Exploring the Diagnostic and Predictive Value of Oral Microbiome in Esophageal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Meta-Analysis
2.5. Quality Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search and Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Sample Collection
3.4. Alpha-Diversity and Beta-Diversity
3.5. Microbiome Changes in Esophageal Cancer Patients Compared to Healthy Controls
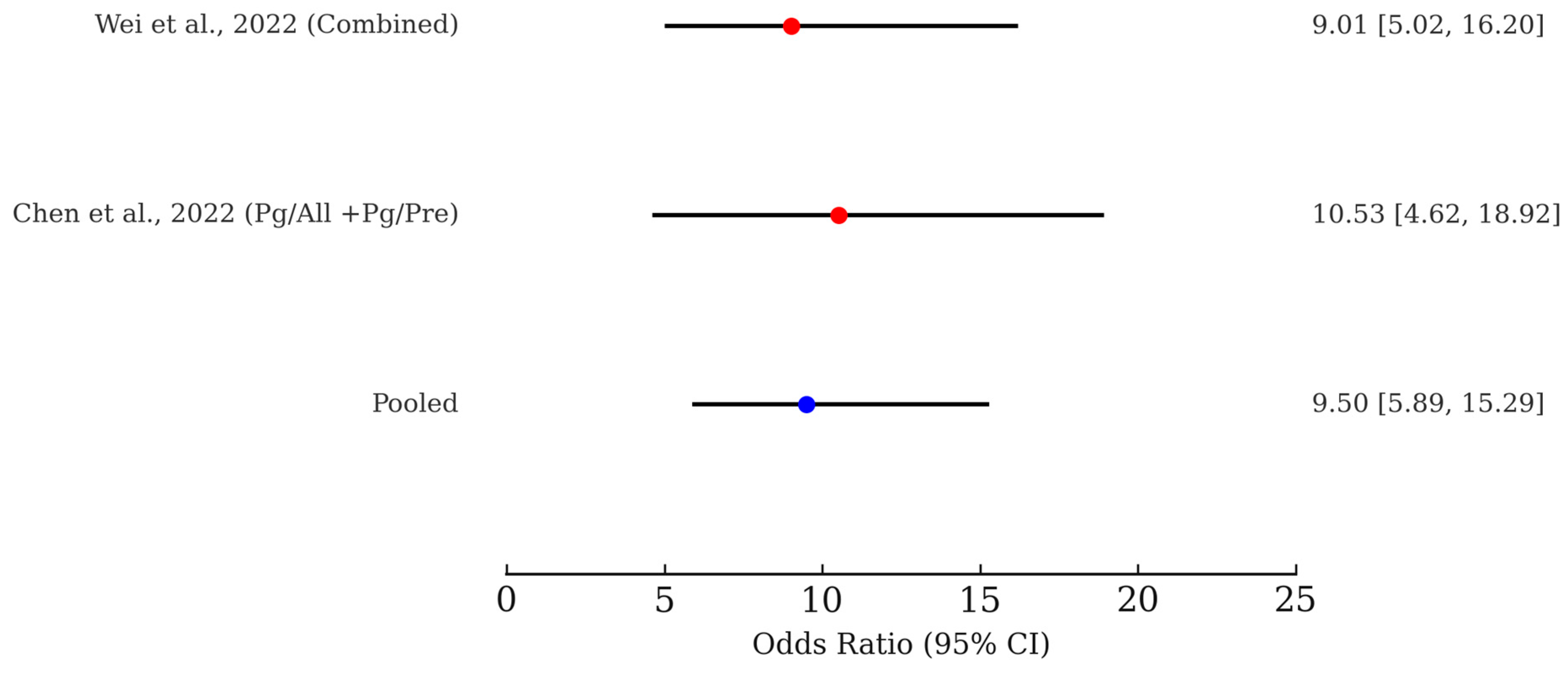
3.6. Meta-Analysis of Microbiome-Based Risk Prediction for ESCC
3.7. Quality Assessment of the Included Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | area under the curve |
| CASP | Critical Appraisal Skills Program |
| CIs | confidence intervals |
| EC | esophageal cancer |
| EAC | esophageal adenocarcinoma |
| ESCC | esophageal squamous cell carcinoma |
| GERD | gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| LEfSe | Linear discriminant analysis effect size |
| ORs | odds ratios |
| OTU | operational taxonomic unit |
| PRISMA | Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| PROSPERO | International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews |
References
- El-Sayed, A.; Aleya, L.; Kamel, M. Microbiota’s role in health and diseases. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 36967–36983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehner, C.; Fine, R.; Kriegel, M.A. The microbiome in systemic autoimmune disease: Mechanistic insights from recent studies. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Takeshita, T. The oral microbiome and human health. J. Oral Sci. 2017, 59, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Chen, T.; Izard, J.; Paster, B.J.; Tanner, A.C.; Yu, W.H.; Lakshmanan, A.; Wade, W.G. The human oral microbiome. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5002–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, P.; Xuedong, Z.; Xin, X.; Yuqing, L.; Yan, L.; Jiyao, L.; Xiaoquan, S.; Shi, H.; Jian, X.; Ga, L. The oral microbiome bank of China. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costalonga, M.; Herzberg, M.C. The oral microbiome and the immunobiology of periodontal disease and caries. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 162, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, M.; Polizzi, A.; Santonocito, S.; Romano, A.; Lombardi, T.; Isola, G. Impact of oral microbiome in periodontal health and periodontitis: A critical review on prevention and treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, J.L.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Ge, L. The role of oral microbiome in respiratory health and diseases. Respir. Med. 2021, 185, 106475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietiainen, M.; Liljestrand, J.M.; Kopra, E.; Pussinen, P.J. Mediators between oral dysbiosis and cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 126 (Suppl. 1), 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharlamova, N.; Jiang, X.; Sherina, N.; Potempa, B.; Israelsson, L.; Quirke, A.M.; Eriksson, K.; Yucel-Lindberg, T.; Venables, P.J.; Potempa, J.; et al. Antibodies to Porphyromonas gingivalis indicate interaction between oral infection, smoking, and risk genes in rheumatoid arthritis etiology. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qian, F.; Cheng, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Tian, Y. Dysbiosis of oral microbiota and metabolite profiles associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0379622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Corral, L.; Alves-Gomes, L.; Fernandez-Fernandez, J.A.; Fernandez-Garcia, D.; Casado-Verdejo, I.; Sanchez-Valdeon, L. Implications of gut and oral microbiota in neuroinflammatory responses in Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2023, 333, 122132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, M.; de Martel, C.