Comparative Proteomics, Functional Characterization and Immunological Cross-Reactivity Studies on Russell’s Viper Venom from Two Distinct Geographical Regions in South India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
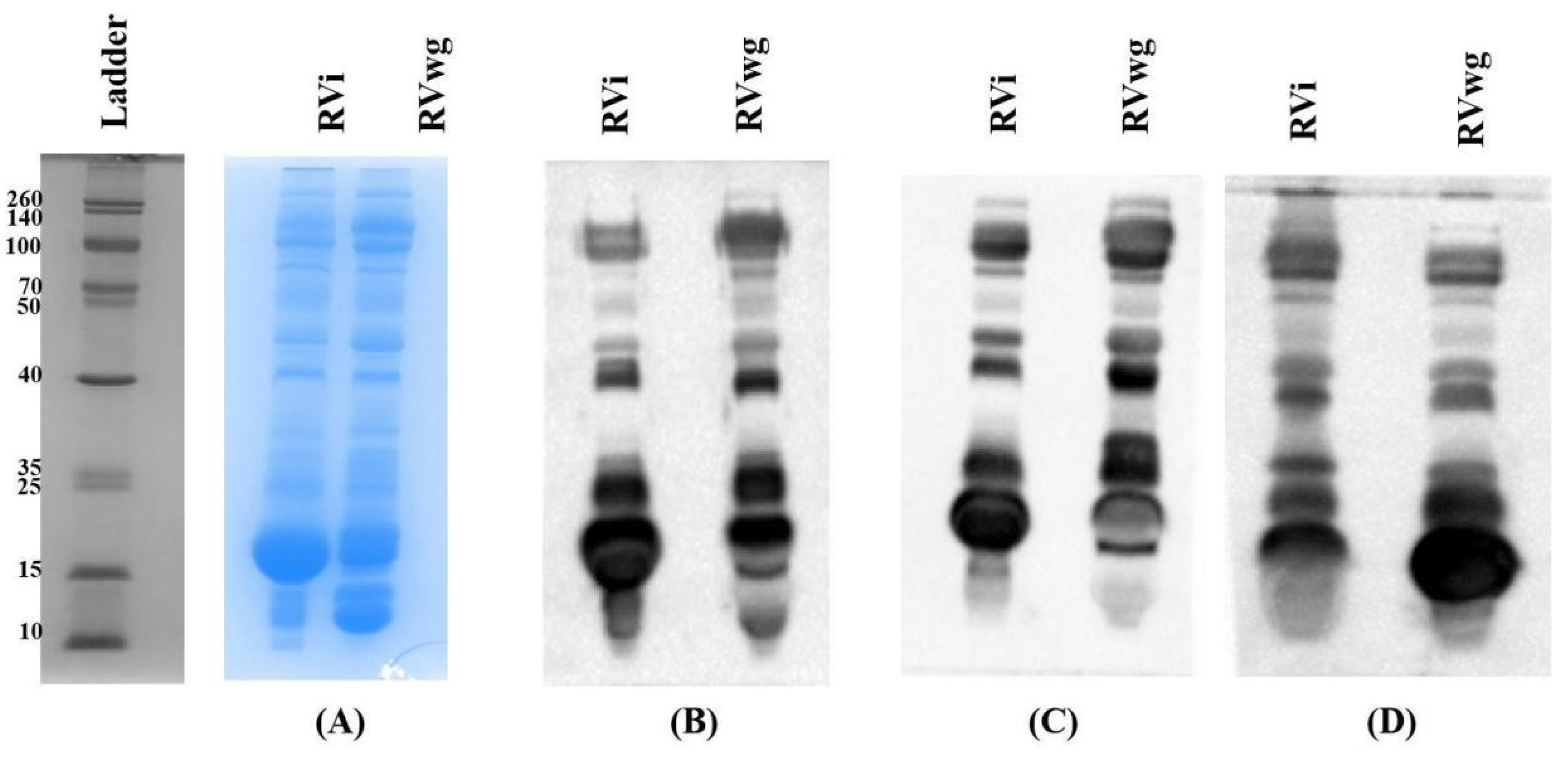
2.1. Proteomics Analysis of RVi and RVwg Venom
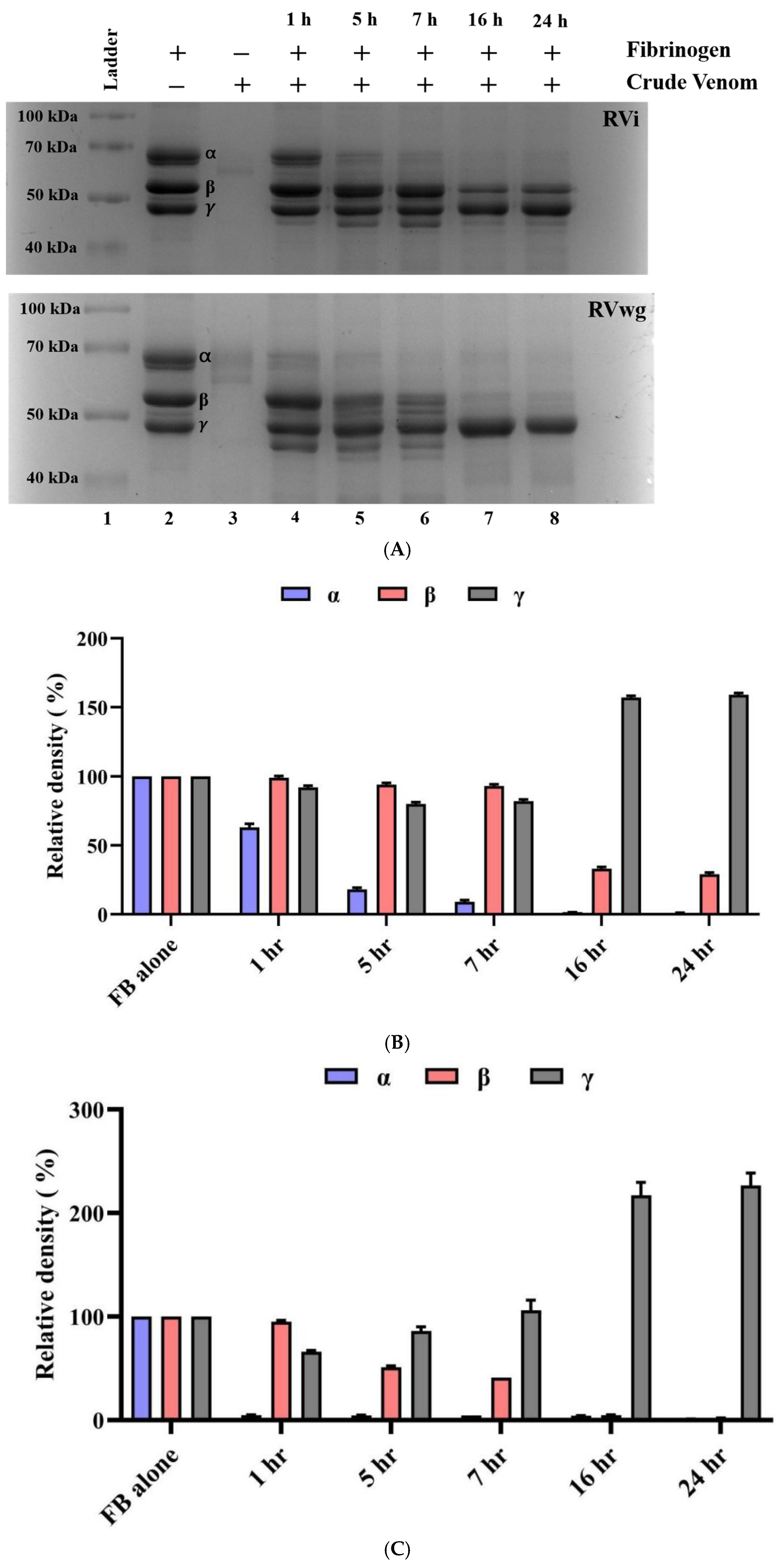
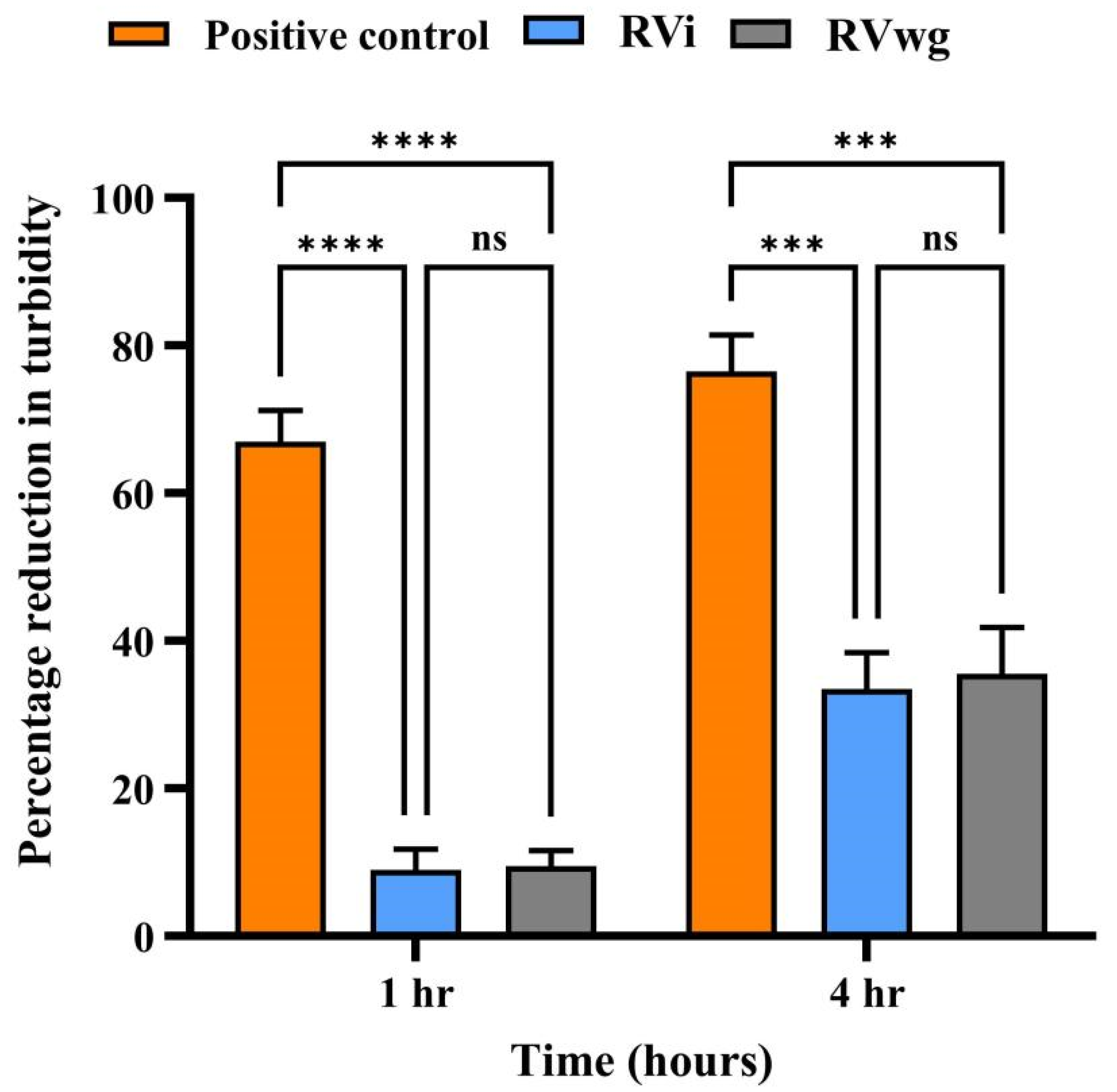
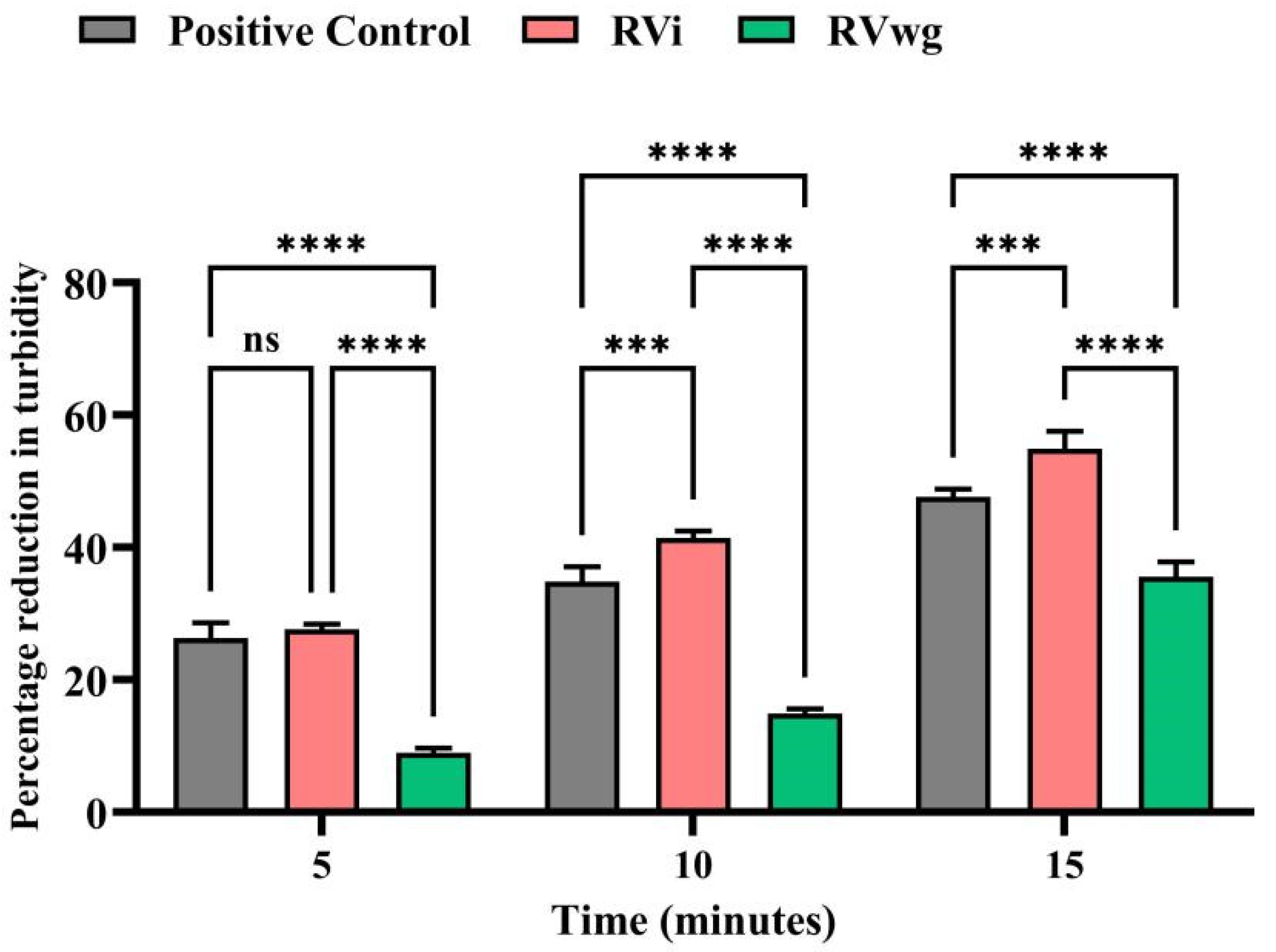
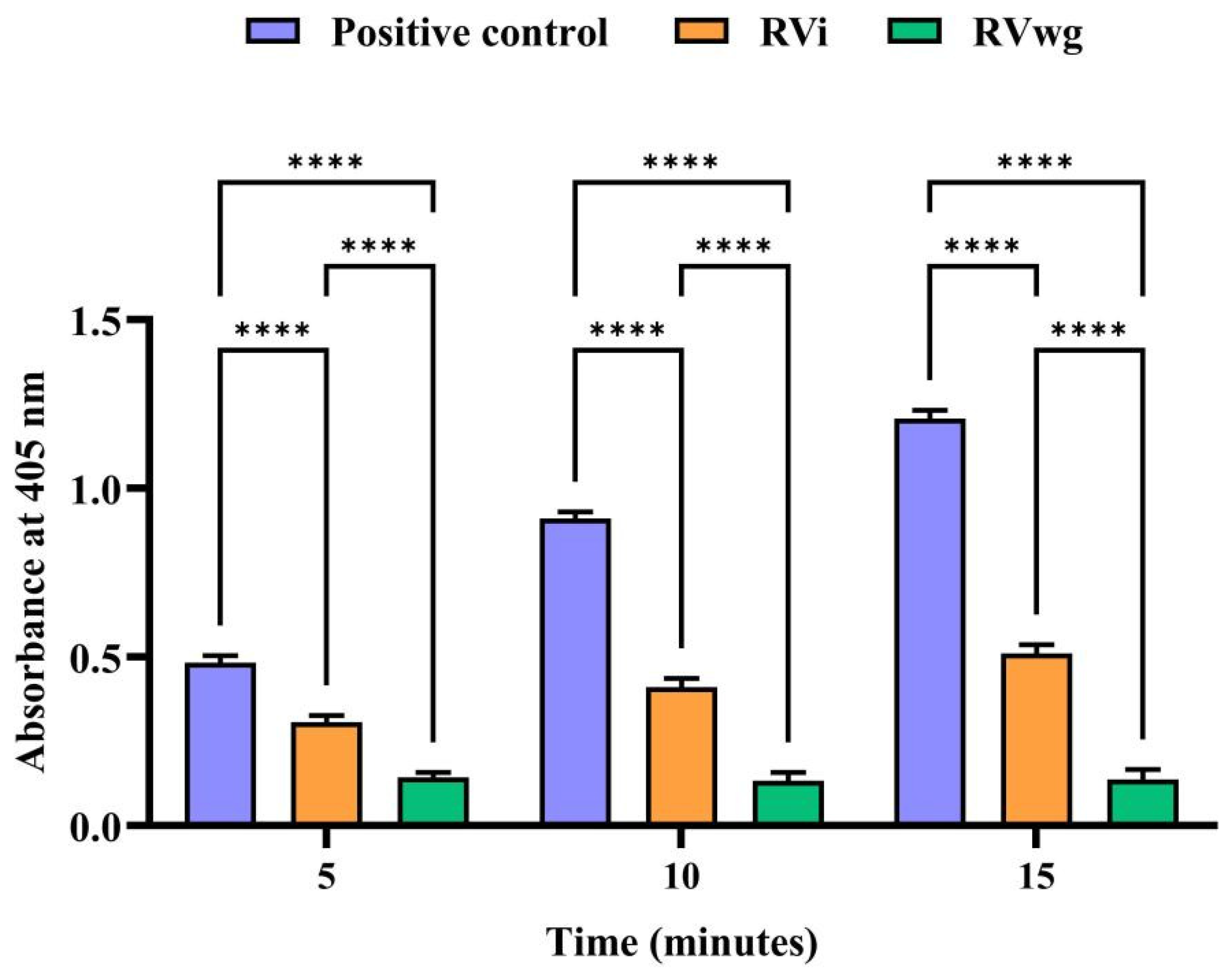
2.2. RVwg Venom Exhibited Higher Fibrinogenolytic and Comparable Hyaluronidase Activities than RVi Venom
2.3. RVi Venom Exhibited Higher Phospholipase A2 and L-Amino Acid Oxidase Activities
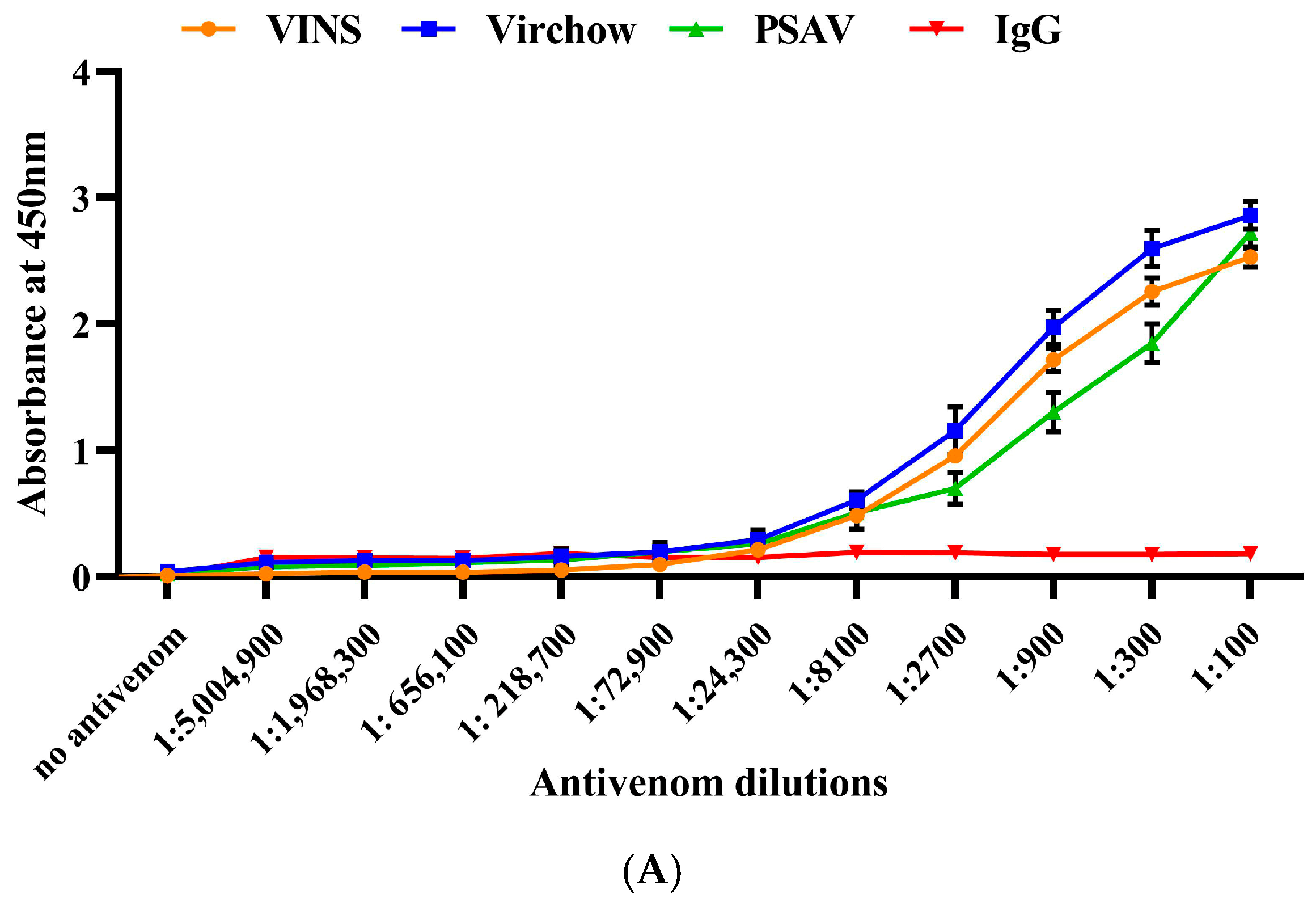
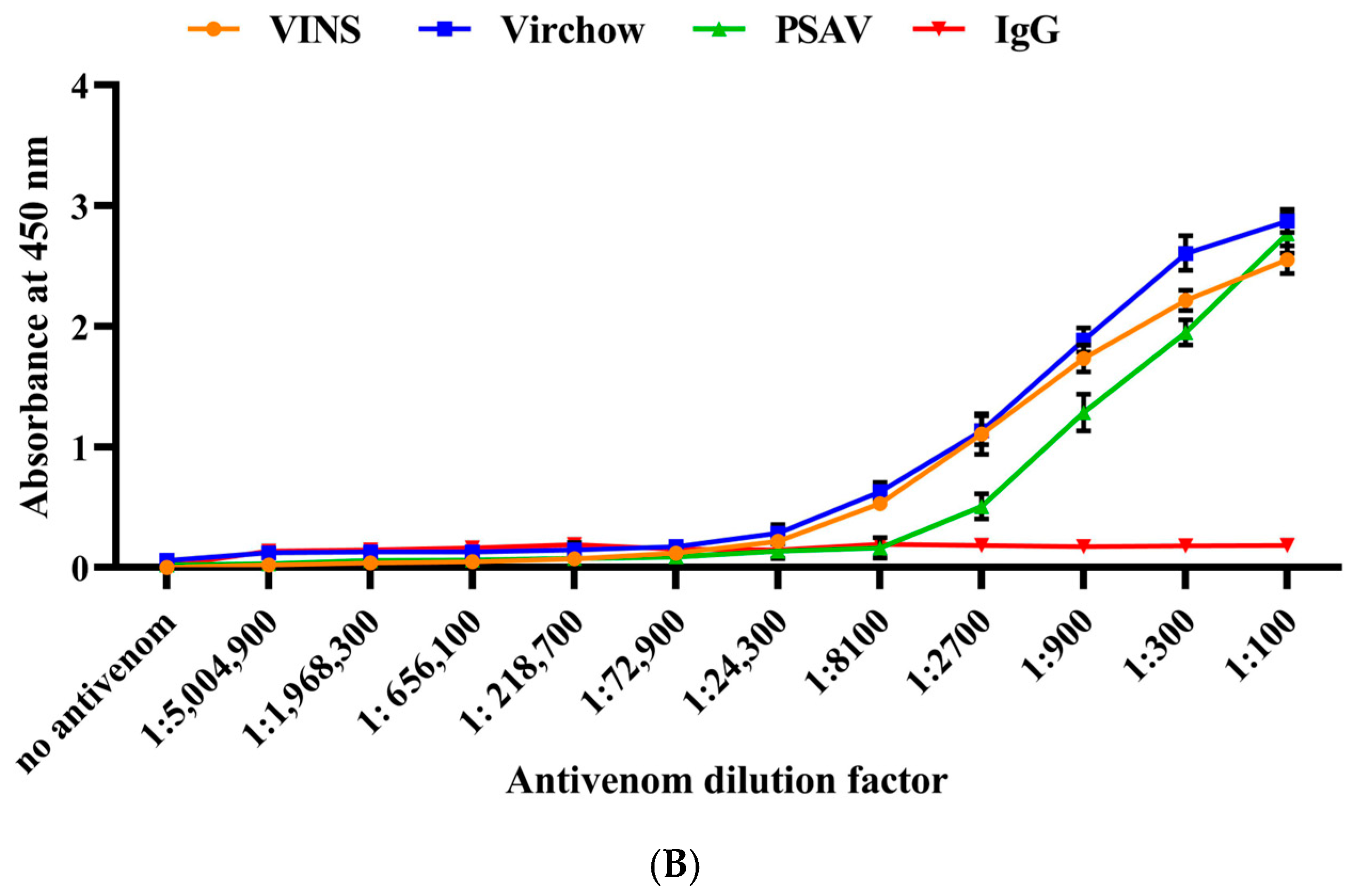
2.4. Immunological Cross-Reactivity of RVi and RVwg Venom Using Indian Polyvalent Antivenoms
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Chemicals
4.2. Venom and Antivenom
4.3. Protein Estimation
4.4. SDS-PAGE and In-Gel Digestion
4.5. Tandem Mass Spectrometry
4.6. Data Analysis by Mascot and Proteome Scaffold
4.7. Functional Assays
4.7.1. PLA2 Assay
4.7.2. Hyaluronidase Assay
4.7.3. L-Amino Acid Oxidase Assay
4.7.4. Fibrinogenolytic Assay
4.8. Immunological Cross-Reactivity Studies
4.8.1. End-Point Titration ELISA
4.8.2. Immunoblotting
4.9. Proteomics Data Availability
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Snakebite Envenoming; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2019 Snakebite Envenomation Collaborators. Global mortality of snakebite envenoming between 1990 and 2019. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, I.D.; Norris, R.L. Snakes of medical importance in India: Is the concept of the “Big 4” still relevant and useful? Wilderness Environ. Med. 2007, 18, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahasandana, S.; Rungruxsirivorn, Y.; Chantarangkul, V. Clinical manifestations of bleeding following Russell’s viper and Green pit viper bites in adults. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1980, 11, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.S.; Narayanan, S.; Udayabhaskaran, V.; Thulaseedharan, N.K. Clinical and epidemiologic profile and predictors of outcome of poisonous snake bites—An analysis of 1,500 cases from a tertiary care center in Malabar, North Kerala, India. