Photobiomodulation at 660 nm Alleviates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology Through Amyloid-β Reduction and SIRT1 Upregulation in the Hippocampus of 5xFAD Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
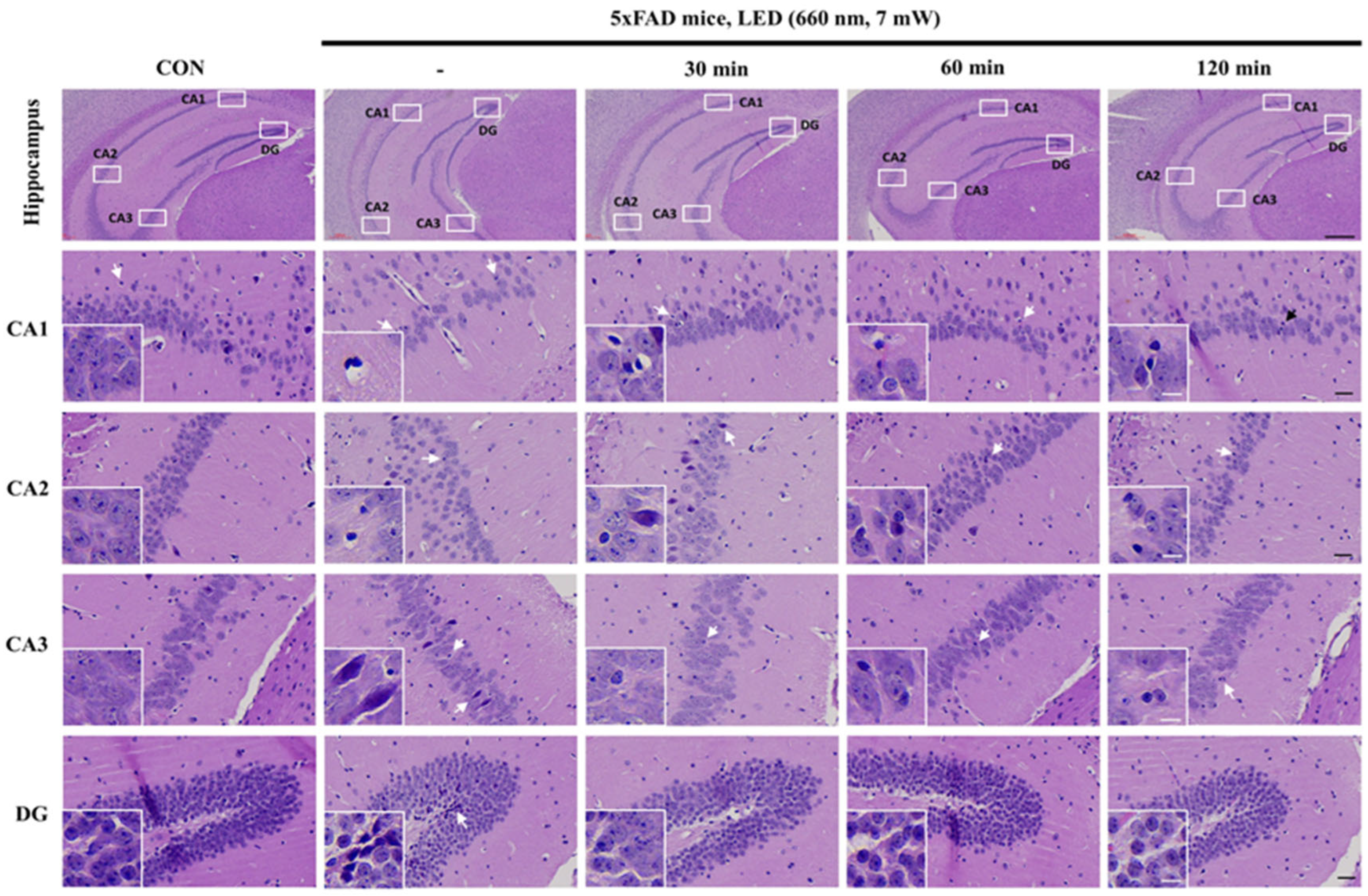
2.1. PBMT at 660 nm Restores Cellular Morphology of 5xFAD Mice Hippocampus
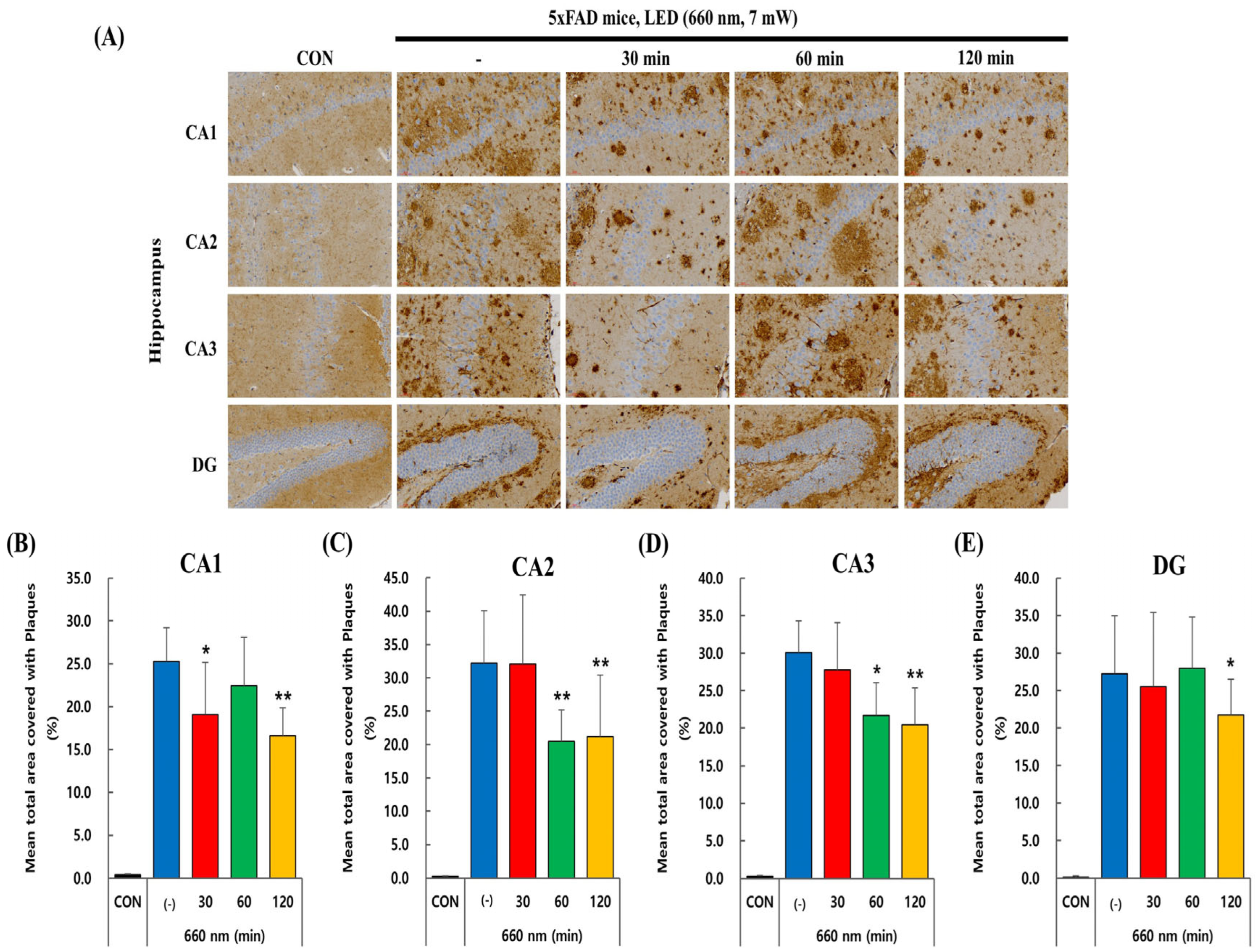
2.2. PBMT at 660 nm Reduces Aβ Plaque Load in 5xFAD Mice Hippocampus
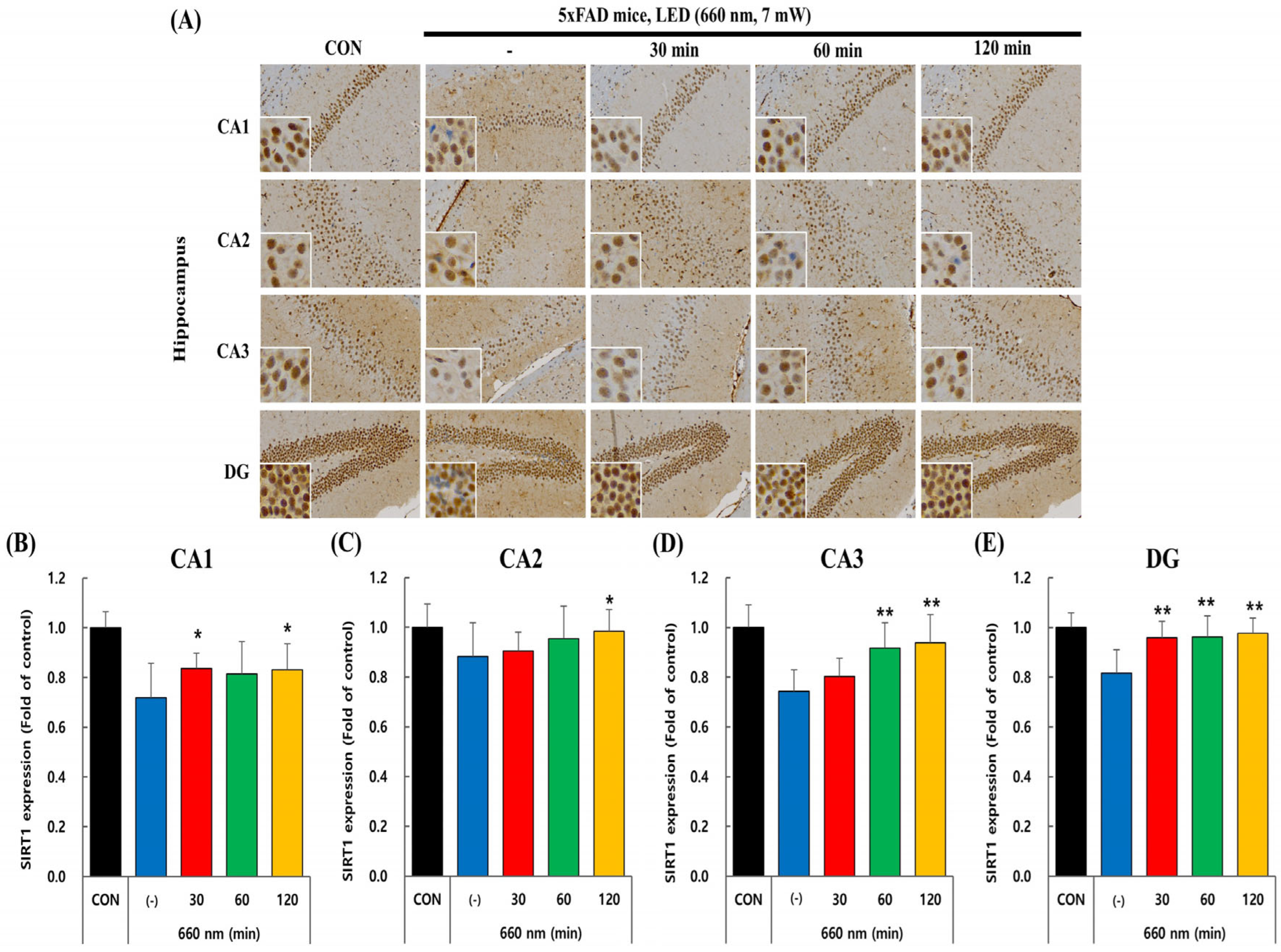
2.3. PBMT at 660 nm Modulates SIRT1 Expression in 5xFAD Mice Hippocampus
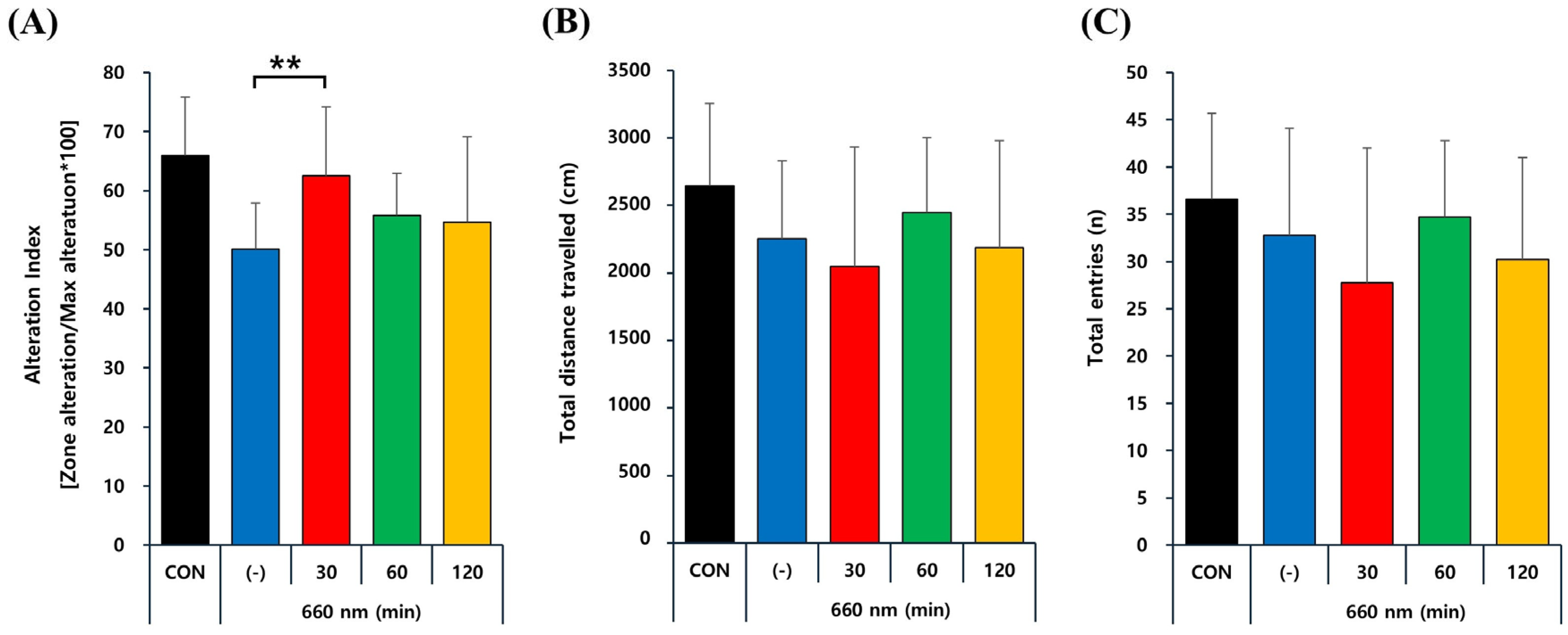
2.4. PBMT at 660 nm Improves Memory Deficits in 5xFAD Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
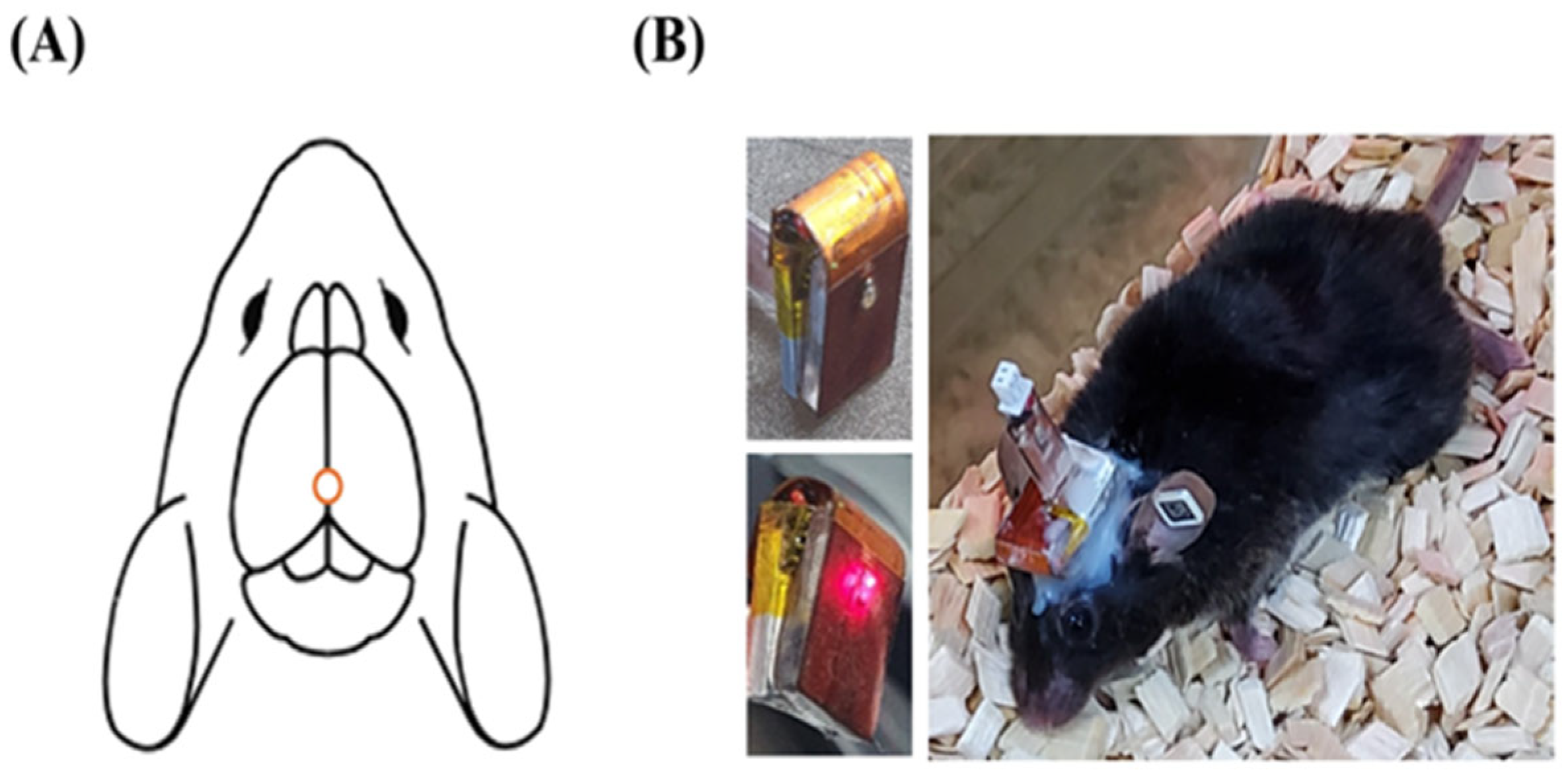
4.2. PBM Treatment Procedure Using LED Device
4.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Antibodies
4.5. Image Acquisition and Quantification of Histology Data
4.6. Y-Maze Test for Behavioral Assessment
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nichols, E.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Vollset, S.E.; Fukutaki, K.; Chalek, J.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdoli, A.; Abualhasan, A.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Akram, T.T. Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e105–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatham, P.T.; Shukla, R.; Khatri, D.K.; Vora, L.K. Pathogenesis, diagnostics, and therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease: Breaking the memory barrier. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 101, 102481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.-Z. Updates in Alzheimer’s disease: From basic research to diagnosis and therapies. