CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Targeted Mutagenesis of GmAS1/2 Genes Alters Leaf Shape in Soybean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
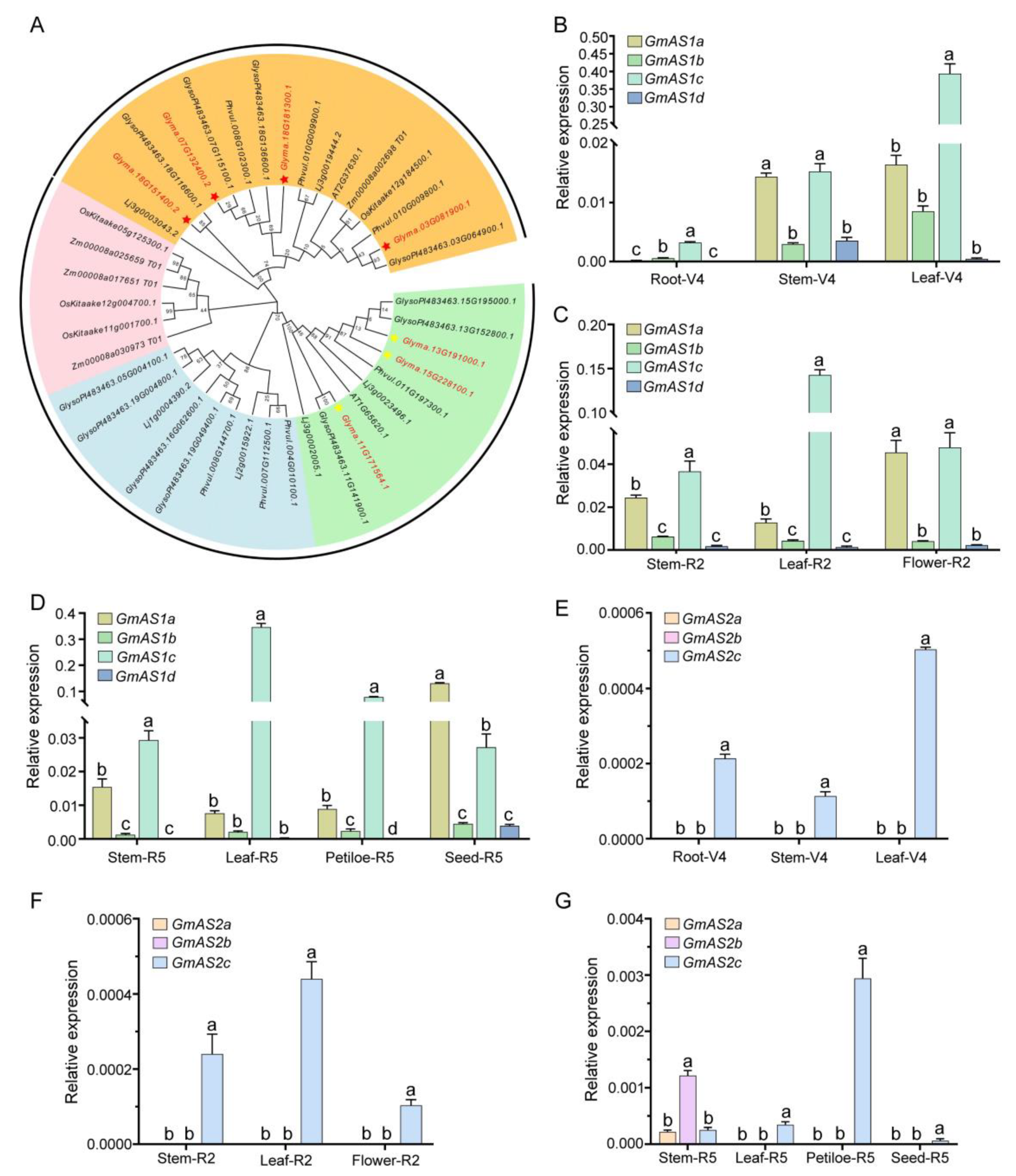
2.1. Expression Pattern of GmAS1 and GmAS2 Family Genes in Soybean
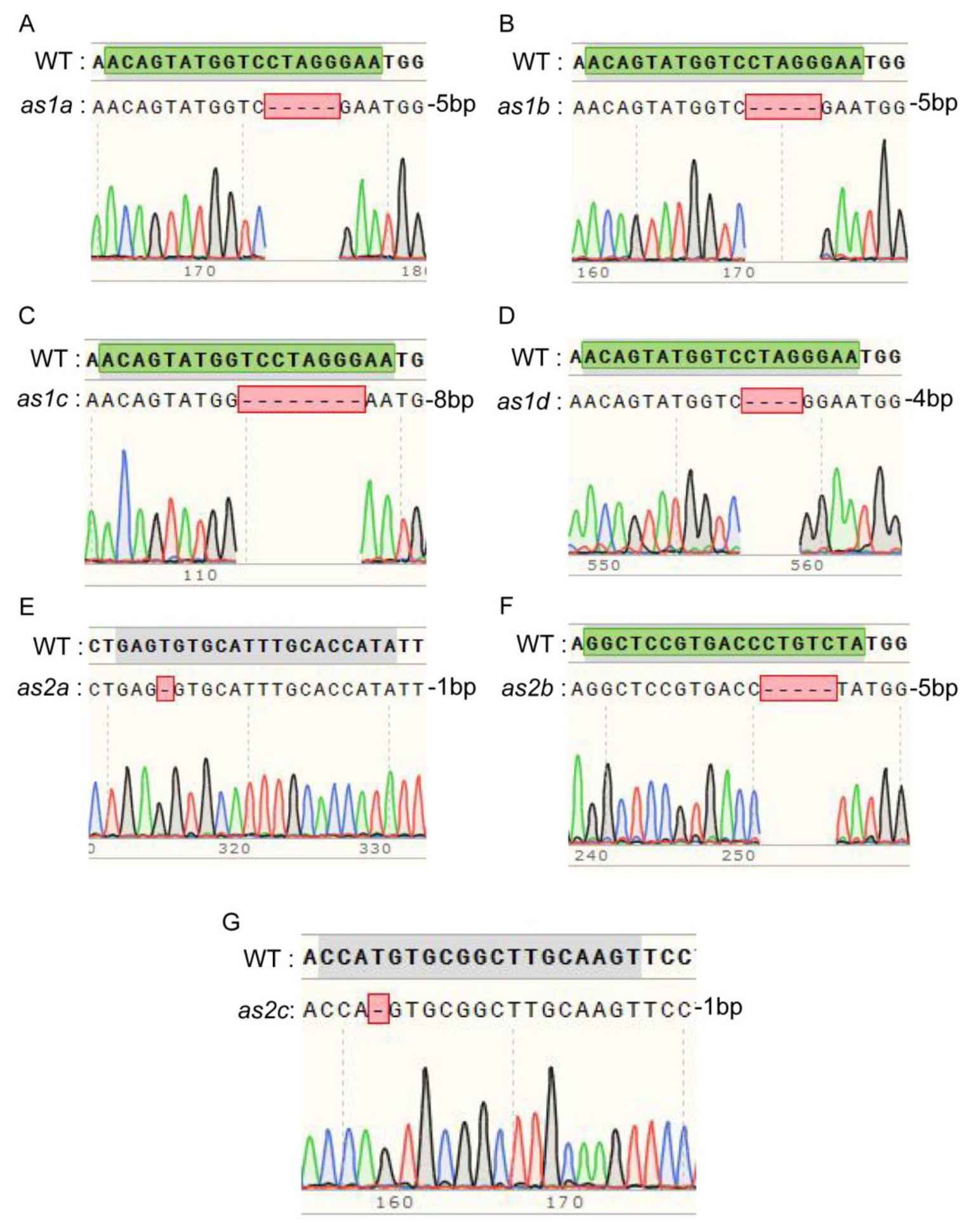
2.2. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Mutagenesis of GmAS1 and GmAS2 Gene Families in Soybean
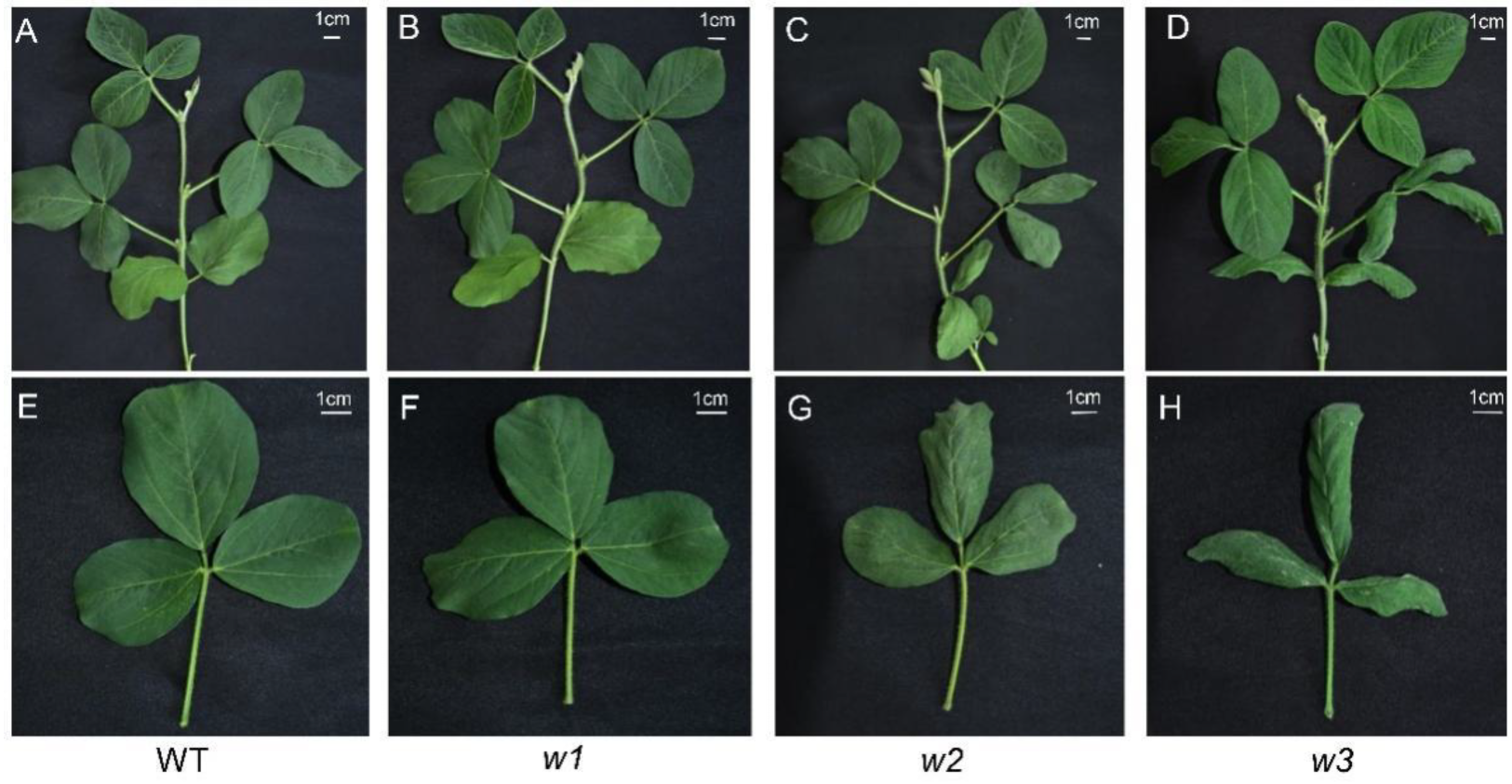
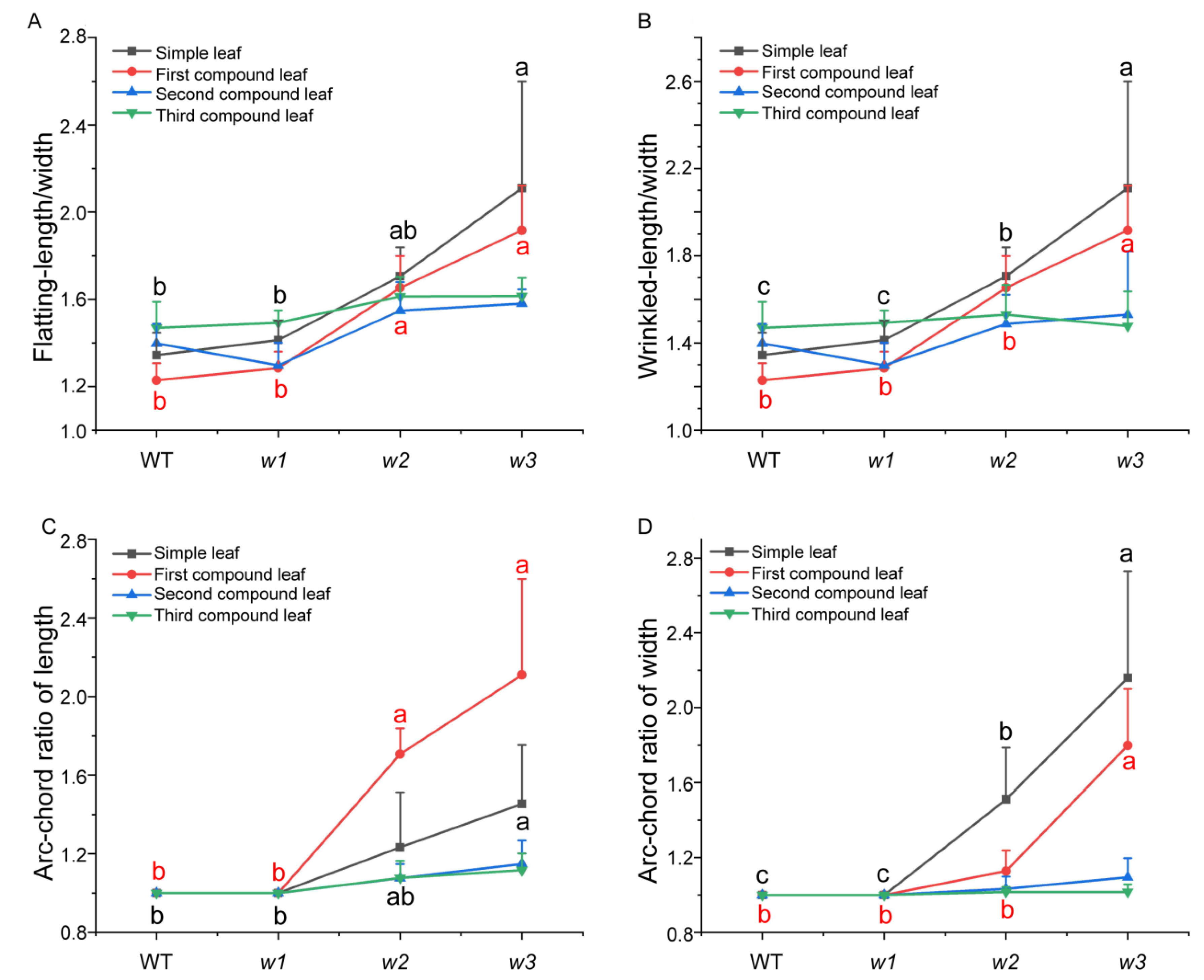
2.3. Phenotypic Characterization and Analysis
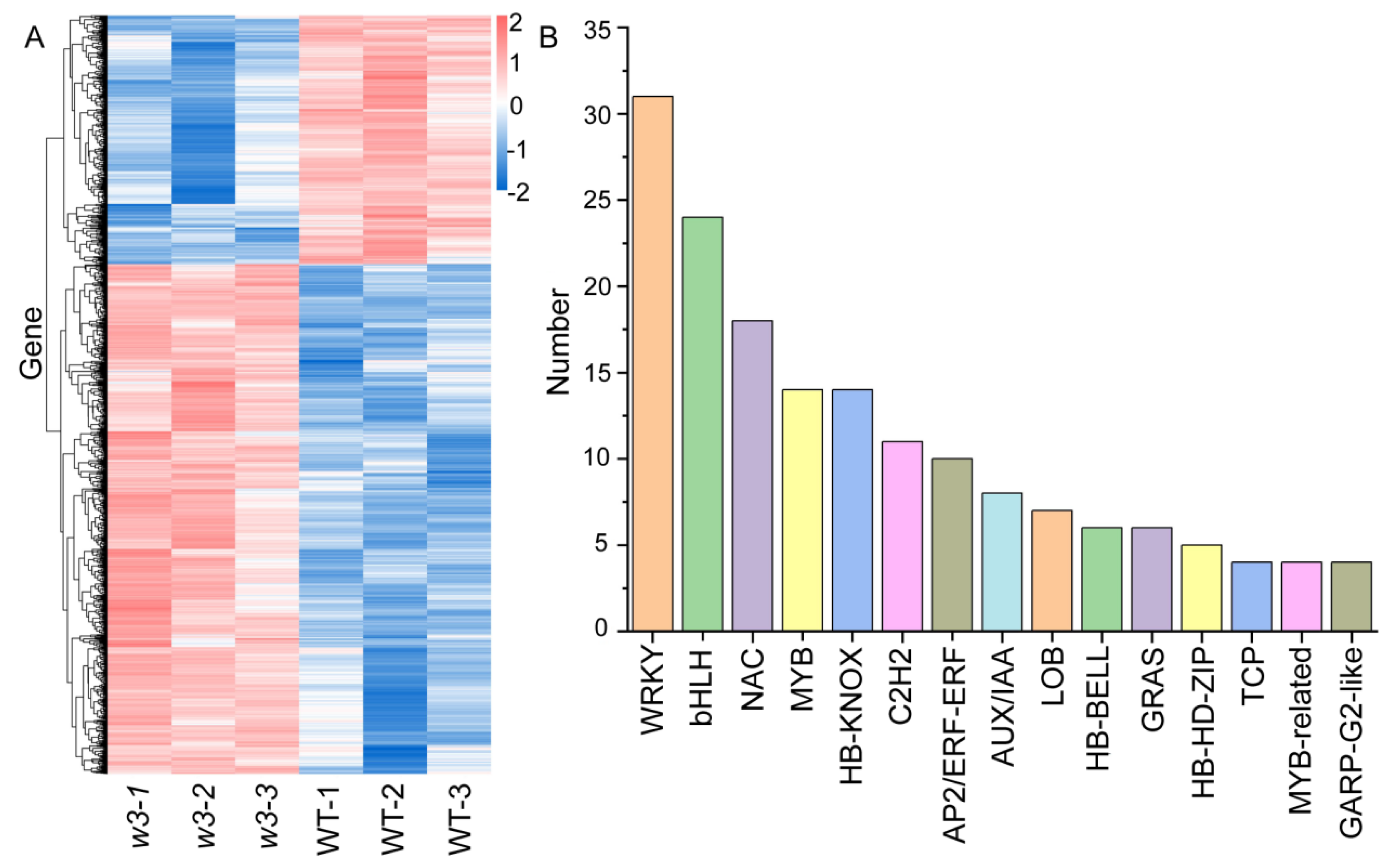
2.4. Comparative Analysis of WT and w3 Transcriptomes
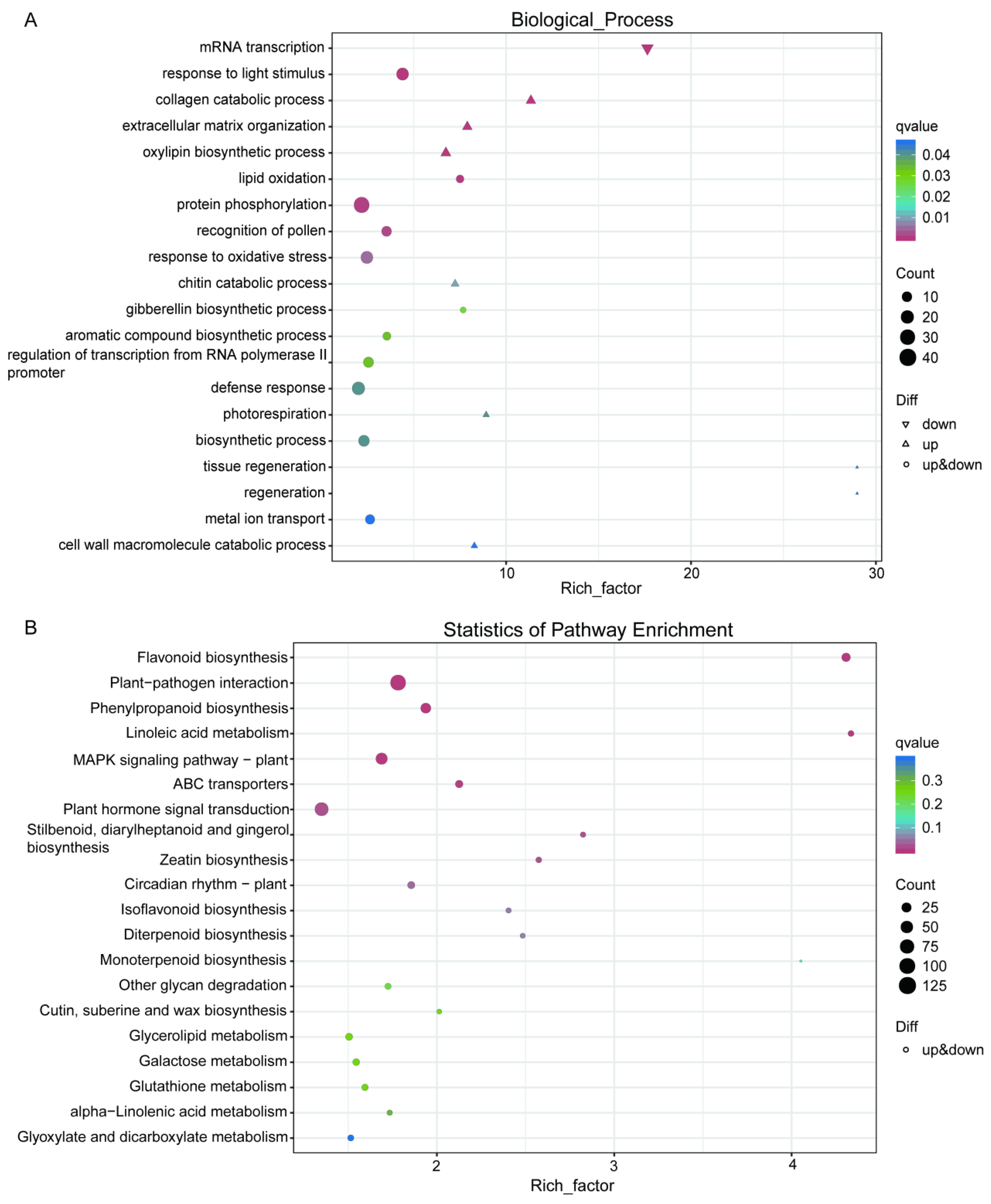
2.5. Analysis of DEGs Using Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathway Methods
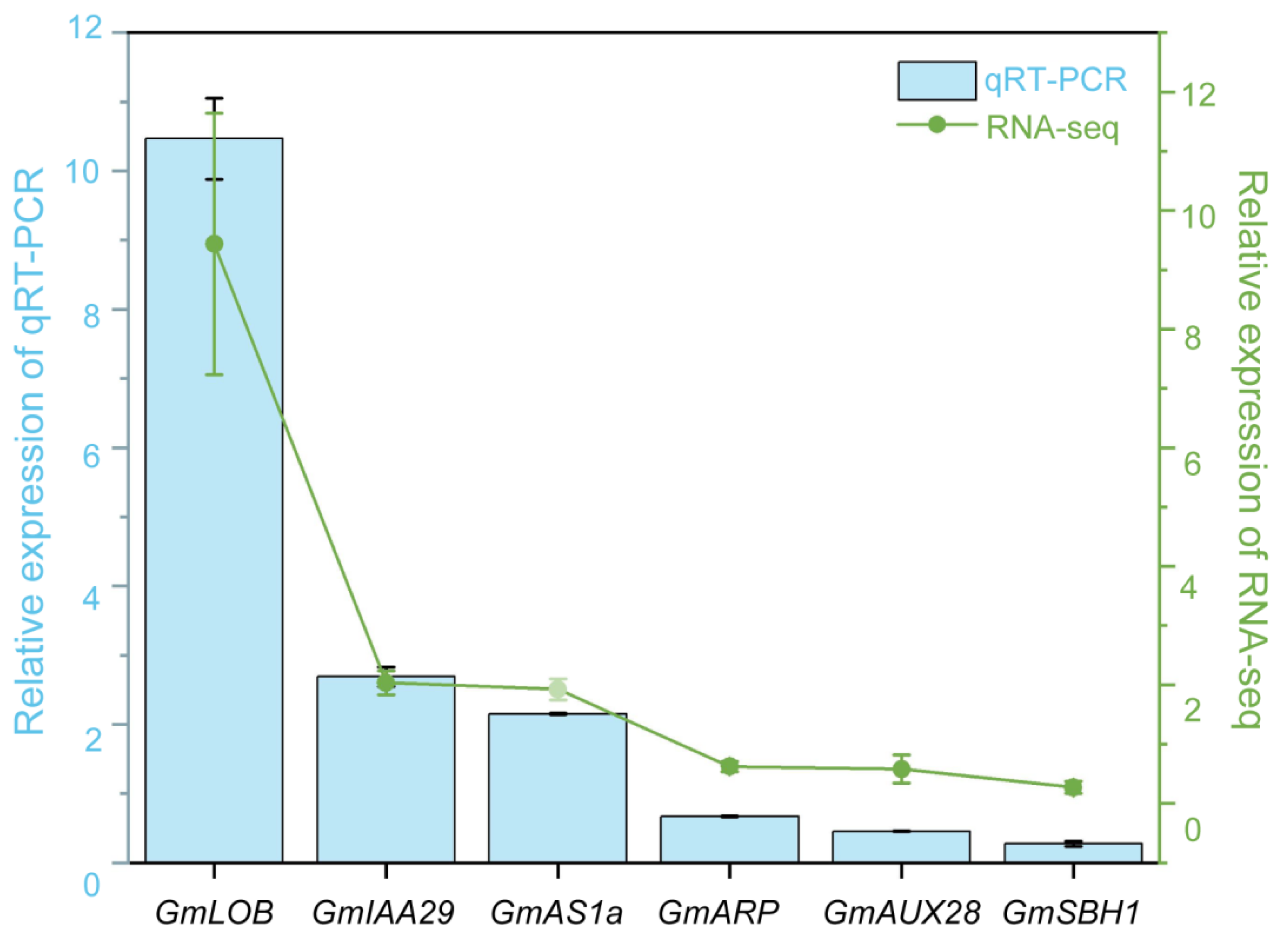
2.6. Confirmation of Chosen DEGs Through Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Cultivation and Growth Conditions
4.2. Bioinformatics Analysis and Phylogenetic Assessment
4.3. qRT-PCR Analysis
4.4. Creation of CRISPR Mutants
4.5. DNA Extraction and Mutation Screening of GmAS1 and 2 Mutant Soybean Lines
4.6. Phenotypic Assessment
4.7. RNA-Seq Based Transcriptome Analysis
4.8. Data Analysis Using Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, B.; Watanabe, S.; Uchiyama, T.; Kong, F.; Kanazawa, A.; Xia, Z.; Nagamatsu, A.; Arai, M.; Yamada, T.; Kitamura, K.; et al. The soybean stem growth habit gene Dt1 is an ortholog of Arabidopsis TERMINAL FLOWER1. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Scaboo, A.; Pantalone, V.; Li, Z.; Bilyeu, K. Utilization of plant architecture genes in soybean to positively impact adaptation to high yield environments. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 891587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ping, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Ma, J. Innovation of a regulatory mechanism modulating semi-determinate stem growth through artificial selection in soybean. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhao, M.; Li, Y.; She, M.; Sui, Y.; Lin, F.; Liu, X.; Tang, Z.; et al. Dt2 is a gain-of-function MADS-domain factor gene that specifies semideterminacy in soybean. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2831–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Lee, R.; Li, Y.; Specht, J.E.; Nelson, R.L.; McClean, P.E.; Qiu, L.; Ma, J. Artificial selection for determinate growth habit in soybean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8563–8568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.K. Twenty years on: The inner workings of the shoot apical meristem, a developmental dynamo. Dev. Biol. 2010, 341, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Huang, H. Transcriptional, post-transcriptional and post-translational regulations of gene expression during leaf polarity formation. Cell Res. 2007, 17, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husbands, A.Y.; Chitwood, D.H.; Plavskin, Y.; Timmermans, M.C. Signals and prepatterns: New insights into organ polarity in plants. Genes. Dev. 2009, 23, 1986–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efroni, I.; Eshed, Y.; Lifschitz, E. Morphogenesis of simple and compound leaves: A critical review. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, J.L.; Floyd, S.K. Patterning and polarity in seed plant shoots. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Iwakawa, H.; Ishibashi, N.; Kojima, S.; Matsumura, Y.; Prananingrum, P.; Iwasaki, M.; Takahashi, A.; Ikezaki, M.; Luo, L.; et al. Meta-analyses of microarrays of Arabidopsis asymmetric leaves1 (as1), as2 and their modifying mutants reveal a critical role for the ETT pathway in stabilization of adaxial-abaxial patterning and cell division during leaf development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Research progress in the role of AS1/AS2 genes in leaf morphogenesis. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2022, 23, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Liu, B.; Wu, J.; Cheng, F.; Wang, X. Genetic variation and divergence of genes involved in leaf adaxial-abaxial polarity establishment in Brassica rapa. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merelo, P.; Paredes, E.B.; Heisler, M.G.; Wenkel, S. The shady side of leaf development: The role of the REVOLUTA/KANADI1 module in leaf patterning and auxin-mediated growth promotion. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 35, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, Y.; Dong, A.; Sun, Y.; Pi, L.; Xu, Y.; Huang, H. Novel as1 and as2 defects in leaf adaxial-abaxial polarity reveal the requirement for ASYMMETRIC LEAVES1 and 2 and ERECTA functions in specifying leaf adaxial identity. Development 2003, 130, 4097–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semiarti, E.; Ueno, Y.; Tsukaya, H.; Iwakawa, H.; Machida, C.; Machida, Y. The ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana regulates formation of a symmetric lamina, establishment of venation and repression of meristem-related homeobox genes in leaves. Development 2001, 128, 1771–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps-Durr, T.L.; Thomas, J.; Vahab, P.; Timmermans, M.C. Maize rough sheath2 and its Arabidopsis orthologue ASYMMETRIC LEAVES1 interact with HIRA, a predicted