Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Biofilms: Antibiotic Pressure and Interaction with Human Neutrophils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Antibiotic Sensitivity of Studied UPEC Strain DL82
2.2. Plankton Growth and Biofilm Formation of UPEC Strain DL82 at Different Ciprofloxacin Concentrations
2.3. Effect of Different Antibiotics Supplemented in Pre-Sub-MIC, Sub-MIC, and MIC on Plankton Growth and Biofilm Formation of UPEC Strain DL82
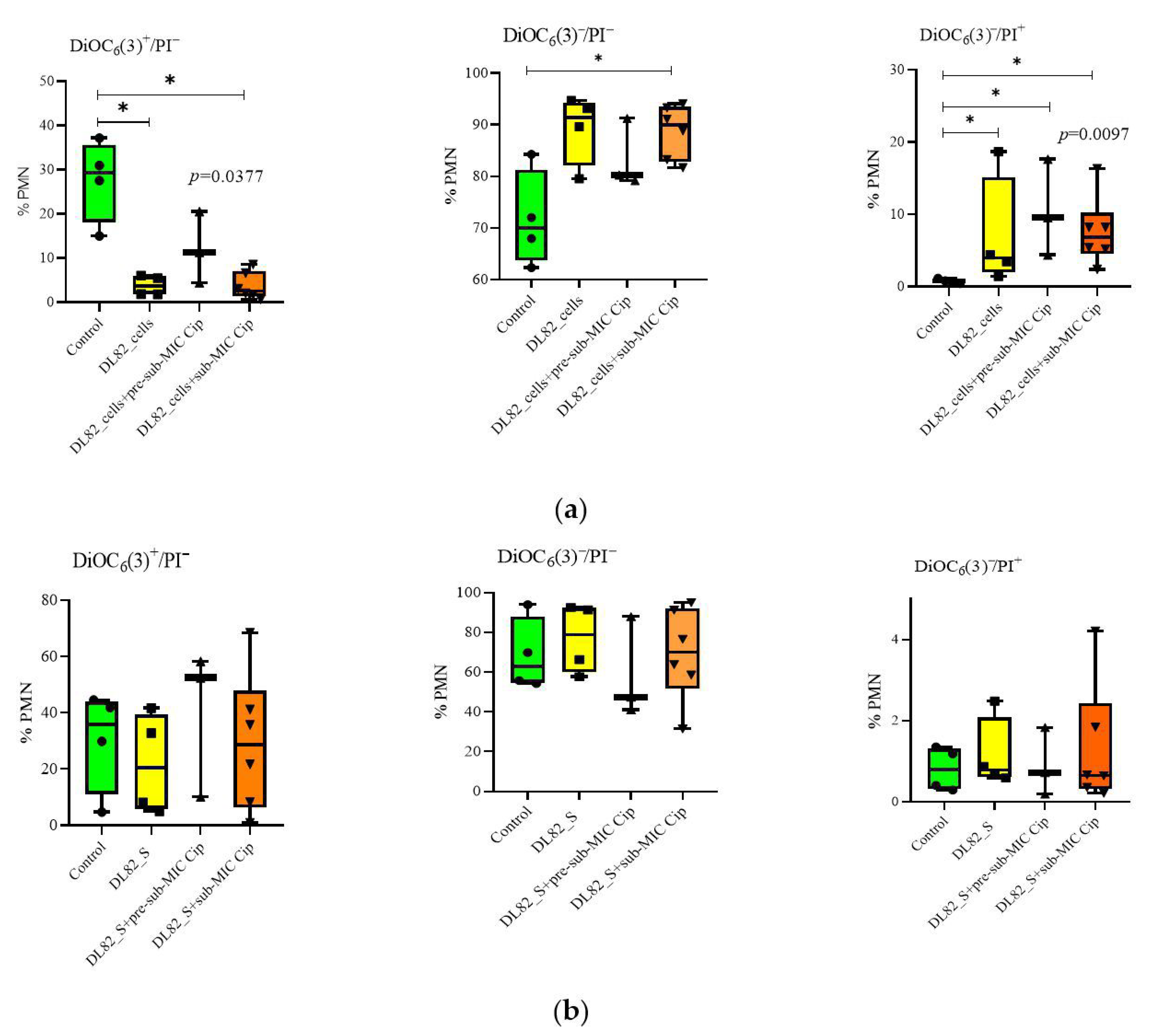
2.4. Neutrophil Viability, Apoptosis, and Necrosis After Interaction of UPEC Strain DL82 Cells and Biofilm Supernatants of Cells Grown in LB Supplemented with Different Ciprofloxacin Concentrations
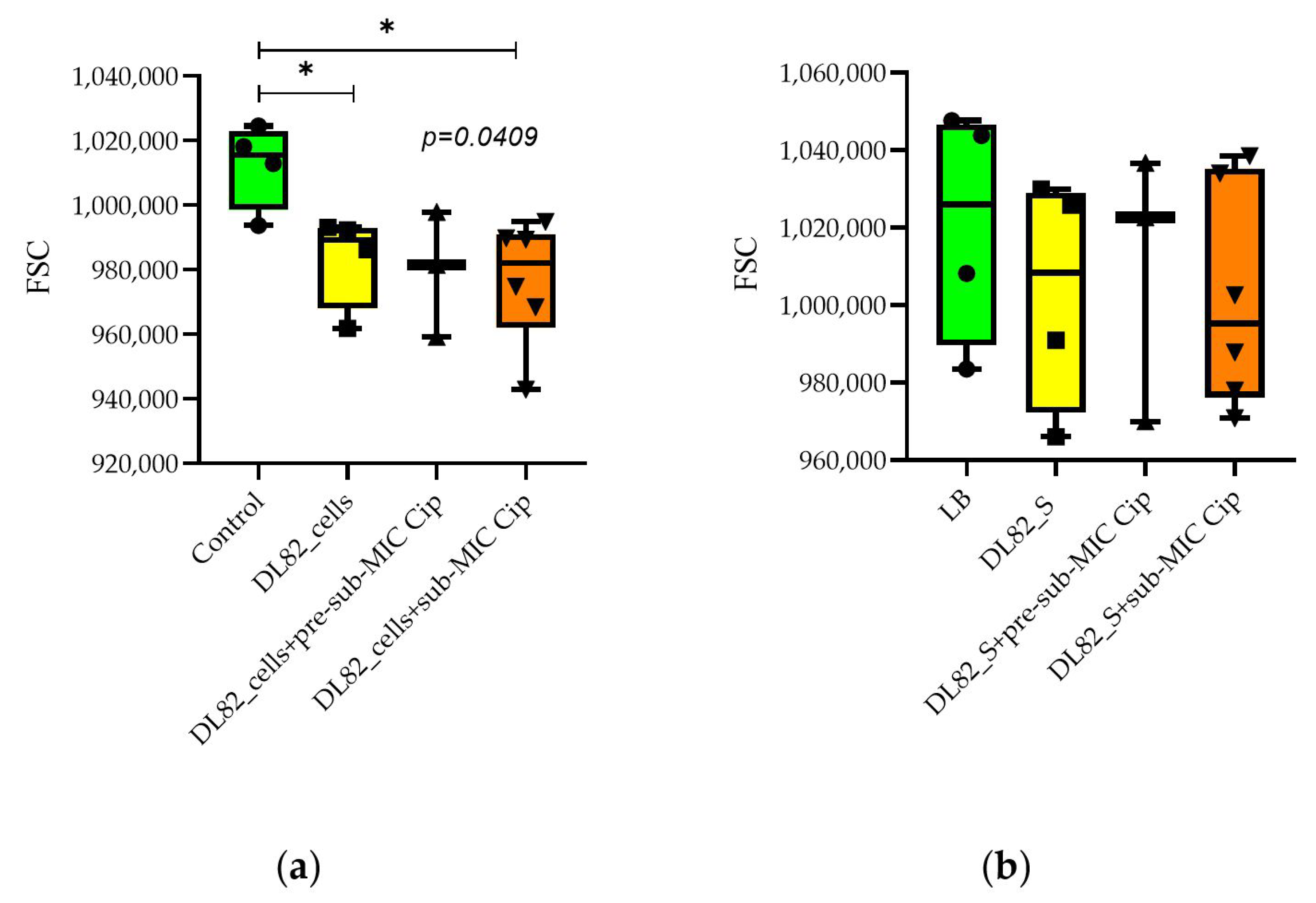
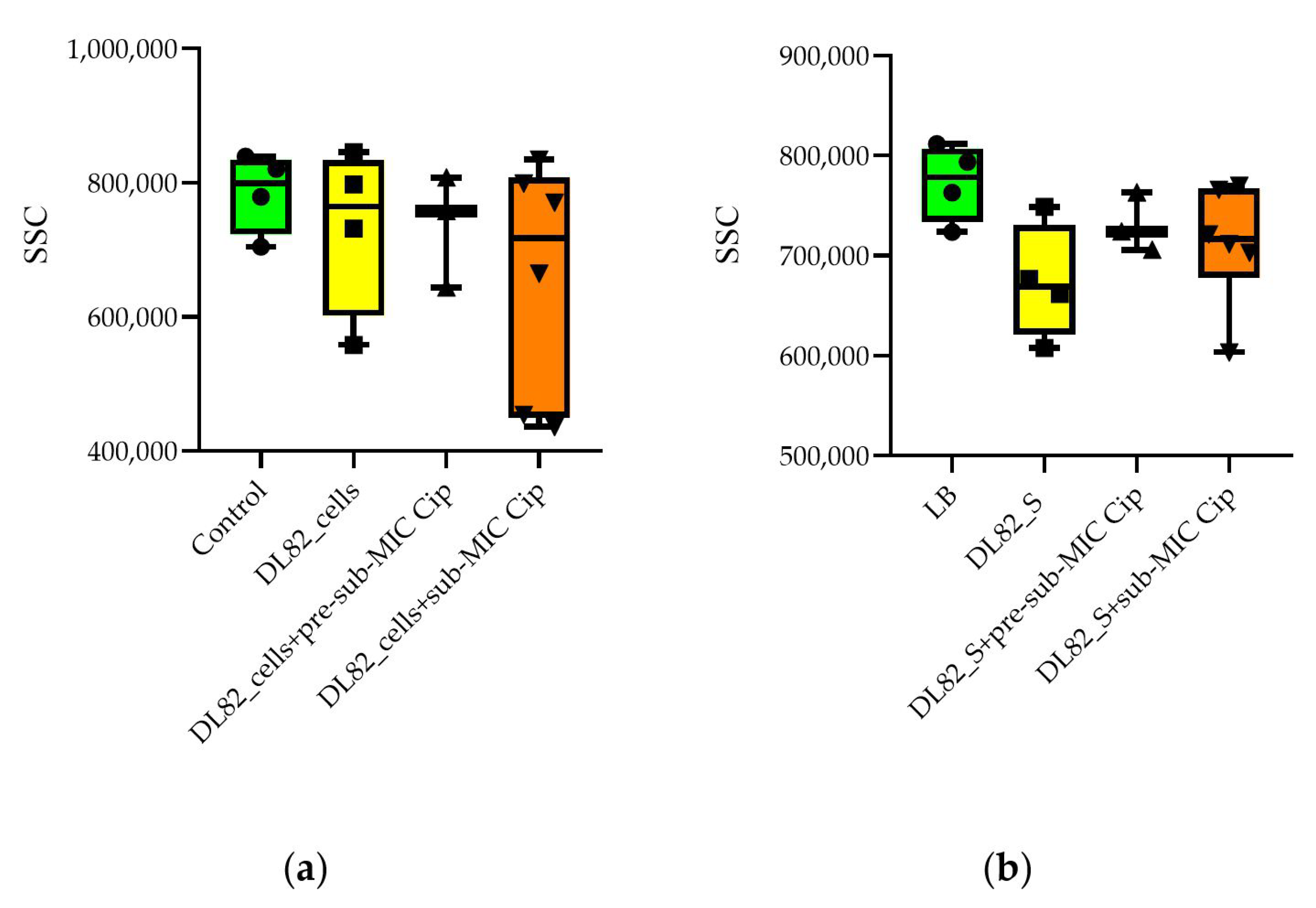
2.5. Neutrophil Size and Granularity After Interaction of UPEC Strain DL82 Cells and Supernatants of Biofilms Formed at Pre-Sub-MIC and Sub-MIC of Cip
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strain
4.2. Antibiotics
4.3. Estimation of MIC, Sub-MIC, and Pre-Sub-MIC of Antibiotics
4.4. Estimation of MBC
4.5. Estimation of MBEC
4.6. Estimation of Biofilm Biomass
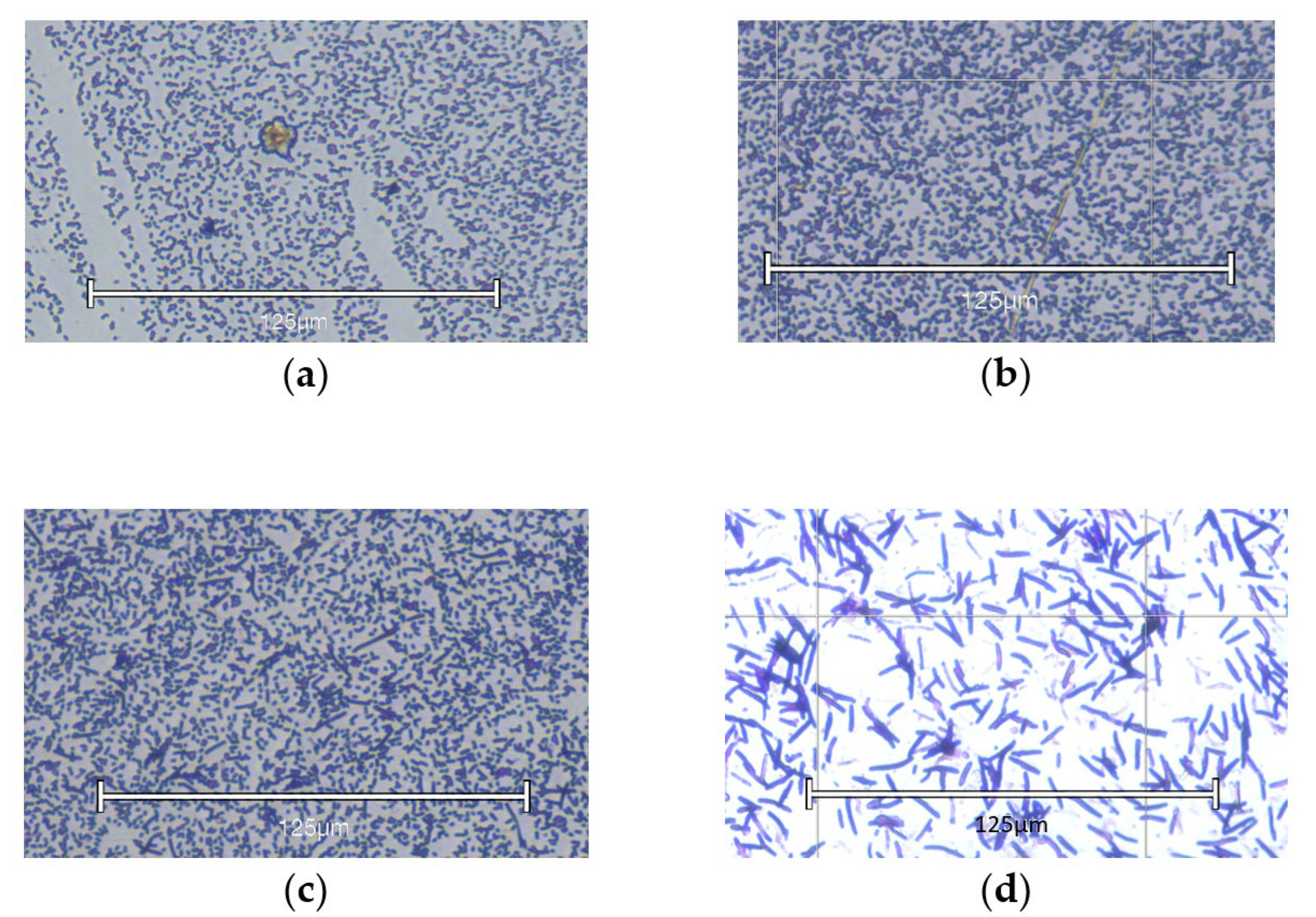
4.7. Microscopy of Biofilm
4.8. Assessment of Neutrophil Viability/Apoptosis/Necrosis
4.9. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Cip | Ciprofloxacin |
| FSC | Forward Scatter |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| MBC | Minimum Bactericidal Concentration |
| MBEC | Minimum Biofilm Eradication Concentration |
| PMN | Polymorphonuclear Neutrophil |
| SSC | Side Scatter |
| UPEC | Uropathogenic |
| UTI | Urinary Tract Infection |
References
- Bonkat, G.; Kranz, J.; Cai, T.; Geerlings, S.E.; Köves, B.; Pilatz, A.; Medina-Polo, J.; Schneidewind, L.; Schubert, S.; Veeratterapillay, R.; et al. EAU Guidelines: Urological Infections [Uroweb]. 2015. Available online: https://uroweb.org/guideline/urological-infections/ (accessed on 24 July 2020).
