Identification of Plasma-Generated Reactive Species in Water and Their DNA-Damaging Effects on Plasmid and Lymphocyte DNA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of NTP on Plasmid DNA in the Presence of Specific Scavengers
2.2. Effects of NTP on Concentration of Hydrogen Peroxide, Nitrates, and Nitrites
2.3. NTP Impact on pH and Evaporation
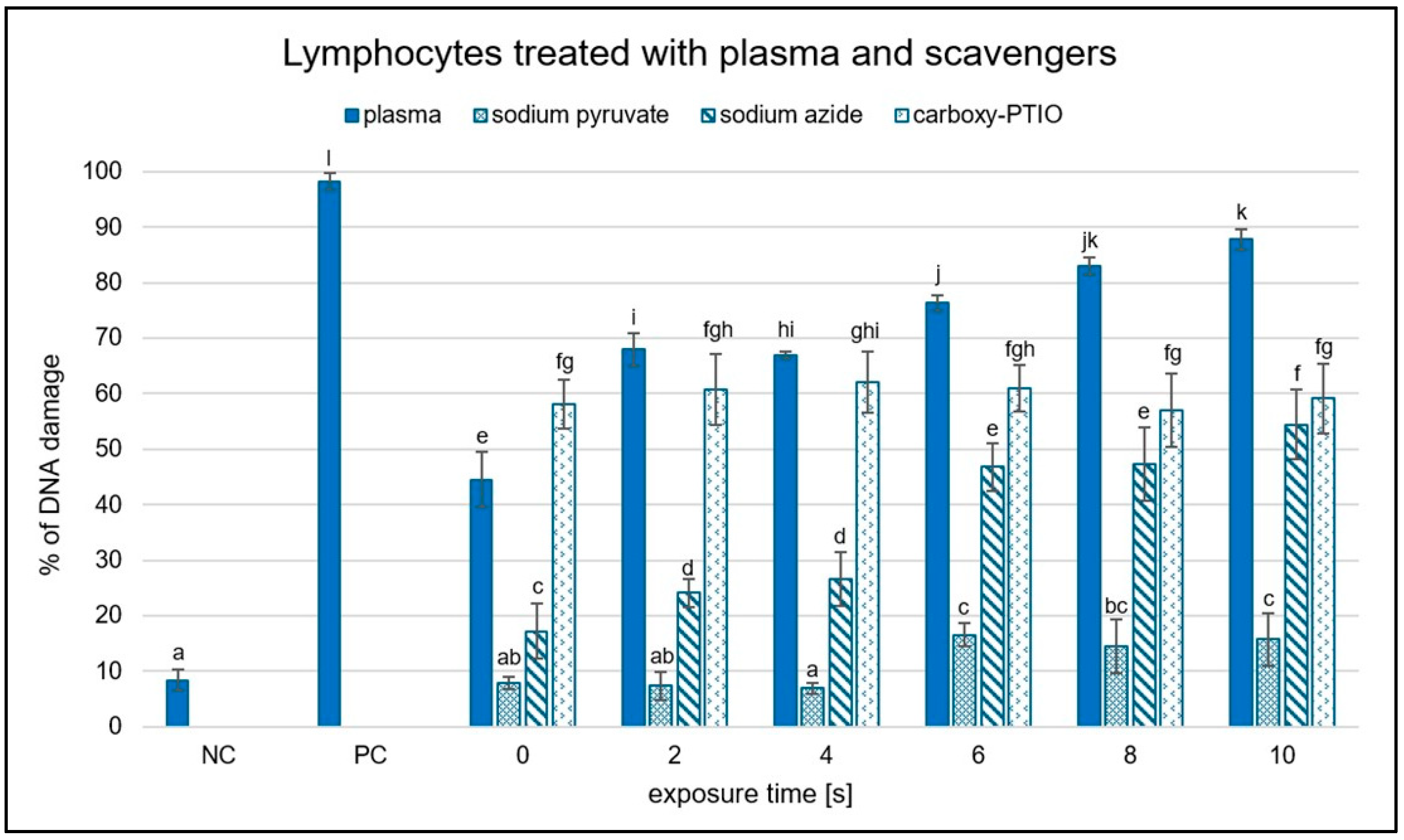
2.4. Differential Scavenger Efficacy on Lymphocyte DNA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
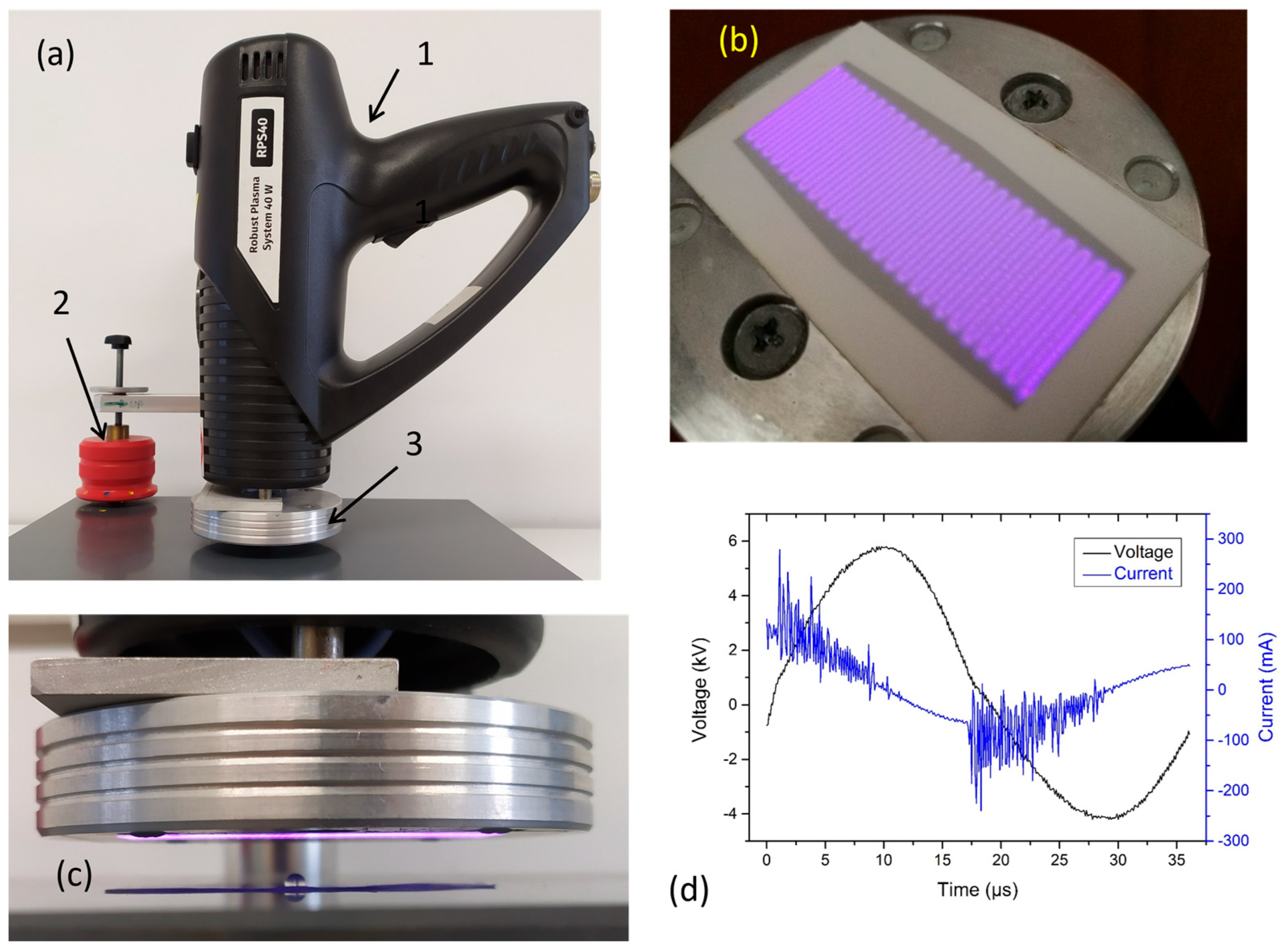
4.1. Plasma Treatment
4.2. DNA Topology Assay
4.3. Measurement of Hydrogen Peroxide, Nitrites, and Nitrates Concentrations
4.4. Measurement of pH Values and Estimation of Water Evaporation
4.5. Comet Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nehra, V.; Kumar, A.; Dwivedi, H.K. Atmospheric non-thermal plasma sources. Int. J. Eng. 2008, 2, 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Haertel, B.; von Woedtke, T.; Weltmann, K.D.; Lindequist, U. Non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma possible application in wound healing. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czapka, T.; Maliszewska, I.; Olesiak-Bańska, J. Influence of atmospheric pressure non-thermal plasma on inactivation of biofilm cells. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2018, 38, 1181–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, P.J.; Kushner, M.J.; Locke, B.R.; Gardeniers, J.G.; Graham, W.G.; Graves, D.B.; Hofman-Caris, R.C.H.M.; Maric, D.; Reid, J.P.; Ceriani, E.; et al. Plasma–liquid interactions: A review and roadmap. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2016, 25, 053002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Rosenstein, B.S.; Wang, Y.; Lebwohl, M.; Wei, H. Identification of possible reactive oxygen species involved in ultraviolet radiation-induced oxidative DNA damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 23, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukes, P.; Clupek, M.; Babicky, V.; Sunka, P. Ultraviolet radiation from the pulsed corona discharge in water. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2008, 17, 024012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, M.; Guay, D.; Leask, R.L.; Coulombe, S. Cell permeabilization using a non-thermal plasma. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 115021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.G.; Cooper, M.; Yost, A.; Paff, M.; Ercan, U.K.; Fridman, G.; Fridman, A.; Brooks, A.D. Nonthermal dielectric-barrier discharge plasma-induced inactivation involves oxidative DNA damage and membrane lipid peroxidation in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, N.; Kurita, H.; Oh, J.S.; Miyachika, S.; Ito, M.; Mizuno, A.; Cowin, A.J.; Allinson, S.; Short, R.D.; Szili, E.J. On cold atmospheric-pressure plasma jet induced DNA damage in cells. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 54, 035203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švubová, R.; Válková, N.; Bathoová, M.; Kyzek, S.; Gálová, E.; Medvecká, V.; Slováková, Ľ. Enhanced in situ activity of peroxidases and lignification of root tissues after exposure to non-thermal plasma increases the resistance of pea seedlings. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2021, 41, 903–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvrdá, E.; Lovíšek, D.; Kyzek, S.; Kováčik, D.; Gálová, E. The effect of non-thermal plasma on the structural and functional characteristics of human spermatozoa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Kim, J.I. Decomposition of biological macromolecules by plasma generated with helium and oxygen. J. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 466–471. [Google Scholar]
- Ptasińska, S.; Bahnev, B.; Stypczyńska, A.; Bowden, M.; Mason, N.J.; Braithwaite, N.S.J. DNA strand scission induced by a non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma jet. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 7779–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkawareek, M.Y.; Nid’a, H.A.; Higginbotham, S.; Flynn, P.B.; Algwari, Q.T.; Gorman, S.P.; Grahan, W.G.; Gilmore, B.F. Plasmid DNA damage following exposure to atmospheric pressure nonthermal plasma: Kinetics and influence of oxygen admixture. Plasma Med. 2014, 4, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, H.P.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.X.; Sun, W.T.; Xing, X.H.; Bao, C.Y. Genetic effects of radio-frequency, atmospheric-pressure glow discharges with helium. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 221504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Mizuno, M.; Nakamura, K.; Kajiyama, H.; Kano, H.; Uchida, K.; Kikkawa, F.; Hori, M.; et al. Direct exposure of non-equilibrium atmospheric pressure plasma confers simultaneous oxidative and ultraviolet modifications in biomolecules. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2014, 55, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, P.; Kumar, N.; Park, J.H.; Yadav, D.K.; Choi, S.; Uhm, H.S.; Kim, I.T.; Cho, E.H.; Lee, W. Influence of reactive species on the modification of biomolecules generated from the soft plasma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walk, R.M.; Snyder, J.A.; Srinivasan, P.; Kirsch, J.; Diaz, S.O.; Blanco, F.C.; Shashurin, A.; Keidar, M.; Sandler, A.D. Cold atmospheric plasma for the ablative treatment of neuroblastoma. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2013, 48, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babajani, A.; Eftekharinasab, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Mehdian, H.; Vakhshiteh, F.; Madjd, Z. Reactive oxygen species from non-thermal gas plasma (CAP): Implication for targeting cancer stem cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Poschkamp, B.; van der Linde, J. Medical gas plasma promotes blood coagulation via platelet activation. Biomaterials 2021, 278, 120433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arguello-Sánchez, R.; López-Callejas, R.; Rodríguez-Méndez, B.G.; Scougall-Vilchis, R.; Velázquez-Enríquez, U.; Mercado-Cabrera, A.; Peña-Eguiluz, R.; Valencia-Alvarado, R.; Medina-Solís, C.E. Innovative curved-tip reactor for non-thermal plasma and plasma-treated water generation: Synergistic impact comparison with sodium hypochlorite in dental root canal disinfection. Materials 2023, 16, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tan, M.; Chen, H.; Wu, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Lian, X.; et al. Non-thermal plasma suppresses bacterial colonization on skin wound and promotes wound healing in mice. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2011, 31, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackert, S.; Haertel, B.; Wende, K.; Von Woedtke, T.; Lindequist, U. Influence of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma on cellular structures and processes in human keratinocytes (HaCaT). J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 70, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Joh, H.M.; Park, J.M.; Kim, M.J.; Chung, T.H.; Kang, T.H. Non-thermal plasma-induced apoptosis is modulated by ATR-and PARP1-mediated DNA damage responses and circadian clock. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serment-Guerrero, J.H.; Giron Romero, K.; López-Callejas, R.; Peña-Eguiluz, R. In vitro assessment of murine melanoma cells sensitivity to non-thermal atmospheric plasma. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2019, 17, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švubová, R.; Kyzek, S.; Medvecká, V.; Slováková, Ľ.; Gálová, E.; Zahoranová, A. Novel insight at the effect of cold atmospheric pressure plasma on the activity of enzymes essential for the germination of pea (Pisum sativum L. cv. Prophet) seeds. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2020, 40, 1221–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holubová, Ľ.; Švubová, R.; Slováková, Ľ.; Bokor, B.; Chobotová Kročková, V.; Renčko, J.; Uhrin, F.; Medvecká, V.; Zahoranová, A.; Gálová, E. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma treatment of maize grains—Induction of growth, enzyme activities and heat shock proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pet’ková, M.; Švubová, R.; Kyzek, S.; Medvecká, V.; Slováková, Ľ.; Ševčovičová, A.; Gálová, E. The effects of cold atmospheric pressure plasma on germination parameters, enzyme activities and induction of DNA damage in barley. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboubakr, H.A.; Gangal, U.; Youssef, M.M.; Goyal, S.M.; Bruggeman, P.J. Inactivation of virus in solution by cold atmospheric pressure plasma: Identification of chemical inactivation pathways. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 204001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Xu, R.; Gou, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Kong, M.G. Mechanism of virus inactivation by cold atmospheric-pressure plasma and plasma-activated water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00726-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarabová, B.; Lukeš, P.; Hammer, M.U.; Jablonowski, H.; von Woedtke, T.; Reuter, S.; Machala, Z. Fluorescence measurements of peroxynitrite/peroxynitrous acid in cold air plasma treated aqueous solutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 8883–8896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willach, S.; Lutze, H.V.; Eckey, K.; Loeppenberg, K.; Lüling, M.; Terhalle, J.; Wolbert, J.B.; Jochmann, M.A.; Karst, U.; Schmidt, T.C. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole using ozone and chlorine dioxide-Compound-specific stable isotope analysis, transformation product analysis and mechanistic aspects. Water Res. 2017, 122, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Ebselen, a selenoorganic compound as glutathione peroxidase mimic. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1993, 14, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, S.; Kadoma, Y. Kinetic studies of the radical-scavenging activity of ebselen, a seleno-organic compound. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 3989–3994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akaike, T.; Yoshida, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Sato, K.; Kohno, M.; Sasamoto, K.; Miyazaki, K.; Ueda, S.; Maeda, H. Antagonistic action of imidazolineoxyl N-oxides against endothelium-derived relaxing factor/•NO (nitric oxide) through a radical reaction. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishibayashi, S.; Asanuma, M.; Kohno, M.; Gómez-Vargas, M.; Ogawa, N. Scavenging effects of dopamine agonists on nitric oxide radicals. J. Neurochem. 1996, 67, 2208–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Diaz-Rivera, D.; He, Z.; Weavers, L.K. Using pulsed wave ultrasound to evaluate the suitability of hydroxyl radical scavengers in sonochemical systems. Ultrason. Sonochem 2013, 20, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Cheng, J.H.; Sun, D.W. Oxidative lesions and post-treatment viability attenuation of listeria monocytogenes triggered by atmospheric non-thermal plasma. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 2348–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, C.; Mori, M.; Nakamura, K.; Tanaka, H.; Mizuno, M.; Hori, M.; Iwase, A.; Kikkawa, F.; Toyokuni, S. Non-thermal plasma prevents progression of endometriosis in mice. Free Radic. Res. 2016, 50, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirst, A.M.; Simms, M.S.; Mann, V.M.; Maitland, N.J.; O’Connell, D.; Frame, F.M. Low-temperature plasma treatment induces DNA damage leading to necrotic cell death in primary prostate epithelial cells. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welz, C.; Emmert, S.; Canis, M.; Becker, S.; Baumeister, P.; Shimizu, T.; Morfill, G.E.; Harréus, U.; Zimmermann, J.L. Cold atmospheric plasma: A promising complementary therapy for squamous head and neck cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, D.; Cox, L.J.; Hyland, W.B.; McMahon, S.J.; Reuter, S.; Graham, W.G.; Gans, T.; Currell, F.J. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma jet interactions with plasmid DNA. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 043701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young Kim, J.; Lee, D.H.; Ballato, J.; Cao, W.; Kim, S.O. Reactive oxygen species controllable non-thermal helium plasmas for evaluation of plasmid DNA strand breaks. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 224101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.M.; Sulyman, S.A.A. The effect of non-thermal plasma Jet on bacterial biofilms and plasmid DNA. Al-Mustansiriyah J. Sci. 2021, 32, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Qiao, J.J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, D.Z.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Xiong, Q. Plasma-enhanced evaporation and its impact on plasma properties and gaseous chemistry in a pin-to-water pulsed discharge. Plasma Process. Polym. 