L.; He, Z.; Ouyang, X.; Liang, S.; Dai, S.; Sha, W.; Chen, C. Dysbiosis of Intestinal Microbiota in Critically Ill Patients and Risk of in-Hospital Mortality. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 1548. [Google Scholar]
- Ojima, M.; Shimizu, K.; Motooka, D.; Ishihara, T.; Nakamura, S.; Shintani, A.; Ogura, H.; Iida, T.; Yoshiya, K.; Shimazu, T. Gut Dysbiosis Associated with Antibiotics and Disease Severity and Its Relation to Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 67, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwannimit, B. A Comparison of Three Organ Dysfunction Scores: MODS, SOFA and LOD for Predicting ICU Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2007, 90, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Cheng, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Fan, H.; Hu, Q.; Han, M.; Su, L.; He, H.; Tong, Y.; et al. Classification of the Gut Microbiota of Patients in Intensive Care Units During Development of Sepsis and Septic Shock. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2020, 18, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernevskaya, E.; Klimenko, N.; Pautova, A.; Buyakova, I.; Tyakht, A.; Beloborodova, N. Host-Microbiome Interactions Mediated by Phenolic Metabolites in Chronically Critically Ill Patients. Metabolites 2021, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.E.; Cox, C.E.; Hope, A.A.; Carson, S.S. Chronic Critical Illness. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, A.K.; Ghita, G.L.; Wang, Z.; Ozrazgat-Baslanti, T.; Raymond, S.L.; Mankowski, R.T.; Brumback, B.A.; Efron, P.A.; Bihorac, A.; Moore, F.A.; et al. The Development of Chronic Critical Illness Determines Physical Function, Quality of Life, and Long-Term Survival Among Early Survivors of Sepsis in Surgical ICUs. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.M.; Le, T.; Angus, D.C.; Cox, C.E.; Hough, C.L.; White, D.B.; Yende, S.; Carson, S.S.; ProVent Study Group Investigators. The Epidemiology of Chronic Critical Illness in the United States*. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoller, J.K.; Xu, M.; Mascha, E.; Rice, R. Long-Term Outcomes for Patients Discharged from a Long-Term Hospital-Based Weaning Unit. Chest 2003, 124, 1892–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Xiao, K.; Yan, P.; Duan, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhao, N.; Cao, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Correlation Analysis of the Microbiome and Immune Function in the Lung-Gut Axis of Critically Ill Patients in the ICU. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 808302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zou, Z.; Wu, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Tu, X.; Huang, W.; Chen, C.; Zhu, S.; Weng, Q.; et al. The Gut-Lung Axis in Critical Illness: Microbiome Composition as a Predictor of Mortality at Day 28 in Mechanically Ventilated Patients. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kritikos, A.; Bernasconi, E.; Choi, Y.; Scherz, V.; Pagani, J.-L.; Greub, G.; Bertelli, C.; Guery, B. Lung and Gut Microbiota Profiling in Intensive Care Unit Patients: A Prospective Pilot Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Gu, S.; Gong, Y.; Li, B.; Lu, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, R.; Gao, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; et al. Clinical Significance of the Correlation between Changes in the Major Intestinal Bacteria Species and COVID-19 Severity. Engineering 2020, 6, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín Giménez, V.M.; Modrego, J.; Gómez-Garre, D.; Manucha, W.; de Las Heras, N. