Catalytic IgG Antibodies Hydrolyze DNA, Histones, and HMGB1 in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Characteristics of Sample
2.2. IgG Isolation from Serum and Confirmation of Purity and Homogeneity of the Obtained Samples
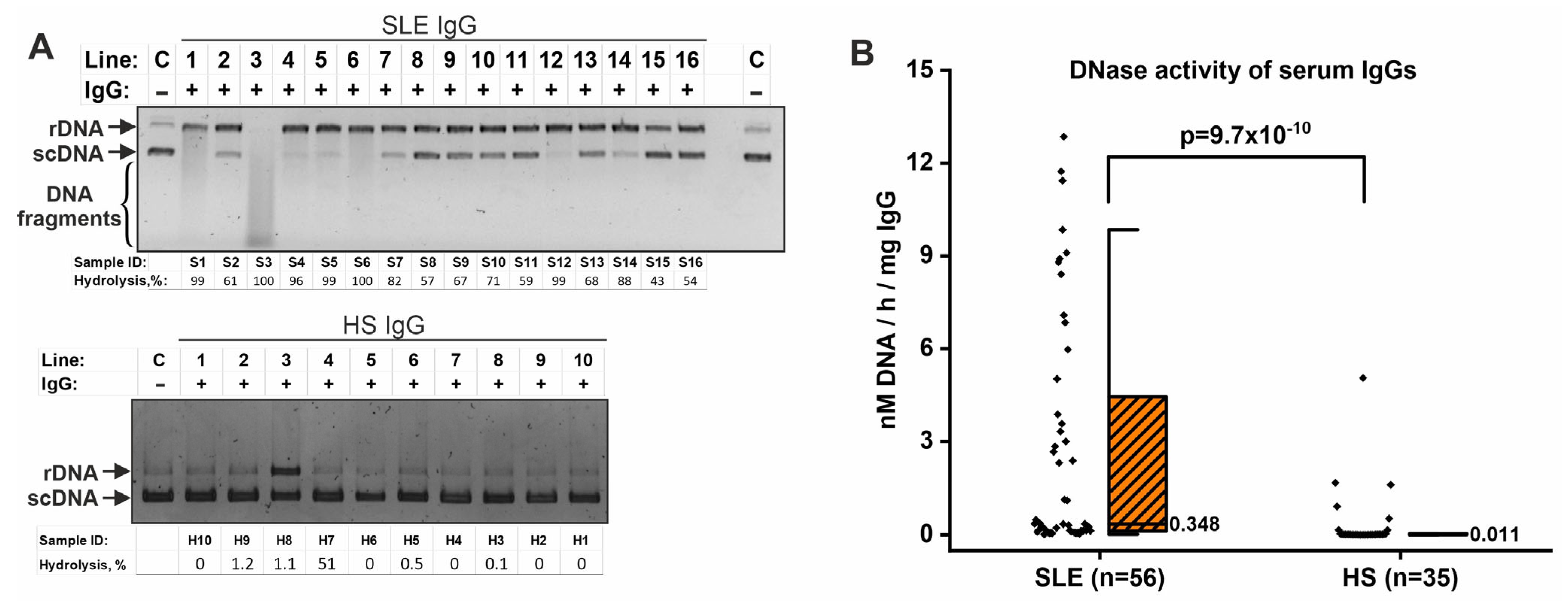
2.3. IgG-Dependent Hydrolysis of DNA
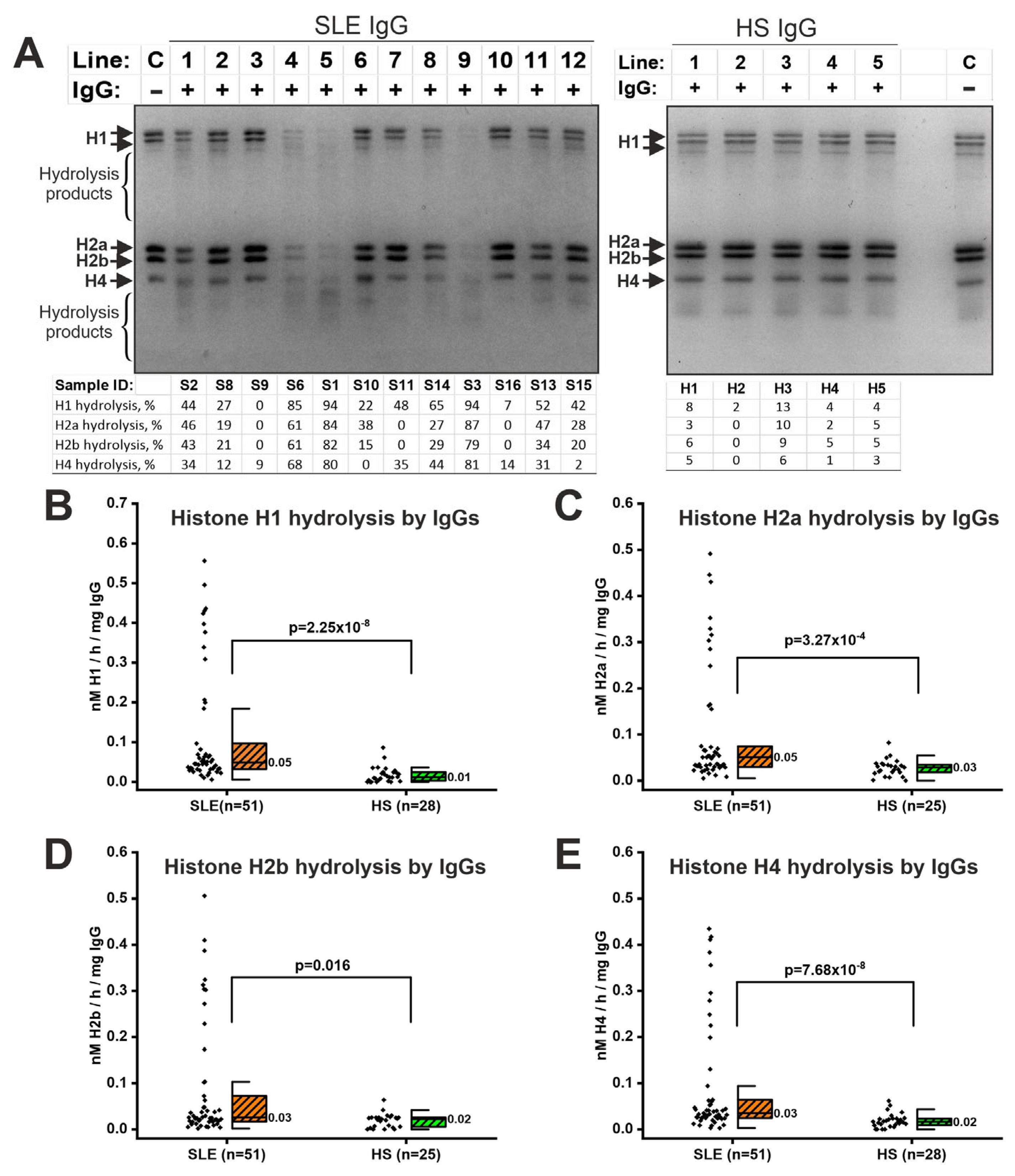
2.4. IgG-Dependent Hydrolysis of Histones
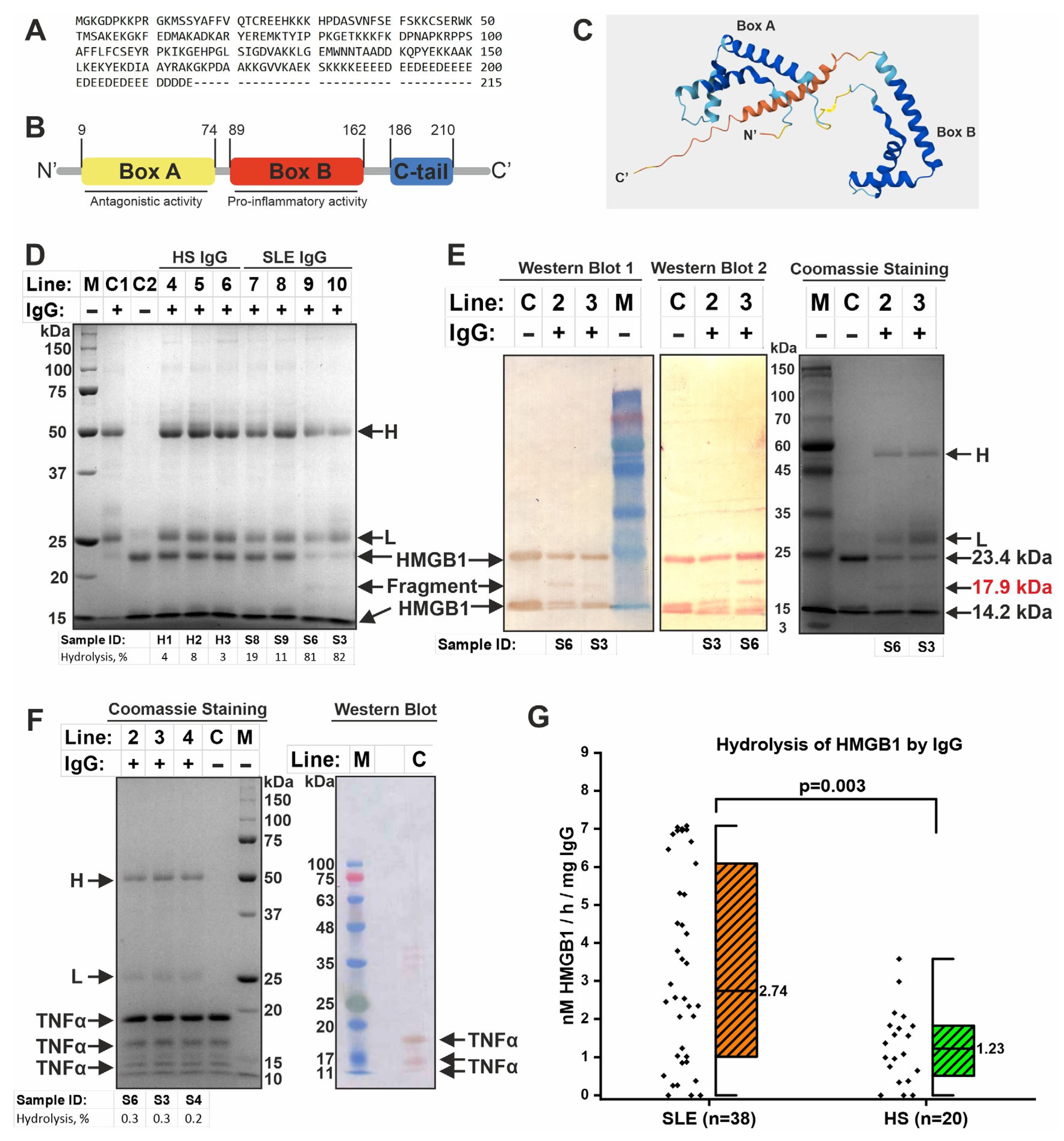
2.5. IgG-Dependent Hydrolysis of HMGB1
2.6. Catalase-like Activity of IgGs
2.7. Verification That Catalytic Activity Belongs to Antibodies
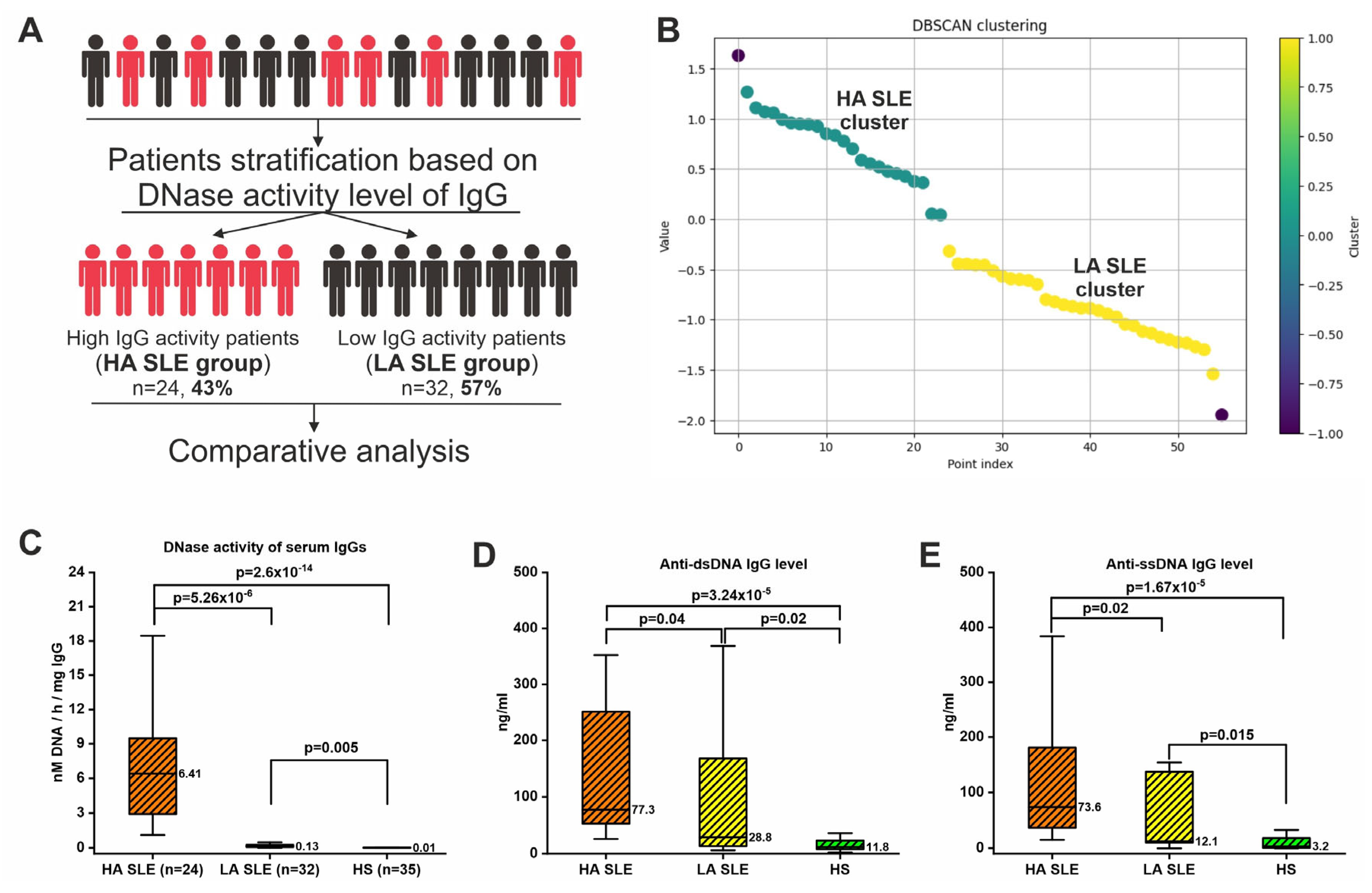
2.8. Patients’ Stratification Based on IgG DNase Activity Level
2.9. Clinical Associations
2.10. Correlation Analysis: The Levels of DNA-, Histone-, and HMGB1-Hydrolyzing Activity of IgG Are Closely Correlated
3. Discussion
3.1. IgG-Dependent Hydrolysis of DNA and DNA-Associated Proteins in SLE
3.2. Associations with Clinical Symptoms
3.3. Catalase-like Activity of IgG in SLE
3.4. The Possible Role of Catalytic Antibodies in SLE
3.5. Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Isolation and Characterization of IgG Samples from Serum
4.3. IgG-Dependent DNA-Hydrolyzing Activity Assay
4.4. Zymographic (In Situ) Analysis of DNA-Hydrolyzing Activity of IgG Samples
4.5. IgG-Dependent Histone-Hydrolyzing Activity Assay
4.6. IgG-Dependent HMGB1-Hydrolyzing Activity Assay
4.7. Analysis of TNFα Hydrolysis by Antibodies
4.8. IgG-Dependent Catalase-like Activity Assay
4.9. Analysis of Catalytic Activity of Fractions After IgG Sorption from the Mixture
4.10. Determination of Anti-DNA IgG Concentration
4.11. Statistical Processing and Visualization of Data
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| DNase1L3 | Deoxyribonuclease 1 Like 3 |
| DBSCAN | The density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise algorithm |
| KDE | Kernel Density Estimation algorithm |
| dsDNA | Double-stranded DNA |
| ssDNA | Single-stranded DNA |
| scDNA | Supercoiled DNA |
| rDNA | Relaxed DNA |
| SELENA-SLEDAI | Safety of Estrogens in Lupus Erythematosus National Assessment—Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index |
| HA SLE | High-activity SLE group |
| LA SLE | Low-activity SLE group |
| HMGB1 | High-mobility group protein B1 |
| NMDAR | N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor |
| HS | Healthy subjects |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
References
- Carter, E.E.; Barr, S.G.; Clarke, A.E. The Global Burden of SLE: Prevalence, Health Disparities and Socioeconomic Impact. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, K.; Pope, J. Employment and Work Disability in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review. Rheumatology 2008, 48, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huscher, D.; Merkesdal, S.; Thiele, K.; Zeidler, H.; Schneider, M.; Zink, A.; The German Collaborative Arthritis Centres. Cost of Illness in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Germany. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, L.; Chasset, F.; Martin, T. Immunopathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: An Update. Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, E.; Kandil, R.; Dorgham, D.; Ghorab, R.; Kholoussi, N. Lymphocyte Apoptosis and Its Association with the Inflammatory Markers and Disease Severity in Juvenile-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2024, 22, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, M.C.; Botto, M. Canonical and Noncanonical Functions of Complement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Eur. J. Immunol. 2024, 54, e2350918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, M.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, T. Imbalance of Th17 Cells, Treg Cells and Associated Cytokines in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1425847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenbrock, K.; Rauen, T. T Cell Dysregulation in SLE. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 239, 109031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrar, S.; Cunninghame Graham, D.S. Review: Abnormal B Cell Development in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: What the Genetics Tell Us. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infantino, M.; Nagy, E.; Bizzaro, N.; Fischer, K.; Bossuyt, X.; Damoiseaux, J. Anti-dsDNA Antibodies in the Classification Criteria of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2022, 5, 100139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xia, Y. Anti-Double Stranded DNA Antibodies: Origin, Pathogenicity, and Targeted Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T. An Emerging Role for Anti-DNA Antibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magna, M.; Pisetsky, D.S. The Alarmin Properties of DNA and DNA-Associated Nuclear Proteins. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvvuri, B.; Lood, C. Cell-Free DNA as a Biomarker in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Kim, M.; Seo, Y.; Ham, Y.; Cho, M.-Y.; Kwon, M.-H. Cytosolic Internalization of Anti-DNA Antibodies by Human Monocytes Induces Production of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Independently of the Tripartite Motif-Containing 21 (TRIM21)-Mediated Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.Y.; Jeong, J.G.; Jun, H.R.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kwon, M.H. A Nucleic Acid-Hydrolyzing Antibody Penetrates into Cells via Caveolae-Mediated Endocytosis, Localizes in the Cytosol and Exhibits Cytotoxicity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.-R.; Im, S.-W.; Chung, H.-Y.; Pravinsagar, P.; Jang, Y.-J. Cell- and Nuclear-Penetrating Anti-dsDNA Autoantibodies Have Multiple Arginines in CDR3 of VH and Increase Cellular Level of pERK and Bcl-2 in Mesangial Cells. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Ishizawa, M.; Kubota, T. Monoclonal Anti-dsDNA Antibody 2C10 Escorts DNA to Intracellular DNA Sensors in Normal Mononuclear Cells and Stimulates Secretion of Multiple Cytokines Implicated in Lupus Pathogenesis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 199, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño-Trives, A.M.; Pérez-Sánchez, C.; Pérez-Sánchez, L.; Luque-Tévar, M.; Ábalos-Aguilera, M.C.; Alcaide-Ruggiero, L.; Arias-de La Rosa, I.; Román-Rodríguez, C.; Seguí, P.; Espinosa, M.; et al. Anti-dsDNA Antibodies Increase the Cardiovascular Risk in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Promoting a Distinctive Immune and Vascular Activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2417–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T. The Multifunctional Protein HMGB1: 50 Years of Discovery. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 824–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, U.; Yang, H.; Harris, H. High-Mobility Group Box 1 Protein (HMGB1) Operates as an Alarmin Outside as Well as inside Cells. Semin. Immunol. 2018, 38, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulahad, D.A.; Westra, J.; Bijzet, J.; Limburg, P.C.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Bijl, M. High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) and Anti-HMGB1 Antibodies and Their Relation to Disease Characteristics in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirestam, L.; Schierbeck, H.; Skogh, T.; Gunnarsson, I.; Ottosson, L.; Erlandsson-Harris, H.; Wetterö, J.; Sjöwall, C. Antibodies against High Mobility Group Box Protein-1 (HMGB1) versus Other Anti-Nuclear Antibody Fine-Specificities and Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, A.; Nagafuchi, H.; Ito, I.; Hirota, K.; Yoshida, M.; Ozaki, S. Lupus Antibodies to the HMGB1 Chromosomal Protein: Epitope Mapping and Association with Disease Activity. Mod. Rheumatol. 2009, 19, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dema, B.; Charles, N. Autoantibodies in SLE: Specificities, Isotypes and Receptors. Antibodies 2016, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, F.J.; Cohen, I.R. The Natural Autoantibody Repertoire and Autoimmune Disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2004, 58, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skevaki, C.; Wesemann, D.R. Antibody Repertoire and Autoimmunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevinsky, G.A.; Buneva, V.N. Catalytic Antibodies in Healthy Humans and Patients with Autoimmune and Viral Diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2003, 7, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevinsky, G.A. Immune Response and Production of Abzymes in Patients with Autoimmune and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biochem. Mosc. 2025, 90, S373–S400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, E.A.; Nevinsky, G.A.; Buneva, V.N. Immunoglobulins with Non-Canonical Functions in Inflammatory and Autoimmune Disease States. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, J.D.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S. Noncanonical Functions of Antibodies. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wootla, B.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Warrington, A.E.; Bieber, A.J.; Kaveri, S.V.; Rodriguez, M. Autoantibodies with Enzymatic Properties in Human Autoimmune Diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2011, 37, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnov, I.; Belogurov, A.; Golovin, A.; Stepanov, A.; Zhang, H.; Blackburn, G.M.; Gabibov, A. Immunoglobulin Go: Synergy of Combinatorics for Catalysis. Isr. J. Chem. 2023, 63, e202300078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, A.; Wear, M.; Casadevall, A. Antibody-Mediated Catalysis in Infection and Immunity. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00202-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Nishiyama, Y.; Planque, S.; Taguchi, H. Theory of Proteolytic Antibody Occurrence. Immunol. Lett. 2006, 103, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuda, Y.; Hifumi, E.; Tsuruhata, K.; Fujinami, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Uda, T. Catalytic Antibody Light Chain Capable of Cleaving a Chemokine Receptor CCR-5 Peptide with a High Reaction Rate Constant. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 86, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzheinikov, S.N.; Muranova, T.A.; Sedelnikova, S.E.; Partridge, L.J.; Blackburn, G.M.; Murray, I.A.; Kakinuma, H.; Takahashi-Ando, N.; Shimazaki, K.; Sun, J.; et al. High-Resolution Crystal Structure of the Fab-Fragments of a Family of Mouse Catalytic Antibodies with Esterase Activity. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 332, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S. Catalytic Antibodies: Design, Expression, and Their Applications in Medicine. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 1514–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, A.M.; Gololobov, G.V.; Kvashuk, O.A.; Bogomolova, A.E.; Smirnov, I.V.; Gabibov, A.G. DNA Hydrolyzing Autoantibodies. Science 1992, 256, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, T.S.; Ermakov, E.A.; Kostina, E.V.; Sinyakov, A.N.; Sizikov, A.E.; Nevinsky, G.A.; Buneva, V.N. Hydrolysis of Oligodeoxyribonucleotides on the Microarray Surface and in Solution by Catalytic Anti-DNA Antibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 9887–9903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, R.; Sundaresh, A.; Rajkumar, R.P.; Negi, V.S.; Vijayalakshmi, M.A.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Tamouza, R.; Leboyer, M.; Kamalanathan, A.S. DNA Hydrolysing IgG Catalytic Antibodies: An Emerging Link between Psychoses and Autoimmunity. Npj Schizophr. 2021, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassov, A.; Florentz, C.; Helm, M.; Naumov, V.; Buneva, V.; Nevinsky, G.; Giege, R. Characterization and Selectivity of Catalytic Antibodies from Human Serum with RNase Activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 5243–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrievskaya, O.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Baranovskii, A.G.; Gal’vita, A.V.; Benzo, E.S.; Naumov, V.A.; Nevinsky, G.A. Catalytic Diversity of Polyclonal RNA-Hydrolyzing IgG Antibodies from the Sera of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunol. Lett. 2002, 81, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermakov, E.A.; Kabirova, E.M.; Sizikov, A.E.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. IgGs-Abzymes from the Sera of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Hydrolyzed miRNAs. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 681–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulminskaya, A.A.; Saveliev, A.N.; Neustroev, K.N. Human Abzymes with Amylolytic Activity. Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol. 2004, 16, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Magorivska, I.B.; Bilyy, R.O.; Havrylyuk, A.M.; Chop’yak, V.V.; Stoika, R.S.; Kit, Y.Y. Anti-histone H1 IgGs from Blood Serum of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients Are Capable of Hydrolyzing Histone H1 and Myelin Basic Protein. J. Mol. Recognit. 2010, 23, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezuglova, A.M.; Konenkova, L.P.