Signaling via C-C Chemokine Ligand 19 and Extracellular Regulated Kinase 5 in T Cells Limits the Humoral Adaptive Immune Response in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
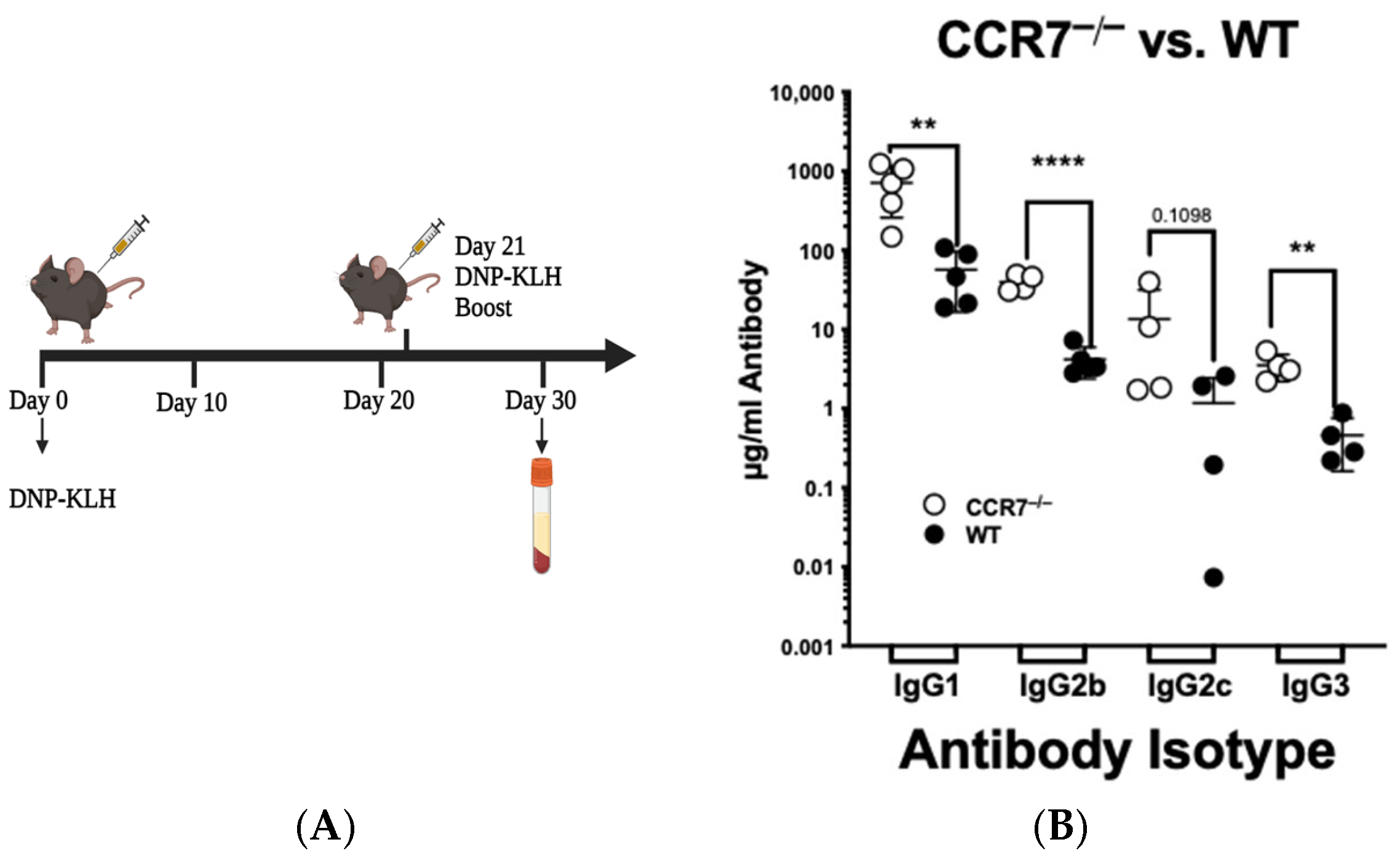
2.1. CCR7 Signals to Limit the Extent of the Secondary Immune Response
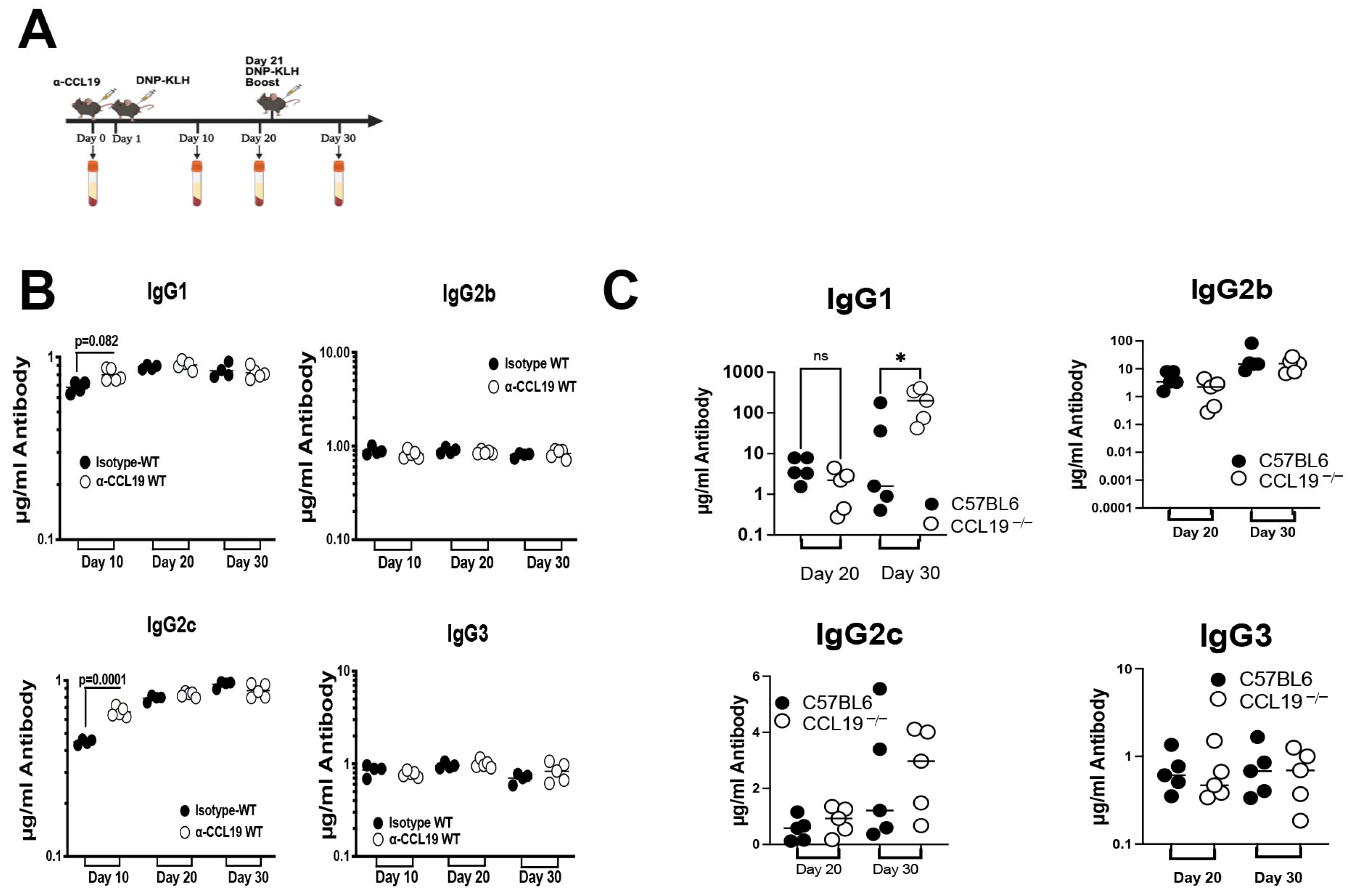
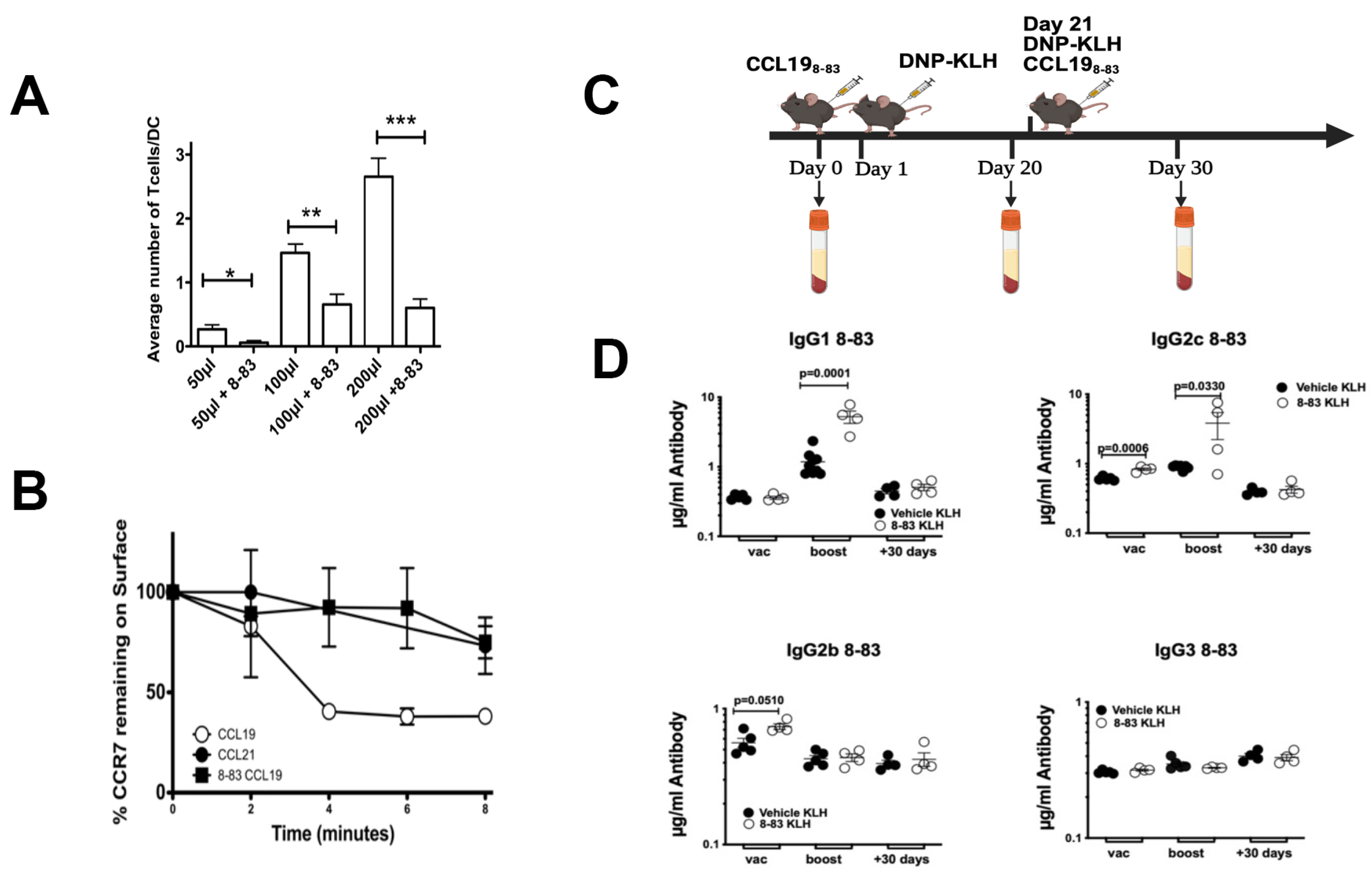
2.2. CCL19 Limits Levels of IgG1
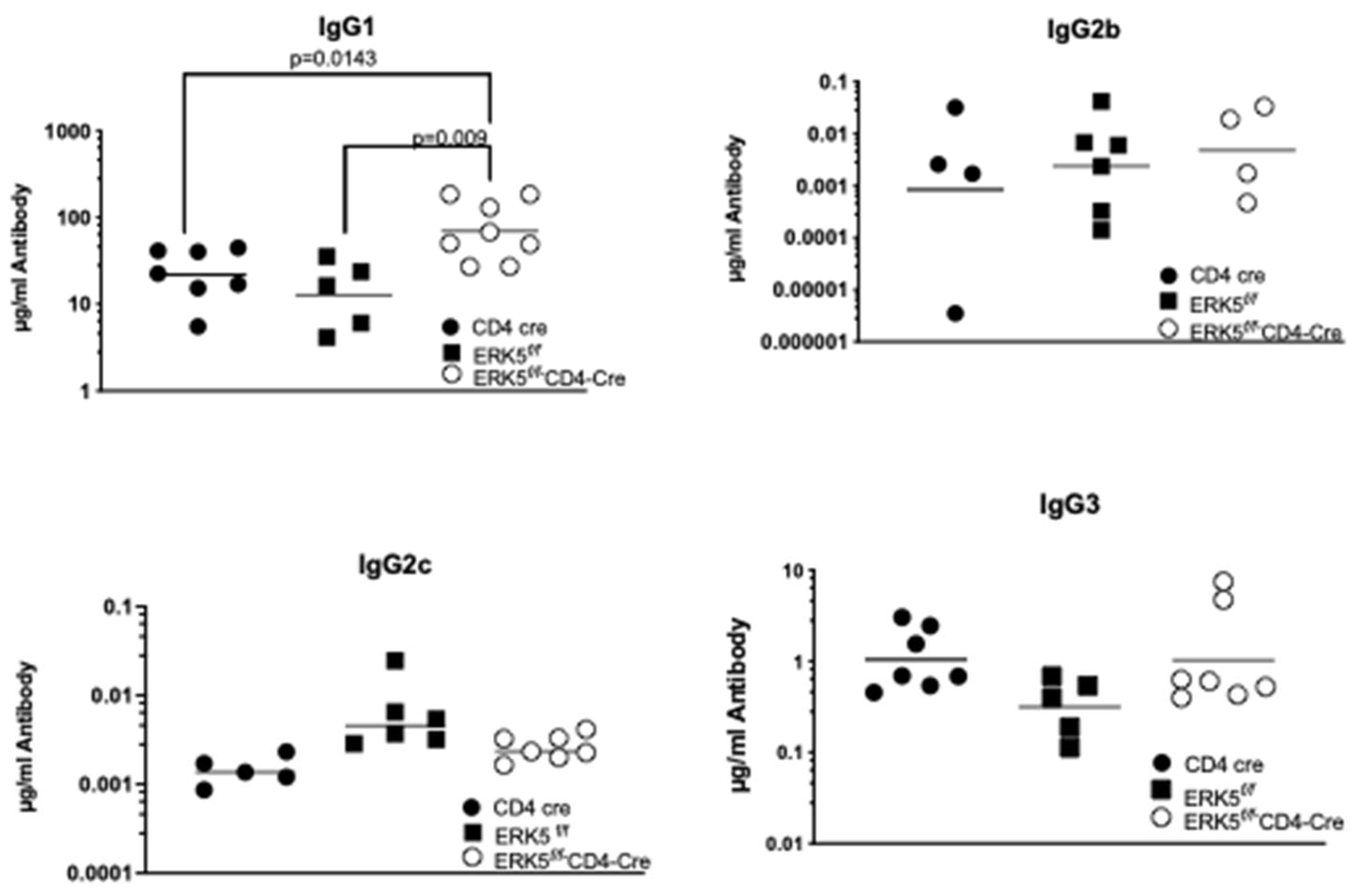
2.3. CCR7 Regulation of ERK5 Controls Antibody Production
2.4. Cytokines Regulated by ERK5 Do Not Limit the Immune Response
2.5. B-Cell Populations Do Not Differ in Response to Signaling via ERK5
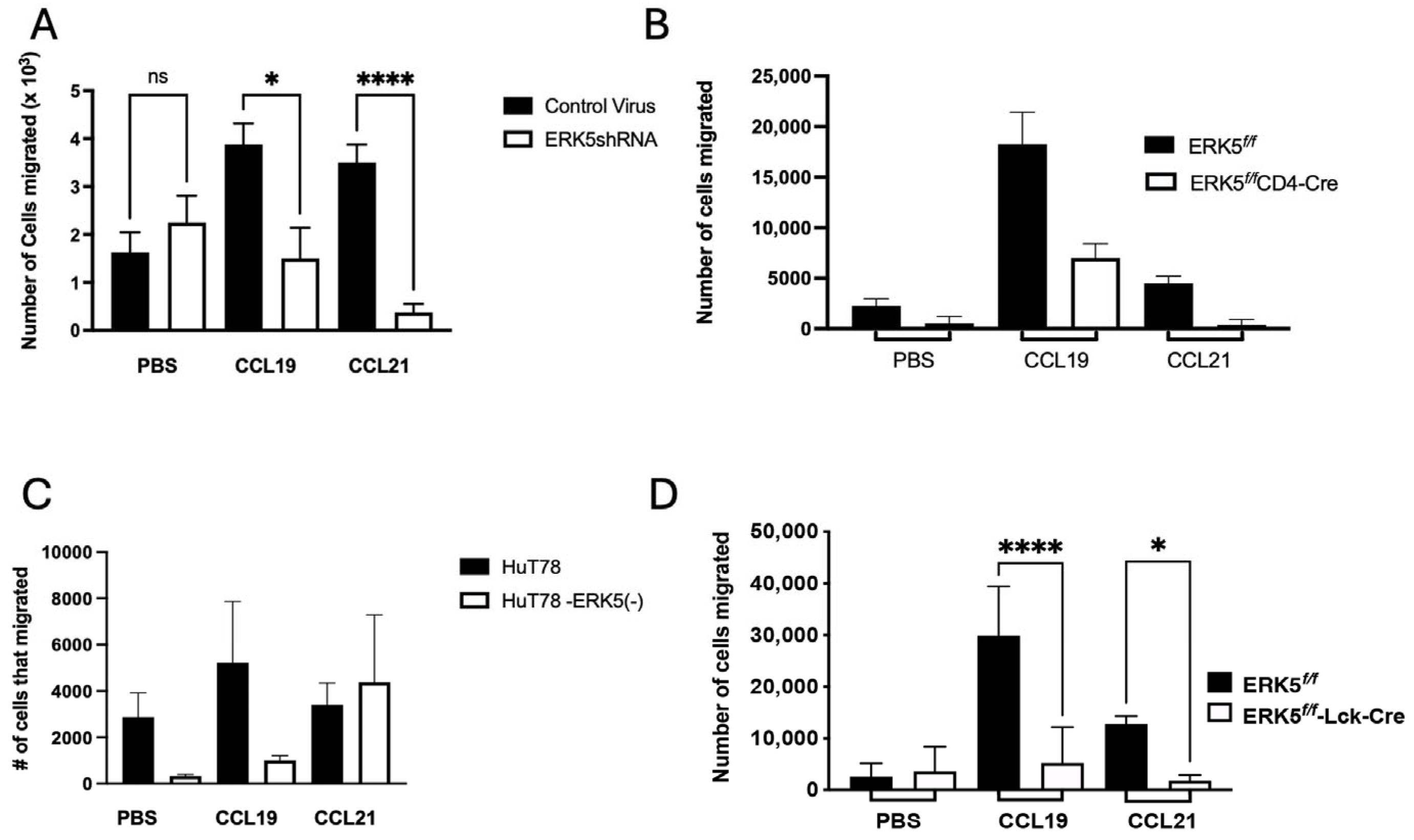
2.6. ERK5 Promotes Chemotactic Migration via CCL19
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice and Reagents
4.2. Induction of a Humoral Immune Response in Mice
4.3. ELISA Measurements of Antibody Levels
4.4. Receptor Internalization Assay
4.5. T-Cell Isolation
4.6. Generation of Bone-Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells
4.7. Chemotaxis Assays
4.8. DC/T-Cell Adhesion Assay
4.9. Recall Assays
4.10. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) Analysis of Lymphocytes
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCL19 | C-C chemokine ligand 19 |
| CCL198-83 | Amino acids 8-83 of murine CCL19; a CCL19 antagonist |
| CCL21 | C-C chemokine ligand 21 |
| CCR7 | C-C chemokine receptor 7 |
| Cre | Cre recombinase |
| DNP-KLH | Dinitrophenyl-keyhole limpet hemocyanin |
| EBI | Epstein-Barr virus-induced molecule 1 |
| EDG-1 | Endothelial differentiation gene 1 |
| ERK5 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 |
| Flox | Flanking loxp sites |
| Lck | A T-cell-specific src family kinase that is expressed in the thymus |
References
