Genetic Diversity and Infection Prevalence of Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Krauss, 1848), the Intermediate Snail Host of Schistosoma mansoni in Gezira State, Sudan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
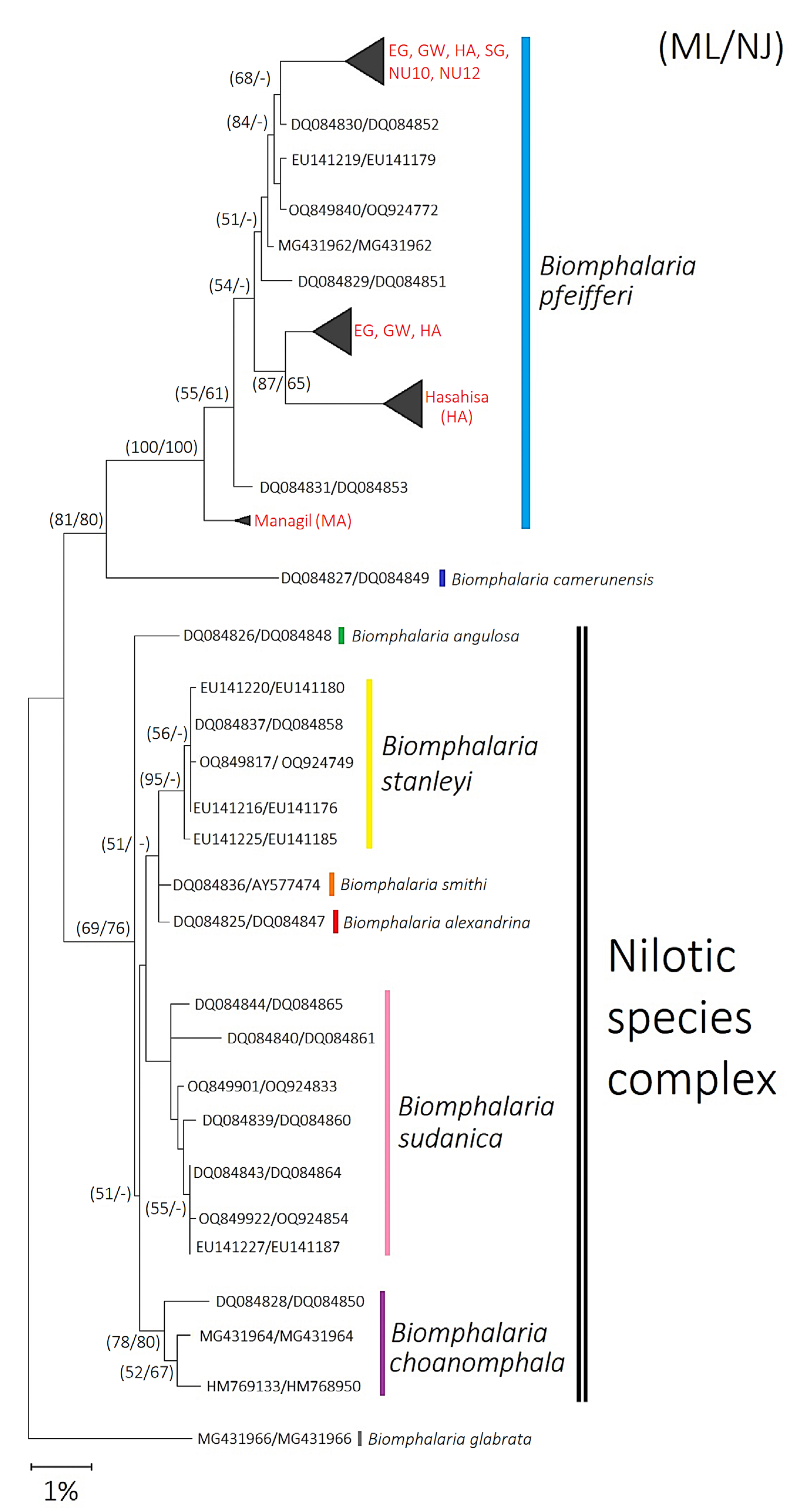
2.1. Species Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.2. Haplotype Analysis, Diversity Parameters, and Neutrality Tests
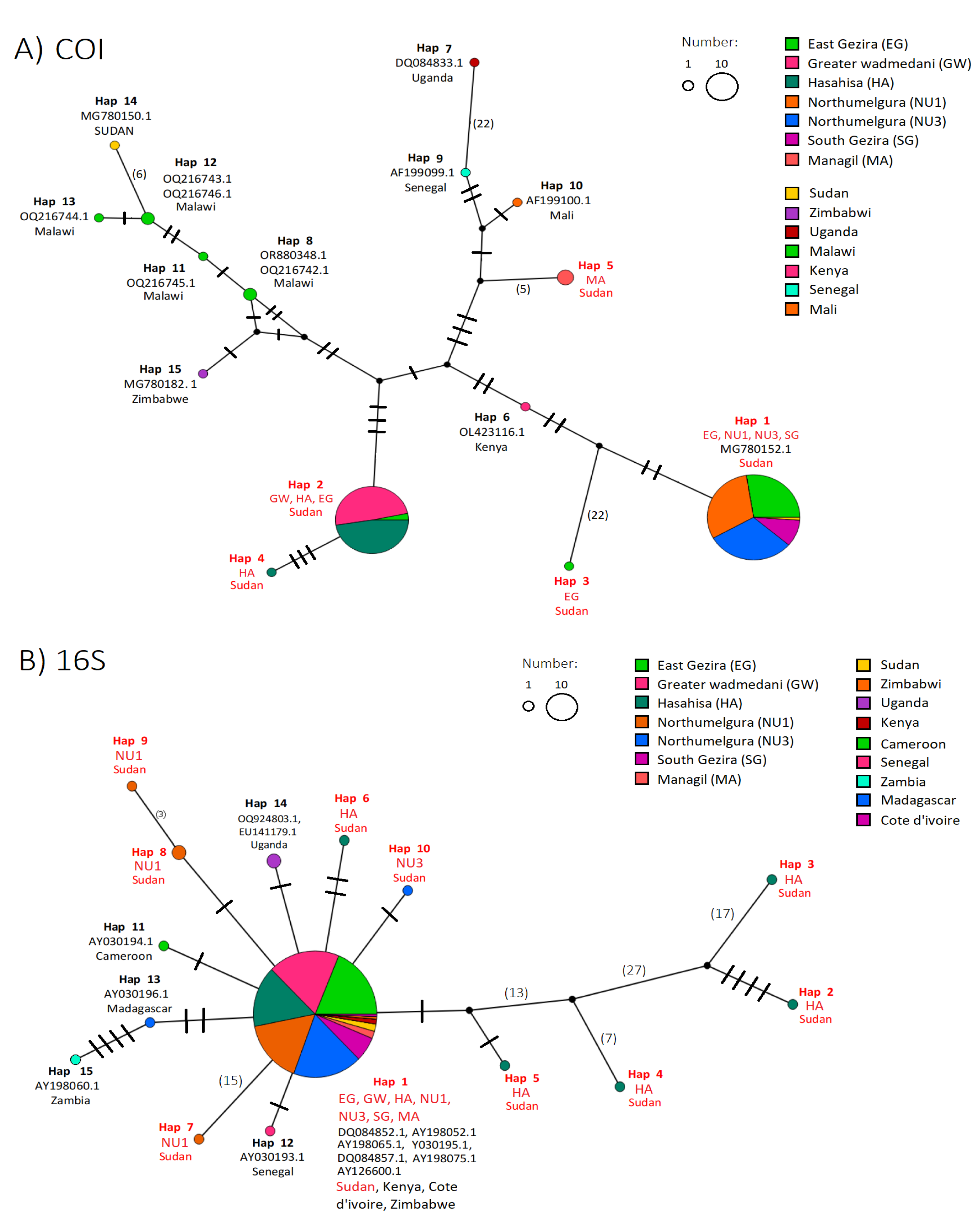
2.3. Haplotypes Network Inference
2.4. Genetic Divergence and Population Differentiation
2.5. Analyses of Molecular Variation (AMOVA)
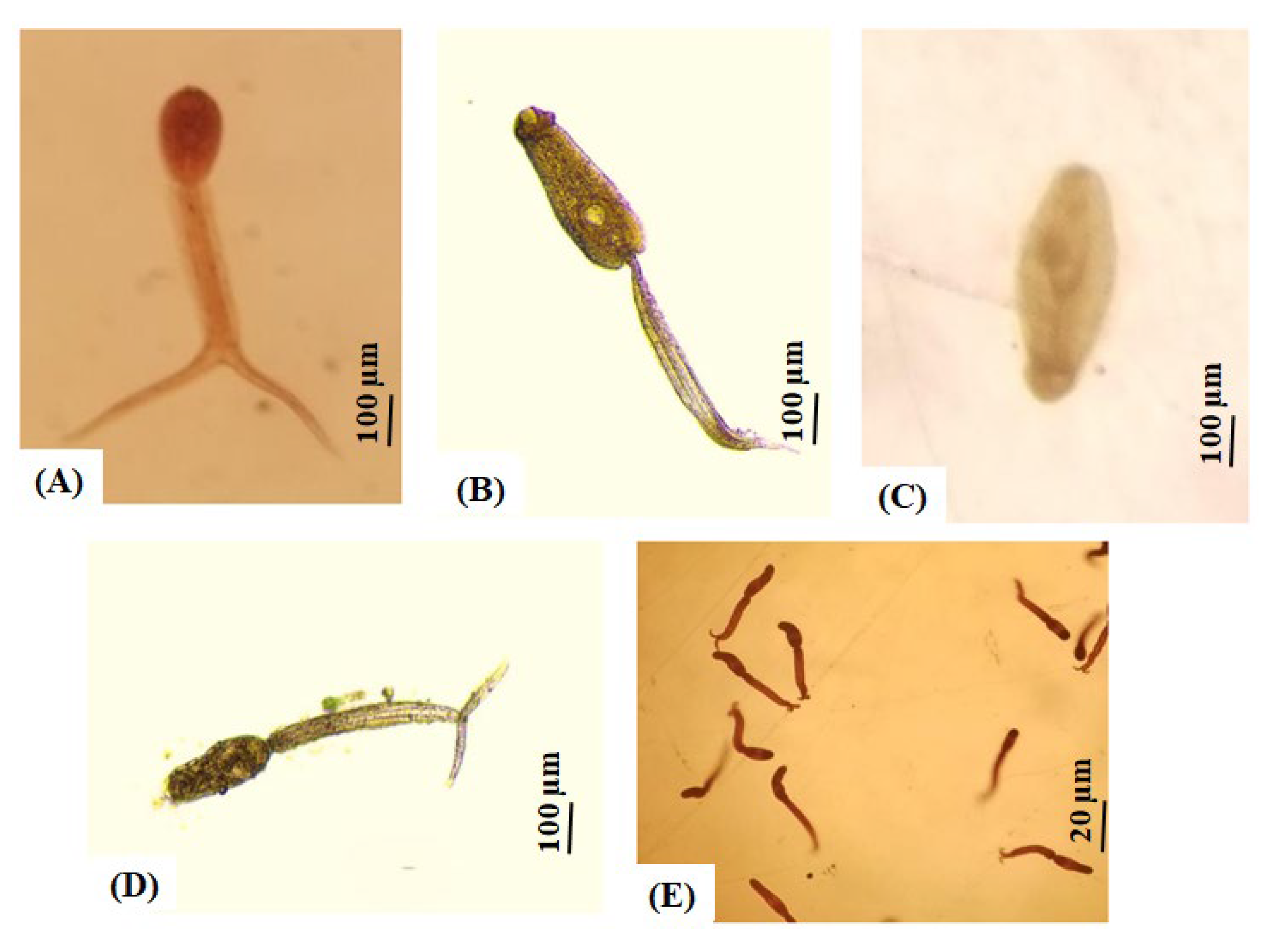
2.6. Cercariae Shedding and PCR Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area, Site Selection, and Sample Collection
4.2. Snail Screening (Cercaria Shedding)
4.3. DNA Extraction
4.4. Molecular Identification
4.4.1. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.4.2. Haplotype and Population Genetic Analysis
4.5. PCR Infection Detection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Brown, D.S. Freshwater Snails of Africa and Their Medical Importance; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; ISBN 0-429-09494-9. [Google Scholar]