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paroni, G.; Bisceglia, P.; Seripa, D. Understanding the amyloid hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 68, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimić, G.; Babić Leko, M.; Wray, S.; Harrington, C.; Delalle, I.; Jovanov-Milošević, N.; Bažadona, D.; Buée, L.; De Silva, R.; Di Giovanni, G. Tau protein hyperphosphorylation and aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies, and possible neuroprotective strategies. Biomolecules 2016, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, R.; Sterling, K.; Song, W. Amyloid β-based therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: Challenges, successes and future. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-J.; Zhang, T.-N.; Chen, H.-H.; Yu, X.-F.; Lv, J.-L.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zheng, G.; Zhao, J.-Q.; Wei, Y.-F. The sirtuin family in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Moglad, E.; Afzal, M.; Gupta, G.; Bhat, A.A.; Kazmi, I.; Alzarea, S.I.; Singh, T.G.; Singh, S.K.; Ali, H. The role of sirtuin 1 in ageing and neurodegenerative disease: A molecular perspective. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 102, 102545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Yang, T.; Ho, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, W.; Thiyagarajan, M.; MacGrogan, D.; Rodgers, J.T. Neuronal SIRT1 activation as a novel mechanism underlying the prevention of Alzheimer disease amyloid neuropathology by calorie restriction. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21745–21754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albani, D.; Polito, L.; Batelli, S.; De Mauro, S.; Fracasso, C.; Martelli, G.; Colombo, L.; Manzoni, C.; Salmona, M.; Caccia, S. The SIRT1 activator resveratrol protects SK-N-BE cells from oxidative stress and against toxicity caused by α-synuclein or amyloid-β (1-42) peptide. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michán, S.; Li, Y.; Chou, M.M.-H.; Parrella, E.; Ge, H.; Long, J.M.; Allard, J.S.; Lewis, K.; Miller, M.; Xu, W. SIRT1 is essential for normal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9695–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, D.; Xing, D. Activation of PKA/SIRT1 signaling pathway by photobiomodulation therapy reduces Aβ levels in Alzheimer’s disease models. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Hamblin, M.R.; Zhang, Q. Photobiomodulation in experimental models of Alzheimer’s disease: State-of-the-art and translational perspectives. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arany, P.R. Photobiomodulation therapy. JADA Found. Sci. 2025, 4, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairuz, T.; Lee, J.-H. Photobiomodulation Therapy on Brain: Pioneering an Innovative Approach to Revolutionize Cognitive Dynamics. Cells 2024, 13, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.C.; Bruchey, A.K.; Gonzalez-Lima, F. Low-level light therapy improves cortical metabolic capacity and memory retention. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 32, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalikova, S.; Ennaceur, A.; van Rensburg, R.; Chazot, P. Emotional responses and memory performance of middle-aged CD1 mice in a 3D maze: Effects of low infrared light. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2008, 89, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Taboada, L.; Yu, J.; El-Amouri, S.; Gattoni-Celli, S.; Richieri, S.; McCarthy, T.; Streeter, J.; Kindy, M.S. Transcranial laser therapy attenuates amyloid-β peptide neuropathology in amyloid-β protein precursor transgenic mice. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 23, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfara, D.; Tuby, H.; Trudler, D.; Doron-Mandel, E.; Maltz, L.; Vassar, R.J.; Frenkel, D.; Oron, U. Low-level laser therapy ameliorates disease progression in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 55, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, V.E.; Spana, S.; Ashkan, K.; Benabid, A.L.; Stone, J.; Baker, G.E.; Mitrofanis, J. Neuroprotection of midbrain dopaminergic cells in MPTP-treated mice after near-infrared light treatment. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010, 518, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagdeo, J.R.; Adams, L.E.; Brody, N.I.; Siegel, D.M. Transcranial red and near infrared light transmission in a cadaveric model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeTaboada, L.; Ilic, S.; Leichliter-Martha, S.; Oron, U.; Oron, A.; Streeter, J. Transcranial application of low-energy laser irradiation improves neurological deficits in rats following acute stroke. Lasers Surg. Med. 2006, 38, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.; Ersen, A.; Sahin, M. Near-infrared light penetration profile in the rodent brain. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 075001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, C.; El Massri, N.; Torres, N.; Ratel, D.; De Jaeger, X.; Chabrol, C.; Perraut, F.; Bourgerette, A.; Berger, M.; Purushothuman, S. Photobiomodulation inside the brain: A novel method of applying near-infrared light intracranially and its impact on dopaminergic cell survival in MPTP-treated mice. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darlot, F.; Moro, C.; El Massri, N.; Chabrol, C.; Johnstone, D.M.; Reinhart, F.; Agay, D.; Torres, N.; Bekha, D.; Auboiroux, V. Near-infrared light is neuroprotective in a monkey model of P arkinson disease. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, F.; van den Berg, M.; Mirjebreili, M.; Kosten, L.; Verhoye, M.; Amiri, M.; Keliris, G.A. Early classification of Alzheimer’s disease phenotype based on hippocampal electrophysiology in the TgF344-AD rat model. Iscience 2023, 26, 107454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boza-Serrano, A.; Yang, Y.; Paulus, A.; Deierborg, T. Innate immune alterations are elicited in microglial cells before plaque deposition in the Alzheimer’s disease mouse model 5xFAD. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, S.; Kawauchi, S.; Balderrama-Gutierrez, G.; Kramár, E.A.; Matheos, D.P.; Phan, J.; Javonillo, D.I.; Tran, K.M.; Hingco, E.; Da Cunha, C. Systematic phenotyping and characterization of the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donmez, G. The neurobiology of sirtuins and their role in neurodegeneration. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herskovits, A.Z.; Guarente, L. SIRT1 in neurodevelopment and brain senescence. Neuron 2014, 81, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachurin, S.O.; Bovina, E.V.; Ustyugov, A.A. Drugs in clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease: The major trends. Med. Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 1186–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.R. Mechanisms and applications of the anti-inflammatory effects of photobiomodulation. AIMS Biophys. 2017, 4, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, H.; Cole, S.L.; Logan, S.; Maus, E.; Shao, P.; Craft, J.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.; Ohno, M.; Disterhoft, J.; Van Eldik, L. Intraneuronal β-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration, and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations: Potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10129–10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawhar, S.; Trawicka, A.; Jenneckens, C.; Bayer, T.A.; Wirths, O. Motor