- Morales-Espinosa, R.; Hernandez-Castro, R.; Delgado, G.; Mendez, J.L.; Navarro, A.; Manjarrez, A.; Cravioto, A. UPEC strain characterization isolated from Mexican patients with recurrent urinary infections. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, N.; Leslie, S.W. Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections. 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557479/ (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Canales-Huerta, N.; Cádiz, M.; Ulloa, M.T.; Chilet, L.A.; Palma, K.; Jara-Wilde, J.; Cuevas, F.; González, M.J.; Navarro, N.; Toledo, J.; et al. Delayed biofilm formation in non-motile uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain in static and dynamic growth conditions. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 206, 107712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballén, V.; Cepas, V.; Ratia, C.; Gabasa, Y.; Soto, S.M. Clinical Escherichia coli: From Biofilm Formation to New Antibiofilm Strategies. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Zhou, Y.H.; Chen, J.Q.; Huang, Q.Y.; Han, Q.; Liu, B.; Cheng, G.D.; Li, Y.H. Quantitative proteomic analysis of sub-MIC erythromycin inhibiting biofilm formation of S. suis in vitro. J. Proteom. 2015, 116, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaji, M.; Shahidi, S.; Atapour, A.; Ataei, B.; Feizi, A.; Havaei, S.A. Characterization of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Among Iranian Kidney Transplant Patients. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palagin, I.S.; Sukhorukova, M.V.; Dekhnich, A.V.; Edelstein, M.V.; Perepanova, T.S.; Kozlov, R.S.; Shipitsyna, E.V.; Khusnutdinova, T.A.; Kulchavenya, E.V. Antimicrobial resistance of pathogens causing community-acquired urinary tract infections in Russia: Results of multicenter study “DARMIS-2018”. Clin. Microbiol Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 2, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yang, H.; Bi, D.; Khaledi, A.; Qiao, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of antibiotic resistance patterns, and the correlation between biofilm formation with virulence factors in uropathogenic E. coli isolated from urinary tract infections. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 144, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goneau, L.W.; Hannan, T.J.; MacPhee, R.A.; Schwartz, D.J.; Macklaim, J.M.; Gloor, G.B.; Razvi, H.; Reid, G.; Hultgren, S.J.; Burton, J.P. Subinhibitory antibiotic therapy alters recurrent urinary tract infection pathogenesis through modulation of bacterial virulence and host immunity. mBio 2015, 6, e00356-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Dhar, N.; Thacker, V.V.; Simonet, T.M.; Signorino-Gelo, F.; Knott, G.W.; McKinney, J.D. Dynamic persistence of UPEC intracellular bacterial communities in a human bladder-chip model of urinary tract infection. eLife 2021, 10, e66481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooton, T.M. Clinical practice. Uncomplicated urinary tract infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.; Choi, E.; Cho, Y.J.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, H.W.; Lee, E.J. A shared mechanism of multidrug resistance in laboratory-evolved uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Virulence 2024, 15, 2367648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starčič Erjavec, M.; Rijavec, M.; Križan-Hergouth, V.; Fruth, A.; Žgur-Bertok, D. Chloramphenicol- and tetracycline-resistant uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) exhibit reduced virulence potential. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2007, 30, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Ding, S.; Shen, J.; Zhu, K. Sublethal levels of antibiotics promotebacterial persistence in epithelial cells. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1900840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamus-Białek, W.; Wawszczak, M.; Arabski, M.; Majchrzak, M.; Gulba, M.; Jarych, D.; Parniewski, P.; Głuszek, S. Ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin, and aminoglycosides stimulate genetic and phenotypic changes in uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Virulence 2019, 10, 260–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T. Toll-like receptors: Critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüthje, P.; Brauner, A. Virulece factors of uropathogenic E. coli and their interaction with the host. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2014, 65, 337–372. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, J.S.; Bakaletz, L.O.; Wozniak, D.J. What’s on the Outside Matters: The Role of the Extracellular Polymeric Substance of Gram-negative Biofilms in Evading Host Immunity and as a Target for Therapeutic Intervention. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 12538–12546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, P.; McLaren, A.; Tavaziva, G.; Overstreet, D. Biofilm Antimicrobial Susceptibility Increases with Antimicrobial Exposure Time. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2016, 474, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, L.; Hartung, A.; Tramm, K.; Klinger-Strobel, M.; Jandt, K.D.; Makarewicz, O.; Pletz, M.W. MBEC Versus MBIC: The Lack of Differentiation between Biofilm Reducing and Inhibitory Effects as a Current Problem in Biofilm Methodology. Biol. Proced. Online 2019, 21, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofu, O.; Rojo-Molinero, E.; Macià, M.D.; Oliver, A. Antibiotic treatment of biofilm infections. APMIS 2017, 125, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.W.; Mah, T.F. Molecular mechanisms of biofilm-based antibiotic resistance and tolerance in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 276–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo, J.L. Biofilm-related disease. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2018, 16, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottier, W.; Seidelman, J.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M. Antimicrobial treatment of patients with a periprosthetic joint infection: Basic principles. Arthroplasty 2023, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geremia, N.; Giovagnorio, F.; Colpani, A.; De Vito, A.; Botan, A.; Stroffolini, G.; Toc, D.A.; Zerbato, V.; Principe, L.; Madeddu, G.; et al. Fluoroquinolones and Biofilm: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.J.; Robino, L.; Iribarnegaray, V.; Zunino, P.; Scavone, P. Effect of different antibiotics on biofilm produced by uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from children with urinary tract infection. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastaldi Guerrieri, C.; Teixeira Gonçalves, M.; Ferreira da Silva, A.; Souza Dos Santos, A.L.; Dos Santos, K.V.; Cruz Spano, L. Remarkable antibiofilm activity of ciprofloxacin, cefoxitin, and tobramycin, by themselves or in combination, against enteroaggregative Escherichia coli in vitro. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 107, 116048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaque, Z.; Abid, N.; Liaqat, N.; Afridi, P.; Siddique, S.; Masood, S.; Kanwal, S.; Dasti, J.I. In-Vitro Investigation of Antibiotics Efficacy Against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Biofilms and Antibiotic Induced Biofilm Formation at Sub-Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Ciprofloxacin. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 2801–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaeger, L.N.; French, S.; Brown, E.D.; Côté, J.P.; Burrows, L.L. Central metabolism is a key player in E. coli biofilm stimulation by sub-MIC antibiotics. PLoS Genet. 2023, 19, e1011013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad Hendri, N.A.; Nor Amdan, N.A.; Dounis, S.O.; Sulaiman Najib, N.; Louis, S.R. Ultrastructural and morphological studies on variables affecting Escherichia coli with selected commercial antibiotics. Cell Surf. 2024, 11, 100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, I.; Culebras, E.; Moreno, F.; Baquero, F. Induction of the SOS response by new 4-quinolones. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1987, 20, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribis, J.P.; García-Villada, L.; Zhai, Y.; Lewin-Epstein, O.; Wang, A.Z.; Liu, J.; Xia, J.; Mei, Q.; Fitzgerald, D.M.; Bos, J.; et al. Gamblers: An Antibiotic-Induced Evolvable Cell Subpopulation Differentiated by Reactive-Oxygen-Induced General Stress Response. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 785–800.