- Dejong, R.J.; Morgan, J.A.; Wilson, W.D.; Al-Jaser, M.H.; Appleton, C.C.; Coulibaly, G.; D’Andrea, P.S.; Doenhoff, M.J.; Haas, W.; Idris, M.A.; et al. Phylogeography of Biomphalaria glabrata and B. pfeifferi, Important Intermediate Hosts of Schistosoma mansoni in the New and Old World Tropics. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 3041–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Fact Sheet 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/schistosomiasis (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- El-Tash, L.A. Inter Relationship of the Socio-Economic Status and Schistosomiasis Infection in the Gunaid Sugar Cane Scheme, Sudan. Faculty of Economics, University of Khartoum: Khartoum, Sudan, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.; Abubaker, H. Control of Schistosomiasis in the Gezira Irrigation Scheme, Sudan. J. Biosoc. Sci. 2017, 49, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenwick, A. Irrigation in the Sudan and Schistosomiasis; Demography and Vector-Borne Disease; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kloos, H.; Thompson, K. Schistosomiasis in Africa: An Ecological Perspective. J. Trop. Geogr. 1979, 48, 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- DeJong, R.J.; Morgan, J.A.; Paraense, W.L.; Pointier, J.P.; Amarista, M.; Ayeh-Kumi, P.F.; Babiker, A.; Barbosa, C.S.; Brémond, P.; Pedro Canese, A.; et al. Evolutionary Relationships and Biogeography of Biomphalaria (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) with Implications Regarding Its Role as Host of the Human Bloodfluke, Schistosoma mansoni. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 2225–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, E.A. Snail Hosts of Schistosomiasis and Other Snail-Transmitted Diseases in Tropical America: A Manual; Pan American Health Organization: Washington, DC, USA, 1985; ISBN 92-75-11478-1. [Google Scholar]
- Frandsen, F.; Christensen, N.O. An Introductory Guide to the Identification of Cercariae from African Freshwater Snails with Special Reference to Cercariae of Trematode Species of Medical and Veterinary Importance. Acta Trop. 1984, 41, 181–202. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, N.A.; Madsen, H.; Ahmed, A.A. Types of Trematodes Infecting Freshwater Snails Found in Irrigation Canals in the East Nile Locality, Khartoum, Sudan. Infect Dis. Poverty 2016, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arwa Osman Yosif Ibrahim Snails’ Population Dynamics and Their Parasitic Infections with Trematode in Barakat Canal, Gezira Scheme) 2011; Blue Nile National Institute for Communicable Diseases, University of Gezira: Wad Madani, Sudan, 2012.
