Chloroplast Genome Diversity and Marker Potentials of Diverse Ensete ventricosum Accessions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
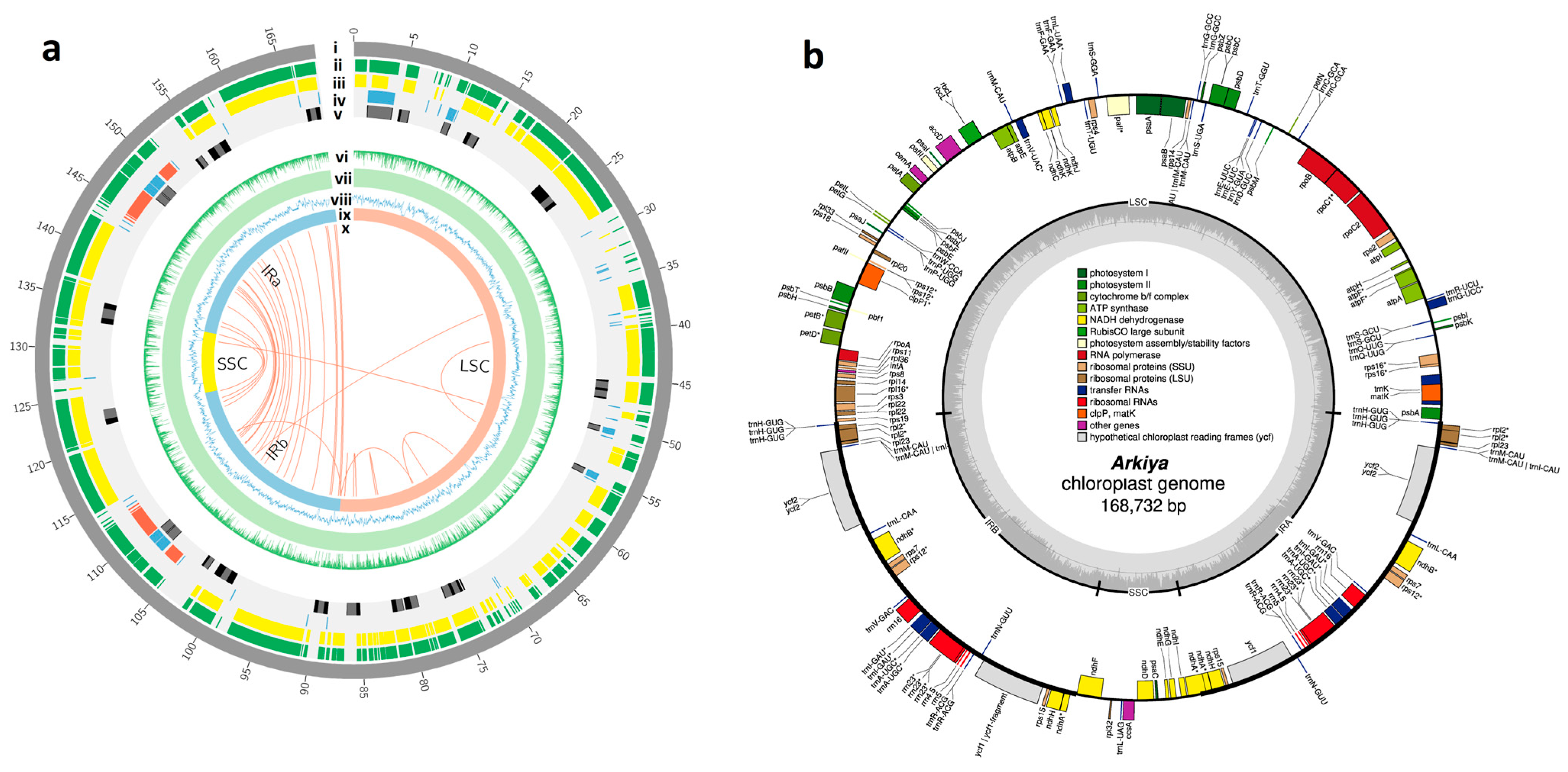
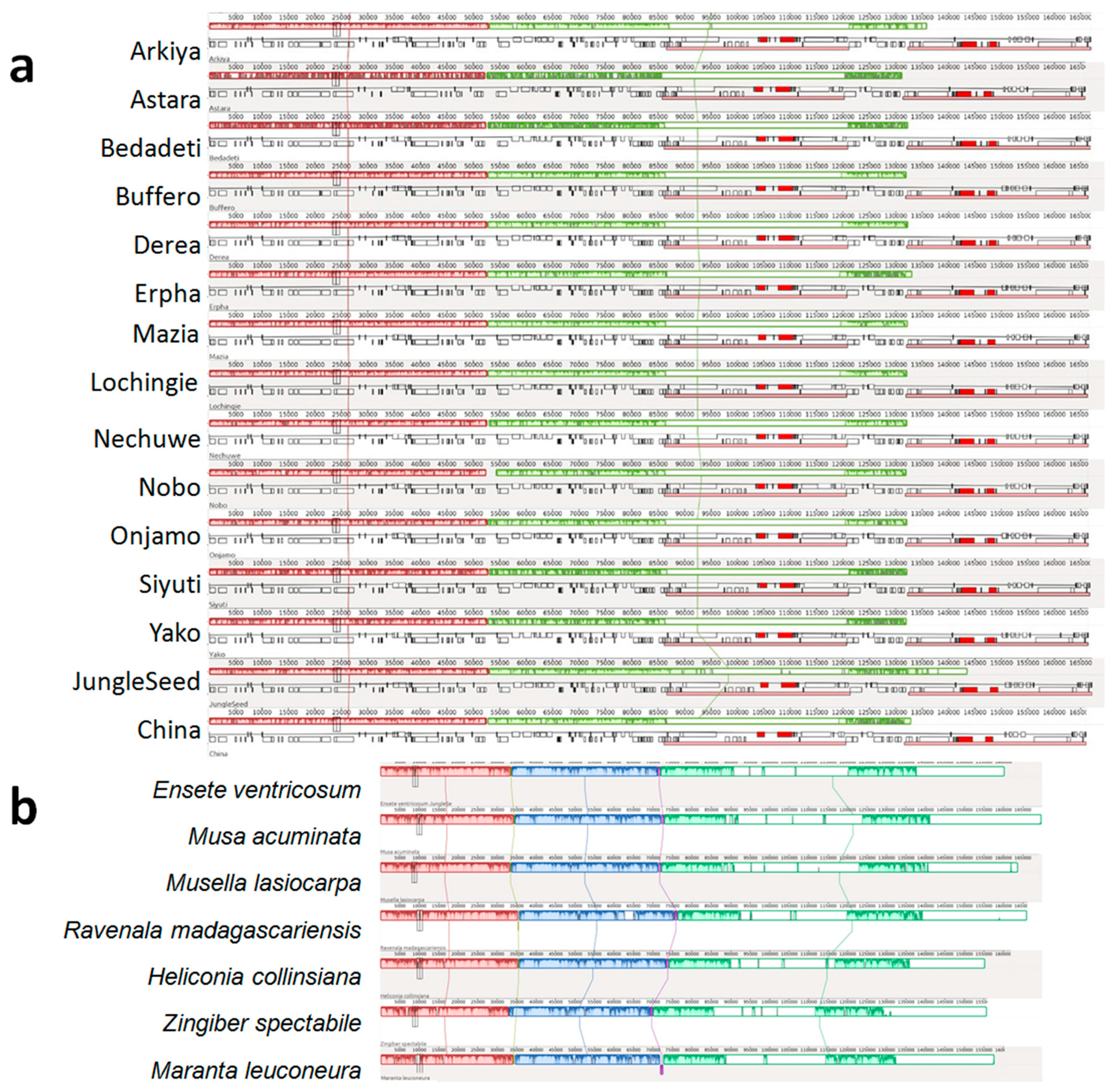
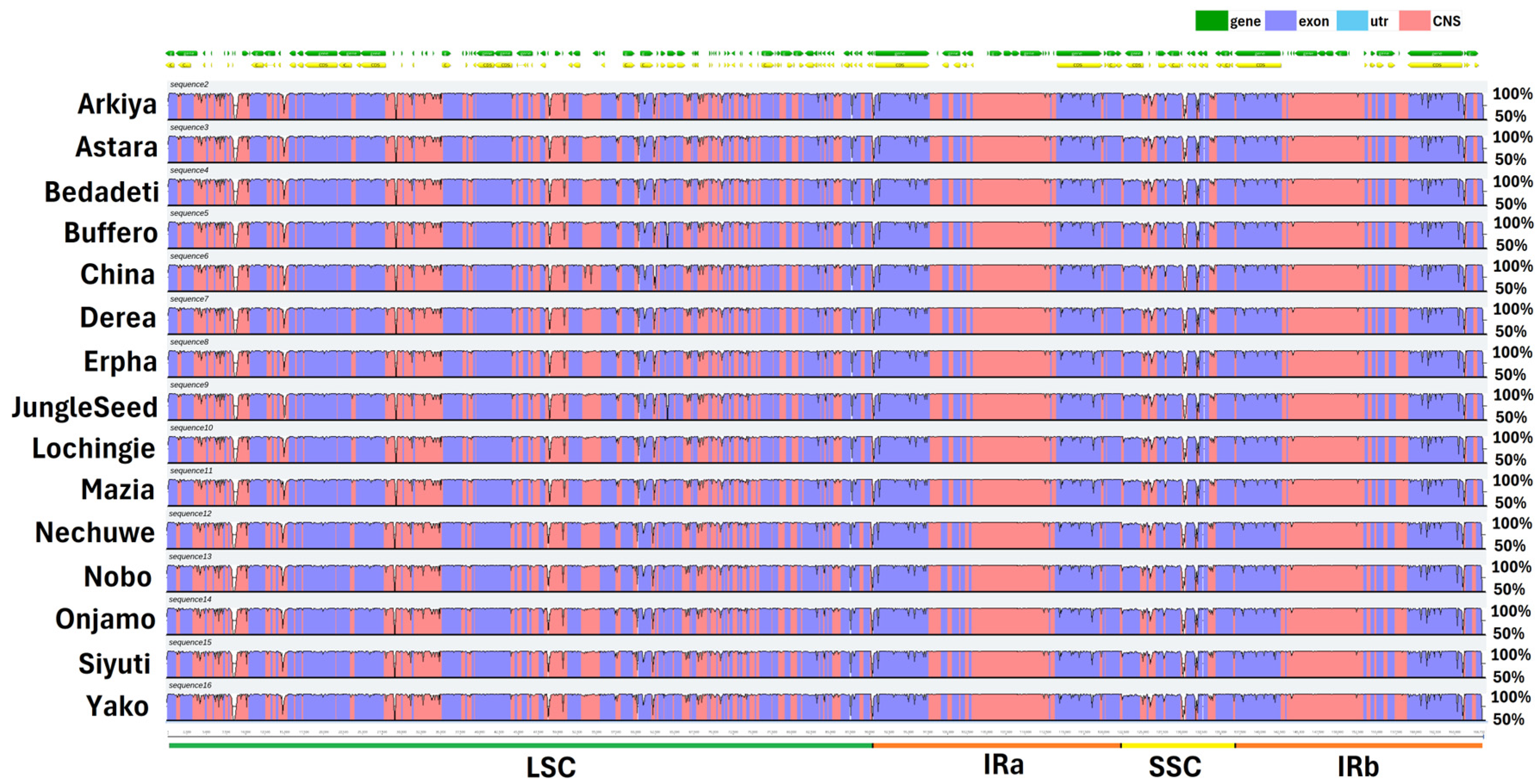
2.1. Chloroplast Genome Assembly, Features, Annotation, and Comparative Genomics
2.2. Codon Usage and Amino Acid Frequency
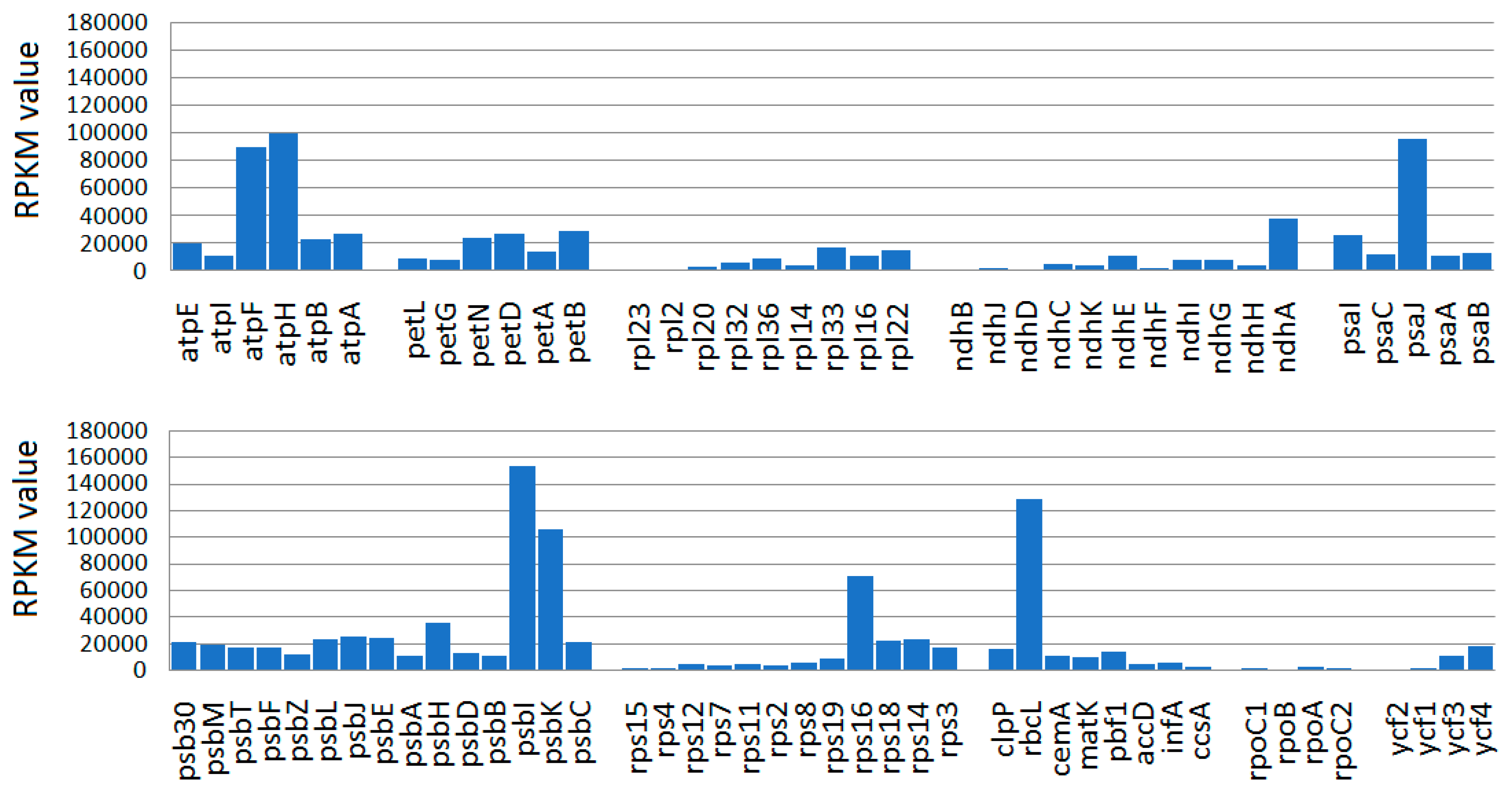
2.3. Transcriptional Evidence in Ensete CP Genes
2.4. Ensete Chloroplast RNA Editing
2.5. Repeat Characterization
2.6. Genome-Wide SNP Distribution
2.7. Molecular Marker Potentiality
2.8. Phylogenetic Relationship, Genomic Diversity, and Structure
3. Discussion
3.1. Chloroplast Genome Assembly, Features, Annotation, and Comparative Genomics
3.2. Codon Usage and Amino Acid Frequency
3.3. Transcriptional Evidence in Ensete Chloroplast Genes
3.4. Ensete Chloroplast RNA Editing
3.5. Repeat Characterization
3.6. Nucleotide Diversity and Mutation Hotspots
3.7. SNP Variation and Marker Potentiality
3.8. Genetic Diversity and Structure
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chloroplast Genome Reconstruction and Annotation
4.2. Comparative Analysis of Chloroplast Genomes
4.3. Transcriptome Sequencing, CP Gene Expression Analysis, and RNA Editing Site Prediction
4.4. Repeat Structure Analysis
4.5. SNP Calling
4.6. Development of Potential Molecular Markers
4.7. Phylogenic Relationship Haplotype Analysis and Structure Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borrell, J.S.; Biswas, M.K.; Goodwin, M.; Blomme, G.; Schwarzacher, T.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S.; Wendawek, A.M.; Berhanu, A.; Kallow, S.; Janssens, S. Enset in Ethiopia: A poorly characterized but resilient starch staple. Ann. Bot. 2019, 123, 747–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, M.K.; Darbar, J.N.; Borrell, J.S.; Bagchi, M.; Biswas, D.; Nuraga, G.W.; Demissew, S.; Wilkin, P.; Schwarzacher, T.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S. The landscape of microsatellites in the enset (Ensete ventricosum) genome and web-based marker resource development. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyissa, T.; Tesfaye, K.; Biswas, M.K.; Schwarzacher, T.; Borrell, J.; Wilkin, P.; Demissew, S.; Tadele, Z.; Heslop-Harrison, J.P. The genotypic and genetic diversity of enset (Ensete ventricosum) landraces used in traditional medicine is similar to the diversity found in starchy landraces. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Haile, M. Cluster analysis for evaluation of genetic diversity inEnset (Enset ventricosum (Welw.): Cheesman) clones at Areka Condition. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 2, 55–69. [Google Scholar]