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. IgGs Containing Light Chains of the λ- and κ- Type and of All Subclasses (IgG1–IgG4) from the Sera of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Hydrolyze Myelin Basic Protein. Int. Immunol. 2012, 24, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, V.; Pandit, P.; Surve, P.; Lecerf, M.; Rajadhyaksha, A.; Nadkar, M.; Khadilkar, P.V.; Chougule, D.A.; Naigaonkar, A.A.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; et al. Catalytic Antibodies in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 5, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Blinova, E.A.; Ermakov, E.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Vasilenko, N.L.; Nevinsky, G.A. IgG Abzymes with Peroxidase and Oxidoreductase Activities from the Sera of Healthy Humans: Oxidoreductase Activities of Human IgGs. J. Mol. Recognit. 2015, 28, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Sedykh, S.E.; Onvumere, M.K.; Timofeeva, A.M.; Maksimenko, L.V.; Gashnikova, N.M.; Nevinsky, G.A. Catalase Activity of IgG and Κκ-IgG, Λλ-IgG, and Κλ-IgG Subfractions in HIV-Infected Patients and Healthy Donors. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2024, 29, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Ermakov, E.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Substrate Specificity of Healthy Human Sera IgG Antibodies with Peroxidase and Oxydoreductase Activities. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermakov, E.A.; Smirnova, L.P.; Bokhan, N.A.; Semke, A.V.; Ivanova, S.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Catalase Activity of IgG Antibodies from the Sera of Healthy Donors and Patients with Schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Onvumere, M.K.; Sedykh, S.E.; Timofeeva, A.M.; Nevinsky, G.A. Catalase Activity of IgGs of Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Nevinsky, G.A. Essential Protective Role of Catalytically Active Antibodies (Abzymes) with Redox Antioxidant Functions in Animals and Humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elloumi, N.; Ben Mansour, R.; Marzouk, S.; Mseddi, M.; Fakhfakh, R.; Gargouri, B.; Masmoudi, H.; Lassoued, S. Differential Reactive Oxygen Species Production of Neutrophils and Their Oxidative Damage in Patients with Active and Inactive Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 184, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravda, J. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Pathogenesis at the Functional Limit of Redox Homeostasis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1651724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, E.A.; Smirnova, L.P.; Parkhomenko, T.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Krotenko, N.M.; Fattakhov, N.S.; Bokhan, N.A.; Semke, A.V.; Ivanova, S.A.; Buneva, V.N.; et al. DNA-Hydrolysing Activity of IgG Antibodies from the Sera of Patients with Schizophrenia. Open Biol. 2015, 5, 150064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, E.A.; Parshukova, D.A.; Nevinsky, G.A.; Buneva, V.N. Natural Catalytic IgGs Hydrolyzing Histones in Schizophrenia: Are They the Link between Humoral Immunity and Inflammation? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetsky, D.S. Anti-DNA Antibodies—Quintessential Biomarkers of SLE. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulova, K.S.; Toporkova, L.B.; Lopatnikova, J.A.; Alshevskaya, A.A.; Sedykh, S.E.; Buneva, V.N.; Budde, T.; Meuth, S.G.; Popova, N.A.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; et al. Changes in Cell Differentiation and Proliferation Lead to Production of Abzymes in EAE Mice Treated with DNA–Histone Complexes. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5816–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, P.; Macovei, L.A.; Mihai, I.R.; Cardoneanu, A.; Burlui, M.A.; Rezus, E. Cytokines in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—Focus on TNF-α and IL-17. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, N.B.; Li, B.-Z.; Leng, R.-X.; Pan, H.-F.; Ye, D.-Q. Circulating Antioxidant Levels in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomark. Med. 2019, 13, 1137–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Volle, D.J.; Beach, C.M.; Johnson, D.R.; Powell, M.J.; Massey, R.J. Catalytic Hydrolysis of Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide by Human Autoantibody. Science 1989, 244, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isenberg, D.A.; Manson, J.J.; Ehrenstein, M.R.; Rahman, A. Fifty Years of Anti-Ds DNA Antibodies: Are We Approaching Journey’s End? Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekvig, O.P.; Van Der Vlag, J.; Seredkina, N. Review: Antinucleosome Antibodies: A Critical Reflection on Their Specificities and Diagnostic Impact. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekvig, O.P. The Anti-DNA Antibody: Origin and Impact, Dogmas and Controversies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekvig, O.P. The Anti-DNA Antibodies: Their Specificities for Unique DNA Structures and Their Unresolved Clinical Impact—A System Criticism and a Hypothesis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 808008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lood, C.; Blanco, L.P.; Purmalek, M.M.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; De Ravin, S.S.; Smith, C.K.; Malech, H.L.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Elkon, K.B.; Kaplan, M.J. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Enriched in Oxidized Mitochondrial DNA Are Interferogenic and Contribute to Lupus-like Disease. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieker, J.; Tel, J.; Pieterse, E.; Thielen, A.; Rother, N.; Bakker, M.; Fransen, J.; Dijkman, H.B.P.M.; Berden, J.H.; De Vries, J.M.; et al. Circulating Apoptotic Microparticles in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients Drive the Activation of Dendritic Cell Subsets and Prime Neutrophils for NETosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbonaviciute, V.; Fürnrohr, B.G.; Meister, S.; Munoz, L.; Heyder, P.; De Marchis, F.; Bianchi, M.E.; Kirschning, C.; Wagner, H.; Manfredi, A.A.; et al. Induction of Inflammatory and Immune Responses by HMGB1–Nucleosome Complexes: Implications for the Pathogenesis of SLE. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 3007–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoenfeld, Y.; Rauch, J.; Massicotte, H.; Datta, S.K.; André-Schwartz, J.; Stollar, B.D.; Schwartz, R.S. Polyspecificity of Monoclonal Lupus Autoantibodies Produced by Human-Human Hybridomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 308, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jacobi, A.M.; Wang, T.; Berlin, R.; Volpe, B.T.; Diamond, B. Polyreactive Autoantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Have Pathogenic Potential. J. Autoimmun. 