Inflammation-Based Cell Ratios Beyond White Blood Cell Count for Predicting Postimplantation Syndrome After EVAR and TEVAR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
4.2. Exclusion Criteria
4.3. Technique
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| CABG | Coronary artery bypass grafting |
| CAD | Coronary artery disease |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| ELR | Eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| EVAR | Endovascular aneurysm repair |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PAD | Peripheral artery disease |
| PIS | Postimplantation syndrome |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| SIRI | Systemic inflammatory response index |
| TEVAR | Thoracic endovascular aortic repair |
References
- Mazzolai, L.; Teixido-Tura, G.; Lanzi, S.; Boc, V.; Bossone, E.; Brodmann, M.; Bura-Rivière, A.; De Backer, J.; Deglise, S.; Della Corte, A.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Peripheral Arterial and Aortic Diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3538–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilo, F.; Catanese, V.; Nenna, A.; Montelione, N.; Codispoti, F.A.; Verghi, E.; Gabellini, T.; Jawabra, M.; Chello, M.; Spinelli, F. Biomarkers in EndoVascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Pathophysiology and Clinical Implications. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galle, C.; De Maertelaer, V.; Motte, S.; Zhou, L.; Stordeur, P.; Delville, J.P.; Li, R.; Ferreira, J.; Goldman, M.; Capel, P.; et al. Early Inflammatory Response after Elective Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair: A Comparison between Endovascular Procedure and Conventional Surgery. J. Vasc. Surg. 2000, 32, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schürmann, K.; Vorwerk, D.; Bücker, A.; Neuerburg, J.; Klosterhalfen, B.; Müller, G.; Uppenkamp, R.; Günther, R.W. Perigraft Inflammation due to Dacron-Covered Stent-Grafts in Sheep Iliac Arteries: Correlation of MR Imaging and Histopathologic Findings. Radiology 1997, 204, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez, O.C.; Carpenter, J.P.; Baum, R.A.; Barker, C.F.; Golden, M.; Criado, F.; Pyeron, A.; Fairman, R.M. Perigraft Air, Fever, and Leukocytosis after Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Am. J. Surg. 1999, 178, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikmen, N.; Ozcinar, E.; Hasde, A.I.; Kayan, A.; Polat, N.; Ardakani, A.; Kadiroğlu Yuruyen, E.; Eyileten, Z. Stent-Induced Inflammation: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study of Post-Implantation Syndrome in Venous and Arterial Procedures. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, U.; Voshage, G.; Lammer, J.; Beyersdorf, F.; Töllner, D.; Kretschmer, G.; Spillner, G.; Polterauer, P.; Nagel, G.; Hölzenbein, T. Endoluminal Stent-Grafts for Infrarenal Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares Ferreira, R.; Bastos Gonçalves, F. Postimplantation Syndrome after Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. In Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm—From Basic Research to Clinical Practice; Koncar, I., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytekin, B.; Iscan, H.Z. Postimplantation Syndrome after Endovascular Aortic Repair: Impact of Endograft Material and a Review of the Literature. Turk. J. Vasc. Surg. 2024, 33, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavda, V.P.; Feehan, J.; Apostolopoulos, V. Inflammation: The Cause of All Diseases. Cells 2024, 13, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; He, J.; Li, H.; Xie, L.; Zeng, W.; Lin, X.; Qiu, Z.; Chen, L. Outcomes of Post-Implantation Syndrome after Endovascular Repair for Stanford Type B Aortic Dissection. J. Vasc. Surg. 2024, 79, 1326–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, N.A.; Roxburgh, C.; Khan, F.; Guthrie, G. Postimplantation Syndrome in Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair—A Systematic Review. Vasa 2021, 50, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaoutoglou, E.; Papas, N.; Milionis, H.; Kouvelos, G.; Koulouras, V.; Matsagkas, M.I. Post-Implantation Syndrome after Endovascular Repair of Aortic Aneurysms: Need for Postdischarge Surveillance. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 11, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaoutoglou, E.; Kouvelos, G.; Milionis, H.; Mavridis, A.; Kolaitis, N.; Papa, N.; Papadopoulos, G.; Matsagkas, M. Post-Implantation Syndrome Following Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair: Preliminary Data. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 12, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, K.S.; Bouchier-Hayes, D.; Leahy, A.L. Consumptive Coagulopathy Following Endovascular Stent Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2000, 19, 94–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohara, N.; Miyata, T.; Oshiro, H.; Shigematsu, H.; Ohki, T. Adverse Outcome Following Transfemoral Endovascular Stent-Graft Repair of an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in a Patient with Severe Liver Dysfunction: Report of a Case. Surg. Today 2000, 30, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaoutoglou, E.; Kouvelos, G.; Koutsoumpelis, A.; Patelis, N.; Lazaris, A.; Matsagkas, M. An Update on the Inflammatory Response after Endovascular Repair for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 945035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.F.; Soares Ferreira, R.; Amaral, C.; Bastos Gonçalves, F.; Ferreira, M.E. The Impact of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio on Short- and Long-Term Prognosis Following Elective Infrarenal EVAR. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2025, 113, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.H.; Schmaier, A.H.; Harth, K.C.; Kumins, N.H.; Wong, V.L.; Zidar, D.A.; Kashyap, V.S.; Cho, J.S. Elevated Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Mortality Following Elective Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 72, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Octeau, D.; Faries, C.; Barnes, H.; Nakazawa, K.R.; Rao, A.J.; Ting, W.; Marin, M.L.; Vouyouka, A.G.; Faries, P.L.; Tadros, R.O. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Associated With Adverse Events After Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR). Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 75, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.X.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhao, N.; Diao, Y.P.; Lan, Y.; Li, Y.J. Novel Systemic Inflammatory Markers Predict All-Cause Mortality in Patients Undergoing Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 25, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, K.; Belayachi, J.; Derras, Y.; Khayari, M.E.; Dendane, T.; Madani, N.; Khoudri, I.; Zeggwagh, A.A.; Abouqal, R. Eosinopenia, an Early Marker of Increased Mortality in Critically Ill Medical Patients. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 37, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhu, H.; Ma, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, Z.; Du, P.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, J.; et al. Peripheral Eosinophil Count Is Associated with the Prognosis of Patients with Type B Aortic Dissection Undergoing Endovascular Aortic Repair: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e027339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Ye, L.; Shi, H.M.; Wang, X.M.; Luo, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, Q.C. Impacts of Eosinophil Percentage on Prognosis Acute Type A Aortic Dissection Patients. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2022, 22, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, D.A. Behavior of Eosinophil Leukocytes in Acute Inflammation. II. Eosinophil Dynamics during Acute Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 1975, 56, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrin, P.; Le Borgne, P.; Sabah, J.; Lefebvre, F.; Kauffenstein, G.; Brossard, C.; Schnee, A.; Trognon, P.; Lavoignet, C.E.; Abensur Vuillaume, L. Eosinophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Early Variation as Predictors of Severity and In-Hospital Mortality in Patients Admitted to the Emergency Department for SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2025, 117, qiaf105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accarino, G.; Silverio, A.; Bellino, M.; Furgiuele, S.; Fimiani, M.; Sica, M.; De Vuono, F.; Fornino, G.; Turchino, D.; Accarino, G.; et al. From Planning to Practice: Impact of Achieved Proximal Sealing Zone in Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR). J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bölke, E.; Jehle, P.M.; Storck, M.; Braun, C.; Schams, S.; Steinbach, G.; Orth, K.; Görich, J.; Scharrer-Pamler, R.; Sunder-Plassmann, L. Endovascular Stent-Graft Placement versus Conventional Open Surgery in Infrarenal Aortic Aneurysm: A Prospective Study on Acute Phase Response and Clinical Outcome. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 314, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, J.R.; Goodall, S.; Thompson, J.P.; Bell, P.R.; Thompson, M.M. Endovascular AAA Repair Attenuates the Inflammatory and Renal Responses Associated with Conventional Surgery. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2000, 7, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartbol, P.; Norgren, L.; Pärsson, H.; Truedsson, L. Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Induces Significant Alterations in Surface Adhesion Molecule Expression on Donor White Blood Cells Exposed to Patient Plasma. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 1997, 14, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorla, R.; Erbel, R.; Eagle, K.A.; Bossone, E. Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndromes in the Era of Interventional Cardiology. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 107, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Turchino, D.; Fanti, C.; Bottino, R.; Ferrara, F.; Mannina, C.; Lerakis, S.; Comentale, G.; Rega, S.; Cittadini, A.; et al. Post-Implantation Syndrome in Patients Undergoing Thoracic and Abdominal Endovascular Aortic Repair: Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2025, 50, 103055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.F.; Soares Ferreira, R.; Amaral, C.; Ferreira, M.E.; Bastos Gonçalves, F. Post-Implantation Syndrome Incidence Is Higher after Complex Endovascular Aortic Procedures than after Standard Infrarenal Repair. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2023, 66, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voûte, M.T.; Bastos Gonçalves, F.M.; van de Luijtgaarden, K.M.; Klein Nulent, C.G.; Hoeks, S.E.; Stolker, R.J.; Verhagen, H.J. Stent Graft Composition Plays a Material Role in the Postimplantation Syndrome. J. Vasc. Surg. 2012, 56, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimidis, T.; Sfyroeras, G.; Trellopoulos, G.; Skoura, L.; Papazoglou, K.; Konstantinidis, K.; Karamanos, D.; Filaktou, A.; Parapanisiou, E. Impact of Endograft Material on the Inflammatory Response after Elective Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair. Angiology 2005, 56, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, E.A.; Locali, R.F.; Romano, C.C.; Duarte, A.J.; Palma, J.H.; Buffolo, E. Analysis of the Inflammatory Response in Endovascular Treatment of Aortic Aneurysms. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2007, 31, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaoutoglou, E.; Kouvelos, G.; Papa, N.; Kallinteri, A.; Milionis, H.; Koulouras, V.; Matsagkas, M. Prospective Evaluation of Post-Implantation Inflammatory Response after EVAR for AAA: Influence on Patients’ 30 Day Outcome. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2015, 49, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storck, M.; Scharrer-Pamler, R.; Kapfer, X.; Gallmeier, U.; Görich, J.; Sunder-Plassmann, L.; Brückner, U.; Mickley, V. Does a Postimplantation Syndrome Following Endovascular Treatment of Aortic Aneurysms Exist? Vasc. Surg. 2001, 35, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, S.; Kavasoğlu, K.; Kısa, U.; Koçoğulları, C.U.; Öztürk, İ. Are Systemic Diseases a Risk Factor for Post-Implantation Syndrome? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Surg. Interv. 2021, 8, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.F.; Soares Ferreira, R.; Bento, R.; Pais, F.; Cardoso, J.; Bastos Gonçalves, F.; Amaral, C.; Ferreira, M.E. Diagnosis and Predictors of Post-Implantation Syndrome Following Endovascular Repair of Aortic Aneurysms—A Narrative Review. Angiol. Cir. Vasc. 2024, 20, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, O.; Di Girolamo, A.; Belli, C.; Gattuso, R.; Baratta, F.; Gossetti, B.; Alunno, A.; Irace, L. Incidence of Post-Implantation Syndrome with Different Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair Modalities and Devices and Related Etiopathogenetic Implications. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 63, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Ko, G.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Han, Y.; Noh, M.; Kwon, T.W.; Cho, Y.P. Effects of Postimplantation Systemic Inflammatory Response on Long-Term Clinical Outcomes after Endovascular Aneurysm Repair of an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Medicine 2016, 95, e4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Oria, M.; Manoranjithan, S.; Scoville, C.; Vogel, T.R.; Cheung, S.; Calvagna, C.; Lepidi, S.; Bath, J. Systematic Review of Risk Factors and Outcomes of Post-Implantation Syndrome Following Endovascular Aortic Repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2024, 79, 1240–1250.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzelas, D.A.; Pitoulias, A.G.; Telakis, Z.C.; Kalogirou, T.E.; Tachtsi, M.D.; Christopoulos, D.C.; Pitoulias, G.A. Incidence and Risk Factors of Postimplantation Syndrome after Elective Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair. Int. Angiol. 2022, 41, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, S.; Ozturk, I.; Yilmaz, H.; Sen, B. Does Postimplantation Syndrome Due to Endovascular Aneurysm Repair Increase Mortality Rate? Ann. Med. Res. 2020, 27, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes Valdivia, A. Post-Implantation Syndromes after Endovascular Aneurysm Repair: Not Good, But Not Bad Either. EJVES Vasc. Forum 2025, 64, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, P.D.; Rastogi, V.; Yadavalli, S.D.; Solomon, Y.; Romijn, A.S.; Dansey, K.; Verhagen, H.J.M.; Giles, K.A.; Lombardi, J.V.; Schermerhorn, M.L. The Rise of Endovascular Repair for Abdominal, Thoracoabdominal, and Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 2025, 81, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilimigras, D.I.; Sigala, F.; Karaolanis, G.