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F.; Franceschi, S. Global burden of cancers attributable to infections in 2012: A synthetic analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2016, 4, e609–e616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Zhou, H.; Xu, S. Oral microbiota as promising diagnostic biomarkers for gastrointestinal cancer: A systematic review. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 11131–11144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.; Onate, M.D.; Pauley, K.M.; Bhattacharyya, I.; Cha, S. Presence of Porphyromonas gingivalis in gingival squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 3, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, S.; Ma, Z.; Liang, S.; Shan, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, G.; Zhou, F.; et al. Presence of Porphyromonas gingivalis in esophagus and its association with the clinicopathological characteristics and survival in patients with esophageal cancer. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2016, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xu, S.; Xiang, C.; Cao, Q.; Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, Z. Tongue coating microbiota community and risk effect on gastric cancer. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 4039–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Wu, J.; Peters, B.A.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; Purdue, M.P.; Abnet, C.C.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; Miller, G.; et al. Human oral microbiome and prospective risk for pancreatic cancer: A population-based nested case-control study. Gut 2018, 67, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellarin, M.; Warren, R.L.; Freeman, J.D.; Dreolini, L.; Krzywinski, M.; Strauss, J.; Barnes, R.; Watson, P.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Moore, R.A.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum infection is prevalent in human colorectal carcinoma. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Then, E.O.; Lopez, M.; Saleem, S.; Gayam, V.; Sunkara, T.; Culliford, A.; Gaduputi, V. Esophageal cancer: An updated surveillance epidemiology and end results database analysis. World J. Oncol. 2020, 11, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narikiyo, M.; Tanabe, C.; Yamada, Y.; Igaki, H.; Tachimori, Y.; Kato, H.; Muto, M.; Montesano, R.; Sakamoto, H.; Nakajima, Y.; et al. Frequent and preferential infection of Treponema denticola, Streptococcus mitis, and Streptococcus anginosus in esophageal cancers. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.F.; Lu, M.S.; Hsieh, C.C.; Chen, W.C. Porphyromonas gingivalis promotes tumor progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell. Oncol. 2021, 44, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Rao, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, N.; Liu, S.; Wen, P.; Li, S.; Li, Y. Oral microbiome in patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Bai, C.; Brown, T.D.; Hood, L.E.; Tian, Q. Human gut microbiota and gastrointestinal cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, E.; Narikiyo, M.; Yano, A.; Nishimura, E.; Igaki, H.; Sasaki, H.; Terada, M.; Hanada, N.; Kawabe, R. Different frequencies of Streptococcus anginosus infection in oral cancer and esophageal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2003, 94, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.A.; Wu, J.; Pei, Z.; Yang, L.; Purdue, M.P.; Freedman, N.D.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; Hayes, R.B.; Ahn, J. Oral microbiome composition reflects prospective risk for esophageal cancers. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6777–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CASP Checklist Case Control Study 2024. Available online: https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/ (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Chen, X.; Winckler, B.; Lu, M.; Cheng, H.