deficits, neuron loss, and reduced anxiety coinciding with axonal degeneration and intraneuronal Aβ aggregation in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 196.e29–196.e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiraboschi, P.; Sabbagh, M.; Hansen, L.; Salmon, D.; Merdes, A.; Gamst, A.; Masliah, E.; Alford, M.; Thal, L.; Corey-Bloom, J. Alzheimer disease without neocortical neurofibrillary tangles: “A second look”. Neurology 2004, 62, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehpour, F.; Mahmoudi, J.; Kamari, F.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Rasta, S.H.; Hamblin, M.R. Brain photobiomodulation therapy: A narrative review. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6601–6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, S.; Duggett, N.; Ennaceur, A.; Chazot, P. Non-invasive infra-red therapy (1072 nm) reduces β-amyloid protein levels in the brain of an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model, TASTPM. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2013, 123, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, G.M.; Lee, S.-Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Park, K.-J.; Choi, B.T.; Shin, Y.-I.; Kim, N.G.; Shin, H.K. Photobiomodulation using a low-level light-emitting diode improves cognitive dysfunction in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Gerontol. A 2020, 75, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.M.; Goette, W.; Farrell, K.; Iida, M.A.; Karlovich, E.; Group, P.W.; White III, C.L.; Crary, J.F.; Richardson, T.E. The relationship between hippocampal amyloid beta burden and spatial distribution of neurofibrillary degeneration. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 3158–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairuz, T.; Heo, J.-C.; Lee, J.