histone chaperone, to maintain knox gene silencing and determinacy during organogenesis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2886–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakawa, H.; Ueno, Y.; Semiarti, E.; Onouchi, H.; Kojima, S.; Tsukaya, H.; Hasebe, M.; Soma, T.; Ikezaki, M.; Machida, C.; et al. The ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana, required for formation of a symmetric flat leaf lamina, encodes a member of a novel family of proteins characterized by cysteine repeats and a leucine zipper. Plant Cell Physiol. 2002, 43, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Hove, C.A.; Heidstra, R. Who begets whom? Plant cell fate determination by asymmetric cell division. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, M.E.; Simorowski, J.; Martienssen, R.A. ASYMMETRIC LEAVES1 reveals knox gene redundancy in Arabidopsis. Development 2002, 129, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, F.L.; Guo, Y.L.; Liu, T.L.; Huang, H. Identification and genetic mapping of four novel genes that regulate leaf development in Arabidopsis. Cell Res. 2000, 10, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Xu, L. Quantitative control of ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2 expression is critical for leaf axial patterning in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 4895–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Thomas, J.; Collins, G.; Timmermans, M.C. Direct repression of KNOX loci by the ASYMMETRIC LEAVES1 complex of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikezaki, M.; Kojima, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Kojima, S.; Ueno, Y.; Machida, C.; Machida, Y. Genetic networks regulated by ASYMMETRIC LEAVES1 (AS1) and AS2 in leaf