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in COVID-19: Modulation and Approaches for Prevention and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Castrellón, P.; Gandara-Martí, T.; Abreu Y Abreu, A.T.; Nieto-Rufino, C.D.; López-Orduña, E.; Jiménez-Escobar, I.; Jiménez-Gutiérrez, C.; López-Velazquez, G.; Espadaler-Mazo, J. Probiotic Improves Symptomatic and Viral Clearance in COVID19 Outpatients: A Randomized, Quadruple-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2018899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuijt, T.J.; Lankelma, J.M.; Scicluna, B.P.; de Sousa e Melo, F.; Roelofs, J.J.T.H.; de Boer, J.D.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; de Beer, R.; de Vos, A.; Belzer, C.; et al. The Gut Microbiota Plays a Protective Role in the Host Defence against Pneumococcal Pneumonia. Gut 2016, 65, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, S.; Bai, L.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X. Efficacy of Preventive Interventions against Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses. J. Hosp. Infect. 2024, 145, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, N.E.; Myburgh, J.; Seppelt, I.; Garside, T.; Vlok, R.; Mahendran, S.; Adigbli, D.; Finfer, S.; Gao, Y.; Goodman, F.; et al. Association Between Selective Decontamination of the Digestive Tract and In-Hospital Mortality in Intensive Care Unit Patients Receiving Mechanical Ventilation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2022, 328, 1922–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpov, O.E.; Gusarov, V.G.; Kamyshova, D.A.; Orlova, O.A.; Petrova, L.V.; Khakulova, A.E.; Pivkina, A.I.; Zamyatin, M.N. Evaluation of the effectiveness of antimicrobial stewardship program: Results from a ten-year study in a multidisciplinary hospital. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 25, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullberg, R.F.J.; Haak, B.W.; Chanderraj, R.; Prescott, H.C.; Dickson, R.P.; Wiersinga, W.J. Empirical Antibiotic Therapy for Sepsis: Save the Anaerobic Microbiota. Lancet Respir. Med. 2025, 13, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanderraj, R.; Baker, J.M.; Kay, S.G.; Brown, C.A.; Hinkle, K.J.; Fergle, D.J.; McDonald, R.A.; Falkowski, N.R.; Metcalf, J.D.; Kaye, K.S.; et al. In Critically Ill Patients, Anti-Anaerobic Antibiotics Increase Risk of Adverse Clinical Outcomes. Eur Respir J 2023, 61, 2200910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, E.; Doan, N.; Evans, T.; Litton, E. Lower Gastrointestinal Tract Dysbiosis in Persistent Critical Illness: A Systematic Review. J. Med. Microbiol. 2024, 73, 001888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborin, A.; Smith, D.; Garfield, K.; Quensen, J.; Shakhsheer, B.; Kade, M.; Tirrell, M.; Tiedje, J.; Gilbert, J.A.; Zaborina, O.; et al. Membership and Behavior of Ultra-Low-Diversity Pathogen Communities Present in the Gut of Humans during Prolonged Critical Illness. mBio 2014, 5, e01361-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szychowiak, P.; Villageois-Tran, K.; Patrier, J.; Timsit, J.-F.; Ruppé, É. The Role of the Microbiota in the Management of Intensive Care Patients. Ann. Intensive Care 2022, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chen, M.; Chen, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Highly Diverse Sputum Microbiota Correlates with the Disease Severity in Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, T.J.; Roth, K.; Schultz, L.; Ma, Z.; Bonavia, A.S.; Broach, J.R.; Hu, B.; Howrylak, J.A. Gut Microbiome Dynamics and Associations with Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. Gut Pathog. 