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Spartalis, E.; Spartalis, M.; Patelis, N.; Papalampros, A.; Long, C.; Moris, D. Cytokines as Biomarkers of Inflammatory Response after Open versus Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: A Systematic Review. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Meganathan, I.; MacArthur, R.; Kassiri, Z. Inflammation in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Cause or Comorbidity? Can. J. Cardiol. 2024, 40, 2378–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakisis, J.D.; Moulakakis, K.G.; Antonopoulos, C.N.; Mylonas, S.N.; Giannakopoulos, T.G.; Sfyroeras, G.S.; Karakitsos, P.; Liapis, C.D. Volume of New-Onset Thrombus Is Associated with the Development of Postimplantation Syndrome after Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 60, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videm, V.; Ødegård, A.; Myhre, H.O. Iohexol-Induced Neutrophil Myeloperoxidase Release and Activation upon Contact with Vascular Stent-Graft Material: A Mechanism Contributing to the Postimplantation Syndrome? J. Endovasc. Ther. 2003, 10, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akowuah, E.; Wilde, P.; Angelini, G.; Bryan, A.J. Systemic Inflammatory Response after Endoluminal Stenting of the Descending Thoracic Aorta. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 6, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norgren, L.; Swartbol, P. Biological Responses to Endovascular Treatment of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. J. Endovasc. Surg. 1997, 4, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.K.; Chuter, T.A.; Niemann, C.U.; Shlipak, M.G.; Cohen, M.J.; Reilly, L.M.; Hiramoto, J.S. Systemic Inflammation, Coagulopathy, and Acute Renal Insufficiency Following Endovascular Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 49, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowlands, T.E.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S. Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Release in Open versus Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Br. J. Surg. 2001, 88, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanos, K.; Karathanos, C.; Giannoukas, A.D. Redefining the Pathophysiology of Post-Implantation Syndrome after Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair. Vascular 2017, 25, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moris, D.; Schizas, D.; Liakakos, T. Regarding “Prospective Evaluation of Postimplantation Syndrome Evolution on Patient Outcomes after Endovascular Aneurysm Repair for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm”. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 1193–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žura, M.; Kozmar, A.; Šakić, K.; Malenica, B.; Hrgovic, Z. Effect of Spinal and General Anesthesia on Serum Concentration of Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic Inflammation in the Etiology of Disease across the Life Span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, S.; Kisa, U.; Kavasoglu, K.; Elci, M.E.; Kahraman, M.A.; Kose, Y.; Sen, S.M.; Ozturk, I.; Kocogullari, C.U. Importance of Biomarkers in Determining Post-Implantation Syndrome Developing Due to Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. EJMO 2019, 3, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliason, J.L.; Hannawa, K.K.; Ailawadi, G.; Sinha, I.; Ford, J.W.; Deogracias, M.P.; Roelofs, K.J.; Woodrum, D.T.; Ennis, T.L.; Henke, P.K.; et al. Neutrophil Depletion Inhibits Experimental Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Formation. Circulation 2005, 112, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. B Lymphocytes in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Atherosclerosis 2015, 242, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seretis, K.G.; Lazaris, A.M.; Kakisis, J.D. The Role of Platelets and Aneurysm Thrombus in the EVAR Post Implantation Syndrome. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2024, 108, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, R.R.; Folsom, A.R.; Poudel, K.; Lutsey, P.L.; Demmer, R.T.; Pankow, J.S.; Chen, L.Y.; Tang, W. Association of Differential Leukocyte Count with Incident Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm over 22.5 Years: The ARIC Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2342–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, N.; Bartolotti, L.A.M.; Migliari, M.; Ferri, A.; Baresi, G.F.; Andreoli, F.; Saitta, G.; Gennai, S. Risk Factors and Perioperative Outcomes of Postimplantation Syndrome after Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2025, 15266028251325764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drăgan, A.; Drăgan, A.Ş.; Ştiru, O. The Predictive Value of Perioperative Inflammatory Indexes in Major Arterial Surgical Revascularization from Leriche Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhong, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Sun, J.; Zhao, S.; Deng, J. Comparison of Systemic Immunoinflammatory Biomarkers for Assessing Severe Abdominal Aortic Calcification among U.S. Adults Aged ≥40 Years: A Cross-Sectional Analysis from NHANES. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0325949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, W.; Wang, L.; Shu, M.; Xue, B.; Wang, R.; Feng, Z.; et al. Combination Model of Neutrophil to High-Density Lipoprotein Ratio and System Inflammation Response Index Is More Valuable for Predicting Peripheral Arterial Disease in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1100453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopf, J.; Zagrapan, B.; Brandau, A.; Lechenauer, P.; Candussi, C.J.; Rossi, P.; Celem, N.D.; Ziegler, M.; Fuchs, L.; Hayden, H.; et al. Circulating Monocyte Populations as Biomarker for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1418625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, Z.; Zheng, L.; He, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. Factors Influencing Early Diagnosis of Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: The Role of Neutrophils. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 5777–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, L.; Liang, T.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Jing, Z. Elevated Preoperative Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Early Adverse Outcomes in Uncomplicated Type B Aortic Dissection Undergoing TEVAR. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishibe, T.; Kano, M.; Maekawa, K.; Matsumoto, R.; Fujiyoshi, T.; Iwahashi, T.; Kamiya, K.; Ogino, H. Association of Neutrophils, Lymphocytes, and Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio to Overall Mortality after Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair. Int. Angiol. 2022, 41, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettrelet, T.; Gigon, L.; Karaulov, A.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.-U. The Enigma of Eosinophil Degranulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, S.P.; Rosenberg, H.F.; Moqbel, R.; Phipps, S.; Foster, P.S.; Lacy, P.; Kay, A.B.; Rothenberg, M.E. Eosinophils: Biological Properties and Role in Health and Disease. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 709–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Deng, Z.; Fang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Luo, S.; Meng, Z.; Liu, J.; et al. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Protect Mice from Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Formation via IL5 and Eosinophils. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2206958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Tai, N.; Kamei, C. Inhibitory Effects of Glucocorticoids on Rat Eosinophil Superoxide Generation and Chemotaxis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2003, 3, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Meijenfeldt, G.C.I.; Chary, S.; van der Laan, M.J.; Zeebregts, C.J.A.M.; Christopher, K.B. Eosinopenia and Post-Hospital Outcomes in Critically Ill Non-Cardiac Vascular Surgery Patients. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochowiecki, T.; Wyczałkowska-Tomasik, A.; Paczek, L.; Jama, K.; Jakimowicz, T.; Cacko, A.; Gałązka, Z.; Michalska, M. Should the PIS Criteria Be More Clarified after Endovascular Aortic Repair of Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm (TAAA)? J. Vasc. Surg. 2024, 79 (Suppl. S1), 69S–70S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.D.; Denaxas, S.; Nicholas, O.; Hingorani, A.D.; Hemingway, H. Low Eosinophil and Low Lymphocyte Counts and the Incidence of 12 Cardiovascular Diseases: A CALIBER Cohort Study. Open Heart 2016, 3, e000477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddi, F.M.; Vacca, F.; Ciattaglia, R.; Fresilli, M.; Fazzini, S.; Ippoliti, A. Polyester Stent Graft Devices and Higher Risk of Post-Implantation Syndrome after EVAR: Single-Center Analysis of 367 Patients. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 75, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvartz, V.; Sokolskaya, M.; Ispiryan, A.; Basieva, M.; Kazanova, P.; Shvartz, E.; Talibova, S.; Petrosyan, A.; Kanametov, T.; Donakanyan, S.; et al. The Role of «Novel» Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation in the Development of Early Hospital Events after Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients with Aortic Stenosis. Life 2023, 13, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hong, X.; Xie, X.; Guo, D.; Chen, B.; Fu, W.; Wang, L. Preoperative Systemic Inflammatory Response Index Predicts Long-Term Outcomes in Type B Aortic Dissection after Endovascular Repair. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 992463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mućka, S.; Jakubiak, G.K.; Pawlas, N. Procalcitonin: Infection or Maybe Something More? Noninfectious Causes of Increased Serum Procalcitonin Concentration: Updated Knowledge. Life 2025, 15, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
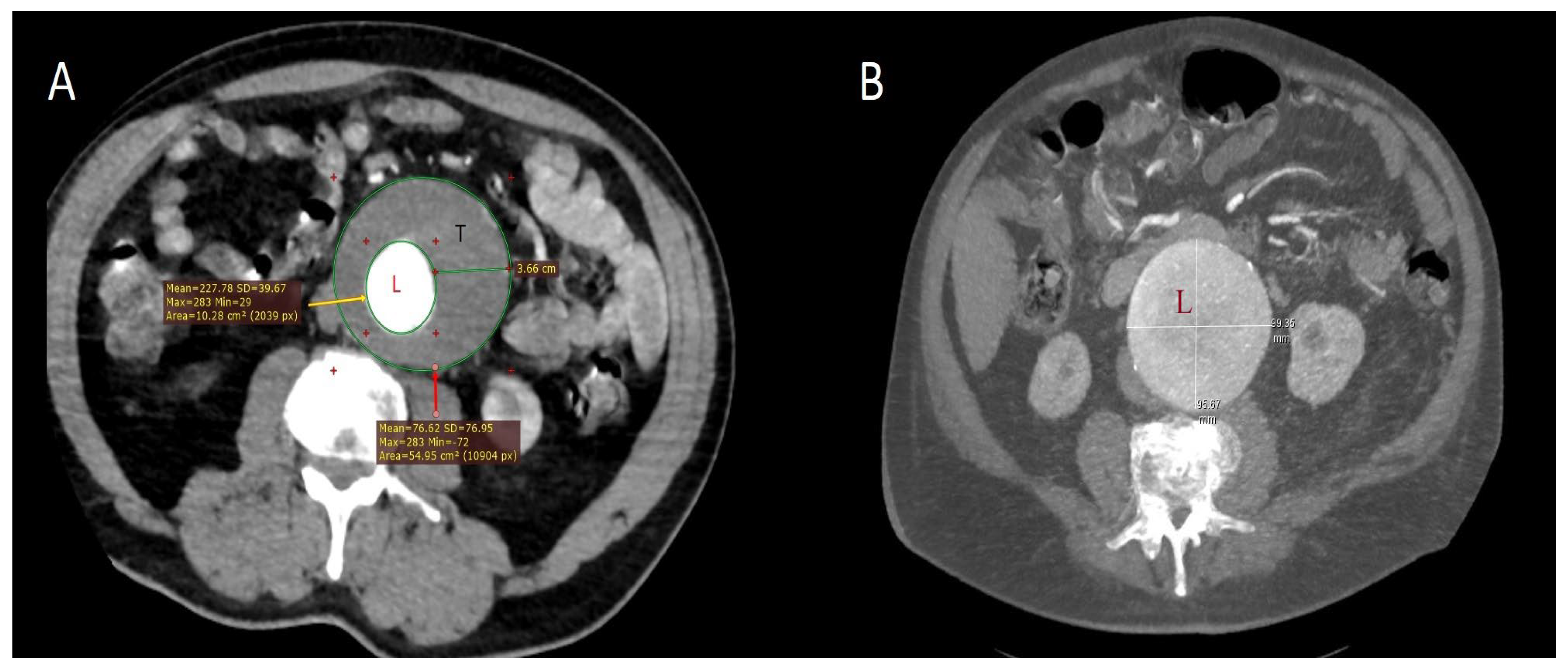
| Patient Demographics | Patients with PIS (n = 55) | Patients Without PIS (n = 245) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female/male | 13/42 | 51/194 | 0.645 |
| Age (years) | 70.1 ± 8.6 | 72.7 ± 7.3 | 0.042 |
| EVAR/TEVAR, n (%) | 40 (72.7)/15 (27.3) | 130 (53.1)/115 (46.9) | 0.010 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 21 (38) | 74 (30) | 0.250 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 51 (92) | 203 (82) | 0.066 |
| Coronary artery disease, n (%) | 20 (36) | 42 (17) | 0.002 |
| Coronary artery bypass grafting, n (%) | 5 (9) | 9 (3.6) | 0.110 |
| Cerebrovascular event, n (%) | 7 (12) | 8 (3.2) | 0.017 |
| Peripheral artery disease, n (%) | 7 (12) | 17 (6.9) | 0.121 |
| COPD, n (%) | 39 (70) | 167 (68) | 0.692 |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 25 (45) | 83 (34) | 0.134 |
| Aneurysm diameter (transverse), mm, median (Q1–Q3) | 77 (65–83) | 65 (61–70) | <0.001 |
| Intramural thrombus thickness, mm, median (Q1–Q3) | 25 (21–28) | 20 (16–25) | <0.001 |