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2018, 11, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, I.; Mohamed, F.; Buckley, N.A.; Gawarammana, I.B.; Dissanayake, D.M.; Chathuranga, U.; Munasinghe, M.; Maduwage, K.; Jayamanne, S.; Endre, Z.H.; et al. Early identification of acute kidney injury in Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) envenoming using renal biomarkers. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, M.; Saurabh, S.; Sagar, P.; Bammigatti, C.; Dutta, T.K. A simple mortality risk prediction score for viper envenoming in India (VENOMS): A model development and validation study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraweera, W.; Warrell, D.; Whitaker, R.; Menon, G.; Rodrigues, R.; Fu, S.H.; Begum, R.; Sati, P.; Piyasena, K.; Bhatia, M.; et al. Trends in snakebite deaths in India from 2000 to 2019 in a nationally representative mortality study. eLife 2020, 9, e54076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.L.; Viegas, M.F.; da Silva, S.L.; Soares, A.M.; Ramos, M.J.; Fernandes, P.A. The chemistry of snake venom and its medicinal potential. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2022, 6, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senji Laxme, R.R.; Khochare, S.; Attarde, S.; Suranse, V.; Iyer, A.; Casewell, N.R.; Whitaker, R.; Martin, G.; Sunagar, K. Biogeographic venom variation in Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) and the preclinical inefficacy of antivenom therapy in snakebite hotspots. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm, M.; Hempel, B.F.; Sussmuth, R.D. Old World Vipers-A Review about Snake Venom Proteomics of Viperinae and Their Variations. Toxins 2021, 13, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanuopadath, M.; Raveendran, D.; Nair, B.G.; Nair, S.S. Venomics and antivenomics of Indian spectacled cobra (Naja naja) from the Western Ghats. Acta Trop. 2022, 228, 106324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, N.B.; Uma, B.; Bhatt, S.K.; Gowda, V.T. Comparative characterisation of Russell’s viper (Daboia/Vipera russelli) venoms from different regions of the Indian peninsula. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1428, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, G.P.; Gowda, T.V. Geographical variation in India in the composition and lethal potency of Russell’s viper (Vipera russelli) venom. Toxicon 1988, 26, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, B.; Patra, A.; Das, A.; Mukherjee, A.K. Proteomic Analysis and Immuno-Profiling of Eastern India Russell’s Viper (Daboia russelii) Venom: Correlation between RVV Composition and Clinical Manifestations Post RV Bite. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2819–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, B.; Patra, A.; Mukherjee, A.K. Unraveling the Proteome Composition and Immuno-profiling of Western India Russell’s Viper Venom for In-Depth Understanding of Its Pharmacological Properties, Clinical Manifestations, and Effective Antivenom Treatment. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisal, T.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, N.H.; Sim, S.M.; Gnanathasan, C.A.; Tan, C.H. Proteomics, toxicity and antivenom neutralization of Sri Lankan and Indian Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) venoms. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 27, e20200177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, B.; Singh, S.; Patra, A.; Mukherjee, A.K. Quantitative proteomic analysis and antivenom study revealing that neurotoxic phospholipase A(2) enzymes, the major toxin class of Russell’s viper venom from southern India, shows the least immuno-recognition and neutralization by commercial polyvalent antivenom. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118 Pt A, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Quesada-Bernat, S.; Villalta, M.; Baal, J.; Chowdhury, M.A.W.; Leon, G.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Kuch, U.; Calvete, J.J. Phylovenomics of Daboia russelii across the Indian subcontinent. Bioactivities and comparative in vivo neutralization and in vitro third-generation antivenomics of antivenoms against venoms from India, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka. J. Proteom. 2019, 207, 103443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Das, D.; Iyer, J.K.; Kini, R.M.; Doley, R. Unveiling the complexities of Daboia russelii venom, a medically important snake of India, by tandem mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2015, 107 Pt B, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, K.; Alangode, A.; Menon, J.C.; Raveendran, D.; Nair, S.S.; Reick, M.; Nair, B.G.; Reick, M.; Vanuopadath, M. Comparative functional characterization and in vitro immunological cross-reactivity studies on Daboia russelii and Craspedocephalus malabaricus venom. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2024, 118, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanuopadath, M.; Rajan, K.; Alangode, A.; Nair, S.S.; Nair, B.G. The Need for Next-Generation Antivenom for Snakebite Envenomation in India. Toxins 2023, 15, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanuopadath, M.; Shaji, S.K.; Raveendran, D.; Nair, B.G.; Nair, S.S. Delineating the venom toxin arsenal of Malabar pit viper (Trimeresurus malabaricus) from the Western Ghats of India and evaluating its immunological cross-reactivity and in vitro cytotoxicity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Rex, D.A.B.; Schuster, D.; Neely, B.A.; Rosano, G.L.; Volkmar, N.; Momenzadeh, A.; Peters-Clarke, T.M.; Egbert, S.B.; Kreimer, S.; et al. Comprehensive Overview of Bottom-Up Proteomics Using Mass Spectrometry. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2024, 4, 338–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Haripriya, V.; Patra, A.; Kalita, B.; Vanuopadath, M.; Nair, B.G.; Mahato, R.; Lalremsanga, H.T.; Khan, M.R.; Bala, A.; et al. Proteomic and functional characterisation of Trimeresurus popeiorum (Pope’s pit viper) venom proteins: Role of enzymatic and non-enzymatic venom toxins in envenomation pathophysiology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 304 Pt 1, 140638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M. Excitement ahead: Structure, function and mechanism of snake venom phospholipase A2 enzymes. Toxicon 2003, 42, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, B.; Mackessy, S.P.; Mukherjee, A.K. Proteomic analysis reveals geographic variation in venom composition of Russell’s Viper in the Indian subcontinent: Implications for clinical manifestations post-envenomation and antivenom treatment. Expert. Rev. Proteom. 2018, 15, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senji Laxme, R.R.; Khochare, S.; Bhatia, S.; Martin, G.; Sunagar, K. From birth to bite: The evolutionary ecology of India’s medically most important snake venoms. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaoba, O.T.; Karina Dos Santos, P.; Selistre-de-Araujo, H.S.; Ferreira de Souza, D.H. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases (SVMPs): A structure-function update. Toxicon X 2020, 7, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, S.M. The long road of research on snake venom serine proteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siigur, E.; Aaspollu, A.; Siigur, J. Anticoagulant serine fibrinogenases from Vipera lebetina venom: Structure-function relationships. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 89, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swenson, S.; Toombs, C.F.; Pena, L.; Johansson, J.; Markland, F.S., Jr. Alpha-fibrinogenases. Curr. Drug Targets Cardiovasc. Haematol. Disord. 2004, 4, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Chijiwa, T.; Oda-Ueda, N.; Ohno, M. Molecular diversity and accelerated evolution of C-type lectin-like proteins from snake venom. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izidoro, L.F.; Sobrinho, J.C.; Mendes, M.M.; Costa, T.R.; Grabner, A.N.; Rodrigues, V.M.; da Silva, S.L.; Zanchi, F.B.; Zuliani, J.P.; Fernandes, C.F.; et al. Snake venom L-amino acid oxidases: Trends in pharmacology and biochemistry. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 196754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadokoro, T.; Modahl, C.M.; Maenaka, K.; Aoki-Shioi, N. Cysteine-Rich Secretory Proteins (CRISPs) From Venomous Snakes: An Overview of the Functional Diversity in A Large and Underappreciated Superfamily. Toxins 2020, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, S.; McManus, D.P. Structure and function of invertebrate Kunitz serine protease inhibitors. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 39, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhananjaya, B.L.; D’souza, C.J.M. An overview on nucleases (DNase, RNase, and phosphodiesterase) in snake venoms. Biochemistry 2010, 75, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechter, O. Studies on Spreading Factors: I. The Importance of Mechanical Factors in Hyaluronidase Action in Skin. J. Exp. Med. 1947, 85, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukrittayakamee, S.; Warrell, D.A.; Desakorn, V.; McMichael, A.J.; White, N.J.; Bunnag, D. The hyaluronidase activities of some Southeast Asian snake venoms. Toxicon 1988, 26, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, S.D. Ophidian envenomation strategies and the role of purines. Toxicon 2002, 40, 335–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Ullah, K.; Ali, H.; Betzel, C.; Ur Rehman, S. The Sequence and a Three-Dimensional Structural Analysis Reveal Substrate Specificity Among Snake Venom Phosphodiesterases. Toxins 2019, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Masood, R. The Sequence and Three-Dimensional Structure Characterization of Snake Venom Phospholipases B. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, R.; Thakur, S.; Blotra, A.; Sahu, A.; Vasudevan, K.; Reza, M.A.; Doley, R. Proteome analysis of Daboia russelii venom, a medically important snake from the Indian sub-continent. Toxicon 2024, 237, 107532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.M.; Huang, K.F.; Tsai, I.H. Snake venom glutaminyl cyclases: Purification, cloning, kinetic study, recombinant expression, and comparison with the human enzyme. Toxicon 2014, 86, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trummal, K.; Tonismagi, K.; Paalme, V.; Jarvekulg, L.; Siigur, J.; Siigur, E. Molecular diversity of snake venom nerve growth factors. Toxicon 2011, 58, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Watson, K.A.; Harrison, R.A.; Gibbins, J.M.; Hutchinson, E.G. Purification and functional characterisation of rhiminopeptidase A, a novel aminopeptidase from the venom of Bitis gabonica rhinoceros. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.G.; Pucca, M.B.; Oliveira, I.S.; Cerni, F.A.; Jacob, B.; Arantes, E.C. Snake venom vascular endothelial growth factors (svVEGFs): Unravelling their molecular structure, functions, and research potential. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2021, 60, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, N.; Laxme, R.R.S.; Sunagar, K. Significant Serpents: Predictive Modelling of Bioclimatic Venom Variation in Russell’s Viper. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2025, 19, e0012949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnan, M.; Saurabh, S.; Dutta, T.K. Clinical profile of viper envenomations in Kerala, India: Some unanswered questions. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2018, 11, 391–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchithra, N.; Pappachan, J.M.; Sujathan, P. Snakebite envenoming in Kerala, South India: Clinical profile and factors involved in adverse outcomes. Emerg. Med. J. 2008, 25, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudresha, G.V.; Khochare, S.; Casewell, N.R.; Sunagar, K. Preclinical evaluation of small molecule inhibitors as early intervention therapeutics against Russell’s viper envenoming in India. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanuopadath, M.; Sajeev, N.; Murali, A.R.; Sudish, N.; Kangosseri, N.; Sebastian, I.R.; Jain, N.D.; Pal, A.; Raveendran, D.; Nair, B.G.; et al. Mass spectrometry-assisted venom profiling of Hypnale hypnale found in the Western Ghats of India incorporating de novo sequencing approaches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118 Pt B, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Reghu, N.; Nair, B.G.; Vanuopadath, M. The Role of Snake Venom Proteins in Inducing Inflammation Post-Envenomation: An Overview on Mechanistic Insights and Treatment Strategies. Toxins 2024, 16, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Kolker, E.; Aebersold, R. Empirical statistical model to estimate the accuracy of peptide identifications made by MS/MS and database search. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5383–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Keller, A.; Kolker, E.; Aebersold, R. A statistical model for identifying proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4646–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizcaino, J.A.; Deutsch, E.W.; Wang, R.; Csordas, A.; Reisinger, F.; Rios, D.; Dianes, J.A.; Sun, Z.; Farrah, T.; Bandeira, N.; et al. ProteomeXchange provides globally coordinated proteomics data submission and dissemination. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizcaino, J.A.; Csordas, A.; del-Toro, N.; Dianes, J.A.; Griss, J.; Lavidas, I.; Mayer, G.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Ternent, T.; et al. 2016 update of the PRIDE database and its related tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D447–D456, Erratum in Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 11033. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, J.C.; Nair, B.; Pati, S.; Pillay, V.V.; Mahapatra, A.; Sreekrishnan, T.P.; Vanuopadath, M.; John, D.; Nair, S.B.; Sahoo, P.K.; et al. From neglect to equity in snakebite envenoming; what the ICMR-Collaborative Centre of Excellence (CCoE) targets. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Protein Family | Central India | Eastern India | Western India | Southern India | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Madhya Pradesh [11] | Burdwan [16] | Nadia [16] | Mumbai [17] | Maharashtra [11] | Tamil Nadu [18] | Tamil Nadu [19] | Tamil Nadu [20] | Tamil Nadu [21] | Tamil Nadu (Current study) * | Kerala (Current Study) * | |
