In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of 40 kDa PEGylated Adrenomedullin in a DSS-Induced Colitis Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
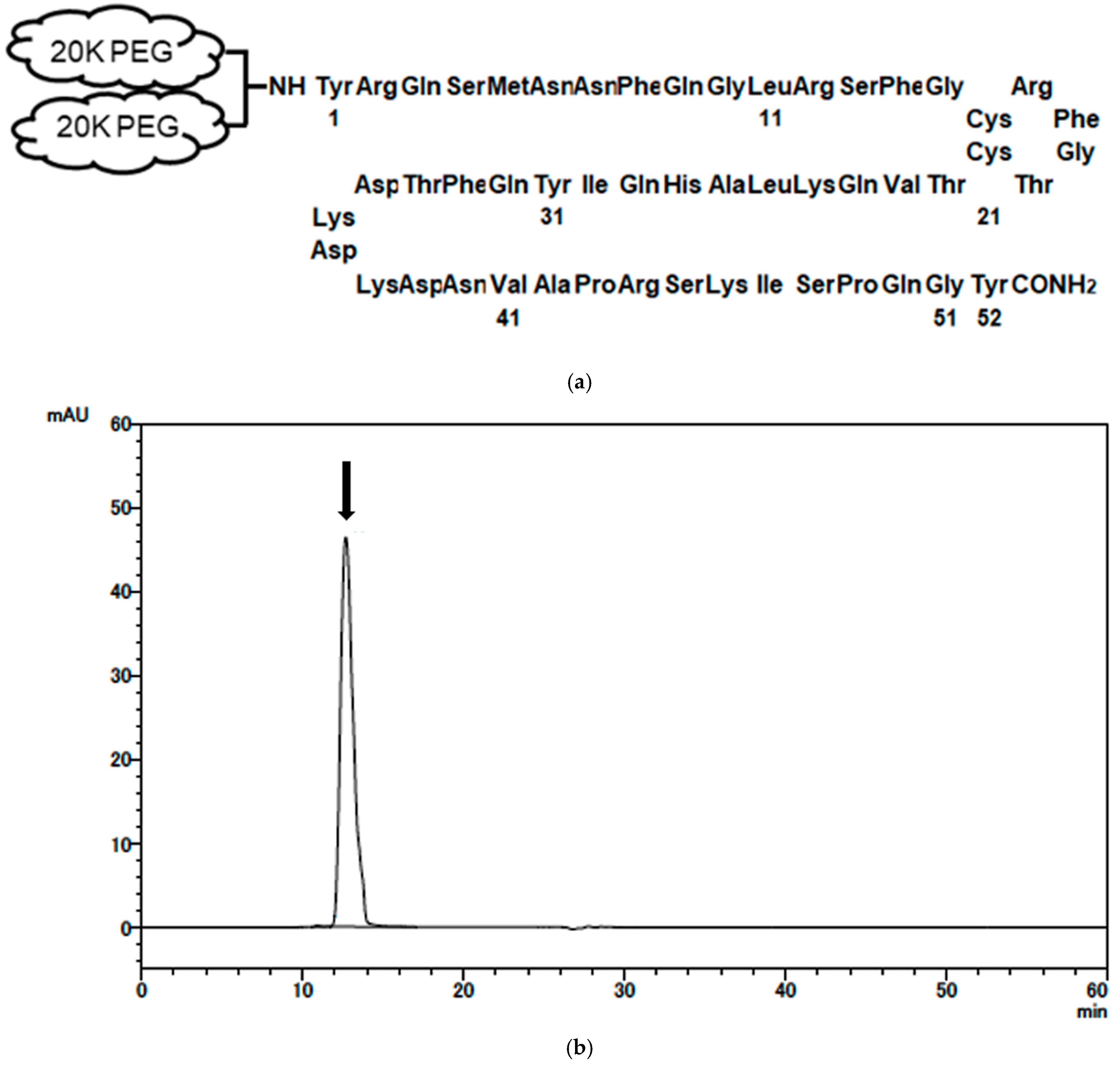
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of PEG-AM
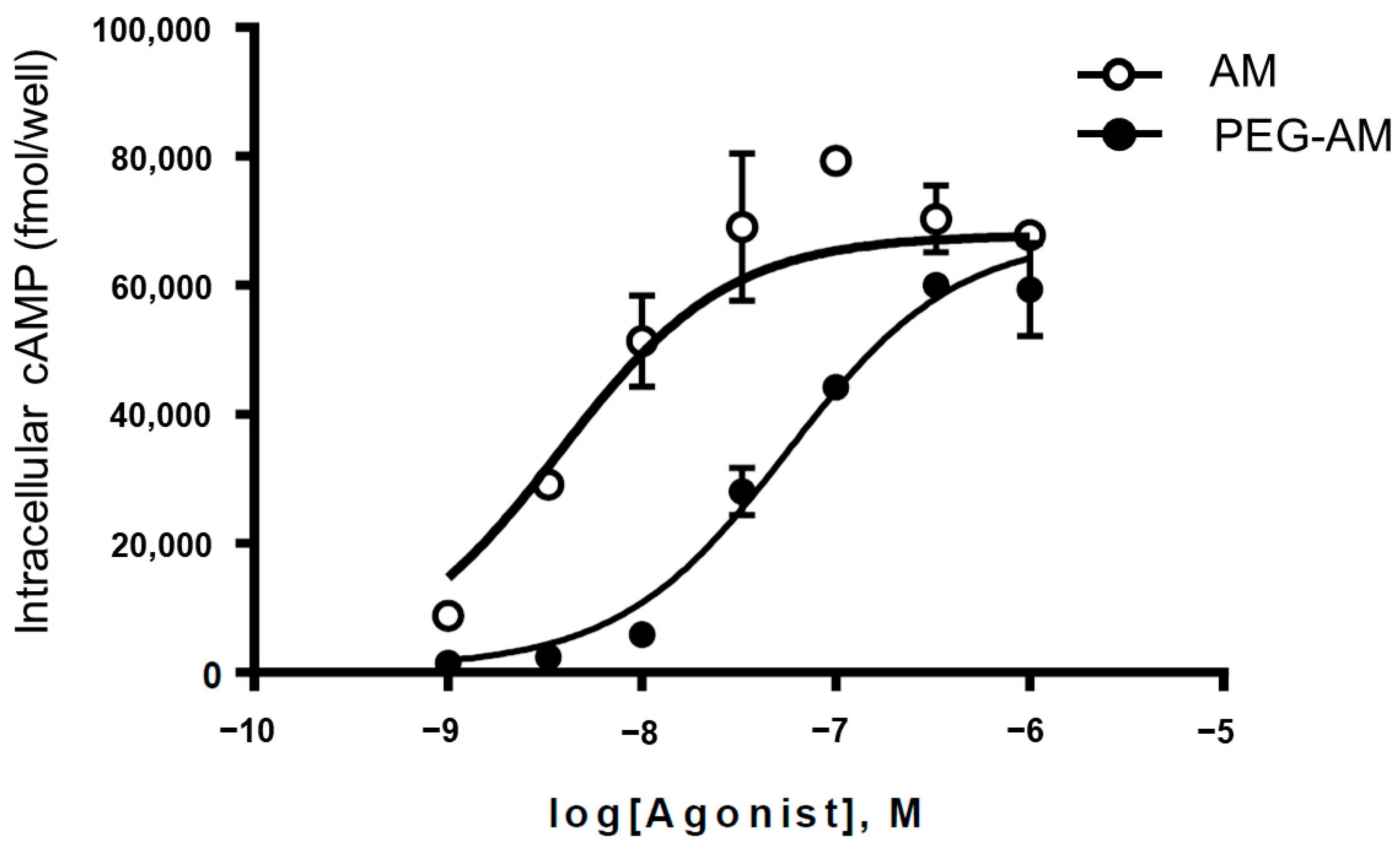
2.2. In Vitro Biological Activity of PEG-AM
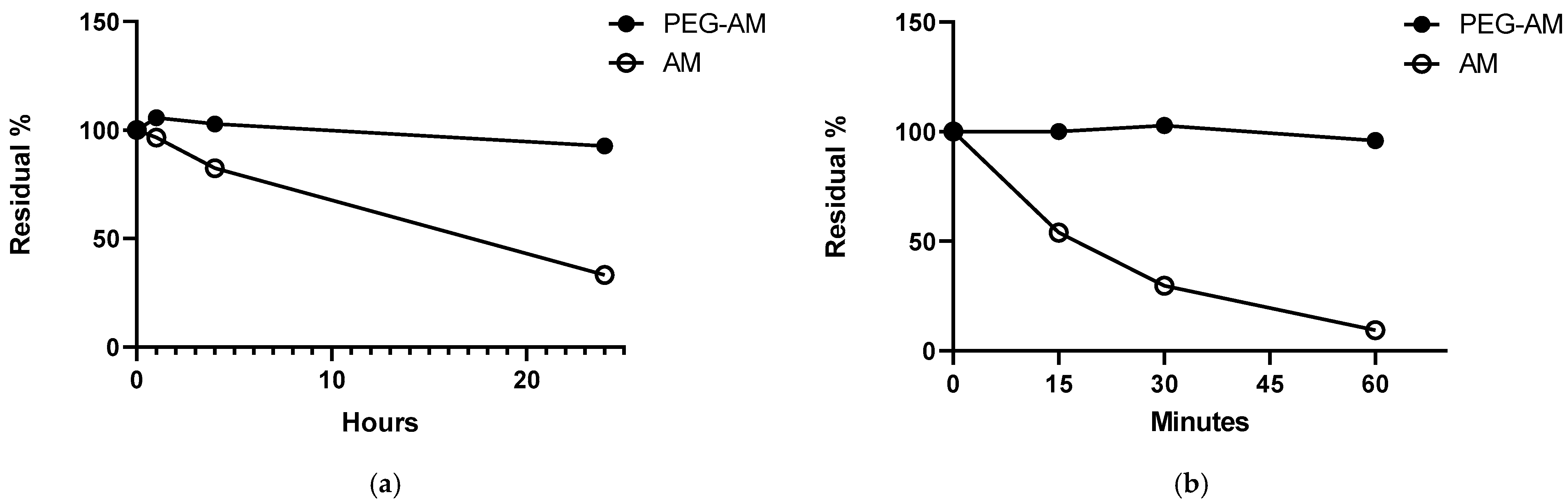
2.3. Stability of PEG-AM and AM
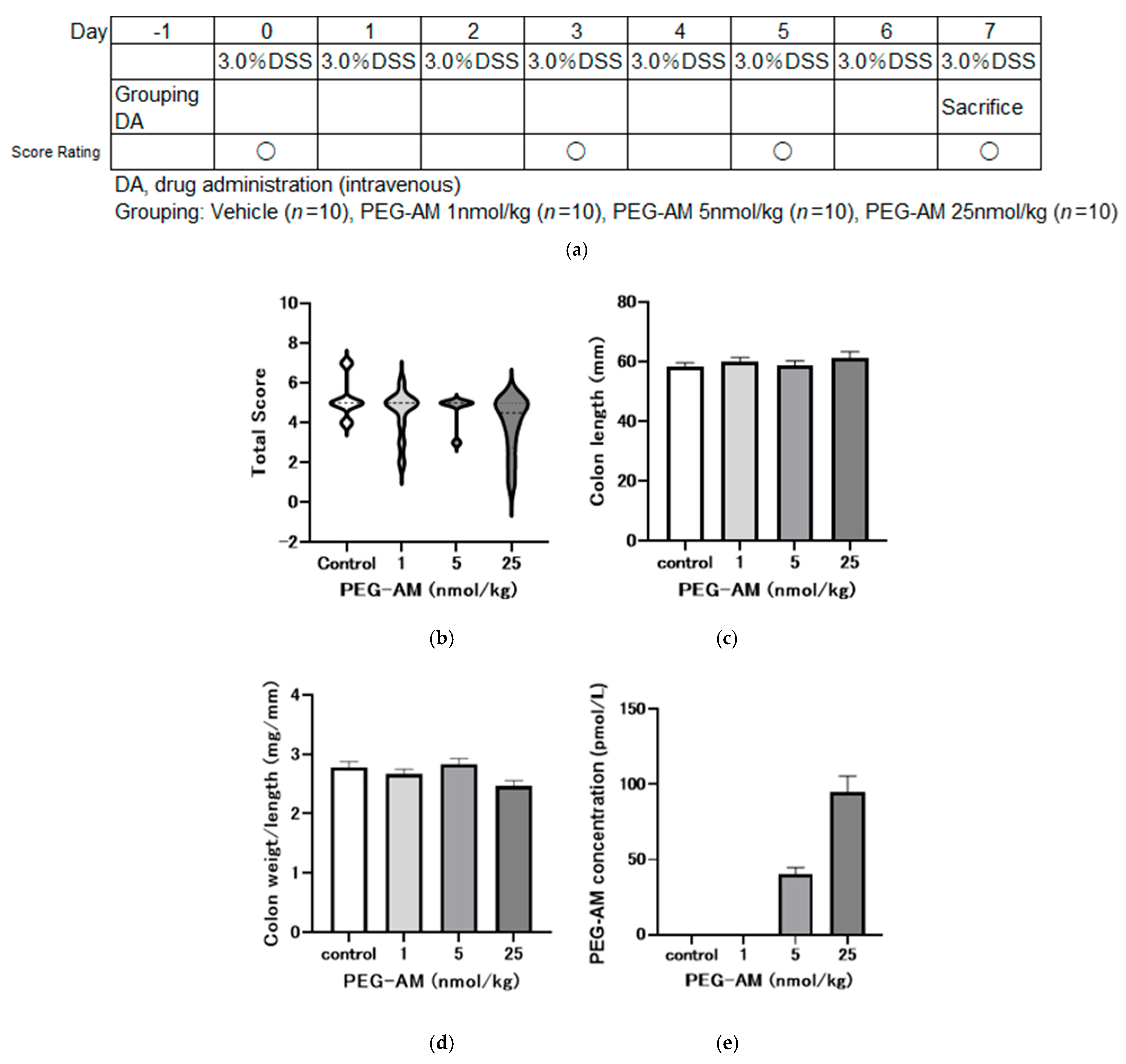
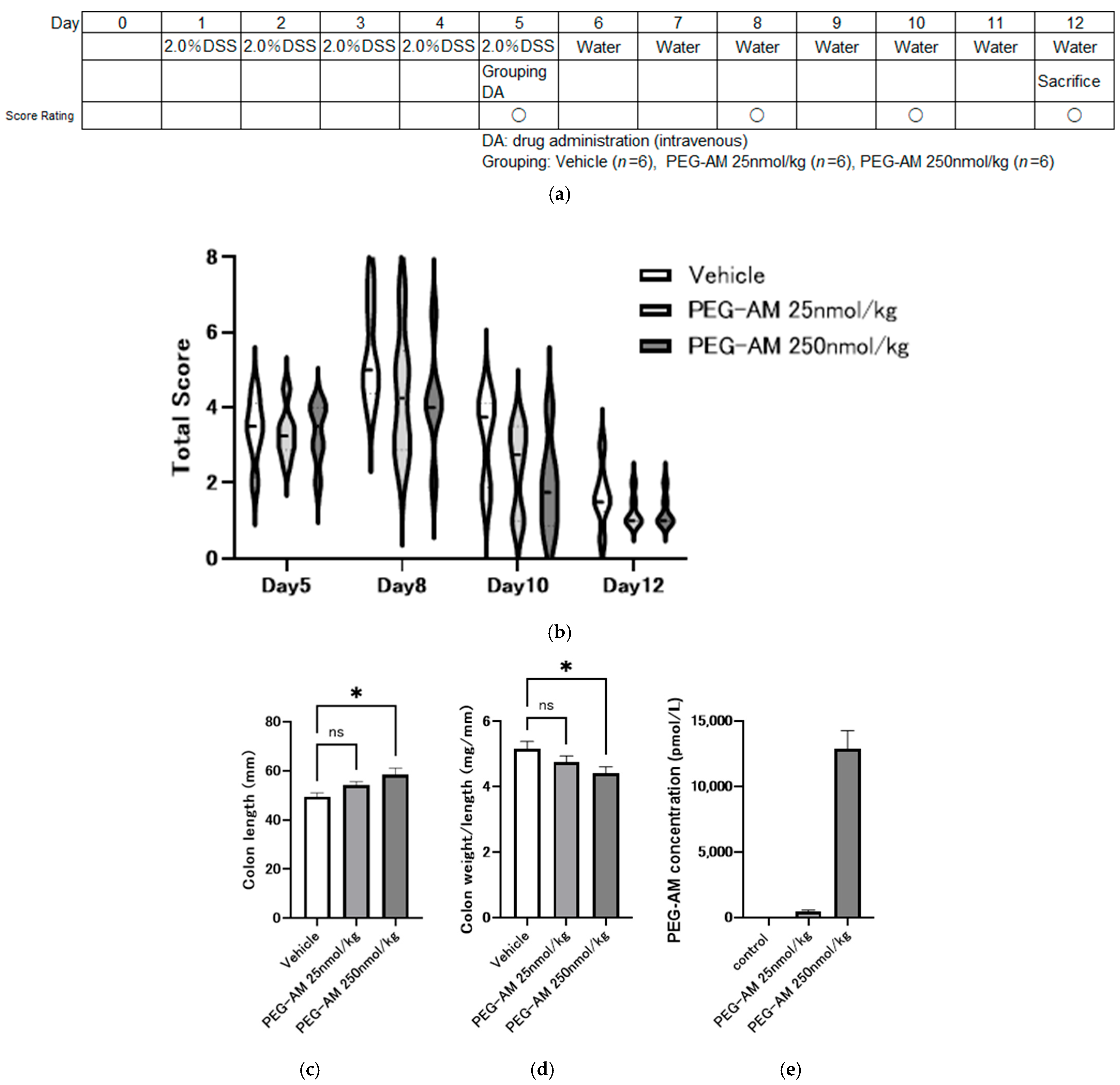
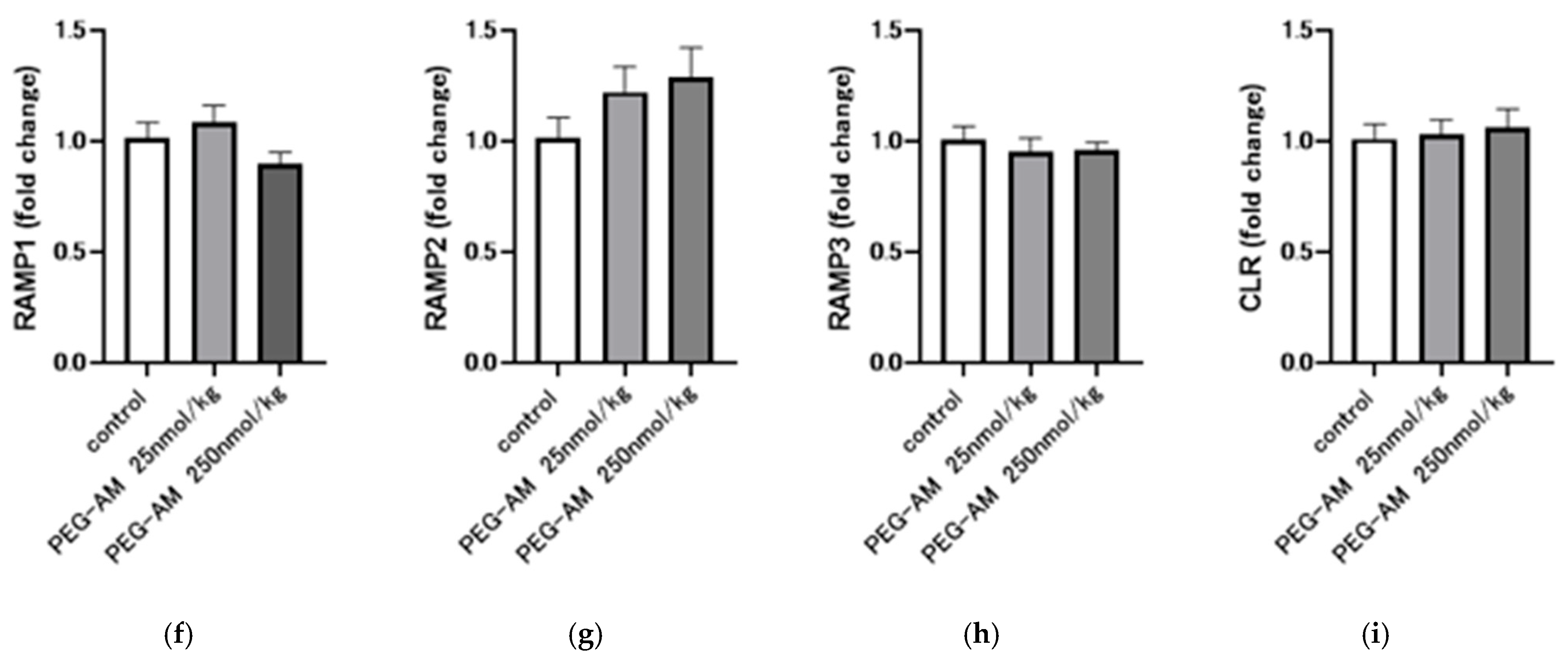
2.4. Dose-Dependent Effects of Intravenous PEG-AM
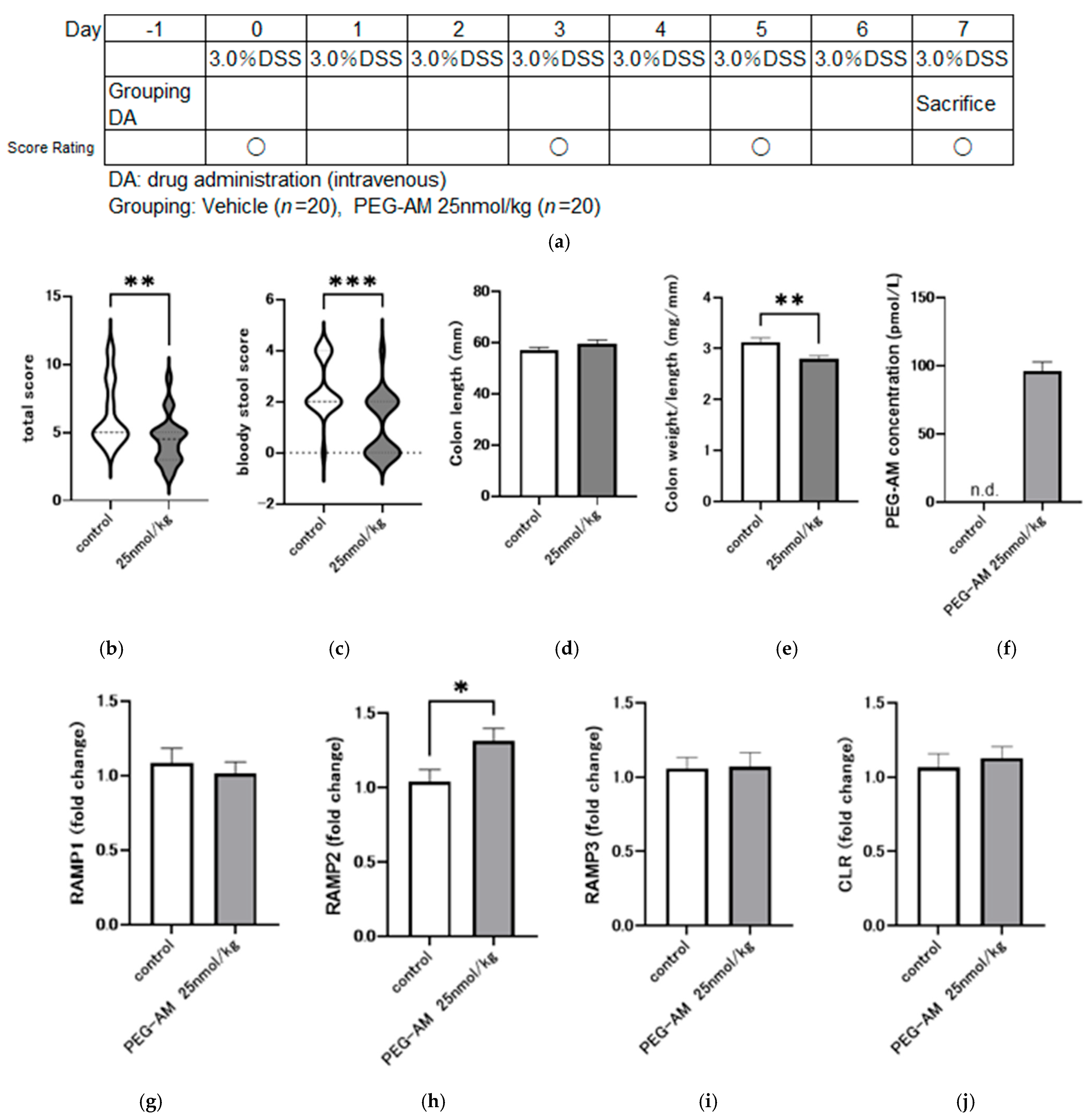
2.5. Effect of 25 nmol/kg PEG-AM in DSS-Induced Colitis
2.6. Therapeutic Effect of PEG-AM After Onset of DSS Colitis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptide and Chemicals
4.2. In Vitro Biological Activity of PEG-AM
4.3. Degradation of AM and PEG-AM
4.4. Quantitative Analysis of AM and PEG-AM
4.5. Gene Expression of Receptor Components
4.6. Induction of DSS-Induced Colitis and PEG-AM Treatment
4.6.1. Dose-Dependent Study (Study No. P170454)
4.6.2. Efficacy of 25 nmol/kg PEG-AM (Study No. P180567)
4.6.3. Therapeutic Effect After Disease Onset (Study No. P200487)
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | Adrenomedullin |
| PEG-AM | 40 kDa PEGylated AM |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| DSS | Dextran sodium sulfate |
| UC | Ulcerative colitis |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| CGRP | Calcitonin gene-related peptide |
| CLR | Calcitonin receptor-like receptor |
| RAMP1 | Receptor activity-modifying protein 1 |
| RAMP2 | Receptor activity-modifying protein 2 |
| RAMP3 | Receptor activity-modifying protein 3 |
| DiPEG-AM | DiPEGylated adrenomedullin |
| 5KPEG-AM | 5 kDa PEGylated AM |
| 20KPEG-AM | 20 kDa PEGylated AM |
| 60KPEG-AM | 60 kDa PEGylated AM |
| HSA | Human serum albumin |
References