| Contrast volume, mL, mean | 106 | 84 | <0.001 |
| Operative time, min, mean | 110 | 90 | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 13.5 ± 2.0 | 13.0 ± 1.8 | 0.574 |
| a White blood cell, 103/μL, median (Q1–Q3) | 10.4 (9.4–11.2) | 8 (6.8–9.1) | <0.001 |
| a Neutrophil count, 103/μL, median (Q1–Q3) | 8.2 (7.2–8.7) | 5.5 (4.5–6.8) | <0.001 |
| a Lymphocyte count, 103/μL, median (Q1–Q3) | 1.3 (1.1–1.8) | 1.8 (1.5–2.0) | <0.001 |
| a Monocyte count, 103/μL, median (Q1–Q3) | 0.6 (0.5–0.9) | 0.6 (0.5–0.7) | 0.014 |
| a Eosinophil count, median (Q1–Q3) | 0.1 (0.05–0.16) | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | <0.001 |
| LDL, mg/dL | 131 ± 28 | 110 ± 25 | <0.001 |
| HDL, mg/dL | 41.1 ± 10.8 | 44.5 ± 12.7 | 0.093 |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL, median (Q1–Q3) | 125 (97–170) | 112 (86–153) | 0.141 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.6 ± 0.3 | 4.0 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| a C-reactive protein, mg/L, median (Q1–Q3) | 11 (9.0–13.2) | 6.3 (5.0–8.2) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.039 |
| HbA1c, % | 6.1 ± 1.0 | 5.7 ± 0.8 | 0.122 |
| Vitamin D level, ng/mL | 12 ± 3.7 | 18 ± 6.3 | <0.001 |
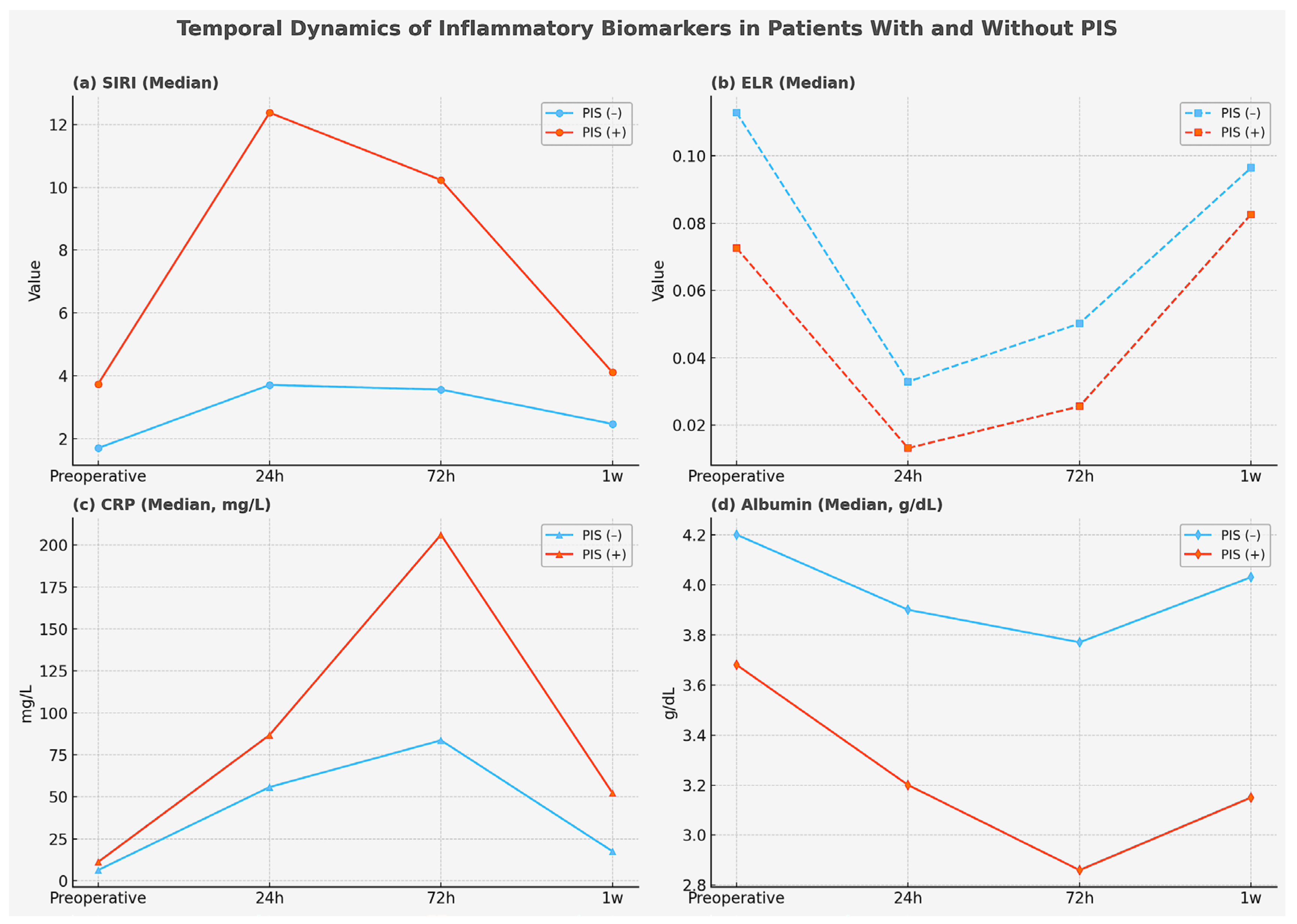
| b NLR; median (Q1–Q3) | 5.6 (4.1–7.6) | 3.0 (2.3–4.0) | <0.001 |
| b SIRI, median (Q1–Q3) | 3.7 (2.5–5.5) | 1.7 (1.3–2.2) | <0.001 |
| b ELR, median (Q1–Q3) | 0.07 (0.03–0.13) | 0.11 (0.07–0.15) | 0.004 |
| Predictor for PIS | OR (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Sex (male) | 1.2 (0.8–5.8) | 0.869 |
| Age, years | 0.83 (0.73–0.95) | 0.008 |
| Aneurysm diameter, mm | 1.2 (1.0–1.3) | 0.003 |
| Mural thrombus thickness, mm | 1.3 (1.0–1.6) | 0.012 |
| Procedure type (EVAR vs. TEVAR) | 3.7 (1.2–6.3) | 0.033 |
| Systemic inflammatory response index | 1.9 (1.2–3.1) | 0.005 |
| Eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio | 0.45 (0.2–0.9) | 0.028 |
| C-reactive protein, mg/L | 1.4 (1.1–3.2) | 0.003 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 0.63 (0.12–0.83) | 0.013 |
| Time Point | Markers | Cut-off Values | AUC | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Accuracy, % | PPV, % | NPV, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At 24 h | SIRI | ≥6.1 | 0.966 | 96.1 | 87.2 | 89.9 | 76.6 | 98.1 |
| ELR | ≤0.02 | 0.660 | 74.5 | 56.8 | 62.1 | 42.7 | 83.8 | |
| CRP, mg/L | ≥70.5 | 0.880 | 90 | 76.1 | 79.3 | 54.5 | 95.1 | |
| Albumin, g/dL | ≤3.4 | 0.851 | 80 | 79.1 | 77.6 | 60.5 | 91.2 | |
| At 72 h | SIRI | ≥6.0 | 0.924 | 90.2 | 85.1 | 86.7 | 73 | 95.1 |
| ELR | ≤0.05 | 0.704 | 83.9 | 51.8 | 63.6 | 45.5 | 85.7 | |
| CRP, mg/L | ≥160 | 0.980 | 98.1 | 97.7 | 97.8 | 94.1 | 96.9 | |
| Albumin, g/dL | ≤3.2 | 0.885 | 91.1 | 78.2 | 81.2 | 62.2 | 83.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sönmez, E.; Jalalzai, İ.; Arslan, Ü. Inflammation-Based Cell Ratios Beyond White Blood Cell Count for Predicting Postimplantation Syndrome After EVAR and TEVAR. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199753
Sönmez E, Jalalzai İ, Arslan Ü. Inflammation-Based Cell Ratios Beyond White Blood Cell Count for Predicting Postimplantation Syndrome After EVAR and TEVAR. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199753
Chicago/Turabian StyleSönmez, Ebubekir, İzatullah Jalalzai, and Ümit Arslan. 2025. "Inflammation-Based Cell Ratios Beyond White Blood Cell Count for Predicting Postimplantation Syndrome After EVAR and TEVAR" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199753
APA StyleSönmez, E., Jalalzai, İ., & Arslan, Ü. (2025). Inflammation-Based Cell Ratios Beyond White Blood Cell Count for Predicting Postimplantation Syndrome After EVAR and TEVAR. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199753