2023, 20, e2300002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putchala, M.C.; Ramani, P.; Sherlin, H.J.; Premkumar, P.; Natesan, A. Ascorbic acid and its pro-oxidant activity as a therapy for tumours of oral cavity–a systematic review. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2013, 58, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurita, R.; Barbieri, D.; Gherardi, M.; Colombo, V.; Lukes, P. Chemical analysis of reactive species and antimicrobial activity of water treated by nanosecond pulsed DBD air plasma. Clin. Plasma Med. 2015, 3, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neretti, G.; Taglioli, M.; Colonna, G.; Borghi, C.A. Characterization of a dielectric barrier discharge in contact with liquid and producing a plasma activated water. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2016, 26, 015013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julák, J.; Hujacová, A.; Scholtz, V.; Khun, J.; Holada, K. Contribution to the chemistry of plasma-activated water. Plasma Phys. Rep. 2018, 44, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Jangra, R.; Ahlawat, K.; Mishra, R.; Mishra, A.; Jangra, S.; Prakash, R. Selective generation of nitrate and nitrite in plasma activated water and its physicochemical parameters analysis. Phys. Lett. A 2023, 474, 128832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wartel, M.; Faubert, F.; Dirlau, I.D.; Rudz, S.; Pellerin, N.; Astanei, D.; Burlica, R.; Hnatiuc, B.; Pellerin, S. Analysis of plasma activated water by gliding arc at atmospheric pressure: Effect of the chemical composition of water on the activation. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 233301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machala, Z.; Tarabová, B.; Sersenová, D.; Janda, M.; Hensel, K. Chemical and antibacterial effects of plasma activated water: Correlation with gaseous and aqueous reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, plasma sources and air flow conditions. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2018, 52, 034002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Prasad, K.; Fang, Z.; Speight, R.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K.K. Cold atmospheric plasma activated water as a prospective disinfectant: The crucial role of peroxynitrite. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 5276–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentheour, R.; Machala, Z. Coupled antibacterial effects of plasma-activated water and pulsed electric field. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 895813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanusová, J.; Kováčik, D.; Stupavská, M.; Černák, M.; Novák, I. Atmospheric pressure plasma treatment of polyamide-12 foils. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buček, A.; Brablec, A.; Kováčik, D.; Sťahel, P.; Černák, M. Glass bond adhesive strength improvement by DCSBD atmospheric-pressure plasma treatment. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 78, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvecká, V.; Kováčik, D.; Zahoranová, A.; Černák, M. Atmospheric pressure plasma assisted calcination by the preparation of TiO2 fibers in submicron scale. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 428, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoranová, A.; Hoppanová, L.; Šimončicová, J.; Tučeková, Z.; Medvecká, V.; Hudecová, D.; Kaliňáková, B.; Kováčik, D.; Černák, M. Effect of cold atmospheric pressure plasma on maize seeds: Enhancement of seedlings growth and surface microorganisms inactivation. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2018, 38, 969–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwig, C.; Leslie, A.; Meneses, N.; Reineke, K.; Rauh, C.; Schlüter, O. Inactivation of Salmonella Enteritidis PT30 on the surface of unpeeled almonds by cold plasma. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2017, 44, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mošovská, S.; Medvecká, V.; Halászová, N.; Ďurina, P.; Valík, Ľ.; Mikulajová, A.; Zahoranová, A. Cold atmospheric pressure ambient air plasma inhibition of pathogenic bacteria on the surface of black pepper. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mošovská, S.; Medvecká, V.; Gregová, M.; Tomeková, J.; Valík, Ľ.; Mikulajová, A.; Zahoranová, A. Plasma inactivation of Aspergillus flavus on hazelnut surface in a diffuse barrier discharge using different working gases. Food Control 2019, 104, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, G. Colorimetric determination of hydrogen peroxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1943, 15, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, G.; Adatia, I.; Yazdanpanah, M.; Makela, S.K. Nitrite and nitrate analyses: A clinical biochemistry perspective. Clin. Biochem. 1998, 31, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, D.; Rossi, R.; Milzani, A.; Dalle-Donne, I. Nitrite and nitrate measurement by Griess reagent in human plasma: Evaluation of interferences and standardization. Meth Enzymol. 2008, 440, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.R. The comet assay for DNA damage and repair: Principles, applications, and limitations. Mol. Biotechnol. 2004, 26, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajičková, T.; Kyzek, S.; Ďurovcová, I.; Ševčovičová, A.; Gálová, E. Ratio-dependent effects of photoactivated hypericin and manumycin A on their genotoxic and mutagenic potential. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2023, 374, 110421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