development in Arabidopsis thaliana: KNOX genes control five morphological events. Plant J. 2010, 61, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmberg, P.L.; Knox, K.A.; Yun, B.W.; Morris, P.C.; Shafiei, R.; Hudson, A.; Loake, G.J. The developmental selector AS1 is an evolutionarily conserved regulator of the plant immune response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18795–18800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Sha, A.; Cao, D. Application of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated multiplex genome editing system in soybean genome editing. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2021, 43, 149. [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz, M.; Benske, A.; Smith, R.A.; Watanabe, Y.; Tobimatsu, Y.; Ralph, J.; Demura, T.; Ellis, B.; Samuels, A.L. Laccases direct lignification in the discrete secondary cell wall domains of protoxylem. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, T.Q.; Keta, S.; Asai, T.; Kojima, S.; Nakagawa, A.; Micol, J.L.; Xia, S.; Machida, Y.; Machida, C. A genetic link between epigenetic repressor AS1-AS2 and DNA replication factors in establishment of adaxial-abaxial leaf polarity of Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol. 2018, 35, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, Y.; Lei, P.; Song, W.; Zheng, W.; Nie, X. Genome-wide identification, evolution, and expression analysis of LBD transcription factor family in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 721253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, B.; Reynaga-Peña, C.G.; Springer, P.S. The lateral organ boundaries gene defines a novel, plant-specific gene family. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, M.K.; McKinney, E.C.; Deal, R.B.; Smith, A.P.; Meagher, R.B. Arabidopsis actin-related protein ARP5 in multicellular development and DNA repair. Dev. Biol. 2009, 335, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Wu, B.; Yu, T.; Wang, Q.; Krogan, N.T.; Liu, X.; Jiao, Y. Spatial auxin signaling controls leaf flattening in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 2940–2950.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.Z.; Liang, Y.; Anwar, M.; Fatima, A.; Hassan, M.J.; Ali, A.; Tang, Q.; Peng, Y. Overexpression of auxin/indole-3-acetic acid gene TrIAA27 enhances biomass, drought, and salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 2024, 13, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, H.; Zhai, L.; Xie, X.; Li, X.; Bian, S. Identification and functional characterization of the Aux/IAA gene VcIAA27 in blueberry. Plant Signal Behav 2020, 15, 1700327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Lin, P.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, D.; Qin, L.; Xu, F.; Su, Y.; Wu, Q.; Que, Y. Genome-wide identification of auxin-responsive GH3 gene family in Saccharum and the expression of ScGH3-1 in stress response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Long, J.; Zhao, K.; Peng, A.; Chen, M.; Long, Q.; He, Y.; Chen, S. Overexpressing GH3.1 and GH3.1L reduces susceptibility to Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri by repressing auxin signaling in citrus (Citrus sinensis Osbeck). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Wu, N.; Fu, J.