- Brown, D.S.; Kristensen, T.K. A Field Guide to African Freshwater Snails I. West African Species; Danish Bilharziasis Laboratory: Charlottenlund, Denmark, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Mandahl-Barth, G. Intermediate Hosts of Schistosoma; African Biomphalaria and Bulinus. I. Bull. World Health Organ. 1957, 16, 1103–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen, A.; Kristensen, T.K.; Stothard, J.R. Phylogeny and Biogeography of African Biomphalaria (Gastropoda: Planorbidae), with Emphasis on Endemic Species of the Great East African Lakes. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2007, 151, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidigal, T.; Kissinger, J.C.; Caldeira, R.L.; Pires, E.C.R.; Monteiro, E.; Simpson, A.J.G.; Carvalho, O.S. Phylogenetic Relationships among Brazilian Biomphalaria Species (Mollusca: Planorbidae) Based upon Analysis of Ribosomal ITS2 Sequences. Parasitology 2000, 121, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrus, P.S.; Stothard, J.R.; Kabatereine, N.B.; Wade, C.M. Comparing Shell Size and Shape with Canonical Variate Analysis of Sympatric Biomphalaria Species within Lake Albert and Lake Victoria, Uganda. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2023, 199, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, F.; Sousa-Figueiredo, J.C.; Paulo, R.; Emery, A.M.; Mirante, C.; Sebastiao, A.; Luciano, A.; Ficato, A.; Van-Dúnem, P.; Brito, M. Mapping Freshwater Snails in Angola: Distribution, Identity and Molecular Diversity of Medically Important Taxa. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2015, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.; Lu, L.; Laidemitt, M.R.; Zhang, S.-M.; Mutuku, M.; Mkoji, G.; Steinauer, M.; Loker, E.S. A Genome Sequence for Biomphalaria pfeifferi, the Major Vector Snail for the Human-Infecting Parasite Schistosoma mansoni. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, R.A.; Stothard, J.R.; Emery, A.M.; Rollinson, D. Molecular Characterization of Freshwater Snails in the Genus Bulinus: A Role for Barcodes? Parasites Vectors 2008, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, M.H.; Condemine, C.; Hesketh, J.; Kayuni, S.A.; Arme, T.M.; Archer, J.; Jones, S.; LaCourse, E.J.; Makaula, P.; Musaya, J. Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) in Lake Malawi and Upper Shire River, Mangochi District, Malawi: Distribution, Genetic Diversity and Pre-Patent Schistosome Infections. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Araújo, A.D.; Carvalho, O.d.S.; Gava, S.G.; Caldeira, R.L. DNA Barcoding as a Valuable Tool for Delimiting Mollusk Species of the Genus Biomphalaria Preston, 1910 (Gastropoda: Planorbidae). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, J.; Cunningham, L.J.; Juhász, A.; Jones, S.; O’Ferrall, A.M.; Rollason, S.; Mainga, B.; Chammudzi, P.; Kapira, D.R.; Lally, D.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology and Population Genetics of Schistosoma mansoni Infecting School-Aged Children Situated along the Southern Shoreline of Lake Malawi, Malawi. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.R.; Lv, S.; Guo, Y.-H.; Gu, W.-B.; Standley, C.J.; Caldeira, R.L.; Zhou, X.-N. Morphological and Molecular Characterization of Invasive Biomphalaria straminea in Southern China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2018, 7, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsaka-Makuvaza, M.J.; Zhou, X.-N.; Tshuma, C.; Abe, E.; Manasa, J.; Manyangadze, T.; Allan, F.; Chin’ombe, N.; Webster, B.; Midzi, N. Genetic Diversity of Biomphalaria pfeifferi, the Intermediate Host of Schistosoma mansoni in Shamva District, Zimbabwe: Role on Intestinal Schistosomiasis Transmission. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 4975–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plam, M.; Jørgensen, A.; Kristensen, T.; Madsen, H. Sympatric Biomphalaria Species (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) in Lake Albert, Uganda, Show Homoplasies in Shell Morphology. Afr. Zool. 2008, 43, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.; Jones, C.S.; Lockyer, A.E.; Hughes, S.; Brown, D.; Noble, L.R.; Rollinson, D. Molecular Evidence Supports an African Affinity of the Neotropical Freshwater Gastropod, Biomphalaria glabrata, Say 1818, an Intermediate Host for Schistosoma mansoni. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 267, 2351–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrus, P.S.; Stothard, J.R.; Wade, C.M. Seasonal Patterns of Schistosoma mansoni Infection within Biomphalaria Snails at the Ugandan Shorelines of Lake Albert and Lake Victoria. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolmarans, C.T.; de Kock, K.N.; Strauss, H.D.; Bornman, M. Daily Emergence of Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium Cercariae from Naturally Infected Snails under Field Conditions. J. Helminthol. 2002, 76, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamburger, J.; Weil, M.; Ouma, J.H.; Koech, D.; Sturrock, R.F. Identification of Schistosome-Infected Snails by Detecting Schistosomal Antigens and DNA Sequences. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 1992, 87 (Suppl. 4), 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannotti-Passos, L.K.; Vidigal, T.H.; Dias-Neto, E.; Pena, S.D.; Simpson, A.J.; Dutra, W.O.; Souza, C.P.; Carvalho-Parra, J.F. PCR Amplification of the Mitochondrial DNA Minisatellite Region to Detect Schistosoma Mansoni Infection in Biomphalaria glabrata Snails. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakuza, J.S.; Gillespie, R.; Nkwengulila, G.; Adam, A.; Kilbride, E.; Mable, B.K. Assessing S. mansoni Prevalence in Biomphalaria Snails in the Gombe Ecosystem of Western Tanzania: The Importance of DNA Sequence Data for Clarifying Species Identification. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, N.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Pérez-Arellano, J.L.; Carranza, C.; Puente, S.; López-Abán, J.; Muro, A. A New PCR-Based Approach for the Specific Amplification of DNA from Different Schistosoma Species Applicable to Human Urine Samples. Parasitology 2006, 133, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joof, E.; Andrus, P.S.; Sowunmi, K.; Onyango, V.M.; Wade, C.M. Comparing PCR Techniques against Conventional Cercarial Shedding Methods for Detecting Schistosoma mansoni Infection in Biomphalaria Snails. Acta Trop. 2020, 212, 105716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennance, T.; Lam, Y.; Bigot, N.; Trapp, J.; Spaan, J.M.; Ogara, G.; Rawago, F.; Andiego, K.; Mulonga, B.; Odhiambo, M.; et al. A Rapid Diagnostic PCR Assay for The Detection of Schistosoma mansoni In Their Snail Vectors. J. Parasitol. 2024, 110, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrus, P.S.; Standley, C.J.; Stothard, J.R.; Wade, C.M. Molecular Xenomonitoring of Schistosoma mansoni Infections in Biomphalaria choanomphala at Lake Victoria, East Africa: Assessing Roles of Abiotic and Biotic Factors. PLoS Negl. Trop Dis. 2025, 19, e0012771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born-Torrijos, A.; Poulin, R.; Raga, J.A.; Holzer, A.S. Estimating Trematode Prevalence in Snail Hosts Using a Single-Step Duplex PCR: How Badly Does Cercarial Shedding Underestimate Infection Rates? Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockyer, A.E.; Olson, P.D.; Littlewood, D.T.J. Utility of Complete Large and Small Subunit rRNA Genes in Resolving the Phylogeny of the Neodermata (Platyhelminthes): Implications and a Review of the Cercomer Theory. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2003, 78, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protasio, A.V.; Tsai, I.J.; Babbage, A.; Nichol, S.; Hunt, M.; Aslett, M.A.; De Silva, N.; Velarde, G.S.; Anderson, T.J.C.; Clark, R.C.; et al. A Systematically Improved High Quality Genome and Transcriptome of the Human Blood Fluke Schistosoma mansoni. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibwana, F. Molecular Identification of Larval Schistosoma Species (Schistosomatidae: Digenea) in Intermediate Hosts (Biomphalaria) from Mwanza Gulf of Lake Victoria in Tanzania. East Afr. Med. J. 2018, 95, 2102–2112. [Google Scholar]
- Avise, J.C.; Neigel, J.E.; Arnold, J. Demographic Influences on Mitochondrial DNA Lineage Survivorship in Animal Populations. J. Mol. Evol. 1984, 20, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avise, J.C. Phylogeography: The History and Formation of Species; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Manzoor, A.; Wang, X. Mitochondrial DNA Analysis Reveals Spatial Genetic Structure and High Genetic Diversity of Massicus raddei (Blessig) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in China. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 11657–11670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. Variability within and among Natural Populations. In Evolution and the Genetics of Populations; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1978; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Standley, C.J.; Goodacre, S.L.; Wade, C.M.; Stothard, J.R. The Population Genetic Structure of Biomphalaria choanomphala in Lake Victoria, East Africa: Implications for Schistosomiasis Transmission. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angers, B.; Charbonnel, N.; Galtier, N.; Jarne, P. The Influence of Demography, Population Structure and Selection on Molecular Diversity in the Selfing Freshwater Snail Biomphalaria pfeifferi. Genet. Res. 2003, 81, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palasio, R.G.S.; Chiaravalloti-Neto, F.; Tuan, R. Distribution of Genetic Diversity of Neotropical Biomphalaria (Preston 1910) (Basommatophora: Planorbidae) Intermediate Hosts for Schistosomiasis in Southeast Brazil. Front. Trop. Dis. 2023, 4, 1143186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein-Eddine, R.; Djuikwo-Teukeng, F.F.; Dar, Y.; Dreyfuss, G.; Van den Broeck, F. Population Genetics of the Schistosoma Snail Host Bulinus truncatus in Egypt. Acta Trop. 2017, 172, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.P.; Davies, C.M.; Hoffman, J.I.; Ndamba, J.; Noble, L.R.; Woolhouse, M.E.J. Population Genetics of the Schistosome Intermediate Host Biomphalaria pfeifferi in the Zimbabwean Highveld: Implications for Co-Evolutionary Theory. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2001, 95, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonnel, N.; Quesnoit, M.; Razatavonjizay, R.; Bremond, P.; Jarne, P. A Spatial and Temporal Approach to Microevolutionary Forces Affecting Population Biology in the Freshwater Snail Biomphalaria pfeifferi. Am. Nat. 2002, 160, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonnel, N.; Angers, B.; Rasatavonjizay, R.; Bremond, P.; Debain, C.; Jarne, P. The Influence of Mating System, Demography, Parasites and Colonization on the Population Structure of Biomphalaria pfeifferi in Madagascar. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 2213–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarne, P.; Charlesworth, D. The Evolution of the Selfing Rate in Functionally Hermaphrodite Plants and Animals. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1993, 24, 441–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian-Bi, Y.-N.T.; Konan, J.-N.K.; Sangaré, A.; Ortega-Abboud, E.; Utzinger, J.; N’Goran, E.K.; Jarne, P. Spatio-Temporal Population Genetic Structure, Relative to Demographic and Ecological Characteristics, in the Freshwater Snail Biomphalaria pfeifferi in Man, Western Côte d’Ivoire. Genetica 2019, 147, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, M.A.; Denno, R.F. The Influence of Dispersal and Diet Breadth on Patterns of Genetic Isolation by Distance in Phytophagous Insects. Am. Nat. 1998, 152, 428–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, V.E. The Importance of ATP in the Immune System of Molluscs. ISJ-Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2011, 8, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Matoo, O.B.; Neiman, M. Bringing Disciplines and People Together to Characterize the Plastic and Genetic Responses of Molluscs to Environmental Change. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2021, 61, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.S. Freshwater Snails of Africa and Their Medical Importance; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: London, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, J.P.; Davies, C.M.; Ndamba, J.; Noble, L.R.; Jones, C.S.; Woolhouse, M.E.J. Spatio-Temporal Genetic Variability in the Schistosome Intermediate Host Biomphalaria pfeifferi. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2001, 95, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandoni, S.M.; Mulvey, M.; KOECH, D.K.; LOKER, E.S. Genetic Structure of Kenyan Populations of Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Gastropoda: Planorbidae). J. Molluscan Stud. 1990, 56, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.I.; Webster, J.P.; Ndamba, J.; Woolhouse, M.E. Extensive Genetic Variation Revealed in Adjacent Populations of the Schistosome Intermediate Host Biomphalaria pfeifferi from a Single River System. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1998, 92, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchami Mbagnia, M.C.; Melachio Tanekou, T.T.; Kengne Fokam, A.C.; Nguiffo Nguete, D.; Wondji, C.S.; Njiokou, F. PCR-Based Molecular Identification of Two Intermediate Snail Hosts of Schistosoma mansoni in Cameroon. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburger, J. Molecular Tools and Schistosomiasis Transmission Elimination. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1376–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webbe, G. Transmission of Bilharziasis. 2. Production of Cercariae. Bull. World Health Organ. 1965, 33, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- King, C.H.; Sturrock, R.F.; Kariuki, H.C.; Hamburger, J. Transmission Control for Schistosomiasis—Why It Matters Now. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamburger, J.; Hoffman, O.; Kariuki, H.C.; Muchiri, E.M.; Ouma, J.H.; Koech, D.K.; Sturrock, R.F.; King, C.H. Large-Scale, Polymerase Chain Reaction-Based Surveillance of Schistosoma haematobium DNA in Snails from Transmission Sites in Coastal Kenya: A New Tool for Studying the Dynamics of Snail Infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 71, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hailegebriel, T.; Nibret, E.; Munshea, A. Prevalence of Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium in Snail Intermediate Hosts in Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Trop. Med. 2020, 2020, 8850840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, S.M.; Mutuku, M.W.; Mkoji, G.M.; Loker, E.S. Relative Compatibility of Schistosoma mansoni with Biomphalaria sudanica and B. pfeifferi from Kenya as Assessed by PCR Amplification of the S. mansoni ND5 Gene in Conjunction with Traditional Methods. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannotti-Passos, L.K.; Magalhães, K.G.; Carvalho, O.S.; Vidigal, T.H. Multiplex PCR for Both Identification of Brazilian Biomphalaria Species (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) and Diagnosis of Infection by Schistosoma mansoni (Trematoda: Schistosomatidae). J. Parasitol. 2006, 92, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, I.; King, C.H.; Muchiri, E.M.; Hamburger, J. Detection of Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma haematobium DNA by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification: Identification of Infected Snails from Early Prepatency. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutuku, M.W.; Dweni, C.K.; Mwangi, M.; Kinuthia, J.M.; Mwangi, I.N.; Maina, G.M.; Agola, L.E.; Zhang, S.M.; Maranga, R.; Loker, E.S.; et al. Field-Derived Schistosoma mansoni and Biomphalaria pfeifferi in Kenya: A Compatible Association Characterized by Lack of Strong Local Adaptation, and Presence of Some Snails Able to Persistently Produce Cercariae for over a Year. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, P.-Y.; Chen, X. Detection of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2003, 5, 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, J.P.; Shrivastava, J.; Johnson, P.J.; Blair, L. Is Host-Schistosome Coevolution Going Anywhere? BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltoum, M.A. Sudan Climate; Institute of Arab Research and Studies: Cairo, Egypt, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Eltoum, I.A.; Sulaiman, S.M.; Elturabi, H.; Mahgoub, E.; Homeida, M.M. Infection with Schistosoma mansoni in Two Different Endemic Areas: A Comparative Population-Based Study in Elziedab and Gezira-Managil Irrigation Schemes, Sudan. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1993, 96, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hilali, A.H.; Madsen, H.; Daffalla, A.A.; Wassila, M.; Christensen, N.O. Infection and Transmission Pattern of Schistosoma mansoni in the Managil Irrigation Scheme, Sudan. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1995, 89, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oomen, J.M.V.; De Wolf, J.; Jobin, W.R. Health and Irrigation: Incorporation of Disease Control Measures in Irrigation: A Multi-Faceted Task in Design, Construction, and Operation: Volume 2; ILRI Publication: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1988; ISBN 90-70754-17-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, S.; Elhag, M.S.; Lee, Y.-H.; Cho, D.-S.; Ismail, H.A.H.A.; Hong, S.-T. Epidemiological Findings and Policy Implications from the Nationwide Schistosomiasis and Intestinal Helminthiasis Survey in Sudan. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadawi, S.; Aldawabi Abdelbagi, T.; Mohamed, S.; Mohamed, A.; Ibrahim, E.; Ali, E.; Abakar, A.; Abdalla Elsharief, U.; Nour, B.Y.M. Prevalence of Intestinal and Urinary Schistosomaisis in Five Localities in Gezira State. Int. J. Med. Sci. Health Res. 2018, 2, 88–99. [Google Scholar]
- Frandsen, F.; McCullough, F.; Madsen, H.; WHO; Danish Bilharziasis, L. A Practical Guide to the Identification of African Freshwater Snails; Malacological review; World Health Organization, Danish Bilharziasis Laboratory: Geneva, Switzerland, 1980; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. A Field Guide to African Fresh Water Snails: Introduction, Danish Bilharziasis Laboratory WHO Collaborating Center for Applied Malacology; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schell, S.C. Handbook of Trematodes of North America North of Mexico; University Press of Idaho: Moscow, ID, USA, 1985; ISBN 0-89301-095-2. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA Primers for Amplification of Mitochondrial Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit I from Diverse Metazoan Invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Palumbi, S.R.; Martin, A.; Romano, S.; McMillan, W.O.; Stice, L.; Grabowski, G.; University of Hawaii at Manoa Department of Zoology; Kewalo Marine, L. The Simple Fool’s Guide to PCR; Version 2.0; Department of Zoology and Kewalo Marine Laboratory, University of Hawaii Honolulu : Honolulu, HI, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Vrijenhoek, R.C. Genetic Diversity and Fitness in Small Populations. In Conservation Genetics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT; Scientific Research: Oxford, UK, 1999; Volume 41, pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Messeguer, X.; Rozas, R. DnaSP, DNA Polymorphism Analyses by the Coalescent and Other Methods. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2496–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukes, T.H.; Cantor, C.R. Evolution of Protein Molecules; Munro, H.N., Ed.; Mammalian Protein Metabolism; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Tajima, F. Statistical Method for Testing the Neutral Mutation Hypothesis by DNA Polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.X.; Li, W.H. Statistical Tests of Neutrality of Mutations. Genetics 1993, 133, 693–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.X. Statistical Tests of Neutrality of Mutations against Population Growth, Hitchhiking and Background Selection. Genetics 1997, 147, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, D.R. Variation in Gene Flow Levels among Predominantly Self-pollinated Plants. J. Evol. Biol. 1989, 2, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, T.; Bouvier, J.-C.; Beslay, D.; Sauphanor, B. Variability in Diapause Propensity within Populations of a Temperate Insect Species: Interactions between Insecticide Resistance Genes and Photoperiodism. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2004, 83, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, M.; Snell, Q.; Walker, P.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K. TCS: Estimating Gene Genealogies. Parallel Distrib. Process. Symp. Int. Proc. 2002, 2, 184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.M.; Bu, L.; Laidemitt, M.R.; Lu, L.; Mutuku, M.W.; Mkoji, G.M.; Loker, E.S. Complete mitochondrial and rDNA complex sequences of important vector species of Biomphalaria, obligatory hosts of the human-infecting blood fluke, Schistosoma mansoni. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidemitt, M.R.; Gleichsner, A.M.; Ingram, C.D.; Gay, S.D.; Reinhart, E.M.; Mutuku, M.W.; Oraro, P.O.; Minchella, D.J.; Mkoji, G.M.; Loker, E.S.; et al. Host preference of field-derived Schistosoma mansoni is influenced by snail host compatibility and infection status. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Site | H | S | K | Hd ±SD | HV | π (JC)± SD | Fu’ Fs | Fu Li’ D | Fu Li’ F | Tajima’s D | Theta Θ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COI | Overall | 5 | 41 | 5.387 | 0.5 ± 0.022 | 0.0005 | 0.01 ± 0.0007 | 13.62 | −5.01 ** | −3.91 ** | −0.867 | 0.014 |
| EG | 3 | 31 | 2.80 | 0.191 ± 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.0055 ± 0.003 | 5.57 | −2.84 * | −3.17 * | −2.36 ** | 0.015 | |
| GW | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| HA | 2 | 3 | 0.2 | 0.067 ± 0.06 | 0.004 | 0.0003 ± 0.0003 | 0.135 | −2.68 * | −2.79 * | −1.731 | 0.001 | |