2023, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurabov, F.M.; Chernevskaya, E.A.; Beloborodova, N.V.; Zurabov, A.Y.; Petrova, M.V.; Yadgarov, M.Y.; Popova, V.M.; Fatuev, O.E.; Zakharchenko, V.E.; Gurkova, M.M.; et al. Bacteriophage Cocktails in the Post-COVID Rehabilitation. Viruses 2022, 14, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyatchenkov, M.O.; Sherbakov, E.V.; Trandina, A.E.; Glushakov, R.I.; Leonov, K.A.; Kazey, V.I. Changes in the Composition of the Gut Microbiota and Content of Microbial-Derived Uremic Toxins in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. Bull. Russ. Mil. Med. Acad. 2024, 26, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodpoor, A.; Hamishehkar, H.; Asghari, R.; Abri, R.; Shadvar, K.; Sanaie, S. Effect of a Probiotic Preparation on Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit: A Prospective Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, S.; Li, N.; Yu, C. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis via Modulating Bile Acid Metabolism and Regulating FXR Signaling. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihurov, M.; Păcularu-Burada, B.; Cotârleţ, M.; Vasile, M.A.; Bahrim, G.E. Novel Insights for Metabiotics Production by Using Artisanal Probiotic Cultures. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleskin, A.V.; Shenderov, B.A. Probiotics and Psychobiotics: The Role of Microbial Neurochemicals. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderov, B.A. Metabiotics: Novel Idea or Natural Development of Probiotic Conception. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2013, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Lee, N.-K.; Paik, H.-D. A Narrative Review on the Advance of Probiotics to Metabiotics. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, I.; Das Mohapatra, P.K. Recent Advancement in Metabiotics: A Consortium with Bioactive Molecules after Fermentation by Probiotic Bacteria with Multidisciplinary Application Potential and Future Solution in Health Sector. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 23, 101583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasyan, R.; Jafari, P.; Farjanikish, G.; Noorbazargan, H. Metabiotic Extracted from Modulates Antioxidant Capacity and Inflammatory Responses during Peptic Ulcer Healing in Male Wistar Rats: A Preliminary Study. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2023, 15, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toropov, V.A.; Shalaeva, O.N.; Roshchina, E.K.; Vakhitov, T.Y.; Sitkin, S.I. Identification of Bacteriocin Genes in Probiotic Strains of Lactic Acid Bacteria Lactobacllus acidophilus D-75 and Lactobacillus acidophilus D-76. Eksp. Klin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 10, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- El Far, M.S.; Zakaria, A.S.; Kassem, M.A.; Edward, E.A. Characterization of Probiotics Isolated from Dietary Supplements and Evaluation of Metabiotic-Antibiotic Combinations as Promising Therapeutic Options against Antibiotic-Resistant Pathogens Using Time-Kill Assay. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Rajendraprasad, S.; Ozkan, M.; Ramachandran, D.; Ahmad, S.; Bakken, J.S.; Laudanski, K.; Gajic, O.; Bauer, B.; Zec, S.; et al. Safety, Feasibility, and Impact on the Gut Microbiome of Kefir Administration in Critically Ill Adults. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grechko, A.V.; Gurkova, M.M.; Zhdanova, M.A.; Zurabov, A.Y.; Zurabov, F.M.; Kuzovlev, A.N.; Petrova, M.V.; Polyakov, P.A.; Cheboksarov, D.V.; Chernevskaya, E.A.; et al. Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia Recurrence Using a Bacteriophage Cocktail in Intensive Care Unit. Anesteziol. Reanimatol. 2024, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloborodova, N.V.; Grechko, A.V.; Gurkova, M.M.; Zurabov, A.Y.; Zurabov, F.M.; Kuzovlev, A.N.; Megley, A.Y.; Petrova, M.V.; Popova, V.M.; Redkin, I.V.; et al. Adaptive Phage Therapy in the Treatment of Patients with Recurrent Pneumonia (pilot Study). Gen. Reanimatol. 