- Yemataw, Z.; Tesfaye, K.; Grant, M.; Studholme, D.J.; Chala, A. Multivariate analysis of morphological variation in enset (Ensete ventricosum (Welw.) Cheesman) reveals regional and clinal variation in germplasm from South and South Western Ethiopia. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2018, 12, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negash, A.; Tsegaye, A.; van Treuren, R.; Visser, B. AFLP analysis of enset clonal diversity in South and Southwestern Ethiopia for conservation. Crop Sci. 2002, 42, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmeta, G.; Nybom, H.; Bekele, E. RAPD analysis of genetic diversity among clones of the Ethiopian crop plant Ensete ventricosum. Euphytica 2002, 124, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiaw, D.C.; Bekele, E. Analysis of genetic diversity among cultivated enset (Ensete ventricosum) populations from Essera and Kefficho, Southwestern part of Ethiopia using inter simple sequence repeats (ISSRs) marker. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 15697–15709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, S.; Mekbib, F.; Admassu, B.; Kelemu, S.; Kidane, S.; Negisho, K.; Djikeng, A.; Nzuki, I. A look into genetic diversity of enset (Ensete ventricosum (Welw.) cheesman) using transferable microsatellite sequences of banana in Ethiopia. J. Crop Improv. 2014, 28, 159–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olango, T.M.; Tesfaye, B.; Pagnotta, M.A.; Pè, M.E.; Catellani, M. Development of SSR markers and genetic diversity analysis in enset (Ensete ventricosum (Welw.) Cheesman), an orphan food security crop from Southern Ethiopia. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, G.L.; Dorman, H.E.; Buchanan, A.; Challagundla, L.; Wallace, L.E. A review of the prevalence, utility, and caveats of using chloroplast simple sequence repeats for studies of plant biology. Appl. Plant Sci. 2014, 2, 1400059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xue, Q. Comparative studies on codon usage pattern of chloroplasts and their host nuclear genes in four plant species. J. Genet. 2005, 84, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Li, H.; Milne, R.; Zhang, T.; Ma, P.; Yang, J.; Li, D.; Gao, L. Comparative analyses of plastid genomes from fourteen Cornales species: Inferences for phylogenetic relationships and genome evolution. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, M. The Chloroplast Genome; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Cusimano, N.; Wicke, S. Massive intracellular gene transfer during plastid genome reduction in nongreen Orobanchaceae. New Phytol. 