| NU1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| NU3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| SG | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MA | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 16S | Overall | 10 | 84 | 2.056 | 0.11± 0.035 | 0.0012 | 0.008 ± 0.003 | −0.043 | −2.57 *** | −3.16 ** | −2.710 *** | 0.051 |
| EG | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| GW | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| HA | 6 | 72 | 9.40 | 0.31 ± 0.109 | 0.012 | 0.035 ± 0.013 | 8.825 | 0.031 | −0.69 | −1.84 * | 0.052 | |
| NU1 | 4 | 18 | 1.32 | 0.25 ± 0.102 | 0.01 | 0.004 ± 0.003 | 1.38 | −4.24 ** | −4.3 *** | −2.425 *** | 0.014 | |
| NU3 | 2 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.067 ± 0.061 | 0.004 | 0.0002 ± 0.0002 | −1.21 | −1.68 | −1.76 | −1.147 | 0.001 | |
| SG | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MA | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| (A) COI Gene Fragment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EG | GW | HA | NU1 | NU3 | SG | MA | |
| EG | - | ||||||
| GW | 0.86 | - | |||||
| HA | 0.85 | 0 | - | ||||
| NU1 | 0.02 | 1 | 0.99 | - | |||
| NU3 | 0.02 | 1 | 0.99 | 0 | - | ||
| SG | 0.02 | 1 | 0.99 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| MA | 0.9 | 1 | 0.99 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| Overall Fst = 0.94, Overall Nm = 0.03 | |||||||
| (B) 16S Gene Fragment | |||||||
| EG | GW | HA | NU1 | NU3 | SG | MA | |
| EG | - | ||||||
| GW | 0 | - | |||||
| HA | 0.05 | 0.05 | - | ||||
| NU1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | - | |||
| NU3 | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.01 | - | ||
| SG | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0 | - | |
| MA | 0 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Overall Fst = 0.04, Overall Nm = 5.72 | |||||||
| Sum of Variation | Degree of Freedom (df) | Sigma Squared (σ2) | %Variation | Fixation Index (ΦST) * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COI | 0.9 (p > 0.001) | ||||
| Among populations | 4203.261 | 6 | 25.616 | 84.6 | |
| Within populations | 724.800 | 156 | 4.646 | 15.4 | |
| Total | 4928.061 | 162 | 30.262 | ||
| 16S | 0.04 (p > 0.001) | ||||
| Among populations | 556.691 | 6 | 1.727 | 3.6 | |
| Within populations | 7154.567 | 156 | 45.863 | 96.4 | |
| Total | 7711.258 | 162 | 47.590 |
| Site (ID) | Number of B. pfeifferi Tested | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collected | Cercaria Shedding | PCR (SmF/R) | Type of Cercariae | |
| SG (S3) | 10 | 0 | 0 | None |
| GW (S6) | 38 | 0 | 0 | None |
| NU1 (S10) | 31 | 0 | 0 | None |
| NU3 (S12) | 30 | 16.6% (5/30) | 0 | Echinostome (n:5) and Cotylomicrocercous spp. (n:4) |
| EG (S13) | 66 | 1.5% (1/66) | 0 | Apharyngostrigea sp. |
| HA (S19) | 39 | 5.1% (2/39) | 40% (12/30) | S. mansoni |
| MA (S23) | 3 | 0 | 0 | None |
| Overall infection rate | 3.6% (8/219) | 7.4% (12/163) * | ||
| Locality/Administrative Unit | Site ID | No. DNA Extracted (n = 163) | Latitude | Longitude | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Gezira/Barakat | S3: Barakat | (SG) | 10 | 14.357 | 33.526 |
| Greater Wadmedani | S6: Atraa | (GW) | 30 | 14.445 | 33.487 |
| North Umelgura/Elhediba | S10: Elhediba | (NU1) | 30 | 14.484 | 33.658 |
| S12: Elhediba | (NU3) | 30 | 14.484 | 33.657 | |
| East Gezira/Elgineid | S13: Elgineid | (EG) | 30 | 14.866 | 33.277 |
| Hasahisa/Wadelfadni | S19: Wadelfadni | (HA) | 30 | 14.670 | 33.343 |
| Managil/Eboud | S23: Eboud/Alnegeer village | (MA) | 3 | 14.230 | 33.173 |
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′→3′) | Primer Length (bp) | Annealing Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LCO 1490 | GGT CAA CAA ATC ATA AAG ATA TTG G | 25 | 45 |
| HCO 2198 | TAA ACT TCA GGG TGA CCA AAA AAT CA | 26 | |
| 16Sar | CTT CTC GAC TGT TTA TCA AAA ACA | 24 | 48 |
| 16Sbr | GCC GGT CTG AAC TCA GAT CAT | 21 | |
| SmF | GAG ATC AAG TGT GAC AGT TTT GC | 23 | 61 |
| SmR | ACA GTG CGC GCG TCG TAA GC | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osman, A.; Andrus, P.S.; Fang, Y.; Elhassan, I.; Zhou, X.; Nour, B.Y.M.; Zhao, L. Genetic Diversity and Infection Prevalence of Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Krauss, 1848), the Intermediate Snail Host of Schistosoma mansoni in Gezira State, Sudan. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199567
Osman A, Andrus PS, Fang Y, Elhassan I, Zhou X, Nour BYM, Zhao L. Genetic Diversity and Infection Prevalence of Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Krauss, 1848), the Intermediate Snail Host of Schistosoma mansoni in Gezira State, Sudan. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199567
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsman, Arwa, Peter S. Andrus, Yuan Fang, Ibrahim Elhassan, Xiaonong Zhou, Bakri Y. M. Nour, and Liming Zhao. 2025. "Genetic Diversity and Infection Prevalence of Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Krauss, 1848), the Intermediate Snail Host of Schistosoma mansoni in Gezira State, Sudan" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199567
APA StyleOsman, A., Andrus, P. S., Fang, Y., Elhassan, I., Zhou, X., Nour, B. Y. M., & Zhao, L. (2025). Genetic Diversity and Infection Prevalence of Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Krauss, 1848), the Intermediate Snail Host of Schistosoma mansoni in Gezira State, Sudan. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199567