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponmalar, I.I.; Swain, J.; Basu, J.K. Modification of bacterial cell membrane dynamics and morphology upon exposure to sub inhibitory concentrations of ciprofloxacin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2022, 1864, 183935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, G.; Bos, J.; Austin, R.H.; Amend, S.R.; Pienta, K.J. Escherichia coli survival in response to ciprofloxacin antibiotic stress correlates with increased nucleoid length and effective misfolded protein management. R Soc. Open Sci. 2023, 10, 230338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, D.S.; Koo, H. Targeted, triggered drug delivery to tumor and biofilm microenvironments. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanenko, N.O. Biofilm and tumor: Interpretation of interaction and treatment strategies. Med. Sci. Ukr. (MSU) 2021, 17, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangui-Panchi, S.P.; Ñacato-Toapanta, A.L.; Enríquez-Martínez, L.J.; Salinas-Delgado, G.A.; Reyes, J.; Garzon-Chavez, D.; Machado, A. Battle royale: Immune response on biofilms—Host-pathogen interactions. Curr. Res. Immunol. 2023, 4, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.P.; Aleandri, M.; Marazzato, M.; Conte, A.L.; Ambrosi, C.; Nicoletti, M.; Zagaglia, C.; Gambara, G.; Palombi, F.; De Cesaris, P.; et al. The adherent/invasive Escherichia coli strain LF82 invades and persists in human prostate cell line RWPE-1, activating a strong inflammatory response. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 3105–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Sharma, M.; Chaudhary, U. Biofilm and multidrug resistance in uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Pathog. Glob. Health 2015, 109, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, S.K.S.; Najar-Peerayeh, S.; Mobarez, A.M.; Parizi, M.K. Characterization of uropathogenic E. coli O25b-B2-ST131, O15:K52:H1, and CGA: Neutrophils apoptosis, serum bactericidal assay, biofilm formation, and virulence typing. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 18272–18282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, A.; Bracci, L. Immunomodulatory properties of CNF1 toxin from E. coli: Implications for colorectal carcinogenesis. Am J Cancer Res. 2022, 12, 651–660. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, J.; Shao, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, W.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Chang, Z. Expression of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 and CD14 during differentiation of HL-60 cells induced by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxy-vitamin D(3). Cell Growth Differ. 2002, 13, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomasek, K.; Leithner, A.; Glatzova, I.; Lukesch, M.S.; Guet, C.C.; Sixt, M. Type 1 piliated uropathogenic Escherichia coli hijack the host immune response by binding to CD14. Elife 2022, 11, e78995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, M.V.; Maslennikova, I.L.; Nekrasova, I.V.; Shirshev, S.V. Effect of mixed culture supernatants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli on apoptosis, necrosis, and oxidative activity of neutrophils. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2015, 461, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borenstein, A.; Fine, N.; Hassanpour, S.; Sun, C.; Oveisi, M.; Tenenbaum, H.C.; Glogauer, M. Morphological characterization of para- and proinflammatory neutrophil phenotypes using transmission electron microscopy. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, L.A.; Melo-González, F.; Sebastián, V.P.; Vallejos, O.P.; Noguera, L.P.; Suazo, I.D.; Schultz, B.M.; Manosalva, A.H.; Peñaloza, H.F.; Soto, J.A.; et al. Characterization of the Anti-Inflammatory Capacity of IL-10-Producing Neutrophils in Response to Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 638917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrover, J.M.; Nicolás-Ávila, J.A.; Hidalgo, A. Aging: A Temporal Dimension for Neutrophils. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, I.; Pascual, A.; Ballesta, S.; Joyanes, P.; Perea, E.J. Intracellular penetration and activity of gemifloxacin in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 3193–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovkin, A.S.; Zurochka, A.V.; Hajdukov, S.V.; Kudryavcev, I.V. Modern methods and approaches to the study of apoptosis in experimental biology. Medicinskaya immunologiya. 2012, 6, 461–482. Available online: https://www.elibrary.ru/pesfxj (accessed on 10 August 2025). (In Russian).