- Han, L.; Zhang, L. CCL21/CCR7 axis as a therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 121, 110431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, S.C.; Pasvanis, S.; Bounou, S.; Dumais, N. CCR7-specific migration to CCL19 and CCL21 is induced by PGE(2) stimulation in human monocytes: Involvement of EP(2)/EP(4) receptors activation. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 2682–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauvillain, C.; Cunin, P.; Doni, A.; Scotet, M.; Jaillon, S.; Loiry, M.L.; Magistrelli, G.; Masternak, K.; Chevailler, A.; Delneste, Y.; et al. CCR7 is involved in the migration of neutrophils to lymph nodes. Blood 2011, 117, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, R.; Schubel, A.; Breitfeld, D.; Kremmer, E.; Renner-Müller, I.; Wolf, E.; Lipp, M. CCR7 coordinates the primary immune response by establishing functional microenvironments in secondary lymphoid organs. Cell 1999, 99, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandum, E.P.; Jorgensen, A.S.; Calvo, M.B.; Spiess, K.; Peterson, F.C.; Yang, Z.; Volkman, B.F.; Veldkamp, C.T.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Goth, C.K.; et al. Selective Boosting of CCR7-Acting Chemokines; Short Peptides Boost Chemokines with Short Basic Tails, Longer Peptides Boost Chemokines with Long Basic Tails. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Okada, T.; Matloubian, M.; Lo, C.G.; Cyster, J.G. S1P1 receptor signaling overrides retention mediated by G alpha i-coupled receptors to promote T cell egress. Immunity 2008, 28, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.N.; Tang, H.L.; Cyster, J.G. Epstein-Barr virus-induced molecule 1 ligand chemokine is expressed by dendritic cells in lymphoid tissues and strongly attracts naive T cells and activated B cells. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, L.A.; McBurney, T.M.; Wells, M.A.; Roth, M.E.; Calloway, P.A.; Bill, C.A.; Islam, S.; Vines, C.M. CCR7/CCL19 controls expression of EDG-1 in T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11656–11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, A.; Donnadieu, E.; Abastado, J.P.; Trautmann, A.; Nardin, A. CC chemokine ligand 19 secreted by mature dendritic cells increases naive T cell scanning behavior and their response to rare cognate antigen. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monks, C.R.; Freiberg, B.A.; Kupfer, H.; Sciaky, N.; Kupfer, A. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature 1998, 395, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dustin, M.L.; Olszowy, M.W.; Holdorf, A.D.; Li, J.; Bromley, S.; Desai, N.; Widder, P.; Rosenberger, F.; van der Merwe, P.A.; Allen, P.M.; et al. A novel adaptor protein orchestrates receptor patterning and cytoskeletal polarity in T-cell contacts. Cell 1998, 94, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grakoui, A.; Bromley, S.K.; Sumen, C.; Davis, M.M.; Shaw, A.S.; Allen, P.M.; Dustin, M.L. The immunological synapse: A molecular machine controlling T cell activation. Science 1999, 285, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.C.; Chin, R.K.; Lee, Y.; Kang, H.-S.; Wang, Y.; Weinstock, J.V.; Banks, T.; Ware, C.F.; Franzoso, G.; Fu, Y.-X. Differential regulation of CCL21 in lymphoid/nonlymphoid tissues for effectively attracting T cells to peripheral tissues. J. Clin. Invest. 2003, 112, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Nakano, H.; Aritomi, K.; Wang, C.R.; Gunn, M.D.; Kakiuchi, T. Mice lacking expression of the chemokines CCL21-ser and CCL19 (plt mice) demonstrate delayed but enhanced T cell immune responses. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baekkevold, E.S.; Yamanaka, T.; Palframan, R.T.; Carlsen, H.S.; Reinholt, F.P.; von Andrian, U.H.; Brandtzaeg, P.; Haraldsen, G. The CCR7 ligand elc (CCL19) is transcytosed in high endothelial venules and mediates T cell recruitment. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Martin, B.; Zepp, J.A.; Ko, J.S.; Gu, C.; Cai, G.; Ouyang, W.; Sen, G.; et al. A novel IL-17 signaling pathway controlling keratinocyte proliferation and tumorigenesis via the TRAF4-ERK5 axis. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1571–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, I.; Donovan, K.A.; Krupnick, N.M.; Boghossian, A.S.; Rees, M.G.; Ronan, M.M.; Roth, J.A.; Fischer, E.S.; Wang, E.S.; Gray, N.S. Acute pharmacological degradation of ERK5 does not inhibit cellular immune response or proliferation. Cell Chem. Biol. 2022, 29, 1630–1638.e1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Sun, H.; Qu, J.; Sun, Y. Tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 exacerbates psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice via ERK5-dependent NETosis. MedComm 2022, 3, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, J.I.; Imanishi, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, A.; Ko, K.A.; Samanthapudi, V.S.K.; Lee, L.L.; Bojorges, A.P.; Gi, Y.J.; Hobbs, B.P.; et al. An ERK5-NRF2 Axis Mediates Senescence-Associated Stemness and Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2023, 133, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, J.J. Action of Pertussigen (Pertussis toxin) on the Host Immune System in Pathogenesis and Immunity in Pertussis. In Pathogenesis and Immunity in Pertussis; Wardlaw, A.C., Parton, R., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1988; 482p, pp. 173–192. [Google Scholar]
