Edible Herb Aster glehni Alleviates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Chondrocytes by Regulating p38 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways with Partial Involvement of Its Major Component, 3,5-Dicaffeoylqunic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
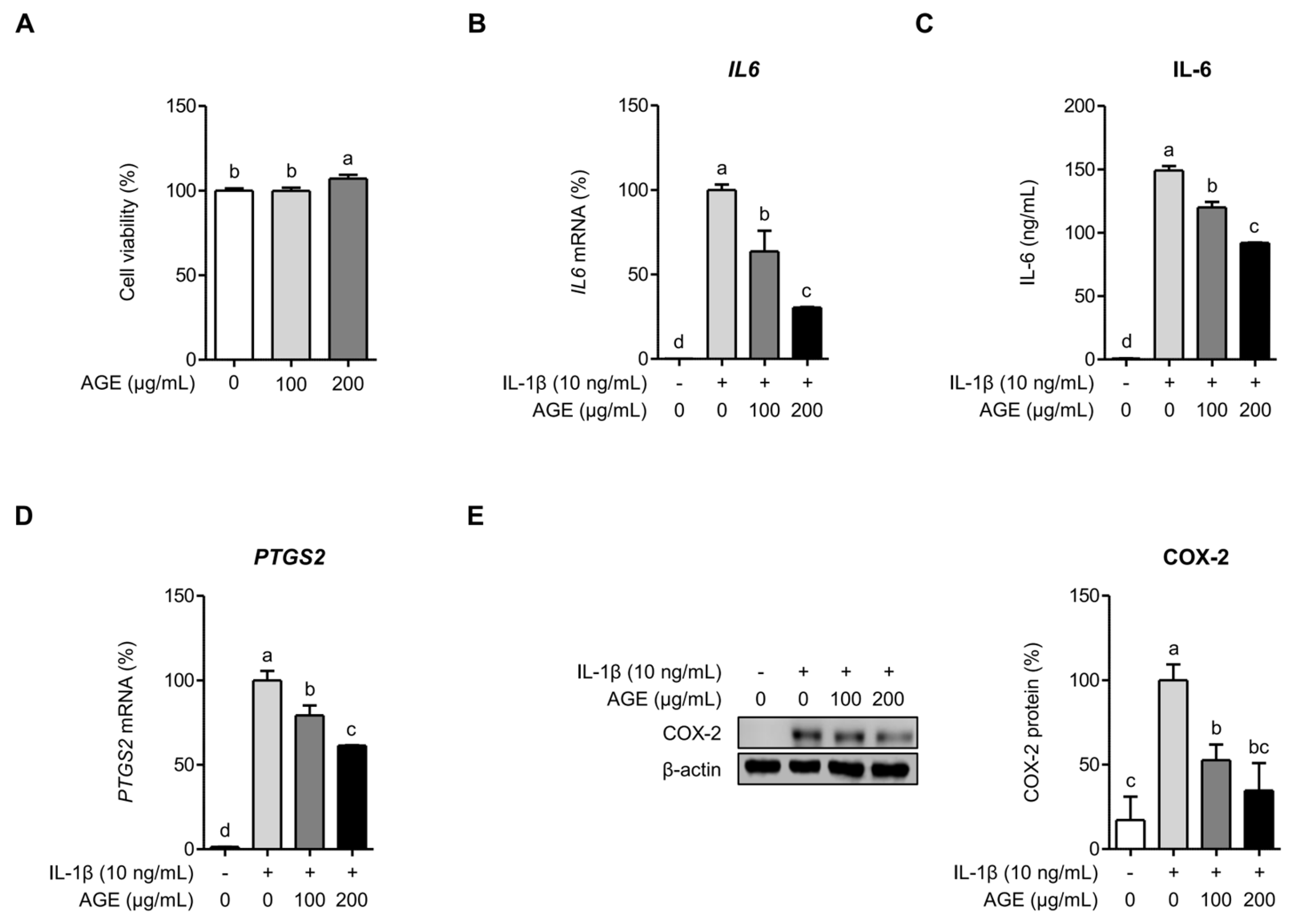
2.1. AGE Suppresses IL-6 and COX-2 Expressions in Chondrocytes
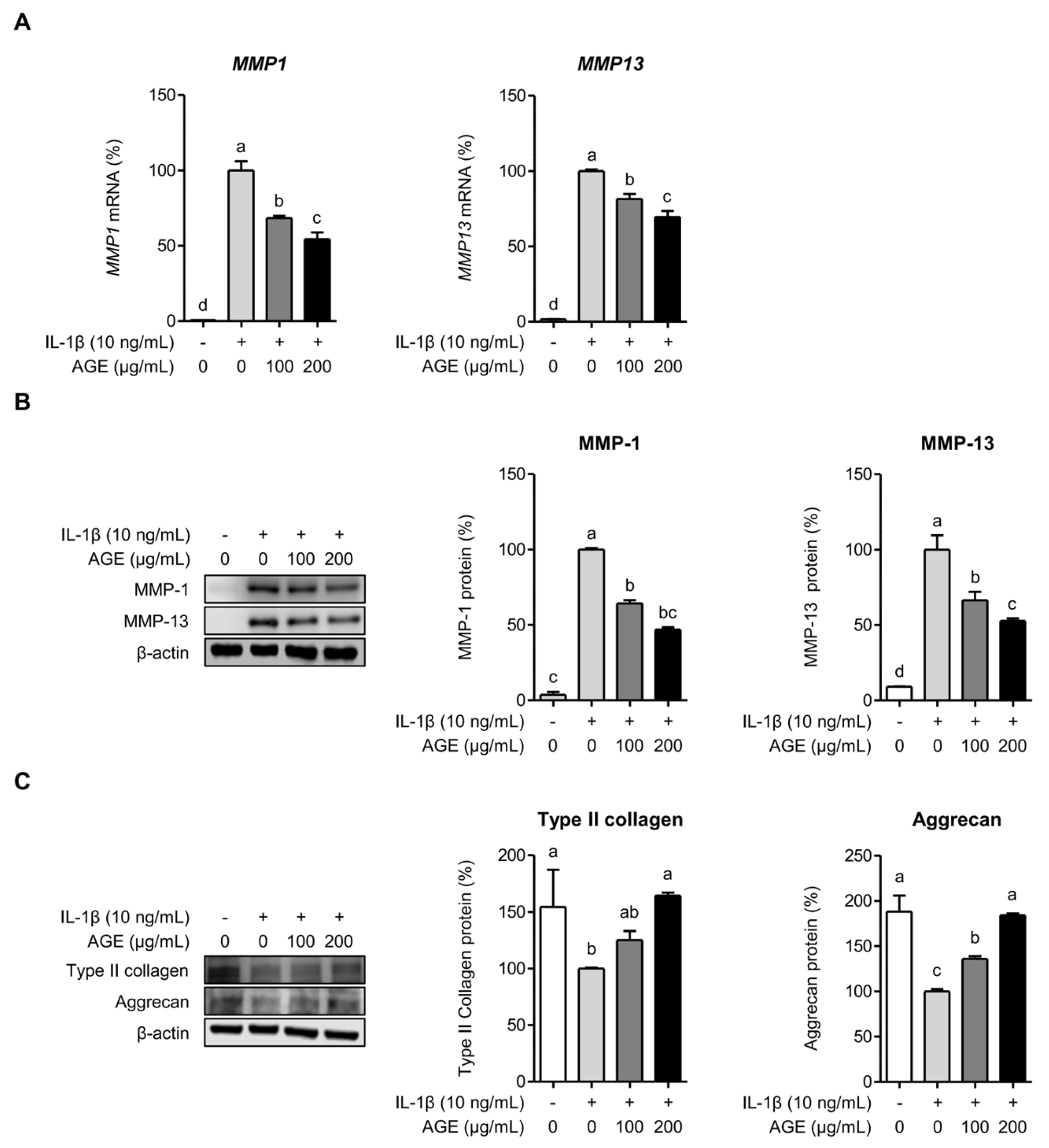
2.2. AGE Inhibits MMP Expressions but Enhances Type II Collagen and Aggrecan Expressions in Chondrocytes
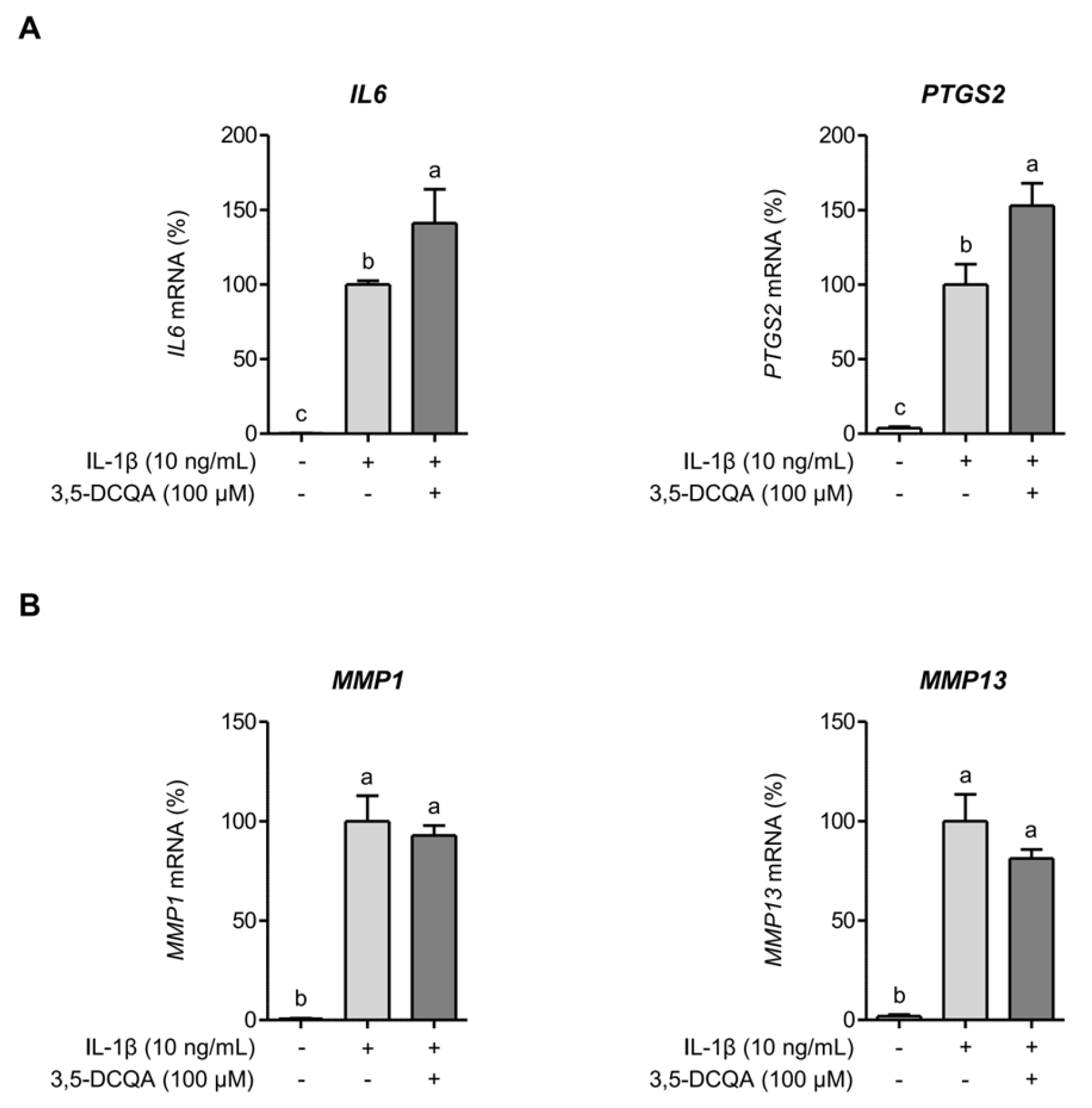
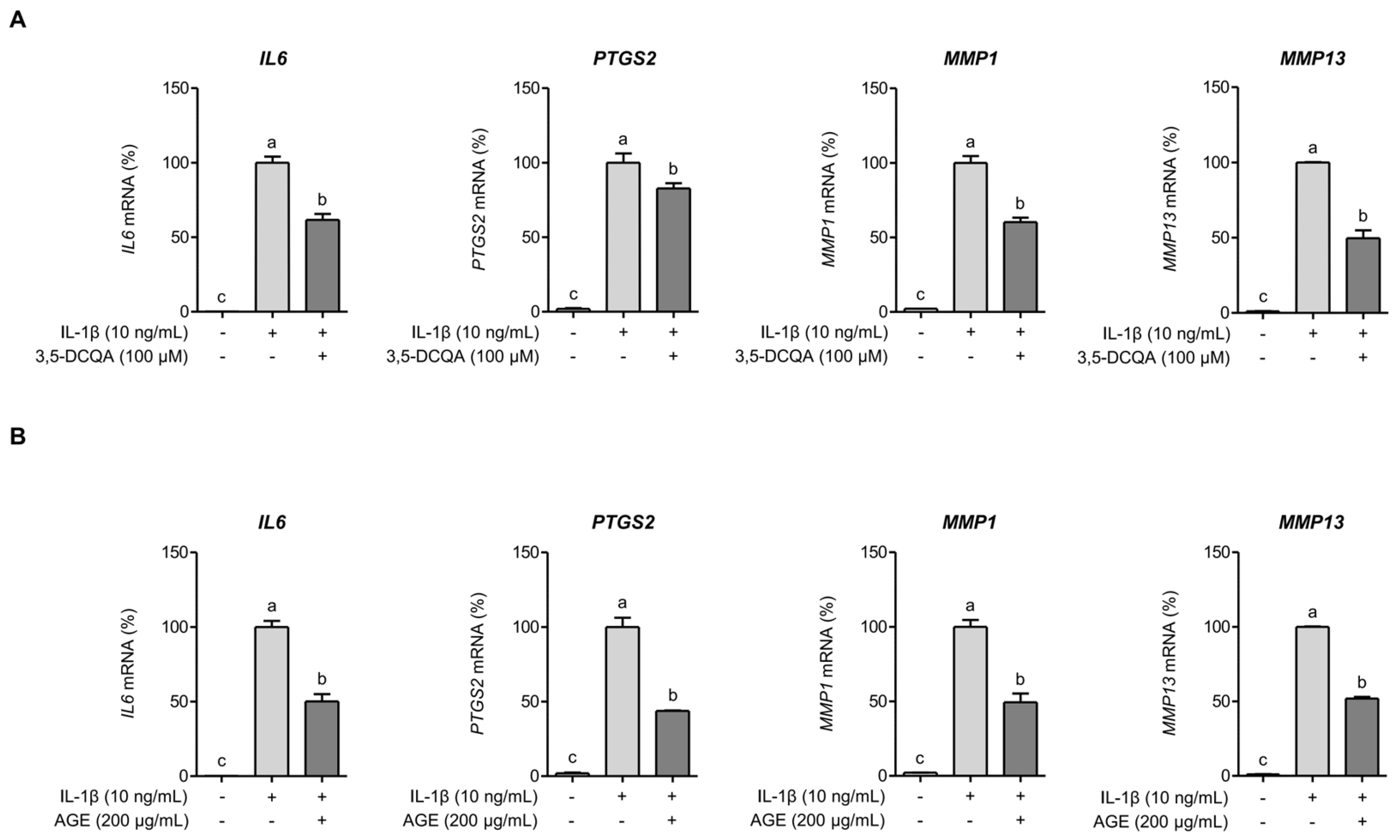
2.3. 3,5-DCQA Is Partly Involved in the Suppression of IL-1β-Induced Inflammatory Mediators and MMPs in Chondrocytes
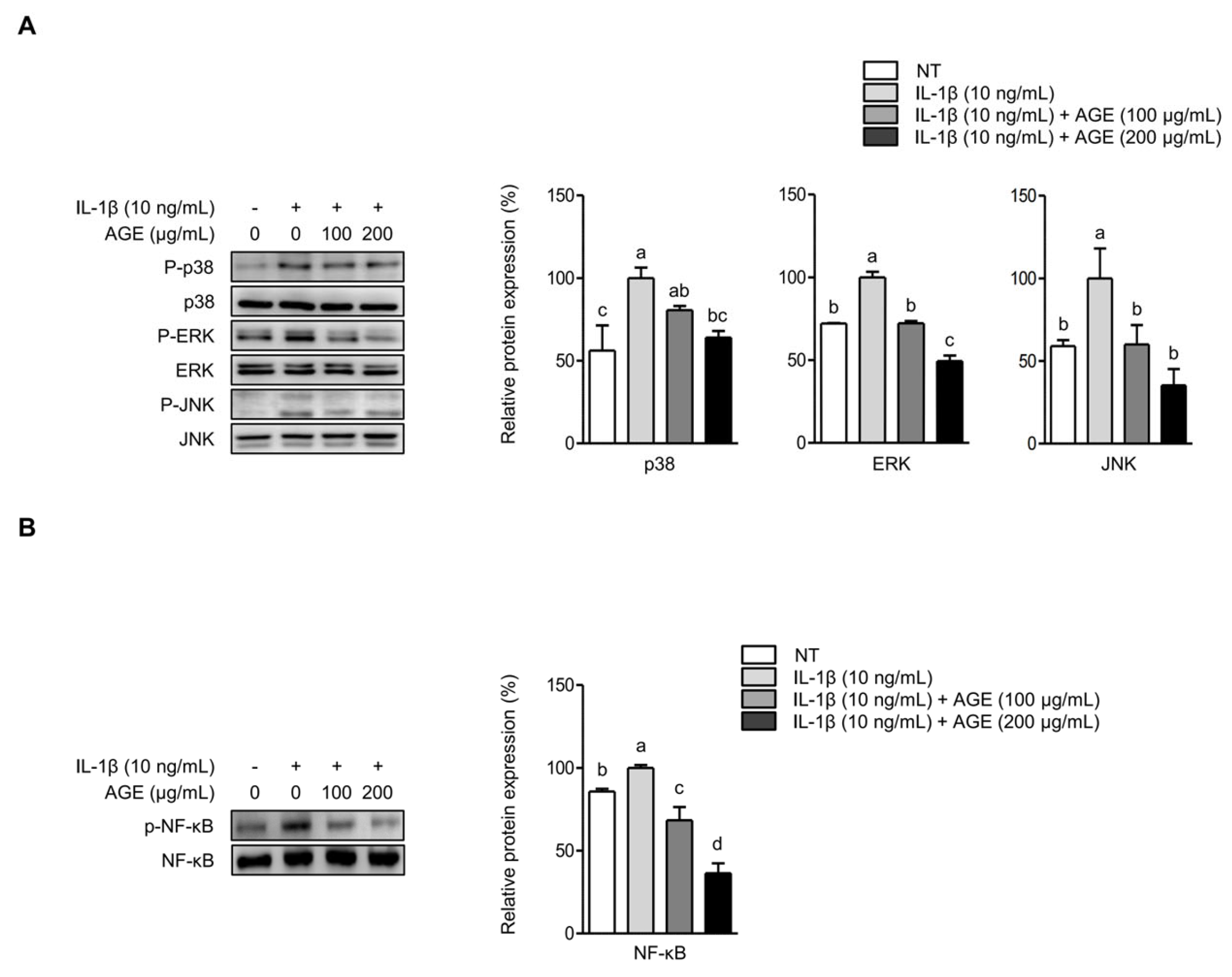
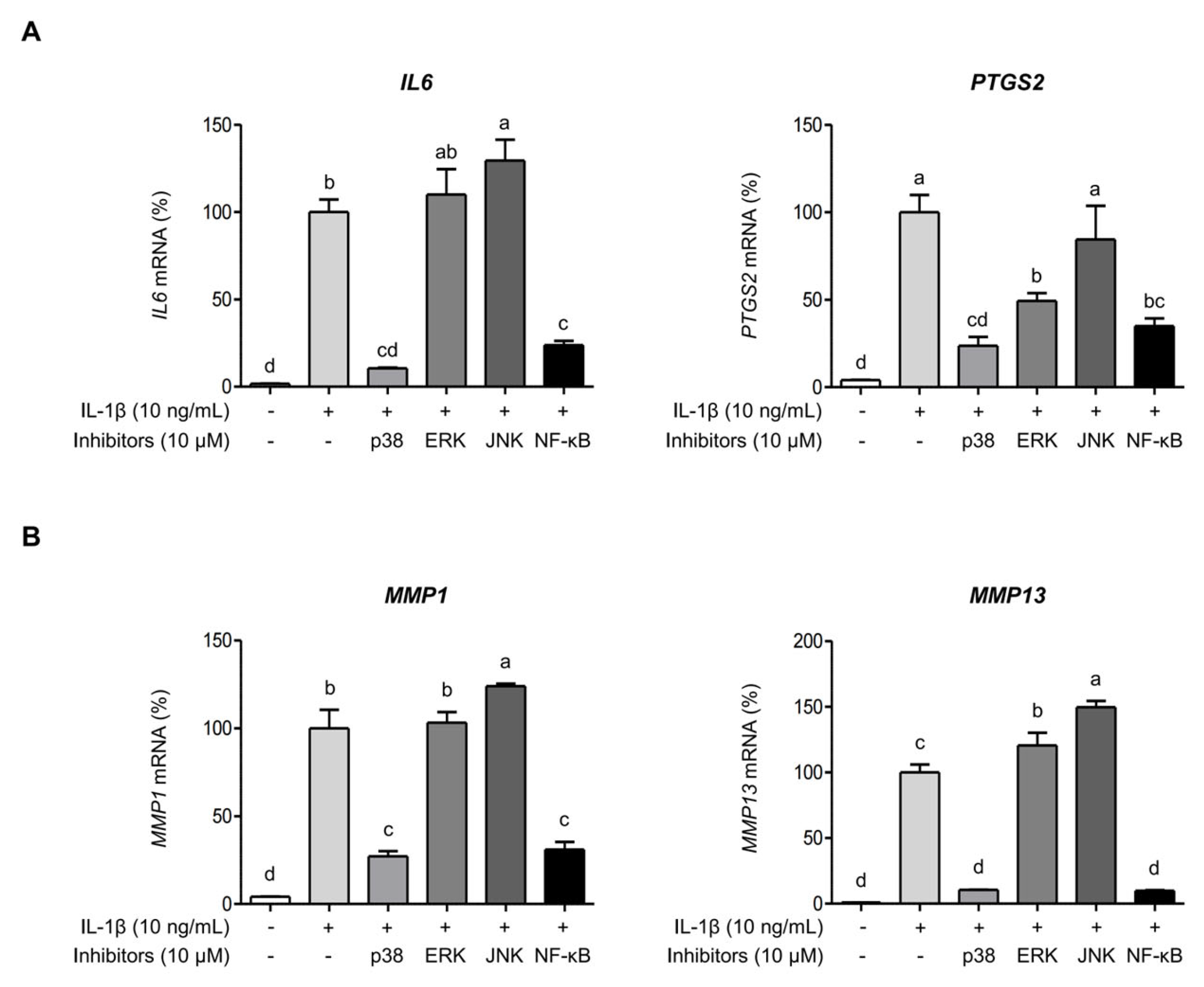
2.4. AGE Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Expressions of IL-6, COX-2, and MMPs Through the Suppression of p38 Kinase and NF-κB Signaling Pathways
2.5. AGE Attenuates Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2)-Induced Oxidative Stress in Chondrocytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. AGE Preparation
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.4. Determination of IL-6 Protein
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Confirmation of Intracellular Signaling Pathways