2009, 33, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGiorgio, L.A.; Konstantinov, K.N.; Lee, S.C.; Hardin, J.A.; Volpe, B.T.; Diamond, B. A Subset of Lupus Anti-DNA Antibodies Cross-Reacts with the NR2 Glutamate Receptor in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Bañuelos, E.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Cashman, K.S.; Paz, M.; Trejo-Zambrano, M.I.; Bugrovsky, R.; Wang, Y.; Chida, A.S.; Sherman-Baust, C.A.; et al. Affinity Maturation Generates Pathogenic Antibodies with Dual Reactivity to DNase1L3 and dsDNA in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, J.; Serpas, L.; Wang, Y.; Rashidfarrokhi, A.; Perez, O.A.; Sally, B.; Sisirak, V.; Soni, C.; Khodadadi-Jamayran, A.; Tsirigos, A.; et al. Autoantibody-Mediated Impairment of DNASE1L3 Activity in Sporadic Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20201138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevinsky, G.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Dmitrienok, P.S. Autoimmune Diseases: Enzymatic Cross Recognition and Hydrolysis of H2B Histone, Myelin Basic Protein, and DNA by IgGs against These Antigens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Eryilmaz, E.; Zhang, Q.; Cowburn, D.; Putterman, C. Anti-DNA Antibody Mediated Catalysis Is Isotype Dependent. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 69, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mansour, R.B.; Lassoued, S.; Gargouri, B.; El Gaïd, A.; Attia, H.; Fakhfakh, F. Increased Levels of Autoantibodies against Catalase and Superoxide Dismutase Associated with Oxidative Stress in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 37, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-T.; Wu, T.-H.; Lin, C.-S.; Lee, C.-S.; Wei, Y.-H.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Chang, D.-M. The Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—From the Viewpoint of Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Mitochondrion 2016, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perl, A. Oxidative Stress in the Pathology and Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.Z.; Gheita, T.A.; Kenawy, S.A.; Fahim, A.T.; El-Sorougy, I.M.; Abdou, M.S. Oxidative Stress in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Relationship to Disease Manifestations and Activity: Oxidative Stress in SLE and RA Patients. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 14, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeruva, S.; Stangner, K.; Jungwirth, A.; Hiermaier, M.; Shoykhet, M.; Kugelmann, D.; Hertl, M.; Egami, S.; Ishii, N.; Koga, H.; et al. Catalytic Antibodies in Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy Patients Cleave Desmoglein 2 and N-Cadherin and Impair Cardiomyocyte Cohesion. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, M.; Kim, M.Y.; Kalunian, K.C.; Grossman, J.; Hahn, B.H.; Sammaritano, L.R.; Lockshin, M.; Merrill, J.T.; Belmont, H.M.; Askanase, A.D.; et al. Combined Oral Contraceptives in Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2550–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. [13] Catalase in Vitro. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; Volume 105, pp. 121–126. ISBN 978-0-12-182005-3. [Google Scholar]