2021, 17, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokina, E.; Pautova, A.; Fatuev, O.; Zakharchenko, V.; Onufrievich, A.; Grechko, A.; Beloborodova, N.; Chernevskaya, E. Promising Markers of Inflammatory and Gut Dysbiosis in Patients with Post-COVID-19 Syndrome. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautova, A.K.; Burnakova, N.A.; Beloborodova, N.B.; Revelsky, A.I. Simultaneous determination of aromatic, short-chain fatty and dicarboxylic acids in blood serum and cerebrospinal fluid by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 79, 1942–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Points | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Previous antibiotic therapy | NO | YES | Received upon admission to the ICU |
| PCT, ng/mL | <0.25 | 0.25–0.5 | >0.5 |
| Presence of a confirmed infectious focus (on CT) | NO | Suspected diagnosis | Confirmed diagnosis |
| ESKAPE group microorganisms detected at clinically significant titers (>104 CFU/mL) | NO | YES | YES In several locations |
| Presence of resistance genes | NO | YES | - |
| Assessment of the colonic microbiota (by PCR/or cultured techniques | Reference values | Deficiency of obligate anaerobes | Deficiency of obligate anaerobes with detection of pathogenic microorganisms at clinically significant titers (>104 CFU/mL) |
| SOFA score | 0–2 | >2 | - |
| Parameter | Mild (n = 21) | Moderate (n = 8) | Severe (n = 14) | The Pearson Chi-Square or Kruskal–Wallis Tests |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline characteristics | ||||
| Age, years | 58 (40; 65) | 53 (38; 58.5) | 60 (48; 70) | 0.561 |
| Sex (males) n, % | 12 (57.1) | 4 (50) | 8 (57.1) | >0.999 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| CRS-R, points | 16 (6; 20) | 10 (6; 21) | 11 (5; 18) | 0.419 |
| Vasoactive drugs, % | 1 (4.8) | 0 (0) | 1 (8.3) | >0.999 |
| Spontaneous breathing, % | 16 (76.2) | 6 (75) | 9 (64.3) | 0.805 |
| Spontaneous Breathing with 30% Oxygen, % | 1 (4.8%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| BIPAP, % | 2 (9.5) | 0 (0) | 2 (14.3) | |
| IMV, % | 2 (9.5) | 2 (25) | 3 (21.4%) | |
| Length of stay, days | 56 (43; 76) | 54 (38; 71.5) | 49.5 (41; 78) | 0.770 |
| Length of ICU stay, days | 42 (20; 56) | 37.5 (25; 59) | 29.5 (22; 48) | 0.643 |
| Parameter | Healthy Volunteers (n = 48) Me (Q1; Q3)/N (%) n = 48 | Patients Me (Q1; Q3)/ n = 43 | p-Value | AUC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA, µmol/L | 0.5 (0.5;0.6) | 0.8 (0.7; 1) | <0.001 | 0.816 (0.706–0.926) |
| PhPA, µmol/L | >0.5 (>0.5;0.5) | >0.5 (>0.5; >0.5) | <0.001 | 0.868 (0.789–0.948) |
| PhLA, µmol/L | >0.5 (>0.5; >0.5) | >0.5 (>0.5; >0.5) | 0.080 | 0.22 (0.17; 0.3) |
| p-HBA, µmol/L | >0.5 (>0.5; >0.5) | 1.7 (>0.5; 3.5) | <0.001 | 0.919 (0.852–0.985) |
| p-HPhAA, µmol/L | >0.5 (>0.5; >0.5) | 0.9 (>0.5; 2.2) | <0.001 | 0.887 (0.812–0.962) |
| p-HPhLA, µmol/L | 1.3 (1;1.6) | 1 (0.7; 1.2) | 0.001 | 0.712 (0.599–0.825) |
| Σ3AMM, µmol/L | 1.9 (1.5;2.2) | 2.1 (1.5; 3.5) | 0.037 | 0.632 (0.507–0.756) |
| Parameter | Day 1 of Admission | Day 7 of Admission | Day 14 of Admission | p-Value Friedman Test: Day 1 vs. Day 7 vs. Day 14) | p-Value Day 1 vs. Day 7 | p-Value Day 1 vs. Day 14 | p-Value Day 7 vs. Day 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomarkers | |||||||
| PCT, ng/mL | 0.13 (0.06; 0.26) | 0.07 (0.04; 0.22) | 0.08 (0.05; 0.17) | 0.151 | |||
| CORT, nmol/L | 416.3 (268; 826.2) | 478.6 (324.6; 552.7) | 455.4 (372.4; 576.6) | 0.636 | |||
| IL-6, pg/mL | 31.8 (19.2; 59.9) | 21.1 (11.9; 55.2) | 23.3 (11.1; 47) | 0.492 | |||
| S100, mkg/L | 0.08 (0.05; 0.12) | 0.08 (0.05; 0.19) | 0.05 (0.03; 0.1) | 0.034 | >0.999 | 0.071 | 0.085 |
| NSE, ng/mL | 12.1 (6.56; 15.2) | 12.2 (6.9; 21.8) | 15.8 (7.4; 21.6) | 0.686 | |||