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jin, L.; Ye, W. Oral microbiota and risk for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a high-risk area of China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, S.; Takeshita, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Asakawa, M.; Matsumi, R.; Furuta, M.; Shibata, Y.; Nagai, K.; Ikebe, M.; Morita, M.; et al. Characteristics of the salivary microbiota in patients with various digestive tract cancers. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, F.; Xu, R.; Liu, Z.; Deng, Q.; Li, X.; et al. Oral microbiome and risk of malignant esophageal lesions in a high-risk area of China: A nested case-control study. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 32, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, T.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Xia, Y.; Xiao, H.; Han, H.; et al. Alterations of oral microbiota in Chinese patients with esophageal cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 541144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, N.; Li, D.; Luo, C.; Wang, T. Characteristics of oral microbiota in patients with esophageal cancer in China. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 2259093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dou, L.; Zhang, Y.; He, S.; Zhao, D.; Hao, C.; Song, G.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G. Characterization of the oral and esophageal microbiota in esophageal precancerous lesions and squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 714162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, R.; Lu, Y.; Meng, F.; Xian, B.; Lai, X.; Lin, X.; Deng, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; et al. Salivary microbiota may predict the presence of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Genes Dis. 2022, 9, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Hua, Z.; Kang, X.; Lu, B.; Li, M.; Wu, J.; Dong, W.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, C. Influence of oral intaking habit on tongue coating microbiota in patients with esophageal precancerous lesions. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 1168–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xian, B.; Wei, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, D.; Lai, X.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Lin, X.; Deng, Y.; et al. Predictive value of the presence of Prevotella and the ratio of Porphyromonas gingivalis to Prevotella in saliva for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 997333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Karaoz, U.; Yang, L.; Yachimski, P.S.; Tseng, W.; Nossa, C.W.; Ye, W.; Tseng, M.; Poles, M.; Francois, F.; et al. Progressive dysbiosis of human orodigestive microbiota along the sequence of gastroesophageal reflux, Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 1703–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, J.; Qian, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S. Oral microbiota may predict the presence of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 4731–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, F.; Yang, R.; Yu, X.; Zhou, X.; Tang, N. Characteristics of the oral and gastric microbiome in patients with early-stage intramucosal esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shao, D.; Fan, Z.; Qin, J.; Xu, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, X.; Hua, Z.; Li, J.; Hao, C.; et al. Non-invasive early detection on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and precancerous lesions by microbial biomarkers combining epidemiological factors in China. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfisburg, Q.S.; Baldini, F.; Baldwin-Hunter, B.; Austin, G.I.; Lee, H.H.; Park, H.; Freedberg, D.E.; Lightdale, C.J.; Korem, T.; Abrams, J.A. The salivary microbiome and predicted metabolite production are associated with Barrett’s esophagus and high-grade dysplasia or adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2024, 33, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Hu, A.Q.; Qian, D. Salivary microbiome is associated with the response to chemoradiotherapy in initially inoperable patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Microbiol. 2024, 16, 2359887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlenhopp, D.J.; Then, E.O.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: Update in global trends, etiology and risk factors. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, L.; Ou, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, E.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Identification of genomic alterations in oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Nature 2014, 509, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Lin, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Miao, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Luo, Y.; et al. Multi-omic characterization of genome-wide abnormal DNA methylation reveals diagnostic and prognostic markers for esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Li, N.; Duan, X.; Niu, H. Interaction between the gut microbiome and mucosal immune system. Mil. Med. Res. 2017, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Mazmanian, S.K. Has the microbiota played a critical role in the evolution of the adaptive immune system? Science 2010, 330, 1768–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, M.C.; McKenney, P.T.; Pamer, E.G. Clostridium difficile colitis: Pathogenesis and host defence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.; Kitano, S.; Puah, G.R.Y.; Kittelmann, S.; Hwang, I.Y.; Chang, M.W. Microbiome and human health: Current understanding, engineering, and enabling technologies. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 31–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, N.; Zouiouich, S.; Vanderbauwhede, B.; Vanacker, J.; Indave Ruiz, B.I.; Huybrechts, I. Human microbiome and metabolic health: An overview of systematic reviews. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Chang, H.W.; Yan, D.; Lee, K.M.; Ucmak, D.; Wong, K.; Abrouk, M.; Farahnik, B.; Nakamura, M.; Zhu, T.H.; et al. Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Delgado, R.Z.R.; Frias-Lopez, J. The oral microbiome and cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 591088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuominen, H.; Rautava, J. Oral microbiota and cancer development. Pathobiology 2021, 88, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Hwang, B.O.; Lim, M.; Ok, S.H.; Lee, S.K.; Chun, K.S.; Park, K.K.; Hu, Y.; Chung, W.Y.; Song, N.Y. Oral-gut microbiome axis in gastrointestinal disease and cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosgood, H.D.; Cai, Q.; Hua, X.; Long, J.; Shi, J.; Wan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Abnet, C.; Bassig, B.A.; Hu, W.; et al. Variation in oral microbiome is associated with future risk of lung cancer among never-smokers. Thorax 2021, 76, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Byrd, D.A.; Wan, Y.; Ansong, D.; Clegg-Lamptey, J.N.; Wiafe-Addai, B.; Edusei, L.; Adjei, E.; Titiloye, N.; Dedey, F.; et al. The oral microbiome and breast cancer and nonmalignant breast disease, and its relationship with the fecal microbiome in the Ghana Breast Health Study. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; He, C.; Qiu, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Fu, B. Association of oral microbiota and periodontal disease with lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2023, 23, 101897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.H.; Wang, J.; Chai, X.Q.; Li, Z.C.; Jiang, Y.H.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Fan, J.; Cai, J.B.; Liu, F. The intratumoral bacterial metataxonomic signature of hepatocellular carcinoma. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0098322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Madhulika, A.; Deepika, G.; Rao, G.V.; Reddy, D.N.; Subramanyam, C.; Sasikala, M.; Talukdar, R. Altered intestinal microbiota in patients with chronic pancreatitis: Implications in diabetes and metabolic abnormalities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.H.; Meng, Y.T.; Xu, J.J.; Fang, X.; Zhao, J.L.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, J.; Han, J.C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, K.X.; et al. Altered diversity and composition of gut microbiota in Chinese patients with chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocan, D.; Rebours, V.; Voican, C.S.; Wrzosek, L.; Puchois, V.; Cassard, A.M.; Perlemuter, G. Characterization of intestinal microbiota in alcoholic patients with and without alcoholic hepatitis or chronic alcoholic pancreatitis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiński, T.M. Role of oral microbiota in cancer development. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.M. The immune response to Prevotella bacteria in chronic inflammatory disease. Immunology 2017, 151, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Shao, R.R.; Zhang, S.; Tan, Z.W.; Guo, Y.T.; He, Y. The mechanism on Prevotella melaninogenica promoting the inflammatory progression of oral lichen planus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 209, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.; Ma, X.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, W.; Ma, J. Periodontitis pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis promotes pancreatic tumorigenesis via neutrophil elastase from tumor-associated neutrophils. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2073785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Wen, L.; Mu, W.; Wu, X.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Fang, J.; Luan, Y.; Chen, P.; et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis promotes colorectal carcinoma by activating the hematopoietic NLRP3 inflammasome. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2745–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, G.H. Porphyromonas gingivalis and digestive system cancers. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeger, S.; Jarzina, F.; Domann, E.; Meyle, J. Porphyromonas gingivalis activates NFκB and MAPK pathways in human oral epithelial cells. BMC Immunol. 2017, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhjiri, S.F.; Park, Y.; Yilmaz, O.; Chung, W.O.; Watanabe, K.; El-Sabaeny, A.; Park, K.; Lamont, R.J. Inhibition of epithelial cell apoptosis by Porphyromonas gingivalis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 200, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, B.; Węsierska, A.; Zalewska, K.; Sokołowska, M.M.; Bursiewicz, W.; Socha, M.; Ozorowski, M.; Pawlak-Osińska, K.; Wiciński, M. The role of Tannerella forsythia and Porphyromonas gingivalis in pathogenesis of esophageal cancer. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2019, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engevik, M.A.; Danhof, H.A.; Ruan, W.; Engevik, A.C.; Chang-Graham, A.L.; Engevik, K.A.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Brand, C.K.; Krystofiak, E.S.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum secretes outer membrane vesicles and promotes intestinal inflammation. mBio 2021, 12, 02706–02720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, P.; Nuccio, F.; Piattelli, A.; Curia, M.C. The role of Fusobacterium nucleatum in oral and colorectal carcinogenesis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, F.; Sohrabi, A.; Zagai, U.; Andreasson, A.; Vieth, M.; Talley, N.J.; Agréus, L.; Ye, W. Oral Microbiome Dysbiosis Is Associated With Precancerous Lesions and Disorders of Upper Gastrointestinal Tract: A Population-Based Study. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol.|ACG 2025, 120, 2173–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Kim, J.; Shin, C.M.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Park, K.U. Metagenomic characterization of oral microbiome signatures to predict upper gastrointestinal and pancreaticobiliary cancers: A case-control study. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinyu, K.; Jian, W.; Yiwen, L.; Ruonan, L.; Shegan, G. Role of Oral and Esophageal Microbiota in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2025, 19, 11795549251350185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Xia, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, T.; Zhao, L.; Fan, S. A cross-cohort study identifies potential oral microbial markers for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. iScience 2024, 27, 111453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, J.; Tangney, M. Bacteria and tumours: Causative agents or opportunistic inhabitants? Infect. Agent. Cancer 2013, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mager, D.L. Bacteria and cancer: Cause, coincidence or cure? A review. J. Transl. Med. 2006, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Huang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhou, H. A causal association between esophageal cancer and the oral microbiome: A Mendelian randomization study based on an Asian population. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1420625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| P (Population) | Patients diagnosed with esophageal cancer (including ESCC and EAC) as well as healthy controls. |
| I (Intervention/Exposure) | Analysis of oral microbiota composition, primarily via 16S rRNA gene sequencing from saliva or other oral samples (e.g., oral swabs, tongue coating). |
| C (Comparison) | Comparison of oral microbiome profiles between esophageal cancer patients and healthy controls. |
| O (Outcome) | Differences in microbial diversity (alpha- and beta- diversity), abundance of specific taxa, and diagnostic performance metrics such as sensitivity, specificity, and odds ratios for microbial biomarkers. |
| First Author | Year | Country | Study Design | Cancer Type | Participants (Case/Control) | Sex (Male %) (Case/Control) | Age (Case/Control) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen, X. | 2015 | China | Case–control study | ESCC | 87/85 | 67.82/72.94 | 64.8/66 a | [29] |
| Peters, B.A. | 2017 | USA | Nested case–control study | EAC and ESCC | EAC: 81/160, ESCC: 25/50 | EAC: 92.6/92.5, ESCC: 40/40 | EAC: 68.0/62.4 a ESCC: 66.6/66.8 a | [27] |
| Wang, Q. | 2019 | China | Case–control study | ESCC | 20/21 | 70.0/57.14 | 65.9/65.14 a | [24] |
| Kageyama, S. | 2019 | Japan | Case–control study | Esophageal cancer | 12/118 | 66.7/71.2 | 68.4/66.4 a | [30] |
| Liu, F. | 2020 | China | Nested case–control study | ESCC | 84/168 | 52.38/52.38 | 57/56 b | [31] |
| Zhao, Q. | 2020 | China | Case–control study | Esophageal cancer | 39/51 | 59.0/45.1 | 60.39/49.18 a | [32] |
| Chen, M. F. | 2021 | Taiwan | Case–control study | ESCC | 34/18 | // | // | [23] |
| Li, H. | 2021 | China | Case–control study | ESCC | 33/35 | 84.9/65.7 | 66/61 b | [33] |
| Li, Z. | 2021 | China | Case–control study | ESCC | 70/82 | 65.7/58.5 | 63.64/58.51 a | [34] |
| Wei, J. | 2022 | China | Case–control study | ESCC | 178/101 | 78.09/49.50 | Screening: 61.71/43.90 a, Verification: 61.41/44.45 a | [35] |
| Xiao, P. | 2022 | China | Case–control study | Esophageal Precancerous Lesions | 123/176 | 57.7/54.5 | 59.71/58.99 a | [36] |
| Chen, X. | 2022 | China | Case–control study | ESCC | 90/50 | 78.89/54.00 | 60.8/47.7 a | [37] |
| Hao, Y. | 2022 | USA | Case–control study | EAC | 19/27 | 94.74/62.96 | 59.9/56.3 a | [38] |
| Jiang, Z. | 2023 | China | Case–control study | ESCC | 56/53 | 53.57/49.06 | 54.56/49.32 a | [39] |
| Chen, H. | 2024 | China | Case–control study | Early-stage intramucosal ESCC | 31/21 | 61.3/52.4 | 70/64 b | [40] |