- Beers, R.F.; Sizer, I.W. A Spectrophotometric Method for Measuring the Breakdown of Hydrogen Peroxide by Catalase. J. Biol. Chem. 1952, 195, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | SLE (n = 56) | HS (n = 35) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (F/M, %) | 100/0 | 100/0 | - |
| Age, years | 50.5 (40, 59) | 45 (38, 59) | 0.35 |
| SLE duration, years | 8.5 (4, 17) | - | - |
| SELENA-SLEDAI, score | 6 (4, 10) | - | - |
| Anti-ssDNA IgG, ng/mL | 39.6 (12, 154) | 3 (1, 17) | 0.00003 |
| Anti-dsDNA IgG, ng/mL | 61.5 (28, 189) | 12 (8, 21) | 0.00006 |
| Course (acute/subacute/chronic, %) | 2/27/71 | - | - |
| SLE activity (high/moderate/low/minimal, %) | 16/49/2/33 | - | - |
| Phase (active/inactive, %) | 96/4 | - | - |
| Parameter | HA SLE (n = 24) | LA SLE (n = 32) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 48 (41, 58) | 53 (41, 61) | 0.62 |
| Disease duration, years | 6 (3, 14) | 12 (7, 20) | 0.03 |
| SELENA-SLEDAI, score | 6 (4, 8) | 8 (5, 10) | 0.33 |
| Course (chronic/subacute, %) | 17%/83% | 42%/58% | 0.048 |
| SLE activity (high/moderate/low/minimal, %) | 8%/50%/0%/42% | 21%/36%/4%/39% | 0.73 |
| Exacerbation (yes/no), % | 92%/8% | 71%/29% | 0.08 |
| Variable | β | Standard Error of β | t-Statistic | p-Value | Adjusted R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG DNase activity | −0.147 | 0.060 | −2.458 | 0.019 | 0.092 |
| IgG H1-hydrolysing activity | 0.146 | 0.118 | 1.236 | 0.224 | |
| IgG catalase-like activity | 0.015 | 0.106 | 0.140 | 0.889 | |
| Anti-dsDNA Abs level | 0.187 | 0.117 | 1.599 | 0.118 | |
| Age | −0.026 | 0.310 | −0.083 | 0.934 | |
| Disease duration | −0.190 | 0.087 | −2.189 | 0.035 |
| Variable | β | Standard Error of β | t-Statistic | p-Value | Adjusted R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG H1-hydrolysing activity | 1.129 | 0.214 | 5.267 | 0.0001 | 0.446 |
| IgG catalase-like activity | 0.252 | 0.209 | 1.209 | 0.232 | |
| Anti-dsDNA Abs level | 0.604 | 0.281 | 2.152 | 0.036 | |
| SELENA-SLEDAI | −1.027 | 0.397 | −2.585 | 0.013 | |
| Age | −0.840 | 0.803 | −1.046 | 0.301 | |
| Disease duration | −0.504 | 0.212 | −2.371 | 0.022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melamud, M.M.; Ermakov, E.A.; Tolmacheva, A.S.; Kostrikina, I.A.; Sizikov, A.E.; Nevinsky, G.A.; Buneva, V.N. Catalytic IgG Antibodies Hydrolyze DNA, Histones, and HMGB1 in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199635
Melamud MM, Ermakov EA, Tolmacheva AS, Kostrikina IA, Sizikov AE, Nevinsky GA, Buneva VN. Catalytic IgG Antibodies Hydrolyze DNA, Histones, and HMGB1 in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199635
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelamud, Mark M., Evgeny A. Ermakov, Anna S. Tolmacheva, Irina A. Kostrikina, Alexey E. Sizikov, Georgy A. Nevinsky, and Valentina N. Buneva. 2025. "Catalytic IgG Antibodies Hydrolyze DNA, Histones, and HMGB1 in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199635
APA StyleMelamud, M. M., Ermakov, E. A., Tolmacheva, A. S., Kostrikina, I. A., Sizikov, A. E., Nevinsky, G. A., & Buneva, V. N. (2025). Catalytic IgG Antibodies Hydrolyze DNA, Histones, and HMGB1 in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199635