4.7. Cell Viability and Fluorometric Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vina, E.R.; Kwoh, C.K. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: Literature update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleton, C. Osteoarthritis year in review 2017: Biology. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Lin, J.; Wei, M.; Teng, Y.; He, Q.; Yang, G.; Yang, X. Sustained Akt signaling in articular chondrocytes causes osteoarthritis via oxidative stress-induced senescence in mice. Bone Res. 2019, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengprasert, P.; Kamenkit, O.; Tanavalee, A.; Reantragoon, R. The Immunological Facets of Chondrocytes in Osteoarthritis: A Narrative Review. J. Rheumatol. 2023, 51, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.R.; Attur, M.; Patel, R.N.; Thakker, G.D.; Marshall, P.J.; Rediske, J.; Stuchin, S.A.; Patel, I.R.; Abramson, S.B. Superinduction of cyclooxygenase-2 activity in human osteoarthritis-affected cartilage. Influence of nitric oxide. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; He, C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 44, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Zhang, B.; Xiang, W.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Feng, D.; Gong, Y.; Wu, J. Natural products in osteo-arthritis treatment: Bridging basic research to clinical applications. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Jang, Y.-N.; Han, Y.-M.; Kim, H.-M.; Jin, C.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, H.S. Aster glehni extract containing caffeoylquinic compounds protects human keratinocytes through the TRPV4-PPARδ-AMPK Pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 9616574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Chung, K.-S.; Jin, B.-R.; Cheon, S.-Y.; Nugroho, A.; Roh, S.-S.; An, H.-J. Anti-inflammatory effects of an ethanol extract of Aster glehni via inhibition of NF-κB activation in mice with DSS-induced colitis. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.K.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Jeong, J.; Han, E.H.; Lee, S.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, J. Neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory effects of ethanolic extract from leaves and stems of Aster glehni. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 79, 104400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Jang, Y.-N.; Han, Y.-M.; Kim, H.-M.; Jeong, J.-M.; Son, M.J.; Jin, C.B.