| Li, M. | 2024 | China | Case–control study | ESCC | 52/52 | // | // | [41] |
| Solfisburg, Q.S. | 2024 | USA | Case–control study | EAC | 78/125 | 79.49/36.00 | 65/50 b | [42] |
| He, Y. | 2024 | China | Case–control study | ESCC | Before: 79/10, After: 8/10 | Before: 74.6/50.0, After: 50.0/50.0 | Before: 72/70 b After: 75/70 b | [43] |
| First Author | Year | Sample Type | 16S Region | Sequencing Platform | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen, X. | 2015 | Saliva | V3–V4 | 454 Roche FLX Titanium adapters (454 Life Sciences, Branford, CT, USA) | [29] |
| Peters, B.A. | 2017 | Oral wash | V4 | Illumina MiSeq (-) | [27] |
| Wang, Q. | 2019 | Saliva | V3–V4 | Illumina MiSeq (Illumina, San Diago, CA, USA) | [24] |
| Kageyama, S. | 2019 | Saliva | V1–V2 | Ion PGM Hi-Q view (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) | [30] |
| Liu, F. | 2020 | Oral swabs | V3–V4 | Ion S5 XL (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) | [31] |
| Zhao, Q. | 2020 | Saliva | V3–V4 | Illumina MiSeq PE250 (Illumina, San Diago, CA, USA) | [32] |
| Chen, M. F. | 2021 | Oral biofilms | Not reported | Illumina MiSeq (Illumina, San Diago, CA, USA) | [23] |
| Li, H. | 2021 | Saliva | V3–V4 | Illumina MiSeq 2×300 bp (Illumina, San Diago, CA, USA) | [33] |
| Li, Z. | 2021 | Saliva | V4 | Ion S5TM XL (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA) | [34] |
| Wei, J. | 2022 | Saliva | V4 | Illumina HiSeq 2500 (Illumina, San Diago, CA, USA) | [35] |
| Xiao, P. | 2022 | Tongue coating | V3–V4 | Illumina MiSeq PE (Illumina, San Diago, CA, USA) | [36] |
| Chen, X. | 2022 | Saliva | V4 | Illumina HiSeq2500 (Illumina, San Diago, CA, USA) | [37] |
| Hao, Y. | 2022 | Buccal mucosa | V3–V5 | Not reported | [38] |
| Jiang, Z. | 2023 | Oral swabs | V3–V4 | Illumina NovaSeq6000 PE250 (Illumina, San Diago, CA, USA) | [39] |
| Chen, H. | 2024 | Saliva | V3–V4 | Illumina NovaSeq (Illumina, San Diago, CA, USA) | [40] |
| Li, M. | 2024 | Saliva | V4 | Illumina MiniSeq (Illumina, San Diago, CA, USA) | [41] |
| Solfisburg, Q.S. | 2024 | Saliva | V3–V4 | Illumina MiSeq (Illumina, San Diago, CA, USA) | [42] |
| He, Y. | 2024 | Saliva | V3–V4 | Illumina NovaSeq 6000 (Illumina, San Diago, CA, USA) | [43] |
| First Author | Alpha Diversity | Beta Diversity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chen, X. | ↓ Shannon (3.7 → 3.4), Chao1 (147.2 → 120.8) | Significant (p < 0.05, UniFrac) | [29] |
| Peters, B.A. | Not significant | Not significant (UniFrac) | [27] |
| Wang, Q. | Not significant | Significant (p = 0.037, Bray-Curtis) | [24] |
| Kageyama, S. | ↑ Shannon (~3.4 → ~3.6), Chao1 (~200 → ~220) | Significant (p = 0.01, UniFrac) | [30] |
| Liu, F. | ↑ Shannon | Not significant (UniFrac) | [31] |
| Zhao, Q. | Not significant | Significant (p = 0.001, Bray-Curtis) | [32] |
| Chen, M. F. | ↑ Shannon | Significant (p = 0.001) | [23] |
| Li, H. | Not significant | Unweighted: significant (p = 0.001), Weighted: not significant | [33] |
| Li, Z. | ↓ Shannon (~6.1 → ~5.8) | Significant (p = 0.001, Bray-Curtis) | [34] |
| Wei, J. | ↑ S. salivarius, etc. (no Shannon shown) | Not reported | [35] |
| Xiao, P. | Not significant | Not reported | [36] |
| Chen, X. | ↑ Shannon | Not significant | [37] |
| Hao, Y. | ↑ Shannon | Significant (p < 0.01, UniFrac) | [38] |
| Jiang, Z. | Not significant | Significant (p < 0.05) | [39] |
| Chen, H. | Not significant | Not significant (Bray-Curtis) | [40] |
| Li, M. | Not significant | Significant (p < 0.01, UniFrac) | [41] |
| Solfisburg, Q.S. | ↓ Shannon, ↓ Simpson | Significant (p < 0.01, UniFrac) | [42] |
| He, Y. | ↓ Chao1 | Significant (Bray-Curtis) | [43] |
| First Author | Key Microbial Changes | Potential Biomarkers | Sensitivity/Specificity | Notes | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | |||||