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Xiong, L. A GH3 family member, OsGH3-2, modulates auxin and abscisic acid levels and differentially affects drought and cold tolerance in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 6467–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Yokota, S.; Hirayama, Y.; Imaichi, R.; Kato, M.; Gasser, C.S. Ancestral expression patterns and evolutionary diversification of YABBY genes in angiosperms. Plant J. 2011, 67, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, N.A. YABBY genes and the development and origin of seed plant leaves. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial-Pradel, S.; Keta, S.; Nomoto, M.; Luo, L.; Takahashi, H.; Suzuki, M.; Yokoyama, Y.; Sasabe, M.; Kojima, S.; Tada, Y.; et al. Arabidopsis zinc-finger-like protein ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2 (AS2) and two nucleolar proteins maintain gene body DNA methylation in the leaf polarity gene ETTIN (ARF3). Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, C.; Nakagawa, A.; Kojima, S.; Takahashi, H.; Machida, Y. The complex of ASYMMETRIC LEAVES (AS) proteins plays a central role in antagonistic interactions of genes for leaf polarity specification in Arabidopsis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2015, 4, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakawa, H.; Takahashi, H.; Machida, Y.; Machida, C. Roles of ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2 (AS2) and nucleolar proteins in the adaxial-abaxial polarity specification at the perinucleolar region in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husbands, A.Y.; Benkovics, A.H.; Nogueira, F.T.; Lodha, M.; Timmermans, M.C. The ASYMMETRIC LEAVES complex employs multiple modes of regulation to affect adaxial-abaxial patterning and leaf complexity. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 3321–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Finer, J.J. Soybean actin, heat shock protein, and ribosomal protein promoters direct tissue-specific transgene expression in transgenic soybean. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2014, 51, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 (-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, A.; Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, S.; Hao, Q.; Guo, W.; Qiu, D.; Shan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, S.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis of GmSPL9 genes alters plant architecture in soybean. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Pan, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, P.; Jiang, L.; Xu, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Guo, W.; Yang, H.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Targeted Mutagenesis of GmAS1/2 Genes Alters Leaf Shape in Soybean. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199657
Xu J, Pan M, Zhu Y, Wang P, Jiang L, Xu D, Wang X, Chen L, Guo W, Yang H, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Targeted Mutagenesis of GmAS1/2 Genes Alters Leaf Shape in Soybean. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199657
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Juan, Mengyue Pan, Yu Zhu, Peiguo Wang, Liwei Jiang, Dami Xu, Xinyang Wang, Limiao Chen, Wei Guo, Hongli Yang, and et al. 2025. "CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Targeted Mutagenesis of GmAS1/2 Genes Alters Leaf Shape in Soybean" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199657
APA StyleXu, J., Pan, M., Zhu, Y., Wang, P., Jiang, L., Xu, D., Wang, X., Chen, L., Guo, W., Yang, H., & Cao, D. (2025). CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Targeted Mutagenesis of GmAS1/2 Genes Alters Leaf Shape in Soybean. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199657