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, H.S. Caffeoylquinic Acid-Rich Extract of Aster glehni F. Schmidt Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver through the Regulation of PPARδ and Adiponectin in ApoE KO Mice. PPAR Res. 2017, 2017, 3912567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Joo, T.; Jhoo, J.-W. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid isolated from Ligularia fischeri leaves. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, C.; Kim, Y.T. 3, 5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid attenuates microglial activation-mediated inflammatory pain by enhancing autophagy through the suppression of MCP3/JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Yu, X.; Liang, S.; Cheng, P.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.-Y.; Lv, Z.-T.; Wan, J.; Mo, H.; Zhu, W.-T.; et al. Physalin A Inhibits MAPK and NF-κB Signal Transduction Through Integrin αVβ3 and Exerts Chondroprotective Effect. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 761922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, I.-C.; Chuang, S.-T.; Hsu, C.-H.; Sun, Y.-J.; Lin, F.-H. C-phycocyanin alleviates osteoarthritic injury in chondrocytes stimulated with H2O2 and compressive stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.T.; Yunus, M.H.M.; Ugusman, A.; Yazid, M.D. Natural Compounds Affecting Inflammatory Pathways of Osteoarthritis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, A.; Jung, S.H.; Pyo, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Jo, S.; Kim, L.; Lee, E.