| Chen, X. | Prevotella (↑), Streptococcus (↑), Porphyromonas (↑); Lautropia (↓), Corynebacterium (↓) | - | Prevotella, Streptococcus, Porphyromonas | Not reported | First ESCC saliva study; 454 sequencing | [29] |
| Peters, B.A. | - | Porphyromonas gingivalis (↑), Prevotella nanceiensis (↑), Treponema vincentii (↑) | Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella nanceiensis | Not reported | ESCC and EAC separation | [27] |
| Wang, Q. | Actinomyces (↑), Atopobium (↑); Fusobacterium (↓), Porphyromonas (↓) | - | Actinomyces, Atopobium | Not reported | Small sample; diversity not significant | [24] |
| Kageyama, S. | - | Porphyromonas gingivalis (↑), Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. vincentii (↑) | Porphyromonas gingivalis, Fusobacterium nucleatum | Not reported | OTU-rich profile in EC | [30] |
| Liu, F. | - | Fusobacterium nucleatum (↑), Actinomyces naeslundii (↑), Prevotella intermedia (↑), Treponema vincentii (↑) | Fusobacterium nucleatum, Actinomyces naeslundii | Not reported | Enriched taxa profiled | [31] |
| Zhao, Q. | Prevotella (↑); Neisseria (↓) | - | Prevotella, Neisseria | Not reported | Clear Prevotella ↑/Neisseria ↓ pattern | [32] |
| Chen, M. F. | - | Porphyromonas gingivalis (↑), Veillonella parvula (↑) | Porphyromonas gingivalis, Veillonella parvula | Not reported | Clinical + mechanistic focus | [23] |
| Li, H. | Streptococcus (↑), Prevotella_7 (↑); Neisseria (↓) | - | Streptococcus, Prevotella_7 * | Not reported | Diversity mixed; taxa significant | [33] |
| Li, Z. | Parvimonas (↑), Helicobacter (↑), Peptostreptococcus (↑) | - | Parvimonas, Helicobacter | Not reported | Disease progression correlated | [34] |
| Wei, J. | - | Streptococcus salivarius (↑), Fusobacterium nucleatum (↑), Porphyromonas gingivalis (↑) | Streptococcus salivarius, Fusobacterium nucleatum, Porphyromonas gingivalis | 69.3–86.4%/58.8–96.1% | qPCR validation used | [35] |
| Xiao, P. | Capnocytophaga (↑); Atopobium (↓), Hydrobacter (↓) | Eubacterium yurii (↑) | Eubacterium yurii, Capnocytophaga | Not reported | Focused on pre-cancerous lesion comparison | [36] |
| Chen, X. | Leptotrichia (↑), Porphyromonas (↑) | - | Leptotrichia, Porphyromonas | 68.2–86.4%/64.4–86.0% | V4 analysis; genus-level resolution | [37] |
| Hao, Y. | - | Actinomyces bowdenii (↑), Atopobium parvulum (↑) | Actinomyces bowdenii, Atopobium parvulum | Not reported | Staged analysis with species detail | [38] |
| Jiang, Z. | Leptotrichia (↑) | - | Leptotrichia | Not reported | Genus-focused significant taxa | [39] |
| Chen, H. | Shigella (↑), Leptotrichia (↑) | Porphyromonas endodontalis (↑) | Porphyromonas endodontalis, Leptotrichia | Not reported | Species-level marker clarity | [40] |
| Li, M. | - | Prevotella histicola (↑), Fusobacterium nucleatum (↑), Prevotella intermedia (↑) | Prevotella spp., Fusobacterium nucleatum | Not reported | Expanded Prevotella panel | [41] |
| Solfisburg, Q.S. | Streptococcus spp. (↑) | - | Streptococcus spp. | Not reported | Dysplasia stratification | [42] |
| He, Y. | Veillonellaceae (↑) | Prevotella salivae (↑) | Prevotella salivae, Veillonellaceae | Not reported | Pre-/post-treatment comparison | [43] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.-C.; Hsu, M.-H.; Hu, S.-W.; Lin, Y.-Y. Exploring the Diagnostic and Predictive Value of Oral Microbiome in Esophageal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199457
Chen J-C, Hsu M-H, Hu S-W, Lin Y-Y. Exploring the Diagnostic and Predictive Value of Oral Microbiome in Esophageal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199457
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jie-Chi, Min-Hsun Hsu, Suh-Woan Hu, and Yuh-Yih Lin. 2025. "Exploring the Diagnostic and Predictive Value of Oral Microbiome in Esophageal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199457
APA StyleChen, J.-C., Hsu, M.-H., Hu, S.-W., & Lin, Y.-Y. (2025). Exploring the Diagnostic and Predictive Value of Oral Microbiome in Esophageal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199457