- Bretto, E.; Urpì-Ferreruela, M.; Casanova, G.R.; González-Suárez, B. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Gastrointestinal Immune Homeostasis and Inflammation: Implications for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Bouwknegt, D.G.; Weersma, R.K.; Dijkstra, G.; van der Sloot, K.W.J.; Festen, E.A.M. Gene-Environment Interactions in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review of Human Epidemiologic Studies. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2025, 19, jjaf061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solitano, V.; Bernstein, C.N.; Dotan, I.; Dignass, A.; Domilici, R.; Dubinsky, M.C.; Gearry, R.B.; Hart, A.; Kaplan, G.G.; Ma, C.; et al. Shaping the future of inflammatory bowel disease: A global research agenda for better management and public health response. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 22, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.C.; Helsingen, L.M.; Refsum, E.; Högdén, A.; Perrin, V.; Løberg, M.; Gantzel, R.H.; Bretthauer, M.; Berglund, A.; Holme, Ø.; et al. Temporal trends in characteristics and management of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 60, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksic, M.; Corovic, I.; Maksic, T.; Zivic, J.; Zivic, M.; Zdravkovic, N.; Begovic, A.; Medovic, M.; Kralj, D.; Todorovic, Z.; et al. Molecular Insight into the Role of HLA Genotypes in Immunogenicity and Secondary Refractoriness to Anti-TNF Therapy in IBD Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; da Silva, B.C.; Hanauer, S.B. The role of immunogenicity in optimizing biological therapies for inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 19, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Kangawa, K.; Kawamoto, M.; Ichiki, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Matsuo, H.; Eto, T. Adrenomedullin: A novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 192, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, H.C.; Nussdorfer, G.G.; Kadowitz, P.J. Structure-activity relationships of adrenomedullin in the circulation and adrenal gland. Regul. Pept. 1999, 85, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.X.; Itahara, Y.; Inui, T.; Yoshizawa-Kumagaye, K.; Nakajima, K.; Sakakibara, S. Vasopressor activities of N-terminal fragments of adrenomedullin in anesthetized rat. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 219, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.P.; Els-Heindl, S.