2016, 210, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.W.; Lam, V.K.; Merckx, V.S. Plastomes on the edge: The evolutionary breakdown of mycoheterotroph plastid genomes. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, D.; He, X.; Zhou, S. Comparative chloroplast genomics of Fritillaria (Liliaceae), inferences for phylogenetic relationships between Fritillaria and Lilium and plastome evolution. Plants 2020, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.J.; Soltis, P.S.; Bell, C.D.; Burleigh, J.G.; Soltis, D.E. Phylogenetic analysis of 83 plastid genes further resolves the early diversification of eudicots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4623–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edger, P.P.; Hall, J.C.; Harkess, A.; Tang, M.; Coombs, J.; Mohammadin, S.; Schranz, M.E.; Xiong, Z.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Meyers, B.C. Brassicales phylogeny inferred from 72 plastid genes: A reanalysis of the phylogenetic localization of two paleopolyploid events and origin of novel chemical defenses. Am. J. Bot. 2018, 105, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, R. Analysis of distribution of bases in the coding sequences by a digrammatic technique. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 6313–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiu, X.; Qin, Y.; Tang, H.; Tang, J.; Liu, T.; Xiao, L.; Luo, H. The chloroplast genome of Camellia sinensis var. assamica cv. Duntsa (Theaceae) and comparative genome analysis: Mutational hotspots and phylogenetic relationships. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2024, 72, 845–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, R.H.M.; Majeský, L’.; Schwarzacher, T.; Gornall, R.; Heslop-Harrison, P. Complete chloroplast genomes from apomictic Taraxacum (Asteraceae): Identity and variation between three microspecies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.K.; Bagchi, M.; Biswas, D.; Harikrishna, J.A.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Sheng, O.; Mayer, C.; Yi, G.; Deng, G. Genome-wide novel genic microsatellite marker resource development and validation for genetic diversity and population structure analysis of banana. Genes 2020, 11, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Baurens, F.; Cardi, C.; Aury, J.; D’Hont, A. The complete chloroplast genome of banana (Musa acuminata, Zingiberales): Insight into plastid monocotyledon evolution. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Luo, H.; Wu, Y.; He, C. The complete chloroplast genome of Musa beccarii. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 2384–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.M.; Md Shah, M.U.; Makale, K.; Mohd-Yusuf, Y.; Khalid, N.; Othman, R.Y. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Musa balbisiana corroborates structural heterogeneity of inverted repeats in wild progenitors of cultivated bananas and plantains. Plant Genome 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Gao, C.; Liu, J. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of wild banana, Musa balbisiana variety ‘Pisang Klutuk Wulung’ (Musaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2018, 3, 460–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L. The complete chloroplast genome of the endangered wild Musa itinerans (Zingiberales: Musaceae). Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2017, 9, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nock, C.J.; Waters, D.L.; Edwards, M.A.; Bowen, S.G.; Rice, N.; Cordeiro, G.M.; Henry, R.J. Chloroplast genome sequences from total DNA for plant identification. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriquez, C.L.; Ahmed, I.; Carlsen, M.M.; Zuluaga, A.; Croat, T.B.; McKain, M.R. Evolutionary dynamics of chloroplast genomes in subfamily Aroideae (Araceae). Genomics 2020, 112, 2349–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, A.P.; Resende-Moreira, L.C.; Buzatti, R.S.; Nazareno, A.G.; Carlsen, M.; Lobo, F.P.; Kalapothakis, E.; Lovato, M.B. Chloroplast genomes of Byrsonima species (Malpighiaceae): Comparative analysis and screening of high divergence sequences. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, F.; Shahzadi, I.; Waseem, S.; Mirza, B.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T. Chloroplast genome of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis (Malvaceae): Comparative analyses and identification of mutational hotspots. Genomics 2020, 112, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, F.; Shahzadi, I.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T.; Mirza, B. Characterization of Withania somnifera chloroplast genome and its comparison with other selected species of Solanaceae. Genomics 2020, 112, 1522–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzadi, I.; Mehmood, F.; Ali, Z.; Ahmed, I.; Mirza, B. Chloroplast genome sequences of Artemisia maritima and Artemisia absinthium: Comparative analyses, mutational hotspots in genus Artemisia and phylogeny in family Asteraceae. Genomics 2020, 112, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez, C.L.; Abdullah; Ahmed, I.; Carlsen, M.M.; Zuluaga, A.; Croat, T.B.; McKain, M.R. Molecular evolution of chloroplast genomes in Monsteroideae (Araceae). Planta 2020, 251, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Messing, J. High-throughput sequencing of three Lemnoideae (duckweeds) chloroplast genomes from total DNA. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Deng, P.; Feng, K.; Liu, P.; Du, X.; You, F.M.; Weining, S. Comparative analysis of codon usage patterns in chloroplast genomes of the Asteraceae family. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 32, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Long, W.; Li, X. Patterns of synonymous codon usage bias in chloroplast genomes of seed plants. For. Stud. China 2008, 10, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Xu, W.; Schwarzacher, T.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S. Comparative chloroplast genome analyses of Avena: Insights into evolutionary dynamics and phylogeny. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Wang, S.; Xia, E.; Jiang, J.; Zeng, F.; Gao, L. Full transcription of the chloroplast genome in photosynthetic eukaryotes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. The chloroplast genome sequence of bittersweet (Solanum dulcamara): Plastid genome structure evolution in Solanaceae. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.R.; Diaz, Y.C.; Penha, H.A.; Pinheiro, D.G.; Fernandes, C.C.; Miranda, V.F.; Michael, T.P.; Varani, A.M. The chloroplast genome of Utricularia reniformis sheds light on the evolution of the ndh gene complex of terrestrial carnivorous plants from the Lentibulariaceae family. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury, N.W.; Roberts, L.L.; Palmer, J.D.; Thompson, W.F. A transcription map of the pea chloroplast genome. Curr. Genet. 1988, 14, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, R.M.; Hoch, B.; Zeltz, P.; Kössel, H. Internal editing of the maize chloroplast ndhA transcript restores codons for conserved amino acids. Plant Cell 1992, 4, 609–616. [Google Scholar]
- Ramadan, A.M.; Mohammed, T.; Firoz, A.; Alameldin, H.F.; Ali, H.M. RNA editing in chloroplast NADH dehydrogenase (ndhA) of salt stressed wild barley revealed novel type G to A. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2023, 35, 102755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, U.J.B.d.; Nunes, R.; Targueta, C.P.; Diniz-Filho, J.A.F.; Telles, M.P.d.C. The complete chloroplast genome of Stryphnodendron adstringens (Leguminosae-Caesalpinioideae): Comparative analysis with related Mimosoid species. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Jung, J.D.; Lee, J.; Park, H.; Oh, K.; Jeong, W.; Choi, D.; Liu, J.R.; Cho, K.Y. Complete sequence and organization of the cucumber (Cucumis sativus L. cv. Baekmibaekdadagi) chloroplast genome. Plant Cell Rep. 2006, 25, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, C.M. Deoxyribonucleic acid. In Encyclopedia of Earth; Draggan, S., Cleveland, C., Eds.; National Council for Science and the Environment: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Lee, H. Complete chloroplast genome sequences from Korean ginseng (Panax schinseng Nees) and comparative analysis of sequence evolution among 17 vascular plants. DNA Res. 2004, 11, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.; Kim, K. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of important oilseed crop Sesamum indicum L. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35872. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Ji, C.; Chen, Z.; Cai, H.; Wu, X.; Shi, C.; Wang, S. Comparative analysis the complete chloroplast genomes of nine Musa species: Genomic features, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic implications. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 832884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, Y.; He, M.; Zhang, B.; Wu, W.; Cai, P.; Huo, D.; Hong, Y. Comparative chloroplast genomes: Insights into the evolution of the chloroplast genome of Camellia sinensis and the phylogeny of Camellia. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Peng, G.; Zhao, L.; Dai, W.; Xu, M.; Xu, X.; Tang, M. Comparative and evolutionary analysis of chloroplast genomes from five rare Styrax species. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giang, V.N.L.; Waminal, N.E.; Park, H.; Kim, N.; Jang, W.; Lee, J.; Yang, T. Comprehensive comparative analysis of chloroplast genomes from seven Panax species and development of an authentication system based on species-unique single nucleotide polymorphism markers. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Kim, T.; Park, Y. Rice chloroplast genome variation architecture and phylogenetic dissection in diverse Oryza species assessed by whole-genome resequencing. Rice 2016, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Shahzad, K.; Li, Z. Comparative chloroplast genomics of Dipsacales species: Insights into sequence variation, adaptive evolution, and phylogenetic relationships. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherry, S.; Xiao, C.; Durbrow, K.; Kimelman, M.; Rodarmer, K.; Shumway, M.; Yaschenko, E. Ncbi sra toolkit technology for next generation sequence data. In Proceedings of the Plant and Animal Genome XX Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 14–18 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, A.E.; Mau, B.; Perna, N.T. progressiveMauve: Multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudno, M.; Malde, S.; Poliakov, A.; Do, C.B.; Couronne, O.; Dubchak, I.; Batzoglou, S. Glocal alignment: Finding rearrangements during alignment. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, i54–i62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mower, J.P. The PREP suite: Predictive RNA editors for plant mitochondrial genes, chloroplast genes and user-defined alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W253–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Schleiermacher, C. REPuter: Fast computation of maximal repeats in complete genomes. Bioinformatics 1999, 15, 426–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, T. MISA—Microsatellite Identification Tool. Available online: http://pgrc.ipk-gatersleben.de/misa/ (accessed on 17 June 2016).
- Mayer, C.; Leese, F.; Tollrian, R. Genome-wide analysis of tandem repeats in Daphnia pulex-a comparative approach. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
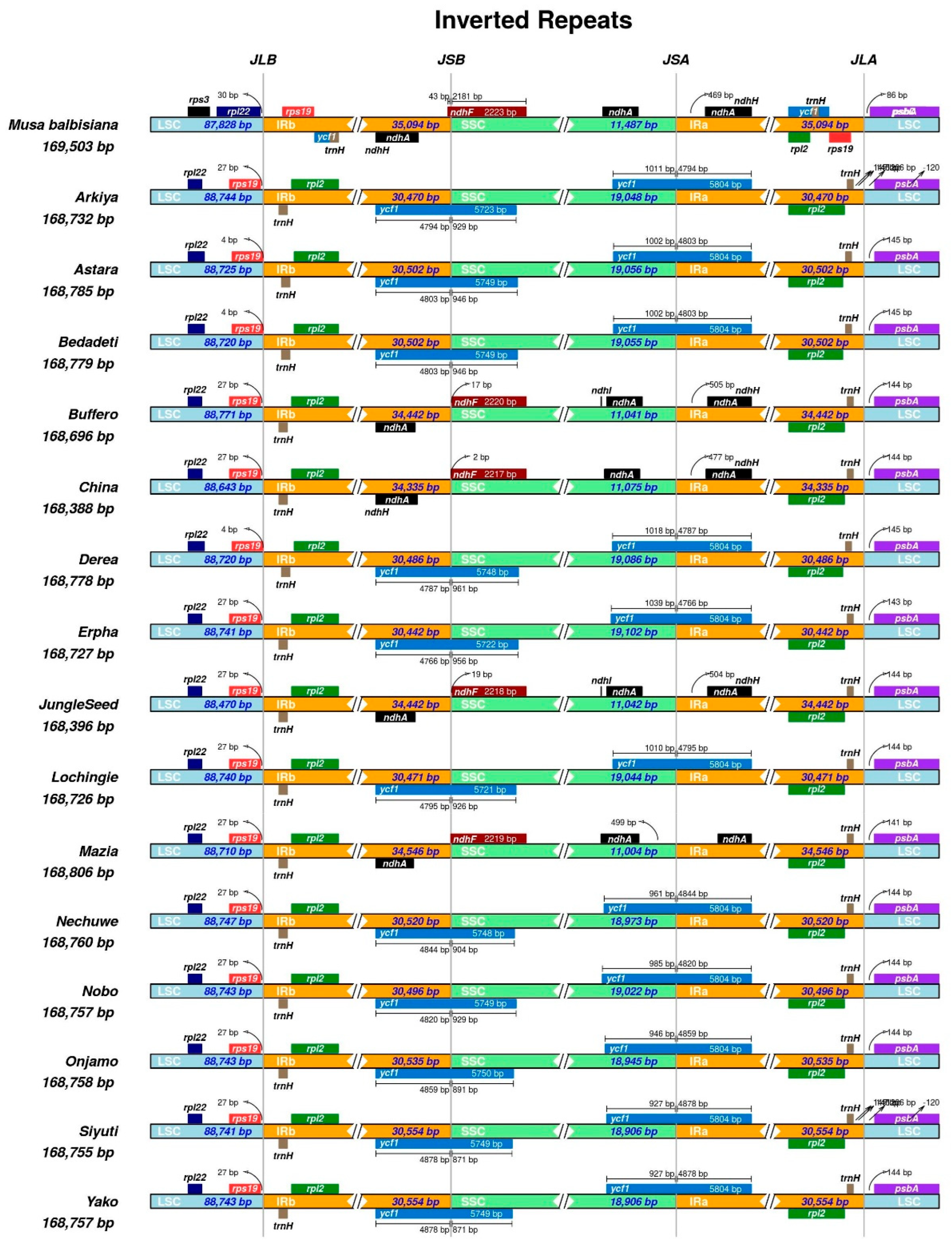

| Landraces | Genome Size (bp) | LSC Size (bp) | SSC Size (bp) | IR Size (bp) | Total No of Genes | No of Unique Genes | No of Genes Found in Duplicate Copy | tRNA (t/u) | rRNA (t/u) | Protein-Coding Gene (t/u) | Exon | Intron | GC% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arkiya | 168,732 | 88,743 | 11,076 | 34,414/34,495 | 137 | 105 | 23 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Astara | 168,785 | 88,724 | 11,080 | 34,461/34,516 | 137 | 105 | 23 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Bedadeti | 168,779 | 88,719 | 11,075 | 34,463/34,518 | 137 | 105 | 23 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Buffero | 168,696 | 88,768 | 11,040 | 34,442/34,254 | 138 | 105 | 25 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 92/75 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| China | 168,388 | 88,642 | 11,074 | 34,334/34,334 | 135 | 105 | 22 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 89/75 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Derea | 168,778 | 88,719 | 11,075 | 34,462/34,518 | 137 | 105 | 23 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Erpha | 168,727 | 88,740 | 11,075 | 34,413/34,495 | 137 | 105 | 23 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| JungleSeed | 168,396 | 88,469 | 11,040 | 34,441/34,442 | 138 | 105 | 24 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 