| Assessment Scores | |||||||
| SOFA | 2 (1; 4) | 2 (1; 3) | 2 (1; 3) | 0.059 | |||
| CRS-R | 12 (6; 20) | 12.5 (7; 20) | 15.5 (10; 20) | <0.001 | >0.999 | 0.114 | 0.008 |
| CGS | 13 (10; 15) | 13 (11; 15) | 14 (11; 15) | 0.011 | >0.999 | 0.272 | 0.826 |
| The blood cells | |||||||
| WBC, ×109/L | 9.1 (6.8; 11,2) | 7.5 (6.09; 11,2) | 8 (6.3; 11) | 0.164 | |||
| Lymphocytes, % | 14.8 (9.2; 19.9) | 18.2 (12.1; 24.2) | 22.7 (14.1; 28.4) | 0.002 | 0.268 | 0.001 | 0.185 |
| Neutrophil, % | 74.2 (69; 81) | 66.8 (59; 77.5) | 62 (58.7; 77.3) | 0.055 | |||
| Platelet, ×109/ | 295 (225; 399) | 307 (255; 338) | 335 (281; 381) | 0.010 | 0.468 | 0.341 | 0.008 |
| Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) | 4.99 (3.52; 8.27) | 3.1 (2.24; 5.52) | 2.68 (2.06; 5.52) | 0.005 | 0.185 | 0.004 | 0.523 |
| Biochemistry parameters | |||||||
| Total Protein, g/L | 58.8 (55.6; 65) | 57.9 (54; 62) | 58.65 (55.6; 64.5) | 0.025 | 0.023 | 0.826 | 0.341 |
| Albumin, g/L | 30.5 (27.8; 33.8) | 29 (26.2; 33.4) | 31.6 (26.3; 34.1) | 0.891 | |||
| C-Reactive Protein (CRP), mg/L | 48.8 (25.49; 95.7) | 41.63 (23.23; 118) | 31 (18.5; 52) | 0.043 | >0.999 | 0.141 | 0.061 |
| Urea, μmol/L | 4.9 (3.7; 7.1) | 4.5 (2.8; 7.7) | 4.2 (2.7; 7) | 0.888 | |||
| Alanine Transaminase (ALT), U/L | 34.1 (17.6; 56.5) | 28.8 (16.2; 37.5) | 18.4 (11.9; 40.3) | 0.05 | |||
| Aspartate Transaminase (AST), U/L | 34.2 (18.3; 49.2) | 29.7 (18.4; 43.8) | 19 (15.1; 30.8) | 0.004 | 0.149 | 0.003 | 0.571 |
| α-Amylase, U/L | 68.2 (45.7; 107) | 49.8 (40.2; 74.6) | 50.7 (38.5; 73.7) | 0.137 | |||
| C-Reactive Protein/Albumin ratio | 1.5 (0.9; 3) | 1.5 (0.8; 3.8) | 1.1 (0.6; 1.8) | 0.025 | >0.999 | 0.247 | 0.023 |
| Parameter | Study Group n = 21 | Control Group n = 38 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 58 (40; 65) | 59 (40.3; 69) | 0.511 |
| Sex (female), n% | 12 (57.1%) | 19 (50%) | 0.599 |
| Acute Cerebrovascular Accident, n (%) | 10 (48%) | 23 (60%) | 0.339 |
| Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, % | 7 (33%) | 9 (24%) | 0.425 |
| Anoxia, % | 4 (19%) | 6 (16%) | 0.733 |
| PCT, ng/mL | 0.05 (0.03; 0.11) | 0.1 (0.06; 0.1) | 0.101 |
| C-Reactive Protein (CRP), mg/L | 46 (22.5; 83.36) | 40.7 (21.6; 105.4) | 0.672 |
| Total Protein, g/L | 60.5 (57.1; 64) | 59.65 (54.37; 66.35) | 0.823 |
| Urea, μmol/L | 4.8 (2.9; 7.7) | 5.3 (3.3; 7.4) | 0.674 |
| Creatinine, μmol/L | 71.9 (55.6; 87.8) | 68.7 (54.6; 83.5) | 0.551 |
| White Blood Cell Count (WBC), ×109/L | 7.8 (6.4; 9.6) | 8.7 (6.4; 10.7) | 0.360 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chernevskaya, E.; Sorokina, E.; Polyakov, P.; Gorshkov, K.; Kovaleva, N.; Zakharchenko, V.; Beloborodova, N. Evaluation and Modulation of Gut Microbiome Dysfunction in Chronically Critically Ill Patients: A Prospective Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199778
Chernevskaya E, Sorokina E, Polyakov P, Gorshkov K, Kovaleva N, Zakharchenko V, Beloborodova N. Evaluation and Modulation of Gut Microbiome Dysfunction in Chronically Critically Ill Patients: A Prospective Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199778
Chicago/Turabian StyleChernevskaya, Ekaterina, Ekaterina Sorokina, Petr Polyakov, Kirill Gorshkov, Nadezda Kovaleva, Vladislav Zakharchenko, and Natalia Beloborodova. 2025. "Evaluation and Modulation of Gut Microbiome Dysfunction in Chronically Critically Ill Patients: A Prospective Pilot Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199778
APA StyleChernevskaya, E., Sorokina, E., Polyakov, P., Gorshkov, K., Kovaleva, N., Zakharchenko, V., & Beloborodova, N. (2025). Evaluation and Modulation of Gut Microbiome Dysfunction in Chronically Critically Ill Patients: A Prospective Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199778