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Adrenomedullin–Current perspective on a peptide hormone with significant therapeutic potential. Peptides 2020, 131, 170347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLatchie, L.M.; Fraser, N.J.; Main, M.J.; Wise, A.; Brown, J.; Thompson, N.; Solari, R.; Lee, M.G.; Foord, S.M. RAMPs regulate the transport and ligand specificity of the calcitonin-receptor-like receptor. Nature 1998, 393, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamitani, S.; Asakawa, M.; Shimekake, Y.; Kuwasako, K.; Nakahara, K.; Sakata, T. The RAMP2/CRLR complex is a functional adrenomedullin receptor in human endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1999, 448, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pioszak, A.A.; Hay, D.L. RAMPs as allosteric modulators of the calcitonin and calcitonin-like class B G protein-coupled receptors. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 88, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso Martinez, L.M.; Harel, F.; Létourneau, M.; Finnerty, V.; Fournier, A.; Dupuis, J.; DaSilva, J.N. SPECT and PET imaging of adrenomedullin receptors: A promising strategy for studying pulmonary vascular diseases. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 9, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dupuis, J.; Caron, A.; Ruel, N. Biodistribution, plasma kinetics and quantification of single-pass pulmonary clearance of adrenomedullin. Clin. Sci. 2005, 109, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, L.; Nelson-Maney, N.P.; Tian, Y.; Serafin, S.D.; Caron, K.M. Clinical Potential of Adrenomedullin Signaling in the Cardiovascular System. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 1185–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, T.; Kitamura, K. Translational studies of adrenomedullin and related peptides regarding cardiovascular diseases. Hypertens. Res. 2022, 45, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, T.; Ashizuka, S.; Ohmiya, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Kanai, T.; Motoya, S.; Hirai, F.; Nakase, H.; Moriyama, T.; Nakamura, M.; et al. Adrenomedullin for steroid-resistant ulcerative colitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase-2a clinical trial. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, T.; Ashizuka, S.; Takeda, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Ohmiya, N.; Nakase, H.; Motoya, S.; Ohi, H.; Mitsuyama, K.; Hisamatsu, T.; et al. Adrenomedullin for biologic-resistant Crohn’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2a clinical trial. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashizuka, S.; Kita, T.; Inatsu, H.; Kitamura, K. Adrenomedullin: A Novel Therapeutic for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacManus, C.F.; Campbell, E.L.; Keely, S.; Burgess, A.; Kominsky, D.J.; Colgan, S.P. Anti-inflammatory actions of adrenomedullin through fine tuning of HIF stabilization. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 1856–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Narumi, K.; Tsuji, S.; Tsubokawa, T.; Nakaya, M.A.; Wakayama, T.; Zuka, M.; Ohshima, T.; Yamagishi, M.; Okada, T. Impact of adrenomedullin on dextran sulfate sodium-induced inflammatory colitis in mice: Insights from in vitro and in vivo experimental studies. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2011, 26, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Kataoka, H.; Kiwaki, T.; Weiting, L.; Nagata, S.; Kitamura, K.; Fukushima, T. Adrenomedullin alleviates mucosal injury in experimental colitis and increases claudin-4 expression in the colonic epithelium. FEBS Open Bio 2023, 13, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Fan, H.; Liu, X.; Tang, Q.; Zuo, D.; Yang, J. Adrenomedullin improves intestinal epithelial barrier function by downregulating myosin light chain phosphorylation in ulcerative colitis rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 3615–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geven, C.; Kox, M.; Pickkers, P. Adrenomedullin and Adrenomedullin-Targeted Therapy As Treatment Strategies Relevant for Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, Y.; Miyazaki, S.; Yasuda, S.; Nagaya, N.; Noguchi, T.; Yamada, N.; Morii, I.; Kawamura, A.; Doi, K.; Miyatake, K.; et al. The first clinical pilot study of intravenous adrenomedullin administration in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2010, 56, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, T.; Kaji, Y.; Kitamura, K. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Adrenomedullin in Healthy Males: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 1 Clinical Trial. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akashi, E.; Nagata, S.; Yamasaki, M.; Kitamura, K. Activation of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Adrenomedullin Receptors by PEGylated Adrenomedullin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 1799–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, G.; Kuroishi, N.; Tokashiki, M.; Nagata, S.; Tamura, M.; Yoshiya, T.; Yoshizawa-Kumagaye, K.; Ashizuka, S.; Kato, J.; Yamasaki, M.; et al. 20 kDa PEGylated Adrenomedullin as a New Therapeutic Candidate for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastrointest. Disord. 2020, 2, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, S.; Yamasaki, M.; Kitamura, K. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of PEGylated Human Adrenomedullin in a Mouse DSS-Induced Colitis Model. Drug Dev. Res. 2017, 78, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Joshi, M.; Zhao, Z.; Mitragotri, S. PEGylated therapeutics in the clinic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2024, 9, e10600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, S.; Wang, T.; Chen, Q. Comparison between long-acting pegylated and daily recombinant human growth hormone for pediatric growth hormone deficiency a systematic review. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 26746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwasako, K.; Shimekake, Y.; Masuda, M.; Nakahara, K.; Yoshida, T.; Kitaura, M.; Kitamura, K.; Eto, T.; Sakata, T. Visualization of the calcitonin receptor-like receptor and its receptor activity-modifying proteins during internalization and recycling. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 29602–29609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.Y.; Kowalczyk, R.; Desai, A.; Brimble, M.A.; Marshall, J.F.; Harris, P.W.R. Synthesis and Systematic Study on the Effect of Different PEG Units on Stability of PEGylated, Integrin-αvβ6-Specific A20FMDV2 Analogues in Rat Serum and Human Plasma. Molecules 2022, 27, 4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, R.; Burnett, J.C., Jr.; Rouleau, J.L.; Ruschitzka, F.; Lüscher, T.F. Vasopeptidase inhibitors: A new therapeutic concept in cardiovascular disease? Circulation 2001, 104, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, Y.; Nagata, S.; Akashi, E.; Yamasaki, M.; Kitamura, K. Thrombin rapidly digests adrenomedullin: Synthesis of adrenomedullin analogs resistant to thrombin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 529, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonauer, R.; Els-Heindl, S.; Fischer, J.P.; Kobberling, J.; Riedl, B.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Adrenomedullin 2.0: Adjusting Key Levers for Metabolic Stability. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 5695–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pío, R.; Elsasser, T.H.; Martínez, A.; Cuttitta, F. Identification, characterization, and physiological actions of factor H as an adrenomedullin binding protein present in human plasma. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2002, 57, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pio, R.; Martinez, A.; Unsworth, E.J.; Kowalak, J.A.; Bengoechea, J.A.; Zipfel, P.F.; Elsasser, T.H.; Cuttitta, F. Complement factor H is a serum-binding protein for adrenomedullin, and the resulting complex modulates the bioactivities of both partners. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 12292–12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.M.; Chess, R.B. Effect of pegylation on pharmaceuticals. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroishi, N.; Nagata, S.; Akashi, E.; Ashizuka, S.; Kato, J.; Yamasaki, M.; Kitamura, K. Development of a novel human adrenomedullin derivative: Human serum albumin-conjugated adrenomedullin. J. Biochem. 