| PLA2 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| SVMP | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| SVSP | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| CRISPS | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| LAAO | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| CTLs | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + |
| PLB | - | - | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | + | + |
| KPI | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 3FTx | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| NGF | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| VEGF | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + |
| HYAL | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + |
| PDE | - | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| 5′NUC | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| Dis | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | - |
| AP | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| DNase | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + |
| GC | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | + | + |
| CP | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reghu, N.; Rao, S.; Raveendran, D.; Nair, B.G.; Vanuopadath, M. Comparative Proteomics, Functional Characterization and Immunological Cross-Reactivity Studies on Russell’s Viper Venom from Two Distinct Geographical Regions in South India. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199734
Reghu N, Rao S, Raveendran D, Nair BG, Vanuopadath M. Comparative Proteomics, Functional Characterization and Immunological Cross-Reactivity Studies on Russell’s Viper Venom from Two Distinct Geographical Regions in South India. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199734
Chicago/Turabian StyleReghu, Nisha, Sudharshan Rao, Dileepkumar Raveendran, Bipin Gopalakrishnan Nair, and Muralidharan Vanuopadath. 2025. "Comparative Proteomics, Functional Characterization and Immunological Cross-Reactivity Studies on Russell’s Viper Venom from Two Distinct Geographical Regions in South India" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199734
APA StyleReghu, N., Rao, S., Raveendran, D., Nair, B. G., & Vanuopadath, M. (2025). Comparative Proteomics, Functional Characterization and Immunological Cross-Reactivity Studies on Russell’s Viper Venom from Two Distinct Geographical Regions in South India. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199734