92/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Lochingie | 168,726 | 88,739 | 11,080 | 34,410/34,493 | 137 | 105 | 23 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Mazia | 168,806 | 88,707 | 11,076 | 34,523/34,310 | 137 | 105 | 24 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/75 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Nechuwe | 168,760 | 88,746 | 11,076 | 34,439/34,495 | 137 | 105 | 23 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Nobo | 168,757 | 88,740 | 11,076 | 34,441/34,261 | 137 | 105 | 23 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Onjamo | 168,758 | 88,740 | 11,080 | 34,440/34,264 | 137 | 105 | 23 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Siyuti | 168,755 | 88,740 | 11,076 | 34,440/34,495 | 137 | 105 | 23 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Yako | 168,757 | 88,740 | 11,080 | 34,439/34,263 | 137 | 105 | 23 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Musa | 169,503 | 87,828 | 11,487 | 35,094 | 148 | 104 | 30 | 38/26 | 8/4 | 106/76 | 58 | 37 | 37 |
| Average | 168,707 | 88,712 | 11,098 | 34,437/34,410 | 137 | 105 | 23 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 91/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Min | 168,388 | 88,469 | 11,040 | 34,334/34,254 | 135 | 105 | 22 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 89/75 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
| Max | 168,806 | 88,768 | 11,080 | 34,523/34,518 | 138 | 105 | 25 | 37/28 | 8/4 | 92/76 | 56 | 37 | 37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biswas, M.K.; Ahmed, B.; Hijri, M.; Schwarzacher, T.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S. Chloroplast Genome Diversity and Marker Potentials of Diverse Ensete ventricosum Accessions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199561
Biswas MK, Ahmed B, Hijri M, Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison JS. Chloroplast Genome Diversity and Marker Potentials of Diverse Ensete ventricosum Accessions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199561
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiswas, Manosh Kumar, Bulbul Ahmed, Mohamed Hijri, Trude Schwarzacher, and J. S. (Pat) Heslop-Harrison. 2025. "Chloroplast Genome Diversity and Marker Potentials of Diverse Ensete ventricosum Accessions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199561
APA StyleBiswas, M. K., Ahmed, B., Hijri, M., Schwarzacher, T., & Heslop-Harrison, J. S. (2025). Chloroplast Genome Diversity and Marker Potentials of Diverse Ensete ventricosum Accessions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199561