-H. Differential Glial Response and Neurodegenerative Patterns in CA1, CA3, and DG Hippocampal Regions of 5XFAD Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miners, J.S.; Baig, S.; Palmer, J.; Palmer, L.E.; Kehoe, P.G.; Love, S. SYMPOSIUM: Clearance of Aβ from the Brain in Alzheimer’s Disease: Aβ-Degrading Enzymes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Pathol. 2008, 18, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Wang, W.-Y.; Mao, Y.-W.; Gräff, J.; Guan, J.-S.; Pan, L.; Mak, G.; Kim, D.; Su, S.C.; Tsai, L.-H. A novel pathway regulates memory and plasticity via SIRT1 and miR-134. Nature 2010, 466, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Yoon, G.; Chung, S.; Abid, M.; Kim, T.; Lee, H.; Kim, M. Novel osmotin inhibits SREBP2 via the AdipoR1/AMPK/SIRT1 pathway to improve Alzheimer’s disease neuropathological deficits. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.R.; Shin, H.K.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, W.S.; Rhim, B.Y.; Hong, K.W.; Kim, C.D. Cilostazol suppresses β-amyloid production by activating a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 10 via the upregulation of SIRT1-coupled retinoic acid receptor-β. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, J.T.; Lerin, C.; Gerhart-Hines, Z.; Puigserver, P. Metabolic adaptations through the PGC-1α and SIRT1 pathways. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, J.J.; Diao, S.; Kwak, Y.-D.; Liu, L.; Zhi, L.; Büeler, H.; Bhat, N.R.; Williams, R.W.; Park, E.A. Metabolic stress modulates Alzheimer’s β-secretase gene transcription via SIRT1-PPARγ-PGC-1 in neurons. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamblin, M.R. Shining light on the head: Photobiomodulation for brain disorders. BBA Clin. 2016, 6, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowsky, J.L.; Zheng, H. Practical considerations for choosing a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2017, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Prior, M.; He, W.; Tang, X.; Hu, X.; Yan, R. Reduced amyloid deposition in mice overexpressing RTN3 is adversely affected by preformed dystrophic neurites. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9163–9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters [Unit] | Value |
|---|---|
| Center wavelength [nm] | 660 |
| Output mode | Continuous |
| Average radiant power [mW] | 7 |
| Spot area [mm2] | 1.28 |
| Beam profile | Square |
| Beam divergence [°] | 120 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nairuz, T.; Heo, J.-C.; Park, H.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Photobiomodulation at 660 nm Alleviates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology Through Amyloid-β Reduction and SIRT1 Upregulation in the Hippocampus of 5xFAD Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199569
Nairuz T, Heo J-C, Park H-J, Lee J-H. Photobiomodulation at 660 nm Alleviates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology Through Amyloid-β Reduction and SIRT1 Upregulation in the Hippocampus of 5xFAD Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199569
Chicago/Turabian StyleNairuz, Tahsin, Jin-Chul Heo, Hee-Jun Park, and Jong-Ha Lee. 2025. "Photobiomodulation at 660 nm Alleviates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology Through Amyloid-β Reduction and SIRT1 Upregulation in the Hippocampus of 5xFAD Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199569
APA StyleNairuz, T., Heo, J.-C., Park, H.-J., & Lee, J.-H. (2025). Photobiomodulation at 660 nm Alleviates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology Through Amyloid-β Reduction and SIRT1 Upregulation in the Hippocampus of 5xFAD Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199569