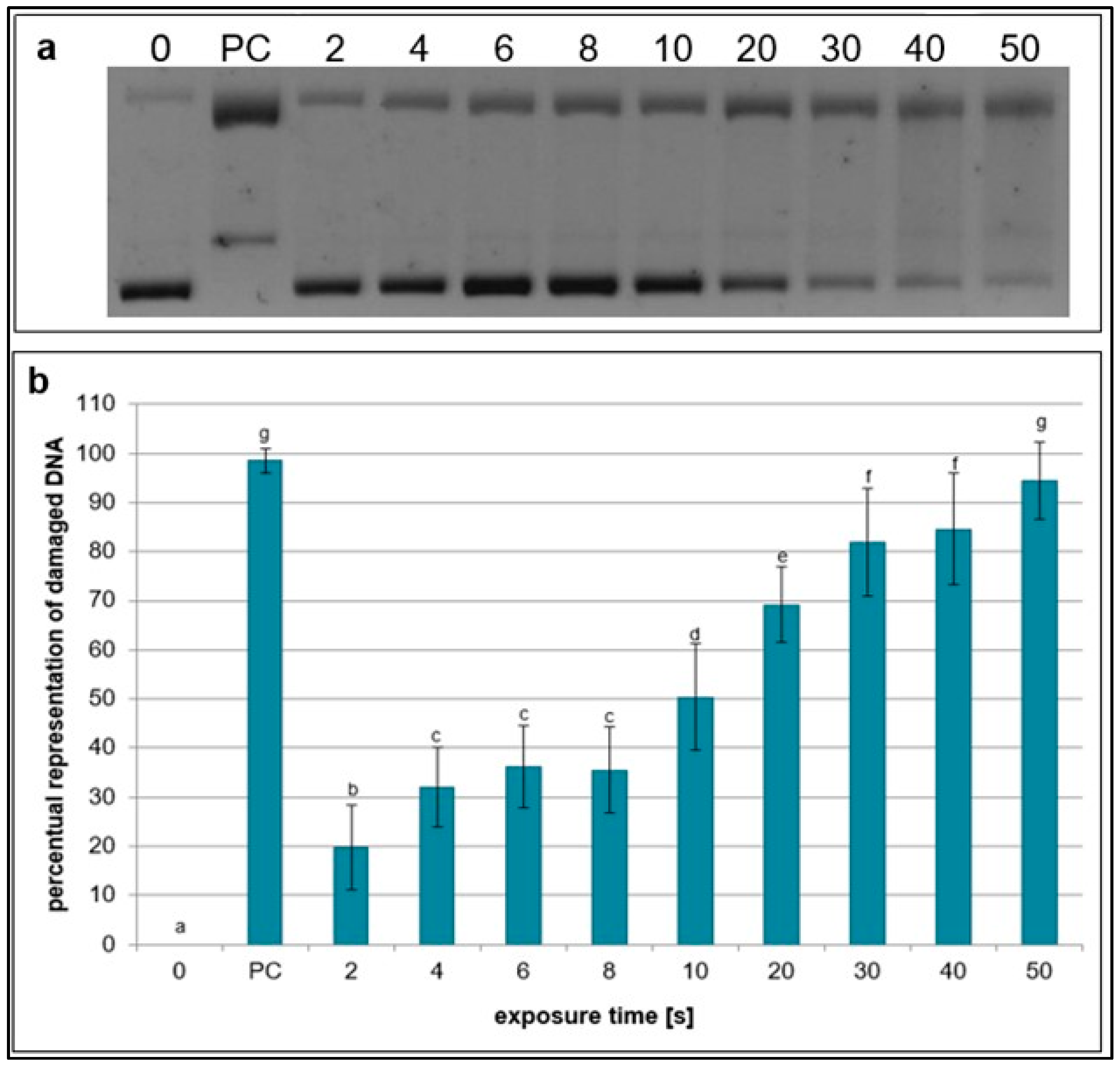
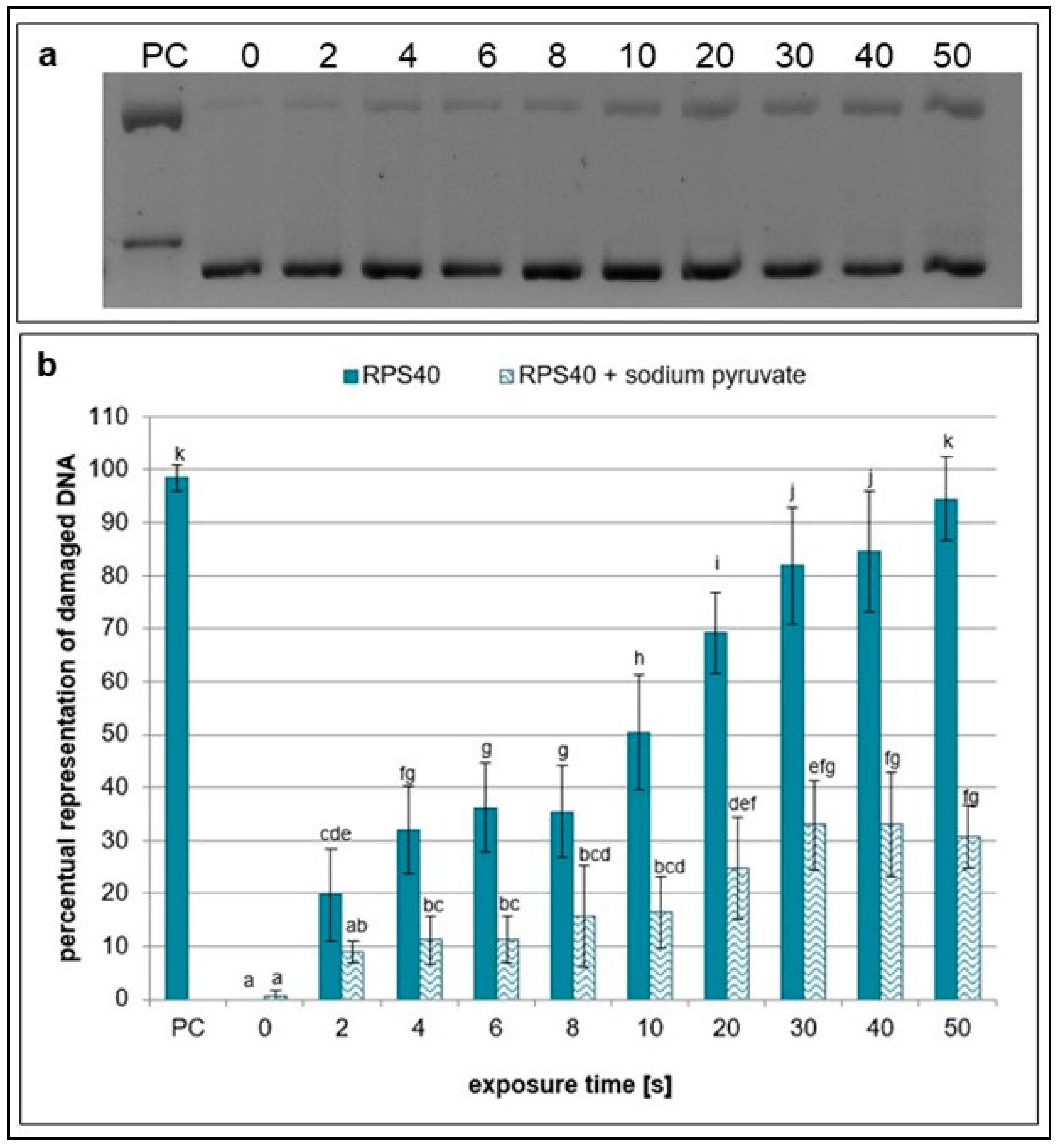

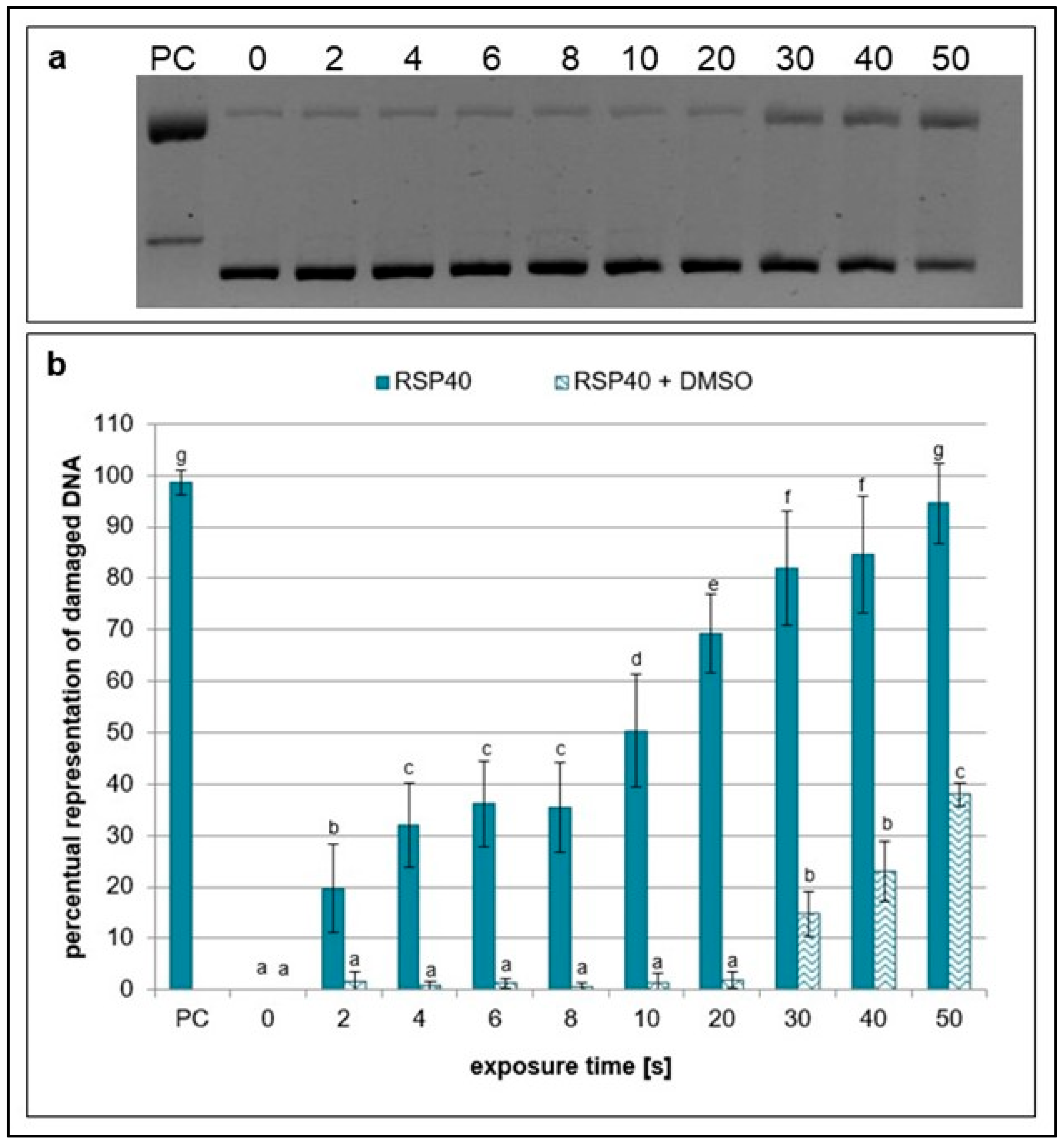
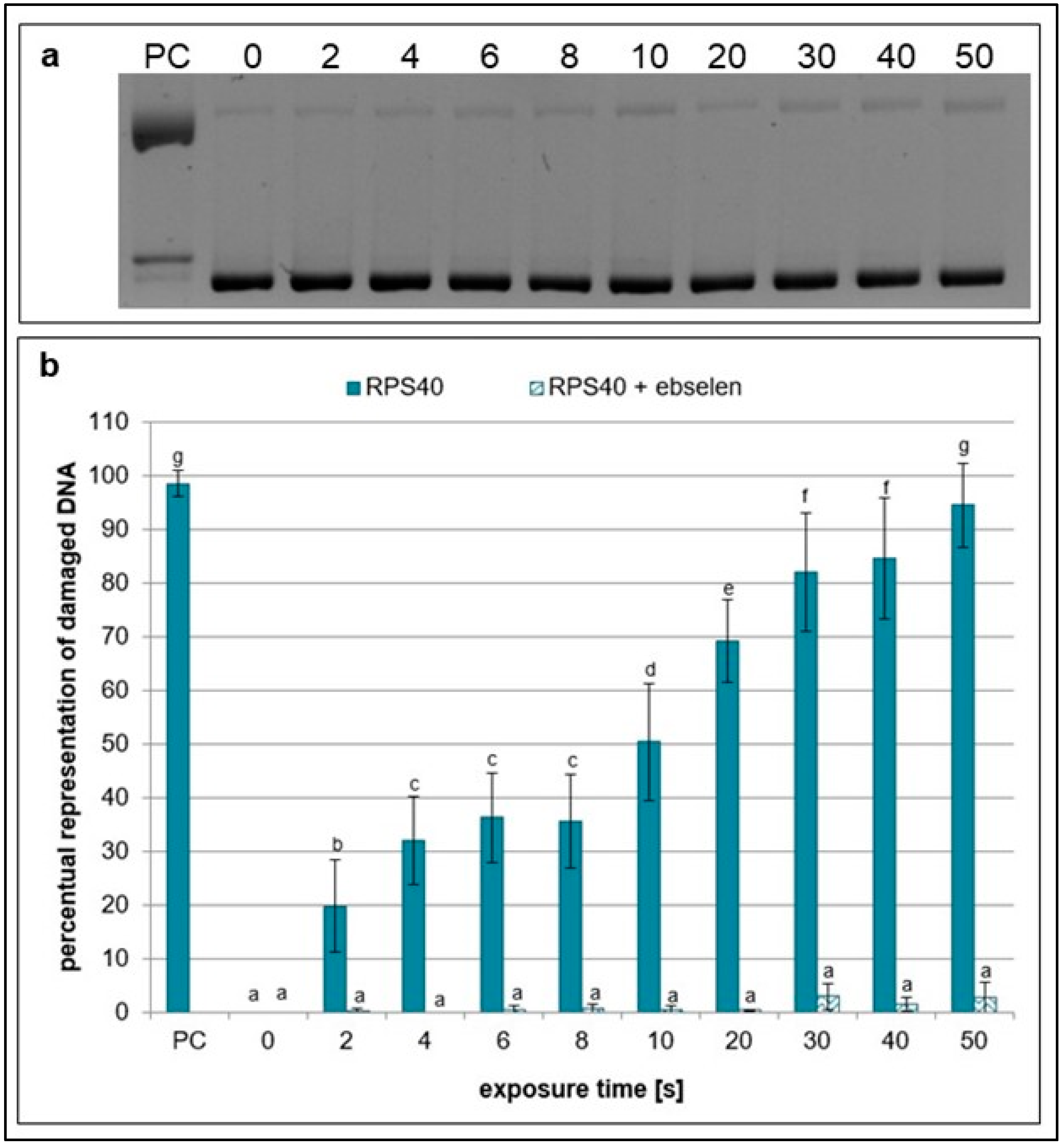
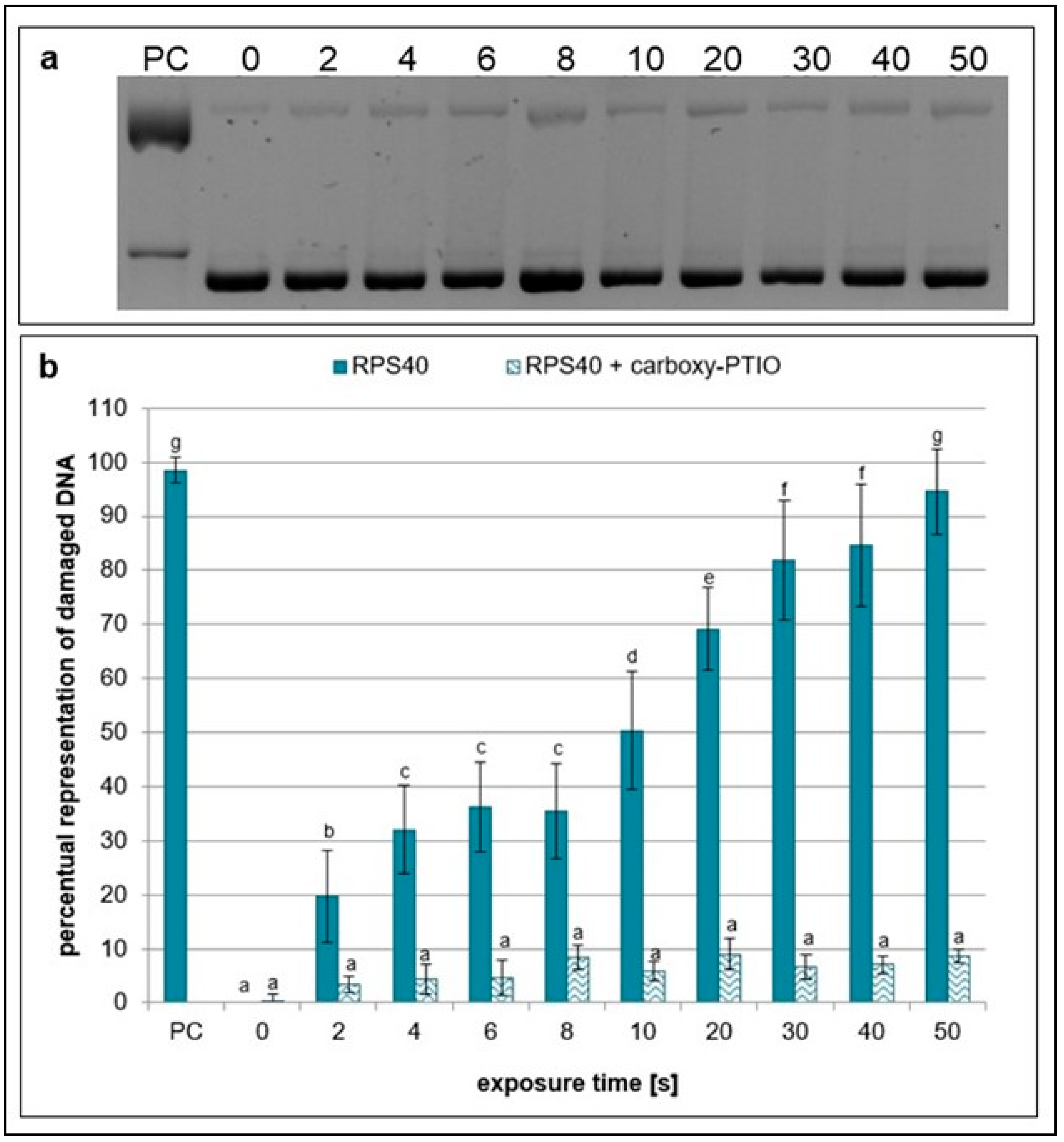
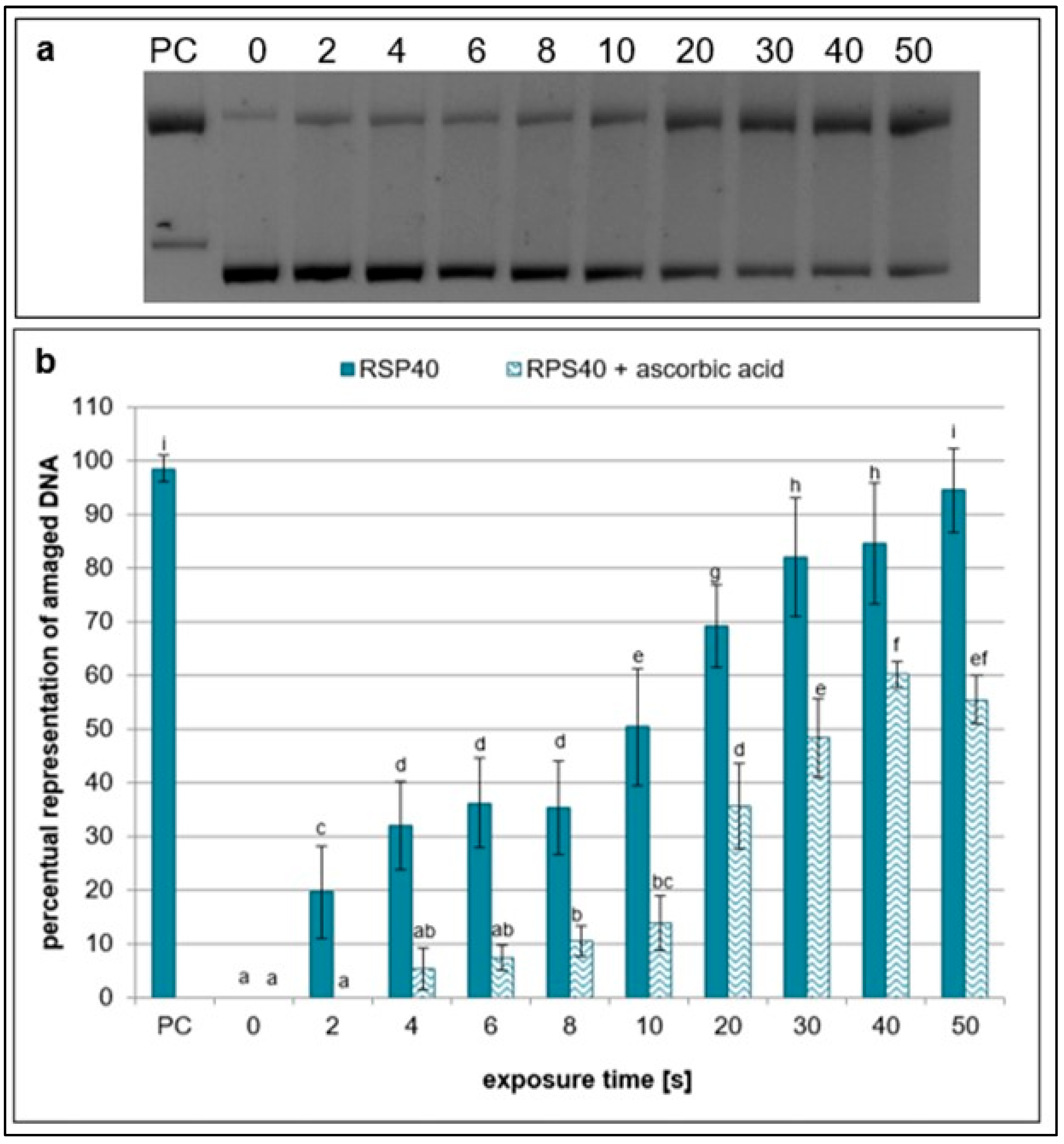
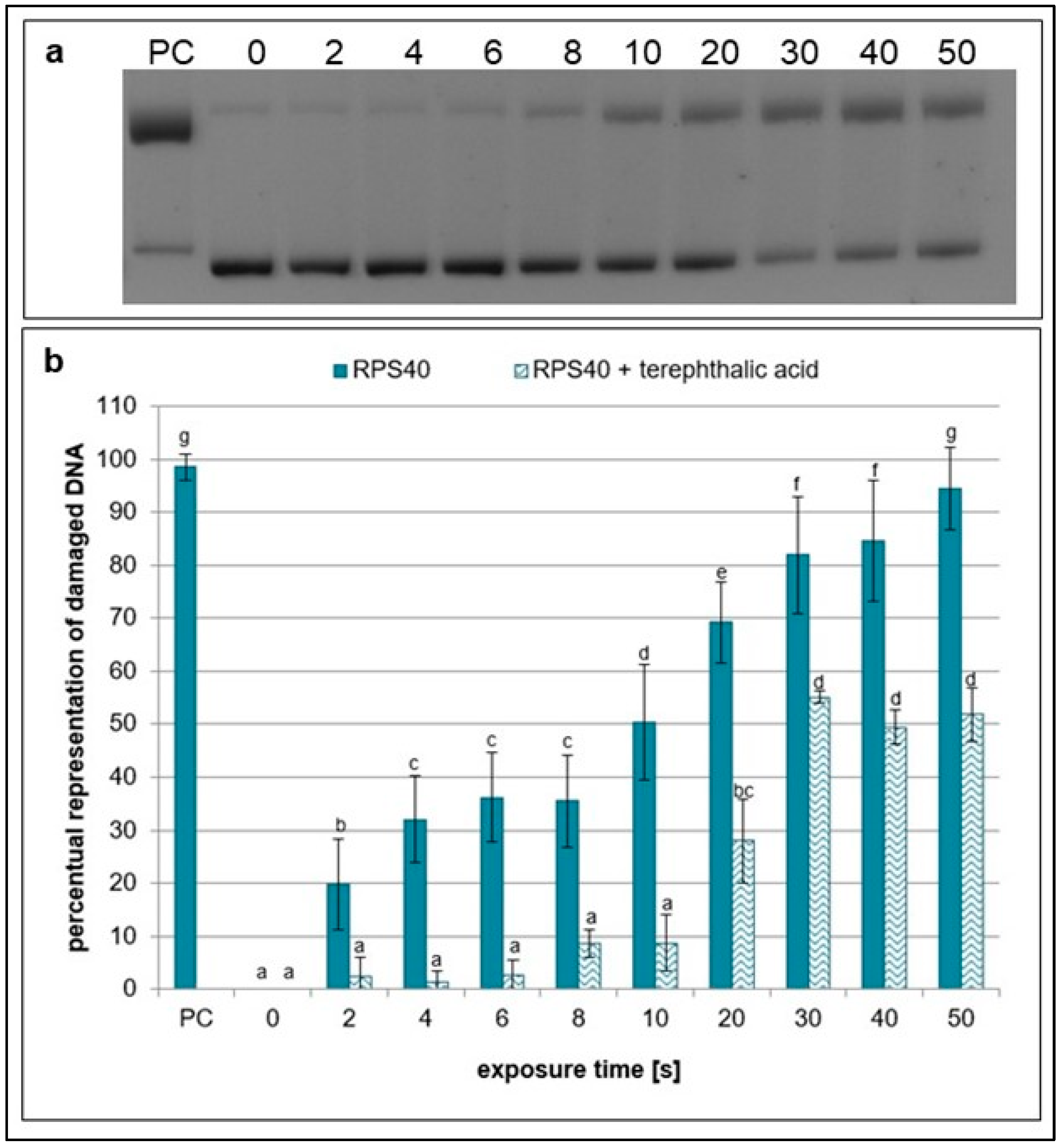
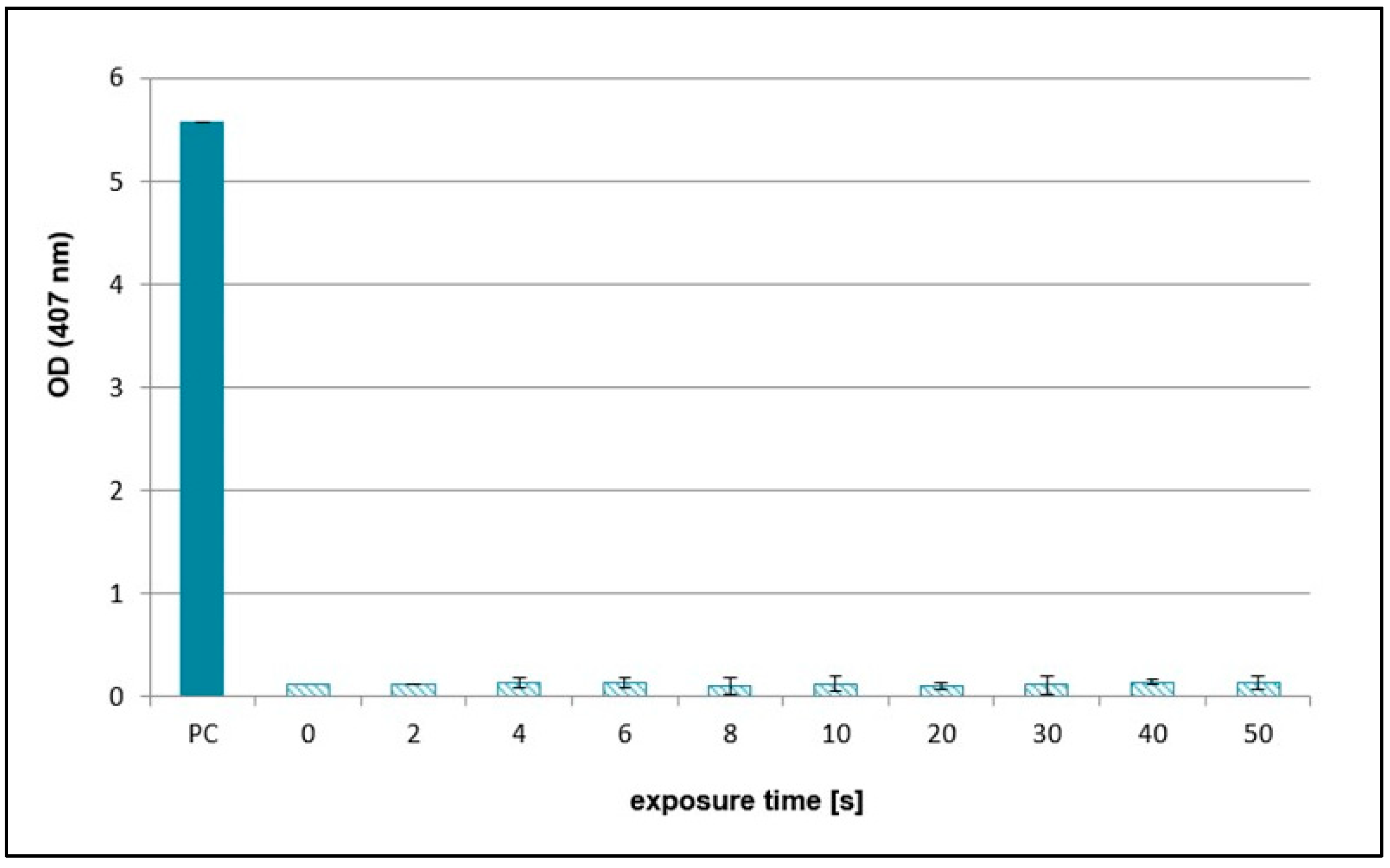


| Exposure Times [s] | pH Value | Sample Weight [mg] |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 c | 8.67 ± 0.12 g |
| 2 | 5 c | 8.50 ± 0.10 fg |
| 4 | 5 c | 8.57 ± 0.12 ef |
| 6 | 5 c | 8.40 ± 0.10 de |
| 8 | 5 c | 8.37 ± 0.06 de |
| 10 | 5 c | 8.33 ± 0.06 d |
| 20 | 5 c | 8.17 ± 0.06 c |
| 30 | 4 b | 8.17 ± 0.06 c |
| 40 | 3 a | 7.77 ± 0.06 b |
| 50 | 3 a | 7.57 ± 0.06 a |
| Scavenger | ROS/RNS | Concentration * | Solvent | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sodium pyruvate | H2O2 | 100 mM | H2O | [29] |
| sodium azide | 1O2, •OH, NO2− | 50 mM | H2O | [29,30,31] |
| carboxy-PTIO | ONOO−, ONOOH, H2O2 | 1 mM | H2O | [30,35,36] |
| ebselen | NO, •NO | 10 mM | DMSO | [33,34] |
| ascorbic acid | ONOOH, •OH | 20 mM | H2O | [29] |
| dimethyl sulfoxide | •OH, O3 | 99% | - | [5,32] |
| terephthalic acid | •OH | 1 mM | DMSO | [37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kyzek, S.; Pišteková, S.; Kyzeková, I.; Ševčovičová, A.; Kováčik, D.; Zahoranová, A.; Gálová, E. Identification of Plasma-Generated Reactive Species in Water and Their DNA-Damaging Effects on Plasmid and Lymphocyte DNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199385
Kyzek S, Pišteková S, Kyzeková I, Ševčovičová A, Kováčik D, Zahoranová A, Gálová E. Identification of Plasma-Generated Reactive Species in Water and Their DNA-Damaging Effects on Plasmid and Lymphocyte DNA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199385
Chicago/Turabian StyleKyzek, Stanislav, Sára Pišteková, Ivana Kyzeková, Andrea Ševčovičová, Dušan Kováčik, Anna Zahoranová, and Eliška Gálová. 2025. "Identification of Plasma-Generated Reactive Species in Water and Their DNA-Damaging Effects on Plasmid and Lymphocyte DNA" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199385
APA StyleKyzek, S., Pišteková, S., Kyzeková, I., Ševčovičová, A., Kováčik, D., Zahoranová, A., & Gálová, E. (2025). Identification of Plasma-Generated Reactive Species in Water and Their DNA-Damaging Effects on Plasmid and Lymphocyte DNA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199385