| Antibiotic | MIC | MBC | MBEC |
|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | |
| Ampicillin | 8192 | 8192 | 5 × 104 |
| Gentamicin | 4 | 16 | 32 |
| Chloramphenicol | 1 | 16 | 512 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.008 | 0.032 | 0.062 |
| Levofloxacin | 0.016 | 0.032 | 1 |
| Antibiotic (Concentration Range) | r 1 | p |
|---|---|---|
| Ampicilin (0–8192 mg/L) | 0.95 | 0.001 |
| Gentamicin (0–16 mg/L) | 0.84 | 0.072 |
| Chloramphenicol (0–4 mg/L) | 0.99 | 0.0002 |
| Ciprofloxacin (0–0.016 mg/L) | 0.76 | 0.085 |
| Levofloxacin (0–0.032 mg/L) | 0.26 | 0.566 |
| Characteristic | UPEC DL82 |
|---|---|
| Phenotypic | |
| Biofilm, OD580 | 0.985 |
| Bacteriocin production | – 1 |
| Genotypic | |
| tra | – |
| papC | + |
| sfaDE | + |
| afa/draBC | – |
| cnf1 | + |
| hly A | + |
| iroN | + |
| ibeA | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maslennikova, I.L.; Nekrasova, I.V.; Starčič Erjavec, M.; Karimova, N.V.; Kuznetsova, M.V. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Biofilms: Antibiotic Pressure and Interaction with Human Neutrophils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199484
Maslennikova IL, Nekrasova IV, Starčič Erjavec M, Karimova NV, Kuznetsova MV. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Biofilms: Antibiotic Pressure and Interaction with Human Neutrophils. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199484
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaslennikova, Irina L., Irina V. Nekrasova, Marjanca Starčič Erjavec, Nina V. Karimova, and Marina V. Kuznetsova. 2025. "Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Biofilms: Antibiotic Pressure and Interaction with Human Neutrophils" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199484
APA StyleMaslennikova, I. L., Nekrasova, I. V., Starčič Erjavec, M., Karimova, N. V., & Kuznetsova, M. V. (2025). Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Biofilms: Antibiotic Pressure and Interaction with Human Neutrophils. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199484