- Whary, M.; Baumgarth, N.; Fox, J.G.; Barthold, S.W. Biology and Diseases of MIce. In Laboratory Animal Medicine; Elsevier, Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tomei, A.A.; Siegert, S.; Britschgi, M.R.; Luther, S.A.; Swartz, M.A. Fluid flow regulates stromal cell organization and CCL21 expression in a tissue-engineered lymph node microenvironment. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4273–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misslitz, A.; Pabst, O.; Hintzen, G.; Ohl, L.; Kremmer, E.; Petrie, H.T.; Forster, R. Thymic T cell development and progenitor localization depend on CCR7. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohl, L.; Mohaupt, M.; Czeloth, N.; Hintzen, G.; Kiafard, Z.; Zwirner, J.; Blankenstein, T.; Henning, G.; Forster, R. CCR7 governs skin dendritic cell migration under inflammatory and steady-state conditions. Immunity 2004, 21, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeki, H.; Moore, A.M.; Brown, M.J.; Hwang, S.T. Cutting edge: Secondary lymphoid-tissue chemokine (SLC) and CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) participate in the emigration pathway of mature dendritic cells from the skin to regional lymph nodes. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 2472–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G.; Hopken, U.E.; Stein, H.; Lipp, M. Systemic immunoregulatory and pathogenic functions of homeostatic chemokine receptors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 72, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MartIn-Fontecha, A.; Sebastiani, S.; Hopken, U.E.; Uguccioni, M.; Lipp, M.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Sallusto, F. Regulation of dendritic cell migration to the draining lymph node: Impact on T lymphocyte traffic and priming. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, A.; Vogt, T.K.; Favre, S.; Britschgi, M.R.; Acha-Orbea, H.; Hinz, B.; Cyster, J.G.; Luther, S.A. Fibroblastic reticular cells in lymph nodes regulate the homeostasis of naive T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, T.R.; Lio, F.M.; Olshefski, D.; Liu, X.J.; Struthers, R.S.; Ling, N. Determinants of high-affinity binding and receptor activation in the N-terminus of CCL-19 (MIP-3 beta). Biochemistry 2004, 43, 3670–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilkington, K.R.; Clark-Lewis, I.; McColl, S.R. Inhibition of generation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity by a CCL19/macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-3beta antagonist. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40276–40282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogquist, K.A.; Jameson, S.C.; Heath, W.R.; Howard, J.L.; Bevan, M.J.; Carbone, F.R. T cell receptor antagonist peptides induce positive selection. Cell 1994, 76, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Noma, T.; Kou, K.; Yoshizawa, I.; Yata, J. Regulation of human IgG subclass production by cytokines: Human IgG subclass production enhanced differentially by interleukin-6. Immunology 1995, 84, 278–284. [Google Scholar]
- Samore, M.H.; Siber, G.R. Pertussis toxin enhanced IgG1 and IgE responses to primary tetanus immunization are mediated by interleukin-4 and persist during secondary responses to tetanus alone. Vaccine 1996, 14, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittasupho, C.; Shannon, L.; Siahaan, T.J.; Vines, C.M.; Berkland, C. Nanoparticles targeting dendritic cell surface molecules effectively block T cell conjugation and shift response. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestak, J.O.; Sullivan, B.P.; Thati, S.; Northrup, L.; Hartwell, B.; Antunez, L.; Forrest, M.L.; Vines, C.M.; Siahaan, T.J.; Berkland, C. Codelivery of antigen and an immune cell adhesion inhibitor is necessary for efficacy of soluble antigen arrays in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2014, 1, 14008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northrup, L.; Sestak, J.O.; Sullivan, B.P.; Thati, S.; Hartwell, B.L.; Siahaan, T.J.; Vines, C.M.; Berkland, C. Co-delivery of autoantigen and b7 pathway modulators suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. AAPS J. 2014, 16, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, J.A. C-C Chemokine Receptor 7 Limits the T cell Receptor Repertoire Submitted. PhD Thesis, The University of Texas at El Paso, El Paso, TX, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, C.M.; Endrizzi, B.T.; Wu, J.; Ding, X.; Weinreich, M.A.; Walsh, E.R.; Wani, M.A.; Lingrel, J.B.; Hogquist, K.A.; Jameson, S.C. Kruppel-like factor 2 regulates thymocyte and T-cell migration. Nature 2006, 442, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izawa, Y.; Yoshizumi, M.; Ishizawa, K.; Fujita, Y.; Kondo, S.; Kagami, S.; Kawazoe, K.; Tsuchiya, K.; Tomita, S.; Tamaki, T. Big mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (BMK1)/extracellular signal regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) is involved in platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Hypertens. Res. 2007, 30, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovida, E.; Navari, N.; Caligiuri, A.; Dello Sbarba, P.; Marra, F. ERK5 differentially regulates PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of hepatic stellate cells. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiering, D.; Schmolke, M.; Ohnesorge, N.; Schmidt, M.; Goebeler, M.; Wegener, J.; Wixler, V.; Ludwig, S. MEK5/ERK5 signaling modulates endothelial cell migration and focal contact turnover. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 24972–24980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananieva, O.; Macdonald, A.; Wang, X.; McCoy, C.E.; McIlrath, J.; Tournier, C.; Arthur, J.S. ERK5 regulation in naive T-cell activation and survival. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 2534–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschovakis, G.L.; Bubke, A.; Dittrich-Breiholz, O.; Braun, A.; Prinz, I.; Kremmer, E.; Forster, R. Deficient CCR7 signaling promotes T(H) 2 polarization and B-cell activation in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cervantes, J.A.; Welch, T.P.; Kaiser, B.; Bill, C.A.; Torres, A.; Bill, G.L.; Bill, C.A.; Vines, C.M. Signaling via C-C Chemokine Ligand 19 and Extracellular Regulated Kinase 5 in T Cells Limits the Humoral Adaptive Immune Response in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199744
Cervantes JA, Welch TP, Kaiser B, Bill CA, Torres A, Bill GL, Bill CA, Vines CM. Signaling via C-C Chemokine Ligand 19 and Extracellular Regulated Kinase 5 in T Cells Limits the Humoral Adaptive Immune Response in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199744
Chicago/Turabian StyleCervantes, Jaisel A., T. Paul Welch, Brian Kaiser, Charles A. Bill, Angel Torres, Gareth L. Bill, Colin A. Bill, and Charlotte M. Vines. 2025. "Signaling via C-C Chemokine Ligand 19 and Extracellular Regulated Kinase 5 in T Cells Limits the Humoral Adaptive Immune Response in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199744
APA StyleCervantes, J. A., Welch, T. P., Kaiser, B., Bill, C. A., Torres, A., Bill, G. L., Bill, C. A., & Vines, C. M. (2025). Signaling via C-C Chemokine Ligand 19 and Extracellular Regulated Kinase 5 in T Cells Limits the Humoral Adaptive Immune Response in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199744