2021, 170, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, S.; Yamasaki, M.; Kuroishi, N.; Kitamura, K. Development of Long-Acting Human Adrenomedullin Fc-Fusion Proteins. Biology 2022, 11, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.M.; Cheng, T.L.; Roffler, S.R. Polyethylene Glycol Immunogenicity: Theoretical, Clinical, and Practical Aspects of Anti-Polyethylene Glycol Antibodies. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 14022–14048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, T.; Tian, X.; An, W.; Wang, Z.; Han, B.; Tao, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Research progress on the PEGylation of therapeutic proteins and peptides (TPPs). Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1353626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, V.T.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Otagiri, M. Pharmaceutical strategies utilizing recombinant human serum albumin. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Yang, K.; Wu, Y.; Yu, G.; Yan, Y.; Hao, M.; Song, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, L. Telitacicept: A novel horizon in targeting autoimmunity and rheumatic diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2024, 148, 103291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, H.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshihara, F. Plasma Clearance of Intravenously Infused Adrenomedullin in Rats with Acute Renal Failure. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, T.; Tanaka, M.; Zhao, Y.; Kamiyoshi, A.; Sakurai, T.; Ichikawa-Shindo, Y.; Kawate, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Q.; et al. Receptor activity-modifying proteins of adrenomedullin (RAMP2/3): Roles in the pathogenesis of ARDS. Peptides 2024, 171, 171118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstead, W.M.; Kiessling, J.W.; Bdeir, K.; Kofke, W.A.; Vavilala, M.S. Adrenomedullin prevents sex-dependent impairment of autoregulation during hypotension after piglet brain injury through inhibition of ERK MAPK upregulation. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trincot, C.E.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Kulikauskas, M.R.; Caranasos, T.G.; Jensen, B.C.; Sabine, A.; Petrova, T.V.; Caron, K.M. Adrenomedullin Induces Cardiac Lymphangiogenesis After Myocardial Infarction and Regulates Cardiac Edema Via Connexin 43. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halasi, M.; Grinstein, M.; Adini, A.; Adini, I. Fibromodulin Ablation Exacerbates the Severity of Acute Colitis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 4515–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koboziev, I.; Karlsson, F.; Zhang, S.; Grisham, M.B. Pharmacological intervention studies using mouse models of the inflammatory bowel diseases: Translating preclinical data into new drug therapies. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 1229–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.J.; Bentley, M.D.; Harris, J.M. Chemistry for peptide and protein PEGylation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto, N.; Maemura, K.; Hirata, I.; Murano, M.; Sasaki, S.; Katsu, K. Inhibition of dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice by intracolonically administered antibodies against adhesion molecules (endothelial leucocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) or intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1)). Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1999, 117, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kitamura, K.; Akashi, E.; Nagata, S.; Kita, T.; Yamasaki, M. In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of 40 kDa PEGylated Adrenomedullin in a DSS-Induced Colitis Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199373
Kitamura K, Akashi E, Nagata S, Kita T, Yamasaki M. In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of 40 kDa PEGylated Adrenomedullin in a DSS-Induced Colitis Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199373
Chicago/Turabian StyleKitamura, Kazuo, Emiko Akashi, Sayaka Nagata, Toshihiro Kita, and Motoo Yamasaki. 2025. "In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of 40 kDa PEGylated Adrenomedullin in a DSS-Induced Colitis Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199373
APA StyleKitamura, K., Akashi, E., Nagata, S., Kita, T., & Yamasaki, M. (2025). In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of 40 kDa PEGylated Adrenomedullin in a DSS-Induced Colitis Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199373