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, S.-R. 3′-Sialyllactose Protects SW1353 Chondrocytic Cells from Interleukin-1β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 609817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.A.; Yoon, S.R.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kang, M.-S.; Kim, H.-R.; Shin, H.-S.; Kang, S.-S. Antiperiodontitis impact of extract from edible herb Aster glehni and its bioactive compound, 3,5-dicaffeolyquinic acid. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roover, A.; Escribano-Núñez, A.; Monteagudo, S.; Lories, R. Fundamentals of osteoarthritis: Inflammatory mediators in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2023, 31, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegertjes, R.; Loo, F.A.J.v.d.; Davidson, E.N.B. A roadmap to target interleukin-6 in osteoarthritis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2681–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepetsos, P.; Papavassiliou, K.A.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Redox and NF-κB signaling in osteoarthritis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 132, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, M.; Nam, J. The role of changes in extracellular matrix of cartilage in the presence of inflammation on the pa-thology of osteoarthritis. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 284873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, G.; Knäuper, V.; Atkinson, S.; Butler, G.; English, W.; Hutton, M.; Stracke, J.; Clark, I. Matrix metalloproteinases in arthritic disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2002, 4, S39–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, K.; Kawato, T.; Morita, T.; Iinuma, T.; Kamio, N.; Zhao, N.; Maeno, M. Angiotensin II induces the production of MMP-3 and MMP-13 through the MAPK signaling pathways via the AT1 receptor in osteoblasts. Biochimie 2013, 95, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondergaard, B.-C.; Schultz, N.; Madsen, S.; Bay-Jensen, A.-C.; Kassem, M.; Karsdal, M. MAPKs are essential upstream sig-naling pathways in proteolytic cartilage degradation–divergence in pathways leading to aggrecanase and MMP-mediated ar-ticular cartilage degradation. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcu, K.B.; Otero, M.; Olivotto, E.; Maria Borzi, R.; Goldring, M.B. NF-κB signaling: Multiple angles to target OA. Curr. Drug Targets 2010, 11, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.Y.; Ahmad, N.; Haqqi, T.M. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salucci, S.; Falcieri, E.; Battistelli, M. Chondrocyte death involvement in osteoarthritis. Cell Tissue Res. 2022, 389, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Sequence |
|---|---|
| IL-6 (IL6) | 5′-TCCTACCCCAATTTCCAATGCT-3′ 5′-TCTGACCACAGTGAGGAATGTC-3′ |
| COX-2 (PTGS2) | 5′-GGCCATGGGGTGGACTTAAA-3′ 5′-CCCCACAGCAAACCGTAGAT-3′ |
| MMP-1 (MMP1) | 5′-AAGGCCAGTATGCACAGCTT-3′ 5′-TTTTCAACCACTGGGCCACTA-3′ |
| MMP-13 (MMP13) | 5′-AGACCTCCAGTTTGCAGAGC-3′ 5′-ATCAGGAACCCCGCATCTTG-3′ |
| SOD1 (SOD1) | 5′-AGGCATGTTGGAGACTTGGG-3′ 5′-AACGACTTCCAGCGTTTCCT-3′ |
| CAT (CAT) | 5′-TCTCACCAAGGTTTGGCCTC-3′ 5′-GCGGTGAGTGTCAGGATAGG-3′ |
| GAPDH (GAPDH) | 5′-AAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCAA-3′ 5′-ATGACAAGCTTCCCGTTCTC-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, J.; Choi, H.; Yoon, S.R.; Jeong, Y.J.; Oh, S.Y.; Kang, M.-S.; Kim, H.-R.; Shin, H.-S.; Kang, S.-S. Edible Herb Aster glehni Alleviates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Chondrocytes by Regulating p38 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways with Partial Involvement of Its Major Component, 3,5-Dicaffeoylqunic Acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199691
Baek J, Choi H, Yoon SR, Jeong YJ, Oh SY, Kang M-S, Kim H-R, Shin H-S, Kang S-S. Edible Herb Aster glehni Alleviates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Chondrocytes by Regulating p38 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways with Partial Involvement of Its Major Component, 3,5-Dicaffeoylqunic Acid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199691
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Jihyeon, Hanhee Choi, Sung Ran Yoon, Yong Jin Jeong, Shin Young Oh, Min-Sook Kang, Haeng-Ran Kim, Han-Seung Shin, and Seok-Seong Kang. 2025. "Edible Herb Aster glehni Alleviates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Chondrocytes by Regulating p38 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways with Partial Involvement of Its Major Component, 3,5-Dicaffeoylqunic Acid" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199691
APA StyleBaek, J., Choi, H., Yoon, S. R., Jeong, Y. J., Oh, S. Y., Kang, M.-S., Kim, H.-R., Shin, H.-S., & Kang, S.-S. (2025). Edible Herb Aster glehni Alleviates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Chondrocytes by Regulating p38 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways with Partial Involvement of Its Major Component, 3,5-Dicaffeoylqunic Acid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199691








